Fault-Tolerant Computing
|
|
|
- Nathaniel McCarthy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fault-Tolerant Computing Dealing with Mid-Level Impairments Oct Error Detection Slide 1
2 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing) by Behrooz Parhami, Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of California, Santa Barbara. The material contained herein can be used freely in classroom teaching or any other educational setting. Unauthorized uses are prohibited. Behrooz Parhami Edition Released Revised Revised First Oct Oct Oct Error Detection Slide 2
3 Error Detection Oct Error Detection Slide 3
4 Oct Error Detection Slide 4
5 Multilevel Model Ideal Component Logic Information System Legend: Legned: Initial Entry Entry Deviation This lecture Defective Faulty Erroneous Malfunctioning Next lecture Low-Level Impaired Mid-Level Impaired Service Result Remedy Tolerance Degraded Failed High-Level Impaired Oct Error Detection Slide 5
6 High-Redundancy Codes Duplication is a form of error coding: x represented as xx (100% redundancy) Detects any error in one version Two-rail encoding x represented as xx (100% redundancy) e.g., 0 represented as 01; 1 as 10 Detects any error in one version Detects all unidirectional errors Encoding x Encoding x f(x) f(x) f(x) f(x) Decoding Decoding XOR Error checking XNOR Error checking y Error signal y Error signal Two-rail logic elements AND: (a 0, a 1 ) (b 0, b 1 ) = (a 0 b 0, a 1 b 1 ) OR: (a 0, a 1 ) (b 0, b 1 ) = (a 0 b 0, a 1 b 1 ) NOT: (a 0, a 1 ) = (a 1, a 0 ) XOR: (a 0, a 1 ) (b 0, b 1 ) = (a 0 b 1 a 1 b 0, a 0 b 0 a 1 b 1 ) X X Oct Error Detection Slide 6
7 The Concept of Error-Detecting Codes Data space Data words Encoding Decoding Code space Codewords Errors Noncodewords Error space The simplest possible error-detecting code: Attach an even parity bit to each k-bit data word Check bit = XOR of all data bits Data space: All 2 k possible k-bit words Code space: All 2 k possible even-parity (k + 1)-bit codewords Error space: All 2 k possible odd-parity (k + 1)-bit noncodewords Detects all single-bit errors Oct Error Detection Slide 7
8 Evaluation of Error-Detecting Codes Redundancy: k data bits encoded in n = k + r bits (r redundant bits) Encoding: Complexity (cost / time) to form codeword from data word Decoding: Complexity (cost / time) to obtain data word from codeword Separable codes have computation-free decoding Capability: Classes of error that can be detected Greater detection capability generally involves more redundancy To detect d bit-errors, a minimum code distance of d + 1 is required Examples of code detection capabilities: Single, double, b-bit burst, byte, unidirectional,... errors Closure: Arithmetic and other operations done directly on codewords (rather than in 3 stages: decode, operate, and encode) Oct Error Detection Slide 8
9 Error Detection in UPC-A To obtain the check digit for 12-digit UPC-A universal product code: Add the odd-indexed digits and multiply the sum by 3 Add the sum of even-indexed digits to previous result Subtract the total from the next higher multiple of 10 Example: Sum odd indexed digits: = 14 Multiply by 3: 14 3 = 42 Add even-indexed digits: = 58 Compute check digit: = 2 Checking: Verify that weighted mod-10 sum of all 12 digits is 0 Capabilities: Detects all single-digit errors Detects most, but not all, transposition errors Bar code uses 7 bits per digit, with different encodings on the right and left halves and different parities at various positions Oct Error Detection Slide 9
10 Checksum Codes Given a data vector x 1, x 2,..., x n, encode the data by attaching the checksum x n+1 to the end, such that Σ j=1 to n+1 w j x j = 0 mod A The elements w j of the weight vector w are predetermined constants Example: For the UPC-A checksum scheme, we have w = 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1 A = 10 Checking: Verify that weighted mod-a sum of all elements is Capabilities: Detects all errors adding an error magnitude that is not a multiple of A Variant: Vector elements may be XORed rather than added together Oct Error Detection Slide 10
11 Hamming Distance Definition: Hamming distance between two bit-vectors is the number of positions in which they differ A distance-2 code: (0 1 error) (1 0 error) Codeword Noncodeword Correctable error Codeword Min H-dist Code capability 2 d = 1; SED 3 c = 1; SEC or (d = 2; DED) 4 c = 1 and d = 2; SEC/DED 5 c = 2 or (c = 1 and d = 3; SEC/3ED) h cec/ded such that h = c + d + 1 Oct Error Detection Slide 11 Detectable error
12 Error Classification and Models Goal of error tolerance methods: Allow uninterrupted operation despite presence of certain errors Error model Relationship between errors and faults (or other causes) Errors are detected/corrected through: Encoded (redundant) data, plus code checkers Reasonableness checks, activity monitoring, retry Errors are classified as: Single or Multiple (according to the number of bits affected) Inversion or Erasure (symbol or bit changed or lost)* Random or Correlated (correlation in the form of byte or burst error) Symmetric or Asymmetric (regarding 0 1 and 1 0 inversions) * Nonbinary codes have substitution rather than inversion errors Also of interest for nonelectronic systems are transposition errors Errors are permanent by nature; transient faults, not transient errors Oct Error Detection Slide 12
13 Application of Coding to Error Control Ordinary codes can be used for storage and transmission errors; they are not closed under arithmetic / logic operations INPUT ENCODE Error-detecting, error-correcting, or combination codes (e.g., Hamming SEC/DED) Arithmetic codes can help detect (or correct) errors during data manipulations: Protected by Encoding SEND STORE SEND Unprotected MANIPULATE 1. Product codes (e.g., 15x) 2. Residue codes (x mod 15) DECODE A common way of applying information coding techniques OUTPUT Oct Error Detection Slide 13
14 Constant-Weight Codes Definition: All codewords have the same number of 1s A weight-2 code: Can detect all unidirectional errors Maximum number of codewords obtained when weight of n-bit codewords is n/2 Oct Error Detection Slide 14
15 Berger Codes Definition: Separable code that has the count of 0s within the data part attached as a binary number that forms the check part Alternative attach the 1 s-complement of the number of 1s A Berger code: Can detect all unidirectional errors log 2 (k + 1) check bits for k data bits Check part Oct Error Detection Slide 15
16 Cyclic Codes Definition: Any cyclic shift of a codeword produces another codeword A k-bit data word corresponds to a polynomial of degree k 1 Data = : D(x) = 1 + x + x 3 + x 6 (addition is mod 2) The code has a generator polynomial of degree r = n k G(x) = 1 + x + x 3 To encode data ( ), multiply its associated polynomial by G(x) 1 + x + x 3 + x x + x x + x 3 + x 6 + x + x 2 + x 4 + x 7 + x 3 + x 4 + x 6 + x x 2 + x 7 + x Detects all burst errors of width less than n k Burst error polynomial x j E(x), where E(x) is of degree less than n k Oct Error Detection Slide 16
17 Cyclic Codes: Encoding and Decoding Encoding: Multiplication by the generator polynomial G(x) G(x): x 3 x 1 FF FF FF V(x) D(x) Decoding: Division by the generator polynomial G(x) B(x) V(x) D(x) G(x): x 3 x 1 FF FF FF B(x) = (x + x 3 ) D(x) V(x) = D(x) + B(x) = (1 + x + x 3 ) D(x) Oct Error Detection Slide 17
18 Separable Cyclic Codes Let D(x) and G(x) be the data and generator polynomials Encoding: Multiply D(x) by x n k and divide the result by G(x) to get the remainder polynomial R(x) of degree less than n k Form the codeword V(x) = R(x) + x n k D(x), which is divisible by G(x) Example: 7-bit code with 4 data bits and 3 check bits, G(x) = 1 + x + x 3 Data = , D(x) = 1 + x 3 x 3 D(x) = x 3 + x 6 = (x + x 2 ) mod (1 + x + x 3 ) V(x) = x + x 2 + x 3 + x 6 Codeword = Check part Data part aka CRC = cyclic redundancy check Single parity bit: G(x) = x + 1 Oct Error Detection Slide 18
19 The Arithmetic Weight of an Error Unsigned addition How a single carry error can lead to an arbitrary Correct sum number of bit-errors Erroneous sum (inversions) Stage generating an erroneous carry of 1 The arithmetic weight of an error: Min number of signed powers of 2 that must be added to the correct value to turn it into the erroneous result (contrast with Hamming weight of an error) Example 1 Example 2 Correct value Erroneous value Difference (error) 16 = = Min-weight BSD Arithmetic weight 1 2 Error type Single, positive Double, negative Oct Error Detection Slide 19
20 Codes for Arithmetic Operations Arithmetic error-detecting codes: Are characterized by arithmetic weights of detectable errors Allow direct arithmetic on coded operands We will discuss two classes of arithmetic error-detecting codes, both of which are based on a check modulus A (usually a small odd number) Product or AN codes Represent the value N by the number AN Residue (or inverse residue) codes Represent the value N by the pair (N, C), where C is N mod A or (N N mod A) mod A Oct Error Detection Slide 20
21 Product or AN Codes For odd A, all weight-1 arithmetic errors are detected Arithmetic errors of weight 2 may go undetected e.g., the error = undetectable with A = 3, 11, or 31 Error detection: check divisibility by A Encoding/decoding: multiply/divide by A Arithmetic also requires multiplication and division by A Product codes are nonseparate (nonseparable) codes Data and redundant check info are intermixed Oct Error Detection Slide 21
22 Low-Cost Product Codes Use low-cost check moduli of the form A = 2 a 1 Multiplication by A = 2 a 1: done by shift-subtract (2 a 1)N = 2 a N N Division by A = 2 a 1: done a bits at a time as follows Given y = (2 a 1)x, find x by computing 2 a x y... xxxx xxxx xxxx =... xxxx xxxx Unknown 2 a x Known (2 a 1)x Unknown x Theorem: Any unidirectional error with arithmetic weight of at most a 1 is detectable by a low-cost product code based on A = 2 a 1 Oct Error Detection Slide 22
23 Arithmetic on AN-Coded Operands Add/subtract is done directly: Ax ± Ay = A(x ± y) Direct multiplication results in: Aa Ax = A 2 ax The result must be corrected through division by A For division, if z = qd + s, we have: Az = q(ad) + As Thus, q is unprotected Possible cure: premultiply the dividend Az by A The result will need correction Square rooting leads to a problem similar to division A 2 x = A x which is not the same as A x Oct Error Detection Slide 23
24 Residue and Inverse Residue Codes Represent N by the pair (N, C(N)), where C(N) = N mod A Residue codes are separate (separable) codes Separate data and check parts make decoding trivial Encoding: Given N, compute C(N) = N mod A Low-cost residue codes use A = 2 a 1 To compute N mod (2 a 1), add a-bit segments of N, modulo 2 a 1 (no division is required) Example: Compute mod = 0011 (addition with end-around carry) = = 1100 The final residue mod 15 Oct Error Detection Slide 24
25 Arithmetic on Residue-Coded Operands Add/subtract: Data and check parts are handled separately (x, C(x)) ± (y, C(y)) = (x ± y, (C(x) ± C(y)) mod A) Multiply (a, C(a)) (x, C(x)) = (a x, (C(a) C(x)) mod A) Divide/square-root: difficult x C(x) y C(y) Main Arithmetic Processor Check Processor mod A Compare Error Indicator z C(z) Arithmetic processor with residue checking Oct Error Detection Slide 25
26 Higher-Level Error Coding Methods We have applied coding to data at the bit-string or word level It is also possible to apply coding at higher levels Data structure level Robust data structures Application level Algorithm-based error tolerance Oct Error Detection Slide 26
Oct Part IV Errors: Informational Distortions Slide 1
 Oct. 2015 Part IV Errors: Informational Distortions Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation is intended to support the use of the textbook Dependable Computing: A Multilevel Approach (traditional
Oct. 2015 Part IV Errors: Informational Distortions Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation is intended to support the use of the textbook Dependable Computing: A Multilevel Approach (traditional
Fault-Tolerant Computing
 Fault-Tolerant Computing Hardware Design Methods Nov. 2007 Hardware Implementation Strategies Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant
Fault-Tolerant Computing Hardware Design Methods Nov. 2007 Hardware Implementation Strategies Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant
Fault-Tolerant Computing
 Fault-Tolerant Computing Hardware Design Methods Nov 2007 Self-Checking Modules Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing)
Fault-Tolerant Computing Hardware Design Methods Nov 2007 Self-Checking Modules Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing)
Ch. 7 Error Detection and Correction
 Ch. 7 Error Detection and Correction Error Detection and Correction Data can be corrupted during transmission. Some applications require that errors be detected and corrected. 2 1. Introduction Let us
Ch. 7 Error Detection and Correction Error Detection and Correction Data can be corrupted during transmission. Some applications require that errors be detected and corrected. 2 1. Introduction Let us
CS321: Computer Networks Error Detection and Correction
 CS321: Computer Networks Error Detection and Correction Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Error Detection and Correction Objective: System must
CS321: Computer Networks Error Detection and Correction Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Error Detection and Correction Objective: System must
EE 6900: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING SYSTEMS
 EE 6900: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING SYSTEMS LECTURE 6: CODING THEORY - 2 Fall 2014 Avinash Kodi kodi@ohio.edu Acknowledgement: Daniel Sorin, Behrooz Parhami, Srinivasan Ramasubramanian Agenda Hamming Codes
EE 6900: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING SYSTEMS LECTURE 6: CODING THEORY - 2 Fall 2014 Avinash Kodi kodi@ohio.edu Acknowledgement: Daniel Sorin, Behrooz Parhami, Srinivasan Ramasubramanian Agenda Hamming Codes
Advanced Computer Networks. Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS. Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Advanced Computer Networks Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Rab Nawaz Jadoon Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
Advanced Computer Networks Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Rab Nawaz Jadoon Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
Fault-Tolerant Computing
 Fault-Tolerant Computing Dealing with Low-Level Impairments Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing) by Behrooz Parhami,
Fault-Tolerant Computing Dealing with Low-Level Impairments Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation has been prepared for the graduate course ECE 257A (Fault-Tolerant Computing) by Behrooz Parhami,
Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction 0. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note The Hamming distance between two words is the number of differences
Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction 0. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note The Hamming distance between two words is the number of differences
Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction 10.1
 Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction 10.1 10-1 INTRODUCTION some issues related, directly or indirectly, to error detection and correction. Topics discussed in this section: Types of Errors Redundancy
Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction 10.1 10-1 INTRODUCTION some issues related, directly or indirectly, to error detection and correction. Topics discussed in this section: Types of Errors Redundancy
MYcsvtu Notes DATA REPRESENTATION. Data Types. Complements. Fixed Point Representations. Floating Point Representations. Other Binary Codes
 DATA REPRESENTATION Data Types Complements Fixed Point Representations Floating Point Representations Other Binary Codes Error Detection Codes Hamming Codes 1. DATA REPRESENTATION Information that a Computer
DATA REPRESENTATION Data Types Complements Fixed Point Representations Floating Point Representations Other Binary Codes Error Detection Codes Hamming Codes 1. DATA REPRESENTATION Information that a Computer
ENEE x Digital Logic Design. Lecture 3
 ENEE244-x Digital Logic Design Lecture 3 Announcements Homework due today. Homework 2 will be posted by tonight, due Monday, 9/2. First recitation quiz will be tomorrow on the material from Lectures and
ENEE244-x Digital Logic Design Lecture 3 Announcements Homework due today. Homework 2 will be posted by tonight, due Monday, 9/2. First recitation quiz will be tomorrow on the material from Lectures and
Lecture 6: Reliable Transmission. CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex Snoeren (guest lecture) Alex Sn
 Lecture 6: Reliable Transmission CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex Snoeren (guest lecture) Alex Sn Lecture 6 Overview Finishing Error Detection Cyclic Remainder Check (CRC) Handling errors Automatic Repeat
Lecture 6: Reliable Transmission CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex Snoeren (guest lecture) Alex Sn Lecture 6 Overview Finishing Error Detection Cyclic Remainder Check (CRC) Handling errors Automatic Repeat
Lecture / The Data Link Layer: Framing and Error Detection
 Lecture 2 6.263/16.37 The Data Link Layer: Framing and Error Detection MIT, LIDS Slide 1 Data Link Layer (DLC) Responsible for reliable transmission of packets over a link Framing: Determine the start
Lecture 2 6.263/16.37 The Data Link Layer: Framing and Error Detection MIT, LIDS Slide 1 Data Link Layer (DLC) Responsible for reliable transmission of packets over a link Framing: Determine the start
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS
 FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/koren/faulttolerantsystems Part 6 Coding I Chapter 3 Information Redundancy Part.6.1 Information Redundancy - Coding A data word with d bits is encoded
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/koren/faulttolerantsystems Part 6 Coding I Chapter 3 Information Redundancy Part.6.1 Information Redundancy - Coding A data word with d bits is encoded
CMSC 2833 Lecture 18. Parity Add a bit to make the number of ones (1s) transmitted odd.
 Parity Even parity: Odd parity: Add a bit to make the number of ones (1s) transmitted even. Add a bit to make the number of ones (1s) transmitted odd. Example and ASCII A is coded 100 0001 Parity ASCII
Parity Even parity: Odd parity: Add a bit to make the number of ones (1s) transmitted even. Add a bit to make the number of ones (1s) transmitted odd. Example and ASCII A is coded 100 0001 Parity ASCII
Data Link Layer. Srinidhi Varadarajan
 Data Link Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Data Link Layer: Functionality The data link layer must: Detect errors (using redundancy bits) Request retransmission if data is lost (using automatic repeat request
Data Link Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Data Link Layer: Functionality The data link layer must: Detect errors (using redundancy bits) Request retransmission if data is lost (using automatic repeat request
CSN Telecommunications. 5: Error Coding. Data, Audio, Video and Images Prof Bill Buchanan
 CSN874 Telecommunications 5: Error Coding Data, Audio, Video and Images http://asecuritysite.com/comms Prof Bill Buchanan CSN874 Telecommunications 5: Error Coding: Modulo-2 Data, Audio, Video and Images
CSN874 Telecommunications 5: Error Coding Data, Audio, Video and Images http://asecuritysite.com/comms Prof Bill Buchanan CSN874 Telecommunications 5: Error Coding: Modulo-2 Data, Audio, Video and Images
TYPES OF ERRORS. Data can be corrupted during transmission. Some applications require that errors be detected and corrected.
 Data can be corrupted during transmission. Some applications require that errors be detected and corrected. TYPES OF ERRORS There are two types of errors, 1. Single Bit Error The term single-bit error
Data can be corrupted during transmission. Some applications require that errors be detected and corrected. TYPES OF ERRORS There are two types of errors, 1. Single Bit Error The term single-bit error
Chapter 3. The Data Link Layer. Wesam A. Hatamleh
 Chapter 3 The Data Link Layer The Data Link Layer Data Link Layer Design Issues Error Detection and Correction Elementary Data Link Protocols Sliding Window Protocols Example Data Link Protocols The Data
Chapter 3 The Data Link Layer The Data Link Layer Data Link Layer Design Issues Error Detection and Correction Elementary Data Link Protocols Sliding Window Protocols Example Data Link Protocols The Data
Fault Tolerance & Reliability CDA Chapter 2 Additional Interesting Codes
 Fault Tolerance & Reliability CDA 5140 Chapter 2 Additional Interesting Codes m-out-of-n codes - each binary code word has m ones in a length n non-systematic codeword - used for unidirectional errors
Fault Tolerance & Reliability CDA 5140 Chapter 2 Additional Interesting Codes m-out-of-n codes - each binary code word has m ones in a length n non-systematic codeword - used for unidirectional errors
CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability Rodrigo Fonseca
 CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Janno< Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Link layer framing Today Getting
CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Janno< Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Link layer framing Today Getting
CSE123A discussion session
 CSE23A discussion session 27/2/9 Ryo Sugihara Review Data Link Layer (3): Error detection sublayer CRC Polynomial representation Implementation using LFSR Data Link Layer (4): Error recovery sublayer Protocol
CSE23A discussion session 27/2/9 Ryo Sugihara Review Data Link Layer (3): Error detection sublayer CRC Polynomial representation Implementation using LFSR Data Link Layer (4): Error recovery sublayer Protocol
CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren. HW 1 due Thursday!
 CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 1 due Thursday! Error handling through redundancy Adding extra bits to the frame Hamming Distance When we can detect When we can correct Checksum Cyclic Remainder
CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 1 due Thursday! Error handling through redundancy Adding extra bits to the frame Hamming Distance When we can detect When we can correct Checksum Cyclic Remainder
ISO/OSI Reference Model. Data Link Layer. 7. Application. 6. Presentation. 5. Session. 4. Transport. 3. Network. 2. Data Link. 1.
 Data Link Layer 1 ISO/OSI Reference Model 7. Application E-Mail, Terminal, Remote login 6. Presentation System dependent presentation of data (EBCDIC/ASCII) 5. Session Connection establishment, termination,
Data Link Layer 1 ISO/OSI Reference Model 7. Application E-Mail, Terminal, Remote login 6. Presentation System dependent presentation of data (EBCDIC/ASCII) 5. Session Connection establishment, termination,
EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L3: Data Link layer. Stefan Höst
 EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L3: Data Link layer Stefan Höst Communication on physical layer To transmit on the physical medium use signals At each computer it can be seen as transmitting
EITF25 Internet Techniques and Applications L3: Data Link layer Stefan Höst Communication on physical layer To transmit on the physical medium use signals At each computer it can be seen as transmitting
CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability John Jannotti
 CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability John Jannotti Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, Rodrigo Fonseca Roadmap Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Link layer framing Today
CSCI-1680 Link Layer Reliability John Jannotti Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, Rodrigo Fonseca Roadmap Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Link layer framing Today
Link Layer: Error detection and correction
 Link Layer: Error detection and correction Topic Some bits will be received in error due to noise. What can we do? Detect errors with codes Correct errors with codes Retransmit lost frames Later Reliability
Link Layer: Error detection and correction Topic Some bits will be received in error due to noise. What can we do? Detect errors with codes Correct errors with codes Retransmit lost frames Later Reliability
Lecture 2 Error Detection & Correction. Types of Errors Detection Correction
 Lecture 2 Error Detection & Correction Types of Errors Detection Correction Basic concepts Networks must be able to transfer data from one device to another with complete accuracy. Data can be corrupted
Lecture 2 Error Detection & Correction Types of Errors Detection Correction Basic concepts Networks must be able to transfer data from one device to another with complete accuracy. Data can be corrupted
CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems
 CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems 2.1 Introduction 37 2.2 Positional Numbering Systems 38 2.3 Decimal to Binary Conversions 38 2.3.1 Converting Unsigned Whole Numbers 39 2.3.2 Converting
CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems 2.1 Introduction 37 2.2 Positional Numbering Systems 38 2.3 Decimal to Binary Conversions 38 2.3.1 Converting Unsigned Whole Numbers 39 2.3.2 Converting
EC500. Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware. Lecture 9. Mark Karpovsky
 EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 9 Mark Karpovsky 1 1 Arithmetical Codes 1.1 Detection and Correction of errors in arithmetical channels (adders, multipliers, etc) Let = 0,1,,2 1 and
EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 9 Mark Karpovsky 1 1 Arithmetical Codes 1.1 Detection and Correction of errors in arithmetical channels (adders, multipliers, etc) Let = 0,1,,2 1 and
CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems
 CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems 2.1 Introduction 37 2.2 Positional Numbering Systems 38 2.3 Decimal to Binary Conversions 38 2.3.1 Converting Unsigned Whole Numbers 39 2.3.2 Converting
CHAPTER 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems 2.1 Introduction 37 2.2 Positional Numbering Systems 38 2.3 Decimal to Binary Conversions 38 2.3.1 Converting Unsigned Whole Numbers 39 2.3.2 Converting
Error Detection Codes. Error Detection. Two Dimensional Parity. Internet Checksum Algorithm. Cyclic Redundancy Check.
 Error Detection Two types Error Detection Codes (e.g. CRC, Parity, Checksums) Error Correction Codes (e.g. Hamming, Reed Solomon) Basic Idea Add redundant information to determine if errors have been introduced
Error Detection Two types Error Detection Codes (e.g. CRC, Parity, Checksums) Error Correction Codes (e.g. Hamming, Reed Solomon) Basic Idea Add redundant information to determine if errors have been introduced
CSEP 561 Error detection & correction. David Wetherall
 CSEP 561 Error detection & correction David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Codes for Error Detection/Correction ti ti Error detection and correction How do we detect and correct messages that are garbled
CSEP 561 Error detection & correction David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Codes for Error Detection/Correction ti ti Error detection and correction How do we detect and correct messages that are garbled
Telecom Systems Chae Y. Lee. Contents. Flow Control Error Detection/Correction Link Control (Error Control) Link Performance (Utility)
 Data Link Control Contents Flow Control Error Detection/Correction Link Control (Error Control) Link Performance (Utility) 2 Flow Control Flow control is a technique for assuring that a transmitting entity
Data Link Control Contents Flow Control Error Detection/Correction Link Control (Error Control) Link Performance (Utility) 2 Flow Control Flow control is a technique for assuring that a transmitting entity
Lecture 5. Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1
 Lecture 5 Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 5 Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Error Correction and Detection using Cyclic Redundancy Check
 Error Correction and Detection using Cyclic Redundancy Check Dr. T. Logeswari Associate Professor, Dept of Computer Science, New Horizon College, Banglore, Karnataka, India ABSTRACT: In this paper Cyclic
Error Correction and Detection using Cyclic Redundancy Check Dr. T. Logeswari Associate Professor, Dept of Computer Science, New Horizon College, Banglore, Karnataka, India ABSTRACT: In this paper Cyclic
Lecture 4: CRC & Reliable Transmission. Lecture 4 Overview. Checksum review. CRC toward a better EDC. Reliable Transmission
 1 Lecture 4: CRC & Reliable Transmission CSE 123: Computer Networks Chris Kanich Quiz 1: Tuesday July 5th Lecture 4: CRC & Reliable Transmission Lecture 4 Overview CRC toward a better EDC Reliable Transmission
1 Lecture 4: CRC & Reliable Transmission CSE 123: Computer Networks Chris Kanich Quiz 1: Tuesday July 5th Lecture 4: CRC & Reliable Transmission Lecture 4 Overview CRC toward a better EDC Reliable Transmission
2.4 Error Detection Bit errors in a frame will occur. How do we detect (and then. (or both) frames contains an error. This is inefficient (and not
 CS475 Networks Lecture 5 Chapter 2: Direct Link Networks Assignments Reading for Lecture 6: Sections 2.6 2.8 Homework 2: 2.1, 2.4, 2.6, 2.14, 2.18, 2.31, 2.35. Due Thursday, Sept. 15 2.4 Error Detection
CS475 Networks Lecture 5 Chapter 2: Direct Link Networks Assignments Reading for Lecture 6: Sections 2.6 2.8 Homework 2: 2.1, 2.4, 2.6, 2.14, 2.18, 2.31, 2.35. Due Thursday, Sept. 15 2.4 Error Detection
4. Error correction and link control. Contents
 //2 4. Error correction and link control Contents a. Types of errors b. Error detection and correction c. Flow control d. Error control //2 a. Types of errors Data can be corrupted during transmission.
//2 4. Error correction and link control Contents a. Types of errors b. Error detection and correction c. Flow control d. Error control //2 a. Types of errors Data can be corrupted during transmission.
PART III. Data Link Layer MGH T MGH C I 204
 PART III Data Link Layer Position of the data-link layer Data link layer duties LLC and MAC sublayers IEEE standards for LANs Chapters Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction Chapter 11 Data Link Control
PART III Data Link Layer Position of the data-link layer Data link layer duties LLC and MAC sublayers IEEE standards for LANs Chapters Chapter 10 Error Detection and Correction Chapter 11 Data Link Control
High Level View. EE 122: Error detection and reliable transmission. Overview. Error Detection
 High Level View EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 22 Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise Solution
High Level View EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 22 Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise Solution
On-Line Error Detecting Constant Delay Adder
 On-Line Error Detecting Constant Delay Adder Whitney J. Townsend and Jacob A. Abraham Computer Engineering Research Center The University of Texas at Austin whitney and jaa @cerc.utexas.edu Parag K. Lala
On-Line Error Detecting Constant Delay Adder Whitney J. Townsend and Jacob A. Abraham Computer Engineering Research Center The University of Texas at Austin whitney and jaa @cerc.utexas.edu Parag K. Lala
Introduction to Computer Networks. 03 Data Link Layer Introduction
 Introduction to Computer Networks 03 Data Link Layer Introduction Link Layer 1 Introduction and services 2 Link Layer Services 2.1 Framing 2.2 Error detection and correction 2.3 Flow Control 2.4 Multiple
Introduction to Computer Networks 03 Data Link Layer Introduction Link Layer 1 Introduction and services 2 Link Layer Services 2.1 Framing 2.2 Error detection and correction 2.3 Flow Control 2.4 Multiple
EITF25 Internet- - Techniques and Applica8ons Stefan Höst. L4 Data link (part 1)
 EITF25 Internet- - Techniques and Applica8ons Stefan Höst L4 Data link (part 1) Previously on EITF25 (or digital signal) 2 Data Link Layer Medium Access Control Access to network Logical Link Control Node-
EITF25 Internet- - Techniques and Applica8ons Stefan Höst L4 Data link (part 1) Previously on EITF25 (or digital signal) 2 Data Link Layer Medium Access Control Access to network Logical Link Control Node-
EE 122: Error detection and reliable transmission. Ion Stoica September 16, 2002
 EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 2002 High Level View Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise
EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 2002 High Level View Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer:
 UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
(Refer Slide Time: 2:20)
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-15 Error Detection and Correction Hello viewers welcome to today s lecture
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-15 Error Detection and Correction Hello viewers welcome to today s lecture
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
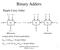 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
CSCI-1680 Link Layer I Rodrigo Fonseca
 CSCI-1680 Link Layer I Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Jannotti Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Today Link layer framing Getting frames
CSCI-1680 Link Layer I Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Jannotti Last time Physical layer: encoding, modulation Today Link layer framing Getting frames
CS254 Network Technologies. Lecture 2: Network Models & Error Detection and Correction. Dr Nikos Antonopoulos
 CS254 Network Technologies Lecture 2: Network Models & Error Detection and Correction Dr Nikos Antonopoulos Department of Computing University of Surrey Autumn 2006 2.1 Layered Tasks Sender, Receiver,
CS254 Network Technologies Lecture 2: Network Models & Error Detection and Correction Dr Nikos Antonopoulos Department of Computing University of Surrey Autumn 2006 2.1 Layered Tasks Sender, Receiver,
CSE 123A Computer Networks
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Data-Link I: Framing and Errors Some portions courtesy Robin Kravets and Steve Lumetta Last time How protocols are organized & why Network layer Data-link
CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Data-Link I: Framing and Errors Some portions courtesy Robin Kravets and Steve Lumetta Last time How protocols are organized & why Network layer Data-link
Digital Fundamentals
 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Decimal Numbers The position of each digit in a weighted
Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Decimal Numbers The position of each digit in a weighted
Part VII Implementation Topics
 Part VII Implementation Topics Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
Part VII Implementation Topics Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
Announcement. (CSC-3501) Lecture 3 (22 Jan 2008) Today, 1 st homework will be uploaded at our class website. Seung-Jong Park (Jay)
 Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 3 (22 Jan 2008) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Announcement Today, 1 st homework will be uploaded at our class website Due date is the beginning
Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 3 (22 Jan 2008) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Announcement Today, 1 st homework will be uploaded at our class website Due date is the beginning
Lecture 5: Data Link Layer Basics
 Lecture 5: Data Link Layer Basics Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE426: Communication Networks Layer 2 PDU: Frame 2 1 Bit-oriented vs. Byte-oriented Layer 2 protocols
Lecture 5: Data Link Layer Basics Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE426: Communication Networks Layer 2 PDU: Frame 2 1 Bit-oriented vs. Byte-oriented Layer 2 protocols
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ERROR DETECTION
 HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ERROR DETECTION Ravishankar K. Iyer, Zbigniew Kalbarczyk Center for Reliable and High-Performance Computing Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ERROR DETECTION Ravishankar K. Iyer, Zbigniew Kalbarczyk Center for Reliable and High-Performance Computing Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
I. INTRODUCTION. each station (i.e., computer, telephone, etc.) directly connected to all other stations
 I. INTRODUCTION (a) Network Topologies (i) point-to-point communication each station (i.e., computer, telephone, etc.) directly connected to all other stations (ii) switched networks (1) circuit switched
I. INTRODUCTION (a) Network Topologies (i) point-to-point communication each station (i.e., computer, telephone, etc.) directly connected to all other stations (ii) switched networks (1) circuit switched
Chapter 2. Positional number systems. 2.1 Signed number representations Signed magnitude
 Chapter 2 Positional number systems A positional number system represents numeric values as sequences of one or more digits. Each digit in the representation is weighted according to its position in the
Chapter 2 Positional number systems A positional number system represents numeric values as sequences of one or more digits. Each digit in the representation is weighted according to its position in the
Where we are in the Course
 Link Layer Where we are in the Course Moving on up to the Link Layer! Application Transport Network Link Physical CSE 461 University of Washington 2 Scope of the Link Layer Concerns how to transfer messages
Link Layer Where we are in the Course Moving on up to the Link Layer! Application Transport Network Link Physical CSE 461 University of Washington 2 Scope of the Link Layer Concerns how to transfer messages
Implementing CRCCs. Introduction. in Altera Devices
 Implementing CRCCs in Altera Devices July 1995, ver. 1 Application Note 49 Introduction Redundant encoding is a method of error detection that spreads the information across more bits than the original
Implementing CRCCs in Altera Devices July 1995, ver. 1 Application Note 49 Introduction Redundant encoding is a method of error detection that spreads the information across more bits than the original
CSE123A discussion session
 CSE123A discussion session 2007/02/02 Ryo Sugihara Review Data Link layer (1): Overview Sublayers End-to-end argument Framing sublayer How to delimit frame» Flags and bit stuffing Topics Data Link Layer
CSE123A discussion session 2007/02/02 Ryo Sugihara Review Data Link layer (1): Overview Sublayers End-to-end argument Framing sublayer How to delimit frame» Flags and bit stuffing Topics Data Link Layer
Number Representation
 ECE 645: Lecture 5 Number Representation Part 2 Floating Point Representations Rounding Representation of the Galois Field elements Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and
ECE 645: Lecture 5 Number Representation Part 2 Floating Point Representations Rounding Representation of the Galois Field elements Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and
Time redundancy. Time redundancy
 redundancy redundancy Both hardware and information redundancy can require large amount of extra hardware time redundancy attempt to reduce the amount of extra hardware at the expense of additional time
redundancy redundancy Both hardware and information redundancy can require large amount of extra hardware time redundancy attempt to reduce the amount of extra hardware at the expense of additional time
Data Link Control Layer, Error Detection, Error Correction, and Framing
 Data Link Control Layer, Error Detection, Error Correction, and Framing EEE 538, WEEK 2 Dr. Nail Akar Bilkent University Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department 1 Error Detection Techniques Used
Data Link Control Layer, Error Detection, Error Correction, and Framing EEE 538, WEEK 2 Dr. Nail Akar Bilkent University Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department 1 Error Detection Techniques Used
Operations On Data CHAPTER 4. (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions
 CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
Inst: Chris Davison
 ICS 153 Introduction to Computer Networks Inst: Chris Davison cbdaviso@uci.edu ICS 153 Data Link Layer Contents Simplex and Duplex Communication Frame Creation Flow Control Error Control Performance of
ICS 153 Introduction to Computer Networks Inst: Chris Davison cbdaviso@uci.edu ICS 153 Data Link Layer Contents Simplex and Duplex Communication Frame Creation Flow Control Error Control Performance of
CSE 461: Framing, Error Detection and Correction
 CSE 461: Framing, Error Detection and Correction Next Topics Framing Focus: How does a receiver know where a message begins/ends Error detection and correction Focus: How do we detect and correct messages
CSE 461: Framing, Error Detection and Correction Next Topics Framing Focus: How does a receiver know where a message begins/ends Error detection and correction Focus: How do we detect and correct messages
Redundancy in fault tolerant computing. D. P. Siewiorek R.S. Swarz, Reliable Computer Systems, Prentice Hall, 1992
 Redundancy in fault tolerant computing D. P. Siewiorek R.S. Swarz, Reliable Computer Systems, Prentice Hall, 1992 1 Redundancy Fault tolerance computing is based on redundancy HARDWARE REDUNDANCY Physical
Redundancy in fault tolerant computing D. P. Siewiorek R.S. Swarz, Reliable Computer Systems, Prentice Hall, 1992 1 Redundancy Fault tolerance computing is based on redundancy HARDWARE REDUNDANCY Physical
Some portions courtesy Robin Kravets and Steve Lumetta
 CSE 123 Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 4: Data-Link I: Framing and Errors Some portions courtesy Robin Kravets and Steve Lumetta Administrative updates I m Im out all next week no lectures, but You
CSE 123 Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 4: Data-Link I: Framing and Errors Some portions courtesy Robin Kravets and Steve Lumetta Administrative updates I m Im out all next week no lectures, but You
Chapter 2. Data Representation in Computer Systems
 Chapter 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems Chapter 2 Objectives Understand the fundamentals of numerical data representation and manipulation in digital computers. Master the skill of converting
Chapter 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems Chapter 2 Objectives Understand the fundamentals of numerical data representation and manipulation in digital computers. Master the skill of converting
Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) Bits and bitwise operations. Outline. Unsigned and signed integers. Floating point numbers. Number representation
 Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) CSci 2021: Review Lecture 1 Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Number representation Bits and bitwise operators Unsigned and signed
Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) CSci 2021: Review Lecture 1 Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Number representation Bits and bitwise operators Unsigned and signed
COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT I. 1. What are the three criteria necessary for an effective and efficient networks?
 Question Bank COMPUTER NETWORKS Short answer type questions. UNIT I 1. What are the three criteria necessary for an effective and efficient networks? The most important criteria are performance, reliability
Question Bank COMPUTER NETWORKS Short answer type questions. UNIT I 1. What are the three criteria necessary for an effective and efficient networks? The most important criteria are performance, reliability
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data
 Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators. JAVA Standard Edition
 Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
CSMC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala. Nov 1,
 CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala 1 Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment TCP router router IP IP packet IP IP packet
CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala 1 Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame host host HTTP HTTP message HTTP TCP TCP segment TCP router router IP IP packet IP IP packet
LECTURE #34. Data Communication (CS601)
 LECTURE #34 Error Detection And Correction Methods Longitudinal Red Check(LRC) o In LRC, a block of bits is organized in a table (rows and columns) o For example instead of sending 32 bits, we organize
LECTURE #34 Error Detection And Correction Methods Longitudinal Red Check(LRC) o In LRC, a block of bits is organized in a table (rows and columns) o For example instead of sending 32 bits, we organize
Part III The Arithmetic/Logic Unit. Oct Computer Architecture, The Arithmetic/Logic Unit Slide 1
 Part III The Arithmetic/Logic Unit Oct. 214 Computer Architecture, The Arithmetic/Logic Unit Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation is intended to support the use of the textbook Computer Architecture:
Part III The Arithmetic/Logic Unit Oct. 214 Computer Architecture, The Arithmetic/Logic Unit Slide 1 About This Presentation This presentation is intended to support the use of the textbook Computer Architecture:
Positional Number System
 Positional Number System A number is represented by a string of digits where each digit position has an associated weight. The weight is based on the radix of the number system. Some common radices: Decimal.
Positional Number System A number is represented by a string of digits where each digit position has an associated weight. The weight is based on the radix of the number system. Some common radices: Decimal.
Using Error Detection Codes to detect fault attacks on Symmetric Key Ciphers
 Using Error Detection Codes to detect fault attacks on Symmetric Key Ciphers Israel Koren Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Univ. of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA collaborating with Luca Breveglieri,
Using Error Detection Codes to detect fault attacks on Symmetric Key Ciphers Israel Koren Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Univ. of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA collaborating with Luca Breveglieri,
SPM90 MODBUS PROTOCOL AND REGISTER LIST V1.0
 SPM90 MODBUS PROTOCOL AND REGISTER LIST V1.0 目 录 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Purpose of the Communication Protocol... 1 1.2 Version of Communication Protocol... 1 2. Detailed Description of the SPM90 Modbus
SPM90 MODBUS PROTOCOL AND REGISTER LIST V1.0 目 录 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Purpose of the Communication Protocol... 1 1.2 Version of Communication Protocol... 1 2. Detailed Description of the SPM90 Modbus
COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT-3
 COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT-3 Syllabus: The Data Link Layer - Data Link Layer Design Issues, Services Provided to the Network Layer Framing Error Control Flow Control, Error Detection and Correction Error-Correcting
COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT-3 Syllabus: The Data Link Layer - Data Link Layer Design Issues, Services Provided to the Network Layer Framing Error Control Flow Control, Error Detection and Correction Error-Correcting
INF Data Communication Data Link Layer
 INF3190 - Data Communication Data Link Layer Carsten Griwodz Email: griff@ifi.uio.no most slides from: Ralf Steinmetz, TU Darmstadt and a few from Olav Lysne, J. K. Kurose og K. W. Ross Function, Services
INF3190 - Data Communication Data Link Layer Carsten Griwodz Email: griff@ifi.uio.no most slides from: Ralf Steinmetz, TU Darmstadt and a few from Olav Lysne, J. K. Kurose og K. W. Ross Function, Services
CHW 261: Logic Design
 CHW 261: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed14 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby14# Slide 1 Slide 2 Slide 3 Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER
CHW 261: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed14 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby14# Slide 1 Slide 2 Slide 3 Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER
SRI RAMAKRISHNA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT - II DATA LINK LAYER
 SRI RAMAKRISHNA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT - II DATA LINK LAYER 1. What are the responsibilities of data link layer? Specific responsibilities of
SRI RAMAKRISHNA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT - II DATA LINK LAYER 1. What are the responsibilities of data link layer? Specific responsibilities of
Chapter 3. The Data Link Layer
 Chapter 3 The Data Link Layer 1 Data Link Layer Algorithms for achieving reliable, efficient communication between two adjacent machines. Adjacent means two machines are physically connected by a communication
Chapter 3 The Data Link Layer 1 Data Link Layer Algorithms for achieving reliable, efficient communication between two adjacent machines. Adjacent means two machines are physically connected by a communication
Point-to-Point Links. Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm. Fall 2004 CS 691 1
 Point-to-Point Links Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm Fall 2004 CS 691 1 Encoding Signals propagate over a physical medium modulate electromagnetic waves e.g., vary voltage
Point-to-Point Links Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm Fall 2004 CS 691 1 Encoding Signals propagate over a physical medium modulate electromagnetic waves e.g., vary voltage
Communication Fundamentals in Computer Networks
 Lecture 7 Communication Fundamentals in Computer Networks M. Adnan Quaium Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Room 4A07
Lecture 7 Communication Fundamentals in Computer Networks M. Adnan Quaium Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Room 4A07
Computer Networks. Shyam Gollakota
 Computer Networks Shyam Gollakota Topic Some bits will be received in error due to noise. What can we do? Detect errors with codes» Correct errors with codes» Retransmit lost frames Later Reliability is
Computer Networks Shyam Gollakota Topic Some bits will be received in error due to noise. What can we do? Detect errors with codes» Correct errors with codes» Retransmit lost frames Later Reliability is
Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1. Graph 1: y = (x 1) Graph 2: y = (x 1)(x + 2) Graph 3: y =(x 1)(x + 2)(x 3)
 Part I: Polynomial Functions when a = 1 Directions: Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1 1. For each set of factors, graph the zeros first, then use your calculator to determine
Part I: Polynomial Functions when a = 1 Directions: Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1 1. For each set of factors, graph the zeros first, then use your calculator to determine
EE 486 Winter The role of arithmetic. EE 486 : lecture 1, the integers. SIA Roadmap - 2. SIA Roadmap - 1
 EE 486 Winter 2-3 The role of arithmetic EE 486 : lecture, the integers M. J. Flynn With increasing circuit density available with sub micron feature sizes, there s a corresponding broader spectrum of
EE 486 Winter 2-3 The role of arithmetic EE 486 : lecture, the integers M. J. Flynn With increasing circuit density available with sub micron feature sizes, there s a corresponding broader spectrum of
Computer and Network Security
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 6 Announcements First project: Due: 6 Feb. 2009 at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 6 Announcements First project: Due: 6 Feb. 2009 at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
CS422 Computer Networks
 CS422 Computer Networks Lecture 3 Data Link Layer Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS422 DataLinkLayer.1 Data Link Layer Design Issues Services Provided to the Network Layer Provide service
CS422 Computer Networks Lecture 3 Data Link Layer Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS422 DataLinkLayer.1 Data Link Layer Design Issues Services Provided to the Network Layer Provide service
The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include. Figure 2-1. Relationship between packets and frames.
 Module 2 Data Link Layer: - Data link Layer design issues - Error Detection and correction Elementary Data link protocols, Sliding window protocols- Basic Concept, One Bit Sliding window protocol, Concept
Module 2 Data Link Layer: - Data link Layer design issues - Error Detection and correction Elementary Data link protocols, Sliding window protocols- Basic Concept, One Bit Sliding window protocol, Concept
CSMC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala Set 4. September 09 CMSC417 Set 4 1
 CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2009 Ashok Agrawala Set 4 1 The Data Link Layer 2 Data Link Layer Design Issues Services Provided to the Network Layer Framing Error Control Flow Control
CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2009 Ashok Agrawala Set 4 1 The Data Link Layer 2 Data Link Layer Design Issues Services Provided to the Network Layer Framing Error Control Flow Control
Chapter 6 Digital Data Communications Techniques
 Chapter 6 Digital Data Communications Techniques Asynchronous and Synchronous Transmission timing problems require a mechanism to synchronize the transmitter and receiver receiver samples stream at bit
Chapter 6 Digital Data Communications Techniques Asynchronous and Synchronous Transmission timing problems require a mechanism to synchronize the transmitter and receiver receiver samples stream at bit
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan. Data Communication Netwotks (Graduate level) Data Link Layer
 Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Data Communication Netwotks (Graduate level) Data Link Layer By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Data Link Layer 2 Data Link Layer Application
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Data Communication Netwotks (Graduate level) Data Link Layer By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Data Link Layer 2 Data Link Layer Application
3. Data Link Layer 3-2
 3. Data Link Layer 3.1 Transmission Errors 3.2 Error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes 3.3 Bit Stuffing 3.4 Acknowledgments and Sequence Numbers 3.5 Flow Control 3.6 Examples: HDLC, PPP 3. Data Link
3. Data Link Layer 3.1 Transmission Errors 3.2 Error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes 3.3 Bit Stuffing 3.4 Acknowledgments and Sequence Numbers 3.5 Flow Control 3.6 Examples: HDLC, PPP 3. Data Link
Link layer, LANs: outline. Chapter 5-1 Link Layer. Link layer: introduction. Link layer services
 Chapter 5 Link Layer Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Link layer, LANs: outline 5.1 introduction, services 5.2 error detection, correction
Chapter 5 Link Layer Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Link layer, LANs: outline 5.1 introduction, services 5.2 error detection, correction
Data Link Technology. Suguru Yamaguchi Nara Institute of Science and Technology Department of Information Science
 Data Link Technology Suguru Yamaguchi Nara Institute of Science and Technology Department of Information Science Agenda Functions of the data link layer Technologies concept and design error control flow
Data Link Technology Suguru Yamaguchi Nara Institute of Science and Technology Department of Information Science Agenda Functions of the data link layer Technologies concept and design error control flow
