TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 ( ) H04L 9/32 (2006.
|
|
|
- Jasmin Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
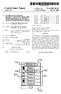
1 (19) TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 ( ) H04L 9/32 ( ) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR Designated Extension States: BA ME (71) Applicant: Siemens Aktiengesellschaft München (DE) (72) Inventor: Boulila, Naoufel München (DE) (4) Network device in a smart grid power network and method of encrypting communication between network devices (7) The invention provides for a method (20) of encrypting communication between network devices () in a smart grid power network, the method (20) comprising the steps of, encrypting (S4), by a first network device (a), an identification code of the first network device (a) with a first private key and a second public key, decrypting (S6), by a second network device (b), the identification code of the first network device (a) using a second private key matching the second public key and a first public key matching the first private key and validating (S7, S8) the identification code at a validation server (13), negotiating (S9) a symmetric key between the first network device (a) and the second network device (b), and encrypting (S, S11) subsequent communication between the first network device (a) and the second network device (b) using the negotiated symmetric key. EP A1 Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR) (Cont. next page)
2 EP A1 2
3 1 EP A1 2 Description FIELD OF THE INVENTION [0001] The present invention relates to a network device in a smart grid power network and a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION [0002] Smart grid power networks comprise a large number of physically distributed network components that may communicate among each other in order to control, measure and dispatch power to consumers. [0003] The communication between network components has to be secured against malicious attacks on the power network, such as spoofing, exploiting, identity theft, data theft, spreading of malware or worms, and remote controlling critical network nodes. [0004] The document US 20/ A1 discloses methods for securing communication over an energy grid between electric meters and application servers of a power grid by requiring human authorization. [000] The document US 2011/02711 A1 discloses a key management system for generating and managing keys used in a communication between network devices in a smart energy grid. [0006] The document Open Metering System Specification, Vol.2 Primary Communication, Issue 3.0.1, January 2011, online available at download/oms-spec_vol2_primary_v301.pdf, discloses in chapter 4.2. a method for encrypting communication messages in a smart meter network using Rijndael algorithms. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION [0007] In a first aspect, the invention provides a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network, the method comprising encrypting, by a first network device, an identification code of the first network device with a first private key and a second public key, decrypting, by a second network device, the identification code of the first network device using a second private key matching the second public key and a first public key matching the first private key and validating the identification code at a validation server, negotiating a symmetric key between the first network device and the second network device, and encrypting subsequent communication between the first network device and the second network device using the negotiated symmetric key. [0008] With the method according to the first aspect, it is a lot more complicated to gain possession of the encryption keys used to secure communication between the network devices, since the symmetric key negotiated between the network devices is generated dynamically rather than being static within the network. [0009] Furthermore, with the pre-communication authentication protocol only registered network devices may gain access to the smart grid power network, thus reducing the possibility of spoofing attacks or imposters gaining access to the network. [00] The symmetric key does not need to be stored permanently on any of the network devices, thereby reducing the possibility of a third person getting knowledge of the symmetric key. [0011] According to one embodiment of the method according to the first aspect the first and/or the second network device are smart meters in the smart grid power network. Especially for smart meters which are usually located in non-surveyed remote sites of the power network it is important to guarantee safety against malicious attacks on the smart grid power network. [0012] According to another embodiment of the method according to the first aspect the negotiated symmetric key has a temporally limited validity. This limits the chance of a third person getting illicit access to the network even further, since the time span during which a symmetric key is valid is too short to reengineer the key. [0013] According to another embodiment of the method according to the first aspect negotiating the symmetric key comprises using a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol. This allows the two network devices to define a common secret key over an otherwise insecure communication channel, which key may be used to encrypt subsequent communication securely. [0014] According to another embodiment of the method according to the first aspect the first private key is a hardware serial number unique to the first network device, and wherein the hardware serial number is stored in the first network device. This has the advantage that the identification code may be attached to the first network device in a secure environment such as a manufacturing facility for network device. [001] According to another embodiment of the method according to the first aspect the validation server is a remote server of the manufacturer of the first network device. The validation server may advantageously also be under the surveillance of the manufacturer, thus increasing the security against a third person illegitimately gaining possession of the identity of the first network device. [0016] In a second aspect, the invention provides for a network device in a smart grid power network, the network device comprising a storage unit configured to store an identification code of the network device and an asymmetric key pair including a public key and a private key, an authentication unit configured to read out the identification code and the private key of the storage unit and to encrypt the identification code using the private key, a communication unit configured to send the encrypted identification code to another network device in the smart grid power network, and an encryption unit configured to negotiate a symmetric key with the other network device 3
4 3 EP A1 4 and to encrypt communication between the network device and the other network device using the negotiated symmetric key. [0017] According to one embodiment of the network device according to the second aspect the network device is a smart meter in the smart grid power network. Especially for smart meters which are usually located in non-surveyed remote sites of the power network it is important to guarantee safety against malicious attacks on the smart grid power network. [0018] According to another embodiment of the network device according to the second aspect the negotiated symmetric key has a temporally limited validity. This limits the chance of a third person getting illicit access to the network even further, since the time span during which a symmetric key is valid is too short to reengineer the key. [0019] According to another embodiment of the network device according to the second aspect the encryption unit is configured to negotiate a symmetric key with the other network device using a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol. This allows the two network devices to define a common secret key over an otherwise insecure communication channel, which key may be used to encrypt subsequent communication securely. [0020] According to another embodiment of the network device according to the second aspect the identification code is a hardware serial number unique to the network device. This has the advantage that the identification code may be attached to the first network device in a secure environment such as a manufacturing facility for network device. [0021] According to another embodiment of the network device according to the second aspect the hardware serial number is stored in a validation server or a remote server of the manufacturer of the network device. The validation server may advantageously also be under the surveillance of the manufacturer, thus increasing the security against a third person illegitimately gaining possession of the identity of the first network device. [0022] In yet another aspect, the invention provides for a smart grid power network comprising a plurality of network devices according to the second aspect of the invention. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0023] The accompanying drawings are included to provide a further understanding of the present invention and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this specification. The drawings illustrate the embodiments of the present invention and together with the description serve to explain the principles of the invention. Other embodiments of the present invention and many of the intended advantages of the present invention will be readily appreciated as they become better understood by reference to the following detailed description. The elements of the drawings are not necessarily drawn to scale relative to each other. Like reference numerals designate corresponding similar parts. Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Fig. Fig. 6 schematically illustrates an embodiment of a smart grid power network comprising a plurality of network devices. schematically illustrates an embodiment of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. schematically illustrates an embodiment of a method step of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. schematically illustrates an embodiment of another method step of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. schematically illustrates an embodiment of a further method step of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. schematically illustrates an embodiment of yet a further method step of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS [0024] Although specific embodiments have been illustrated and described herein, it will be appreciated by those of ordinary skill in the art that a variety of alternate and/or equivalent implementations may be substituted for the specific embodiments shown and described without departing from the scope of the present invention. Generally, this application is intended to cover any adaptations or variations of the specific embodiments discussed herein. [002] Network devices as used herein refer to components or nodes of a network that are part of a network and may actively take part in network related communication, in particular the exchange of communication messages in a smart grid power network. Network devices may for example comprise smart meters, electrical appliances, application servers of power plants, energy trading sites, energy distributors and so on, validation servers of manufacturers of network devices, and similar components. The smart grid power network may provide communication lines, for example wire-bound communication over PowerLAN or telephone landlines, wireless communication over WANs, BANs or HANs, radio communication or similar communication technologies. The network itself may be a virtual part of a physical network, such as the Internet or similar physical network struc- 4
5 EP A1 6 tures. [0026] FIG. 1 schematically illustrates a smart grid power network 0 comprising a plurality of network devices. The smart grid power network 0 may also comprise one or more validation servers 13, which may be remote servers of a facility or manufacturer of network devices. The network devices may be interconnected by communication connections 11, 12. Two network devices may for example be connected by a communication connection 11. A network device may for example be connected to a validation server 13 by a communication connection 12. The number of network devices and validation servers 13 in the smart grid power network 0 in FIG. 1 is only exemplary, and there may in fact be any number of network devices and validation servers 13 in the smart grid power network 0. Similarly, the number of communication connections 11, 12 is only exemplarily shown in FIG. 1 and there may be any number of communication connections 11, 12 between any network devices and validation servers 13. In particular, the communication connections 11, 12 may be set up or torn down dynamically, especially in the scenario of a virtual communication network 0 as part of a larger physical network, for example a power line communication (PLC) network as virtual part of a power line network. [0027] One network device in FIG. 1 is shown in greater detail, and it is to be understood that other network devices of the smart grid power network 0 may comprise similar or identical components as the particular network device shown in greater detail. [0028] The network device may comprise an encryption unit 1, an authentication unit 2, a storage unit 3 and a communication unit 4. The encryption unit 1 may be coupled to the communication unit 4 and the authentication unit 2. The authentication unit 2 may be coupled to the communication unit 4 and the storage unit 3. [0029] The storage unit 3 may for example be a random access memory (RAM), a read-only access memory (ROM), a flash card, a smart card, a USB memory device or any other similar device configured to retrievably store data on a permanent or temporary basis. The storage unit 3 may be configured to store an identification code of the network device. The identification code may for example be a Media Access Control (MAC) number, a hardware serial number or any other alphanumerical code sequence that is used to uniquely identify the network device. The storage unit 3 may further be configured to store an asymmetric key pair including a public key and a private key. The identification code and the asymmetric key pair may for example be stored in the storage unit 3 at a manufacturing facility of the network device. The identification code and the asymmetric key pair may be stored in the storage unit 3 in a manner secured against illicit or inappropriate accesses, for example such that the identification code and the asymmetric key pair are deleted upon manipulation or tampering of the storage unit 3. For that purpose, the storage unit 3 may for example be equipped with a tampering mechanism, for example a tamper wire mesh or similar tampering detection means. [0030] The authentication unit 2 may be configured to read out the identification code and the private key of the storage unit 3. The authentication unit 2 may be configured to encrypt the identification code using the private key. The authentication unit 2 may be configured to relay the encrypted identification code to other network devices in the smart grid power network 0, for example by means of the communication unit 4 which may be configured to send the encrypted identification code to another network device. Additionally, the communication unit 4 may be configured to send the public key to other network devices, for example as a broadcast ("push") service or on request by other network devices ("pull" service). [0031] The encryption unit 1 may be configured to negotiate a symmetric key with other network devices. The encryption unit 1 may be configured to encrypt communication between the network device and other network devices using the negotiated symmetric key. The encryption unit 1 may for example employ a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol for negotiating a symmetric key with other network devices. Alternatively, other key exchange protocols may be used in the encryption unit 1 as well. [0032] FIG. 2 schematically illustrates a method 200 of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network. The method 200 may for example be performed by network devices in a smart grid power network, such as the smart grid power network 0 as depicted in FIG. 1. The method 200 of FIG. 2 will be explained in conjunction with FIGS. 3 to 6 which schematically illustrate method steps of a method of encrypting communication between network devices in a smart grid power network, in particular of a method 200 as exemplarily illustrated in FIG. 2. [0033] In a first step S1, a first network device a may direct a communication request to a second network device b. The second network device b may respond by sending an authentication request to the first network device a in a second step S2. In a third step S3, the network devices a and b may exchange their public keys of the respective asymmetric key pairs associated with the respective network device a or b. In FIG. 3, the method step S3 is shown in more detail. The first network device a may send in a step S31 a first public key over an insecure communication channel to the second network device b. Simultaneously or subsequently, the second network device b may send a second public key in a step S32 over the same or another insecure communication channel to the first network device a. [0034] Returning to FIG. 2, in a step S4, the first network device a may encrypt an identification code stored in its storage unit 3 and send the encrypted identification code in a step S to the second network device
6 7 EP A1 8 b, which in turn decrypts the encrypted identification code in a step S6. A possible implementation for the steps S4, S and S6 is exemplarily shown in greater detail in FIG. 4. The first network device a retrieves the identification code from the storage unit 3 in a step S41. The retrieved identification code may then be encrypted by an authentication unit 2 of the first network device a. The authentication unit 2 may in a step S42 first encrypt the identification code with its own first private key, which may be retrieved from the storage unit 3 as well. In a step S43, the authentication unit 2 may encrypt the already encrypted identification code again with the second public key as received in step S32. The encrypted identification code may then be sent by a communication unit 4 of the first network device a in a step S to the second network device b. In the second network device b, the encrypted identification code is first decrypted using the second private key of the second network device b in a step S61. Then, the second network device b decrypts the already decrypted identification code again with the first public key as received in step S31. In a step S63, the second network device b may check the decrypted identification code for validity. [003] In order to check the validity of the identification code of the first network device a, the second network device b may either look up the identification code in its own registration lists. Alternatively, the second network device b may send a validation request in a step S7 to a validation server 13, for example a remote server of a manufacturer of the first network device a. The validation server 13 may keep a list of all identification codes of network devices manufactured by the manufacturer. [0036] FIG. shows an exemplary embodiment of the validation process of a first network device a at a validation server 13. The validation server 13 may receive a validation request in a step S7 by a second network device b and may in a step S81 check the received identification code with a registration list. In a step S82, a decision is made whether the identification code matches one of the items in the registration list or not. In a step S8, the validation server 13 may return a response to the second network device b which confirms or denies the authenticity of the first network device a. [0037] Upon reception of the response of the validation server 13, the second network device b may selectively reject communication with the first network device a or establish a communication channel with the first network device a. Returning to FIG. 2, in case a communication channel with the first network device a is established, the network devices a and b may in a step S9 negotiate a symmetric key that may be used to encrypting subsequent communication between the first network device a and the second network device b using the negotiated symmetric key. A possible implementation, for example a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol, for negotiating a symmetric key is exemplarily shown in FIG [0038] In a step S91, the first network device a may send a prime number p and a primitive root g modulo p over the established communication channel to the second network device b. Additionally, the first network device a may choose a random number a and compute a first key generator u = g a mod p which may be sent to the second network device b. The second network device b may choose a random number b and compute a second key generator v = g b mod p which may be sent back to the first network device a in a step S92. Each of the network devices a and b may then use the received key generator v and u, respectively, in order to generate a symmetric key k using its own chosen random number a and b, respectively. For example, in a step S93 the first network device a may calculate the symmetric key k as k = v a = g ba mod p. In a step S94 the second network device b may calculate the symmetric key k as k = u b = g ab mod p. Both network devices a and b are now in possession of the same symmetric key k which may be used to encrypt subsequent communication over the established communication channel. [0039] The symmetric key k may only be valid for a certain predefined time span. For example, the symmetric key k may only be valid for the duration of a communication session between the network devices a and b. After the session expires, the network devices a and b will have to negotiate a new symmetric key k again. It may also be possible that the symmetric key k may only be valid for a predefined number of sessions between the network devices a and b, or for a certain fixed duration, for example a few seconds or a few minutes. All these implementations have the advantage, that the symmetric key used for communication between the network devices a and b is generated on the fly and does not need to be stored permanently on any of the network devices a or b. That way, it is not possible for a third person to gain unauthorized access to the network by reading out the communication key from one of the network devices. [0040] With the method 20, each communication channel between a distinct pair of two network devices will have its own symmetric communication key. That way, whenever one of the symmetric keys is compromised, the rest of the network will be able to still communicate securely. Moreover, none of the symmetric communication keys will be known a priori, thereby enhancing the security of the communication within the smart grid power network. [0041] In the foregoing detailed description, various features are grouped together in one or more examples or examples for the purpose of streamlining the disclosure. It is understood that the above description is intended to be illustrative, and not restrictive. It is intended to cover all alternatives, modifications and equivalents as may be included within the scope of the invention. Many other examples will be apparent to one skilled in the art upon reviewing the above specification. [0042] Specific nomenclature used in the foregoing 6
7 9 EP A1 specification is used to provide a thorough understanding of the invention. However, it will be apparent to one skilled in the art in light of the specification provided herein that the specific details are not required in order to practice the invention. Thus, the foregoing descriptions of specific embodiments of the present invention are presented for purposes of illustration and description. They are not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise forms disclosed; obviously many modifications and variations are possible in view of the above teachings. The embodiments were chosen and described in order to best explain the principles of the invention and its practical applications, to thereby enable others skilled in the art to best utilize the invention and various embodiments with various modifications as are suited to the particular use contemplated. Throughout the specification, the terms "including" and "in which" are used as the plain-english equivalents of the respective terms "comprising" and "wherein," respectively. Moreover, the terms "first," "second," and "third," etc., are used merely as labels, and are not intended to impose numerical requirements on or to establish a certain ranking of importance of their objects. Claims 1. A method (20) of encrypting communication between network devices () in a smart grid power network (0), the method (20) comprising: by a first network device (a), encrypting (S4) an identification code of the first network device (a) with a first private key and a second public key; by a second network device (b), decrypting (S6) the identification code of the first network device (a) using a second private key matching the second public key and a first public key matching the first private key and validating (S7, S8) the identification code at a validation server (13); negotiating (S9) a symmetric key between the first network device (a) and the second network device (b); and encrypting (S, S11) subsequent communication between the first network device (a) and the second network device (b) using the negotiated symmetric key. 2. The method (20) according to claim 1, wherein the first and/or the second network device () are smart meters in the smart grid power network (0) , wherein negotiating the symmetric key comprises using a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol.. The method (20) according to one of the claims 1 to 4, wherein the first private key is a hardware serial number unique to the first network device (a), and wherein the hardware serial number is stored in the first network device (a). 6. The method (20) according to claim, wherein the validation server (13) is a remote server of the manufacturer of the first network device (a). 7. A network device () in a smart grid power network (0), the network device () comprising: a storage unit (3) configured to store an identification code of the network device () and an asymmetric key pair including a public key and a private key; an authentication unit (2) configured to read out the identification code and the private key of the storage unit (3) and to encrypt the identification code using the private key; a communication unit (4) configured to send the encrypted identification code to another network device in the smart grid power network (0); and an encryption unit (1) configured to negotiate a symmetric key with the other network device and to encrypt communication between the network device () and the other network device using the negotiated symmetric key. 8. The network device () according to claim 7, wherein the network device () is a smart meter in the smart grid power network (0). 9. The network device () according to one of the claims 7 and 8, wherein the negotiated symmetric key has a temporally limited validity.. The network device () according to one of the claims 7 to 9, wherein the encryption unit (1) is configured to negotiate a symmetric key with the other network device using a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol. 11. The network device () according to one of the claims 7 to, wherein the identification code is a hardware serial number unique to the network device (). 3. The method (20) according to one of the claims 1 and 2, wherein the negotiated symmetric key has a temporally limited validity. 4. The method (20) according to one of the claims 1 to 12. The network device () according to claim 11, wherein the hardware serial number is stored in a validation server (13) of the manufacturer of the network device (). 7
8 11 EP A A smart grid power network (0), comprising a plurality of network devices () according to one of the claims 7 to
9 EP A1 9
10 EP A1
11 EP A1 11
12 EP A1 12
13 EP A1 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Patent documents cited in the description US A1 [0004] US A1 [000] Non-patent literature cited in the description Open Metering System Specification. Primary Communication, January 2011, vol. 2 [0006] 13
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/34
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ Z47A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
TEPZZ _968ZZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 234 069 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.09.2010 Bulletin 2010/39 (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09364002.7 (22) Date of filing:
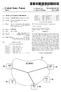
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 234 069 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.09.2010 Bulletin 2010/39 (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09364002.7 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 74_475A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 74_47A_T (11) EP 2 741 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.06.14 Bulletin 14/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 131968.6 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 74_47A_T (11) EP 2 741 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.06.14 Bulletin 14/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 131968.6 (22) Date of
TEPZZ 8_8997A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 ( ) G11B 20/00 ( ) G06Q 10/00 ( )
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
TEPZZ 6 8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/13
 (19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/24 ( ) WU, Qin
 (19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
TEPZZ Z7999A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B05B 15/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 98 _55A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60W 30/14 ( ) B60W 50/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
(19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/37
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/56 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
TEPZZ Z5_748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
TEPZZ 78779ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
TEPZZ 85 9Z_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
TEPZZ 99894ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ _4748 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ _9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/29
 (19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/45
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/33
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
TEPZZ _7655_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
(19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
TEPZZ_5 695B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ _Z_56ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 5976 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G08G 5/00 ( ) H04M 1/725 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
(19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS
 FCOOK.001PR PATENT SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0001] Embodiments of various inventive features will now be described with reference to the
FCOOK.001PR PATENT SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0001] Embodiments of various inventive features will now be described with reference to the
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/32
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application
 From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/08 ( ) G06K 17/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /08 (12.01) G06K 17/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417090.
(19) TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /08 (12.01) G06K 17/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417090.
TEPZZ Z99Z87A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 4/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z99Z87A_T (11) EP 3 099 087 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.11.16 Bulletin 16/48 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/00 (09.01) (21) Application number: 169669.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ Z99Z87A_T (11) EP 3 099 087 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.11.16 Bulletin 16/48 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/00 (09.01) (21) Application number: 169669.7 (22) Date of filing:
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
TEPZZ 7989 ZA T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 ( ) A01B 79/02 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7989 ZA T (11) EP 2 798 9 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 0.11.14 Bulletin 14/4 (1) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 (06.01) A01B 79/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 14166701.4
(19) TEPZZ 7989 ZA T (11) EP 2 798 9 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 0.11.14 Bulletin 14/4 (1) Int Cl.: A01C 21/00 (06.01) A01B 79/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 14166701.4
A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING
 A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING 5 The present invention relates generally to a system and method for enabling short-term financing, and finds particular, although not exclusive, utility in invoice
A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING 5 The present invention relates generally to a system and method for enabling short-term financing, and finds particular, although not exclusive, utility in invoice
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK
 SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
TEPZZ 8_8995A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8_899A_T (11) EP 2 818 99 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.14 Bulletin /01 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1317396.1 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 8_899A_T (11) EP 2 818 99 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.14 Bulletin /01 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1317396.1 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen
 l 1 L L IL L. I 1 L _ I L L L L US008536920B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2013 (54) CLOCK CIRCUIT WITH DELAY FUNCTIONS AND RELATED METHOD
l 1 L L IL L. I 1 L _ I L L L L US008536920B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2013 (54) CLOCK CIRCUIT WITH DELAY FUNCTIONS AND RELATED METHOD
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9660456B2 (12) United States Patent Dwelley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SWITCHING OF CONDUCTOR PAIR IN POWER
USOO9660456B2 (12) United States Patent Dwelley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SWITCHING OF CONDUCTOR PAIR IN POWER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
(19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(51) Int Cl.: H04N 5/232 ( ) H04N 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
(19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM
 Technical Disclosure Commons InVue Defensive Publications Defensive Publications Series August 11, 2017 ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM InVue Security Products
Technical Disclosure Commons InVue Defensive Publications Defensive Publications Series August 11, 2017 ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM InVue Security Products
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/14
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News
 August 2008 INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News All patent publication events including grants are now covered in the INPADOC Legal Status for all authorities In the INPADOCDB and INPAFAMDB files, all patent publication
August 2008 INPADOCDB/INPAFAMDB News All patent publication events including grants are now covered in the INPADOC Legal Status for all authorities In the INPADOCDB and INPAFAMDB files, all patent publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager
 Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
System and method for encoding and decoding data files
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 7,246,177 Anton, et al. July 17, 2007 System and method for encoding and decoding data files Abstract Distributed compression of a data file can comprise a master server
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 7,246,177 Anton, et al. July 17, 2007 System and method for encoding and decoding data files Abstract Distributed compression of a data file can comprise a master server
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
-3- Additionally or alternatively, the invention may comprise a method of controlling access to a digital wallet, the method comprising the steps:
 -1- Secure Multiparty loss resistant Storage and Transfer of Cryptographic Keys for blockchain based systems in conjunction with a wallet management system 1 This invention relates generally to computer
-1- Secure Multiparty loss resistant Storage and Transfer of Cryptographic Keys for blockchain based systems in conjunction with a wallet management system 1 This invention relates generally to computer
Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport. Contract n ILSE - User manual
 Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport Contract n 4810020050102005367 GIM Geographic Information Management nv C05474B June 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 ABOUT ILSE... 1 1.1 Purpose of ILSE... 1 1.2 System
Eurostat - Unit D4: Energy and Transport Contract n 4810020050102005367 GIM Geographic Information Management nv C05474B June 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 ABOUT ILSE... 1 1.1 Purpose of ILSE... 1 1.2 System
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
402\ USER SENDs TO TIME SIAMPING SMTP SERVER
 US 2004.0003255A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0003255A1 ApVrille et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2004 (54) SECURE EMAIL TIME STAMPING Publication Classification
US 2004.0003255A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0003255A1 ApVrille et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2004 (54) SECURE EMAIL TIME STAMPING Publication Classification
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 11/14 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 014 266 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.01.08 Bulletin 08/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 11/14 (06.01) (21) Application number:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 014 266 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.01.08 Bulletin 08/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 11/14 (06.01) (21) Application number:
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/56 ( ) (54) Packet flow control in a communication network based on flow control agents
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 892 894 A1 (43) Date of publication: 27.02.08 Bulletin 08/09 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06119460.1 (22) Date of filing: 24.08.06
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 892 894 A1 (43) Date of publication: 27.02.08 Bulletin 08/09 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06119460.1 (22) Date of filing: 24.08.06
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2
 USOO6649849B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2 Bass et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) HANDHELD MAILING SYSTEM 5,710.706 A * 1/1998 Marklet al.... 177/25.15 6,153,835
USOO6649849B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2 Bass et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) HANDHELD MAILING SYSTEM 5,710.706 A * 1/1998 Marklet al.... 177/25.15 6,153,835
TEPZZ 7565ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/931 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 76ZB_T (11) EP 2 37 60 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 11.09.13 Bulletin 13/37 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/931 (13.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 76ZB_T (11) EP 2 37 60 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 11.09.13 Bulletin 13/37 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/931 (13.01) (21) Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
(51) Int Cl.: H04Q 1/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002
 US006418141B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) MULTI-CAST ENABLED WEB SERVER 6,011,782 A * 1/2000 DeSimone et al...... 370/260 6,038,601
US006418141B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) MULTI-CAST ENABLED WEB SERVER 6,011,782 A * 1/2000 DeSimone et al...... 370/260 6,038,601
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
Utility Patent Application Number 15/486,987
 Utility Patent Application Number 15/486,987 Electronic Filing System ID 28922251 Application Number 15486987 Confirmation Number 1044 Title of Invention Method of Authenticating and Exchanging Virtual
Utility Patent Application Number 15/486,987 Electronic Filing System ID 28922251 Application Number 15486987 Confirmation Number 1044 Title of Invention Method of Authenticating and Exchanging Virtual
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
Method and system for processing event-triggered transactions
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent Application 20050289014 Kind Code A1 Butler, James M. December 29, 2005 Method and system for processing event-triggered transactions Abstract The invention relates to a
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent Application 20050289014 Kind Code A1 Butler, James M. December 29, 2005 Method and system for processing event-triggered transactions Abstract The invention relates to a
Core Wireless Licensing S.a.r.l. v. Apple, Inc. Doc. 1 Att. 3 EXHIBIT 2. Dockets.Justia.com
 Core Wireless Licensing S.a.r.l. v. Apple, Inc. Doc. 1 Att. 3 EXHIBIT 2 Dockets.Justia.com 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007606910B2 (12) United States Patent Bajko
Core Wireless Licensing S.a.r.l. v. Apple, Inc. Doc. 1 Att. 3 EXHIBIT 2 Dockets.Justia.com 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007606910B2 (12) United States Patent Bajko
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/29
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 477 149 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/29 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/02 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 12150906.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 477 149 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/29 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/02 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 12150906.1 (22) Date of filing:
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
eifu Trauma and Extremities
 Electronic Instructions for Use eifu Trauma and Extremities 1 Instructions for use of T&E products are available on the Stryker eifu website 2 Benefits Environmental aspect less paper, possible smaller
Electronic Instructions for Use eifu Trauma and Extremities 1 Instructions for use of T&E products are available on the Stryker eifu website 2 Benefits Environmental aspect less paper, possible smaller
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) GCRP - November 2009
 European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) GCRP - November 2009 Contents Who are ENTSO-E? Background and legal standing Activities and Remit European Network Code Development
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) GCRP - November 2009 Contents Who are ENTSO-E? Background and legal standing Activities and Remit European Network Code Development
BASIC PRICE LIST. The price of transportation is added toll in the amount of CZK 1,30 / kg and the current fuel surcharge.
 BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
BASIC PRICE LIST Shipping weight Shipment to 1 kg 5 kg 10 kg 15 kg 20 kg 25 kg 30 kg 40 kg 50 kg Delivery time BE BELGIUM 445 700 720 760 830 860 890 1050 1120 2-3 days BG BULGARIA 520 915 1485 2050 2620
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2
 USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Ray, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2011
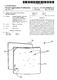 US 2011 0302835A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0302835 A1 Ray, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2011 (54) SEED LABELS AND MANUFACTURING B32B 37/6 (2006.01)
US 2011 0302835A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0302835 A1 Ray, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2011 (54) SEED LABELS AND MANUFACTURING B32B 37/6 (2006.01)
TMCH Report March February 2017
 TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
