EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 ( )
|
|
|
- Cecilia Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP A1 (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/39 (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 ( ) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (84) Designated Contracting States: AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR Designated Extension States: AL BA RS (71) Applicant: Thomson Licensing Issy-les-Moulineaux (FR) Marvie, Jean-Eudes Issy les Moulineaux (FR) Briand, Gérard Issy les Moulineaux (FR) (74) Representative: Huchet, Anne Technicolor 1-5 rue Jeanne d Arc Issy-les-Moulineaux (FR) (72) Inventors: Gautron, Pascal Issy les Moulineaux (FR) (54) Method for generating shadows in an image EP A1 (57) The invention concerns a method for generating shadows in an image (10) comprising the steps of: - Computing (E2) a depth-map (6) that comprises an array of pixels, wherein pixels in the depth-map (6) have a depth value (d sm ) that indicates a depth from the light source (2) to a portion of the nearest occluding object (4) visible through the pixel, - projecting (E6) each point (P ix ) visible from a virtual camera (1) into the light space, - calculating (E7) the distance (d p ) between the said visible projected point (P) and the light source (2), - fetching (E8) the depth value (d sm ) in the depth-map (6) corresponding to the light ray from the light source to said visible projected point (P), The method further comprises the steps of - computing (E9), for each pixel, an adaptive bias (b) as a function of a predetermined base bias (b base ) and the orientation of the surface (3) on which the said visible point is located, - comparing (E10) for each pixel (P ix ) in the image, the distance (d p ) between said visible projected point (P) and the light source (2) with the sum of the corresponding depth map value ((d sm ) and said adaptive bias (b base ), - labelling (E11, E12) said pixel (P ix ) as lit or shadowed according to said comparison. Printed by Jouve, PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP A1 2 Description [0001] In graphics rendering, it is important to produce images that are realistic on a real-time basis. The basic difficulty in achieving total visual realism is the complexity of quickly and accurately representing real world visual effects. A scene can include a variety of textures, color gradations, reflections, translucency, and, most particularly, shadows. Shadows enhance the realism of an image because they give a two-dimensional (2D) image the appearance of being three-dimensional. [0002] The generation of shadows is critical in games environment for instance as it has to be generated in realtime according to the movements in the scene which are guided by the games users. [0003] In the past, there have been a number of different ways to determine how objects in a scene would cast shadows and how these shadows should be represented in the rendered image. [0004] A common shadowing method, called shadow volumes is described in the document from F. Crow entitled "Shadow Algorithms for Computer Graphics" published in the proceedings of SIGGRAPH in [0005] In this document, the silhouette of shadow-casting objects is extruded to determine the shadowing. While this method provides high quality shadows, it is limited to simple scenes and is computationally intensive. [0006] A more general technique for real-time shadow generation is described in the document from L. Williams entitled "Casting curved shadows on curved surfaces" published in the proceedings of SIGGRAPH in [0007] While this method is very efficient and easy to implement, it suffers from sampling drawbacks due to the finite resolution of the shadow map: most, of the time a single shadow map texel gets used in several pixels of the final image, yielding several aliasing artifacts. The most known artifact is the apparition of shadow blocks in the final image. [0008] This artifact can typically be reduced using percentage-closer filtering disclosed in the article from M. Bunnell and F. Pellacini entitled "Shadow Map Antialiasing" published in GPU Gems, Addison Wesley Edition in 2004, in which several shadow map texels are used to determine the percentage of lighting incoming to the point. Many other methods have been devised to reduce such aliasing artifacts by focusing the shadow map only on the visible parts of the scene. However all those methods are view-dependent, and hence require regenerating the shadow map for each movement of the user. Furthermore, the quality of the shadow map is not constant depending on the user location. [0009] Another artifact is due both to the precision of the distance information and to the limited resolution of the map: the distance comparison may return erroneous values for occluding objects very close to each other, or on surfaces nearly tangent to the light direction. To overcome this problem, the user-defined bias value offsets the distance comparisons so that erroneous shadowing is removed. However, this results in an undesired shifting of the shadows. As a same bias value is used for rendering the entire scene, problematic objects force a shifting of all the other shadows to avoid artifacts. [0010] US 5,870,097 filed on January 27, 1996 in the name of Snyder, proposes a method for improving shadowing in a graphics rendering system. It proposes an automatic calculation of a bias for shadow-mapping. However, the method proposed in this patent requires complex computations, and namely a computation of the distance from the source to the two closest surfaces. [0011] The present invention proposes to solve at least one of these drawbacks. To this end, the present invention concerns a method for generating shadows in an image comprising the steps of: - Computing a depth-map that comprises an array of pixels, wherein pixels in the depth-map have a depth value that indicates a depth from the light source to a portion of the nearest occluding object visible through the pixel, - projecting each point visible from a virtual camera into the light space, - calculating the distance between the said visible projected point and the light source, - fetching the depth value in the depth-map corresponding to the light ray from the light source to said visible projected point. The method further comprises the steps of - computing, for each pixel, an adaptive bias as a function of a predetermined base bias and the orientation of the surface on which the said visible point is located, - comparing for each pixel in the image, the distance between said visible projected point and the light source with the sum of the corresponding depth map value and said adaptive bias, - labelling said pixel as lit or shadowed according to said comparison. [0012] Preferentially, said adaptive bias is dependant on said surface normal. [0013] According to a preferred embodiment, said adaptive bias is defined as the division of said predetermined base bias by the dot product of the surface normal by the incident light direction. [0014] Preferentially, said adaptive bias is limited to a maximum value. [0015] According to a second aspect, the invention concerns also a graphics processing unit comprising code instructions for performing the method according to any of the previous claims. [0016] According to a third aspect, the invention concerns also a computer program product for computing shadows for an image, the computer program product comprising a computer-readable medium containing 2
3 3 EP A1 4 computer program code for performing the steps of the method according to any of claims 1 to 4. [0017] According to a second aspect, the invention concerns a graphics processing unit comprising code instructions for performing the method according to any of the previous claims. [0018] According to a third aspect, the invention concerns a computer program product for computing shadows for an image, the computer program product comprising a computer-readable medium containing computer program code for performing the steps of the method according to the invention. [0019] Other characteristics and advantages of the invention will appear through the description of a non-limiting embodiment of the invention, which will be illustrated, with the help of the enclosed drawings. - Figure 1 represents an overview of a scene for which shadows have to be generated, - Figure 2 represents an algorithm of shadow mapping, with adaptive bias, - Figure 3 represents the values used in the bias calculation according to a preferred embodiment of the invention, - Figure 4 represents the aliasing phenomenon on surfaces. [0020] On figure 1, the scene for which shadows have to be generated is represented. The proposed method enables the generation of shadows in real-time. When a video game is played, according to the displacement of persons in a scene, guided by the user, the shadows have to be generated in real-time. Therefore, the method is advantageously executed thanks to a Graphics Processing unit, known under the acronym of GPU, on a computer or graphics processing board of a computer. The GPU will execute the software instructions to execute the method which is disclosed hereafter. The code instructions are stored on a computer-readable medium, such as a memory. [0021] The method is based on the fact that a light source and a virtual camera are positioned in the scene. One embodiment is shown on figure 1. [0022] A virtual camera 1 captures the scene for which shadows have to be generated. A light source 2 is positioned as shown on figure 1. A sphere 4 is located in the scene and represents an occluding object for an image 10. The pixels are projected on a surface plane 3. The light source 2 projects light rays 5 which illuminate part of the sphere 4. The image 10 comprises an array of pixels that represent a three-dimensional scene as viewed from a particular point of the virtual camera 1. For a given light source 2, a depth map 6 is computed. The depth map 6 includes an array of pixels, where instead of having a color value, each pixel has a depth value. Each pixel in the depth map has coordinates (x sm, y sm ). In one embodiment, the depth value is defined with reference to a z-axis, which is normal to the depth-map [0023] The flowchart given in figure 2 is based on a real-time shadow-mapping algorithm but it is not limited to this method and the invention can be based on any shadow mapping-based technique. [0024] In the case of perspective shadow mapping methods, steps E2 and E7 described later on are different. [0025] In a step E1, a camera is positioned at the light source location, thanks to the facilities offered by virtual reality. [0026] In a step E2, the scene is rendered from the camera positioned at the light source location. The distance d sm (x sm, y sm ), visible on figure 1 with reference numeral 8, to each point which is visible from this camera position is stored in the shadow map. The shadow map is a depth-map texture stored in a graphics memory. [0027] In a step E3, the rendering process is initialized and in the following steps the camera is located in its original position. [0028] In a step E4, the user defines the bias b base which depends only on the scene scale. For instance, the value 0,1 is suitable for a scene which length unit is the meter. [0029] In a step E5 a first pixel Pix as in the final image is chosen. All the pixels will be chosen one after the others. In other embodiments, depending on the processor capabilities, several pixels can be processed simultaneously. [0030] In a step E6, the point P visible through pixel Pix is projected into the light space. [0031] In a step E7, the distance dp from P to the light source is computed. It is shown on figure 1 as reference numeral 9. [0032] This light ray, from the light source to the point P, crosses the depth map at pixel of coordinates (x sm, y sm ) and the corresponding distance d sm (x sm, y sm ) to the nearest occluder is fetched from the shadow map in a step E8. [0033] In a step E9, an adaptive bias is computed. As shown in figure 4, in conventional methods, there is aliasing on surfaces. Aliasing artifacts tend to appear when the rendered surface gets tangent to the lighting direction. [0034] As each pixel of the shadow map stores the distance to the point visible in the middle of the pixel, the limited sampling rate yields zones in which points are successively labeled as lit or shadowed. [0035] To remove the artifacts, the bias value must be raised. Conversely, surfaces nearly perpendicular to the lighting direction do not require a high bias value. [0036] According to the present embodiment of the invention, based on the surface orientation at each visible point, a per-pixel bias adaptation function is defined. Given the user-defined base bias value b base which only depends on the scene scale, the actual bias b used to determine the shadowing is computed according to the following equation: 3
4 5 EP A1 6 [0037] where. is the vector dot product operator, N is the surface normal, L is the incident light direction and ε is a minimum value, typically 0.05, to prevent the bias value to go to infinity when N gets nearly perpendicular to L. [0038] Figure 3 illustrates this by showing the L and N representations. [0039] In a step E10, a test is performed. D p represents the distance from the light source to the point P and D sm represents the distance from the light source to the shadow map. [0040] If d p d sm +b, then one moves forward to a step E11 in which the pixel Pix is labeled as a shadowed pixel. [0041] If d p < d sm +b, then one moves forward to a step E12 in which the pixel is labeled as a lit pixel. [0042] Then one moves further to step E13, in which a test is performed in order to check whether this is the last pixel of the scene. If yes, the whole scene has been processed, otherwise, one moves further to step E15, in which a next pixel is chosen and one moves back to step E6, and so on and so forth until all pixels have been reviewed (step E14). [0043] When all the pixels of the image have been labeled either lit or shadowed, an image processing method is performed on these pixels to respectively light or shadow them. [0044] The invention as described in the preferred embodiments, is advantageously computed using a Graphics processing unit (GPU) on a graphics processing board. [0045] The invention is also therefore implemented preferentially as software code instructions and stored on a computer-readable medium such as a memory (flash, SDRAM...), said instructions being read by a graphics processing unit. [0046] The foregoing description of the embodiments of the invention has been presented for the purposes of illustration and description. It is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise form disclosed. Persons skilled in the relevant art can appreciate that many modifications and variations are possible in light of the above teaching. It is therefore intended that the scope of the invention is not limited by this detailed description, but rather by the claims appended hereto. Claims a depth from the light source (2) to a portion of the nearest occluding object (4) visible through the pixel, - projecting (E6) each point (P ix ) visible from a virtual camera (1) into the light space, - calculating (E7) the distance (dp) between the said visible projected point (P) and the light source (2), - fetching (E8) the depth value (d sm ) in the depthmap (6) corresponding to the light ray from the light source to said visible projected point (P), Characterized in that it further comprises the steps of - computing (E9), for each pixel, an adaptive bias (b) as a function of a predetermined base bias (b base ) and the orientation of the surface (3) on which the said visible point is located, - comparing (E10) for each pixel (P ix ) in the image, the distance (dp) between said visible projected point (P) and the light source (2) with the sum of the corresponding depth map value ((d sm ) and said adaptive bias (b base ), - labelling (E11, E12) said pixel (P ix ) as lit or shadowed according to said comparison. 2. Method according to claim 1 characterized in that said adaptive bias (b base ) is dependant on said surface normal (N). 3. Method according to claim 2 characterized in that said adaptive bias (b) is defined as the division of said predetermined base bias (b base ) by the dot product of the surface normal (N) by the incident light direction (L). 4. Method according to any of the previous claims characterized in that said adaptive bias is limited to a maximum value. 5. Graphics processing unit comprising code instructions for performing the method according to any of the previous claims. 6. Computer program product for computing shadows for an image, the computer program product comprising a computer-readable medium containing computer program code for performing the steps of the method according to any of claims 1 to Method for generating shadows in an image (10) comprising the steps of: - Computing (E2) a depth-map (6) that comprises an array of pixels, wherein pixels in the depthmap (6) have a depth value (d sm ) that indicates 55 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 10
11 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Patent documents cited in the description US A, Snyder [0010] Non-patent literature cited in the description M. Bunnell ; F. Pellacini. Shadow Map Antialiasing. Addison Wesley Edition, 2004 [0008] 11
TEPZZ Z47A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/00 ( )
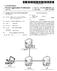
 (19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/34
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ _968ZZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 ( ) H04L 9/32 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T (11) EP 2 608 446 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 (2006.01) H04L 9/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T (11) EP 2 608 446 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 (2006.01) H04L 9/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ 6 8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
TEPZZ Z7999A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B05B 15/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
TEPZZ 98 _55A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 ( ) G11B 20/00 ( ) G06Q 10/00 ( )
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60W 30/14 ( ) B60W 50/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
(19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
TEPZZ 85 9Z_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/13
 (19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/37
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
TEPZZ 8_8997A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
TEPZZ Z5_748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/24 ( ) WU, Qin
 (19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/56 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
TEPZZ 74_475A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 74_47A_T (11) EP 2 741 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.06.14 Bulletin 14/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 131968.6 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 74_47A_T (11) EP 2 741 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.06.14 Bulletin 14/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 131968.6 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/45
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 99894ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
TEPZZ _7655_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
(19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
TEPZZ _Z_56ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 78779ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/33
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ _9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/29
 (19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
TEPZZ _4748 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/32
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/14
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms
 Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Last Time. Why are Shadows Important? Today. Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
TEPZZ 8_8995A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8_899A_T (11) EP 2 818 99 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.14 Bulletin /01 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1317396.1 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 8_899A_T (11) EP 2 818 99 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.14 Bulletin /01 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1317396.1 (22) Date of
For Intuition about Scene Lighting. Today. Limitations of Planar Shadows. Cast Shadows on Planar Surfaces. Shadow/View Duality.
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
eifu Trauma and Extremities
 Electronic Instructions for Use eifu Trauma and Extremities 1 Instructions for use of T&E products are available on the Stryker eifu website 2 Benefits Environmental aspect less paper, possible smaller
Electronic Instructions for Use eifu Trauma and Extremities 1 Instructions for use of T&E products are available on the Stryker eifu website 2 Benefits Environmental aspect less paper, possible smaller
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion
 TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques
 Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
TEPZZ 7989 ZA T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 ( ) A01B 79/02 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7989 ZA T (11) EP 2 798 9 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 0.11.14 Bulletin 14/4 (1) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 (06.01) A01B 79/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 14166701.4
(19) TEPZZ 7989 ZA T (11) EP 2 798 9 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 0.11.14 Bulletin 14/4 (1) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 (06.01) A01B 79/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 14166701.4
TEPZZ 5976 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G08G 5/00 ( ) H04M 1/725 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
(19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
Last Time. Reading for Today: Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
TMCH Report March February 2017
 TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Textures can Alias. Schedule. Questions? Quiz 1: Tuesday October 26 th, in class (1 week from today!
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
BoR (14) 142. Presented by ECTA in relation to the public hearing on the draft BEREC Strategy and draft BEREC Work Programme 2015
 BoR (14) 142 Presented by ECTA in relation to the public hearing on the draft BEREC Strategy 2015-2017 and draft BEREC Work Programme 2015 NGA investments are steadily increasing Source: Implementation
BoR (14) 142 Presented by ECTA in relation to the public hearing on the draft BEREC Strategy 2015-2017 and draft BEREC Work Programme 2015 NGA investments are steadily increasing Source: Implementation
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Today. Why are Shadows Important? Shadows as a Depth Cue. For Intuition about Scene Lighting
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
(51) Int Cl.: H04N 5/232 ( ) H04N 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
(19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
Real-Time Shadows. Computer Graphics. MIT EECS Durand 1
 Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
TEPZZ 858 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/15
 (19) TEPZZ 88 A_T (11) EP 2 88 323 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04. Bulletin / (21) Application number: 13637.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) G06Q /00 (12.01) G06F
(19) TEPZZ 88 A_T (11) EP 2 88 323 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04. Bulletin / (21) Application number: 13637.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) G06Q /00 (12.01) G06F
Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport. Contract n ILSE - User manual
 Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport Contract n 4810020050102005367 GIM Geographic Information Management nv C05474B June 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 ABOUT ILSE... 1 1.1 Purpose of ILSE... 1 1.2 System
Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport Contract n 4810020050102005367 GIM Geographic Information Management nv C05474B June 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 ABOUT ILSE... 1 1.1 Purpose of ILSE... 1 1.2 System
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination. Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker
 Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
Texture Mapping II. Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1. 7.
 Texture Mapping II Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1 Light Maps Simulates the effect of a local light source + = Can be pre-computed
Texture Mapping II Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1 Light Maps Simulates the effect of a local light source + = Can be pre-computed
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager
 Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1. Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO665537OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1 Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) FIRECRACKER LAUNCHING DEVICE 3,794,325 * 2/1974 Stender 4,995,371. A 2/1991 Kuizinas...
USOO665537OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1 Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) FIRECRACKER LAUNCHING DEVICE 3,794,325 * 2/1974 Stender 4,995,371. A 2/1991 Kuizinas...
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/29
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 477 149 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/29 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/02 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 12150906.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 477 149 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/29 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/02 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 12150906.1 (22) Date of filing:
Country
 Total EU-12 31,2 26,6 21,1 22,5 25,9 29,2 29,6 29,7 30,5 29,9 25,3 25,1 EU-15 28,1 28,6 28,6 29,4 28,8 24,3 24,2 EU-25 25,0 25,0 A 15,0 13,4 14,3 15,6 14,9 16,6 13,6 5,3 10,9 10,8 B 41,9 44,7 51,6 53,5
Total EU-12 31,2 26,6 21,1 22,5 25,9 29,2 29,6 29,7 30,5 29,9 25,3 25,1 EU-15 28,1 28,6 28,6 29,4 28,8 24,3 24,2 EU-25 25,0 25,0 A 15,0 13,4 14,3 15,6 14,9 16,6 13,6 5,3 10,9 10,8 B 41,9 44,7 51,6 53,5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
BASIC PRICE LIST. The price of transportation is added toll in the amount of CZK 1,30 / kg and the current fuel surcharge.
 BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
TEPZZ_5 695B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms
 In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms Alex Wiens and Gitta Domik, University of Paderborn, Germany Abstract: We are describing two exercises to deepen the understanding of two popular real-time shadow
In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms Alex Wiens and Gitta Domik, University of Paderborn, Germany Abstract: We are describing two exercises to deepen the understanding of two popular real-time shadow
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015
 CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Final Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Final Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
WO 2013/ Al. 17 January 2013 ( ) P O P C T
 (12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International
TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
(19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Schedule. Questions? Today. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
Real-Time Shadows. MIT EECS 6.837, Durand and Cutler
 Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
Connevans.info. DeafEquipment.co.uk. This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at
 Connevans.info Solutions to improve the quality of life Offering you choice Helping you choose This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at www.deafequipment.co.uk DeafEquipment.co.uk
Connevans.info Solutions to improve the quality of life Offering you choice Helping you choose This product may be purchased from Connevans Limited secure online store at www.deafequipment.co.uk DeafEquipment.co.uk
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
Eurostat s s Information Society Statistics
 3rd workshop on Information Society Measurement for www.europa.eu.int/comm/eurostat/ Directorate F: Social Statistics and Information Society Unit F-6: Information Society and Tourism Statistics Latin
3rd workshop on Information Society Measurement for www.europa.eu.int/comm/eurostat/ Directorate F: Social Statistics and Information Society Unit F-6: Information Society and Tourism Statistics Latin
Reading. 18. Projections and Z-buffers. Required: Watt, Section , 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
Shadow and Environment Maps
 CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #8 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Monday, 28 September 2009 Shadow and Environment Maps Lecture #8: Monday, 28 September 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #8 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Monday, 28 September 2009 Shadow and Environment Maps Lecture #8: Monday, 28 September 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
Cybersecurity in the EU Steve Purser Head of Operational Departments, ENISA Regional Cybersecurity Forum Sofia, Bulgaria 29 th November 2016 European
 Cybersecurity in the EU Steve Purser Head of Operational Departments, ENISA Regional Cybersecurity Forum Sofia, Bulgaria 29 th November 2016 European Union Agency for Network and Information Security Positioning
Cybersecurity in the EU Steve Purser Head of Operational Departments, ENISA Regional Cybersecurity Forum Sofia, Bulgaria 29 th November 2016 European Union Agency for Network and Information Security Positioning
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (11) EP 2 377 493 A1 (43) Date of publication: 19..11 Bulletin 11/42 (21) Application number: 09837427. (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (11) EP 2 377 493 A1 (43) Date of publication: 19..11 Bulletin 11/42 (21) Application number: 09837427. (22) Date of filing:
Multi-View Soft Shadows. Louis Bavoil
 Multi-View Soft Shadows Louis Bavoil lbavoil@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1.0 March 16, 2011 Louis Bavoil Initial release Overview The Multi-View Soft Shadows
Multi-View Soft Shadows Louis Bavoil lbavoil@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1.0 March 16, 2011 Louis Bavoil Initial release Overview The Multi-View Soft Shadows
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker. Herbst 2010
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Ray Tracing. Kjetil Babington
 Ray Tracing Kjetil Babington 21.10.2011 1 Introduction What is Ray Tracing? Act of tracing a ray through some scene Not necessarily for rendering Rendering with Ray Tracing Ray Tracing is a global illumination
Ray Tracing Kjetil Babington 21.10.2011 1 Introduction What is Ray Tracing? Act of tracing a ray through some scene Not necessarily for rendering Rendering with Ray Tracing Ray Tracing is a global illumination
Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007
 Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007 Lightmaps, as do other precomputed lighting methods, provide an efficient and pleasing solution for lighting and shadowing of relatively static
Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007 Lightmaps, as do other precomputed lighting methods, provide an efficient and pleasing solution for lighting and shadowing of relatively static
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Thesis Report. Thesis Title: Soft Shadow Rendering in Real Time. Shihab Rezwan Manzur ID: CSE Department BRAC University
 Thesis Report Thesis Title: Soft Shadow Rendering in Real Time Shihab Rezwan Manzur ID: 09201028 CSE Department BRAC University Supervisor: Professor Dr. Mumit Khan Date: 13-08 - 12 Abstract Shadows have
Thesis Report Thesis Title: Soft Shadow Rendering in Real Time Shihab Rezwan Manzur ID: 09201028 CSE Department BRAC University Supervisor: Professor Dr. Mumit Khan Date: 13-08 - 12 Abstract Shadows have
Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
HANDBOOK ON INDUSTRIAL PROPERTY INFORMATION AND DOCUMENTATION. Ref.: Standards ST.10/B page: STANDARD ST.10/B
 Ref.: Standards ST.10/B page: 3.10.2.1 STANDARD ST.10/B LAYOUT OF BIBLIOGRAPHIC DATA COMPONENTS Revision adopted by the SCIT Standards and Documentation Working Group at its tenth session on November 21,
Ref.: Standards ST.10/B page: 3.10.2.1 STANDARD ST.10/B LAYOUT OF BIBLIOGRAPHIC DATA COMPONENTS Revision adopted by the SCIT Standards and Documentation Working Group at its tenth session on November 21,
1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg
 BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps
 Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps Christoph Peters 2017-07-30 High-Performance Graphics 2017 These slides include presenter s notes for your convenience. 1 In this presentation we discuss non-linearly
Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps Christoph Peters 2017-07-30 High-Performance Graphics 2017 These slides include presenter s notes for your convenience. 1 In this presentation we discuss non-linearly
Shadows. Real-Time Hard Shadows. Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec
 Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
(51) Int Cl.: H04Q 1/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
Lecture 17: Shadows. Projects. Why Shadows? Shadows. Using the Shadow Map. Shadow Maps. Proposals due today. I will mail out comments
 Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Rendering. Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image. Camera. Light. Rendering. View Plane
 Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Computer Graphics. Lecture 13. Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity. Taku Komura
 Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
EPO INPADOC 44 years. Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo. November 2016
 EPO INPADOC 44 years Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo November 2016 Content The INPADOC period Integration into the EPO establishment of principal directorate patent information
EPO INPADOC 44 years Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo November 2016 Content The INPADOC period Integration into the EPO establishment of principal directorate patent information
INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News
 August 2008 INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News All patent publication events including grants are now covered in the INPADOC Legal Status for all authorities In the INPADOCDB and INPAFAMDB files, all patent publication
August 2008 INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News All patent publication events including grants are now covered in the INPADOC Legal Status for all authorities In the INPADOCDB and INPAFAMDB files, all patent publication
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT. Directorate G :Global Business Statistics Unit G-2: Structural business statistics and global value chains
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate G :Global Business Statistics Unit G-2: Structural business statistics and global value chains MEETING OF THE BUSINESS DEMOGRAPHY WORKING GROUP 18 MAY 2015 BECH
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate G :Global Business Statistics Unit G-2: Structural business statistics and global value chains MEETING OF THE BUSINESS DEMOGRAPHY WORKING GROUP 18 MAY 2015 BECH
