The Next Step. Mathematics Applications for Adults. Book Measurement
|
|
|
- Janice Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Next Step Mathematics Applications for Adults Book Measurement
2 OUTLINE Mathematics - Book Measurement The Metric System use correct metric units to measure length, volume, capacity, mass, time, and temperature. convert from any given metric unit to any stated metric unit. Area, Perimeter, and Volume find the perimeter of various regular and irregular geometric figures and shapes. find the area of various regular and irregular geometric figures and shapes. find the volume of various regular geometric figures.
3 THE NEXT STEP Book Measurement The Metric System In the 1790s, French scientists worked out a system of measurement based on the meter. The meter is one tenmillionth of the distance between the North Pole and the Equator. The French scientists made a metal rod equal to the length of the standard meter. By the 1980s, the French metal bar was no longer a precise measure for the meter. Scientists figured out a new standard for the meter. They made it equal to 1/299,792,548 of the distance light travels in a vacuum in one second. Since the speed of light in a vacuum never changes, the distance of the meter will not change. The French scientists developed the metric system to cover measurement of length, area, volume, and weight.
4 Metric Length Equivalents Metric Unit Abbreviation Metric Equivalent millimeter mm.1 centimeter centimeter cm 10 millimeters decimeter dm 10 centimeters meter m 100 centimeters dekameter dam 10 meters hectometer hm 100 meters kilometer km 1000 meters Metric Weight Equivalents Metric Unit Abbreviation Metric Equivalent milligram mg.001 gram centigram cg 10 milligrams decigram dg 10 centigrams gram g 1,000 milligrams decagram dag 10 grams hectogram hg 100 grams kilogram kg 1,000 grams Metric Volume Measures Metric Unit Abbreviation Metric Equivalent milliliter ml.001 liter centiliter cl 10 milliliters
5 deciliter dl 10 centiliters liter l 1,000 milliliters dekaliter dal 10 liters hectoliter hl 100 liters kiloliter kl 1,000 liters Decimal Point A period that separates the whole numbers from the fractional part of a number; or that separates dollars from cents Example: Kilometers Hectometers Decameters Meters Decimeters Centimeters Millimeters Kilograms Hectograms Decagrams Grams Decigrams Centigrams Milligrams Kiloliters Hectoliters Decaliters Liters Deciliters Centiliters Milliliters To use this chart, if a question asks you how many grams that you can get from 200 centigrams, for example, try this: Start by putting down the number: 200
6 If we don t see a decimal point, the number is a whole number; and therefore, a decimal point may be inserted to the right of the last digit: 200. Now, using your chart, start at centigrams and count back to grams (two spaces to the left). Move the decimal point in your number the same amount of spaces in the same direction: 2.00 The answer to the question is that 200 centigrams is equal to 2 grams. If a question asks you to tell how many millimeters are is 8.3 decimeters, try this: Write down the number: 8.3 We already see a decimal point, so there is no need to guess where to place it: 8.3 Now, using your chart, start at decimeters and count forward to millimeters (two spaces to the right).
7 Move the decimal point in your number the same amount of spaces in the same direction: 830. The answer to the question is that 830 millimeters is equal to 8.3 decimeters. Change larger to smaller units by multiplying. 3 meters =? cm 3 x 100 (100 centimeters to a meter) = 300 centimeters Change smaller to larger units by dividing 5000 grams =? kg grams = 5 kg Fill in the answer cl = ml 4. 8 g = cg L = kl cm = mm mg = cg 6. 8 kg = g
8 cg = mg cm = m m = mm L = cl cl = ml mm = m cg = g km = m cl = ml cl = L g = kg ml = cl ml = L cl = L kl = L m = mm cg = mg cm = m m = km mm = cm L = kl cm = m kl = L L = ml cl = L km = m km = m The Centigrade Scale In 1742, Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius ( ) invented a scale for measuring heat. His scale is called the centigrade or Celsius scale. Celsius s scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. The freezing point of water is equal to 0 degrees Celsius. The boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius. While the Fahrenheit scale is used in the United States, the centigrade scale is used in most
9 countries throughout the world. It is the scale preferred by scientists. The markings on a thermometer are in degrees. We read the degrees as: above zero +1, +2, +3, below zero -1, -2, -3,.. The temperature on the Celsius thermometer below is -78 degrees. This can be written as -78. A degree Celsius memory device: There are several memory aids that can be used to help the novice understand the degree Celsius temperature scale. One such device is: When it's zero it's freezing, when it's 10 it's not, when it's 20 it's warm, when it's 30 it's hot! Or, another one to remember:
10 30's hot 20's nice 10's cold zero's ice
11 Area, Perimeter, and Volume To measure flat spaces we calculate perimeter. Perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional or flat shape. Calculating Perimeter Perimeter is calculated in different ways, depending upon the shape of the surface. The perimeter of a surface outlined by straight lines is calculated by adding together the lengths of its sides = 102 yds. perimeter of the rectangular lot = 4 x 8 = 32 4s (4 sides) = perimeter of a square = 32 3s (3 sides) = perimeter of a triangle = 4 x 8 = 32 4s = perimeter of a rhombus
12 = 26 8s = perimeter of an irregular octagon = 25 all sides = perimeter of an irregular polygon A regular polygon is a polygon whose sides are all the same length, and whose angles are all the same. To calculate the perimeter of regular polygons like squares or rhombuses, multiply the number of sides by the length of a side. This is possible, because all the sides are the same length. Find the perimeter. 1. a = 7 ft c = 6 ft b = c 19 ft 2. v = 5 cm t = 8 cm r = 12 cm s = t
13 3. All sides equal 5 cm 4. e = 8 in f = 17 in 5. a = 6 mi c = 5 mi b = c 6. The side d of this square is 27 mi 7. e = 3 ft f = 9 ft 8. m = 19 yd All sides are equal
14 9. The side d of this square is 28 m 10. v = 8 cm t = 11 cm r = 16 cm s = t Calculating Area The area of a figure is the size of the region it covers. Area is a measurement of only two dimensions, usually length and width. Area is calculated in different ways, depending on the shape of the surface. Area is expressed in squares: square inches, square meters, etc. An area with a perimeter made up of straight lines is calculated in different ways for different shapes.
15 S ² = area of a square base x height = area of a 2 triangle base x height = area of a rhombus b x h = area of a rectangle The area of a rectangle, square, or rhombus is sometimes referred to as length x width (l x w) instead of base x height. The area of a triangle is so metimes expressed as ½ the base x height (1/2 b x h). A parallelogram has 4 sides and the opposite sides are parallel. The area of a parallelogram is found by multiplying the length of the base by the height. Height is the distance straight down from a point on one non-slanting side to its opposite side, or the base. The formula for the area of a parallelogram can be written: A = bh, where b = base and h = height.
16 Example Find the area of the parallelogram below. Use the formula for finding the area of a parallelogram: A = bh = 10 x 8 = 80 sq cm Answer: The area of the parallelogram is 80 sq cm. The area of a circle has a special calculation: 2 a = r The equation is read area equals pi times radius squared.
17 Find the area for each squared cm All sides are 12 cm All sides are 9 cm 7.
18
19 Complete the table for each triangle. Round to the nearest hundredth. base height area 1. 9 in 2 in square in 2. 9 cm 5 cm square cm 3. 9 m 3 m square m 4. 9 mm 7 mm square mm yd 8 yd square yd ft 13 ft square ft mi mi square mi km 19.8 km square km cm cm square cm 10. yd 12 yd 66.6 square yd 11. mm 19.6 mm square mm ft ft square ft m m square m in 14 in square in 2
20 km 10 5 km square km Find the Area for each. Round to the nearest hundredth. Assume = g = 20 m 314 m 2 3. s = 9 m 5. e = 27.1 mi 7. s = 7 mi 2. m = 61 m 4. e = 28 cm 6. g = yd 8. m = in
21 Complete the table for each circle. Round to the nearest hundredth. Assume = Assume = 3 1/7 for questions radius diameter area 1. 3 in in in² 2. yd 10 yd yd² 3. 6 m 12 m m² ft 20 ft ft² 5. 7 mm 14 mm mm² 6. km 13.2 km km² 7. mi mi mi² cm cm cm² 9. yd yd yd² km 14.6 km km² ft in ft ft² in in² 13. mm mm mm² m m m²
22 cm cm cm² In some problems you may be asked to find the area of irregular shapes. These figures are often made up of two or more simple figures. Example Find the area of the figure shown below. Step 1 Separate the figure into two familiar shapes---in this case rectangles. Decide what measurements you are missing and label them (x and y in this figure).
23 Step 2 Find the missing lengths of the sides by subtracting values you do know. Side x is 12 ft 8 ft = 4 ft Side y is 10 ft 3 ft = 7 ft Step 3 Find the area of each rectangle by using the correct formula. First replace l with 4 and w with 3 in the formula A = lw. Then replace l with 12 and w with 7 in the formula A = lw. Area I = lw = 4 x 3 = 12 sq ft
24 Area II = lw = 12 x 7 = 84 sq ft Step 4 Add the areas of the two rectangles. Area I + Area II = = 96 sq ft Answer: The total area of the figure is 96 sq ft. Find the area of each figure
25 3. Surface Area The surface area is the sum of the areas of the outside surface of a three-dimensional shape. Surface Area of a Cube = 6 a 2 cube) (a is the length of the side of each edge of the In words, the surface area of a cube is the area of the six squares that cover it. The area of one of them is aa, or a 2. Since these are all the same, you can multiply one of them by six, so the surface area of a cube is 6 times one of the sides squared.
26 Example Find the total area of a cube whose edges measure 15 inches. A = 6a 2 A = 6 x (15) 2 A = 6 x 225 A = 1,350 square inches. Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac (a, b, and c are the lengths of the 3 sides) In words, the surface area of a rectangular prism is the area of the six rectangles that cover it. But we don't have to figure out all six because we know that the top and bottom are the same, the front and back are the same, and the left and right sides are the same. The area of the top and bottom (side lengths a and c) = ac. Since there are two of them, you get 2ac. The front and back have side lengths of b and c. The area of one of them is bc, and there are two of them, so the surface area of those two is 2bc. The left and right
27 side have side lengths of a and b, so the surface area of one of them is ab. Again, there are two of them, so their combined surface area is 2ab. Example Find the total area of a rectangular prism 9 meters long, 6 meters wide, and 7 meters high. A = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac A = 2 x 9 x x 9 x x 6 x 7 A = A = 318 square meters. Surface Area of a Cylinder = 2(pi r 2 ) + (2 pi r)h (h is the height of the cylinder, r is the radius of the top) Surface Area = Areas of top and bottom + Area of the side Surface Area = 2(Area of top) + (circumference of top) x height Surface Area = 2(pi r 2) + (2 pi r)h
28 In words, the easiest way is to think of a can. The surface area is the areas of all the parts needed to cover the can. That's the top, the bottom, and the paper label that wraps around the middle. You can find the area of the top (or the bottom). That's the formula for area of a circle (pi r 2 ). Since there is both a top and a bottom, that gets multiplied by two. The side is like the label of the can. If you peel it off and lay it flat it will be a rectangle. The area of a rectangle is the product of the two sides. One side is the height of the can, the other side is the circumference of the circle, since the label wraps once around the can. So the area of the rectangle is (2 pi r)h. Add those two parts together and you have the formula for the surface area of a cylinder. Surface Area = 2(pi r 2) + (2 pi r)h Example Find the total area of a cylinder whose radius is 21 feet and whose height is 30 feet.
29 A = 2(pi r 2 ) + (2 pi r)h A = 2 x 22/7 x (21) x 22/7 x 21 x 30 A = 2, ,960 A = 6,732 square feet Find the total areas of each of the following rectangular prisms. 1. Find the total area of a rectangular prism measuring 5 feet by 4 feet by 3 feet. 2. Find the total area of a rectangular prism measuring 16 meters by 6 meters by 2 meters. 3. Find the total area of a rectangular prism measuring 17 centimeters by 11 centimeters by 8 centimeters. 4. Find the total area of a rectangular prism measuring 16.4 meters by 13.7 meters by 14.5 meters.
30 Find the total area of each cube. 1. Find the total area of a cube whose edges measure 7 centimeters. 2. Find the total area of a cube whose edges measure 5.5 feet. 3. Find the total area of a cube whose edges measure 11.6 meters. 4. Find the total area of a cube whose edges measure 9 inches. Find the total area of each cylinder. 1. Find the total area of a cylinder whose diameter is 9 inches and whose height is 15 inches. 2. Find the total area of a cylinder whose radius is 10 inches and whose height is 13 inches.
31 3. Find the total area of a cylinder whose radius is 27 centimeters and whose height is 32 centimeters. 4. Find the total area of a cylinder whose radius is 14 meters and whose height is 12 meters. Calculating Volume Volume is the amount of space contained in a threedimensional shape. Area is a measurement of only two dimensions, usually length and width. Volume is a measurement of three dimensions, usually length, width, and height, and is measured in cubic units. To find the volume of a cube or a rectangular prism, multiply length by width by height. l x w x h = volume of a rectangular prism 8 x 3 x 4 = 96 Since a cube has sides of equal length, multiply the length of one side by itself three times, S³ :
32 S³ = volume of a cube To find the volume of a cylinder, multiply the area of the base (B) (or r²) by the height of the cylinder. B x h = volume of a cylinder r² x h = Find the volume. 1. All sides are 9 yd 3. D = 28 yd E = 33 yd F = 4 yd 2. A = 15 m B = 7 m G = 29 m 4. A = 12 ft B = 6 ft C = 24 ft
33 Fill in the missing spaces and complete the table. Round to the nearest hundredth. length width height volume 5. 5 mm 7 mm 13 mm cubic millimeters 6. 8 m 10 m 9 m cubic meters mm 33 mm 36 mm cubic millimeters yd 15 yd 30 yd cubic yards 9. ft 15 ft 12 ft 720 cubic feet cm cm 16 cm 960 cubic centimeters m m 9 m 1512 cubic meters yd 13 yd 10.3 yd cubic yards ft 4.2 ft 4 ft cubic feet cm 8.41 cm 14 cm cubic centimeters m 11 m 5.92 m cubic meters Find the volume. Use 3.14 for. Round to the nearest hundredth. 1. B = 3 ft A = 6 ft 2. E = 4 mm D = 9 mm 3. B = 5 mm A = 8 mm 4. E = 10 in D = 17 in
34 Fill in the missing spaces and complete the table. Use 3.14 for. Round to the nearest hundredth. diameter radius height volume ft 5 ft 8 ft 628 cubic feet 6. 6 cm 3 cm 9 cm cubic centimeters in 8 in 3 in cubic inches ft ft 8 ft cubic feet m 6 m m cubic meters yd 14 yd yd cubic yards 11. m 7 m 9 m cubic meters m m 6 m cubic meters cm 16.2 cm 7.5 cm cubic centimeters mm 11.6 mm 9.6 mm cubic millimeters m m 3 m cubic meters
35 Pyramids and Cones A pyramid has one base with sides of the same length. The base is connected to a single point, called a vertex, by triangular faces (sides). A cone has one circular base and one vertex. A curved surface connects the base and vertex. The volume of a pyramid or a cone is of the area of its base multiplied by its height. V = x Area of base x height V = Ah
36 pyramid cone Volume = x (area of square) x height = x (l x w) x height Volume = x (area of circle) x height = x x radius squared x height Example Find the volume of the pyramid shown below in cubic feet. Step 1 Find the area of the base (a square). Choose the formula. Substitute and solve. A = length x width A = 6 x 6 = 36 square feet Step 2 Choose the volume formula. Substitute. Solve. V = Ah V = (36)(5) V = 60 cubic ft.
37 Example Find the volume of the cone shown below in cubic centimeters. Step 1 Use the formula for finding the volume of a cone. V = 1/3 x x radius squared x height Step 2 Substitute. V = 1/3(3.14)(3 x 3)(9) Step 3 Solve. V = 1/3(3.14)(9)(9) = The volume of the cone is cubic centimeters. 1. A cone has a height of 16 centimeters and a base with an area of 18 square centimeters. What is the volume of the cone in cubic centimeters?
38 2. Find the volume of a pyramid if the area of the base is 12 square meters and the height is 4 meters. 3. Find the volume of a cone if the area of the base is 4 square centimeters and the height is 9 centimeters. 4. The base of a pyramid has an area of 9 square meters. The height of the pyramid is 12 ½ meters. What is the volume of the pyramid in cubic meters? You may also be asked to find the volume of irregular figures made up of common solid shapes. Example Find the volume of the object shown below.
39 Step 1 Find the area of the base of the pyramid. A = length x width = 12(11) = 132 square centimeters Step 2 Find the volume of the pyramid. V = 1/3Ah = 1/3(132)(12) = 44(12) = 528 cubic centimeters Step 3 Find the volume of the rectangular solid. Step 4 Add the results. V = lwh = 12(11)(10) = 132(10) = 1320 cubic centimeters = 1848 cubic centimeters The volume of the object is 1848 cubic centimeters.
40 1. Find the volume of the object shown below. 2. What is the volume in cubic centimeters of the figure shown below?
41 FORMULAS Perimeter Polygon P = sum of the lengths of the sides Rectangle P = 2(l + w) Circumference Circle C = 2 r, or C = d Area Circle A = r 2 Parallelogram A = bh Rectangle A = lw Square A = s 2 Triangle A = bh Volume Cube V = e 3 Cylinder V = Bh, or V = r 2 h Prism V = Bh Cone V =1/3Bh Pyramid V = 1/3Bh
42 Answer Key Book Measurement Page ml 2. 2 kl 3. 4 cg cg mm g mg L 9. 4 km m kg cm mm cl kl cl L m ml L L m L ml g mm L m mg m ml m m Page cm cm in mi mi ft yd m cm Page square yd square cm square in square cm square cm square m square yd square mi square m Page / / / /25
43 Page m² m² cm² mi² yd² mi² in² Page ; ; ; ; ; ; / / /5; / / ; Page ft² cm² cm² Page ft² m² cm² m² Page cm² ft² m² in² Page in² in² cm² m² Page yd³ m³ yd³ ft³ Page ft³ mm³ mm³
44 in³ ; ; ; Page cm³ m³ cm³ m³ Page m³ cm³
Volume of Cylinders. Volume of Cones. Example Find the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth.
 Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Measurement and Geometry
 8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
Practice A Introduction to Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Brunswick School Department: Grade 5
 Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
2-dimensional figure. 3-dimensional figure. about. acute angle. addend. addition. angle. area. array. bar graph. capacity
 2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
PASIG CATHOLIC COLLEGE Grade School Department MATHEMATICS 5 FOURTH QUARTER Activity Sheet No. 1. TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Concept Development
 PASIG CATHOLIC COLLEGE MATHEMATICS 5 Activity Sheet No. 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Concept Development : Percentage, Base and Rate LEARNING OBJECTIVE : Identify the elements of percent in a give problem. REFERENCE
PASIG CATHOLIC COLLEGE MATHEMATICS 5 Activity Sheet No. 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Concept Development : Percentage, Base and Rate LEARNING OBJECTIVE : Identify the elements of percent in a give problem. REFERENCE
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade
 Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
CCBC Math 081 Geometry Section 2.2
 2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES. The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power.
 UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
10-1. Enrichment. You Can Count On It!
 10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Sect Volume. 3 ft. 2 ft. 5 ft
 199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
3 Dimensional Solids. Table of Contents. 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres
 Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Someone else might choose to describe the closet by determining how many square tiles it would take to cover the floor. 6 ft.
 Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS
 MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018
 Class: Date: TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018 Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 1. 5. Find the area. All lengths are in centimeters. Round answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 6. A can of
Class: Date: TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018 Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 1. 5. Find the area. All lengths are in centimeters. Round answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 6. A can of
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 11 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon
 Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Reteaching. Solids. These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids. A cylinder has two congruent circular bases.
 9- Solids These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids A B C D cylinder cone prism pyramid A cylinder has two congruent circular bases AB is a radius A cone has one circular base CD is
9- Solids These three-dimensional figures are space figures, or solids A B C D cylinder cone prism pyramid A cylinder has two congruent circular bases AB is a radius A cone has one circular base CD is
STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS
 STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to fractions and to repeated
STRAND 1 NUMBER and OPERATIONS Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to fractions and to repeated
Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A3; B2; C1. 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can.
 Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A; B2; C1 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can. 2. Name the geometric solid suggested by a beach ball.. Name the geometric solid suggested
Geometry Review Chapter 10: Volume PA Anchors: A; B2; C1 1. Name the geometric solid suggested by a frozen juice can. 2. Name the geometric solid suggested by a beach ball.. Name the geometric solid suggested
1.1 Metric Systems. Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units. Main Ideas:
 1.1 Metric Systems Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units Formula sheet Multiplying and dividing fractions Definitions Metric System The International System of Units, abbreviated
1.1 Metric Systems Learning Target: to practice converting between different metric units Formula sheet Multiplying and dividing fractions Definitions Metric System The International System of Units, abbreviated
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
C in. 2. D in Find the volume of a 7-inch tall drinking glass with a 4-inch diameter. C lateral faces. A in. 3 B in.
 Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
GEOMETRY. slide #3. 6th Grade Math Unit 7. 6th Grade Unit 7: GEOMETRY. Name: Table of Contents. Area of Rectangles
 Name: 6th Grade Math Unit 7 GEOMETRY 2012 10 17 www.njctl.org 1 Table of Contents Area of Rectangles Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of Trapezoids Mixed Review Area of Irregular Figures Area
Name: 6th Grade Math Unit 7 GEOMETRY 2012 10 17 www.njctl.org 1 Table of Contents Area of Rectangles Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of Trapezoids Mixed Review Area of Irregular Figures Area
Lesson 9. Three-Dimensional Geometry
 Lesson 9 Three-Dimensional Geometry 1 Planes A plane is a flat surface (think tabletop) that extends forever in all directions. It is a two-dimensional figure. Three non-collinear points determine a plane.
Lesson 9 Three-Dimensional Geometry 1 Planes A plane is a flat surface (think tabletop) that extends forever in all directions. It is a two-dimensional figure. Three non-collinear points determine a plane.
February 07, Dimensional Geometry Notebook.notebook. Glossary & Standards. Prisms and Cylinders. Return to Table of Contents
 Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of
 Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Notes: Geometry (6.G.1 4)
 Perimeter Add up all the sides (P =s + s + s...) Square A = side 2 A = S 2 Perimeter The distance around a polygon. Rectangle w s L A = Length x Width A = lw Parallelogram A = Base x Height A = h h Triangle
Perimeter Add up all the sides (P =s + s + s...) Square A = side 2 A = S 2 Perimeter The distance around a polygon. Rectangle w s L A = Length x Width A = lw Parallelogram A = Base x Height A = h h Triangle
Revision Booklet. Grade 6
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Mathematics RIT Score:
 Mathematics RIT Score: 201-210 Number Sense and Operations Whole Numbers Understand the concept of division using pictorial representation Use front-end estimation strategy for multiplication and division
Mathematics RIT Score: 201-210 Number Sense and Operations Whole Numbers Understand the concept of division using pictorial representation Use front-end estimation strategy for multiplication and division
Geometry: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Rectangular Prism:
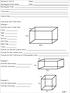 : Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids. Use the formula. Substitute for l and w. Use the formula. Substitute for B and h.
 ? LESSON 10.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids How do you find the volume of a rectangular prism and a rectangular pyramid? Finding the Volume of a Rectangular Prism Remember
? LESSON 10.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids How do you find the volume of a rectangular prism and a rectangular pyramid? Finding the Volume of a Rectangular Prism Remember
Write Euler s Theorem. Solving Problems Using Surface Area and Volume. Figure Surface Area Volume. Cl V 5 1 } 3
 CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
North Adams Public Schools
 Unit 1: Place Value and Multi-Digit Addition and Subtraction Place value drawings to represent numbers. Place value drawings to add and subtract whole numbers. Different methods to add and subtract whole
Unit 1: Place Value and Multi-Digit Addition and Subtraction Place value drawings to represent numbers. Place value drawings to add and subtract whole numbers. Different methods to add and subtract whole
Understand the concept of volume M.TE Build solids with unit cubes and state their volumes.
 Strand II: Geometry and Measurement Standard 1: Shape and Shape Relationships - Students develop spatial sense, use shape as an analytic and descriptive tool, identify characteristics and define shapes,
Strand II: Geometry and Measurement Standard 1: Shape and Shape Relationships - Students develop spatial sense, use shape as an analytic and descriptive tool, identify characteristics and define shapes,
The School District of Palm Beach County Fifth Grade Mathematics Scope rd Trimester
 Unit & Go Math! & lessons from each Measurement and Data MA.5.G.5.3 MD.1.1 Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within
Unit & Go Math! & lessons from each Measurement and Data MA.5.G.5.3 MD.1.1 Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within
Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes
 26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
North Adams Public Schools 5 th Grade Math Curriculum Map Unit: 1 - Addition and Subtraction with Fractions
 Unit: 1 - Addition and Subtraction with Fractions Pacing: 20 Days (Sept.) From the previous year, students should have mastered: Representing fractions as sums of unit fractions Composed and decomposed
Unit: 1 - Addition and Subtraction with Fractions Pacing: 20 Days (Sept.) From the previous year, students should have mastered: Representing fractions as sums of unit fractions Composed and decomposed
Lesson 6 Reteach. Perimeter of the base = 14. S. A. = area of the 2 bases + lateral area = = 52 m^.
 Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms The sum of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. The area of
Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms The sum of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. The area of
Section 9.4. Volume and Surface Area. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area What You Will Learn Volume Surface Area 9.4-2 Volume Volume is the measure of the capacity of a three-dimensional figure. It is the amount of material you can put inside
Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area What You Will Learn Volume Surface Area 9.4-2 Volume Volume is the measure of the capacity of a three-dimensional figure. It is the amount of material you can put inside
CHAPTER. Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC. Three-Dimensional Figures 217
 CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Geometry: Notes
 Geometry: 11.5-11.8 Notes NAME 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Date: Define Vocabulary: volume Cavalieri s Principle density similar solids Examples: Finding Volumes of Prisms 1 Examples: Finding
Geometry: 11.5-11.8 Notes NAME 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Date: Define Vocabulary: volume Cavalieri s Principle density similar solids Examples: Finding Volumes of Prisms 1 Examples: Finding
Lesson 6 Reteach. Surface Area of Prisms. Example. Exercises. 232 in^ tt^^ Find the surface area of the rectangular prism.
 Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms T h e s u m of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. T h e surface area of a rectangular prism with length f,
Lesson 6 Reteach Surface Area of Prisms T h e s u m of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces, of a three-dimensional shape is the surface area. T h e surface area of a rectangular prism with length f,
= 25)(10) 10. =
 8.5 Volume of Rounded Objects A basic definition of volume is how much space an object takes up. Since this is a three-dimensional measurement, the unit is usually cubed. For example, we might talk about
8.5 Volume of Rounded Objects A basic definition of volume is how much space an object takes up. Since this is a three-dimensional measurement, the unit is usually cubed. For example, we might talk about
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z
 o o o. 5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
o o o. 5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
Measurement and Geometry
 Name Date Class Review for Mastery: Converting Customary Units You can use the table below to convert customary units. Length 1 foot = 1 inches 1 yard = 36 inches 1 yard = 3 feet 1 mile = 5,80 feet 1 mile
Name Date Class Review for Mastery: Converting Customary Units You can use the table below to convert customary units. Length 1 foot = 1 inches 1 yard = 36 inches 1 yard = 3 feet 1 mile = 5,80 feet 1 mile
Area. Domain 4 Lesson 25. Getting the Idea
 Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all its outer surfaces or faces.
 Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
9 Find the area of the figure. Round to the. 11 Find the area of the figure. Round to the
 Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
GRADE 5. Operations & Algebraic Thinking - Domain
 Write and interpret numerical expressions. CLUSTERS: 1. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. 2. Write simple expressions that record
Write and interpret numerical expressions. CLUSTERS: 1. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. 2. Write simple expressions that record
Free Response. Test A. 1. What is the estimated area of the figure?
 Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume. Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms.
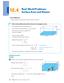 12.4 Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume Lesson Objective Solve problems involving surface area and volume of prisms. Learn Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms. A rectangular
12.4 Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume Lesson Objective Solve problems involving surface area and volume of prisms. Learn Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms. A rectangular
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. no no R89. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
11.6 Start Thinking Warm Up Cumulative Review Warm Up
 11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
Volume and Surface Area Unit 28 Remember Volume of a solid figure is calculated in cubic units and measures three dimensions.
 Volume and Surface Area Unit 28 Remember Volume of a solid figure is calculated in cubic units and measures three dimensions. Surface Area is calculated in square units and measures two dimensions. Prisms
Volume and Surface Area Unit 28 Remember Volume of a solid figure is calculated in cubic units and measures three dimensions. Surface Area is calculated in square units and measures two dimensions. Prisms
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Measurement Unit 2 Surface Area, Volume and 3-D Shapes
 Warden Ave PS Measurement Unit 2 Surface Area, Volume and 3-D Shapes Mr. D. Leavitt Math LEARNING GOALS By the end of this unit, you should be able to: Identify and use the correct formula for calculating
Warden Ave PS Measurement Unit 2 Surface Area, Volume and 3-D Shapes Mr. D. Leavitt Math LEARNING GOALS By the end of this unit, you should be able to: Identify and use the correct formula for calculating
This booklet is designed to be used by the homeschooling parent, tutor, or parent who wants to track their elementary math students progress.
 This booklet is designed to be used by the homeschooling parent, tutor, or parent who wants to track their elementary math students progress. I intentionally present this information with each subject
This booklet is designed to be used by the homeschooling parent, tutor, or parent who wants to track their elementary math students progress. I intentionally present this information with each subject
Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area
 Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
Section 9.4. Volume and Surface Area. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 6, 2013 Area and Perimeter Table 36 February 6, 2013 Section 9.3 Notes 37 February 11, 2013 Volume and Surface Area
Section 9.4 Volume and Surface Area INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 6, 2013 Area and Perimeter Table 36 February 6, 2013 Section 9.3 Notes 37 February 11, 2013 Volume and Surface Area
PYRAMIDS AND CONES WHAT YOU LL LEARN. Ø Finding the surface areas and volume of pyramids Ø Finding the surface areas and volume of cones
 PYRAMIDS AND CONES A pyramid is a solid with a polygonal base and triangular lateral faces that meet at a vertex. In this lesson, you will work with regular pyramids. The base of a regular pyramid is a
PYRAMIDS AND CONES A pyramid is a solid with a polygonal base and triangular lateral faces that meet at a vertex. In this lesson, you will work with regular pyramids. The base of a regular pyramid is a
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
Read, write, order and compare numbers up to and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
 Autumn Term Area Year 6 Year 5 Number and place value Addition Multiplication and division up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
Autumn Term Area Year 6 Year 5 Number and place value Addition Multiplication and division up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
Chapter 12 Review Period:
 Chapter 12 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the number of vertices, faces, and edges for the figure. 9. A polyhedron has 6 faces and 7 vertices. How many edges does it have? Explain your answer. 10. Find the
Chapter 12 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the number of vertices, faces, and edges for the figure. 9. A polyhedron has 6 faces and 7 vertices. How many edges does it have? Explain your answer. 10. Find the
Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education
 Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
Math Supplement: Grade 3 Vocabulary. Compiled by: Katherine Dunlap. District Math Coach
 Math Supplement: Grade 3 Vocabulary Compiled by: Katherine Dunlap District Math Coach 1 Number of Votes Third Grade Math Vocabulary accurate: Precise. angle: A figure that is formed by two rays with a
Math Supplement: Grade 3 Vocabulary Compiled by: Katherine Dunlap District Math Coach 1 Number of Votes Third Grade Math Vocabulary accurate: Precise. angle: A figure that is formed by two rays with a
3.1 Deepening Understandings of Volume Parts 1_2.notebook. September 05, 2018 M Jun 27 10:28 AM
 M1 115 Jun 27 10:28 AM 1 Learning Targets Jun 20 10:53 AM 2 9/4 /18 # Glue pages 1 & 2 into notebook M1: 3.1 Deepening Understanding of Volume Essential Question: How can you use what you know to calculate
M1 115 Jun 27 10:28 AM 1 Learning Targets Jun 20 10:53 AM 2 9/4 /18 # Glue pages 1 & 2 into notebook M1: 3.1 Deepening Understanding of Volume Essential Question: How can you use what you know to calculate
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, D Geometry Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
ROCHESTER COMMUNITY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS SCOPE AND SEQUENCE, K-5 STRAND: NUMERATION
 STRAND: NUMERATION Shows one-to-one correspondence for numbers 1-30 using objects and pictures Uses objects and pictures to show numbers 1 to 30 Counts by 1s to 100 Counts by 10s to 100 Counts backwards
STRAND: NUMERATION Shows one-to-one correspondence for numbers 1-30 using objects and pictures Uses objects and pictures to show numbers 1 to 30 Counts by 1s to 100 Counts by 10s to 100 Counts backwards
8th Grade. Slide 1 / 97. Slide 2 / 97. Slide 3 / 97. 3D Geometry. Table of Contents. 3-Dimensional Solids. Volume. Glossary & Standards
 Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
ADW GRADE 5 Math Standards, revised 2017
 NUMBER SENSE (NS) Students compute with whole numbers, decimals and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers.
NUMBER SENSE (NS) Students compute with whole numbers, decimals and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers.
Math Tool: Grid Paper
 Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
8.5 Volume of Rounded Objects
 8.5 Volume of Rounded Objects A basic definition of volume is how much space an object takes up. Since this is a three-dimensional measurement, the unit is usually cubed. For example, we might talk about
8.5 Volume of Rounded Objects A basic definition of volume is how much space an object takes up. Since this is a three-dimensional measurement, the unit is usually cubed. For example, we might talk about
Practice Test Unit 8. Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it!
 Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
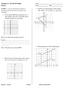 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula
 Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP
 Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP UNIT 14: SOLIDS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Face Edge Vertex Cross section Prism Height Surface area Lateral surface area Net Volume Scale
Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP UNIT 14: SOLIDS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Face Edge Vertex Cross section Prism Height Surface area Lateral surface area Net Volume Scale
Alignment of Destination Math Courseware with GRADE 4 Benchmarks (B1-B3)
 NUMBER SENSE SAM04101- B1 Read write whole numbers in the millions (1.1) 1.1 Read write whole numbers in the millions. I Number Sense Unit: Large Small Whole to One Million Ordering Rounding Whole SAM04102a-B1
NUMBER SENSE SAM04101- B1 Read write whole numbers in the millions (1.1) 1.1 Read write whole numbers in the millions. I Number Sense Unit: Large Small Whole to One Million Ordering Rounding Whole SAM04102a-B1
Unit 5. Area & Volume. Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume. Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18. Name: Math Teacher:
 Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Chapter Test A For use after Chapter 12
 Chapter Test A For use after Chapter Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, find the number of faces, vertices, and edges.. 2. 3.. Determine whether the polyhedron is regular and/or conve. 2.
Chapter Test A For use after Chapter Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, find the number of faces, vertices, and edges.. 2. 3.. Determine whether the polyhedron is regular and/or conve. 2.
Geometry Unit 10 Note Sheets Date Name of Lesson. 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures Areas of Circles and Sectors
 Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
Math Vocabulary Grades PK - 5
 Math Vocabulary ades P - 5 P 1 2 3 4 5 < Symbol used to compare two numbers with the lesser number given first > Symbol used to compare two numbers with the greater number given first a. m. The time between
Math Vocabulary ades P - 5 P 1 2 3 4 5 < Symbol used to compare two numbers with the lesser number given first > Symbol used to compare two numbers with the greater number given first a. m. The time between
Correlation of the Math Diagnosis and Intervention System and Grade 5 to the Michigan Mathematics Grade-Level Content Expectations
 and and Correlation Strand 1: Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers through 03. through 03. N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with
and and Correlation Strand 1: Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers through 03. through 03. N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with
Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms
 CONDENSED LESSON 8.1 Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms In this lesson, you Review the formula for the area of a rectangle Use the area formula for rectangles to find areas of other shapes Discover
CONDENSED LESSON 8.1 Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms In this lesson, you Review the formula for the area of a rectangle Use the area formula for rectangles to find areas of other shapes Discover
