Exam Monday. Lecture 19: Binary Search & Splay Trees. Assignment BST
|
|
|
- June Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eam Monda Lecture 19: inar Search & Sla Trees S 62 Srin 2015 Kim ruce & merica hambers In class: 50 minutes Samle Eams on-line overs everthin throuh Sla trees Studin essential Do form stud rous Do roblems from samle eams Do roblems from tet ssinment ST Work first on World & Secies classes Need JUnit for both and turn in World Each creature kees a reference to its secies so it can follow the roram. Moves ho, left, riht, and infect use u turn if s and oto are free binar tree is a binar search tree iff it is emt or if the value of ever node is both reater than or equal to ever value in its left subtree and less than or equal to ever value in its riht subtree.
2 Imlementation Focus on trickiest methods: add, et, & remove rotected methods: locate, redecessor, and removeto root and value are non-null 1 - eistin tree node with the desired value, or // 2 - the node to which value should be added rotected inartree<e> locate(inartree<e> root, E value) { E rootvalue = root.value(); inartree<e> child; if (rootvalue.equals(value)) return root; // found at root // look left if less-than, riht if reater-than if (orderin.comare(rootvalue,value) < 0) { child = root.riht(); else { child = root.left(); // no child there: not in tree, return this node, // else kee searchin if (child.isemt()) { return root; else { return locate(child, value); rotected inartree<e> redecessor(inartree<e> root) { inartree<e> result = root.left(); while (!result.riht().isemt()) { result = result.riht(); return result; rotected inartree<e> successor(inartree<e> root) { inartree<e> result = root.riht(); while (!result.left().isemt()) { result = result.left(); return result; ublic void add(e value) { inartree<e> newnode = new inartree<e>(value,empty,empty); // add value to binar search tree // if there's no root, create value at root if (root.isemt()) { root = newnode; else { inartree<e> insertlocation = locate(root,value); E nodevalue = insertlocation.value(); // The location returned is the successor or redecessor // of the to-be-inserted value if (orderin.comare(nodevalue,value) < 0) { insertlocation.setriht(newnode); else { if (!insertlocation.left().isemt()) { // if value is in tree, we insert just before redecessor(insertlocation).setriht(newnode); else { insertlocation.setleft(newnode); count++;
3 Remove node General ase Remove tomost node. Left hild has a riht subtree: Eas cases: no left subtree, or no riht subtree -- eas, the are new tree left child has no riht subtree 3 redecessor( ) Remove method omleit Locate element to be deleted RemoveTo of node rooted at element Hook u resultin tree as child of elt s arent. O(h), where h is heiht of tree. O(h) to find, ould be another O(h) to find redecessor onstant to atch back toether. dd, et, contains, remove Proortional to heiht of tree an we uarantee O(lo n)? Onl if we can kee them balanced!! Secial binar search trees that sta balanced: VL trees Red-black trees We ll do sla tree, which doesn t uarantee balance but uarantees ood averae behavior easier to understand than alternatives better than others if likel to o back to recent nodes
4 Rotatin Trees Ke idea: Rotate node hiher in tree while keein it in order. Sla Trees Riht rotation Left rotation Rotatin Trees Shiftin elements toward root Rotate to root, while maintain ST structure ll nodes in subtree o u one level, all in o down one level, all in sta same. Move u two levels w/ two rotations If is left child of a left child... See code in inartree Riht rotation Left rotation
5 Shiftin elements toward root Sla Tree If is a riht child of a left child. Idea behind sla tree. Ever time find, et, add: or remove an element, move it to the root b a series of rotations. b) Other elements rotate out of wa while maintainin order. Sla means to sread outwards Smmetric if interchane left and riht
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees
 Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Best-Case upper limit on the time for insert/delete/find of an element for a BST withnelements?
 S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
S673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees 1 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)>(value stored in left subtree) For each node n, (value stored at node n)
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
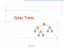 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
2. We ll add new nodes to the AVL as leaves just like we did for Binary Search Trees (BSTs). a) Add the key 90 to the tree?
 eam #: bsent:. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that
eam #: bsent:. n VL ree is a special type of inary Search ree (S) that it is balanced. y balanced I mean that the of every s left and right subtrees differ by at most one. his is enough to guarantee that
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 9: AVL TREES definition, properties, insertion
 CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 9: AVL TREES definition, roerties, insertion v 6 3 8 4 BST Performance BST ith n nodes and of height h methods find, insert and remove take O(h) time h is
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 9: AVL TREES definition, roerties, insertion v 6 3 8 4 BST Performance BST ith n nodes and of height h methods find, insert and remove take O(h) time h is
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
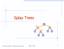 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
B Tree. Also, every non leaf node must have at least two successors and all leaf nodes must be at the same level.
 B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
CSE 326: Data Structures Splay Trees
 Announcements (//08) CSE : Data Structures Slay Trees Brian Curless Srin 008 No homewor assined this wee Midterm next Friday Closed notes, boo It will cover everythin throuh today, maybe art of Monday
Announcements (//08) CSE : Data Structures Slay Trees Brian Curless Srin 008 No homewor assined this wee Midterm next Friday Closed notes, boo It will cover everythin throuh today, maybe art of Monday
CSC 263 Lecture 4. September 13, 2006
 S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
Splay Trees 3/20/14. Splay Trees. Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees. note that two keys of equal value may be wellseparated (7,T) (1,Q) (1,C) (5,H)
 Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Binomial Queue deletemin ADTs Seen So Far
 Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Lecture Overview. Readings. Recall: Binary Search Trees (BSTs) The importance of being balanced. AVL trees. Balance Insert. Other balanced trees
 alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
Where we are. CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 4: Dictionaries; Binary Search Trees. The Dictionary (a.k.a. Map) ADT
 Where we are Studying the absolutely essential DTs of computer science and classic data structures for implementing them SE: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Dictionaries; inary Search Trees Dan rossman
Where we are Studying the absolutely essential DTs of computer science and classic data structures for implementing them SE: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Dictionaries; inary Search Trees Dan rossman
CS350: Data Structures Tree Traversal
 Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Tree Traversal James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Defining Trees Recursively Trees can easily be defined recursively Definition of a binary
Advanced Tree Structures
 Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018
 Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018 Red-black trees Symmetric binary B-tree, Rudolf Bayer, 1972. The balancing is maintained by using a coloring of the nodes. The red-black trees are binary search trees
Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018 Red-black trees Symmetric binary B-tree, Rudolf Bayer, 1972. The balancing is maintained by using a coloring of the nodes. The red-black trees are binary search trees
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
search(i): Returns an element in the data structure associated with key i
 CS161 Lecture 7 inary Search Trees Scribes: Ilan Goodman, Vishnu Sundaresan (2015), Date: October 17, 2017 Virginia Williams (2016), and Wilbur Yang (2016), G. Valiant Adated From Virginia Williams lecture
CS161 Lecture 7 inary Search Trees Scribes: Ilan Goodman, Vishnu Sundaresan (2015), Date: October 17, 2017 Virginia Williams (2016), and Wilbur Yang (2016), G. Valiant Adated From Virginia Williams lecture
CS 303 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 inal Exam S 0 esign and nalsis of lgorithms Review or inal Exam ong Xu (Based on class note of avid Luebke) am-0am, onda, a 0 lose book Bring our calculator 40% of our final score Office hours during final
inal Exam S 0 esign and nalsis of lgorithms Review or inal Exam ong Xu (Based on class note of avid Luebke) am-0am, onda, a 0 lose book Bring our calculator 40% of our final score Office hours during final
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees. Linda Shapiro Spring 2016
 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 nnouncements HW2 due start of class Wednesday pril 13 on paper. Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms
CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 6: Binary Search Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 nnouncements HW2 due start of class Wednesday pril 13 on paper. Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms
Balanced search trees
 Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES WEEK - 6
 Ashish Jamuda Week 6 CS 331 DATA STRUCTURES & ALGORITHMS BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES OBJECTIVES: Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Tree
Ashish Jamuda Week 6 CS 331 DATA STRUCTURES & ALGORITHMS BINARY TREES, THE SEARCH TREE ADT BINARY SEARCH TREES, RED BLACK TREES, TREE TRAVERSALS, B TREES OBJECTIVES: Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Tree
Binary Trees. Binary Search Trees
 Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Linear Data Structure Linked List
 . Definition. Reresenting List in C. Imlementing the oerations a. Inserting a node b. Deleting a node c. List Traversal. Linked imlementation of Stack 5. Linked imlementation of Queue 6. Circular List
. Definition. Reresenting List in C. Imlementing the oerations a. Inserting a node b. Deleting a node c. List Traversal. Linked imlementation of Stack 5. Linked imlementation of Queue 6. Circular List
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
AVL Trees. Reading: 9.2
 AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
CS 361, Lecture 21. Outline. Things you can do. Things I will do. Evaluation Results
 HW Difficulty CS 361, Lecture 21 Jared Saia University of New Mexico The HW in this class is inherently difficult, this is a difficult class. You need to be able to solve problems as hard as the problems
HW Difficulty CS 361, Lecture 21 Jared Saia University of New Mexico The HW in this class is inherently difficult, this is a difficult class. You need to be able to solve problems as hard as the problems
B + -trees. Kerttu Pollari-Malmi
 B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
Binary Trees and Huffman Encoding Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees and Huffman Encoding Binary Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Motivation: Maintaining a Sorted Collection of Data A data dictionary is a
Binary Trees and Huffman Encoding Binary Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Motivation: Maintaining a Sorted Collection of Data A data dictionary is a
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Why Trees? Alternatives. Want: Ordered arrays. Linked lists. A data structure that has quick insertion/deletion, as well as fast search
 Why Trees? Alternatives Ordered arrays Fast searching (binary search) Slow insertion (must shift) Linked lists Want: Fast insertion Slow searching (must start from head of list) A data structure that has
Why Trees? Alternatives Ordered arrays Fast searching (binary search) Slow insertion (must shift) Linked lists Want: Fast insertion Slow searching (must start from head of list) A data structure that has
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Some Search Structures. Balanced Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. A Binary Search Tree. Review Binary Search Trees
 Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees IV. Lecture 21. Prof.
 ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
a graph is a data structure made up of nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges
 1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium
![[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists, Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium [6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. McCreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \A new. representation for linear lists, Proc. Ninth Annual ACM Symposium](/thumbs/88/117928360.jpg) [6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. Mcreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \ new representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth nnual M Smposium on Theor of omputing, (1977), pp.49-60. [7] L. J. Guibas, R. Sedgewick,
[6] L. J. Guibas, E. M. Mcreight, M. F. Plass, and J. R. Roberts \ new representation for linear lists," Proc. Ninth nnual M Smposium on Theor of omputing, (1977), pp.49-60. [7] L. J. Guibas, R. Sedgewick,
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
CS 261 Data Structures. AVL Trees
 CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Motivation Computer Information Systems Storage Retrieval Updates. Binary Search Trees. OrderedStructures. Binary Search Tree
 Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI Section E01 AVL Trees AVL Property While BST structures have average performance of Θ(log(n))
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI Section E01 AVL Trees AVL Property While BST structures have average performance of Θ(log(n))
4/18/ Binary Search Trees (BSTs) 17.1 Adding an Element to a BST Removing an Element from a BST. 17.
 17.1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) 17.1 Adding an Element to a BST! Write the inorder traversal of this tree. What do you observe?! A search tree is a tree whose elements are organized to facilitate finding
17.1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) 17.1 Adding an Element to a BST! Write the inorder traversal of this tree. What do you observe?! A search tree is a tree whose elements are organized to facilitate finding
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
COMP 250. Lecture 22. binary search trees. Oct. 30, 2017
 COMP 250 Lecture 22 binary search trees Oct. 30, 2017 1 (binary search) tree binary (search tree) 2 class BSTNode< K >{ K BSTNode< K > BSTNode< K > : } key; leftchild; rightchild; The keys are comparable
COMP 250 Lecture 22 binary search trees Oct. 30, 2017 1 (binary search) tree binary (search tree) 2 class BSTNode< K >{ K BSTNode< K > BSTNode< K > : } key; leftchild; rightchild; The keys are comparable
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
Outline. Computer Science 331. Insertion: An Example. A Recursive Insertion Algorithm. Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion.
 Outline Computer Science Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture # 2 BST Deletion Case Case 2 Case Case 4 Complexity Discussion
Outline Computer Science Binary Search Trees Insertion and Deletion Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture # 2 BST Deletion Case Case 2 Case Case 4 Complexity Discussion
List: a sequence of cells in which each cell contains a data item of type Object a reference to the next cell in the sequence (null if this
 Lists 1 Overview Arrays Random access:! Fixed size: cannot grow on demand after creation: " Characteristics of some alications: do not need random access require a data structure that can grow and shrink
Lists 1 Overview Arrays Random access:! Fixed size: cannot grow on demand after creation: " Characteristics of some alications: do not need random access require a data structure that can grow and shrink
Search Trees. Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees
 Unit 9, Part 2 Search Trees Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees Search-tree property: for each node k: all nodes in k s left subtree are < k all nodes
Unit 9, Part 2 Search Trees Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Binary Search Trees Search-tree property: for each node k: all nodes in k s left subtree are < k all nodes
Binary search trees :
 Binary search trees Binary search trees : Search trees are data structures that generally offer the following dynamic-set operations : SEARCH MINIMUM MAXIMUM PREDECESSOR SUCCESSOR INSERT DELETE Basic operations
Binary search trees Binary search trees : Search trees are data structures that generally offer the following dynamic-set operations : SEARCH MINIMUM MAXIMUM PREDECESSOR SUCCESSOR INSERT DELETE Basic operations
CSC148 Week 7. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 7 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 can be picked up in DH-3008 A1 due this Saturday Next week is reading week no lecture, no labs no office hours 2 Recap Last week, learned about binary trees
CSC148 Week 7 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 can be picked up in DH-3008 A1 due this Saturday Next week is reading week no lecture, no labs no office hours 2 Recap Last week, learned about binary trees
Week 2. TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400 home pages) Peer Mentoring available - Friday 8am-12pm, 12:15-1:30pm in 1289CS
 ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
Announcements. Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18. Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps. Break around 11:45am
 Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 7: Dictionaries; Binary Search Trees. Ruth Anderson Winter 2019
 CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 7: Dictionaries; Binary Search Trees Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Today Dictionaries Trees 1/23/2019 2 Where we are Studying the absolutely essential ADTs of
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 7: Dictionaries; Binary Search Trees Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Today Dictionaries Trees 1/23/2019 2 Where we are Studying the absolutely essential ADTs of
Red-Black Trees 10/19/2009. Red-Black Trees. Example. Red-Black Properties. Black Height. Example
 lgorithms Red-lak Trees 13-2 Red-lak Trees Red-lak Trees ll binar searh tree operations take O(h) time, here h is the height of the tree Therefore, it is important to `balane the tree so that its height
lgorithms Red-lak Trees 13-2 Red-lak Trees Red-lak Trees ll binar searh tree operations take O(h) time, here h is the height of the tree Therefore, it is important to `balane the tree so that its height
B-trees. It also makes sense to have data structures that use the minimum addressable unit as their base node size.
 B-trees Balanced BSTs such as RBTs are great for data structures that can fit into the main memory of the computer. But what happens when we need to use external storage? Here are some approximate speeds
B-trees Balanced BSTs such as RBTs are great for data structures that can fit into the main memory of the computer. But what happens when we need to use external storage? Here are some approximate speeds
Algorithms. Red-Black Trees
 Algorithms Red-Black Trees Red-Black Trees Balanced binary search trees guarantee an O(log n) running time Red-black-tree Binary search tree with an additional attribute for its nodes: color which can
Algorithms Red-Black Trees Red-Black Trees Balanced binary search trees guarantee an O(log n) running time Red-black-tree Binary search tree with an additional attribute for its nodes: color which can
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees
 Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
Advanced Tree. Structures. AVL Tree. Outline. AVL Tree Recall, Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special case of. Splay Tree (Ch 13.2.
 ttp://1...0/csd/ Data tructure Capter 1 Advanced Tree tructures Dr. atrick Can cool of Computer cience and Engineering out Cina Universit of Tecnolog AVL Tree Recall, Binar earc Tree (BT) is a special
ttp://1...0/csd/ Data tructure Capter 1 Advanced Tree tructures Dr. atrick Can cool of Computer cience and Engineering out Cina Universit of Tecnolog AVL Tree Recall, Binar earc Tree (BT) is a special
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Binary Tree Implementation
 Binary Tree Implementation Lecture 31 Sections 12.2-12.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 5, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Implementation Mon, Apr 5, 2010 1 /
Binary Tree Implementation Lecture 31 Sections 12.2-12.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 5, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Implementation Mon, Apr 5, 2010 1 /
Maps & Dictionaries Searching for Information
 Maps & Dictionaries Searching for Information Maps 1 Definition Map is the mathematical name for a dictionary» It is a function that, given a key, returns corresponding data > Hence the notion of mapping
Maps & Dictionaries Searching for Information Maps 1 Definition Map is the mathematical name for a dictionary» It is a function that, given a key, returns corresponding data > Hence the notion of mapping
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree -
 Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree - AVL, Red-Black, B-tree Hanyang University Jong-Il Park AVL TREE Division of Computer Science and Engineering, Hanyang University Balanced binary trees Non-random
Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree - AVL, Red-Black, B-tree Hanyang University Jong-Il Park AVL TREE Division of Computer Science and Engineering, Hanyang University Balanced binary trees Non-random
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CS 314H Honors Data Structures Fall 2017 Programming Assignment #6 Treaps Due November 12/15/17, 2017
 CS H Honors Data Structures Fall 207 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November 2//7, 207 In this assignment ou will work individuall to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure called
CS H Honors Data Structures Fall 207 Programming Assignment # Treaps Due November 2//7, 207 In this assignment ou will work individuall to implement a map (associative lookup) using a data structure called
Binary Search Trees 1
 Binary Search Trees 1 The Problem with Linked Lists 8Accessing a item from a linked list takes O(N) time for an arbitrary element 8Binary trees can improve upon this and reduce access to O( log N ) time
Binary Search Trees 1 The Problem with Linked Lists 8Accessing a item from a linked list takes O(N) time for an arbitrary element 8Binary trees can improve upon this and reduce access to O( log N ) time
CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013
 CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop
CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop
TREES 11/1/18. Prelim Updates. Data Structures. Example Data Structures. Tree Overview. Tree. Singly linked list: Today: trees!
 relim Updates Regrades are live until next Thursday @ :9M A few rubric changes are happening Recursion question: -0pts if you continued to print Exception handling write the output of execution of that
relim Updates Regrades are live until next Thursday @ :9M A few rubric changes are happening Recursion question: -0pts if you continued to print Exception handling write the output of execution of that
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Multi-Way Search Tree
 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
CS350: Data Structures AA Trees
 AA Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to AA Trees A type of balanced binary search tree Developed as a simpler alternative
AA Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to AA Trees A type of balanced binary search tree Developed as a simpler alternative
Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park
 Data Structures and Algorithms Binary Search Trees Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park Copyright Notice: This material is modified version of the lecture slides by Prof. Rada Mihalcea in Univ. of North Texas.
Data Structures and Algorithms Binary Search Trees Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park Copyright Notice: This material is modified version of the lecture slides by Prof. Rada Mihalcea in Univ. of North Texas.
AVL Trees. Data and File Structures Laboratory. DFS Lab (ISI) AVL Trees 1 / 18
 AVL Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2018/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) AVL Trees 1 / 18 Recap: traditional vs. alternative implementations nodelist p Data Left Right
AVL Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2018/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) AVL Trees 1 / 18 Recap: traditional vs. alternative implementations nodelist p Data Left Right
Data Structure. Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang. National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan
 Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
A set of nodes (or vertices) with a single starting point
 Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Red-Black Trees (2) Antonio Carzaniga. Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano. April 26, Antonio Carzaniga 1
 Red-lack Trees (2) ntonio arzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano pril 26, 2012 2006 ntonio arzaniga 1 Recap on Red-lack Trees 12 5 18 2 9 15 19 4 13 17 Red-black-tree property 2. 4. 5. 1.
Red-lack Trees (2) ntonio arzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano pril 26, 2012 2006 ntonio arzaniga 1 Recap on Red-lack Trees 12 5 18 2 9 15 19 4 13 17 Red-black-tree property 2. 4. 5. 1.
DELETION WITHOUT REBALANCING IN BINARY SEARCH TREES
 DELETION WITHOUT RELNING IN INRY SERH TREES SIDDHRTH SEN, ROERT E. TRJN, ND DVID HONG KYUN KIM bstract. We address the veing issue of deletions in balanced trees. Rebalancing after a deletion is generall
DELETION WITHOUT RELNING IN INRY SERH TREES SIDDHRTH SEN, ROERT E. TRJN, ND DVID HONG KYUN KIM bstract. We address the veing issue of deletions in balanced trees. Rebalancing after a deletion is generall
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
Crit-bit Trees. Adam Langley (Version )
 Crit-bit Trees Adam Langley (agl@imperialviolet.org) (Version 20080926) 1. Introduction This code is taken from Dan Bernstein s qhasm and implements a binary crit-bit (alsa known as PATRICA) tree for NUL
Crit-bit Trees Adam Langley (agl@imperialviolet.org) (Version 20080926) 1. Introduction This code is taken from Dan Bernstein s qhasm and implements a binary crit-bit (alsa known as PATRICA) tree for NUL
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
AVL Trees. Version of September 6, AVL Trees Version of September 6, / 22
 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Multi-way Search Trees! M-Way Search! M-Way Search Trees Representation!
 Lecture 10: Multi-way Search Trees: intro to B-trees 2-3 trees 2-3-4 trees Multi-way Search Trees A node on an M-way search tree with M 1 distinct and ordered keys: k 1 < k 2 < k 3
Lecture 10: Multi-way Search Trees: intro to B-trees 2-3 trees 2-3-4 trees Multi-way Search Trees A node on an M-way search tree with M 1 distinct and ordered keys: k 1 < k 2 < k 3
If you took your exam home last time, I will still regrade it if you want.
 Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
