Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
|
|
|
- Carmel Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles share the same centroid G, and are homothetic at G with ratio 1 : 2. The superior triangle of is the triangle bounded by the parallels of the sides through the opposite vertices. The two triangles also share the same centroid G, and are homothetic at G with ratio 2 : 1.
2 216 Some triangle centers The orthocenter and the Euler line The three altitudes of a triangle are concurrent. This is because the line containing an altitude of triangle is the perpendicular bisector of a side of its superior triangle. The three lines therefore intersect at the circumcenter of the superior triangle. This is the orthocenter of the given triangle. H G O The circumcenter, centroid, and orthocenter of a triangle are collinear. This is because the orthocenter, being the circumcenter of the superior triangle, is the image of the circumcenter under the homothety h(g, 2). The line containing them is called the Euler line of the reference triangle (provided it is non-equilateral). The orthocenter of an acute (obtuse) triangle lies in the interior (exterior) of the triangle. The orthocenter of a right triangle is the right angle vertex.
3 7.2 The nine-point circle The nine-point circle Theorem 7.1. The following nine points associated with a triangle are on a circle whose center is the midpoint between the circumcenter and the orthocenter: (i) the midpoints of the three sides, (ii) the pedals (orthogonal projections) of the three vertices on their opposite sides, (iii) the midpoints between the orthocenter and the three vertices. D F E G N O H E F D Proof. (1) Let N be the circumcenter of the inferior triangle DEF. Since DEF and are homothetic at G in the ratio 1 : 2, N, G, O are collinear, and NG : GO = 1 : 2. Since HG : GO = 2 : 1, the four are collinear, and HN : NG : GO = 3 : 1 : 2, and N is the midpoint of OH. (2) Let be the pedal of H on. Since N is the midpoint of OH, the pedal of N is the midpoint of D. Therefore, N lies on the perpendicular bisector of D, and N = ND. Similarly, NE = N, and NF = N for the pedals of H on and respectively. This means that the circumcircle of DEF also contains,,. (3) Let D, E, F be the midpoints of H, H, H respectively. The triangle D E F is homothetic to at H in the ratio 1 : 2. Denote by N its circumcenter. The points N, G, O are collinear, and N G : GO = 1 : 2. t follows that N = N, and the circumcircle of DEF also contains D, E, F. This circle is called the nine-point circle of triangle. ts center N is called the nine-point center. ts radius is half of the circumradius of.
4 218 Some triangle centers Exercise 1. Let H be the orthocenter of triangle. Show that the Euler lines of triangles, H, H and H are concurrent For what triangles is the Euler line parallel (respectively perpendicular) to an angle bisector? 2 3. Prove that the nine-point circle of a triangle trisects a median if and only if the side lengths are proportional to its medians lengths in some order. P F E H N G D Proof. ( ) 1 3 m2 a = 1 4 (b2 + c 2 a 2 ); 4m 2 a = 3(b2 + c 2 a 2 ); 2b 2 + 2c 2 a 2 = 3(b 2 + c 2 a 2 ), 2a 2 = b 2 + c 2. Therefore, is a root-mean-square triangle. 4. Let P be a point on the circumcircle. What is the locus of the midpoint of HP? Why? 5. f the midpoints of P, P, P are all on the nine-point circle, must P be the orthocenter of triangle? 3 1 Hint: find a point common to them all. 2 The Euler line is parallel (respectively perpendicular) to the bisector of angle if and only if α = 120 (respectively 60 ). 3 P. iu and J. oung, Problem 2437 and solution, rux Math. 25 (1999) 173; 26 (2000) 192.
5 7.3 The incircle and the Gergonne point The incircle and the Gergonne point f the incircle of triangle touches,, at,, respectively, = s b s c s c s a s a s b = 1. y eva s theorem, the lines,, are concurrent. The intersection is called the Gergonne point G e of the triangle. s a s a s b G e s c s b s c Triangle is called the intouch triangle of. learly, = + 2 t is always acute angled, and, = + 2, = +. 2 = 2r cos 2, = 2r cos 2, = 2r cos 2.
6 220 Some triangle centers Exercise 1. Given three points,, not on the same line, construct three circles, with centers at,,, mutually tangent to each other externally. 2. Show that if the incenter of triangle lies on the Gergonne cevian, then is isosceles with =. Deduce that the triangle is equilateral if and only if its Gergonne point and incenter coincide. 3. The incircle of triangle touches the sides and at and respectively. Suppose =. Show that the triangle is isosceles.
7 7.3 The incircle and the Gergonne point is a triangle with = 25, = 21, and = 28. The incircle touches at and at. Let D and E be the midpoints of and respectively. Show that (i) the lines and E intersect on the bisector of angle ; (ii) the lines D and also intersect on the bisector of angle. E D P 5. Given triangle, construct a circle tangent to at and at such that the line passes through the centroid G. Show that G : G = c : b. G
8 222 Some triangle centers 6. Suppose the incircle of triangle touches the side at. Show that the incircles of triangles and touch the side at the same point. 7. Two circles are orthogonal to each other if their tangents at an intersection are perpendicular to each other. Given three points,, not on a line, construct three circles with these as centers and orthogonal to each other. (1) onstruct the tangents from to the circle (b), and the circle tangent to these two lines and to (a) internally. (2) onstruct the tangents from to the circle (a), and the circle tangent to these two lines and to (b) internally. (3) The two circles in (1) and (2) are congruent. 8. Given a point on a line segment, construct a right-angled triangle whose incircle touches the hypotenuse at Let be a triangle with incenter. (1a) onstruct a tangent to the incircle at the point diametrically opposite to its point of contact with the side. Let this tangent intersect at 1 and at 1. (1b) Same in part (a), for the side, and let the tangent intersect at 2 and at 2. (1c) Same in part (a), for the side, and let the tangent intersect at 3 and at 3. (2) Note that 3 = 2. onstruct the circle tangent to and at 3 and 2. How does this circle intersect the circumcircle of triangle? 10. The incircle of touches the sides,, at D, E, F respectively. is a point inside such that the incircle of touches at D also, and touches and at and respectively. (1) The four points E, F,, are concyclic. (2) What is the locus of the center of the circle EF? 4 P. iu, G. Leversha, and T. Seimiya, Problem 2415 and solution, rux Math. 25 (1999) 110; 26 (2000)
9 7.4 The excircles and the Nagel point The excircles and the Nagel point Let,, be the points of tangency of the excircles ( a ), ( b ), ( c ) with the corresponding sides of triangle. The lines,, are concurrent. The common point N a is called the Nagel point of triangle. b c N a a
10 224 Some triangle centers Exercise 1. onstruct the tritangent circles of a triangle. (1) Join each excenter to the midpoint of the corresponding side of. These three lines intersect at a point M i. (This is called the Mittenpunkt of the triangle). (2) Join each excenter to the point of tangency of the incircle with the corresponding side. These three lines are concurrent at another point T. (3) The lines M i and T are symmetric with respect to the bisector of angle ; so are the lines M i, T and M i, T (with respect to the bisectors of angles and ). b c T M i a
11 7.4 The excircles and the Nagel point onstruct the excircles of a triangle. (1) Let D, E, F be the midpoints of the sides,,. onstruct the incenter S p of triangle DEF, 5 and the tangents from S to each of the three excircles. (2) The 6 points of tangency are on a circle, which is orthogonal to each of the excircles. b c S p a 5 This is called the Spieker point of triangle.
12 226 Some triangle centers 3. Let D, E, F be the midpoints of the sides,,, and let the incircle touch these sides at,, respectively. The lines through parallel to D, through to E and through to F are concurrent. 6 F E P D 6 rux Math. Problem The reflection of the Nagel point N a in the incenter. This is 145 of ET.
13 7.5 the excentral triangle the excentral triangle The excentral triangle has vertices the excenters a, b, c. ts sides are the external bisectors of the angles of triangle, so that the internal bisectors are its altitudes, and its orthocenter. Thus, is the orthic triangle of a b c, and its circumcircle is the nine-point circle of the excentral triangle. Therefore, the line O is the Euler line of the excentral triangle. b M c O M a We also have the following interesting facts. (i) The midpoints of the segments a, b, and c are on the circumcircle of. (ii) The midpoints of b c, c a, and a b are also on the circumcircle of. (iii) n particular, the midpoints M of a and M of b c are antipodal on the circumcircle, and MM is the perpendicular bisector of. b c O M a More surprising are the following facts about the circumcirle of the excentral triangle. (iv) The circumradius of the excentral circle is 2R.
14 228 Some triangle centers (v) Since the excentral triangle has nine-point center O and orthocenter, its circumcenter is the reflection of in O, i.e., := 2O. Note that the line a is perpendicular to. t therefore contains the point of tangency with the -excircle. From this, we deduce two more interesting facts. Proposition 7.1. The perpendiculars from three excenters to the corresponding sides concur at the reflection of the incenter in the circumcenter. b M c O c D a b M a Theorem 7.2. r a + r b + r c = 4R + r. Proof. onsider the diameter MM of the circumcircle (of ) perpendicular to. (i) r b + r c = 2 DM = 2(R + OD). (ii) 2 OD = r + a = r + 2R r a. (iii) t follows that r a + r b + r c = 4R + r.
Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles
 1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles. Cevian. Cevian Triangle & Circle 10/5/2011. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16
 Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
CLASSICAL THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY. September 2007 BC 1 AC 1 CA 1 BA 1 = 1.
 SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) FORUM GEOM ISSN Harcourt s Theorem. Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan Carlos Salazar
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 117 124. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Harcourt s Theorem Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan arlos Salazar bstract. We give a proof of Harcourt s theorem that if the signed distances
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 117 124. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Harcourt s Theorem Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan arlos Salazar bstract. We give a proof of Harcourt s theorem that if the signed distances
The Orthic-of-Intouch and Intouch-of-Orthic Triangles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
On the Complement of the Schiffler Point
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (005) 149 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the omplement of the Schiffler Point Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. onsider a triangle with excircles (), ( ), (), tangent to the nine-point
Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (005) 149 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the omplement of the Schiffler Point Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. onsider a triangle with excircles (), ( ), (), tangent to the nine-point
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
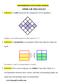 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
IX GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN.
 IX GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN. THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS. 1. (N.Moskvitin) Let be an isosceles triangle with =. Point E lies on side, and ED is the perpendicular from E to. It is
IX GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN. THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS. 1. (N.Moskvitin) Let be an isosceles triangle with =. Point E lies on side, and ED is the perpendicular from E to. It is
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011
 MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
3. Radius of incenter, C. 4. The centroid is the point that corresponds to the center of gravity in a triangle. B
 1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) FORUM GEOM ISSN Pseudo-Incircles. Stanley Rabinowitz
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
VII GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN
 VII GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN Final round. First day. 8th grade. Solutions. 1. (.linkov) The diagonals of a trapezoid are perpendicular, and its altitude is equal to the medial line. Prove
VII GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN Final round. First day. 8th grade. Solutions. 1. (.linkov) The diagonals of a trapezoid are perpendicular, and its altitude is equal to the medial line. Prove
GEOMETRY. PARALLEL LINES Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal.
 GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE
 CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
VI GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN THE CORRESPONDENCE ROUND. SOLUTIONS
 VI GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS 1. (.Frenkin) (8) Does there exist a triangle, whose side is equal to some its altitude, another side is equal to some its
VI GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS 1. (.Frenkin) (8) Does there exist a triangle, whose side is equal to some its altitude, another side is equal to some its
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle
 Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles
 Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited
 230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
1) If a point lies on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
 5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 170
 YIU: Euclidean Geometry 3 3. is a triangle with a right angle at. If the median on the side a is the geometric mean of the sides b and c, show that c =3b. 4. (a)suppose c = a+kb for a right triangle with
YIU: Euclidean Geometry 3 3. is a triangle with a right angle at. If the median on the side a is the geometric mean of the sides b and c, show that c =3b. 4. (a)suppose c = a+kb for a right triangle with
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Term: Definition: Picture:
 10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
You MUST know the big 3 formulas!
 Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
Semester Test Topic Review. Correct Version
 Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
H.Geometry Chapter 3 Definition Sheet
 Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
University of Sioux Falls. MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry
 University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Warm Up. Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes
 Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
VIII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin
 VIII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. First day. 8th form. Solutions 1. (.linkov) Let M be the midpoint of the base of an acute-angled isosceles triangle. Let N be the reection
VIII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. First day. 8th form. Solutions 1. (.linkov) Let M be the midpoint of the base of an acute-angled isosceles triangle. Let N be the reection
Constructions Quiz Review November 29, 2017
 Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry
 The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) FORUM GEOM ISSN Pedal Polygons. Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario Pennisi
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 153 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 edal olygons Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario ennisi Abstract. We study the pedal polygon H n of a point with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 153 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 edal olygons Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario ennisi Abstract. We study the pedal polygon H n of a point with
Review Packet: Ch. 4 & 5 LT13 LT17
 Review Packet: Ch. 4 & 5 LT13 LT17 Name: Pd. LT13: I can apply the Triangle Sum Theorem and Exterior angle Theorem to classify triangles and find the measure of their angles. 1. Find x and y. 2. Find x
Review Packet: Ch. 4 & 5 LT13 LT17 Name: Pd. LT13: I can apply the Triangle Sum Theorem and Exterior angle Theorem to classify triangles and find the measure of their angles. 1. Find x and y. 2. Find x
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Similar Quadrilaterals
 Similar Quadrilaterals ui, Kadaveru, Lee, Maheshwari Page 1 Similar Quadrilaterals uthors Guangqi ui, kshaj Kadaveru, Joshua Lee, Sagar Maheshwari Special thanks to osmin Pohoata and the MSP ornell 2014
Similar Quadrilaterals ui, Kadaveru, Lee, Maheshwari Page 1 Similar Quadrilaterals uthors Guangqi ui, kshaj Kadaveru, Joshua Lee, Sagar Maheshwari Special thanks to osmin Pohoata and the MSP ornell 2014
Type of Triangle Definition Drawing. Name the triangles below, and list the # of congruent sides and angles:
 Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Name. 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles PQR, and RA is a median, find m QR Q. 4 inches A. 2) Which side is the dot closest to?
 enters of Triangles acket 1 Name 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles QR, and R is a median, find m QR Q 4 inches R 2) Which side is the dot closest to? an you draw a point that is the same distance
enters of Triangles acket 1 Name 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles QR, and R is a median, find m QR Q 4 inches R 2) Which side is the dot closest to? an you draw a point that is the same distance
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS. Jesus Torres. A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of. The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science
 THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson
 Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
CHAPTER 2. Euclidean Geometry
 HPTER 2 Euclidean Geometry In this chapter we start off with a very brief review of basic properties of angles, lines, and parallels. When presenting such material, one has to make a choice. One can present
HPTER 2 Euclidean Geometry In this chapter we start off with a very brief review of basic properties of angles, lines, and parallels. When presenting such material, one has to make a choice. One can present
Chapter. Triangles. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Investigating Properties of Kites
 Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Find the locus of the center of a bicycle wheel touching the floor and two corner walls.
 WFNMC conference - Riga - July 00 Maurice Starck - mstarck@canl.nc Three problems My choice of three problems, ordered in increasing difficulty. The first is elementary, but the last is a very difficult
WFNMC conference - Riga - July 00 Maurice Starck - mstarck@canl.nc Three problems My choice of three problems, ordered in increasing difficulty. The first is elementary, but the last is a very difficult
Construction of Malfatti Squares
 Forum eometricorum Volume 8 (008) 49 59. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 onstruction of Malfatti Squares Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We give a very simple construction of the Malfatti squares of a triangle,
Forum eometricorum Volume 8 (008) 49 59. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 onstruction of Malfatti Squares Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We give a very simple construction of the Malfatti squares of a triangle,
MST Topics in History of Mathematics
 MST Topics in History of Mathematics Euclid s Elements and the Works of rchimedes Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2014 June 30 2.6 ngle properties 11 2.6 ngle properties
MST Topics in History of Mathematics Euclid s Elements and the Works of rchimedes Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2014 June 30 2.6 ngle properties 11 2.6 ngle properties
Unit 2 Triangles Part 1
 Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
TImath.com. Geometry. Special Segments in Triangles
 Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
45 Wyner Math Academy I Spring 2016
 45 Wyner Math cademy I Spring 2016 HPTER FIVE: TRINGLES Review January 13 Test January 21 Other than circles, triangles are the most fundamental shape. Many aspects of advanced abstract mathematics and
45 Wyner Math cademy I Spring 2016 HPTER FIVE: TRINGLES Review January 13 Test January 21 Other than circles, triangles are the most fundamental shape. Many aspects of advanced abstract mathematics and
Segments and Angles. Name Period. All constructions done today will be with Compass and Straight-Edge ONLY.
 Segments and ngles Geometry 3.1 ll constructions done today will be with ompass and Straight-Edge ONLY. Duplicating a segment is easy. To duplicate the segment below: Draw a light, straight line. Set your
Segments and ngles Geometry 3.1 ll constructions done today will be with ompass and Straight-Edge ONLY. Duplicating a segment is easy. To duplicate the segment below: Draw a light, straight line. Set your
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
Math 460: Homework # 6. Due Monday October 2
 Math 460: Homework # 6. ue Monday October 2 1. (Use Geometer s Sketchpad.) onsider the following algorithm for constructing a triangle with three given sides, using ircle by center and radius and Segment
Math 460: Homework # 6. ue Monday October 2 1. (Use Geometer s Sketchpad.) onsider the following algorithm for constructing a triangle with three given sides, using ircle by center and radius and Segment
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate
 Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
Question2: Which statement is true about the two triangles in the diagram?
 Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
- DF is a perpendicular bisector of AB in ABC D
 Geometry 5-1 isectors, Medians, and ltitudes. Special Segments 1. Perpendicular -the perpendicular bisector does what it sounds like, it is perpendicular to a segment and it bisects the segment. - DF is
Geometry 5-1 isectors, Medians, and ltitudes. Special Segments 1. Perpendicular -the perpendicular bisector does what it sounds like, it is perpendicular to a segment and it bisects the segment. - DF is
Some Constructions Related to the Kiepert Hyperbola
 Forum eometricorum Volume 6 2006 343 357. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 Some onstructions Related to the Kiepert yperbola Paul Yiu bstract. iven a reference triangle and its Kiepert hyperbola K, we study several
Forum eometricorum Volume 6 2006 343 357. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 Some onstructions Related to the Kiepert yperbola Paul Yiu bstract. iven a reference triangle and its Kiepert hyperbola K, we study several
Geometry Curriculum Map
 Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
