CS Path Planning
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why Path Planning? CS Path Planning Roderic A. Grupen 4/13/15 Robotics 1 4/13/15 Robotics 2 Why Motion Planning? Origins of Motion Planning Virtual Prototyping! Character Animation! Structural Molecular Biology! Autonomous Control! GE! T. Lozano-Pérez and M.A. Wesley: An Algorithm for Planning Collision-Free Paths Among Polyhedral Obstacles, 1979.! introduced the notion of configuration space (c-space) to robotics! many approaches have been devised since then in configuration space! 4/13/15 Robotics 3 4/13/15 Robotics 4 1
2 Representation given a moving object, A, initially in an unoccupied region of freespace, s, a set of stationary objects, B i, at known locations, and a goal position, g,!! Mapping to Configuration Space - Translational Case (fixed orientation) Obstacle! find a sequence of! collision-free motions! that take A from s to g! Robot! 4/13/15 Robotics 6 Reference Point! changing θ? C-Space! Obstacle! 9 Obstacles in 3D (x,y,q) Exact Cell Decomposition Jean-Claude Latombe! Jean-Claude Latombe! 4/13/15 Robotics 10 4/13/15 Robotics 12 2
3 Exact Cell Decomposition Exact Cell Decomposition Jean-Claude Latombe! 4/13/15 Robotics 13 Jean-Claude Latombe! 4/13/15 Robotics 14 Representation Simplicial Decomposition Approximate Methods: 2 n -Tree Schwartz and Sharir Lozano-Perez Canny 4/13/15 Robotics 15 4/13/15 Robotics 16 3
4 Approximate Cell Decomposition Representation Roadmaps Visibility diagrams: unsmooth sensitive to error again build a graph and search it to find a path! 4/13/15 Robotics 17 Jean-Claude Latombe! 4/13/15 Robotics 18 Roadmap Representations Summary Voronoi diagrams a retraction the continuous freespace is represented as a network of curves Exact Cell Decomposition! Approximate Cell Decomposition!! graph search!! next: potential field methods! state of the art techniques Roadmap Methods! visibility graphs! Voronoi diagrams! next: probabilistic road maps (PRM)! Jean-Claude Latombe! 4/13/15 Robotics 19 4/13/15 Robotics 20 4
5 Attractive Potential Fields Repulsive Potentials Oliver Brock + Oliver Brock Electrostatic (or Gravitational) Field Attractive Potential φ att (q) = 1 2 k (q q ref ) T (q q ref ) F att (q) = φ att (q) = k (q q ref ) depends on! direction!
6 A Repulsive Potential Repulsive Potential F rep (q) = 1 x! 1 φ rep (q) = k (q q obst ) 1 $ # " δ & 0 % 2 if ((q q obs ) < δ 0 = 0 otherwise x F rep (q) = 1 x 1 δ 0 25 F rep (q) = φ(q) ) = k # 1 (q q obs ) 1 & - + % $ δ ( if ((q q obs ) < δ 0 + * 0 '. + +, 0 otherwise / 4/13/15 Robotics 26 Sum Attractive and Repulsive Fields Artificial Potential Function φ att (q) + φ rep (q) = φ total (q) +! =! F total (q) = φ total
7 Potential Fields Goal: avoid local minima Problem: requires global information Solution: Navigation Function F rep! Robot! F att! F rep! Navigation Functions Analyticity navigation functions are analytic because they are infinitely differentiable and their Taylor series converge to φ(q 0 ) as q approaches q 0!! Polar gradients (streamlines) of navigation functions terminate at a unique minima! F att! Obstacle! Goal! 4/13/15 Robotics 29 4/13/15 Robotics 30 Navigation Functions The Hessian Morse - navigation functions have no degenerate critical points where the robot can get stuck short of attaining the goal. Critical points are places where the gradient of φ vanishes, i.e. minima, saddle points, or maxima and their images under φ are called critical values.! multivariable control function, f(q 0,q 1,...,q n )! Admissibility - practical potential fields must always generate bounded torques! if the Hessian is positive semi-definite over! the domain Q, then the function f is convex over Q! 4/13/15 Robotics 31 4/13/15 Robotics 32 7
8 Harmonic Functions Properties of Harmonic Functions if the trace of the Hessian (the Laplacian) is 0! then function f is a harmonic function! laminar fluid flow, steady state temperature distribution, electromagnetic fields, current flow in conductive media! 4/13/15 Robotics 33 Min-Max Property -!...in any compact neighborhood of freespace, the minimum and maximum of the function must occur on the boundary.!! 4/13/15 Robotics 34 Properties of Harmonic Functions Numerical Relaxation Mean-Value - up to truncation error, the value of the harmonic potential at a point in a lattice is the average of the values of its 2n Manhattan neighbors. Jacobi iteration! ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ analog & numerical methods! 4/13/15 Robotics 35 4/13/15 Robotics 36 8
9 Harmonic Relaxation: Numerical Methods Properties of Harmonic Functions Gauss-Seidel Successive Over Relaxation Hitting Probabilities - if we denote p(x) at state x as! the probability that starting from x, a random walk process will reach an obstacle before it reaches a goal p(x) is known as the hitting probability!! greedy descent on the harmonic function minimizes the hitting probability.! 4/13/15 Robotics 37 4/13/15 Robotics 38 Minima in Harmonic Functions Configuration Space for some i, if 2 φ/ x i 2 > 0 (concave upward), then there must exist another dimension, j, where! 2 φ/ x j 2 < 0 to satisfy Laplace s constraint.! therefore, if you re not at a goal, there is always a way downhill......there are no local minima...! 4/13/15 Robotics 39 4/13/15 Robotics 40 9
10 Harmonic Functions for Path Planning Harmonic Functions for Path Planning 4/13/15 Robotics 41 4/13/15 Robotics 42 Harmonic Functions for Path Planning Reactive Admittance Control 4/13/15 Robotics 43 4/13/15 Robotics 44 10
11 Probabilistic Roadmaps (PRM) ok, back to graphical methods Construction! Generate random configurations! Eliminate if they are in collision! Use local planner to connect configurations! Expansion! Identify connected components! Resample gaps! Try to connect components! Query! Connect initial and final configuration to roadmap! Perform graph search! 4/13/15 Robotics 45 4/13/15 Robotics 46 Probabilistic Roadmaps (PRM) Sampling Phase Oliver Brock Construction! R = (V,E)! repeat n times:! generate random configuration! add to V if collision free! attempt to connect to neighbors using local planner, unless in same connected component of R! 4/13/15 Robotics 47 4/13/15 Robotics 49 11
12 Path Extraction Local Planner Connect start and goal configuration to roadmap using local planner! Perform graph search on roadmap! Computational cost of querying negligible compared to construction of roadmap! δ q 2 q 1 tests up to a specified resolution δ! 4/13/15 Robotics 50 4/13/15 Robotics 52 Another Local Planner Summary: PRM Algorithmically very simple! Surprisingly efficient even in high-dimensional C- spaces! Capable of addressing a wide variety of motion planning problems! One of the hottest areas of research! Allows probabilistic performance guarantees! perform random walk of predetermined length; choose new direction randomly after hitting obstacle; attempt to connect to roadmap after random walk 4/13/15 Robotics 53 4/13/15 Robotics 56 12
13 Variations of the PRM Lazy PRM Lazy PRMs! Rapidly-exploring Random Trees! observation: pre-computation of roadmap takes a long time and does not respond well in dynamic environments! 4/13/15 Robotics 59 4/13/15 Robotics 60 Lazy PRM Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees (RRT) Oliver Brock Oliver Brock 4/13/15 Robotics 61 4/13/15 Robotics 65 13
14 Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees (RRT) Steven LaValle! 4/13/15 Robotics 66 14
Robot Motion Planning
 Robot Motion Planning slides by Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science and Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague lecture A4M36PAH - Planning and Games Dpt.
Robot Motion Planning slides by Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science and Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague lecture A4M36PAH - Planning and Games Dpt.
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning
 6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2012 Figures by Nancy Amato, Rodney Brooks, Vijay Kumar Reading:
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2012 Figures by Nancy Amato, Rodney Brooks, Vijay Kumar Reading:
Visibility Graph. How does a Mobile Robot get from A to B?
 Robot Path Planning Things to Consider: Spatial reasoning/understanding: robots can have many dimensions in space, obstacles can be complicated Global Planning: Do we know the environment apriori? Online
Robot Path Planning Things to Consider: Spatial reasoning/understanding: robots can have many dimensions in space, obstacles can be complicated Global Planning: Do we know the environment apriori? Online
Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning
 16.412/6.834J Cognitive Robotics February 7 th, 2005 Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning Based on Past Student Lectures by: Paul Elliott, Aisha Walcott, Nathan Ickes and Stanislav Funiak
16.412/6.834J Cognitive Robotics February 7 th, 2005 Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning Based on Past Student Lectures by: Paul Elliott, Aisha Walcott, Nathan Ickes and Stanislav Funiak
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning
 6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2011 Figures by Nancy Amato, Rodney Brooks, Vijay Kumar Reading:
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 9: Configuration Space and Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2011 Figures by Nancy Amato, Rodney Brooks, Vijay Kumar Reading:
Robotic Motion Planning: Review C-Space and Start Potential Functions
 Robotic Motion Planning: Review C-Space and Start Potential Functions Robotics Institute 16-735 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~motionplanning Howie Choset http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~choset What if the robot is not
Robotic Motion Planning: Review C-Space and Start Potential Functions Robotics Institute 16-735 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~motionplanning Howie Choset http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~choset What if the robot is not
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 Path Planning for Point Robots Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/mpa Class Objectives Motion planning framework Classic motion planning approaches 2 3 Configuration Space:
Path Planning for Point Robots Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/mpa Class Objectives Motion planning framework Classic motion planning approaches 2 3 Configuration Space:
Introduction to State-of-the-art Motion Planning Algorithms. Presented by Konstantinos Tsianos
 Introduction to State-of-the-art Motion Planning Algorithms Presented by Konstantinos Tsianos Robots need to move! Motion Robot motion must be continuous Geometric constraints Dynamic constraints Safety
Introduction to State-of-the-art Motion Planning Algorithms Presented by Konstantinos Tsianos Robots need to move! Motion Robot motion must be continuous Geometric constraints Dynamic constraints Safety
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Autonomous Mobile Robots, Chapter 6 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there? Localization. Cognition. Real World Environment
 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Implementing Motion Planning
 6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Implementing Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by N. Roy and D. Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2011 Reading: Chapter 3, and Craig: Robotics http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.141/!
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Implementing Motion Planning Lecture Notes Prepared by N. Roy and D. Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2011 Reading: Chapter 3, and Craig: Robotics http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.141/!
Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017
 Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017 The Motion Planning Problem Intuition: Find a safe path/trajectory from start to goal More precisely: A path is a series of robot configurations
Geometric Path Planning McGill COMP 765 Oct 12 th, 2017 The Motion Planning Problem Intuition: Find a safe path/trajectory from start to goal More precisely: A path is a series of robot configurations
Path Planning. Marcello Restelli. Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano tel:
 Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Robot Motion Planning and (a little) Computational Geometry
 Images taken from slides b B. Baazit, G. Dudek, J. C. Latombe and A. Moore Robot Motion Planning and (a little) Computational Geometr Topics: Transforms Topological Methods Configuration space Skeletonization
Images taken from slides b B. Baazit, G. Dudek, J. C. Latombe and A. Moore Robot Motion Planning and (a little) Computational Geometr Topics: Transforms Topological Methods Configuration space Skeletonization
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots
 EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture 3: Path Planning Algorithm Prof. Yi Guo ECE Dept. Plan Representing the Space Path Planning Methods A* Search Algorithm D* Search Algorithm Representing
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture 3: Path Planning Algorithm Prof. Yi Guo ECE Dept. Plan Representing the Space Path Planning Methods A* Search Algorithm D* Search Algorithm Representing
Path Planning for Point Robots. NUS CS 5247 David Hsu
 Path Planning for Point Robots NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Problem Input Robot represented as a point in the plane Obstacles represented as polygons Initial and goal positions Output A collision-free path between
Path Planning for Point Robots NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Problem Input Robot represented as a point in the plane Obstacles represented as polygons Initial and goal positions Output A collision-free path between
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Motion Planning III
 6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Motion Planning III Lecture Notes Prepared by N. Roy and D. Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2012 Reading: Chapter 3, and Craig: Robotics http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.141/!
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 10: Motion Planning III Lecture Notes Prepared by N. Roy and D. Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2012 Reading: Chapter 3, and Craig: Robotics http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.141/!
Artificial Potential Biased Probabilistic Roadmap Method
 Artificial Potential Biased Probabilistic Roadmap Method Daniel Aarno, Danica Kragic and Henrik I Christensen Centre for Autonomous Systems Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden Email:bishop@kth.se,
Artificial Potential Biased Probabilistic Roadmap Method Daniel Aarno, Danica Kragic and Henrik I Christensen Centre for Autonomous Systems Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden Email:bishop@kth.se,
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset What is Motion Planning? What is Motion Planning? Determining where to go Overview The Basics Motion Planning Statement The World and Robot Configuration Space Metrics Algorithms
Motion Planning Howie CHoset What is Motion Planning? What is Motion Planning? Determining where to go Overview The Basics Motion Planning Statement The World and Robot Configuration Space Metrics Algorithms
CS 4649/7649 Robot Intelligence: Planning
 CS 4649/7649 Robot Intelligence: Planning Probabilistic Roadmaps Sungmoon Joo School of Interactive Computing College of Computing Georgia Institute of Technology S. Joo (sungmoon.joo@cc.gatech.edu) 1
CS 4649/7649 Robot Intelligence: Planning Probabilistic Roadmaps Sungmoon Joo School of Interactive Computing College of Computing Georgia Institute of Technology S. Joo (sungmoon.joo@cc.gatech.edu) 1
Robot Motion Planning
 Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning
 Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning Computer Science 336 http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager/teaching/cs336 Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Recall Earlier Methods
Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning Computer Science 336 http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager/teaching/cs336 Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Recall Earlier Methods
Configuration Space of a Robot
 Robot Path Planning Overview: 1. Visibility Graphs 2. Voronoi Graphs 3. Potential Fields 4. Sampling-Based Planners PRM: Probabilistic Roadmap Methods RRTs: Rapidly-exploring Random Trees Configuration
Robot Path Planning Overview: 1. Visibility Graphs 2. Voronoi Graphs 3. Potential Fields 4. Sampling-Based Planners PRM: Probabilistic Roadmap Methods RRTs: Rapidly-exploring Random Trees Configuration
Part I Part 1 Sampling-based Motion Planning
 Overview of the Lecture Randomized Sampling-based Motion Planning Methods Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Lecture 05 B4M36UIR
Overview of the Lecture Randomized Sampling-based Motion Planning Methods Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Lecture 05 B4M36UIR
for Motion Planning RSS Lecture 10 Prof. Seth Teller
 Configuration Space for Motion Planning RSS Lecture 10 Monday, 8 March 2010 Prof. Seth Teller Siegwart & Nourbahksh S 6.2 (Thanks to Nancy Amato, Rod Brooks, Vijay Kumar, and Daniela Rus for some of the
Configuration Space for Motion Planning RSS Lecture 10 Monday, 8 March 2010 Prof. Seth Teller Siegwart & Nourbahksh S 6.2 (Thanks to Nancy Amato, Rod Brooks, Vijay Kumar, and Daniela Rus for some of the
Part I Part 1 Sampling-based Motion Planning
 Overview of the Lecture Randomized Sampling-based Motion Planning Methods Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Lecture 06 B4M36UIR
Overview of the Lecture Randomized Sampling-based Motion Planning Methods Jan Faigl Department of Computer Science Faculty of Electrical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague Lecture 06 B4M36UIR
Road Map Methods. Including material from Howie Choset / G.D. Hager S. Leonard
 Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Sampling-Based Robot Motion Planning. Lydia Kavraki Department of Computer Science Rice University Houston, TX USA
 Sampling-Based Robot Motion Planning Lydia Kavraki Department of Computer Science Rice University Houston, TX USA Motion planning: classical setting Go from Start to Goal without collisions and while respecting
Sampling-Based Robot Motion Planning Lydia Kavraki Department of Computer Science Rice University Houston, TX USA Motion planning: classical setting Go from Start to Goal without collisions and while respecting
Path Planning. Jacky Baltes Dept. of Computer Science University of Manitoba 11/21/10
 Path Planning Jacky Baltes Autonomous Agents Lab Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky Path Planning Jacky Baltes Dept. of
Path Planning Jacky Baltes Autonomous Agents Lab Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky Path Planning Jacky Baltes Dept. of
MEV 442: Introduction to Robotics - Module 3 INTRODUCTION TO ROBOT PATH PLANNING
 MEV 442: Introduction to Robotics - Module 3 INTRODUCTION TO ROBOT PATH PLANNING THE PATH PLANNING PROBLEM The robot should find out a path enables the continuous motion of a robot from an initial configuration
MEV 442: Introduction to Robotics - Module 3 INTRODUCTION TO ROBOT PATH PLANNING THE PATH PLANNING PROBLEM The robot should find out a path enables the continuous motion of a robot from an initial configuration
Lecture 3: Motion Planning (cont.)
 CS 294-115 Algorithmic Human-Robot Interaction Fall 2016 Lecture 3: Motion Planning (cont.) Scribes: Molly Nicholas, Chelsea Zhang 3.1 Previously in class... Recall that we defined configuration spaces.
CS 294-115 Algorithmic Human-Robot Interaction Fall 2016 Lecture 3: Motion Planning (cont.) Scribes: Molly Nicholas, Chelsea Zhang 3.1 Previously in class... Recall that we defined configuration spaces.
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo. Motion Planning 1 Retraction and Cell Decomposition
 Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo Motion Planning 1 Retraction and Cell Decomposition motivation robots are expected to perform tasks in workspaces populated by obstacles autonomy requires
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo Motion Planning 1 Retraction and Cell Decomposition motivation robots are expected to perform tasks in workspaces populated by obstacles autonomy requires
Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II. Howie Choset
 Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II Howie Choset Map-Based Approaches: Properties of a roadmap: Roadmap Theory Accessibility: there exists a collision-free path from the start to the road map
Motion Planning, Part IV Graph Search Part II Howie Choset Map-Based Approaches: Properties of a roadmap: Roadmap Theory Accessibility: there exists a collision-free path from the start to the road map
MOBILE ROBOTS NAVIGATION, MAPPING & LOCALIZATION: PART I
 MOBILE ROBOTS NAVIGATION, MAPPING & LOCALIZATION: PART I Lee Gim Hee* CML DSO National Laboratories 20 Science Park Drive Singapore 118230 Tel: (+65) 6796 8427 Email: lgimhee@dso.org.sg Marcelo H. Ang
MOBILE ROBOTS NAVIGATION, MAPPING & LOCALIZATION: PART I Lee Gim Hee* CML DSO National Laboratories 20 Science Park Drive Singapore 118230 Tel: (+65) 6796 8427 Email: lgimhee@dso.org.sg Marcelo H. Ang
Computer Game Programming Basic Path Finding
 15-466 Computer Game Programming Basic Path Finding Robotics Institute Path Planning Sven Path Planning needs to be very fast (especially for games with many characters) needs to generate believable paths
15-466 Computer Game Programming Basic Path Finding Robotics Institute Path Planning Sven Path Planning needs to be very fast (especially for games with many characters) needs to generate believable paths
Planning Techniques for Robotics Planning Representations: Skeletonization- and Grid-based Graphs
 16-350 Planning Techniques for Robotics Planning Representations: Skeletonization- and Grid-based Graphs Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute 2D Planning for Omnidirectional Point Robot Planning for omnidirectional
16-350 Planning Techniques for Robotics Planning Representations: Skeletonization- and Grid-based Graphs Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute 2D Planning for Omnidirectional Point Robot Planning for omnidirectional
Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning
 Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning Computer Science 336 http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager/teaching/cs336 Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Recall Earlier Methods
Algorithms for Sensor-Based Robotics: Sampling-Based Motion Planning Computer Science 336 http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager/teaching/cs336 Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Recall Earlier Methods
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation
 Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Motion Planning. Chapter Motion Planning Concepts. by Lydia E. Kavraki and Steven M. LaValle Configuration Space
 Chapter 5 Motion Planning by Lydia E. Kavraki and Steven M. LaValle A fundamental robotics task is to plan collision-free motions for complex bodies from a start to a goal position among a collection of
Chapter 5 Motion Planning by Lydia E. Kavraki and Steven M. LaValle A fundamental robotics task is to plan collision-free motions for complex bodies from a start to a goal position among a collection of
Roadmaps. Vertex Visibility Graph. Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side.
 Roadmaps Vertex Visibility Graph Full visibility graph Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side. (but keeping endpoints roads) what else might we
Roadmaps Vertex Visibility Graph Full visibility graph Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side. (but keeping endpoints roads) what else might we
Sampling-Based Motion Planning
 Sampling-Based Motion Planning Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many images from Lavalle, Planning Algorithms Motion Planning Problem Given start state x S, goal state x G Asked for: a sequence of control
Sampling-Based Motion Planning Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many images from Lavalle, Planning Algorithms Motion Planning Problem Given start state x S, goal state x G Asked for: a sequence of control
Motion Planning with Dynamics, Physics based Simulations, and Linear Temporal Objectives. Erion Plaku
 Motion Planning with Dynamics, Physics based Simulations, and Linear Temporal Objectives Erion Plaku Laboratory for Computational Sensing and Robotics Johns Hopkins University Frontiers of Planning The
Motion Planning with Dynamics, Physics based Simulations, and Linear Temporal Objectives Erion Plaku Laboratory for Computational Sensing and Robotics Johns Hopkins University Frontiers of Planning The
Approximate path planning. Computational Geometry csci3250 Laura Toma Bowdoin College
 Approximate path planning Computational Geometry csci3250 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Path planning Combinatorial Approximate Combinatorial path planning Idea: Compute free C-space combinatorially
Approximate path planning Computational Geometry csci3250 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Path planning Combinatorial Approximate Combinatorial path planning Idea: Compute free C-space combinatorially
Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012
 COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
Planning in Mobile Robotics
 Planning in Mobile Robotics Part I. Miroslav Kulich Intelligent and Mobile Robotics Group Gerstner Laboratory for Intelligent Decision Making and Control Czech Technical University in Prague Tuesday 26/07/2011
Planning in Mobile Robotics Part I. Miroslav Kulich Intelligent and Mobile Robotics Group Gerstner Laboratory for Intelligent Decision Making and Control Czech Technical University in Prague Tuesday 26/07/2011
Sampling-based Planning 2
 RBE MOTION PLANNING Sampling-based Planning 2 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Problem with KD-tree RBE MOTION PLANNING Curse of dimension
RBE MOTION PLANNING Sampling-based Planning 2 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Problem with KD-tree RBE MOTION PLANNING Curse of dimension
Probabilistic Motion Planning: Algorithms and Applications
 Probabilistic Motion Planning: Algorithms and Applications Jyh-Ming Lien Department of Computer Science George Mason University Motion Planning in continuous spaces (Basic) Motion Planning (in a nutshell):
Probabilistic Motion Planning: Algorithms and Applications Jyh-Ming Lien Department of Computer Science George Mason University Motion Planning in continuous spaces (Basic) Motion Planning (in a nutshell):
f-v v-f f-e e-f f-f e-e-cross e-v v-e degenerate PCs e-e-touch v-v
 Planning Motion Compliant to Complex Contact States Λ uerong Ji, Jing iao Computer Science Department University of North Carolina - Charlotte Charlotte, NC 28223, US xji@uncc.edu, xiao@uncc.edu bstract
Planning Motion Compliant to Complex Contact States Λ uerong Ji, Jing iao Computer Science Department University of North Carolina - Charlotte Charlotte, NC 28223, US xji@uncc.edu, xiao@uncc.edu bstract
CS4733 Class Notes. 1 2-D Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Using Grown Obstacles
 CS4733 Class Notes 1 2-D Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Using Grown Obstacles Reference: An Algorithm for Planning Collision Free Paths Among Poyhedral Obstacles by T. Lozano-Perez and M. Wesley. This
CS4733 Class Notes 1 2-D Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Using Grown Obstacles Reference: An Algorithm for Planning Collision Free Paths Among Poyhedral Obstacles by T. Lozano-Perez and M. Wesley. This
Decomposition-based Motion Planning: Towards Real-time Planning for Robots with Many Degrees of Freedom. Abstract
 Decomposition-based Motion Planning: Towards Real-time Planning for Robots with Many Degrees of Freedom Oliver Brock Lydia E. Kavraki Department of Computer Science Rice University, Houston, Texas 77005
Decomposition-based Motion Planning: Towards Real-time Planning for Robots with Many Degrees of Freedom Oliver Brock Lydia E. Kavraki Department of Computer Science Rice University, Houston, Texas 77005
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space
 ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) How to generate Delaunay Triangulation? (3 pts) Explain the difference
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) How to generate Delaunay Triangulation? (3 pts) Explain the difference
Path Planning. Ioannis Rekleitis
 Path Planning Ioannis Rekleitis Outline Path Planning Visibility Graph Potential Fields Bug Algorithms Skeletons/Voronoi Graphs C-Space CSCE-574 Robotics 2 Mo+on Planning The ability to go from A to B
Path Planning Ioannis Rekleitis Outline Path Planning Visibility Graph Potential Fields Bug Algorithms Skeletons/Voronoi Graphs C-Space CSCE-574 Robotics 2 Mo+on Planning The ability to go from A to B
Motion Planning 2D. Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo
 Motion Planning 2D Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo Tratto dai corsi: CS 326A: Motion Planning ai.stanford.edu/~latombe/cs326/2007/index.htm Prof. J.C. Latombe Stanford
Motion Planning 2D Corso di Robotica Prof. Davide Brugali Università degli Studi di Bergamo Tratto dai corsi: CS 326A: Motion Planning ai.stanford.edu/~latombe/cs326/2007/index.htm Prof. J.C. Latombe Stanford
Motion Planning. Jana Kosecka Department of Computer Science
 Motion Planning Jana Kosecka Department of Computer Science Discrete planning, graph search, shortest path, A* methods Road map methods Configuration space Slides thanks to http://cs.cmu.edu/~motionplanning,
Motion Planning Jana Kosecka Department of Computer Science Discrete planning, graph search, shortest path, A* methods Road map methods Configuration space Slides thanks to http://cs.cmu.edu/~motionplanning,
Outline. Robotics Planning. Example: Getting to DC from Atlanta. Introduction
 Outline Robotics Planning Henrik I Christensen Introduction Representations Planning Basics Search methods Evaluation (or the lack thereof) Summary Introduction Example: Getting to DC from Atlanta Generation
Outline Robotics Planning Henrik I Christensen Introduction Representations Planning Basics Search methods Evaluation (or the lack thereof) Summary Introduction Example: Getting to DC from Atlanta Generation
Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222)
 2017 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222) 1 26-Jul Introduction + 2 2-Aug Representing Position
2017 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222) 1 26-Jul Introduction + 2 2-Aug Representing Position
Trajectory Optimization
 Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
Sampling-based Path Planning for an Autonomous Helicopter
 Linköping Studies in Science and Technology Thesis No. 1229 Sampling-based Path Planning for an Autonomous Helicopter by Per Olof Pettersson Submitted to Linköping Institute of Technology at Linköping
Linköping Studies in Science and Technology Thesis No. 1229 Sampling-based Path Planning for an Autonomous Helicopter by Per Olof Pettersson Submitted to Linköping Institute of Technology at Linköping
Space Robot Path Planning for Collision Avoidance
 Space Robot Path Planning for ollision voidance Yuya Yanoshita and Shinichi Tsuda bstract This paper deals with a path planning of space robot which includes a collision avoidance algorithm. For the future
Space Robot Path Planning for ollision voidance Yuya Yanoshita and Shinichi Tsuda bstract This paper deals with a path planning of space robot which includes a collision avoidance algorithm. For the future
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation
 Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Configuration Space. Ioannis Rekleitis
 Configuration Space Ioannis Rekleitis Configuration Space Configuration Space Definition A robot configuration is a specification of the positions of all robot points relative to a fixed coordinate system
Configuration Space Ioannis Rekleitis Configuration Space Configuration Space Definition A robot configuration is a specification of the positions of all robot points relative to a fixed coordinate system
Func%on Approxima%on. Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS
 Func%on Approxima%on Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Value Itera4on Algorithm: Start with for all s. For i=1,, H For all states s 2 S: Imprac4cal for large state spaces = the expected sum of rewards accumulated
Func%on Approxima%on Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Value Itera4on Algorithm: Start with for all s. For i=1,, H For all states s 2 S: Imprac4cal for large state spaces = the expected sum of rewards accumulated
Probabilistic roadmaps for efficient path planning
 Probabilistic roadmaps for efficient path planning Dan A. Alcantara March 25, 2007 1 Introduction The problem of finding a collision-free path between points in space has applications across many different
Probabilistic roadmaps for efficient path planning Dan A. Alcantara March 25, 2007 1 Introduction The problem of finding a collision-free path between points in space has applications across many different
Robot motion planning using exact cell decomposition and potential field methods
 Robot motion planning using exact cell decomposition and potential field methods DUŠAN GLAVAŠKI, MARIO VOLF, MIRJANA BONKOVIĆ Laboratory for Robotics and Intelligent Systems Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
Robot motion planning using exact cell decomposition and potential field methods DUŠAN GLAVAŠKI, MARIO VOLF, MIRJANA BONKOVIĆ Laboratory for Robotics and Intelligent Systems Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
(1) Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14)z = a + 2
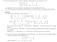 (1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
(1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
Advanced path planning. ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012
 Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Advanced path planning ROS RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Simon Lacroix Toulouse, France Where do I come from? Robotics at LAAS/CNRS, Toulouse, France Research topics Perception, planning and decision-making,
Path Planning Algorithms and Multi Agent Path Planning
 Path Planning Algorithms and Multi Agent Path Planning Fuat Geleri 10.2006 Outline Path Planning Basics Complexity of Path Planning Simulation Related Utilities Collision Checking Integration Sampling
Path Planning Algorithms and Multi Agent Path Planning Fuat Geleri 10.2006 Outline Path Planning Basics Complexity of Path Planning Simulation Related Utilities Collision Checking Integration Sampling
Visual Navigation for Flying Robots. Motion Planning
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Visual Navigation for Flying Robots Motion Planning Dr. Jürgen Sturm Motivation: Flying Through Forests 3 1 2 Visual Navigation for Flying Robots 2 Motion Planning
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Visual Navigation for Flying Robots Motion Planning Dr. Jürgen Sturm Motivation: Flying Through Forests 3 1 2 Visual Navigation for Flying Robots 2 Motion Planning
Manipula0on Algorithms Mo0on Planning. Mo#on Planning I. Katharina Muelling (NREC, Carnegie Mellon University) 1
 16-843 Manipula0on Algorithms Mo0on Planning Mo#on Planning I Katharina Muelling (NREC, Carnegie Mellon University) 1 Configura0on Space Obstacles Star Algorithm Convex robot, transla#on C obs : convex
16-843 Manipula0on Algorithms Mo0on Planning Mo#on Planning I Katharina Muelling (NREC, Carnegie Mellon University) 1 Configura0on Space Obstacles Star Algorithm Convex robot, transla#on C obs : convex
Mobile Robot Path Planning in Static Environments using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Mobile Robot Path Planning in Static Environments using Particle Swarm Optimization M. Shahab Alam, M. Usman Rafique, and M. Umer Khan Abstract Motion planning is a key element of robotics since it empowers
Mobile Robot Path Planning in Static Environments using Particle Swarm Optimization M. Shahab Alam, M. Usman Rafique, and M. Umer Khan Abstract Motion planning is a key element of robotics since it empowers
COMPLETE AND SCALABLE MULTI-ROBOT PLANNING IN TUNNEL ENVIRONMENTS. Mike Peasgood John McPhee Christopher Clark
 COMPLETE AND SCALABLE MULTI-ROBOT PLANNING IN TUNNEL ENVIRONMENTS Mike Peasgood John McPhee Christopher Clark Lab for Intelligent and Autonomous Robotics, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University
COMPLETE AND SCALABLE MULTI-ROBOT PLANNING IN TUNNEL ENVIRONMENTS Mike Peasgood John McPhee Christopher Clark Lab for Intelligent and Autonomous Robotics, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University
LQR-RRT : Optimal Sampling-Based Motion Planning with Automatically Derived Extension Heuristics
 LQR-RRT : Optimal Sampling-Based Motion Planning with Automatically Derived Extension Heuristics Alejandro Perez, Robert Platt Jr., George Konidaris, Leslie Kaelbling and Tomas Lozano-Perez Computer Science
LQR-RRT : Optimal Sampling-Based Motion Planning with Automatically Derived Extension Heuristics Alejandro Perez, Robert Platt Jr., George Konidaris, Leslie Kaelbling and Tomas Lozano-Perez Computer Science
Introduction to Robotics
 Jianwei Zhang zhang@informatik.uni-hamburg.de Universität Hamburg Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften Technische Aspekte Multimodaler Systeme 05. July 2013 J. Zhang 1 Task-level
Jianwei Zhang zhang@informatik.uni-hamburg.de Universität Hamburg Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften Technische Aspekte Multimodaler Systeme 05. July 2013 J. Zhang 1 Task-level
Sensor-based Planning for a Rod-shaped Robot in Three Dimensions: Piecewise Retracts of R 3 S 2
 Ji Yeong Lee Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) Seoul, Korea jiyeongl@andrew.cmu.edu Howie Choset Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA Sensor-based Planning for a Rod-shaped
Ji Yeong Lee Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) Seoul, Korea jiyeongl@andrew.cmu.edu Howie Choset Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA Sensor-based Planning for a Rod-shaped
Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader)
 Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader) Robotics Institute 16-735 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset
Robotic Motion Planning: Cell Decompositions (with some discussion on coverage and pursuer/evader) Robotics Institute 16-735 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset
Unit 5: Part 1 Planning
 Unit 5: Part 1 Planning Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland March 25, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Planning March 25, 2014 1 / 9 Planning Localization
Unit 5: Part 1 Planning Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland March 25, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Planning March 25, 2014 1 / 9 Planning Localization
Robot Motion Control Matteo Matteucci
 Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
A Reduced-Order Analytical Solution to Mobile Robot Trajectory Generation in the Presence of Moving Obstacles
 A Reduced-Order Analytical Solution to Mobile Robot Trajectory Generation in the Presence of Moving Obstacles Jing Wang, Zhihua Qu,, Yi Guo and Jian Yang Electrical and Computer Engineering University
A Reduced-Order Analytical Solution to Mobile Robot Trajectory Generation in the Presence of Moving Obstacles Jing Wang, Zhihua Qu,, Yi Guo and Jian Yang Electrical and Computer Engineering University
II. RELATED WORK. A. Probabilistic roadmap path planner
 Gaussian PRM Samplers for Dynamic Configuration Spaces Yu-Te Lin and Shih-Chia Cheng Computer Science Department Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, USA {yutelin, sccheng}@cs.stanford.edu SUID: 05371954,
Gaussian PRM Samplers for Dynamic Configuration Spaces Yu-Te Lin and Shih-Chia Cheng Computer Science Department Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, USA {yutelin, sccheng}@cs.stanford.edu SUID: 05371954,
Shorter, Smaller, Tighter Old and New Challenges
 How can Computational Geometry help Robotics and Automation: Shorter, Smaller, Tighter Old and New Challenges Dan Halperin School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University Algorithms in the Field/CG, CG
How can Computational Geometry help Robotics and Automation: Shorter, Smaller, Tighter Old and New Challenges Dan Halperin School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University Algorithms in the Field/CG, CG
Search Spaces I. Before we get started... ME/CS 132b Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Perception 4/05/2011
 Search Spaces I b Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Perception 4/05/2011 1 Before we get started... Website updated with Spring quarter grading policy 30% homework, 20% lab, 50% course project Website
Search Spaces I b Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Perception 4/05/2011 1 Before we get started... Website updated with Spring quarter grading policy 30% homework, 20% lab, 50% course project Website
vizmo++: a Visualization, Authoring, and Educational Tool for Motion Planning
 vizmo++: a Visualization, Authoring, and Educational Tool for Motion Planning Aimée Vargas E. Jyh-Ming Lien Nancy M. Amato. aimee@cs.tamu.edu neilien@cs.tamu.edu amato@cs.tamu.edu Technical Report TR05-011
vizmo++: a Visualization, Authoring, and Educational Tool for Motion Planning Aimée Vargas E. Jyh-Ming Lien Nancy M. Amato. aimee@cs.tamu.edu neilien@cs.tamu.edu amato@cs.tamu.edu Technical Report TR05-011
Star-shaped Roadmaps - A Deterministic Sampling Approach for Complete Motion Planning
 Star-shaped Roadmaps - A Deterministic Sampling Approach for Complete Motion Planning Gokul Varadhan Dinesh Manocha University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill http://gamma.cs.unc.edu/motion/ Email: {varadhan,dm}@cs.unc.edu
Star-shaped Roadmaps - A Deterministic Sampling Approach for Complete Motion Planning Gokul Varadhan Dinesh Manocha University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill http://gamma.cs.unc.edu/motion/ Email: {varadhan,dm}@cs.unc.edu
Planning: Part 1 Classical Planning
 Planning: Part 1 Classical Planning Computer Science 6912 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland July 12, 2016 COMP 6912 (MUN) Planning July 12, 2016 1 / 9 Planning Localization
Planning: Part 1 Classical Planning Computer Science 6912 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland July 12, 2016 COMP 6912 (MUN) Planning July 12, 2016 1 / 9 Planning Localization
Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2
 Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2 Jingwei Zhu March 19, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The purpose of this
Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2 Jingwei Zhu March 19, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The purpose of this
Path-Planning for Multiple Generic-Shaped Mobile Robots with MCA
 Path-Planning for Multiple Generic-Shaped Mobile Robots with MCA Fabio M. Marchese and Marco Dal Negro Dipartimento di Informatica, Sistemistica e Comunicazione Università degli Studi di Milano - Bicocca
Path-Planning for Multiple Generic-Shaped Mobile Robots with MCA Fabio M. Marchese and Marco Dal Negro Dipartimento di Informatica, Sistemistica e Comunicazione Università degli Studi di Milano - Bicocca
SPATIAL GUIDANCE TO RRT PLANNER USING CELL-DECOMPOSITION ALGORITHM
 SPATIAL GUIDANCE TO RRT PLANNER USING CELL-DECOMPOSITION ALGORITHM Ahmad Abbadi, Radomil Matousek, Pavel Osmera, Lukas Knispel Brno University of Technology Institute of Automation and Computer Science
SPATIAL GUIDANCE TO RRT PLANNER USING CELL-DECOMPOSITION ALGORITHM Ahmad Abbadi, Radomil Matousek, Pavel Osmera, Lukas Knispel Brno University of Technology Institute of Automation and Computer Science
Minkowski Sums. Dinesh Manocha Gokul Varadhan. UNC Chapel Hill. NUS CS 5247 David Hsu
 Minkowski Sums Dinesh Manocha Gokul Varadhan UNC Chapel Hill NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Last Lecture Configuration space workspace configuration space 2 Problem Configuration Space of a Translating Robot Input:
Minkowski Sums Dinesh Manocha Gokul Varadhan UNC Chapel Hill NUS CS 5247 David Hsu Last Lecture Configuration space workspace configuration space 2 Problem Configuration Space of a Translating Robot Input:
Dependency Tracking for Fast Marching. Dynamic Replanning for Ground Vehicles
 Dependency Tracking for Fast Marching Dynamic Replanning for Ground Vehicles Roland Philippsen Robotics and AI Lab, Stanford, USA Fast Marching Method Tutorial, IROS 2008 Overview Path Planning Approaches
Dependency Tracking for Fast Marching Dynamic Replanning for Ground Vehicles Roland Philippsen Robotics and AI Lab, Stanford, USA Fast Marching Method Tutorial, IROS 2008 Overview Path Planning Approaches
Model-Based Motion Planning
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Computer Science Department Faculty Publication Series Computer Science 2004 Model-Based Motion Planning Brendan Burns University of Massachusetts
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Computer Science Department Faculty Publication Series Computer Science 2004 Model-Based Motion Planning Brendan Burns University of Massachusetts
Path Coordination for Multiple Mobile Robots: A Resolution-Complete Algorithm
 42 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION, VOL. 18, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2002 Path Coordination for Multiple Mobile Robots: A Resolution-Complete Algorithm Thierry Siméon, Stéphane Leroy, and Jean-Paul
42 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION, VOL. 18, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2002 Path Coordination for Multiple Mobile Robots: A Resolution-Complete Algorithm Thierry Siméon, Stéphane Leroy, and Jean-Paul
Saving Time for Object Finding with a Mobile Manipulator Robot in 3D Environment
 Saving Time for Object Finding with a Mobile Manipulator Robot in 3D Environment Centro de Investigación en Matemáticas, CIMAT, Guanajuato, Mexico jespinoza@cimat.mx, murrieta@cimat.mx Abstract. In this
Saving Time for Object Finding with a Mobile Manipulator Robot in 3D Environment Centro de Investigación en Matemáticas, CIMAT, Guanajuato, Mexico jespinoza@cimat.mx, murrieta@cimat.mx Abstract. In this
Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222)
 2017 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222) 1 26-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
2017 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (W: 3:05p-4:50, 7-222) 1 26-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Path and Motion Planning. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Path and Motion Planning Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 Motion Planning Latombe (1991): eminently necessary since,
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Path and Motion Planning Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 Motion Planning Latombe (1991): eminently necessary since,
Lecture 3: Motion Planning 2
 CS 294-115 Algorithmic Human-Robot Interaction Fall 2017 Lecture 3: Motion Planning 2 Scribes: David Chan and Liting Sun - Adapted from F2016 Notes by Molly Nicholas and Chelsea Zhang 3.1 Previously Recall
CS 294-115 Algorithmic Human-Robot Interaction Fall 2017 Lecture 3: Motion Planning 2 Scribes: David Chan and Liting Sun - Adapted from F2016 Notes by Molly Nicholas and Chelsea Zhang 3.1 Previously Recall
University of Nevada, Reno. Dynamic Path Planning and Replanning for Mobile Robot Team Using RRT*
 University of Nevada, Reno Dynamic Path Planning and Replanning for Mobile Robot Team Using RRT* A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Computer
University of Nevada, Reno Dynamic Path Planning and Replanning for Mobile Robot Team Using RRT* A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Computer
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning
 Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Autonomous Robotics 6905
 6905 Lecture 5: to Path-Planning and Navigation Dalhousie University i October 7, 2011 1 Lecture Outline based on diagrams and lecture notes adapted from: Probabilistic bili i Robotics (Thrun, et. al.)
6905 Lecture 5: to Path-Planning and Navigation Dalhousie University i October 7, 2011 1 Lecture Outline based on diagrams and lecture notes adapted from: Probabilistic bili i Robotics (Thrun, et. al.)
Motion Planning. COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures
 Motion Planning COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures Motion Planning Task Planner can tell the robot discrete steps but can t say how to execute them Discrete actions must be turned into operations in
Motion Planning COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures Motion Planning Task Planner can tell the robot discrete steps but can t say how to execute them Discrete actions must be turned into operations in
