Edexcel Mechanics 2 Kinematics of a particle. Section 1: Projectiles
|
|
|
- Delilah West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Edecel Mechanics Kinematics of a particle Section 1: Projectiles Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Investigating projectiles Modelling assumptions General strateg for projectile questions Components of the velocit Finding the time of flight, range and maimum height Height of projection Investigating projectiles There are several resources on the website which allow ou to investigate projectiles. It is worth tring some of these before working through the chapter, to give ourself a feel for the topic. The Component interactive spreadsheet allows ou to investigate the flight of a projectile as the vertical and horizontal components of the velocit var. The Angle interactive spreadsheet allows ou to investigate how varing the angle of projection affects the range of the projectile. The Projectiles interactive spreadsheet allows ou to view the path of a projectile for which ou can set the initial velocit, the angle of projection and the initial height. Instructions are available. The Projectiles application provides four different activities: two investigations and two worked eamples. Instructions are available. Modelling assumptions The modelling assumptions for projectile motion: the object is a particle the onl force acting is gravit (so there is no air resistance) the ground is a horizontal plane are ver important. Without them, analsing projectiles would be much harder. In man situations these assumptions will not make a significant difference to the final answer, so the are reasonable. However, throwing a flat sheet of paper, for eample, could not usefull be analsed without taking account of the effects of air resistance. 1 of 7 18/04/ MEI
2 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples General strateg for projectile questions The standard wa to solve projectiles questions is to split the velocit of the particle into two components, horizontal and vertical. The equations of motion are then applied to each component of velocit. The main ones used are:- V v u at and 1 s ut at Verticall Horizontall a g a 0 vertical velocit (using v u at ) u Vsin u Vcos horizontal velocit (using v u at ) vertical displacement (using v V sin gt v Vcos 1 1 s ut Vt sin gt at ) Vt cos horizontal displacement where t is the time of flight. 1 (using s ut at ) The diagram shows the path of a projectile with initial velocit V, projected at angle to the horizontal. Components of the velocit The vertical component When the vertical component of velocit is positive, the particle is rising. At the instant the vertical component of velocit is 0, the particle is at maimum height. When the vertical component of velocit is negative, the particle is falling. The horizontal component Remember: THE HORIZONTAL VELOCITY REMAINS CONSTANT. It is worth noting that a particle which is fired from the top of a cliff at 100 ms -1 horizontall and another which is dropped from the top of the same cliff at the same time will land on the ground at the same time! This is because the both have an initial vertical component of velocit of 0 ms -1. Their initial horizontal components of velocit will have no effect on their motion in the vertical direction. Direction of flight The direction of flight depends upon the ratio of the horizontal and vertical velocities. of 7 18/04/ MEI
3 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples As the horizontal velocit remains constant, the direction of flight changes because of the change in the vertical velocit. The direction of flight can be obtained b combining the velocit components in the usual wa: V v Vcos v Vsin v tan v Finding the time of flight, range and maimum height Time of flight The time of flight can be found in two was:- Use v 0 in v u at to find the time to maimum height, and then double it. This onl works if the starting and finishing points are on the same level. 1 Put = h in s ut at, where h is the vertical displacement from its starting point when the particle lands, then solve this quadratic to give t. If the projectile starts and stops at the same level, h = 0. There will be two solutions to the quadratic, but the time when the particle lands must be the greater (think about wh this is the case). Range The range is found b multipling the time of flight with the horizontal component of the velocit. (Remember, for a projectile, the horizontal component of velocit is CONSTANT). It ma be stating the obvious, but the range is alwas increasing whilst the particle is off the ground. Maimum height At the maimum height, the vertical component of velocit is 0, so use v 0 in v u as to get the maimum height and in v u at to get the time to maimum height. Eample 1 A projectile is fired with an initial speed V from a point O on a horizontal plane, the 1 angle of elevation being tan. The particle returns to the plane at a point A. Find the distance OA, in terms of V. Show that the same point could have been reached b 1 firing the particle at the same speed from O, but at an angle of elevation tan. Find, in terms of V, the difference in the times of flights of the two trajectories. of 7 18/04/ MEI
4 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples Solution V O Notice how ou can use Pthagoras s theorem to find the sine and cosine of an angle if ou know its tangent as a fraction. tan, sin, cos To find the time of flight, since the particle lands on the same level as it started, we can find the time to maimum height and then double it: A Verticall: u V sin V v u at V v 0 (at ma height) 0 9.8t a 9.8 V t? t 9.8 The time of flight is double this, 4V so the time of flight is t 0.1V seconds ( s.f) 9.8 Alternativel, put = 0 in the equation 1 ut sin gt The horizontal range is the value of when t takes the above value. Vt cos 4V V 9.8 1V V ( d.p.) If the particle is projected at the same speed, V, but at angle, such that then: tan, sin, cos tan, 4 of 7 18/04/ MEI
5 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples To find the time of flight, find the time to maimum height and then double it, as before: Verticall: u V sin V v 0 (at ma height) a 9.8 t? v u at V 0 9.8t V t 9.8 The time of flight is double this, 6V So the time of flight is 0.170V seconds ( s.f). 9.8 The horizontal range is the value of when t takes the above value. Vt cos 6V V 9.8 1V V ( d.p.) So the ranges are the same. The difference in the times of flight is ( s.f.) 6V 4V V V seconds Height of projection If the object is not projected from ground level, then ou need to be careful to include the initial height in our equations. Eample A ball is projected with a velocit find: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) the maimum height, the time of flight, the range, the angle of flight after 1 second. 4 0 from a position. Assuming g = 10ms of 7 18/04/ MEI
6 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples 5ms -1 The curved line shows the path of the projectile 10m -1 4ms Solution (i) At the maimum height, the vertical velocit is 0. So, using the equation v u as 0 5 (-10) 5 s So the maimum height is 1.5 m above the starting point, 11.5 m above the ground. s (ii) 1 The time of flight can be obtained using s ut at, considering the vertical motion of the projectile. Here s will be 10 m, as we want the time when the particle hits the ground. At this time the particle is 10 m below the starting point. 1 s ut t 10 5t 10 t 1 5t 5t10 0 t t So t 1, which is impossible, or t. The time of flight is seconds. (iii) The range is just the horizontal velocit, which remains constant, multiplied b the time of flight. So the range is 4 = 8 m (iv) The direction of the flight is given b the ratio of the velocities. After 1 second, the vertical velocit is found using v = u + at v 5 ( 10) 1 v 5 The horizontal velocit is still 4 ms -1. It does not change. 6 of 7 18/04/ MEI
7 Edecel M Kinematics 1 Notes and Eamples A 4 ms -1 5 ms -1 Angle of flight: 5 tan A 4 A 51. (s.f.) So, after 1 second, the direction of flight is 51. ( s.f.) below the horizontal. Eample A bo throws a ball horizontall from a point 5.1 m above the horizontal ground. (i) What is the minimum speed at which the ball must be thrown to clear a fence.6 m high at a horizontal distance of 8 m from the point of projection? (ii) Find the distance beond the fence at which the ball strikes the ground if it is projected at this speed? Solution Path of projectile 5.1m.6m (i) In the time the ball travels 8 m 8m horizontall, it must fall a maimum distance of =.5 m if it is to clear the fence. Considering the vertical motion: The time to fall.5 m: u 0 a 9.8 ms s.5 m t? 1 s ut at.5 4.9t t seconds ( s.f.) So the ball travels 8 m horizontall in s, 8 so its initial horizontal speed is = 11. ms-1 ( s.f.), or greater. (ii) The time for the ball to fall to ground level is found as above, ecept that now s = 5.1 m, instead of.5 m. 5.1 So t t 1.0s ( s.f.) 4.9 In 1.0 seconds the ball will travel m (4 s.f.) horizontall, so it will land =.4 m ( s.f.) beond the fence. 7 of 7 18/04/ MEI
OCR Maths M2. Topic Questions from Papers. Projectiles
 OCR Maths M2 Topic Questions from Papers Projectiles PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 21 Aparticleisprojectedhorizontallywithaspeedof6ms 1 from a point 10 m above horizontal ground. The particle moves freely under
OCR Maths M2 Topic Questions from Papers Projectiles PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 21 Aparticleisprojectedhorizontallywithaspeedof6ms 1 from a point 10 m above horizontal ground. The particle moves freely under
(ii) Calculate the maximum height reached by the ball. (iii) Calculate the times at which the ball is at half its maximum height.
 1 Inthis question take g =10. A golf ball is hit from ground level over horizontal ground. The initial velocity of the ball is 40 m s 1 at an angle α to the horizontal, where sin α = 0.6 and cos α = 0.8.
1 Inthis question take g =10. A golf ball is hit from ground level over horizontal ground. The initial velocity of the ball is 40 m s 1 at an angle α to the horizontal, where sin α = 0.6 and cos α = 0.8.
PROJECTILE. 5) Define the terms Velocity as related to projectile motion: 6) Define the terms angle of projection as related to projectile motion:
 1) Define Trajectory a) The path traced by particle in air b) The particle c) Vertical Distance d) Horizontal Distance PROJECTILE 2) Define Projectile a) The path traced by particle in air b) The particle
1) Define Trajectory a) The path traced by particle in air b) The particle c) Vertical Distance d) Horizontal Distance PROJECTILE 2) Define Projectile a) The path traced by particle in air b) The particle
Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical
 Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical With no gravity the projectile would follow the straight-line path (dashed line).
Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical With no gravity the projectile would follow the straight-line path (dashed line).
2.3 Projectile Motion
 Figure 1 An Olympic ski jumper uses his own body as a projectile. projectile an object that moves along a two-dimensional curved trajectory in response to gravity projectile motion the motion of a projectile
Figure 1 An Olympic ski jumper uses his own body as a projectile. projectile an object that moves along a two-dimensional curved trajectory in response to gravity projectile motion the motion of a projectile
Do you know where you are?
 Do ou know where ou are? The missile knows where it is at all times. It knows this because it knows where it isn't. B subtracting where it is from where it isn't, or where it isn't from where it is (whichever
Do ou know where ou are? The missile knows where it is at all times. It knows this because it knows where it isn't. B subtracting where it is from where it isn't, or where it isn't from where it is (whichever
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick A Quiz Review LT ,
 4A Quiz Review LT 3.4 3.10, 4.1 4.3 Key Facts Know how to use the formulas for projectile motion. The formulas will be given to you on the quiz, but you ll need to know what the variables stand for Horizontal:
4A Quiz Review LT 3.4 3.10, 4.1 4.3 Key Facts Know how to use the formulas for projectile motion. The formulas will be given to you on the quiz, but you ll need to know what the variables stand for Horizontal:
Name Period. (b) Now measure the distances from each student to the starting point. Write those 3 distances here. (diagonal part) R measured =
 Lesson 5: Vectors and Projectile Motion Name Period 5.1 Introduction: Vectors vs. Scalars (a) Read page 69 of the supplemental Conceptual Physics text. Name at least 3 vector quantities and at least 3
Lesson 5: Vectors and Projectile Motion Name Period 5.1 Introduction: Vectors vs. Scalars (a) Read page 69 of the supplemental Conceptual Physics text. Name at least 3 vector quantities and at least 3
SPH3U1 Lesson 12 Kinematics
 SPH3U1 Lesson 12 Kinematics PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the motion of an object thrown at arbitrary angles through the air. Describe the horizontal and vertical motions of
SPH3U1 Lesson 12 Kinematics PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the motion of an object thrown at arbitrary angles through the air. Describe the horizontal and vertical motions of
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test
 Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
Parametric Equations: Motion in a Plane Notes for Section 6.3. are parametric equations for the curve.
 Parametric Equations: Motion in a Plane Notes for Section 6.3 In Laman s terms: Parametric equations allow us to put and into terms of a single variable known as the parameter. Time, t, is a common parameter
Parametric Equations: Motion in a Plane Notes for Section 6.3 In Laman s terms: Parametric equations allow us to put and into terms of a single variable known as the parameter. Time, t, is a common parameter
Two-Dimensional Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion Objects don't always move in a straight line. When an object moves in two dimensions, we must look at vector components. The most common kind of two dimensional motion you will encounter
Two-Dimensional Motion Objects don't always move in a straight line. When an object moves in two dimensions, we must look at vector components. The most common kind of two dimensional motion you will encounter
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
Projectile Motion SECTION 3. Two-Dimensional Motion. Objectives. Use of components avoids vector multiplication.
 Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
Math Learning Center Boise State 2010, Quadratic Modeling STEM 10
 Quadratic Modeling STEM 10 Today we are going to put together an understanding of the two physics equations we have been using. Distance: Height : Recall the variables: o acceleration o gravitation force
Quadratic Modeling STEM 10 Today we are going to put together an understanding of the two physics equations we have been using. Distance: Height : Recall the variables: o acceleration o gravitation force
Projectile Motion. Remember that the projectile travels vertically (up and down y) in the same time that it is traveling above the horizontal (x)
 Projectile Motion Consider motion in and y separately Ignore air resistance elocity in -direction is constant Write down positions in and y as a function of time Remember that the projectile traels ertically
Projectile Motion Consider motion in and y separately Ignore air resistance elocity in -direction is constant Write down positions in and y as a function of time Remember that the projectile traels ertically
Vector Decomposition
 Projectile Motion AP Physics 1 Vector Decomposition 1 Coordinate Systems A coordinate system is an artificially imposed grid that you place on a problem. You are free to choose: Where to place the origin,
Projectile Motion AP Physics 1 Vector Decomposition 1 Coordinate Systems A coordinate system is an artificially imposed grid that you place on a problem. You are free to choose: Where to place the origin,
Projectile Trajectory Scenarios
 Projectile Trajectory Scenarios Student Worksheet Name Class Note: Sections of this document are numbered to correspond to the pages in the TI-Nspire.tns document ProjectileTrajectory.tns. 1.1 Trajectories
Projectile Trajectory Scenarios Student Worksheet Name Class Note: Sections of this document are numbered to correspond to the pages in the TI-Nspire.tns document ProjectileTrajectory.tns. 1.1 Trajectories
Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations
 Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations. Determine
Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations. Determine
ASSIGNMENT BETA COVER SHEET
 Question Done Backpack Ready for test ASSIGNMENT BETA COVER SHEET Name Teacher Topic Teacher/student comment Drill A indices Drill B tangents Drill C differentiation Drill D normals Drill E gradient Section
Question Done Backpack Ready for test ASSIGNMENT BETA COVER SHEET Name Teacher Topic Teacher/student comment Drill A indices Drill B tangents Drill C differentiation Drill D normals Drill E gradient Section
Zero Launch Angle. since θ=0, then v oy =0 and v ox = v o. The time required to reach the water. independent of v o!!
 Zero Launch Angle y h since θ=0, then v oy =0 and v ox = v o and based on our coordinate system we have x o =0, y o =h x The time required to reach the water independent of v o!! 1 2 Combining Eliminating
Zero Launch Angle y h since θ=0, then v oy =0 and v ox = v o and based on our coordinate system we have x o =0, y o =h x The time required to reach the water independent of v o!! 1 2 Combining Eliminating
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 9 ARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND OLAR COORDINATES So far we have described plane curves b giving as a function of f or as a function of t or b giving a relation between and that defines implicitl as a function
9 ARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND OLAR COORDINATES So far we have described plane curves b giving as a function of f or as a function of t or b giving a relation between and that defines implicitl as a function
SECTION 6-8 Graphing More General Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions
 6-8 Graphing More General Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions 9 duce a scatter plot in the viewing window. Choose 8 for the viewing window. (B) It appears that a sine curve of the form k
6-8 Graphing More General Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions 9 duce a scatter plot in the viewing window. Choose 8 for the viewing window. (B) It appears that a sine curve of the form k
STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs
 UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
Projectile Motion. Honors Physics
 Projectile Motion Honors Physics What is projectile? Projectile -Any object which projected by some means and continues to moe due to its own inertia (mass). Projectiles moe in TWO dimensions Since a projectile
Projectile Motion Honors Physics What is projectile? Projectile -Any object which projected by some means and continues to moe due to its own inertia (mass). Projectiles moe in TWO dimensions Since a projectile
Lab #4: 2-Dimensional Kinematics. Projectile Motion
 Lab #4: -Dimensional Kinematics Projectile Motion A medieval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.iinet.net.au/~rmine/ht/ht0.html#5 Introduction: In medieval das, people had a ver practical knowledge
Lab #4: -Dimensional Kinematics Projectile Motion A medieval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.iinet.net.au/~rmine/ht/ht0.html#5 Introduction: In medieval das, people had a ver practical knowledge
Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function?
 8.5 Graphing Other Trigonometric Functions Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function? Graphing the Tangent Function Work with a partner. a. Complete the table
8.5 Graphing Other Trigonometric Functions Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function? Graphing the Tangent Function Work with a partner. a. Complete the table
Quadratic Functions In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs. Math Background
 Graphing In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Graphing In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
2. Find RS and the component form of RS. x. b) θ = 236, v = 35 y. b) 4i 3j c) 7( cos 200 i+ sin 200. a) 2u + v b) w 3v c) u 4v + 2w
 Pre Calculus Worksheet 6.1 For questions 1-3, let R = ( 5, 2) and S = (2, 8). 1. Sketch the vector RS and the standard position arrow for this vector. 2. Find RS and the component form of RS. 3. Show algebraicall
Pre Calculus Worksheet 6.1 For questions 1-3, let R = ( 5, 2) and S = (2, 8). 1. Sketch the vector RS and the standard position arrow for this vector. 2. Find RS and the component form of RS. 3. Show algebraicall
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
ABSOLUTE EXTREMA AND THE MEAN VALUE THEOREM
 61 LESSON 4-1 ABSOLUTE EXTREMA AND THE MEAN VALUE THEOREM Definitions (informal) The absolute maimum (global maimum) of a function is the -value that is greater than or equal to all other -values in the
61 LESSON 4-1 ABSOLUTE EXTREMA AND THE MEAN VALUE THEOREM Definitions (informal) The absolute maimum (global maimum) of a function is the -value that is greater than or equal to all other -values in the
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE
 IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
2D Kinematics Projectiles Relative motion
 2D Kinematics Projectiles Relative motion Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 4, 2017 Last time 2 dimensional motion projectile motion height of a projectile Overview range of a projectile trajectory equation
2D Kinematics Projectiles Relative motion Lana heridan De Anza College Oct 4, 2017 Last time 2 dimensional motion projectile motion height of a projectile Overview range of a projectile trajectory equation
Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion. Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University
 Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Vectors What is a vector? Examples? Notation:! a or! a or a 2 Vector Addition Graphical Methods Triangle, parallelogram, polygon
Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Vectors What is a vector? Examples? Notation:! a or! a or a 2 Vector Addition Graphical Methods Triangle, parallelogram, polygon
is a plane curve and the equations are parametric equations for the curve, with parameter t.
 MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
Projectile Motion. A.1. Finding the flight time from the vertical motion. The five variables for the vertical motion are:
 Projectile Motion A. Finding the muzzle speed v0 The speed of the projectile as it leaves the gun can be found by firing it horizontally from a table, and measuring the horizontal range R0. On the diagram,
Projectile Motion A. Finding the muzzle speed v0 The speed of the projectile as it leaves the gun can be found by firing it horizontally from a table, and measuring the horizontal range R0. On the diagram,
Investigation Free Fall
 Investigation Free Fall Name Period Date You will need: a motion sensor, a small pillow or other soft object What function models the height of an object falling due to the force of gravit? Use a motion
Investigation Free Fall Name Period Date You will need: a motion sensor, a small pillow or other soft object What function models the height of an object falling due to the force of gravit? Use a motion
Recitation 1-6 Projectile Motion
 Preliminaries Recitation 1-6 Projectile Motion The Recorder is the youngest person at your table. The Recorder Should write down everyone s name on the worksheet and put your Table No. on the worksheet.
Preliminaries Recitation 1-6 Projectile Motion The Recorder is the youngest person at your table. The Recorder Should write down everyone s name on the worksheet and put your Table No. on the worksheet.
2. The diagram shows part of the graph of y = a (x h) 2 + k. The graph has its vertex at P, and passes through the point A with coordinates (1, 0).
 Quadratics Vertex Form 1. Part of the graph of the function y = d (x m) + p is given in the diagram below. The x-intercepts are (1, 0) and (5, 0). The vertex is V(m, ). (a) Write down the value of (i)
Quadratics Vertex Form 1. Part of the graph of the function y = d (x m) + p is given in the diagram below. The x-intercepts are (1, 0) and (5, 0). The vertex is V(m, ). (a) Write down the value of (i)
The Quadratic function f(x) = x 2 2x 3. y y = x 2 2x 3. We will now begin to study the graphs of the trig functions, y = sinx, y = cosx and y = tanx.
 Chapter 7 Trigonometric Graphs Introduction We have alread looked at the graphs of various functions : The Linear function f() = The Quadratic function f() = The Hperbolic function f() = = = = We will
Chapter 7 Trigonometric Graphs Introduction We have alread looked at the graphs of various functions : The Linear function f() = The Quadratic function f() = The Hperbolic function f() = = = = We will
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analysis Section 5. Graph sketching
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analsis Section 5 Graph sketching What ou need to know alread: How to compute and interpret limits How to perform first and second derivative
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analsis Section 5 Graph sketching What ou need to know alread: How to compute and interpret limits How to perform first and second derivative
Unit 4 Trigonometry. Study Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 8.1)
 Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Module 2, Section 2 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Algebra II. Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2
 Algebra II Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2 Name Algebra II 13.1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Day One Today I am using SOHCAHTOA and special right triangle to solve trig problems. I am successful
Algebra II Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2 Name Algebra II 13.1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Day One Today I am using SOHCAHTOA and special right triangle to solve trig problems. I am successful
Projectile Launched Horizontally
 Projectile Launched Horizontally by Nada Saab-Ismail, PhD, MAT, MEd, IB nhsaab.weebly.com nhsaab2014@gmail.com P3.3c Explain the recoil of a projectile launcher in terms of forces and masses. P3.4e Solve
Projectile Launched Horizontally by Nada Saab-Ismail, PhD, MAT, MEd, IB nhsaab.weebly.com nhsaab2014@gmail.com P3.3c Explain the recoil of a projectile launcher in terms of forces and masses. P3.4e Solve
20/06/ Projectile Motion. 3-7 Projectile Motion. 3-7 Projectile Motion. 3-7 Projectile Motion
 3-7 A projectile is an object moving in two dimensions under the influence of Earth's gravity; its path is a parabola. 3-7 It can be understood by analyzing the horizontal and vertical motions separately.
3-7 A projectile is an object moving in two dimensions under the influence of Earth's gravity; its path is a parabola. 3-7 It can be understood by analyzing the horizontal and vertical motions separately.
Using a Table of Values to Sketch the Graph of a Polynomial Function
 A point where the graph changes from decreasing to increasing is called a local minimum point. The -value of this point is less than those of neighbouring points. An inspection of the graphs of polnomial
A point where the graph changes from decreasing to increasing is called a local minimum point. The -value of this point is less than those of neighbouring points. An inspection of the graphs of polnomial
Purpose of the experiment
 Projectile Motion PES 116 Advanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure the velocity of a ball using two photogates and Logger Pro. Apply the concepts of two-dimensional kinematics to predict
Projectile Motion PES 116 Advanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure the velocity of a ball using two photogates and Logger Pro. Apply the concepts of two-dimensional kinematics to predict
Chapter Three Chapter Three
 Chapter Three Chapter Three 90 CHAPTER THREE ConcepTests for Section.. If f () = g (), then f() = g(). (a) True (b) False (b). If f () = g (), then f() = g() + C, where C is some constant. You might point
Chapter Three Chapter Three 90 CHAPTER THREE ConcepTests for Section.. If f () = g (), then f() = g(). (a) True (b) False (b). If f () = g (), then f() = g() + C, where C is some constant. You might point
Practice problems from old exams for math 233
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manually
 Group Members: Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manuall Objective: Find the shape of sine and cosine graphs b plotting them on graph paper. 1 90 180 270 450 540 630 720 1 1 90 180 270 450 540
Group Members: Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manuall Objective: Find the shape of sine and cosine graphs b plotting them on graph paper. 1 90 180 270 450 540 630 720 1 1 90 180 270 450 540
Up and Down or Down and Up
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Up and Down or Down and Up Eploring Quadratic Functions Vocabular Write the given quadratic function in standard form. Then describe the shape of the graph and whether
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Up and Down or Down and Up Eploring Quadratic Functions Vocabular Write the given quadratic function in standard form. Then describe the shape of the graph and whether
Graphing Trigonometric Functions
 LESSON Graphing Trigonometric Functions Graphing Sine and Cosine UNDERSTAND The table at the right shows - and f ()-values for the function f () 5 sin, where is an angle measure in radians. Look at the
LESSON Graphing Trigonometric Functions Graphing Sine and Cosine UNDERSTAND The table at the right shows - and f ()-values for the function f () 5 sin, where is an angle measure in radians. Look at the
Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts. Important Features of Parabolas
 Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts Name: _ Learning Objective: Students will be able to identify the vertex and intercepts of a parabola from its equation. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.A Graph linear and
Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts Name: _ Learning Objective: Students will be able to identify the vertex and intercepts of a parabola from its equation. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.A Graph linear and
Date Course Name Instructor Name Student(s) Name WHERE WILL IT LAND?
 Date Course Name Instructor Name Student(s) Name WHERE WILL IT LAND? You have watched a ball roll off a table and strike the floor. What determines where it will land? Could you predict where it will land?
Date Course Name Instructor Name Student(s) Name WHERE WILL IT LAND? You have watched a ball roll off a table and strike the floor. What determines where it will land? Could you predict where it will land?
Lines and Their Slopes
 8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
4.4. Concavity and Curve Sketching. Concavity
 4.4 Concavit and Curve Sketching 267 4.4 Concavit and Curve Sketching f' decreases CONCAVE DOWN 3 f' increases 0 CONCAVE UP FIGURE 4.25 The graph of ƒsd = 3 is concave down on s - q, 0d and concave up
4.4 Concavit and Curve Sketching 267 4.4 Concavit and Curve Sketching f' decreases CONCAVE DOWN 3 f' increases 0 CONCAVE UP FIGURE 4.25 The graph of ƒsd = 3 is concave down on s - q, 0d and concave up
Section 5: Quadratics
 Chapter Review Applied Calculus 46 Section 5: Quadratics Quadratics Quadratics are transformations of the f ( x) x function. Quadratics commonly arise from problems involving area and projectile motion,
Chapter Review Applied Calculus 46 Section 5: Quadratics Quadratics Quadratics are transformations of the f ( x) x function. Quadratics commonly arise from problems involving area and projectile motion,
Implicit differentiation
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 4: Basic differentiation rules Section 5 Implicit differentiation What ou need to know alread: Basic rules of differentiation, including the chain rule.
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 4: Basic differentiation rules Section 5 Implicit differentiation What ou need to know alread: Basic rules of differentiation, including the chain rule.
Preview. Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
Stomp Rocket Lab Physics
 Stomp Rocket Lab Physics Stomp Rockets are plastic projectiles that are launched when a bladder of air is hit or stomped with a foot. Typically the launch angle can be changed, but should be left at 90
Stomp Rocket Lab Physics Stomp Rockets are plastic projectiles that are launched when a bladder of air is hit or stomped with a foot. Typically the launch angle can be changed, but should be left at 90
Concept: Slope of a Line
 Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
2-D Motion: Projectiles at an Angle Physics
 -D Motion: Projectiles at an Angle Physics Be sure your calculator is set to DEGREES! I. Trigonometry Reiew: 1. Find the alues of the following functions. (Use scientific calculator) i) sin45º ii) cos40º
-D Motion: Projectiles at an Angle Physics Be sure your calculator is set to DEGREES! I. Trigonometry Reiew: 1. Find the alues of the following functions. (Use scientific calculator) i) sin45º ii) cos40º
Solving Quadratics Algebraically Investigation
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 TOPIC Trigonometr [Stage 5.3]. Overview Numerous videos and interactivities are embedded just where ou need them, at the point of learning, in our learnon title at www.jacplus.com.au. The will help ou
TOPIC Trigonometr [Stage 5.3]. Overview Numerous videos and interactivities are embedded just where ou need them, at the point of learning, in our learnon title at www.jacplus.com.au. The will help ou
Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute Value Square Root Exponential Reciprocal
 Topic 2.0 Review Concepts What are non linear equations? Student Notes Unit 2 Non linear Equations Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute
Topic 2.0 Review Concepts What are non linear equations? Student Notes Unit 2 Non linear Equations Types of Functions Here are six common types of functions and examples of each. Linear Quadratic Absolute
Answers Investigation 4
 Answers Investigation Applications. a. At seconds, the flare will have traveled to a maimum height of 00 ft. b. The flare will hit the water when the height is 0 ft, which will occur at 0 seconds. c. In
Answers Investigation Applications. a. At seconds, the flare will have traveled to a maimum height of 00 ft. b. The flare will hit the water when the height is 0 ft, which will occur at 0 seconds. c. In
Projectile Motion. Photogate 2 Photogate 1 Ramp and Marble. C-clamp. Figure 1
 Projectile Motion Purpose Apply concepts from two-dimensional kinematics to predict the impact point of a ball in projectile motion, and compare the result with direct measurement. Introduction and Theory
Projectile Motion Purpose Apply concepts from two-dimensional kinematics to predict the impact point of a ball in projectile motion, and compare the result with direct measurement. Introduction and Theory
4.5 Conservative Forces
 4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
Learning Objectives. Math Prerequisites. Technology Prerequisites. Materials. Math Objectives. Technology Objectives
 Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 2: Dude, Where s My Football? Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 60 minutes Many students expect a falling object graph to look just like the path of the falling
Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 2: Dude, Where s My Football? Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 60 minutes Many students expect a falling object graph to look just like the path of the falling
Topic 2 Transformations of Functions
 Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Trigonometric Graphs
 GCSE MATHEMATICS Trigonometric Graphs X These questions have been taken or modified from previous AQA GCSE Mathematics Papers. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point pen. Draw diagrams in pencil.
GCSE MATHEMATICS Trigonometric Graphs X These questions have been taken or modified from previous AQA GCSE Mathematics Papers. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point pen. Draw diagrams in pencil.
Rational functions and graphs. Section 2: Graphs of rational functions
 Rational functions and graphs Section : Graphs of rational functions Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Graph sketching Turning points and restrictions on values Graph sketching You can
Rational functions and graphs Section : Graphs of rational functions Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Graph sketching Turning points and restrictions on values Graph sketching You can
8.5. Quadratic Function A function f is a quadratic function if f(x) ax 2 bx c, where a, b, and c are real numbers, with a 0.
 8.5 Quadratic Functions, Applications, and Models In the previous section we discussed linear functions, those that are defined b firstdegree polnomials. In this section we will look at quadratic functions,
8.5 Quadratic Functions, Applications, and Models In the previous section we discussed linear functions, those that are defined b firstdegree polnomials. In this section we will look at quadratic functions,
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Verte Form The two forms of a quadratic function that have been eplored previousl are: Factored form: f ( ) a( r)( s) Standard form: f ( ) a b c
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Verte Form The two forms of a quadratic function that have been eplored previousl are: Factored form: f ( ) a( r)( s) Standard form: f ( ) a b c
AA Simulation: Firing Range
 America's Army walkthrough AA Simulation: Firing Range Firing Range This simulation serves as an introduction to uniform motion and the relationship between distance, rate, and time. Gravity is removed
America's Army walkthrough AA Simulation: Firing Range Firing Range This simulation serves as an introduction to uniform motion and the relationship between distance, rate, and time. Gravity is removed
Practice Exams. Exam logistics. Projectile Motion Problem-Solving. ax = 0 m/s2 ay = -9.8 m/s2. You won t do well if you wait then cram.
 1 v projectile is in free fall! ax = 0 m/s2 ay = -9.8 m/s2 Projectile Motion Problem-Solving Last year s exam equation sheet. 2 What are you getting stuck on in problem-solving? Topics: Chapters 1 3 including:
1 v projectile is in free fall! ax = 0 m/s2 ay = -9.8 m/s2 Projectile Motion Problem-Solving Last year s exam equation sheet. 2 What are you getting stuck on in problem-solving? Topics: Chapters 1 3 including:
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
Answers. Chapter 4. Cumulative Review Chapters 1 3, pp Chapter Self-Test, p Getting Started, p a) 49 c) e)
 . 7" " " 7 "7.. "66 ( ") cm. a, (, ), b... m b.7 m., because t t has b ac 6., so there are two roots. Because parabola opens down and is above t-ais for small positive t, at least one of these roots is
. 7" " " 7 "7.. "66 ( ") cm. a, (, ), b... m b.7 m., because t t has b ac 6., so there are two roots. Because parabola opens down and is above t-ais for small positive t, at least one of these roots is
Graphing f ( x) = ax 2 + c
 . Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
. Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
1.1. Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions?
 1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
REMARKS. 8.2 Graphs of Quadratic Functions. A Graph of y = ax 2 + bx + c, where a > 0
 8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
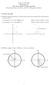 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
(40-455) Student Launcher
 611-1415 (40-455) Student Launcher Congratulations on your purchase of the Science First student launcher. You will find Science First products in almost every school in the world. We have been making
611-1415 (40-455) Student Launcher Congratulations on your purchase of the Science First student launcher. You will find Science First products in almost every school in the world. We have been making
Algebra I. Linear Equations. Slide 1 / 267 Slide 2 / 267. Slide 3 / 267. Slide 3 (Answer) / 267. Slide 4 / 267. Slide 5 / 267
 Slide / 67 Slide / 67 lgebra I Graphing Linear Equations -- www.njctl.org Slide / 67 Table of ontents Slide () / 67 Table of ontents Linear Equations lick on the topic to go to that section Linear Equations
Slide / 67 Slide / 67 lgebra I Graphing Linear Equations -- www.njctl.org Slide / 67 Table of ontents Slide () / 67 Table of ontents Linear Equations lick on the topic to go to that section Linear Equations
Using Characteristics of a Quadratic Function to Describe Its Graph. The graphs of quadratic functions can be described using key characteristics:
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program
 Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program Introduction Finite element analsis (FEA) allows ou analze the stresses and displacements in a bod when forces are applied. FEA determines the stresses and displacements
Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program Introduction Finite element analsis (FEA) allows ou analze the stresses and displacements in a bod when forces are applied. FEA determines the stresses and displacements
Assignment. Pg. 567 #16-33, even pg 577 # 1-17 odd, 32-37
 Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Chapter 3 Practice Test
 1. Complete parts a c for each quadratic function. a. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex. b. Make a table of values that includes the vertex.
1. Complete parts a c for each quadratic function. a. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex. b. Make a table of values that includes the vertex.
Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using
 Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
CHECK Your Understanding
 CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
3.1 Functions. The relation {(2, 7), (3, 8), (3, 9), (4, 10)} is not a function because, when x is 3, y can equal 8 or 9.
 3. Functions Cubic packages with edge lengths of cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm have volumes of 3 or cm 3, 7 3 or 33 cm 3, and 8 3 or 5 cm 3. These values can be written as a relation, which is a set of ordered pairs,
3. Functions Cubic packages with edge lengths of cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm have volumes of 3 or cm 3, 7 3 or 33 cm 3, and 8 3 or 5 cm 3. These values can be written as a relation, which is a set of ordered pairs,
Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form.
 Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Week 3. Topic 5 Asymptotes
 Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Introduction One of the strangest features of a graph is an asmptote. The come in three flavors: vertical, horizontal, and slant (also called oblique).
Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Week 3 Topic 5 Asmptotes Introduction One of the strangest features of a graph is an asmptote. The come in three flavors: vertical, horizontal, and slant (also called oblique).
You are going to need to access the video that was taken of your device - it can be accessed here:
 Part 2: Projectile Launcher Analysis Report Submit Assignment Due Dec 17, 2015 by 10:30am Points 100 Submitting a file upload Available after Dec 17, 2015 at 6am Step 2 - Now We Look At The Real World
Part 2: Projectile Launcher Analysis Report Submit Assignment Due Dec 17, 2015 by 10:30am Points 100 Submitting a file upload Available after Dec 17, 2015 at 6am Step 2 - Now We Look At The Real World
Math 1050 Lab Activity: Graphing Transformations
 Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
Transforming Polynomial Functions
 5-9 Transforming Polnomial Functions Content Standards F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative) find
5-9 Transforming Polnomial Functions Content Standards F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative) find
Falling Balls. Names: Date: About this Laboratory
 Falling Balls Names: Date: About this Laboratory In this laboratory,1 we will explore quadratic functions and how they relate to the motion of an object that is dropped from a specified height above ground
Falling Balls Names: Date: About this Laboratory In this laboratory,1 we will explore quadratic functions and how they relate to the motion of an object that is dropped from a specified height above ground
4.4 Absolute Value Equations. What is the absolute value of a number? Example 1 Simplify a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3. Example 2 Solve x = 2
 4.4 Absolute Value Equations What is the absolute value of a number? Eample Simplif a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3 Eample Solve = Steps for solving an absolute value equation: ) Get the absolute value b itself on one
4.4 Absolute Value Equations What is the absolute value of a number? Eample Simplif a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3 Eample Solve = Steps for solving an absolute value equation: ) Get the absolute value b itself on one
