Limits of Recursive Triangle and Polygon Tunnels
|
|
|
- Meghan Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Limits of Recursive Triangle and Polygon Tunnels Florentin Smarandache University of New Mexico, Gallup Campus, USA Abstract. In this paper we present unsolved problems that involve infinite tunnels of recursive triangles or recursive polygons, either in a decreasing or in an increasing way. The nedians or order i in a triangle are generalized to nedians of ratio r and nedians of angle α or nedians at angle β, and afterwards one considers their corresponding nedian triangles and nedian polygons. This tunneling idea came from physics. A) Open Question 1 (Decreasing Tunnel). 1. Let Δ ABC be a triangle and let Δ A 1 B 1 C 1 be its orthic triangle (i.e. the triangle formed by the feet of its altitudes) and H 1 its orthocenter (the point on intersection of its altitudes). Then, let s consider the triangle Δ A 2 B 2 C 2, which is the orthic triangle of triangle Δ A 1 B 1 C 1, and H 2 its orthocenter. Therefore, let s consider the triangle Δ A n B n C n, which is the orthic triangle of triangle Δ A n-1 B n-1 C n-1, and H n its orthocenter. a) What is the geometric place of the orthocenter points H 1, H 2,, H n,? b) Is this limit: lim Δ A n B n C n convergent to a point? If so, what is this point? c) Calculate the sequences α n = area( ΔAnBnCn) area A B C and β n = perimeter( ΔABC n n n) perimeter A B C. d) We generalize the problem from triangles to polygons. Let AB M be a polygon with m 4 sides. From A we draw a perpendicular on the next polygon s side BC, and note its intersection with this side by A 1. And so on. We get another polygon A 1 B 1 M 1. We continue the recursive construction of this tunnel of polygons and we get the polygon sequence A n B n M n. d1) Calculate the limit: lim Δ A n B n M n
2 d2) And the ratios of areas and perimeters as in question c). e) A version of this polygonal extension d) would be to draw a perpendicular from A not necessarily on the next polygon s side, but on another side (say, for example, on the third polygon s side) and keep a similar procedure for the next perpendiculars from all polygon vertices B, C, etc. In order to tackle the problem in a easier way, one can start by firstly studying particular initial triangles Δ ABC, such as the equilateral and then the isosceles. B) Open Question 2 (Decreasing Tunnel). 2. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but replacing orthic triangle by medial triangle, and respectively orthocenter by center of mass (geometric centroid), and altitude by median. Therefore: Let Δ ABC be a triangle and let Δ A 1 B 1 C 1 be its medial triangle (i.e. the triangle formed by its medians legs) and H 1 its center of mass (the point on intersection of its medians). Then, let s consider the triangle Δ A 2 B 2 C 2, which is the medial triangle of triangle Δ A 1 B 1 C 1, and H 2 its center of mass. Therefore, let s consider the triangle Δ A n B n C n, which is the medial triangle of triangle Δ A n-1 B n-1 C n-1, and H n its center of massy. a) What is the geometric place of the center of mass points H 1, H 2,, H n,? {This has an easy answer; all H i will coincide with H 1 (FS, IP).} b) Is this limit: lim Δ A n B n C n convergent to a point? If so, what is this point? {Same response; the limit is equal to H 1 (FS, IP).} c) Calculate the sequences α n = area( ΔAnBnCn) area ΔA B C ( n 1 n 1 n 1) and β n = perimeter( ΔABC n n n) perimeter A B C. d) We generalize the problem from triangles to polygons. Let AB M be a polygon with m 4 sides. From A we draw a line that connects A with the midpoint of BC, and note its intersection with this side by A 1. And so on. We get another polygon A 1 B 1 M 1. We continue the recursive construction of this tunnel of polygons and we get the polygon sequence A n B n M n. d1 Calculate the limit: lim Δ A n B n M n. d2) And the ratios of areas and perimeters of two consecutive polygons as in question c). e) A version of this polygonal extension d) would be to draw a line that connects A not necessarily on the midpoint of the next polygon s side, but with the midpoint of another
3 side (say, for example, of the third polygon s side) and keep a similar procedure for the next lines from all polygon vertices B, C, etc. C) Open Questions 3-7 (Decreasing Tunnels). 3. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of incentral triangles and their incentral points, and their interior angles bisectors. Incentral triangle is the triangle whose vertices are the intersections of the interior angle bisectors of the reference triangle Δ ABC with the respective opposite sides of Δ ABC. 4. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of contact triangles (intouch triangles) and their incircle center points, and their interior angles bisectors. A contact triangle is a triangle formed by the tangent points of the triangle sides to its incircle. 5. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of pedal triangles and a fixed point P in the plane of triangle Δ ABC. A pedal triangle of P is formed by the feet of the perpendiculars from P to the sides of the triangle Δ ABC. 6. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of symmedial triangles. The symmedial triangle (a term coined by E.W. Weisstein [4]), is the triangle whose vertices are the intersection points of the symmedians with the reference triangle. 7. Same problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of cyclocevian triangles. A cyclocevian triangle of triangle Δ ABC with respect to the planar point P is the Cevian triangle of the cyclocevian conjugate of. D) Open Questions 8-12 (Increasing Tunnels). 8. Similar problem as in Open Question 1, but considering a tunnel of anticevian triangles of the triangle Δ ABC with respect to the same planar point P. For question c) and d1) only. The anticevian triangle of the given triangle Δ ABC with respect to the given point P is the triangle of which Δ ABC is the Cevian triangle with respect to P. 9. Similarly, but considering a tunnel of tangential triangles. The tangential triangle to the given triangle Δ ABC is a triangle formed by the tangents to the circumcircle of Δ ABC at its vertices. 10. Similarly, but considering a tunnel of antipedal triangles. The antipedal triangle of the given triangle Δ ABC with respect to the given point P is the triangle of which Δ ABC is the pedal triangle with respect to P. 11. Similarly, but considering a tunnel of excentral triangles. The excentral triangle (or tritangent triangle) of the triangle Δ ABC is the triangle with vertices corresponding to the excenters of Δ ABC. 12. Similarly, but considering a tunnel of anticomplementary triangles.
4 The anticomplementary (or antimedian) triangle of the triangle Δ ABC is the triangle formed by the parallels drew through the vertices of the triangle Δ ABC to the opposite sides. E) Open Questions Involving Nedians a) One calls nedians of order i [see 4] of the triangle Δ ABC the lines that pass through each of the vertices of the triangle Δ ABC and divide the opposite site of the triangle into the ratio i/n, for 1 i n-1. Let s generalize this to nedians of ratio r, which means lines that pass through each of the vertices of the given triangle Δ ABC and divide the opposite site of the triangle into the ratio r. We introduce the notion of nedian triangles, first the interior nedian triangle of order i (or more general interior nedian triangle of ratio r), which is the triangle formed by the three points of intersections of the three nedians of order i (or respectively of the three nedians of ratio r), taken two by two; and that of exterior nedian triangle of order i (or more general exterior nedian triangle of ratio r), which is the triangle Δ A B C such that A BC, B CA, and C AB - where AA, BB, and CC are nedians of order i (respectively of ratio r) in the triangle Δ ABC. b) Another notion to introduce: nedians of angle α (or α-nedians), which are nedians that each of them forms the same angle α with its respective side of the triangle, i.e. (AA, AB) = (BB, BC) = (CC, CA) = α. And associated with this we have interior α-nedian triangle and exterior α-nedian triangle. c) And one more derivative to introduce now: nedians at angle β to the opposite side (or nedians-β), which are of course nedians that form with the opposite side of the triangle Δ ABC the same angle β. {As a particular case we have the altitudes, which are nedians at an angle of 90 or 90 nedians.} And associated with this we have interior nedian-β triangle and exterior nedian-β triangle. d) All these notions about nedians in a triangle can be extended to nedians in a polygon, and to the formation of corresponding nedian polygons. Then: 13. Let Δ ABC be a triangle and let Δ A 1 B 1 C 1 be its interior nedian triangle of ratio r. Then, let s consider the triangle Δ A 2 B 2 C 2, which is the interior nedian triangle of order i of triangle Δ A 1 B 1 C 1. Therefore, let s consider the triangle Δ A n B n C n, which is the interior nedian triangle of ordedr i of triangle the triangle Δ A n-1 B n-1 C n-1. Same questions b)-e) as in Open Question Similar questions for exterior nedian triangle of ratio r Similar questions for interior α-nedian triangle and exterior α-nedian triangle Similar questions for interior nedian-β triangle and exterior nedian-β triangle Similar questions as the above for the corresponding nedian polygons.
5 F) More Open Questions. The reader can exercise his or her research on other types of decreasing or increasing tunnels of special triangles, such as the: extangential triangle, cotangential triangle, antisuplementary triangle, automedial triangle, altimedial triangle, circumpedal triangle, antiparalel triangle, Napolean triangles, Vecten triangles, Sharygin triangles, Brocard triangles, Smarandache- Pătrașcu triangles, Carnot triangle, Fuhrmann triangle, Morley triangle, Țițeica triangle, Lucas triangle, Lionnet triangle, Schroeter triangle, Grebe triangle, etc. {We don t present their definitions since the reader can find them in books of Geometry of Triangle or in mathematical encyclopedias, see for examples [1] and [5].} References: 1. Cătălin Barbu, Teoreme fundamentale din geometria triunghiului, Ed. Unique, Bacău, Ion Pătrașcu, s to the Author, February-March Florentin Smarandache, Généralisations et généralités, Ed. Nouvelle, Fès, Morocco, 1984, 4. Viorel Gh. Vodă, Surprize în matematica elementară, Ed. Albatros, Bucharest, Eric W. Weisstein, MathWorld -- A Wolfram Web Resource,
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles. Cevian. Cevian Triangle & Circle 10/5/2011. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16
 Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE
 CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011
 MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
A New Proof and an Application of Dergiades Theorem
 A New Proof and an Application of Dergiades Theorem Ion Pătraşcu, Professor, The Frații Buzeşti College, Craiova, Romania Florentin Smarandache, Professor, The University of New Mexico, U.S.A. In this
A New Proof and an Application of Dergiades Theorem Ion Pătraşcu, Professor, The Frații Buzeşti College, Craiova, Romania Florentin Smarandache, Professor, The University of New Mexico, U.S.A. In this
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle
 Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
For all questions, E. NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.
 For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Term: Definition: Picture:
 10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
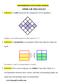 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
Investigating Properties of Kites
 Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Mth 97 Winter 2013 Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
The Orthic-of-Intouch and Intouch-of-Orthic Triangles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
Figure 1. The centroid and the symmedian point of a triangle
 ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
CLASSICAL THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY. September 2007 BC 1 AC 1 CA 1 BA 1 = 1.
 SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Centres of a Triangle. Teacher Notes
 Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Chapter. Triangles. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Type of Triangle Definition Drawing. Name the triangles below, and list the # of congruent sides and angles:
 Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Semester Test Topic Review. Correct Version
 Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Period: Date Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means
 : Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets
 Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center!
 Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center! Justin Dykstra Clinton Peterson Ashley Rall Erika Shadduck March 1, 2006 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Introduction The number of triangle centers is astounding. Upwards
Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center! Justin Dykstra Clinton Peterson Ashley Rall Erika Shadduck March 1, 2006 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Introduction The number of triangle centers is astounding. Upwards
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson
 Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles
 Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles Name Date Assignment Questions I have Day 1 Section 4.1: Triangle Sum, Exterior Angles, and Classifying Triangles Day 2 Assign: Finish Ch. 3 Review Sheet, WS 4.1 Section
Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles Name Date Assignment Questions I have Day 1 Section 4.1: Triangle Sum, Exterior Angles, and Classifying Triangles Day 2 Assign: Finish Ch. 3 Review Sheet, WS 4.1 Section
Teacher: Mr. Samuels. Name: 1. 2
 Teacher: Mr. Samuels Name: 1. 2 As shown in the diagram below of ΔABC, a compass is used to find points D and E, equidistant from point A. Next, the compass is used to find point F, equidistant from points
Teacher: Mr. Samuels Name: 1. 2 As shown in the diagram below of ΔABC, a compass is used to find points D and E, equidistant from point A. Next, the compass is used to find point F, equidistant from points
5-2 Medians and Altitudes of Triangles. In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. 1. PC ANSWER: 12 2.
 In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. In, UJ = 9, VJ = 3, and ZT = 18. Find each length. 1. PC 12 2. AP 10 3. INTERIOR DESIGN An interior designer is creating a custom coffee table
In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. In, UJ = 9, VJ = 3, and ZT = 18. Find each length. 1. PC 12 2. AP 10 3. INTERIOR DESIGN An interior designer is creating a custom coffee table
Points of Concurrency on a Coordinate Graph
 Points of Concurrency on a Coordinate Graph Name Block *Perpendicular bisectors: from the midpoint to the side opposite( ) 1. The vertices of ΔABC are A(1,6), B(5,4), C(5,-2). Find the coordinates of the
Points of Concurrency on a Coordinate Graph Name Block *Perpendicular bisectors: from the midpoint to the side opposite( ) 1. The vertices of ΔABC are A(1,6), B(5,4), C(5,-2). Find the coordinates of the
Let s Get This Started!
 Lesson. Skills Practice Name Date Let s Get This Started! Points, Lines, Planes, Rays, and Line Segments Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement.. A geometric figure created without
Lesson. Skills Practice Name Date Let s Get This Started! Points, Lines, Planes, Rays, and Line Segments Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement.. A geometric figure created without
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
Randolph High School Math League Page 1. Similar Figures
 Randolph High School Math League 2014-2015 Page 1 1 Introduction Similar Figures Similar triangles are fundamentals of geometry. Without them, it would be very difficult in many configurations to convert
Randolph High School Math League 2014-2015 Page 1 1 Introduction Similar Figures Similar triangles are fundamentals of geometry. Without them, it would be very difficult in many configurations to convert
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
3. 4. fraction can not be the length of the third side?
 Name: Teacher: Mrs. Ferry 1. 2 In the construction shown below, is drawn. 3. 4 If two sides of a triangle have lengths of and, which fraction can not be the length of the third side? 1. 2. 3. 4. In ABC,
Name: Teacher: Mrs. Ferry 1. 2 In the construction shown below, is drawn. 3. 4 If two sides of a triangle have lengths of and, which fraction can not be the length of the third side? 1. 2. 3. 4. In ABC,
Question2: Which statement is true about the two triangles in the diagram?
 Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry
 The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
B = the maximum number of unique scalene triangles having all sides of integral lengths and perimeter less than 13
 GEOMETRY TEAM #1 A = the m C in parallelogram ABCD with m B= (4x+ 15), m D= (6x+ ) B = the degree measure of the smallest angle in triangle ABC with m A= ( x+ 0), m B= ( x+ 7), m C= (x 15) Find the value
GEOMETRY TEAM #1 A = the m C in parallelogram ABCD with m B= (4x+ 15), m D= (6x+ ) B = the degree measure of the smallest angle in triangle ABC with m A= ( x+ 0), m B= ( x+ 7), m C= (x 15) Find the value
You MUST know the big 3 formulas!
 Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
Circumference of a Circle
 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2
 Name: Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2 Original Text By Dr. Bradley Material Supplemented by Mrs.de Nobrega 4.8 Points of Concurrency in a Triangle Our last four constructions are our
Name: Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2 Original Text By Dr. Bradley Material Supplemented by Mrs.de Nobrega 4.8 Points of Concurrency in a Triangle Our last four constructions are our
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review
 Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Unit 2 Triangles Part 1
 Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS. Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line.
 GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS. Jesus Torres. A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of. The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science
 THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
Warm Up. Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes
 Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Proving Triangles and Quadrilaterals Satisfy Transformational Definitions
 Proving Triangles and Quadrilaterals Satisfy Transformational Definitions 1. Definition of Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with one line of symmetry. a. If a triangle has two equal sides, it is isosceles.
Proving Triangles and Quadrilaterals Satisfy Transformational Definitions 1. Definition of Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with one line of symmetry. a. If a triangle has two equal sides, it is isosceles.
Computer Discovered Mathematics: Half-Anticevian Triangle of the Incenter
 International Journal of Computer Discovered Mathematics (IJCDM) ISSN 2367-7775 c IJCDM Volume 2, 2017, pp.55-71. Received 20 February 2017. Published on-line 28 February 2017 web: http://www.journal-1.eu/
International Journal of Computer Discovered Mathematics (IJCDM) ISSN 2367-7775 c IJCDM Volume 2, 2017, pp.55-71. Received 20 February 2017. Published on-line 28 February 2017 web: http://www.journal-1.eu/
1) If a point lies on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
 5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees.
 Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles
 1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Park Forest Math Team. Meet #3. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #3 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Polygons, Pythagorean Theorem 3.
Park Forest Math Team Meet #3 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Polygons, Pythagorean Theorem 3.
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles
 Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER 1
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which statement(s) may
Name: Class: Date: Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which statement(s) may
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 Lester s Circle Julie Hoaglund University of
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 Lester s Circle Julie Hoaglund University of
Activity 8. Midsegment of a Triangle. Name. Date
 . Name Date Activity 8 Midsegment of a Triangle Construct the geometric object by following the instructions below, and then answer the questions about the object. 1. From the Lines Toolbar, select Triangle.
. Name Date Activity 8 Midsegment of a Triangle Construct the geometric object by following the instructions below, and then answer the questions about the object. 1. From the Lines Toolbar, select Triangle.
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1
 Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY ( ) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A
 APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles
 Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Warm-Up. Find the domain and range:
 Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
fall08ge Geometry Regents Exam Test Sampler fall08 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
 fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
5.6notes November 13, Based on work from pages , complete In an isosceles triangle, the &
 chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
pd 3notes 5.4 November 09, 2016 Based on work from pages , complete In an isosceles triangle, the &
 chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Boardworks Ltd KS3 Mathematics. S1 Lines and Angles
 1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
Instructional Unit CPM Geometry Unit Content Objective Performance Indicator Performance Task State Standards Code:
 306 Instructional Unit Area 1. Areas of Squares and The students will be -Find the amount of carpet 2.4.11 E Rectangles able to determine the needed to cover various plane 2. Areas of Parallelograms and
306 Instructional Unit Area 1. Areas of Squares and The students will be -Find the amount of carpet 2.4.11 E Rectangles able to determine the needed to cover various plane 2. Areas of Parallelograms and
