and to the following students who assisted in the creation of the Fluid Dynamics tutorials:
|
|
|
- Eunice Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Channel Flow Basic Tutorial # 4 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair Engineering; and to the following students who assisted in the creation of the Fluid Dynamics tutorials: Leslie Tanner, Cole Yarrington, Curtis Rands, Curtis Memory, and Stephen McQuay.
2
3 2D Curved Flow In this tutorial, GAMBIT will be used to create and mesh the flow field geometry for the problem. Once this is complete, FLUENT will be used to solve for the pressure field everywhere in the domain and plot the pressure distribution across the pipe. This tutorial will provide experience in solving 2D flows and creating plots of the results. The methods expressed in these tutorials represent just one approach to modeling, constraining and solving 2D problems. Our goal is the education of students in the use of CAx tools for modeling, constraining and solving fluids application problems. Other techniques and methods will be used and introduced in subsequent tutorials. Water flows around the vertical two-dimensional bend with circular streamlines and constant velocity as shown below. If the pressure is 40 kpa at point (1), determine the pressure at points (2) and (3). Assume that the velocity profile is uniform as indicated. 3
4 Creating Geometry Begin the problem by creating geometry in Gambit. Start Gambit by either typing gambit at the command prompt (Unix or Windows) or clicking on the Gambit icon (Windows). The Gambit standard display should appear. Meshes are generated in Gambit by following left to right the menu icons located in the top right of the display window. The 2-D geometry will consist of two 90 arcs with lines connecting the ends. Create a node which will be used to define the center of curvature for the two arcs. Geometry > Vertex > Create Vertex Enter the Vertex at (0,6,0) as shown: Select Apply and Close. 4
5 Geometry > Edge > Create Real Circular Arc Note: Icons with a red arrow have a pull down menu. The arc button is located in the edges pull down menu. To activate the pull down menu select the icon with MB3. Buttons are then selected with MB1. Select the far right radio button Enter 6 for the radius, 225 and 315 for the angles. Select the center button. Select the vertex by holding the shift button and clicking MB1 over the vertex. Repeat for another arc of radius 4. Channel Flow Creating Geometry Now draw two lines to connect the arcs. Geometry > Edge > Create Edge Create lines to connect the arcs by shift selecting both end points and selecting Apply. Repeat for the other side of the channel. 5
6 Creating Geometry Next, create a face from the edges just created. Geometry > Face > Wireframe Shift select all four edges and click Apply. The edges should now be colored blue to indicate that the face has been created. If problems are encountered in creating the geometry, the geometry can be loaded from the file Bend_Geometry.dbs. 6
7 Meshing Geometry The geometry has now been created. The next step is to generate the mesh. First the edges must be meshed. Mesh > Edge > Mesh Edges Shift Select the left straight edge and the right straight edge. Change the pull-down menu to Interval count and enter 30. Click Apply. Repeat this procedure for the upper and lower walls. The screen should now look like this: Next mesh the face. Mesh > Face > Mesh faces Shift Select any edge of the geometry to select the face. Make sure the Element menu is set to Quad, Type is set to Map and then select Apply. The screen should look like this: If problems are encountered in meshing geometry, the meshed geometry can be loaded from the file Bend_Meshed.dbs. 7
8 Boundary Conditions Now define the boundary conditions for the problem. Since Fluent version 6 is going to be used, select Solver > Fluent5/6 from the pull-down menu across the top of the window. Operation > Zones > Specify Boundary Types Change the pull-down menu at the bottom to edges. This allows for selection of individual edges. Select the top and bottom edges. Name them walls and click Apply. Select the left straight edge, change the type pull-down menu to Velocity-Inlet, name it inlet and click Apply. Select the right straight edge, change the type pull-down menu to Outflow, name it outlet and click Apply. Now the geometry is ready to be exported. From the file pull-down menu, select File>export>mesh Select a location for the *.msh file and Accept. make sure to select the "export 2-D (X-Y) Mesh" radio button. Save and exit from Gambit. 8
9 If problems are encountered in specifying boundary conditions, the completed mesh with boundary conditions specified can be loaded from the file Bend_Complete.dbs. Channel Flow Starting in Fluent Open Fluent from the Desktop or Start menu. Select 2D Select Run The following window should appear. This is the FLUENT user interface. Most tasks are completed using the menus across the top. The menus are designed to guide you through the analysis in an orderly fashion, going from top to bottom through each menu, and left to right across the menu bar. Text commands can also be used in the command window. 9
10 Defining the Problem Start by importing the mesh created in Gambit. File > Read > Case A browse window should appear. Locate the *.msh file and select OK. FLUENT will read the mesh you created. If there are problems reading the mesh, return to the beginning of the tutorial and make sure you follow the steps carefully. If there are no problems the command window should state done. Now check the grid for errors. Grid > Check Any errors will be listed, otherwise the command window should again state done. 10
11 Defining the Problem Because the problem statement assumes a constant velocity profile across the channel, the flow will be modeled as inviscid. Define > Models > Viscous Select the Inviscid radio button and then OK. Now the fluid properties must be specified. The fluid properties are found by selecting: Define > Materials Select database... to browse through the FLUENT library of materials. Scroll down and select water-liquid (h2o<l>). Select Copy to copy these material properties into the current problem. Select Close on the Database Materials windows, followed by Close on the Materials window. Note: it is very important to click on the copy button. The fluid properties will not be loaded if the copy button is not selected. 11
12 Defining the Problem In order to set gravitational conditions as specified in the problem, select: Define > Operating Conditions Click on the Gravity radio button. Set the Operating pressure to be Pa and Gravity to be m/s 2 in the y direction. Click Ok. Now the velocity condition at the inlet and fluid type must be specified. Define > Boundary Conditions Select fluid under zones menu. Select fluid from the type menu. Click on set... From the Material Name pull down menu select the fluid that was previously added to the list, namely water-liquid (h2o<l>). Select Ok. 12
13 Defining the Problem Now to set the inlet conditions, select the inlet on the left, then select Set... Set the velocity magnitude to 10m/s. Select Ok and close the Boundary Conditions window. Specify which discretization functions will be used to calculate the solution. Solve > Controls > Solution In the Solution Control dialogue box, set the under-relaxation coefficients to Pressure = 0.9 Density = 1 Body Forces = 1 Momentum = 0.7 Also, change the Discretization functions to: PRESTO! SIMPLEC 2nd order upwind Click Ok. 13
14 Defining the Problem Next, the solution must be initialized. To do this: Solve > Initialize > Initialize From the Compute From pull-down menu, select the name given to the inlet wall. Select Init then close. Note: Once again, if initialize is not selected before close is, the case will remain un-initialized. By default, while trying to converge to a solution, FLUENT will stop iterating at a prescribed convergence threshold. Since the residuals will be plotted and analyzed graphically, it is not necessary to have FLU- ENT do this. To change this select: Solve > Monitors > Residual Place a check mark next to the Plot option using MB1. Make a new window by incrementing Window from 0 to 1. Deselect all of the check convergence boxes. Select Ok. 14
15 Defining the Problem In order to view the pressure field including the hydrostatic pressure, create a "Custom Field Function Define > Custom Field Function Create the function defined as follows: absolute-pressure - density * 9.81 * y Select absolute-pressure from the pulldown menu as shown: Click Select. Select the subtract sign. Select density from the pull-down menu and click select Select the multiplication (X) sign Enter 9.81 on the calculator pad Select the multiplication sign Select the y-coordinate as follows: First Pull-down menu: Grid Second Pull-down menu: Y-Coordinate Rename the function Press in the new function name box. Click Define and Close. 15
16 Defining the Problem In order to view pressure at discrete points, the points of interest must be created. Surface > Point... Create three points by entering the coordinate values and giving the point a name. If the bottom point surface creation fails, use a value slightly above zero (y=.0001), as shown. Create two points located at the middle (y=1) and top of the channel (y=2), respectively. Now set up monitors for these points under: Solve > Monitors > Surface... Set up three separate monitors (one for each point). Rename the monitors. Check the Print box for all three monitors. Choose Iteration from the Every pulldown menu. Select Define for the first monitor. Choose the point to be monitored from the Surfaces scroll menu. Change Report type to Sum. Verify that the correct Custom Field Function chosen from the Report of menu. Click Ok. Repeat for the remaining two points. Now, while iterating, there will be a column of pressure values displayed in the prompt window for each point. 16
17 Solving the Problem The problem is now ready to be solved. Select: Solve > Iterate Set the number of iterations to 100 and click Iterate. When iterations have completed close the iterate window. Note: It is preferable to have a view of the residuals handy so that they can be visually monitored., as shown. 17
18 Analyzing the Results Notice that the residuals have dropped by 6 to 7 orders of magnitude and have leveled out. This means that the solution has converged. To visually inspect the solutions, select Display > Contours From the pull-down menus select Pressure and select Display. The Pressure Distribution should look like this: 18
19 Analyzing the Results Now, since the pressure along the z-axis is desired, create a line along which to plot pressure vs. position by selecting: Surface > Line/Rake Enter the values as follows to define a line: x0 = 0 y0 = 0 x1 = 0 y1 = 2 Name the line centerline. Click create then close. Display the line in the display window by highlighting centerline in the Grid Display window, and clicking display. It should appear as shown: 19
20 Analyzing the Results Now plot the user-defined function by selecting: Plot > XY Plot From the pull down menu, select: Custom Field Functions... Select the line that was created: Change the plot direction as shown: Select Plot. The plot should look like this: If problems are encountered in setting up this problem in fluent, the solved problem can be read in as a Case and Data from the file Bend.cas. 20
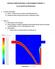
21 Analytical Solution The analytical solution for the pressure along the vertical line from (1) to (3) is derived from ã dy dn p = n ñv R 2 Where γ is the specific weight of the fluid and ρ is the density. Substituting the geometry conditions for this problem and integrating yields P = P1 γy ρv At point (2), y=1m, and P 2 = 12.0kPa. At point (3), y=2m, and P 3 = -20.1kPa. The values predicted by Fluent are: P 2 = 13507kPa P 3 = kPa 2 6 ln 6 y which are in both in error by 13% and 9% respectively. The plot below shows a comparison of the analytical and CFD results Fluent Analytical 20.0 P (kpa) y(m) 21
and to the following students who assisted in the creation of the Fluid Dynamics tutorials:
 Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Pressure Along a Streamline Basic Tutorial #3 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair
Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Pressure Along a Streamline Basic Tutorial #3 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair
Appendix: To be performed during the lab session
 Appendix: To be performed during the lab session Flow over a Cylinder Two Dimensional Case Using ANSYS Workbench Simple Mesh Latest revision: September 18, 2014 The primary objective of this Tutorial is
Appendix: To be performed during the lab session Flow over a Cylinder Two Dimensional Case Using ANSYS Workbench Simple Mesh Latest revision: September 18, 2014 The primary objective of this Tutorial is
2. MODELING A MIXING ELBOW (2-D)
 MODELING A MIXING ELBOW (2-D) 2. MODELING A MIXING ELBOW (2-D) In this tutorial, you will use GAMBIT to create the geometry for a mixing elbow and then generate a mesh. The mixing elbow configuration is
MODELING A MIXING ELBOW (2-D) 2. MODELING A MIXING ELBOW (2-D) In this tutorial, you will use GAMBIT to create the geometry for a mixing elbow and then generate a mesh. The mixing elbow configuration is
Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge
 SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 2 Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification A uniform supersonic stream encounters a wedge
SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 2 Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification A uniform supersonic stream encounters a wedge
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe
 Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Modeling Flow Through Porous Media
 Tutorial 7. Modeling Flow Through Porous Media Introduction Many industrial applications involve the modeling of flow through porous media, such as filters, catalyst beds, and packing. This tutorial illustrates
Tutorial 7. Modeling Flow Through Porous Media Introduction Many industrial applications involve the modeling of flow through porous media, such as filters, catalyst beds, and packing. This tutorial illustrates
Compressible Flow in a Nozzle
 SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1 Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification Consider air flowing at high-speed through a
SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1 Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification Consider air flowing at high-speed through a
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows
 Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models
 Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer
 Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders
 Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate
 Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Step 1: Create Geometry in GAMBIT
 Step 1: Create Geometry in GAMBIT If you would prefer to skip the mesh generation steps, you can create a working directory (see below), download the mesh from here (right click and save as pipe.msh) into
Step 1: Create Geometry in GAMBIT If you would prefer to skip the mesh generation steps, you can create a working directory (see below), download the mesh from here (right click and save as pipe.msh) into
Tutorial: Hydrodynamics of Bubble Column Reactors
 Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for solving a gas-liquid bubble column problem using the multiphase mixture model, including advice on solver
Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for solving a gas-liquid bubble column problem using the multiphase mixture model, including advice on solver
A B C D E. Settings Choose height, H, free stream velocity, U, and fluid (dynamic viscosity and density ) so that: Reynolds number
 Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 By Timur K. Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 By Timur K. Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame
 Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver.
 Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body
 1 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 18, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim, Maysam Mousaviraad,
1 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 18, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim, Maysam Mousaviraad,
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following:
 Tutorial 22. Modeling Solidification Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following: Define a
Tutorial 22. Modeling Solidification Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following: Define a
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert)
 Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert) ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Developing Laminar Flow in a 2D Channel 1 How to use This
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert) ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Developing Laminar Flow in a 2D Channel 1 How to use This
Flow in an Intake Manifold
 Tutorial 2. Flow in an Intake Manifold Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to model turbulent flow in a simple intake manifold geometry. An intake manifold is a system of passages which carry
Tutorial 2. Flow in an Intake Manifold Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to model turbulent flow in a simple intake manifold geometry. An intake manifold is a system of passages which carry
Introduction to CFX. Workshop 2. Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. WS2-1. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
TUTORIAL#3. Marek Jaszczur. Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate W1-1 AGH 2018/2019
 TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for boudary layer 1. Creating 2D simple geometry
TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for boudary layer 1. Creating 2D simple geometry
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing
 Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT
 Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT Introduction This tutorial provides instructions for meshing two internal flows. Pointwise software will be used
Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT Introduction This tutorial provides instructions for meshing two internal flows. Pointwise software will be used
Modeling External Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Solution Domain Boundary Conditions Start-Up
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Solution Domain Boundary Conditions Start-Up
Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow
 Tutorial 21. Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow Introduction Mixing tanks are used to maintain solid particles or droplets of heavy fluids in suspension. Mixing may be required to enhance
Tutorial 21. Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow Introduction Mixing tanks are used to maintain solid particles or droplets of heavy fluids in suspension. Mixing may be required to enhance
µ = Pa s m 3 The Reynolds number based on hydraulic diameter, D h = 2W h/(w + h) = 3.2 mm for the main inlet duct is = 359
 Laminar Mixer Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 March 30, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@pdx.edu 1 Overview Imagine that you are part of a team developing a medical diagnostic device. The device has a millimeter
Laminar Mixer Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 March 30, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@pdx.edu 1 Overview Imagine that you are part of a team developing a medical diagnostic device. The device has a millimeter
3. MODELING A THREE-PIPE INTERSECTION (3-D)
 3. MODELING A THREE-PIPE INTERSECTION (3-D) This tutorial employs primitives that is, predefined GAMBIT modeling components and procedures. There are two types of GAMBIT primitives: Geometry Mesh Geometry
3. MODELING A THREE-PIPE INTERSECTION (3-D) This tutorial employs primitives that is, predefined GAMBIT modeling components and procedures. There are two types of GAMBIT primitives: Geometry Mesh Geometry
Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
 Tutorial 16. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s air-blast atomizer model is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the air flow
Tutorial 16. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s air-blast atomizer model is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the air flow
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM)
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Computational Fluid Dynamics autumn, 1st week
 Computational Fluid Dynamics 2016 autumn, 1st week 1 Tamás Benedek benedek [at] ara.bme.hu www.ara.bme.hu/~benedek/cfd/icem The most important rule: Dont use space or specific characters in: File names,
Computational Fluid Dynamics 2016 autumn, 1st week 1 Tamás Benedek benedek [at] ara.bme.hu www.ara.bme.hu/~benedek/cfd/icem The most important rule: Dont use space or specific characters in: File names,
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe.
 Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Ryian Hunter MAE 598
 Setup: The initial geometry was produced using the engineering schematics provided in the project assignment document using the ANSYS DesignModeler application taking advantage of system symmetry. Fig.
Setup: The initial geometry was produced using the engineering schematics provided in the project assignment document using the ANSYS DesignModeler application taking advantage of system symmetry. Fig.
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 07 Tank Flushing
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 07 Tank Flushing Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations,
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 07 Tank Flushing Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations,
Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
 Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle
 CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle C, Diyoke Mechanical Engineering Department Enugu State University of Science & Tech. Enugu, Nigeria U, Ngwaka
CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle C, Diyoke Mechanical Engineering Department Enugu State University of Science & Tech. Enugu, Nigeria U, Ngwaka
Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
SimCafe. ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited by Benjamin J Mullen on Apr 29, :18
 Page 1 of 5 Search Cornell SimCafe Home Edit Browse/Manage Login Simulation > > ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Search ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited
Page 1 of 5 Search Cornell SimCafe Home Edit Browse/Manage Login Simulation > > ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Search ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited
Use 6DOF solver to calculate motion of the moving body. Create TIFF files for graphic visualization of the solution.
 Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for setting up and solving a moving deforming mesh (MDM) case along with the six degree of freedom (6DOF) solver and
Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for setting up and solving a moving deforming mesh (MDM) case along with the six degree of freedom (6DOF) solver and
Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding This tutorial demonstrates how to use the solution recording and playback module for capturing the results of transient phenomena.
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding This tutorial demonstrates how to use the solution recording and playback module for capturing the results of transient phenomena.
8. BASIC TURBO MODEL WITH UNSTRUCTURED MESH
 8. BASIC TURBO MODEL WITH UNSTRUCTURED MESH This tutorial employs a simple turbine blade configuration to illustrate the basic turbo modeling functionality available in GAMBIT. It illustrates the steps
8. BASIC TURBO MODEL WITH UNSTRUCTURED MESH This tutorial employs a simple turbine blade configuration to illustrate the basic turbo modeling functionality available in GAMBIT. It illustrates the steps
Tutorial: Heat and Mass Transfer with the Mixture Model
 Tutorial: Heat and Mass Transfer with the Mixture Model Purpose The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate the use of mixture model in FLUENT 6.0 to solve a mixture multiphase problem involving heat
Tutorial: Heat and Mass Transfer with the Mixture Model Purpose The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate the use of mixture model in FLUENT 6.0 to solve a mixture multiphase problem involving heat
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3
 APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
SMS v Simulations. SRH-2D Tutorial. Time. Requirements. Prerequisites. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model
 Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate how to set up and solve a problem using the. Moving Deforming Mesh (MDM) using the layering algorithm.
 Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate how to set up and solve a problem using the following two features in FLUENT. Moving Deforming Mesh (MDM) using the layering algorithm.
Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate how to set up and solve a problem using the following two features in FLUENT. Moving Deforming Mesh (MDM) using the layering algorithm.
Computational Flow Analysis of Para-rec Bluff Body at Various Reynold s Number
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
TUTORIAL#4. Marek Jaszczur. Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate W1-1 AGH 2018/2019
 TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for Non-isothermal
TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for Non-isothermal
equivalent stress to the yield stess.
 Example 10.2-1 [Ansys Workbench/Thermal Stress and User Defined Result] A 50m long deck sitting on superstructures that sit on top of substructures is modeled by a box shape of size 20 x 5 x 50 m 3. It
Example 10.2-1 [Ansys Workbench/Thermal Stress and User Defined Result] A 50m long deck sitting on superstructures that sit on top of substructures is modeled by a box shape of size 20 x 5 x 50 m 3. It
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies
 Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Flow over an Ahmed Body
 Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Flow over an Ahmed Body Problem Specification Start Up Geometry Import Geometry Enclose Suppress Mesh Set Mesh Controls Generate
Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Flow over an Ahmed Body Problem Specification Start Up Geometry Import Geometry Enclose Suppress Mesh Set Mesh Controls Generate
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Import Geometry Mesh
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Import Geometry Mesh
Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent
 MEGR 7090-003, Computational Fluid Dynamics :1 7 Spring 2015 Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent Rahul R Upadhyay Master of Science, Dept of Mechanical
MEGR 7090-003, Computational Fluid Dynamics :1 7 Spring 2015 Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent Rahul R Upadhyay Master of Science, Dept of Mechanical
CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report
 26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model
 Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate setup and solution procedure of liquid chemical
Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate setup and solution procedure of liquid chemical
Analysis of an airfoil
 UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH FALL 2010 Analysis of an airfoil using Computational Fluid Dynamics Tanveer Chandok 12/17/2010 Independent research thesis at the Georgia Institute of Technology under the supervision
UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH FALL 2010 Analysis of an airfoil using Computational Fluid Dynamics Tanveer Chandok 12/17/2010 Independent research thesis at the Georgia Institute of Technology under the supervision
Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics. Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4
 UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow 2 Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow This tutorial demonstrates the performance of STAR-CCM+ in solving a traditional square lid-driven cavity
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow 2 Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow This tutorial demonstrates the performance of STAR-CCM+ in solving a traditional square lid-driven cavity
November c Fluent Inc. November 8,
 MIXSIM 2.1 Tutorial November 2006 c Fluent Inc. November 8, 2006 1 Copyright c 2006 by Fluent Inc. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or otherwise used in any form without
MIXSIM 2.1 Tutorial November 2006 c Fluent Inc. November 8, 2006 1 Copyright c 2006 by Fluent Inc. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or otherwise used in any form without
First Steps - Ball Valve Design
 COSMOSFloWorks 2004 Tutorial 1 First Steps - Ball Valve Design This First Steps tutorial covers the flow of water through a ball valve assembly before and after some design changes. The objective is to
COSMOSFloWorks 2004 Tutorial 1 First Steps - Ball Valve Design This First Steps tutorial covers the flow of water through a ball valve assembly before and after some design changes. The objective is to
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366
 FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
Project 2 Solution. General Procedure for Model Setup
 Project 2 Solution MAE598 Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Shashank Kunjibettu General Procedure for Model Setup Step 1: Model the given component using design modeler Step 2: Meshing is done for the
Project 2 Solution MAE598 Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Shashank Kunjibettu General Procedure for Model Setup Step 1: Model the given component using design modeler Step 2: Meshing is done for the
Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil, Page 1 ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil
 Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil, Page 1 ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil Authors: Scott Richards, Keith Martin, and John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 17 January
Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil, Page 1 ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Flow Over an Airfoil Authors: Scott Richards, Keith Martin, and John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 17 January
Tutorial: Modeling Domains with Embedded Reference Frames: Part 2 Sliding Mesh Modeling
 Tutorial: Modeling Domains with Embedded Reference Frames: Part 2 Sliding Mesh Modeling Introduction The motion of rotating components is often complicated by the fact that the rotational axis about which
Tutorial: Modeling Domains with Embedded Reference Frames: Part 2 Sliding Mesh Modeling Introduction The motion of rotating components is often complicated by the fact that the rotational axis about which
Kratos Multi-Physics 3D Fluid Analysis Tutorial. Pooyan Dadvand Jordi Cotela Kratos Team
 Kratos Multi-Physics 3D Fluid Analysis Tutorial Pooyan Dadvand Jordi Cotela Kratos Team Kratos 3D Fluid Tutorial In this tutorial we will solve a simple example using GiD and Kratos Geometry Input data
Kratos Multi-Physics 3D Fluid Analysis Tutorial Pooyan Dadvand Jordi Cotela Kratos Team Kratos 3D Fluid Tutorial In this tutorial we will solve a simple example using GiD and Kratos Geometry Input data
Problem description. The FCBI-C element is used in the fluid part of the model.
 Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 -
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 -
Revolve 3D geometry to display a 360-degree image.
 Tutorial 24. Turbo Postprocessing Introduction This tutorial demonstrates the turbomachinery postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT. In this example, you will read the case and data files (without doing
Tutorial 24. Turbo Postprocessing Introduction This tutorial demonstrates the turbomachinery postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT. In this example, you will read the case and data files (without doing
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 6263
 Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Prerequisites: This tutorial assumes that you are familiar with the menu structure in FLUENT, and that you have solved Tutorial 1.
 Tutorial 22. Postprocessing Introduction: In this tutorial, the postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT are demonstrated for a 3D laminar flow involving conjugate heat transfer. The flow is over a rectangular
Tutorial 22. Postprocessing Introduction: In this tutorial, the postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT are demonstrated for a 3D laminar flow involving conjugate heat transfer. The flow is over a rectangular
Introduction To FLUENT. David H. Porter Minnesota Supercomputer Institute University of Minnesota
 Introduction To FLUENT David H. Porter Minnesota Supercomputer Institute University of Minnesota Topics Covered in this Tutorial What you can do with FLUENT FLUENT is feature rich Summary of features and
Introduction To FLUENT David H. Porter Minnesota Supercomputer Institute University of Minnesota Topics Covered in this Tutorial What you can do with FLUENT FLUENT is feature rich Summary of features and
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells James A. Peitzmeier *1, Steven Kapturowski 2 and Xia Wang
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells James A. Peitzmeier *1, Steven Kapturowski 2 and Xia Wang
Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+
 ME 448/548 February 28, 2012 Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+ Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview Figure 1 depicts a two-dimensional fluid domain bounded by a cylinder of diameter D. Inside
ME 448/548 February 28, 2012 Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+ Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview Figure 1 depicts a two-dimensional fluid domain bounded by a cylinder of diameter D. Inside
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
ISSN(PRINT): ,(ONLINE): ,VOLUME-1,ISSUE-1,
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 08 Vortex Shedding
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 08 Vortex Shedding Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations,
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 08 Vortex Shedding Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry Oriented HPC Simulations,
Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 3927 Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial This tutorial models flow through the catalyst geometry described in the introductory section. In the porous region, the theoretical pressure drop
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 3927 Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial This tutorial models flow through the catalyst geometry described in the introductory section. In the porous region, the theoretical pressure drop
Instructions for Muffler Analysis
 Instructions for Muffler Analysis Part 1: Create the BEM mesh using ANSYS Specify Element Type Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete Add Shell Elastic 4 Node 181 Close Specify Geometry Preprocessor
Instructions for Muffler Analysis Part 1: Create the BEM mesh using ANSYS Specify Element Type Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete Add Shell Elastic 4 Node 181 Close Specify Geometry Preprocessor
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 06 Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 06 Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 06 Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School
Swapnil Nimse Project 1 Challenge #2
 Swapnil Nimse Project 1 Challenge #2 Project Overview: Using Ansys-Fluent, analyze dependency of the steady-state temperature at different parts of the system on the flow velocity at the inlet and buoyancy-driven
Swapnil Nimse Project 1 Challenge #2 Project Overview: Using Ansys-Fluent, analyze dependency of the steady-state temperature at different parts of the system on the flow velocity at the inlet and buoyancy-driven
