Cache Memory and Performance
|
|
|
- Maryann Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cache Memory and Performance Cache Organization 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP) Randal E. Bryant and David R. O'Hallaron The book is used explicitly in CS 2505 and CS 3214 and as a reference in CS 2506.
2 Cache Memories Cache Organization 2 Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and L3), then in main memory. Typical system structure: CPU chip Register file Cache memories ALU System bus Memory bus Bus interface I/O bridge Main memory
3 General Cache Organization (S, E, B) Cache Organization 3 E = 2 e lines (blocks) per set S = 2 s sets e -1 set line (block) 2 s -1 v valid bit tag B-1 B = 2 b bytes per cache block (the data) Cache size: C = S x E x B data bytes
4 Cache Defines View of DRAM Cache Organization 4 The "geometry" of the cache is defined by: S = 2 s E = 2 e B = 2 b the number of sets in the cache the number of lines (blocks) in a set the number of bytes in a line (block) These values define a related way to think about the organization of DRAM: DRAM consists of a sequence of blocks of B bytes. The bytes in a block (line) can be indexed by using b bits. DRAM consists of a sequence of groups of S blocks (lines). The blocks (lines) in a group can be indexed by using s bits. Each group contains SxB bytes, which can be indexed by using s + bbits.
5 Cache (8, 2, 4) and 256-Byte DRAM Cache Organization 5 Cache size: C = S x E x B = 64 data bytes E = 2 1 blocks (lines) per set 0 1 DRAM S = 2 3 sets v tag valid bit B = 2 2 bytes per cache block (the data)
6 Example of Cache View of DRAM Assume a cache has the following geometry: Cache Organization 6 address DRAM S = 2 2 = 8 the number of sets in the cache E = 2 1 = 2 the number of lines (blocks) in a set B = 2 2 = 4 the number of bytes in a line (block) block Suppose that DRAM consists of 256 bytes, so we have 8-bit addresses. Then DRAM consists of: - 64 blocks, each holding 4 bytes - 8 groups, each holding 8 blocks group block 1 block
7 Example of Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 7 Pick an address: group block byte address DRAM byte byte 00 block 000 a 1 a 0 give the byte number and the offset of the byte in the block. group byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte 10 block 100 block 101 block byte
8 Example of Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 8 Pick an address: address DRAM group block byte byte byte 00 block 000 a 4 a 3 a 2 give the block number byte byte 10 block byte byte 00 a 4 a 3 a 2 00* equals the offset of the block in the group. group byte byte byte byte byte byte 10 block 101 block 110 * a 4 a 3 a 2 00 = a 4 a 3 a 2 x byte 11 =a 4 a 3 a 2 x (size of a block)
9 Example of Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 9 Pick an address: group block byte address DRAM byte byte 00 block 000 a 7 a 6 a 5 give the group number byte byte byte 11 block byte 00 a 7 a 6 a * equals the offset of the group in the DRAM group byte byte byte byte byte byte 10 block 101 block 110 * Why? byte
10 The BIG Picture Cache Organization DRAM Group 011 in DRAM Block 101 in Group byte byte byte byte 11
11 Example of Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 11 Pick an address: address DRAM How does this address map into the cache? The DRAM block number determines the cache set used to store the block. Note this means that two DRAM blocks from the same DRAM group cannot map into the same cache set. So the address: maps to set 101 in the cache. Each set in our cache can hold 2 blocks. This block could be stored at either location within the corresponding set byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte block 100 block 101 block 110
12 Example of Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 12 DRAM block containing address: address DRAM Maps to cache set: Cache or valid tag byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte byte block 100 block 101 block 110
13 Cache View of DRAM Cache Organization 13 So, to generalize, suppose a cache has: S = 2 s sets E = 2 e blocks (lines) per set B = 2 b bytes per block (line) And, suppose that DRAM uses N-bit addresses. then for any address: a N-1 : a s+b a s+b-1 : a b a b-1 : a 0 Bits a b-1 :a 0 give the byte index within the block Bits a b+s-1 :a b give the set index Bits a N-1 :a s+b become the tag for the data Note that these bits are only the same for blocks that are within the same DRAM group.
14 Cache Read 1. Locate set 2. Check if anyline in set has matching tag 3. Yes + line valid: hit 4. Locate data starting at offset Address of word: t bits s bits = K b bits = J 1 Set 0 1 K Line Cache Organization e -1 tag set index block offset 2 s -1 2 K data begins at this offset 4 3 v tag 0 1 J 2 b -1
15 Example: Direct Mapped Cache (E = 1) Cache Organization 15 Direct mapped: One line per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes S = 2 s sets v tag v tag v tag Address of int: t bits find set v tag
16 Example: Direct Mapped Cache (E = 1) Cache Organization 16 Direct mapped: One line per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes valid? + matching tags hit Address of int: t bits v tag block offset
17 Example: Direct Mapped Cache (E = 1) Cache Organization 17 Direct mapped: One line per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes valid? + matching tags hit Address of int: t bits v tag block offset int (4 Bytes) is here No match: old line (block) is evicted and replaced by requested block from DRAM
18 Direct-Mapped Cache Simulation Cache Organization 18 t=1 s=2 b=1 x xx x M=16 byte addresses, B=2 bytes/block, S=4 sets, E=1 Blocks/set Address trace (reads, one byte per read): 0 [ ], miss 1 [ ], hit 7 [ ], miss 8 [ ], miss 0 [ ] miss Set 0 Set 1 Set 2 Set 3 v Tag Block ? M[8-9] M[0-1]? 1 0 M[6-7]
19 E-way Set Associative Cache (Here: E = 2) Cache Organization 19 E = 2: Two lines per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes Address of short int: t bits v tag v tag v tag v tag find set v tag v tag v tag v tag
20 E-way Set Associative Cache (Here: E = 2) Cache Organization 20 E = 2: Two lines per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes compare both Address of short int: t bits valid? + matching tags hit v tag v tag block offset
21 E-way Set Associative Cache (Here: E = 2) E = 2: Two lines per set Assume: cache block size 8 bytes compare both Cache Organization 21 Address of short int: t bits valid? + matching tags hit v tag v tag short int (2 Bytes) is here block offset No match: One line in set is selected for eviction and replacement Replacement policies: random, least recently used (LRU),
22 2-Way Set Associative Cache Simulation Cache Organization 22 t=2 s=1 b=1 xx x x M=16 byte addresses, B=2 bytes/block, S=2 sets, E=2 blocks/set Address trace (reads, one byte per read): 0 [ ], miss 1 [ ], hit 7 [ ], miss 8 [ ], miss 0 [ ] hit Set 0 Set 1 v Tag Block 01 00? M[0-1]? M[8-9] M[6-7]
23 Cache Organization Types Cache Organization 23 The "geometry" of the cache is defined by: S = 2 s E = 2 e B = 2 b the number of sets in the cache the number of lines (blocks) in a set the number of bytes in a line (block) E = 1 (e = 0) direct-mapped cache only one possible location in cache for each DRAM block S > 1 E = K > 1 K-way associative cache Kpossible locations (in same cache set) for each DRAM block S = 1 (only one set) fully-associative cache E= # of cache blocks each DRAM block can be at any location in the cache
24 Searching a Set Cache Organization 24 If we have an associative cache (K-way or fully), how do we determine if a given DRAM block occurs within a set? Compare the tag we re trying to match to all of the tags for blocks in the relevant set at the same time! Then factor in the valid bits, also in parallel. And employ a MUX
Cache Memory and Performance
 Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
CISC 360. Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 2009
 Topics ν CISC 36 Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 29 Review of cache memory mapping Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. ν Hold frequently
Topics ν CISC 36 Cache Memories Exercises Dec 3, 29 Review of cache memory mapping Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. ν Hold frequently
Cache Memories. From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6.
 Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Memory hierarchies: caches and their impact on the running time
 Memory hierarchies: caches and their impact on the running time Irene Finocchi Dept. of Computer and Science Sapienza University of Rome A happy coincidence A fundamental property of hardware Different
Memory hierarchies: caches and their impact on the running time Irene Finocchi Dept. of Computer and Science Sapienza University of Rome A happy coincidence A fundamental property of hardware Different
Memory Hierarchy. Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3. Instructor: Joanna Klukowska
 Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed Zahran (NYU)
Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed Zahran (NYU)
Memory Hierarchy. Cache Memory Organization and Access. General Cache Concept. Example Memory Hierarchy Smaller, faster,
 Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Cache Memory Organization and Access Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O
Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Cache Memory Organization and Access Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O
Agenda Cache memory organization and operation Chapter 6 Performance impact of caches Cache Memories
 Agenda Chapter 6 Cache Memories Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal
Agenda Chapter 6 Cache Memories Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal
Today. Cache Memories. General Cache Concept. General Cache Organization (S, E, B) Cache Memories. Example Memory Hierarchy Smaller, faster,
 Today Cache Memories CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization November 7th-9th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory
Today Cache Memories CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization November 7th-9th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory
CS 33. Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware.
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Carnegie Mellon. Cache Memories
 Cache Memories Thanks to Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron from CMU Reading Assignment: Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspec4ve, Third Edi4on, Chapter 6 1 Today Cache memory organiza7on and
Cache Memories Thanks to Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron from CMU Reading Assignment: Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspec4ve, Third Edi4on, Chapter 6 1 Today Cache memory organiza7on and
Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches
 Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
Improving our Simple Cache
 Improving our Simple Cache SI232 Slide Set #17: More More (Hierarchy) (Chapter 7) 1. How to handle a write? 2.Efficient Bit Manipulation 3.How to handle a miss? 4.How to eliminate even more conflicts?
Improving our Simple Cache SI232 Slide Set #17: More More (Hierarchy) (Chapter 7) 1. How to handle a write? 2.Efficient Bit Manipulation 3.How to handle a miss? 4.How to eliminate even more conflicts?
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
Caches Part 1. Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
Cache Memories. Andrew Case. Slides adapted from Jinyang Li, Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron
 Cache Memories Andrew Case Slides adapted from Jinyang Li, Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Topics Cache memory organiza3on and opera3on Performance impact of caches 2 Cache Memories Cache memories are
Cache Memories Andrew Case Slides adapted from Jinyang Li, Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Topics Cache memory organiza3on and opera3on Performance impact of caches 2 Cache Memories Cache memories are
Cache Memories /18-213/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 5, Today s Instructor: Phil Gibbons
 Cache Memories 15-213/18-213/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 5, 2017 Today s Instructor: Phil Gibbons 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact
Cache Memories 15-213/18-213/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 5, 2017 Today s Instructor: Phil Gibbons 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact
Cache Policies. Philipp Koehn. 6 April 2018
 Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
10/16/17. Outline. Outline. Typical Memory Hierarchy. Adding Cache to Computer. Key Cache Concepts
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
Carnegie Mellon. Cache Memories. Computer Architecture. Instructor: Norbert Lu1enberger. based on the book by Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron
 Cache Memories Computer Architecture Instructor: Norbert Lu1enberger based on the book by Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Today Cache memory organiza7on and opera7on Performance impact of caches The
Cache Memories Computer Architecture Instructor: Norbert Lu1enberger based on the book by Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Today Cache memory organiza7on and opera7on Performance impact of caches The
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles. Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!)
 Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
MIPS) ( MUX
 Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Locality. CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture. Locality Example 2. Locality Example
 Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches. Marco Paolieri Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook
 CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
Denison University. Cache Memories. CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems. Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud
 Cache Memories CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud 1 Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally
Cache Memories CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud 1 Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally
Slide Set 9. for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University
 Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 34, Spring 23 Computer Science Cornell University Welcome back from Spring Break! Welcome back from Spring Break! Big Picture: Memory Code
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 34, Spring 23 Computer Science Cornell University Welcome back from Spring Break! Welcome back from Spring Break! Big Picture: Memory Code
Chapter 6 Caches. Computer System. Alpha Chip Photo. Topics. Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM Caches Direct Mapped Associative
 Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
10/11/17. New-School Machine Structures. Review: Single Cycle Instruction Timing. Review: Single-Cycle RISC-V RV32I Datapath. Components of a Computer
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ // Fall - Lecture # Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ // Fall - Lecture # Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Lecture 21: Virtual Memory. Spring 2018 Jason Tang
 Lecture 21: Virtual Memory Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Virtual addressing Page tables Translation lookaside buffer 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices Control Datapath Input Output
Lecture 21: Virtual Memory Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Virtual addressing Page tables Translation lookaside buffer 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices Control Datapath Input Output
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2017 Lecture 15
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 15 LAST TIME: CACHE ORGANIZATION Caches have several important parameters B = 2 b bytes to store the block in each cache line S = 2 s cache sets
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 15 LAST TIME: CACHE ORGANIZATION Caches have several important parameters B = 2 b bytes to store the block in each cache line S = 2 s cache sets
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 1, 2012! Prashanth Mohan!! Slides from Anthony Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Caching!
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 1, 2012! Prashanth Mohan!! Slides from Anthony Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Caching!
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016
 211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - project2 - Structure/ Array Representation - Structure Alignment Rutgers University Liu
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - project2 - Structure/ Array Representation - Structure Alignment Rutgers University Liu
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 411 Computer Organization Fall 2006 Solutions Problem Set #10 Problem 1. Cache accounting The diagram below illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 411 Computer Organization Fall 2006 Solutions Problem Set #10 Problem 1. Cache accounting The diagram below illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: April 5, 2018 at 13:55 CS429 Slideset 19: 1 Cache Vocabulary Much
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: April 5, 2018 at 13:55 CS429 Slideset 19: 1 Cache Vocabulary Much
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/11/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #14 1 Parallel
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/11/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #14 1 Parallel
Computer Organization: A Programmer's Perspective
 A Programmer's Perspective Computer Architecture and The Memory Hierarchy Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il Typical Computer Architecture CPU chip PC (Program Counter) register file ALU Main Components
A Programmer's Perspective Computer Architecture and The Memory Hierarchy Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il Typical Computer Architecture CPU chip PC (Program Counter) register file ALU Main Components
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Warren Hunt, Jr. and Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: August 26, 2014 at 08:54 CS429 Slideset 20: 1 Cache
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Warren Hunt, Jr. and Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: August 26, 2014 at 08:54 CS429 Slideset 20: 1 Cache
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
How to Write Fast Numerical Code
 How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Alen Stojanov, Georg Ofenbeck, Gagandeep Singh Organization Temporal and spatial locality Memory
How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Alen Stojanov, Georg Ofenbeck, Gagandeep Singh Organization Temporal and spatial locality Memory
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Computer Architecture and Organization Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 28.1 Fundamental Questions
Computer Architecture and Organization Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 28.1 Fundamental Questions
Memory hierarchy and cache
 Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz hdp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/13/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #14 1 New-School
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz hdp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/13/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #14 1 New-School
Binghamton University. CS-220 Spring Cached Memory. Computer Systems Chapter
 Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Consider the following 16-bit machine (datapath and register width is 2B).
 Consider the following 16-bit machine (datapath and register width is 2B). -- Virtual memory: -- byte addressable. -- 16-bit virtual addresses. -- the VMAR is 16-bits. -- Physical memory: -- byte addressable.
Consider the following 16-bit machine (datapath and register width is 2B). -- Virtual memory: -- byte addressable. -- 16-bit virtual addresses. -- the VMAR is 16-bits. -- Physical memory: -- byte addressable.
10/7/13! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny CS162 UCB Fall 2013! " (0xE0)" " " " (0x70)" " (0x50)"
 Goals for Todayʼs Lecture" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 7, 2013! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Paging- and
Goals for Todayʼs Lecture" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" October 7, 2013! Anthony D. Joseph and John Canny! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Paging- and
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2015 Lecture 15
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2015 Lecture 15 LAST TIME! Discussed concepts of locality and stride Spatial locality: programs tend to access values near values they have already accessed
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2015 Lecture 15 LAST TIME! Discussed concepts of locality and stride Spatial locality: programs tend to access values near values they have already accessed
CS 31: Intro to Systems Caching. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 2015
 CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
High-Performance Parallel Computing
 High-Performance Parallel Computing P. (Saday) Sadayappan Rupesh Nasre Course Overview Emphasis on algorithm development and programming issues for high performance No assumed background in computer architecture;
High-Performance Parallel Computing P. (Saday) Sadayappan Rupesh Nasre Course Overview Emphasis on algorithm development and programming issues for high performance No assumed background in computer architecture;
How to Write Fast Numerical Code
 How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Daniele Spampinato & Alen Stojanov Left alignment Attractive font (sans serif, avoid Arial) Calibri,
How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Daniele Spampinato & Alen Stojanov Left alignment Attractive font (sans serif, avoid Arial) Calibri,
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2014 Lecture 14
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
6.004 Recitation Problems L13 Caches
 6.004 Recitation Problems L13 Caches Keep the most often-used data in a small, fast SRAM (often local to CPU chip). The reason this strategy works: LOCALITY. Temporal locality: If a location has been accessed
6.004 Recitation Problems L13 Caches Keep the most often-used data in a small, fast SRAM (often local to CPU chip). The reason this strategy works: LOCALITY. Temporal locality: If a location has been accessed
Buffer Overflows. Buffer Overflow. Many of the following slides are based on those from
 s Many of the following slides are based on those from 1 Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP) Randal E. Bryant and David R. O'Hallaron http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/public/lectures.html
s Many of the following slides are based on those from 1 Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP) Randal E. Bryant and David R. O'Hallaron http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/public/lectures.html
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 4: Memory Organization Our goal: understand the basic types of memory in computer understand memory hierarchy and the general process to access memory
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 4: Memory Organization Our goal: understand the basic types of memory in computer understand memory hierarchy and the general process to access memory
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
Chapter Seven. Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Caches. Hiding Memory Access Times
 Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Paging! 2/22! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica CS162 UCB Fall 2012! " (0xE0)" " " " (0x70)" " (0x50)"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
Cache Memories : Introduc on to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 6th, Instructor: Randy Bryant.
 Cache Memories 15-213: Introduc on to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 6th, 2016 Instructor: Randy Bryant 1 Today Cache memory organiza on and opera on Performance impact of caches The memory mountain
Cache Memories 15-213: Introduc on to Computer Systems 12 th Lecture, October 6th, 2016 Instructor: Randy Bryant 1 Today Cache memory organiza on and opera on Performance impact of caches The memory mountain
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
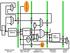 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
The Memory Hierarchy 10/25/16
 The Memory Hierarchy 10/25/16 Transition First half of course: hardware focus How the hardware is constructed How the hardware works How to interact with hardware Second half: performance and software
The Memory Hierarchy 10/25/16 Transition First half of course: hardware focus How the hardware is constructed How the hardware works How to interact with hardware Second half: performance and software
Computer Systems C S Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College
 Computer Systems C S 0 7 Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College 2 Today s Topics TODAY S LECTURE: Caching ANNOUNCEMENTS: Assign6 & Assign7 due Friday! 6 & 7 NO late
Computer Systems C S 0 7 Cynthia Lee Today s materials adapted from Kevin Webb at Swarthmore College 2 Today s Topics TODAY S LECTURE: Caching ANNOUNCEMENTS: Assign6 & Assign7 due Friday! 6 & 7 NO late
Review: Computer Organization
 Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
CS61C : Machine Structures
 CS C L.. Cache I () Design Principles for Hardware CSC : Machine Structures Lecture.. Cache I -- Kurt Meinz inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~csc. Simplicity favors regularity Every instruction has operands, opcode
CS C L.. Cache I () Design Principles for Hardware CSC : Machine Structures Lecture.. Cache I -- Kurt Meinz inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~csc. Simplicity favors regularity Every instruction has operands, opcode
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University
 Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Memory Code Stored in Memory (also, data and stack) memory PC +4 new pc
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Memory Code Stored in Memory (also, data and stack) memory PC +4 new pc
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
associativity terminology
 Caching 1 2 associativity terminology direct-mapped one block per set E-way set associative E blocks per set E ways in the cache fully associative one set total (everything in one set) 3 Tag-Index-Offset
Caching 1 2 associativity terminology direct-mapped one block per set E-way set associative E blocks per set E ways in the cache fully associative one set total (everything in one set) 3 Tag-Index-Offset
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems
 CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
Memory Hierarchy. 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt
 Memory Hierarchy 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt Agenda Review Memory Hierarchy Lab 2 Ques6ons Return Quiz 1 Latencies Comparison Numbers L1 Cache 0.5 ns L2 Cache 7 ns 14x L1 cache Main Memory
Memory Hierarchy 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt Agenda Review Memory Hierarchy Lab 2 Ques6ons Return Quiz 1 Latencies Comparison Numbers L1 Cache 0.5 ns L2 Cache 7 ns 14x L1 cache Main Memory
Memory Hierarchy. Caching Chapter 7. Locality. Program Characteristics. What does that mean?!? Exploiting Spatial & Temporal Locality
 Caching Chapter 7 Basics (7.,7.2) Cache Writes (7.2 - p 483-485) configurations (7.2 p 487-49) Performance (7.3) Associative caches (7.3 p 496-54) Multilevel caches (7.3 p 55-5) Tech SRAM (logic) SRAM
Caching Chapter 7 Basics (7.,7.2) Cache Writes (7.2 - p 483-485) configurations (7.2 p 487-49) Performance (7.3) Associative caches (7.3 p 496-54) Multilevel caches (7.3 p 55-5) Tech SRAM (logic) SRAM
exercise 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00
 Caching (part 2) 1 exercise 3 address (hex) result 00000000 (00) 00000001 (01) 01100011 (63) 01100001 (61) 01100010 (62) 00000000 (00) 01100100 (64) 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00 01 10
Caching (part 2) 1 exercise 3 address (hex) result 00000000 (00) 00000001 (01) 01100011 (63) 01100001 (61) 01100010 (62) 00000000 (00) 01100100 (64) 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00 01 10
Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design
 S 09 L17-1 18-447 Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design James C. Hoe Dept of ECE, CMU March 24, 2009 Announcements: Project 3 is due Midterm 2 is coming Handouts: Practice Midterm 2 solutions The
S 09 L17-1 18-447 Lecture 17: Memory Hierarchy: Cache Design James C. Hoe Dept of ECE, CMU March 24, 2009 Announcements: Project 3 is due Midterm 2 is coming Handouts: Practice Midterm 2 solutions The
Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I. Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB)
 Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Memory Hierarchy On-Chip SRAM Direct-Mapped Cache Review: ARM System Architecture Fast on-chip RAM External
Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Memory Hierarchy On-Chip SRAM Direct-Mapped Cache Review: ARM System Architecture Fast on-chip RAM External
Giving credit where credit is due
 CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches
 Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches A modern memory subsystem combines fast small memory, slower larger memories This lecture looks at why and how Focus today mostly on electronic memories. Next lecture
Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches A modern memory subsystem combines fast small memory, slower larger memories This lecture looks at why and how Focus today mostly on electronic memories. Next lecture
EE 457 Unit 7a. Cache and Memory Hierarchy
 EE 457 Unit 7a Cache and Memory Hierarchy 2 Memory Hierarchy & Caching Use several levels of faster and faster memory to hide delay of upper levels Registers Unit of Transfer:, Half, or Byte (LW, LH, LB
EE 457 Unit 7a Cache and Memory Hierarchy 2 Memory Hierarchy & Caching Use several levels of faster and faster memory to hide delay of upper levels Registers Unit of Transfer:, Half, or Byte (LW, LH, LB
LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches
 EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
VIRTUAL MEMORY: CONCEPTS
 VIRTUAL MEMORY: CONCEPTS CS 45 Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. Donald J. Patterson Adapted from Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition VIRTUAL MEMORY:
VIRTUAL MEMORY: CONCEPTS CS 45 Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. Donald J. Patterson Adapted from Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition VIRTUAL MEMORY:
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
Page 1. Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation "
 Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
Virtual Memory 3. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. P & H Chapter 5.4
 Virtual Memory 3 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University P & H Chapter 5.4 Project3 available now Administrivia Design Doc due next week, Monday, April 16 th Schedule
Virtual Memory 3 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University P & H Chapter 5.4 Project3 available now Administrivia Design Doc due next week, Monday, April 16 th Schedule
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped Caches. Increasing distance from processor, decreasing speed.
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped s 9/27/2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 2 - - Lecture #4 New- School Machine Structures (It
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped s 9/27/2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 2 - - Lecture #4 New- School Machine Structures (It
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
Computer Architecture and Engineering. CS152 Quiz #2. March 3rd, Professor Krste Asanovic. Name:
 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #2 March 3rd, 2008 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal difficulty,
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #2 March 3rd, 2008 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal difficulty,
Virtual Memory. CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming
 Virtual Memory CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming These slides are the product of many rounds of teaching CS 3410 by Professors Weatherspoon, Bala, Bracy, and Sirer. Where are we now and
Virtual Memory CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming These slides are the product of many rounds of teaching CS 3410 by Professors Weatherspoon, Bala, Bracy, and Sirer. Where are we now and
