The Cartesian plane 15B
|
|
|
- Evelyn Robert Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Weblink attleship Game e A bishop can move diagonall an number of (unoccupied) squares at a time. omplete the following sentence: With its net move, the bishop at b could capture the (name the chess piece) at (name the position). 7 The game of attleship uses alphanumeric grids. Navigate to the attleship weblink in our eookplus. Pla the game to test our skills with alphanumeric references. 8 7 elesson oordinates and the artesian plane eles-8 REFLETION When we specif an alphanumeric grid reference, does order matter? (That is, does it matter whether the letter is stated first and the number second, or the other wa around?) The artesian plane The artesian plane is named after its inventor, mathematician René Descartes. It is a visual means of describing locations on a plane b using two numbers as coordinates (rather than a letter and a number). The artesian plane is formed b two perpendicular lines. The horizontal line is called the -ais, while the vertical line is referred to as the -ais. The point where the two aes intersect is called the origin. oth aes must be marked (with marks being evenl spaced) and numbered. The distance between each mark is one unit. To locate an point on the artesian plane we use a pair of numbers called artesian coordinates. The numbers are written in a set of brackets and are separated b a comma. The first number in brackets is called the -coordinate of the point; this shows how far across from the origin the point is located. The second number is called the -coordinate; this shows how far up (or down) from the origin the point is. If the artesian coordinates of the point are known, it can be easil located b moving across and up (or down) from the a b c d e f g h origin the specified number of units. For eample, to find the point with coordinates (, ), start from the origin and move units to the right and units up. Hint: To help remember the order in which artesian coordinates are measured, think about using a ladder. Remember we must alwas walk across with our ladder and then climb up it. (, ) hapter oordinates and the artesian plane 7
2 WORKED EXAMPLE Draw a artesian plane with aes etending from to units. Mark the following points with a dot, and label them. a (, ) b (, ) c (, ) d (, ) DRAW First rule up and label the aes. Mark each point. a b c (, ) means starting at the origin, go across units, and then up units. (, ) means go across units and up units. It lies on the -ais. (, ) means go across units and up units. It lies on the -ais. d (, ) means go across units and up unit. Label each point. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) WORKED EXAMPLE Find the artesian coordinates for each of the points A,, and D. Point A is units across and unit up Point is unit across and units up. Point is units across and units up. Point D is unit across and units up. WRITE A is at (, ) is at (, ) is at (, ) D is at (, ) D A Etending the aes The artesian aes can etend infinitel in both directions. On the -ais, the values to the left of the origin are negative and decreasing. Likewise, on the -ais the values below the origin are negative and decreasing. The aes divide the artesian plane into four sections called quadrants. The quadrants are numbered in an anti-clockwise direction, starting with the top right corner. If both - and -coordinates of the point are positive, it will be located in the first quadrant; if the -coordinate is negative but the -coordinate is positive, the point will be in the second quadrant. If the point is in the third quadrant, both the - and -coordinates of the point will be negative. Finall, if the point is in the fourth quadrant, its -coordinate is positive, while its -coordinate is negative. 8 Maths Quest 7 for the Australian urriculum nd quadrant st quadrant Origin rd quadrant - - th quadrant - -
3 If the point is located on the -ais, its -coordinate is alwas. Likewise, if the point is on the -ais, its -coordinate is alwas. WORKED EXAMPLE Plot the following points on the artesian plane. A(-, ), (, -), (, -), D(, ), E(-, -) State the location of each point on the plane (that is, the quadrant, or the ais on which it sits). Draw a set of aes, ensuring that the are long enough to fit all the values. Plot the points. The first point is one unit to the left and two units up from the origin. The second point is two units to the right and four units down from the origin (and so on). WRITE A D E Look at the plane and state the location of each point. Remember that the quadrants are numbered in an anticlockwise direction, starting at the top right. If the point is on the ais, specif which ais it is. Point A is in the second quadrant. Point is in the fourth quadrant. Point is on the -ais. Point D is on the -ais. Point E is in the third quadrant. REMEMER. artesian coordinates can be used to locate an point on a plane.. The artesian plane is formed b two perpendicular lines called aes. The horizontal ais is called the -ais and the vertical ais is called the -ais. The aes intersect at the point called the origin.. oth aes must be marked (with marks being evenl spaced) and numbered. The distance between each mark is one unit. The aes can etend infinitel in both directions.. The location of an point on the artesian plane is given b its artesian coordinates. The artesian coordinates are a pair of numbers that are separated b a comma and are shown within brackets. The first number is called the -coordinate of the point; this shows how far across (that is, to the left or to the right) from the origin the point is located. The second number is called the -coordinate; this shows how far up (or down) from the origin nd quadrant st quadrant Origin rd quadrant - - th quadrant - - the point is. For eample, the point (, ) is located units to the right and units up from the origin. hapter oordinates and the artesian plane 9
4 EXERISE INDIVIDUAL PATHWAYS Activit -- Introducing the artesian plane doc-9 Activit -- More of the artesian plane doc- Activit -- D planes doc- The artesian plane FLUENY WE Draw a artesian plane with aes etending from to units. Mark the fol lowing points with a dot, and label them. a (, ) b (, ) c (, ) d (, ) e (, ) f (, ) WE Find the artesian coordinates for each of the points A L L J D G Weblink The coordinate plane I K H F A WE Plot the following points on the artesian plane. A(, ), (, ), (, ), D(, ), E(, ), F(, ), G(, ), H(, ), I(, ), J(, ) State the location of each point on the plane (that is, the quadrant, or the ais it sits on). UNDERSTANDING Each of these sets of artesian aes (ecept one) has something wrong with it. From the list below, match the mistake in each diagram with one of the sentences. A The units are not marked evenl. The -ais is not vertical. The aes are labelled incorrectl. D The units are not marked on the aes. E There is nothing wrong. a b E Maths Quest 7 for the Australian urriculum
5 c d e f Digital docs Spreadsheet Plotting points doc- From the diagram at right, write down the coordinates of points which: a have the same -coordinate b have the same -coordinate. Messages can be sent in code using a grid like the one drawn below, where the letter is represented b the D coordinates (, ). A Use the diagram to decode the answer to the following E riddle. Q Where did the put the man who was run over b a steamroller? A (, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, ) U V W X Y (, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, ) P Q R S T (, ) (, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, ) (, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, )(, ) K L M N O 7 Rule up a artesian plane with both aes etending from to F G H I J units. Plot the following points and join them in the order A D E given to make a geometric figure. Name each shape. a (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) b (, ) (8, ) (, 8) (, ) c (, ) (, ) (8, 9) (, 9) (, ) d (, ) (8, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 Here is an eercise which ma require care and concentration. On graph paper or in our eercise book rule up a pair of artesian aes. The -ais must go from to and the -ais from to. Plot the following points and join them in the order given. (, ) (, 7) (9, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (8, 9) (, ) (, 8) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (8, ) (, 7) (, 7) (, ) (, 7) (, 8) (, ) N omplete the picture b joining (9, ) (, ) (, ) (9, ). School 9 What is the area of a rectangle formed b connecting the points (, ), (7, ), (7, ) and (, ) on a artesian plane? Home hapter oordinates and the artesian plane
6 Digital docs WorkSHEET. doc- onsider the following set of points: A(, ) (, ) (, 7) D(, ) E(, ) F(, ) G( 8, ) H( 9, ) I(8, 8) J(, ). Which of the following statements is true? a Points A and J are in the first quadrant. b Points and H are in the third quadrant. c Onl point I is in the fourth quadrant. d Onl one point is in the second quadrant. e Point F is at the origin. f Point J is not on the same ais as point E. g Point D is two units to the left of point F. onsider the triangle A at right. a State the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle A. b Find the area of the triangle. A c Reflect the triangle in the -ais. (You need to cop it into our workbook first.) What are the new coordinates of the vertices? d Now reflect the triangle ou have obtained in part c into the -ais, and state the new coordinates of the vertices. REFLETION Wh must the -coordinate alwas be written first and the -coordinate second? Plotting simple linear relationships When a set of points is plotted on the artesian plane, a pattern ma be formed. If a pattern forms a straight line, we call it a linear pattern. The coordinates of the points that form a pattern can be presented as a set, or in a table. If shown in a table (similar to the one shown below), the coordinates of each point should be read in columns ; that is, the top number in each column gives the -coordinate and the bottom number gives the corresponding -coordinate of the point. onsider, for eample, the table of values and the set of points below. oth show the same information. 8 (, 8) (, ) (, ) (, ) The artesian coordinates of the points are ordered pairs. That is, the first number alwas represents the -coordinate, and the second alwas represents the -coordinate of a point. A set of ordered pairs forms a relation between and. If the points form a linear pattern when plotted, we sa that the relation between and is linear. WORKED EXAMPLE Plot the following set of points on the artesian plane, and comment on an pattern formed. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, 7) WRITE Look at the coordinates of the points in the set: the -values range between and, while the -values range between and 7. Draw a set of aes, ensuring the are long enough to fit all the values. Maths Quest 7 for the Australian urriculum
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA. He opened mathematics to many discoveries and exciting applications.
 PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
STRAND I: Geometry and Trigonometry. UNIT 37 Further Transformations: Student Text Contents. Section Reflections. 37.
 MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mathematics SKE, Strand J UNIT J Further Transformations: Tet STRND J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS and MTRIES J Further Transformations Tet ontents Section J.1 Translations * J. ombined Transformations Mathematics
Mathematics SKE, Strand J UNIT J Further Transformations: Tet STRND J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS and MTRIES J Further Transformations Tet ontents Section J.1 Translations * J. ombined Transformations Mathematics
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane
 Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Chapter12. Coordinate geometry
 Chapter1 Coordinate geometr Contents: A The Cartesian plane B Plotting points from a table of values C Linear relationships D Plotting graphs of linear equations E Horizontal and vertical lines F Points
Chapter1 Coordinate geometr Contents: A The Cartesian plane B Plotting points from a table of values C Linear relationships D Plotting graphs of linear equations E Horizontal and vertical lines F Points
Lesson 11 Skills Maintenance. Activity 1. Model. The addition problem is = 4. The subtraction problem is 5 9 = 4.
 Lesson Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Vocabular Development -coordinate -coordinate point of origin Skills Maintenance ddition and Subtraction of Positive and Negative Integers Problem Solving: We look
Lesson Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Vocabular Development -coordinate -coordinate point of origin Skills Maintenance ddition and Subtraction of Positive and Negative Integers Problem Solving: We look
Key Ideas/ Vocabulary
 Name: Date: Unit 1 oordinates and Design 1.1 The artesian Plane Key Ideas/ Vocabulary P. 9 5 11, 13-15, 18 1.2 reate Designs P. 15 3 6, 9-12 Math 7 hapter 1 1 P a g e 1.3 Transformations P. 24 3-21, 24
Name: Date: Unit 1 oordinates and Design 1.1 The artesian Plane Key Ideas/ Vocabulary P. 9 5 11, 13-15, 18 1.2 reate Designs P. 15 3 6, 9-12 Math 7 hapter 1 1 P a g e 1.3 Transformations P. 24 3-21, 24
Math 1050 Lab Activity: Graphing Transformations
 Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
ACTIVITY: Frieze Patterns and Reflections. a. Is the frieze pattern a reflection of itself when folded horizontally? Explain.
 . Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
. Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING
 LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
More Coordinate Graphs. How do we find coordinates on the graph?
 Lesson Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs How do we find coordinates on the graph? We use coordinates to find where the dot goes on the coordinate graph. From
Lesson Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs Problem Solving: More Coordinate Graphs How do we find coordinates on the graph? We use coordinates to find where the dot goes on the coordinate graph. From
The Coordinate Plane. Have you ever used a street directory? CHAPTER. Points on the Coordinate Plane. Length of Line Segments
 HPTER 9 The oordinate Plane 9. 9. 9. Points on the oordinate Plane Length of Line Segments Real-World Problems: Graphing Have ou ever used a street director? street director is useful for locating a street
HPTER 9 The oordinate Plane 9. 9. 9. Points on the oordinate Plane Length of Line Segments Real-World Problems: Graphing Have ou ever used a street director? street director is useful for locating a street
Rotate. A bicycle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. ACTIVITY: Three Basic Ways to Move Things
 . Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
. Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
Algebra I. Linear Equations. Slide 1 / 267 Slide 2 / 267. Slide 3 / 267. Slide 3 (Answer) / 267. Slide 4 / 267. Slide 5 / 267
 Slide / 67 Slide / 67 lgebra I Graphing Linear Equations -- www.njctl.org Slide / 67 Table of ontents Slide () / 67 Table of ontents Linear Equations lick on the topic to go to that section Linear Equations
Slide / 67 Slide / 67 lgebra I Graphing Linear Equations -- www.njctl.org Slide / 67 Table of ontents Slide () / 67 Table of ontents Linear Equations lick on the topic to go to that section Linear Equations
THE INVERSE GRAPH. Finding the equation of the inverse. What is a function? LESSON
 LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
3.1 Sequences of Transformations
 Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
(0, 2) y = x 1 2. y = x (2, 2) y = 2x + 2
 .5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSG-GPE.B.5 HSG-GPE.B. Essential Question How can ou write an equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given
.5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSG-GPE.B.5 HSG-GPE.B. Essential Question How can ou write an equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T9 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS REVIEW - 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) -INTERCEPT = the point where the graph touches or crosses the -ais. It occurs when = 0. ) -INTERCEPT = the
FOM 11 T9 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS REVIEW - 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) -INTERCEPT = the point where the graph touches or crosses the -ais. It occurs when = 0. ) -INTERCEPT = the
Section 4.2 Graphing Lines
 Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
ACTIVITY: Forming the Entire Coordinate Plane
 .5 The Coordinate Plane How can ou graph and locate points that contain negative numbers in a coordinate plane? You have alread graphed points and polgons in one part of the coordinate plane. In Activit,
.5 The Coordinate Plane How can ou graph and locate points that contain negative numbers in a coordinate plane? You have alread graphed points and polgons in one part of the coordinate plane. In Activit,
Lines and Their Slopes
 8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 10th Grade Unit 9
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 10th Grade Unit 9 Unit 9 Coordinate Geometr MATH 1009 Coordinate Geometr INTRODUCTION 3 1. ORDERED PAIRS 5 POINTS IN A PLANE 5 SYMMETRY 11 GRAPHS OF ALGEBRAIC CONDITIONS 19 SELF TEST
MATH STUDENT BOOK 10th Grade Unit 9 Unit 9 Coordinate Geometr MATH 1009 Coordinate Geometr INTRODUCTION 3 1. ORDERED PAIRS 5 POINTS IN A PLANE 5 SYMMETRY 11 GRAPHS OF ALGEBRAIC CONDITIONS 19 SELF TEST
STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs
 UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
Multiply using the grid method.
 Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
Identify and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid.
 Ordered Pairs Teacher Notes Objective Identif and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid. Use these worksheets if students have trouble graphing on the coordinate plane graphing proportional relationships
Ordered Pairs Teacher Notes Objective Identif and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid. Use these worksheets if students have trouble graphing on the coordinate plane graphing proportional relationships
7/7/2016 Unit 4: Linear Relations Grade 9 Mathematics
 Rene Descartes, a mathematician who lived during the 17 th century, developed a system for graphing ordered pairs on a grid. This system is called the Cartesian Coordinate System. 1 In this system, ordered
Rene Descartes, a mathematician who lived during the 17 th century, developed a system for graphing ordered pairs on a grid. This system is called the Cartesian Coordinate System. 1 In this system, ordered
Transformation Packet
 Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Transforming Coordinates
 # Transforming Coordinates The drawing window in man computer geometr programs is a coordinate grid. You make designs b specifing the endpoints of line segments. When ou transform a design, the coordinates
# Transforming Coordinates The drawing window in man computer geometr programs is a coordinate grid. You make designs b specifing the endpoints of line segments. When ou transform a design, the coordinates
Transformations of Functions. 1. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Symmetry of functions and equations
 Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
About Finish Line New Jersey Math 5
 Table of COntents About Finish Line New Jerse Math Unit : Big Ideas from Grade Lesson.NBT., Multipling and Dividing Whole Numbers [connects to.nbt., ] Lesson.NF., Understanding Decimals [connects to.nbt..a,
Table of COntents About Finish Line New Jerse Math Unit : Big Ideas from Grade Lesson.NBT., Multipling and Dividing Whole Numbers [connects to.nbt., ] Lesson.NF., Understanding Decimals [connects to.nbt..a,
3.2 Exercises. rise y (ft) run x (ft) Section 3.2 Slope Suppose you are riding a bicycle up a hill as shown below.
 Section 3.2 Slope 261 3.2 Eercises 1. Suppose ou are riding a biccle up a hill as shown below. Figure 1. Riding a biccle up a hill. a) If the hill is straight as shown, consider the slant, or steepness,
Section 3.2 Slope 261 3.2 Eercises 1. Suppose ou are riding a biccle up a hill as shown below. Figure 1. Riding a biccle up a hill. a) If the hill is straight as shown, consider the slant, or steepness,
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions
 Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
Plot and connect the points in a coordinate plane to make a polygon. Name the polygon.
 . Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
. Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
Module 2, Section 2 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Lesson 12. Unit 2. Embroidery in Cultures around the World. Measuring Figures on a Coordinate Plane
 Lesson Measuring Figures on a Coordinate Plane Embroider in Cultures around the World One of the oldest forms of embroider is crossstitch. Man countries have a histor of making clothing and art work that
Lesson Measuring Figures on a Coordinate Plane Embroider in Cultures around the World One of the oldest forms of embroider is crossstitch. Man countries have a histor of making clothing and art work that
14 Loci and Transformations
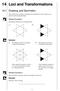 MEP Pupil Tet 1 1 Loci and Transformations 1.1 rawing and Smmetr This section revises the ideas of smmetr first introduced in Unit and gives ou practice in drawing simple shapes. Worked Eample 1 escribe
MEP Pupil Tet 1 1 Loci and Transformations 1.1 rawing and Smmetr This section revises the ideas of smmetr first introduced in Unit and gives ou practice in drawing simple shapes. Worked Eample 1 escribe
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide
 Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide / Unit 04: Suggested Duration: 6 das Unit 04: Geometr: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 das) Possible Lesson 0 (6 das) Possible Lesson
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide / Unit 04: Suggested Duration: 6 das Unit 04: Geometr: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 das) Possible Lesson 0 (6 das) Possible Lesson
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide
 Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide Grade / Unit : Suggested Duration: das Unit : Statistics ( das) Possible Lesson 0 ( das) Possible Lesson 0 ( das) POSSIBLE LESSON 0 ( das) This lesson is one approach
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide Grade / Unit : Suggested Duration: das Unit : Statistics ( das) Possible Lesson 0 ( das) Possible Lesson 0 ( das) POSSIBLE LESSON 0 ( das) This lesson is one approach
For more information, see the Math Notes box in Lesson of the Core Connections, Course 1 text.
 Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Three-Dimensional Coordinates
 CHAPTER Three-Dimensional Coordinates Three-dimensional movies superimpose two slightl different images, letting viewers with polaried eeglasses perceive depth (the third dimension) on a two-dimensional
CHAPTER Three-Dimensional Coordinates Three-dimensional movies superimpose two slightl different images, letting viewers with polaried eeglasses perceive depth (the third dimension) on a two-dimensional
Create Designs. How do you draw a design on a coordinate grid?
 Create Designs Focus on After this lesson, ou will be able to create a design and identif the coordinates used to make the design identif the coordinates of vertices of a -D shape Bahamas Canada Hungar
Create Designs Focus on After this lesson, ou will be able to create a design and identif the coordinates used to make the design identif the coordinates of vertices of a -D shape Bahamas Canada Hungar
Section 2 0: The Rectangular Coordinate System. The Coordinate System
 Section 2 : The Rectangular Coordinate System The rectangular coordinate system is based on two number lines. A horizontal line called the x axis and a vertical line called the y axis. Each axis has marks
Section 2 : The Rectangular Coordinate System The rectangular coordinate system is based on two number lines. A horizontal line called the x axis and a vertical line called the y axis. Each axis has marks
Polygons in the Coordinate Plane
 . Polgons in the Coordinate Plane How can ou find the lengths of line segments in a coordinate plane? ACTIVITY: Finding Distances on a Map Work with a partner. The coordinate grid shows a portion of a
. Polgons in the Coordinate Plane How can ou find the lengths of line segments in a coordinate plane? ACTIVITY: Finding Distances on a Map Work with a partner. The coordinate grid shows a portion of a
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions The Coordinate Plane A coordinate plane is formed b the intersection of a horizontal number line called the -ais and a vertical number line called the -ais.
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 8: Graphs and Functions The Coordinate Plane A coordinate plane is formed b the intersection of a horizontal number line called the -ais and a vertical number line called the -ais.
These are square roots, cube roots, etc. Intermediate algebra Class notes Radicals and Radical Functions (section 10.1)
 Intermediate algebra Class notes Radicals and Radical Functions (section 10.1) These are square roots, cube roots, etc. Worksheet: Graphing Calculator Basics: This will go over basic home screen and graphing
Intermediate algebra Class notes Radicals and Radical Functions (section 10.1) These are square roots, cube roots, etc. Worksheet: Graphing Calculator Basics: This will go over basic home screen and graphing
Name Date. using the vector 1, 4. Graph ABC. and its image. + to find the image
 _.1 ractice 1. Name the vector and write its component form. K J. The vertices of, 3, 1,, and 0, 1. Translate using the vector 1,. Graph and its image. are ( ) ( ) ( ) 3. Find the component form of the
_.1 ractice 1. Name the vector and write its component form. K J. The vertices of, 3, 1,, and 0, 1. Translate using the vector 1,. Graph and its image. are ( ) ( ) ( ) 3. Find the component form of the
3.6 Graphing Piecewise-Defined Functions and Shifting and Reflecting Graphs of Functions
 76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
F8-18 Finding the y-intercept from Ordered Pairs
 F8-8 Finding the -intercept from Ordered Pairs Pages 5 Standards: 8.F.A., 8.F.B. Goals: Students will find the -intercept of a line from a set of ordered pairs. Prior Knowledge Required: Can add, subtract,
F8-8 Finding the -intercept from Ordered Pairs Pages 5 Standards: 8.F.A., 8.F.B. Goals: Students will find the -intercept of a line from a set of ordered pairs. Prior Knowledge Required: Can add, subtract,
Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions. Graphing Equations. Introduction to Functions. Graphing Linear Functions. The Slope of a Line. Equations of Lines Integrated Review Linear Equations in Two Variables.6 Graphing
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions. Graphing Equations. Introduction to Functions. Graphing Linear Functions. The Slope of a Line. Equations of Lines Integrated Review Linear Equations in Two Variables.6 Graphing
Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles October 6, 2010 Graphs and Transformations
 Universit of Waterloo Facult of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7 & 8 Math ircles October, 00 Graphs and Transformations efinition Transformation: a transformation is
Universit of Waterloo Facult of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7 & 8 Math ircles October, 00 Graphs and Transformations efinition Transformation: a transformation is
The Cartesian Coordinate Plane
 The Cartesian Coordinate Plane Air traffic controllers use radar to track tens of thousands of commercial airline flights. Controllers use quadrants to identif the locations, altitudes, and speeds of man
The Cartesian Coordinate Plane Air traffic controllers use radar to track tens of thousands of commercial airline flights. Controllers use quadrants to identif the locations, altitudes, and speeds of man
Transformations in the Plane - Activity 1 Reflections in axes and an oblique line.
 Name: Class: p 5 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set. Copyright 00 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Transformations in the Plane - Activity Reflections in axes and an oblique line. ) On the diagram
Name: Class: p 5 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set. Copyright 00 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Transformations in the Plane - Activity Reflections in axes and an oblique line. ) On the diagram
Mathematics Stage 5 PAS5.1.2 Coordinate geometry
 Mathematics Stage PAS.. Coordinate geometr Part Graphing lines Acknowledgments This publication is copright New South Wales Department of Education and Training (DET), however it ma contain material from
Mathematics Stage PAS.. Coordinate geometr Part Graphing lines Acknowledgments This publication is copright New South Wales Department of Education and Training (DET), however it ma contain material from
Translations. Essential Question How can you translate a figure in a coordinate plane? A B
 . Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
. Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
Worksheet on Line Symmetry & Rotational Symmetry
 Gr. 9 Math 8. - 8.7 Worksheet on Line Smmetr & Rotational Smmetr Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which shapes have at least lines of smmetr?
Gr. 9 Math 8. - 8.7 Worksheet on Line Smmetr & Rotational Smmetr Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which shapes have at least lines of smmetr?
REMARKS. 8.2 Graphs of Quadratic Functions. A Graph of y = ax 2 + bx + c, where a > 0
 8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
Appendix C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities
 Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
2.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals
 Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Lesson 2.1 Exercises, pages 90 96
 Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Fair Game Review. Chapter 11. Name Date. Reflect the point in (a) the x-axis and (b) the y-axis. 2. ( 2, 4) 1. ( 1, 1 ) 3. ( 3, 3) 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Reflect the point in (a) the -ais and (b) the -ais.. (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ) 5. (, ) 6. (, ) Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued)
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Reflect the point in (a) the -ais and (b) the -ais.. (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ) 5. (, ) 6. (, ) Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued)
Let us start with a quick revision of algebra and how to work with variables. Now let us look at the simpler topic, namely Substitution.
 Section F Algebra & Equations Objective In this section, we will be dealing with solving equations for the variable involved, manipulating formulae to get one variable as the subject of the formula and
Section F Algebra & Equations Objective In this section, we will be dealing with solving equations for the variable involved, manipulating formulae to get one variable as the subject of the formula and
Example 1: MATH is a parallelogram. Find the values of w, x, y, and z. Write an equation for each and write the property of parallelograms used.
 Name: Date: Period: Geometr Notes Parallelograms Fab Five Quadrilateral Parallelogram Diagonal Five Fabulous Facts about Parallelograms: ) ) 3) 4) 5) ***This is the Parallelogram Definition and Theorems!
Name: Date: Period: Geometr Notes Parallelograms Fab Five Quadrilateral Parallelogram Diagonal Five Fabulous Facts about Parallelograms: ) ) 3) 4) 5) ***This is the Parallelogram Definition and Theorems!
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
 0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
Derivatives 3: The Derivative as a Function
 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Section 4.3 Features of a Line
 Section.3 Features of a Line Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif the - and -intercepts of a line. Plotting points in the --plane
Section.3 Features of a Line Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif the - and -intercepts of a line. Plotting points in the --plane
The Number Plane THE NUMBER PLANE PASSPORT.
 THE NUMBER PLANE PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.nz Fill in the mind-map below with what you already know about number planes. A start has been made for you! Uses a coordinate system developed by the French
THE NUMBER PLANE PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.nz Fill in the mind-map below with what you already know about number planes. A start has been made for you! Uses a coordinate system developed by the French
Transformations. which the book introduces in this chapter. If you shift the graph of y 1 x to the left 2 units and up 3 units, the
 CHAPTER 8 Transformations Content Summar In Chapter 8, students continue their work with functions, especiall nonlinear functions, through further stud of function graphs. In particular, the consider three
CHAPTER 8 Transformations Content Summar In Chapter 8, students continue their work with functions, especiall nonlinear functions, through further stud of function graphs. In particular, the consider three
23.1 Perpendicular Bisectors of Triangles
 Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
9. f(x) = x f(x) = x g(x) = 2x g(x) = 5 2x. 13. h(x) = 1 3x. 14. h(x) = 2x f(x) = x x. 16.
 Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
ACTIVITY 9 Continued Lesson 9-2
 Continued Lesson 9- Lesson 9- PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Eample A Eample B #1 #3 Lesson Practice M Notes Learning Targets: Graph on a coordinate plane the solutions of a linear inequalit
Continued Lesson 9- Lesson 9- PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Eample A Eample B #1 #3 Lesson Practice M Notes Learning Targets: Graph on a coordinate plane the solutions of a linear inequalit
3x 4y 2. 3y 4. Math 65 Weekly Activity 1 (50 points) Name: Simplify the following expressions. Make sure to use the = symbol appropriately.
 Math 65 Weekl Activit 1 (50 points) Name: Simplif the following epressions. Make sure to use the = smbol appropriatel. Due (1) (a) - 4 (b) ( - ) 4 () 8 + 5 6 () 1 5 5 Evaluate the epressions when = - and
Math 65 Weekl Activit 1 (50 points) Name: Simplif the following epressions. Make sure to use the = smbol appropriatel. Due (1) (a) - 4 (b) ( - ) 4 () 8 + 5 6 () 1 5 5 Evaluate the epressions when = - and
The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations
 The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations that are rigid motions and characteristics of transformations
The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations that are rigid motions and characteristics of transformations
Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines
 Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines WARM UP Identif whether the equation represents a proportional or non-proportional relationship. Then state whether the graph of the line will increase
Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines WARM UP Identif whether the equation represents a proportional or non-proportional relationship. Then state whether the graph of the line will increase
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS
 GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
2.4. Families of Polynomial Functions
 2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. and y = 5. Evaluate the expression when x = xy 2. 4x. Evaluate the expression when a = 9 and b = 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name: Thus, y-intercept is (0,40) (d) y-intercept: Set x = 0: Cover the x term with your finger: 2x + 6y = 240 Solve that equation: 6y = 24 y = 4
 Name: GRAPHING LINEAR INEQUALITIES IN TWO VARIABLES SHOW ALL WORK AND JUSTIFY ALL ANSWERS. 1. We will graph linear inequalities first. Let us first consider 2 + 6 240 (a) First, we will graph the boundar
Name: GRAPHING LINEAR INEQUALITIES IN TWO VARIABLES SHOW ALL WORK AND JUSTIFY ALL ANSWERS. 1. We will graph linear inequalities first. Let us first consider 2 + 6 240 (a) First, we will graph the boundar
Concept: Slope of a Line
 Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
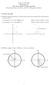 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Graphing Equations. The Rectangular Coordinate System
 3.1 Graphing Equations The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem Ordered pair two numbers associated with a point on a graph. The first number gives the horizontal location of the point. The second gives the vertical
3.1 Graphing Equations The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem Ordered pair two numbers associated with a point on a graph. The first number gives the horizontal location of the point. The second gives the vertical
C URVES AND V ECTORS
 96-ch- SB5-Ostebee June 6, 9:57 C H A P T E R O U T L I N E. Three-Dimensional Space. Curves and Parametric Equations. Polar Coordinates and Polar Curves.4 Vectors.5 Vector-Valued Functions, Derivatives,
96-ch- SB5-Ostebee June 6, 9:57 C H A P T E R O U T L I N E. Three-Dimensional Space. Curves and Parametric Equations. Polar Coordinates and Polar Curves.4 Vectors.5 Vector-Valued Functions, Derivatives,
2.1 The ReCTAngUlAR COORdInATe SySTemS And graphs
 7 CHAPTER equations ANd inequalities learning ObjeCTIveS In this section ou will: Plot ordered pairs in a Cartesian coordinate sstem. Graph equations b plotting points. Graph equations with a graphing
7 CHAPTER equations ANd inequalities learning ObjeCTIveS In this section ou will: Plot ordered pairs in a Cartesian coordinate sstem. Graph equations b plotting points. Graph equations with a graphing
Coordinate geometry Straight lines are an important part of our environment. We play sport on courts with parallel and perpendicular lines, and
 Number and Algebra Coordinate geometr Straight lines are an important part of our environment. We pla sport on courts with parallel and perpendicular lines, and skscrapers would not be standing without
Number and Algebra Coordinate geometr Straight lines are an important part of our environment. We pla sport on courts with parallel and perpendicular lines, and skscrapers would not be standing without
4.4 Absolute Value Equations. What is the absolute value of a number? Example 1 Simplify a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3. Example 2 Solve x = 2
 4.4 Absolute Value Equations What is the absolute value of a number? Eample Simplif a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3 Eample Solve = Steps for solving an absolute value equation: ) Get the absolute value b itself on one
4.4 Absolute Value Equations What is the absolute value of a number? Eample Simplif a) 6 b) 4 c) 7 3 Eample Solve = Steps for solving an absolute value equation: ) Get the absolute value b itself on one
Beecher J.A, Penna J.A., Bittinger M.L. Algebra and Trigonometry (3ed, Addison Wesley, 2007) 58 Chapter 1 Graphs, Functions, and Models
 Beecher J.A, Penna J.A., Bittinger M.L. Algebra and Trigonometr (ed, Addison Wesle, 007) 8 Chapter Graphs, Functions, and Models.. Introduction Polnomial to Functions Graphing and Modeling Plot points.
Beecher J.A, Penna J.A., Bittinger M.L. Algebra and Trigonometr (ed, Addison Wesle, 007) 8 Chapter Graphs, Functions, and Models.. Introduction Polnomial to Functions Graphing and Modeling Plot points.
TRANSFORMATION BOOK. Name:
 TRANSFORMATION BOOK Name: Pg. TRANSLATION NOTES: You are going to Translate point A to point A. First graph the point (-,) and label it A. Now graph the point (,) and label it A. SYMMETRY ASSIGNMENT: Pg.
TRANSFORMATION BOOK Name: Pg. TRANSLATION NOTES: You are going to Translate point A to point A. First graph the point (-,) and label it A. Now graph the point (,) and label it A. SYMMETRY ASSIGNMENT: Pg.
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 7.1.5
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
Making Graphs from Tables and Graphing Horizontal and Vertical Lines - Black Level Problems
 Making Graphs from Tables and Graphing Horizontal and Vertical Lines - Black Level Problems Black Level Hperbola. Give the graph and find the range and domain for. EXPONENTIAL Functions - The following
Making Graphs from Tables and Graphing Horizontal and Vertical Lines - Black Level Problems Black Level Hperbola. Give the graph and find the range and domain for. EXPONENTIAL Functions - The following
L3 Rigid Motion Transformations 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date
 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date Pre-Assessment Which of the following could represent a translation using the rule T (, ) = (, + 4), followed b a reflection over the given line? (The pre-image
3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date Pre-Assessment Which of the following could represent a translation using the rule T (, ) = (, + 4), followed b a reflection over the given line? (The pre-image
14-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
17.1 Translations. Exploring Translations. Explore
 Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Geometry. Slide 1 / 202. Slide 2 / 202. Slide 3 / 202. Analytic Geometry. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 202 Slide 2 / 202 Geometr Analtic Geometr 201--02 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 202 Origin of Analtic Geometr The Distance Formula The Midpoint Formula Partitions of a Line Segment
Slide 1 / 202 Slide 2 / 202 Geometr Analtic Geometr 201--02 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 202 Origin of Analtic Geometr The Distance Formula The Midpoint Formula Partitions of a Line Segment
6th Grade Graphing
 1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13. Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
12.4 Rotations. Learning Objectives. Review Queue. Defining Rotations Rotations
 12.4. Rotations www.ck12.org 12.4 Rotations Learning Objectives Find the image of a figure in a rotation in a coordinate plane. Recognize that a rotation is an isometry. Review Queue 1. Reflect XY Z with
12.4. Rotations www.ck12.org 12.4 Rotations Learning Objectives Find the image of a figure in a rotation in a coordinate plane. Recognize that a rotation is an isometry. Review Queue 1. Reflect XY Z with
9-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary
 9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
