Statistics: Normal Distribution, Sampling, Function Fitting & Regression Analysis (Grade 12) *
|
|
|
- Merry Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OpenStax-CNX module: m Statistics: Normal Distribution, Sampling, Function Fitting & Regression Analysis (Grade 12) * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License Introduction In this chapter, you will use the mean, median, mode and standard deviation of a set of data to identify whether the data is normally distributed or whether it is skewed. You will learn more about populations and selecting dierent kinds of samples in order to avoid bias. You will work with lines of best t, and learn how to nd a regression equation and a correlation coecient. You will analyse these measures in order to draw conclusions and make predictions. 2 A Normal Distribution 2.1 Investigation : You are given a table of data below Table 1 1. Calculate the mean, median, mode and standard deviation of the data. 2. What percentage of the data is within one standard deviation of the mean? 3. Draw a histogram of the data using intervals 60 x < 64, 64 x < 68, etc. 4. Join the midpoints of the bars to form a frequency polygon. If large numbers of data are collected from a population, the graph will often have a bell shape. If the data was, say, examination results, a few learners usually get very high marks, a few very low marks and most get a mark in the middle range. We say a distribution is normal if * Version 1.1: Aug 1, :55 am
2 OpenStax-CNX module: m the mean, median and mode are equal. it is symmetric around the mean. ±68% of the sample lies within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations and 99% within three standard deviations of the mean. Figure 1 What happens if the test was very easy or very dicult? Then the distribution may not be symmetrical. If extremely high or extremely low scores are added to a distribution, then the mean tends to shift towards these scores and the curve becomes skewed. If the test was very dicult, the mean score is shifted to the left. In this case, we say the distribution is positively skewed, or skewed right. If it was very easy, then many learners would get high scores, and the mean of the distribution would be shifted to the right. We say the distribution is negatively skewed, or skewed left. Figure 2 Figure 3
3 OpenStax-CNX module: m Normal Distribution 1. Given the pairs of normal curves below, sketch the graphs on the same set of axes and show any relation between them. An important point to remember is that the area beneath the curve corresponds to 100%. a. Mean = 8, standard deviation = 4 and Mean = 4, standard deviation = 8 b. Mean = 8, standard deviation = 4 and Mean = 16, standard deviation = 4 c. Mean = 8, standard deviation = 4 and Mean = 8, standard deviation = 8 2. After a class test, the following scores were recorded: Test Score Frequency Total 64 Mean 6 Standard Deviation 1,2 Table 2 a. Draw the histogram of the results. b. Join the midpoints of each bar and draw a frequency polygon. c. What mark must one obtain in order to be in the top 2% of the class? d. Approximately 84% of the pupils passed the test. What was the pass mark? e. Is the distribution normal or skewed? 3. In a road safety study, the speed of 175 cars was monitored along a specic stretch of highway in order to nd out whether there existed any link between high speed and the large number of accidents along the route. A frequency table of the results is drawn up below. Speed (km.h 1 ) Number of cars (Frequency)
4 OpenStax-CNX module: m Table 3 The mean speed was determined to be around 82 km.h 1 while the median speed was worked out to be around 84,5 km.h 1. a. Draw a frequency polygon to visualise the data in the table above. b. Is this distribution symmetrical or skewed left or right? Give a reason fro your answer. 3 Extracting a Sample Population Suppose you are trying to nd out what percentage of South Africa's population owns a car. One way of doing this might be to send questionnaires to peoples homes, asking them whether they own a car. However, you quickly run into a problem: you cannot hope to send every person in the country a questionnaire, it would be far to expensive. Also, not everyone would reply. The best you can do is send it to a few people, see what percentage of these own a car, and then use this to estimate what percentage of the entire country own cars. This smaller group of people is called the sample population. The sample population must be carefully chosen, in order to avoid biased results. How do we do this? First, it must be representative. If all of our sample population comes from a very rich area, then almost all will have cars. But we obviously cannot conclude from this that almost everyone in the country has a car! We need to send the questionnaire to rich as well as poor people. Secondly, the size of the sample population must be large enough. It is no good having a sample population consisting of only two people, for example. Both may very well not have cars. But we obviously cannot conclude that no one in the country has a car! The larger the sample population size, the more likely it is that the statistics of our sample population corresponds to the statistics of the entire population. So how does one ensure that ones sample is representative? There are a variety of methods available, which we will look at now. 1. Random Sampling. Every person in the country has an equal chance of being selected. It is unbiased and also independant, which means that the selection of one person has no eect on the selection on another. One way of doing this would be to give each person in the country a number, and then ask a computer to give us a list of random numbers. We could then send the questionnaire to the people corresponding to the random numbers. 2. Systematic Sampling. Again give every person in the country a number, and then, for example, select every hundredth person on the list. So person with number 1 would be selected, person with number 100 would be selected, person with number 200 would be selected, etc. 3. Stratied Sampling. We consider dierent subgroups of the population, and take random samples from these. For example, we can divide the population into male and female, dierent ages, or into dierent income ranges. 4. Cluster Sampling. Here the sample is concentrated in one area. For example, we consider all the people living in one urban area. 3.1 Sampling 1. Discuss the advantages, disadvantages and possible bias when using a. systematic sampling b. random sampling c. cluster sampling 2. Suggest a suitable sampling method that could be used to obtain information on: a. passengers views on availability of a local taxi service. b. views of learners on school meals.
5 OpenStax-CNX module: m c. defects in an item made in a factory. d. medical costs of employees in a large company. 3. 2% of a certain magazines' subscribers is randomly selected. The random number 16 out of 50, is selected. Then subscribers with numbers 16, 66, 116, 166,... are chosen as a sample. What kind of sampling is this? 4 Function Fitting and Regression Analysis In Grade 11 we recorded two sets of data (bivariate data) on a scatter plot and then we drew a line of best t as close to as many of the data items as possible. Regression analysis is a method of nding out exactly which function best ts a given set of data. We can nd out the equation of the regression line by drawing and estimating, or by using an algebraic method called the least squares method, available on most scientic calculators. The linear regression equation is written ^y= a + bx (we say y-hat) or y = A + Bx. Of course these are both variations of a more familiar equation y = mx + c. Suppose you are doing an experiment with washing dishes. You count how many dishes you begin with, and then nd out how long it takes to nish washing them. So you plot the data on a graph of time taken versus number of dishes. This is plotted below. Figure 4 If t is the time taken, and d the number of dishes, then it looks as though t is proportional to d, ie. t = m d, where m is the constant of proportionality. There are two questions that interest us now. 1. How do we nd m? One way you have already learnt, is to draw a line of best-t through the data points, and then measure the gradient of the line. But this is not terribly precise. Is there a better way of doing it? 2. How well does our line of best t really t our data? If the points on our plot don't all lie close to the line of best t, but are scattered everywhere, then the t is not 'good', and our assumption that t = m d might be incorrect. Can we nd a quantitative measure of how well our line really ts the data? In this chapter, we answer both of these questions, using the techniques of regression analysis. Phet simulation for curve tting This media object is a Flash object. Please view or download it at < Figure 5 Exercise 1: Fitting by hand (Solution on p. 7.) Use the data given to draw a scatter plot and line of best t. Now write down the equation of the line that best seems to t the data.
6 OpenStax-CNX module: m x 1,0 2,4 3,1 4,9 5,6 6,2 y 2,5 2,8 3,0 4,8 5,1 5,3 Table 4
7 OpenStax-CNX module: m Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Exercise (p. 5) Step 1. The rst step is to draw the graph. This is shown below. Figure 6 Step 2. The equation of the line is y = mx + c (6) From the graph we have drawn, we estimate the y-intercept to be 1,5. We estimate that y = 3, 5 when x = 3. So we have that points (3; 3, 5) and (0; 1, 5) lie on the line. The gradient of the line, m, is given by m = y2 y1 x 2 x 1 = 3,5 1,5 3 0 = 2 3 So we nally have that the equation of the line of best t is (6) y = 2 x + 1, 5 (6) 3
Slide Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION. Chapter 13. Statistics Sampling Techniques
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide - Chapter Statistics. Sampling Techniques Statistics Statistics is the art and science of gathering, analyzing, and making inferences from numerical information
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide - Chapter Statistics. Sampling Techniques Statistics Statistics is the art and science of gathering, analyzing, and making inferences from numerical information
Further Maths Notes. Common Mistakes. Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry. Write equations in terms of variables
 Further Maths Notes Common Mistakes Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry Remember to interpret data with the multipliers specified (e.g. in thousands) Write equations in terms of variables
Further Maths Notes Common Mistakes Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry Remember to interpret data with the multipliers specified (e.g. in thousands) Write equations in terms of variables
STA 570 Spring Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1
 STA 570 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1 Descriptive Statistics Summarizing Univariate Data o Standard Deviation, Empirical Rule, IQR o Boxplots Summarizing Bivariate Data o Contingency Tables o Row
STA 570 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1 Descriptive Statistics Summarizing Univariate Data o Standard Deviation, Empirical Rule, IQR o Boxplots Summarizing Bivariate Data o Contingency Tables o Row
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
WELCOME! Lecture 3 Thommy Perlinger
 Quantitative Methods II WELCOME! Lecture 3 Thommy Perlinger Program Lecture 3 Cleaning and transforming data Graphical examination of the data Missing Values Graphical examination of the data It is important
Quantitative Methods II WELCOME! Lecture 3 Thommy Perlinger Program Lecture 3 Cleaning and transforming data Graphical examination of the data Missing Values Graphical examination of the data It is important
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
8: Statistics. Populations and Samples. Histograms and Frequency Polygons. Page 1 of 10
 8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Univariate Statistics Summary
 Further Maths Univariate Statistics Summary Types of Data Data can be classified as categorical or numerical. Categorical data are observations or records that are arranged according to category. For example:
Further Maths Univariate Statistics Summary Types of Data Data can be classified as categorical or numerical. Categorical data are observations or records that are arranged according to category. For example:
The first few questions on this worksheet will deal with measures of central tendency. These data types tell us where the center of the data set lies.
 Instructions: You are given the following data below these instructions. Your client (Courtney) wants you to statistically analyze the data to help her reach conclusions about how well she is teaching.
Instructions: You are given the following data below these instructions. Your client (Courtney) wants you to statistically analyze the data to help her reach conclusions about how well she is teaching.
Functions and Graphs: Graphs of Inverse Functions (Grade 12) *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m39282 1 Functions and Graphs: Graphs of Inverse Functions (Grade 12) * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m39282 1 Functions and Graphs: Graphs of Inverse Functions (Grade 12) * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Box Plots. OpenStax College
 Connexions module: m46920 1 Box Plots OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Box plots (also called box-and-whisker
Connexions module: m46920 1 Box Plots OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Box plots (also called box-and-whisker
MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES
 MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES SPECIAL NOTE: These resources were assembled to assist in student readiness for their upcoming Algebra 1 EOC. Although these resources have been compiled for your
MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES SPECIAL NOTE: These resources were assembled to assist in student readiness for their upcoming Algebra 1 EOC. Although these resources have been compiled for your
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution. Measures of center and spread. Features of the normal distribution
 Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Section 4.4: Parabolas
 Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
 11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data. 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data
 Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data 2.2 Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data 2.3 Stem-and-leaf Displays 2.4 Dotplots 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative
Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data 2.2 Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data 2.3 Stem-and-leaf Displays 2.4 Dotplots 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Compare quadrilaterals for similarities and differences *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m31291 1 Compare quadrilaterals for similarities and differences * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m31291 1 Compare quadrilaterals for similarities and differences * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Normal Distribution. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file
 1 SPSS Guide 2009 Content 1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis. 3 2. Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file 3 4 3. Data Analysis/ Frequencies. 5 4. Recoding the variable into classes.. 5 5. Data Analysis/
1 SPSS Guide 2009 Content 1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis. 3 2. Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file 3 4 3. Data Analysis/ Frequencies. 5 4. Recoding the variable into classes.. 5 5. Data Analysis/
M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes.
 M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes. Population: Census: Biased: Sample: The entire group of objects or individuals considered
M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes. Population: Census: Biased: Sample: The entire group of objects or individuals considered
Distributions of Continuous Data
 C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
Averages and Variation
 Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Ex.1 constructing tables. a) find the joint relative frequency of males who have a bachelors degree.
 Two-way Frequency Tables two way frequency table- a table that divides responses into categories. Joint relative frequency- the number of times a specific response is given divided by the sample. Marginal
Two-way Frequency Tables two way frequency table- a table that divides responses into categories. Joint relative frequency- the number of times a specific response is given divided by the sample. Marginal
Elementary Statistics
 1 Elementary Statistics Introduction Statistics is the collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, and then organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing
1 Elementary Statistics Introduction Statistics is the collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, and then organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing
Chapter 5snow year.notebook March 15, 2018
 Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
Lecture Series on Statistics -HSTC. Frequency Graphs " Dr. Bijaya Bhusan Nanda, Ph. D. (Stat.)
 Lecture Series on Statistics -HSTC Frequency Graphs " By Dr. Bijaya Bhusan Nanda, Ph. D. (Stat.) CONTENT Histogram Frequency polygon Smoothed frequency curve Cumulative frequency curve or ogives Learning
Lecture Series on Statistics -HSTC Frequency Graphs " By Dr. Bijaya Bhusan Nanda, Ph. D. (Stat.) CONTENT Histogram Frequency polygon Smoothed frequency curve Cumulative frequency curve or ogives Learning
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data
 Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
OpenStax-CNX module: m Quadratic Functions. OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49337 1 Quadratic Functions OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m49337 1 Quadratic Functions OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA
 CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
Central Limit Theorem Sample Means
 Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1. Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016)
 CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
OpenStax-CNX module: m The Ellipse. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART 2 - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES
 STP 6 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES Chapter covered organizing data into tables, and summarizing data with graphical displays. We will now use
STP 6 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES Chapter covered organizing data into tables, and summarizing data with graphical displays. We will now use
demonstrate an understanding of the exponent rules of multiplication and division, and apply them to simplify expressions Number Sense and Algebra
 MPM 1D - Grade Nine Academic Mathematics This guide has been organized in alignment with the 2005 Ontario Mathematics Curriculum. Each of the specific curriculum expectations are cross-referenced to the
MPM 1D - Grade Nine Academic Mathematics This guide has been organized in alignment with the 2005 Ontario Mathematics Curriculum. Each of the specific curriculum expectations are cross-referenced to the
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I
 UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 1
 MATH 115: Review for Chapter 1 Can you use the Distance Formula to find the distance between two points? (1) Find the distance d P, P between the points P and 1 1, 6 P 10,9. () Find the length of the line
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 1 Can you use the Distance Formula to find the distance between two points? (1) Find the distance d P, P between the points P and 1 1, 6 P 10,9. () Find the length of the line
Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error
 AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department. YEAR 11 GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet
 PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department YEAR GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet Name: _ Class: Teacher: GEOMETRY & MEASURES Area, Perimeter, Volume & Circles AREA FORMULAS Area is the space a 2D
PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department YEAR GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet Name: _ Class: Teacher: GEOMETRY & MEASURES Area, Perimeter, Volume & Circles AREA FORMULAS Area is the space a 2D
Position vs Time Graphs *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m54110 1 Position vs Time Graphs * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m54110 1 Position vs Time Graphs * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this
Chapter 2. Frequency distribution. Summarizing and Graphing Data
 Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Chapter 11. Worked-Out Solutions Explorations (p. 585) Chapter 11 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 583)
 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 3) 1. After School Activities. Pets Frequency 1 1 3 7 Number of activities 3. Students Favorite Subjects Math English Science History Frequency 1 1 1 3 Number of
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 3) 1. After School Activities. Pets Frequency 1 1 3 7 Number of activities 3. Students Favorite Subjects Math English Science History Frequency 1 1 1 3 Number of
1. Determine the population mean of x denoted m x. Ans. 10 from bottom bell curve.
 6. Using the regression line, determine a predicted value of y for x = 25. Does it look as though this prediction is a good one? Ans. The regression line at x = 25 is at height y = 45. This is right at
6. Using the regression line, determine a predicted value of y for x = 25. Does it look as though this prediction is a good one? Ans. The regression line at x = 25 is at height y = 45. This is right at
LASER s Level 2 Maths Course - Summary
 LASER s Level 2 Maths Course - Summary Unit Code Unit Title Credits Level Status SER945 Shape, Space and Measurement 3 2 Mandatory SER946 Collecting, Recording and Analysing Data 3 2 Mandatory SER947 Development
LASER s Level 2 Maths Course - Summary Unit Code Unit Title Credits Level Status SER945 Shape, Space and Measurement 3 2 Mandatory SER946 Collecting, Recording and Analysing Data 3 2 Mandatory SER947 Development
The Normal Distribution
 14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
Algebra II: Strand 3. Quadratic Functions; Topic 2. Digging Deeper; Task 3.2.1
 1 TASK 3..1: PUTTING IT TOGETHER Solutions 1. Each of the following quadratic functions is given in standard form ( y = ax + bx + c ). For each function: Transform the function to the form y = a(x h) +
1 TASK 3..1: PUTTING IT TOGETHER Solutions 1. Each of the following quadratic functions is given in standard form ( y = ax + bx + c ). For each function: Transform the function to the form y = a(x h) +
Vocabulary. 5-number summary Rule. Area principle. Bar chart. Boxplot. Categorical data condition. Categorical variable.
 5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 2.1- #
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version]
![Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version]](/thumbs/72/67574169.jpg) Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data
 Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters. Graphs are
Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters. Graphs are
UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA
 A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means
 Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function
 Lesson 35 Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 2: Functions and Algebra Assessment Standard Generate
Lesson 35 Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 2: Functions and Algebra Assessment Standard Generate
Higher tier unit 6a check in test. Calculator
 Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
Distributions of random variables
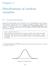 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Female Brown Bear Weights
 CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
St Aloysius College. Mark: Name: Grade 9 Mathematics COMMON ASSESSMENT TASK Graphing Linear Algebra
 St Aloysius College Name: Grade 9 Mathematics COMMON ASSESSMENT TASK Graphing Linear Algebra Mark: Instructions: Neatly show all working out and answers in the space provided. CALCULATORS ALLOWED / Question
St Aloysius College Name: Grade 9 Mathematics COMMON ASSESSMENT TASK Graphing Linear Algebra Mark: Instructions: Neatly show all working out and answers in the space provided. CALCULATORS ALLOWED / Question
1MA1 Practice Tests Set 1: Paper 1F (Regular) mark scheme Version 1.0 Question Working Answer Mark Notes
 1 5, 3, 4, 6, 9 1 B1 cao 2 4.3 1 B1 cao 3 3/10 1 B1 oe 4 70% 1 B1 cao 5 916(30 5 2 M1 30 (16 + 9) or 30 16 9 or 30 9 16 6 4 2 M1 for correct order of operations +7 then 3 M1 for forming the equation 3x
1 5, 3, 4, 6, 9 1 B1 cao 2 4.3 1 B1 cao 3 3/10 1 B1 oe 4 70% 1 B1 cao 5 916(30 5 2 M1 30 (16 + 9) or 30 16 9 or 30 9 16 6 4 2 M1 for correct order of operations +7 then 3 M1 for forming the equation 3x
1MA1 Practice Tests Set 1: Paper 1F (Regular) mark scheme Version 1.0 Question Working Answer Mark Notes
 5, 3, 4, 6, 9 B cao 4.3 B cao 3 3/0 B oe 4 70% B cao 5 96(30 5 M 30 (6 + 9) or 30 6 9 or 30 9 6 6 4 M for correct order of operations +7 then 3 7 60 5.50 3 M for forming the equation 3x 7 = 5 and showing
5, 3, 4, 6, 9 B cao 4.3 B cao 3 3/0 B oe 4 70% B cao 5 96(30 5 M 30 (6 + 9) or 30 6 9 or 30 9 6 6 4 M for correct order of operations +7 then 3 7 60 5.50 3 M for forming the equation 3x 7 = 5 and showing
Key: 5 9 represents a team with 59 wins. (c) The Kansas City Royals and Cleveland Indians, who both won 65 games.
 AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 6.3: Measures of Position
 Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
Year 8 End of Year Exams Revision List
 Year 8 End of Year Exams Revision List All students will expected to be confident with the appropriate year 7 learning objectives as follows Target 1-3 must be confident with year 7 target 1-3 Target 2-4
Year 8 End of Year Exams Revision List All students will expected to be confident with the appropriate year 7 learning objectives as follows Target 1-3 must be confident with year 7 target 1-3 Target 2-4
Chapter 2: Understanding Data Distributions with Tables and Graphs
 Test Bank Chapter 2: Understanding Data with Tables and Graphs Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following would best depict nominal level data? a. pie chart b. line graph c. histogram d. polygon Ans: A
Test Bank Chapter 2: Understanding Data with Tables and Graphs Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following would best depict nominal level data? a. pie chart b. line graph c. histogram d. polygon Ans: A
Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions. Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc
 Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1-1 Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution (or Frequency Table) It shows how a data set is partitioned among
Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1-1 Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution (or Frequency Table) It shows how a data set is partitioned among
Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things.
 + What is Data? Data is a collection of facts. Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things. In most cases, data needs to be interpreted and
+ What is Data? Data is a collection of facts. Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things. In most cases, data needs to be interpreted and
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency
 Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2
 Year 11 General Maths Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 Bivariate Data Chapter 4 Chapter Four 1 st Edition 2 nd Edition 2013 4A 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 2F (FM) 1,
Year 11 General Maths Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 Bivariate Data Chapter 4 Chapter Four 1 st Edition 2 nd Edition 2013 4A 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 2F (FM) 1,
Middle School Math Course 3
 Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Mathematics Grade 8 (2012) (1) Mathematical process standards.
Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Mathematics Grade 8 (2012) (1) Mathematical process standards.
Learner Expectations UNIT 1: GRAPICAL AND NUMERIC REPRESENTATIONS OF DATA. Sept. Fathom Lab: Distributions and Best Methods of Display
 CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
Grade 8 - geometry investigation - Rene Rix *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m35699 1 Grade 8 - geometry investigation - Rene Rix * Pinelands High School This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 An
OpenStax-CNX module: m35699 1 Grade 8 - geometry investigation - Rene Rix * Pinelands High School This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 An
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2. Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Measures of Central Tendency
 Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
[Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment satisfying x = 3] (b) y = x drawn 1 B1 for y = x drawn
![[Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment satisfying x = 3] (b) y = x drawn 1 B1 for y = x drawn [Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment satisfying x = 3] (b) y = x drawn 1 B1 for y = x drawn](/thumbs/85/91731873.jpg) 1. (a) x = 3 drawn 1 B1 for x = 3 drawn (b) y = x drawn 1 B1 for y = x drawn [Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment satisfying x = 3] [Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment
1. (a) x = 3 drawn 1 B1 for x = 3 drawn (b) y = x drawn 1 B1 for y = x drawn [Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment satisfying x = 3] [Note: each line drawn must be a single line segment
2.1 Objectives. Math Chapter 2. Chapter 2. Variable. Categorical Variable EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES
 EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 Objectives 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 Objectives 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
SHAPE, SPACE & MEASURE
 STAGE 1 Know the place value headings up to millions Recall primes to 19 Know the first 12 square numbers Know the Roman numerals I, V, X, L, C, D, M Know the % symbol Know percentage and decimal equivalents
STAGE 1 Know the place value headings up to millions Recall primes to 19 Know the first 12 square numbers Know the Roman numerals I, V, X, L, C, D, M Know the % symbol Know percentage and decimal equivalents
3 Graphical Displays of Data
 3 Graphical Displays of Data Reading: SW Chapter 2, Sections 1-6 Summarizing and Displaying Qualitative Data The data below are from a study of thyroid cancer, using NMTR data. The investigators looked
3 Graphical Displays of Data Reading: SW Chapter 2, Sections 1-6 Summarizing and Displaying Qualitative Data The data below are from a study of thyroid cancer, using NMTR data. The investigators looked
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
Section Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
Getting to Know Your Data
 Chapter 2 Getting to Know Your Data 2.1 Exercises 1. Give three additional commonly used statistical measures (i.e., not illustrated in this chapter) for the characterization of data dispersion, and discuss
Chapter 2 Getting to Know Your Data 2.1 Exercises 1. Give three additional commonly used statistical measures (i.e., not illustrated in this chapter) for the characterization of data dispersion, and discuss
Year 7 Set 1 : Unit 1 : Number 1. Learning Objectives: Level 5
 Year 7 Set 1 : Unit 1 : Number 1 I can place decimals in order of size I can place negative numbers in order of size I can add and subtract negative numbers I can set out and do addition, subtraction,
Year 7 Set 1 : Unit 1 : Number 1 I can place decimals in order of size I can place negative numbers in order of size I can add and subtract negative numbers I can set out and do addition, subtraction,
Year 8 Review 1, Set 1 Number confidence (Four operations, place value, common indices and estimation)
 Year 8 Review 1, Set 1 Number confidence (Four operations, place value, common indices and estimation) Place value Digit Integer Negative number Difference, Minus, Less Operation Multiply, Multiplication,
Year 8 Review 1, Set 1 Number confidence (Four operations, place value, common indices and estimation) Place value Digit Integer Negative number Difference, Minus, Less Operation Multiply, Multiplication,
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs
 Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
5. Compare the volume of a three dimensional figure to surface area.
 5. Compare the volume of a three dimensional figure to surface area. 1. What are the inferences that can be drawn from sets of data points having a positive association and a negative association. 2. Why
5. Compare the volume of a three dimensional figure to surface area. 1. What are the inferences that can be drawn from sets of data points having a positive association and a negative association. 2. Why
