Page 1. Overview : Wireless Networks Lecture 15: WiFi Self-Organization. Client throughput. What determines client performance?
|
|
|
- Georgina Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview : Wireless Networks Lecture 15: WiFi Self-Organization Dina Papagiannaki & Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester Self-organization/Management of WiFi networks Urban, cooperative environments (unmanaged)» Frequency selection» User association» Power control Enteprise WLANs (managed) New application domains (unmanaged +managed) 2 Design of the Wired Overprovisioning the solution of choice! From a managed core to an unmanaged edge A large fraction of the s clients are going wireless (WiFi, 3G, WiMax) Client performance primarily determined by the edge network networks challenge our traditional thinking in network design and management The need for measurement paramount due to the unreliability and dynamics of the medium, the notion of contention domains and mobility 3 4 What determines client performance? Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) Transmitter senses the medium, uses Clear Channel Assessment (CCA) threshold to determine state If medium idle, randomize access When backoff counter=0, transmit Upon ACK, reset backoff counter If no ACK, double contention window, adjust transmission rate and try again Performance = f(access probability, retransmissions, link quality, hidden terminals) Client throughput 11 Mbps 54 Mbps 1 Mbps Effective throughput~ 30 Mbps Effective throughput< 10 Mbps Effective throughput ~Kbps 5 6 Page 1
2 Solutions and operations Minimize the number of transmitters in the same contention domain Frequency selection Power Control Minimize the number of transmitters in the same contention domain Ensure high quality links between clients and APs Frequency selection Power Control User Association Self-Organization in Urban, Collaborative Environments Frequency Selection Minimize the effect of hidden terminals RTS/CTS Scheduling 7 8 WiFi frequency selection Cellular analogue 2.4 GHz band (802.11b/g) 11 channels, 3 orthogonal 5 GHz band (802.11a) 11/12 channels depending on continent Question: Which frequency should each AP operate on for optimal performance? b/g frequencies not enough WiFi scanning tools: NetStumbler Page 2
3 Frequency Selection Effect of Frequency Selection Mbps/11g Client1 Client2 Client3 Before After (*3) 30 (*5) (*2) AP client Alternatives Partially overlapping channels Interference is the outcome of transmissions! Frequency selection could take workload into account» Requires additional measurements» Could lead to instability if based on variable measurements Using partially overlapping channels Minimize the number of transmitters in the same contention domain Frequency selection Power Control Self-Organization in Urban, Collaborative Environments Power Control Partially overlapped channels not considered harmful, In ACM Sigmetrics Page 3
4 Power Control in What is the benefit of power control? Heterogeneous transmit powers across nodes can lead to node starvation! 1 st order starvation Reducing transmission power can reduce interference in the network Increasing transmission power can improve client SINR thus allowing for higher transmission rates There is a tradeoff between the amount of interference we introduce in the network and the additional throughput benefit at the client We need to ensure that there is symmetry in the nodes contention domains Condition for starvation free power control Effect of Power Control We need to ensure network symmetry We have proven that for starvation-free power control we need to keep the product of CCA threshold and transmission power constant CCA * P = C The louder you are going to shout the more carefully you should listen for the nodes that whisper Mbps/11g Client1 Client2 Client3 Interference Mitigation through Power Control in High Density WLANs, IEEE Infocom 2007 Before After (*3) (*4) (*2) AP client Ensure high quality links between clients and APs User Association Self-Organization in Urban, Collaborative Environments User Association User throughput 1. Channel access time 2. Aggregated transmission delay 3. Wireless channel quality State of the art can lead to unnecessarily low throughput! Page 4
5 Overall network fairness improved User association Mean:1428, variance: Mean:1559, variance: Mbps/11g Client1 Before Balance the user associations~ 5for minimal potential delay ~ 8 the personal and social fairness. UsersAfter take into account cost of different association rules. 25 Implementation and Experimental set-up 26 Impact of different algorithms The 3 algorithms are implemented» for both APs and clients» on Intel 2915 prototype driver and firmware Testbed A : U Cambridge, UK» 21 APs, 30 client Technical Characteristics» Nodes: Soekris net4826,» Wireless cards: Intel 2915 a/b/g 5-dBi omnidirectional antennae 27 Minimize the effect of hidden terminals The transformation of enterprise WLANs RTS/CTS Scheduling Self-Organization in Enterprise WLANs: From Collaboration to Coordination 28 Centralization of the control increased security, opportunity for optimal configuration 29 Page 5 30
6 Hidden and Exposed Terminals WLANs HP Labs Seoul National University Exposed Terminals Hidden Terminals 39% 9% 39% 43% 70% 35% Our Testbed Conflict Graph and its measurement Micro-probing can measure the conflict graph of a 20 node network in 20 seconds! In 30% of the hidden terminals (300 cases) performance degradation was greater than 90%! Carrier-sense Interference No client modifications As accurate as state of the art with ~400 times less overhead Centralized Scheduling Implementation Issues C4 X C1 Y C3 (X,C1) (Y,C2) (Y,C3) (X,C4) Need for a conflict graph Tight synchronization among APs Precise knowledge of when a transmission will be over (not easy due to retransmission and changes in transmission rate) C2 Speculation is required! Scheduler DCF performs better in the general case! Hybrid Scheduling The network design space Use speculative centralized scheduling only for hidden terminals management power control, user association Frequency selection, power control Centralized control and scheduling More devices on the same frequency overhearing PHY coding conscious choice reachability, minimal handoff time 35 Network density No single design will fit-all understanding constraints and solution space is essential. Applications will be the main drivers 36 Page 6
7 The FON model large scale WiFi collaboration When collaboration meets coordination The Neighborhood Network Management degree home Neighborhood Network Enterprise Next-generation community networks Community WiFi Community networks today seen as infrastructure for access and services on the move [Cabernet, ViFi, Dome] What if such networks formed the new edge with the ability to provide better and new types of services? New Types of Services in Neighborhood WiFi Today s home use Reliability through broadband provider diversity Higher uplink capacity through wireless-assisted broadband link aggregation Services beyond the limitations of one home s resources Most broadband connections underutilized Wireless speeds far exceed last mile broadband Page 7
8 Large uploads are very slow! Burstable broadband service zzz.. zzz..!?! Burstable broadband service Burstable broadband service Aggregation through wireless What is the best strategy to get efficient aggregation of bandwidth? Wireless unicast Opportunistic wireless reception Wireless unicast Opportunistic broadcast??? Problem: Individual losses can significantly harm performance. 47 Solution needs to minimize redundancy in wired transmissions while making optimal use of the wireless medium 48 Page 8
9 Link-alike offers significant gains through opportunism Open Questions 49 How could such a mechanism be adjusted for real-time content, such as high resolution video conferencing? Automated frequency selection restricts the number of APs in the same frequency, limiting the potential for overhearing What are the mechanisms needed for optimal performance of neighborhood networks? 50 US Spectrum Allocation 700 MHz and white spaces Beyond the ISM bands WiFi 51 References Partially-overlapped Channels not considered harmful, Arunesh Mishra, Vivek Shrivastava, Suman Banerjee, William Arbaugh. In ACM Sigmetrics, St. Malo, France, June MDG: Measurement-Driven Guidelines for WLAN Design, I. Broustis, K. Papagiannaki, S. Krishnamurthy, M. Faloutsos, and V. Mhatre. In ACM Mobicom, Montreal, Canada, September Interference Mitigation through Power Control in High Density WLANs, V. Mhatre, K. Papagiannaki and F. Baccelli. In IEEE Infocom, Anchorage, Alaska, May, Measurement-Based Self Organization of Interfering Wireless Access Networks, B. Kaufmann, F. Baccelli, A. Chaintreau, V. Mhatre, K. Papagiannaki and C. Diot. In IEEE Infocom, Anchorage, Alaska, May, Link-alike: Using Wireless to Share Network Resources in a Neighborhood, S. Jakubczak, D. Andersen, M. Kaminsky, K. Papagiannaki, and S. Seshan. To appear in ACM Sigmobile Mobile Computing and Communications Review (MC2R) 53 Page 9 52
Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs
 Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs Ghazale Hosseinabadi and Nitin Vaidya Department of ECE and Coordinated Science Lab. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs Ghazale Hosseinabadi and Nitin Vaidya Department of ECE and Coordinated Science Lab. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Medium Access Control. MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols
 Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
PIE in the Sky : Online Passive Interference Estimation for Enterprise WLANs
 WiNGS Labs PIE in the Sky : Online Passive Interference Estimation for Enterprise WLANs * Nokia Research Center, Palo Alto Shravan Rayanchu, Suman Banerjee University of Wisconsin-Madison Konstantina Papagiannaki
WiNGS Labs PIE in the Sky : Online Passive Interference Estimation for Enterprise WLANs * Nokia Research Center, Palo Alto Shravan Rayanchu, Suman Banerjee University of Wisconsin-Madison Konstantina Papagiannaki
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks
 ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 11: * Outline. Power Management. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Mohamed Khedr.
 Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 25: CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren. HW4 due NOW
 Lecture 25: 802.11 CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW4 due NOW Lecture 25 Overview 802.11 Wireless PHY layer overview Hidden Terminals Basic wireless challenge RTS/CTS Virtual carrier sense
Lecture 25: 802.11 CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW4 due NOW Lecture 25 Overview 802.11 Wireless PHY layer overview Hidden Terminals Basic wireless challenge RTS/CTS Virtual carrier sense
Lecture 24: CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage. HW4 due NOW
 Lecture 24: 802.11 CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage HW4 due NOW About the final Similar in style to midterm Some combination of easy questions, short answer and more in-depth questions Sample final
Lecture 24: 802.11 CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage HW4 due NOW About the final Similar in style to midterm Some combination of easy questions, short answer and more in-depth questions Sample final
IEEE MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE )
 IEEE 802.11 MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE 802.11-1999) Wireless Networking Sunghyun Choi, Associate Professor Multimedia & Wireless Networking Lab. (MWNL) School of Electrical Engineering Seoul National
IEEE 802.11 MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE 802.11-1999) Wireless Networking Sunghyun Choi, Associate Professor Multimedia & Wireless Networking Lab. (MWNL) School of Electrical Engineering Seoul National
Announcements / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Wireless. Regular Ethernet CSMA/CD.
 Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul
 be in charge Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism WHITE PAPER Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul: Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism
be in charge Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism WHITE PAPER Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul: Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Aloha and 802 Wireless. Regular Ethernet CSMA/CD
 Page 1 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Aloha and 802 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Data link fundamentals» And what changes in wireless Aloha Ethernet Wireless-specific
Page 1 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Aloha and 802 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Data link fundamentals» And what changes in wireless Aloha Ethernet Wireless-specific
Computer Communication III
 Computer Communication III Wireless Media Access IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Advantages of Wireless LANs Using the license free ISM band at 2.4 GHz no complicated or expensive licenses necessary very cost
Computer Communication III Wireless Media Access IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Advantages of Wireless LANs Using the license free ISM band at 2.4 GHz no complicated or expensive licenses necessary very cost
Overview : Computer Networking. Spectrum Use Comments. Spectrum Allocation in US Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi
 Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
Outline. Wireless Channel Characteristics. Multi-path Fading. Opportunistic Communication - with a focus on WLAN environments -
 Outline Opportunistic Communication - with a focus on WLAN environments - Jong-won Lee 2006. 02.20. Background? Wireless Channels? Opportunistic communication? Examples? Basics of WLAN Previous Works?
Outline Opportunistic Communication - with a focus on WLAN environments - Jong-won Lee 2006. 02.20. Background? Wireless Channels? Opportunistic communication? Examples? Basics of WLAN Previous Works?
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Advanced Computer Networks WLAN
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE Networks
 A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE 802.11 Networks Marcel William Rocha da Silva, José Ferreira de Rezende Abstract The great popularity of IEEE 802.11 along with channel scarcity may lead
A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE 802.11 Networks Marcel William Rocha da Silva, José Ferreira de Rezende Abstract The great popularity of IEEE 802.11 along with channel scarcity may lead
ACCESS POINT TUNING IN CHAOTIC WIRELESS NETWORKS
 ACCESS POINT TUNING IN CHAOTIC WIRELESS NETWORKS Adwait Belsare, Richard Skowyra, Robert Kinicki Worcester Polytechnic Institute 100 Institute Road Worcester, MA01609 USA adwait@wpi.edu, rskowyra@wpi.edu,
ACCESS POINT TUNING IN CHAOTIC WIRELESS NETWORKS Adwait Belsare, Richard Skowyra, Robert Kinicki Worcester Polytechnic Institute 100 Institute Road Worcester, MA01609 USA adwait@wpi.edu, rskowyra@wpi.edu,
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Almost all wireless LANs now are IEEE 802.11
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Almost all wireless LANs now are IEEE 802.11
Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Wireless Intro : Computer Networking. Wireless Challenges. Overview. TCP on wireless links Wireless MAC Assigned reading.
 Wireless Intro 15-744: Computer Networking L-9 Wireless TCP on wireless links Wireless MAC Assigned reading [BPSK97] A Comparison of Mechanism for Improving TCP Performance over Wireless Links [BDS+94]
Wireless Intro 15-744: Computer Networking L-9 Wireless TCP on wireless links Wireless MAC Assigned reading [BPSK97] A Comparison of Mechanism for Improving TCP Performance over Wireless Links [BDS+94]
Rahman 1. Application
 Data Link layer Overview of IEEE 802.11 Application Presentation Session Transport LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform
Data Link layer Overview of IEEE 802.11 Application Presentation Session Transport LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform
EVALUATING ADJACENT CHANNEL INTERFERENCE IN IEEE NETWORKS
 EVALUATING ADJACENT CHANNEL INTERFERENCE IN IEEE 802.11 NETWORKS Wee Lum Tan 1, Konstanty Bialkowski 1 1 Queensland Research Laboratory National ICT Australia Brisbane, QLD, Australia Email: {weelum.tan,
EVALUATING ADJACENT CHANNEL INTERFERENCE IN IEEE 802.11 NETWORKS Wee Lum Tan 1, Konstanty Bialkowski 1 1 Queensland Research Laboratory National ICT Australia Brisbane, QLD, Australia Email: {weelum.tan,
4.3 IEEE Physical Layer IEEE IEEE b IEEE a IEEE g IEEE n IEEE 802.
 4.3 IEEE 802.11 Physical Layer 4.3.1 IEEE 802.11 4.3.2 IEEE 802.11b 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a 4.3.4 IEEE 802.11g 4.3.5 IEEE 802.11n 4.3.6 IEEE 802.11ac,ad Andreas Könsgen Summer Term 2012 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a Data
4.3 IEEE 802.11 Physical Layer 4.3.1 IEEE 802.11 4.3.2 IEEE 802.11b 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a 4.3.4 IEEE 802.11g 4.3.5 IEEE 802.11n 4.3.6 IEEE 802.11ac,ad Andreas Könsgen Summer Term 2012 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a Data
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 7: Wireless LAN
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks
 Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
Impact of IEEE n Operation on IEEE Operation
 2009 International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops Impact of IEEE 802.11n Operation on IEEE 802.15.4 Operation B Polepalli, W Xie, D Thangaraja, M Goyal, H Hosseini
2009 International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops Impact of IEEE 802.11n Operation on IEEE 802.15.4 Operation B Polepalli, W Xie, D Thangaraja, M Goyal, H Hosseini
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Lecture 17: Wireless Networking"
 Lecture 17: 802.11 Wireless Networking" CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Lili Qiu, Nitin Vaidya Lecture 17 Overview" Project discussion Intro to 802.11 WiFi Jigsaw discussion
Lecture 17: 802.11 Wireless Networking" CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Lili Qiu, Nitin Vaidya Lecture 17 Overview" Project discussion Intro to 802.11 WiFi Jigsaw discussion
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking
 CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 CMPE 257 Spring'15 1 Next week Announcements April 14: ICN (Spencer Sevilla) April 16: DTN
CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 CMPE 257 Spring'15 1 Next week Announcements April 14: ICN (Spencer Sevilla) April 16: DTN
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Communications & Networks Introduction
 Communications & Networks Introduction Alexander Nelson February 19th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Networking Number of Connected Devices 1 How
Communications & Networks Introduction Alexander Nelson February 19th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Networking Number of Connected Devices 1 How
Co-existence of WiFi and ZigBee
 Co-existence of WiFi and ZigBee Kang G. Shin The University of Michigan Joint work with Xinyu Zhang ACM MobiHoc 2011 Applying Autonomics to Create an Intelligent, Ubiquitous Environment Slide 1 Coexistence
Co-existence of WiFi and ZigBee Kang G. Shin The University of Michigan Joint work with Xinyu Zhang ACM MobiHoc 2011 Applying Autonomics to Create an Intelligent, Ubiquitous Environment Slide 1 Coexistence
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
IEEE Wireless LANs
 Unit 11 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Shyam Parekh IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs References Standards Basics Physical Layer 802.11b 802.11a MAC Framing Details Management PCF QoS (802.11e) Security Take Away Points
Unit 11 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Shyam Parekh IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs References Standards Basics Physical Layer 802.11b 802.11a MAC Framing Details Management PCF QoS (802.11e) Security Take Away Points
CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice
 CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice IEEE 802.11 (WLAN/WiFi) Bhaskaran Raman, Department of CSE, IIT Kanpur http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/braman/courses/wless-spring2007/ IEEE 802.11 (WiFi)
CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice IEEE 802.11 (WLAN/WiFi) Bhaskaran Raman, Department of CSE, IIT Kanpur http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/braman/courses/wless-spring2007/ IEEE 802.11 (WiFi)
Survey Topic: WiFi On The Move Presented by - Abhinav Tekumalla (atekumal) Bahula Gupta (bahulag)
 Outline Survey Topic: WiFi On The Move Presented by - Abhinav Tekumalla (atekumal) Bahula Gupta (bahulag) WiFi on the move : Challenges VanLAN ViFi Cabernet HSPDA/ WiMax WiFi on the move Providing WiFi
Outline Survey Topic: WiFi On The Move Presented by - Abhinav Tekumalla (atekumal) Bahula Gupta (bahulag) WiFi on the move : Challenges VanLAN ViFi Cabernet HSPDA/ WiMax WiFi on the move Providing WiFi
MDG: Measurement-Driven Guidelines for WLAN Design
 MDG: Measurement-Driven Guidelines for 82.11 WLAN Design Ioannis Broustis Dept. of CS&E UC Riverside broustis@cs.ucr.edu Michalis Faloutsos Dept. of CS&E UC Riverside michalis@cs.ucr.edu Konstantina Papagiannaki
MDG: Measurement-Driven Guidelines for 82.11 WLAN Design Ioannis Broustis Dept. of CS&E UC Riverside broustis@cs.ucr.edu Michalis Faloutsos Dept. of CS&E UC Riverside michalis@cs.ucr.edu Konstantina Papagiannaki
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 1 An Analytical Approach: Bianchi Model 2 Real Experimentations HoE on IEEE 802.11b Analytical Models Bianchi s Model Simulations ns-2 3 N links with the
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 1 An Analytical Approach: Bianchi Model 2 Real Experimentations HoE on IEEE 802.11b Analytical Models Bianchi s Model Simulations ns-2 3 N links with the
CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking
 CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 CMPE 257 Winter'11 1 Announcements Accessing secure part of the class Web page: User id: cmpe257.
CMPE 257: Wireless and Mobile Networking Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 CMPE 257 Winter'11 1 Announcements Accessing secure part of the class Web page: User id: cmpe257.
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE
 3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
Wireless Challenges : Computer Networking. Overview. Routing to Mobile Nodes. Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless
 Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless Peter Steenkiste Fall 2010 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f10 Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather
Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless Peter Steenkiste Fall 2010 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f10 Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1
 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.6: Wireless Networks - MAC Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.6: Wireless Networks - MAC Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
IEEE Medium Access Control. Medium Access Control
 IEEE 802.11 Medium Access Control EECS3214 3 April 2018 Medium Access Control reliable data delivery access control MAC layer covers three functional areas: security 2 1 MAC Requirements To avoid interference
IEEE 802.11 Medium Access Control EECS3214 3 April 2018 Medium Access Control reliable data delivery access control MAC layer covers three functional areas: security 2 1 MAC Requirements To avoid interference
CE693: Adv. Computer Networking
 CE693: Adv. Computer Networking L-9 Wireless Fall 1389 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from the graduate level Computer Networks course thought by Srinivasan Seshan at CMU. When slides are obtained
CE693: Adv. Computer Networking L-9 Wireless Fall 1389 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from the graduate level Computer Networks course thought by Srinivasan Seshan at CMU. When slides are obtained
EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12)
 EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12) Intro to Cellular and WiFi Networks Bhaskar Krishnamachari= Acknowledgement These slides were prepared by Dr. Kyuho Son, kyuhoson@usc.edu, visiting scholar at USC.
EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12) Intro to Cellular and WiFi Networks Bhaskar Krishnamachari= Acknowledgement These slides were prepared by Dr. Kyuho Son, kyuhoson@usc.edu, visiting scholar at USC.
Page 1. Outline : Wireless Networks Lecture 11: MAC. Standardization of Wireless Networks. History. Frequency Bands
 Outline 18-759 : Wireless s Lecture 11: 80.11 Peter Steenkiste Dina Papagiannaki Spring Semester 009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/ Peter A. Steenkiste, CMU 1 80 protocol overview Wireless LANs
Outline 18-759 : Wireless s Lecture 11: 80.11 Peter Steenkiste Dina Papagiannaki Spring Semester 009 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wireless09/ Peter A. Steenkiste, CMU 1 80 protocol overview Wireless LANs
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Cisco Cooperative Project. Coexistence of WiFi and LAA: Detection Thresholds. Students: Li Li Advisors: Len Cimini, Chien-Chung Shen
 Cisco Cooperative Project Coexistence of WiFi and LAA: Detection Thresholds Students: Li Li Advisors: Len Cimini, Chien-Chung Shen Nov. 12, 2015 Outline Problem Review Performance of Delay A problem in
Cisco Cooperative Project Coexistence of WiFi and LAA: Detection Thresholds Students: Li Li Advisors: Len Cimini, Chien-Chung Shen Nov. 12, 2015 Outline Problem Review Performance of Delay A problem in
Transmission Control Protocol over Wireless LAN
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 12 Issue 17 Version 1.0 Year 2012 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 12 Issue 17 Version 1.0 Year 2012 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Link Quality based Association Mechanism in IEEE h compliant Wireless LANs
 Link Quality based Association Mechanism in IEEE 802.11h compliant Wireless LANs T. Korakis +, O. Ercetin α, S. Krishnamurthy, L. Tassiulas +, S. Tripathi ρ + Computer Engineering and Telecommunications
Link Quality based Association Mechanism in IEEE 802.11h compliant Wireless LANs T. Korakis +, O. Ercetin α, S. Krishnamurthy, L. Tassiulas +, S. Tripathi ρ + Computer Engineering and Telecommunications
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE WLANs. Presented by Eric Wang
 CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE 802.11 WLANs Presented by Eric Wang 1 Outline Introduction Related Work Preliminaries CARA Performance Evaluation Conclusion and Future Work 2 Basic CSMA/CA
CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE 802.11 WLANs Presented by Eric Wang 1 Outline Introduction Related Work Preliminaries CARA Performance Evaluation Conclusion and Future Work 2 Basic CSMA/CA
Medium Access Control
 Medium Access Control Fundamental Problem N nodes in vicinity want to transmit (to, say, N other nodes). How to do this interference free? Interference free means SINR Otherwise, we say that packets collide.
Medium Access Control Fundamental Problem N nodes in vicinity want to transmit (to, say, N other nodes). How to do this interference free? Interference free means SINR Otherwise, we say that packets collide.
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 8 Wireless Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
A Multi-channel MAC Protocol for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks
 A Multi-channel MAC Protocol for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Jungmin So Dept. of Computer Science, and Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Email: jso1@uiuc.edu Nitin
A Multi-channel MAC Protocol for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Jungmin So Dept. of Computer Science, and Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Email: jso1@uiuc.edu Nitin
Wireless Networks (MAC)
 802.11 Wireless Networks (MAC) Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Academia Sinica 2016.03.18 CSIE, NTU Reference 1. A Technical Tutorial on the IEEE 802.11 Protocol By Pablo Brenner online: http://www.sss-mag.com/pdf/802_11tut.pdf
802.11 Wireless Networks (MAC) Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Academia Sinica 2016.03.18 CSIE, NTU Reference 1. A Technical Tutorial on the IEEE 802.11 Protocol By Pablo Brenner online: http://www.sss-mag.com/pdf/802_11tut.pdf
Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in : Collision or Weak Signal?
 Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in 802.11: Collision or Weak Signal? Shravan Rayanchu Arunesh Mishra Dheeraj Agrawal Sharad Saha Suman Banerjee Wisconsin Wireless and NetworkinG Systems (WiNGS) Lab University
Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in 802.11: Collision or Weak Signal? Shravan Rayanchu Arunesh Mishra Dheeraj Agrawal Sharad Saha Suman Banerjee Wisconsin Wireless and NetworkinG Systems (WiNGS) Lab University
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Lecture 6. Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1
 Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 5 January 31, 2013 Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail: carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 5 January 31, 2013 Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail: carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/
INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS LAN, MAC PROTOCOLS and INTERFERENCE. Choong Seon Hong, KHU
 INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS LAN, MAC PROTOCOLS and INTERFERENCE cshong@khu.ac.kr, Choong Seon Hong, KHU Outline 2 Introduction Wireless LAN Architecture Wireless LAN standards Media Access Problem The IEEE
INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS LAN, MAC PROTOCOLS and INTERFERENCE cshong@khu.ac.kr, Choong Seon Hong, KHU Outline 2 Introduction Wireless LAN Architecture Wireless LAN standards Media Access Problem The IEEE
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview. Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University
 Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
CSE 6811 Ashikur Rahman
 Data Link layer Application Overview of IEEE 802.11 LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform address recognition and CRC validation.
Data Link layer Application Overview of IEEE 802.11 LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform address recognition and CRC validation.
Logical Link Control (LLC) Medium Access Control (MAC)
 Overview of IEEE 802.11 Data Link layer Application Presentation Session Transport LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform
Overview of IEEE 802.11 Data Link layer Application Presentation Session Transport LLC: On transmission, assemble data into a frame with address and CRC fields. On reception, disassemble frame, perform
Advanced Computer Networks. WLAN, Cellular Networks
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN, Cellular Networks Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2013 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Medium Access COPE Today Last week Short
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN, Cellular Networks Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2013 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Medium Access COPE Today Last week Short
CSMC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala. Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1
 CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
Analysis of IEEE e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs
 Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
TACKLING THE CHALLENGES OF WIRELESS INTERFERENCE AND COEXISTENCE
 TACKLING THE CHALLENGES OF WIRELESS INTERFERENCE AND COEXISTENCE By Jun Huang A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF
TACKLING THE CHALLENGES OF WIRELESS INTERFERENCE AND COEXISTENCE By Jun Huang A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
CSE 461: Wireless Networks
 CSE 461: Wireless Networks Wireless IEEE 802.11 A physical and multiple access layer standard for wireless local area networks (WLAN) Ad Hoc Network: no servers or access points Infrastructure Network
CSE 461: Wireless Networks Wireless IEEE 802.11 A physical and multiple access layer standard for wireless local area networks (WLAN) Ad Hoc Network: no servers or access points Infrastructure Network
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
MAC protocols. Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov
 MAC protocols Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2616/ OUTLINE: Problems for MAC to deal with; Design goals; Classification of MAC protocols Contention-based
MAC protocols Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2616/ OUTLINE: Problems for MAC to deal with; Design goals; Classification of MAC protocols Contention-based
Dynamic Rate Adaptation in IEEE WLANs
 Dynamic Rate Adaptation in IEEE 802.11 WLANs SongYiLin@ICT August 10, 2008 References [1] On the Performance Characteristics of WLANs: Revisited (SIGMETRICS 2005) [2] CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation
Dynamic Rate Adaptation in IEEE 802.11 WLANs SongYiLin@ICT August 10, 2008 References [1] On the Performance Characteristics of WLANs: Revisited (SIGMETRICS 2005) [2] CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation
APPLICATION NOTE. XCellAir s Wi-Fi Radio Resource Optimization Solution. Features, Test Results & Methodology
 APPLICATION NOTE XCellAir s Wi-Fi Radio Resource Optimization Solution Features, Test Results & Methodology Introduction Multi Service Operators (MSOs) and Internet service providers have been aggressively
APPLICATION NOTE XCellAir s Wi-Fi Radio Resource Optimization Solution Features, Test Results & Methodology Introduction Multi Service Operators (MSOs) and Internet service providers have been aggressively
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 9: MAC Protocols for WLANs Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) 1 Reference 1. A Technical Tutorial on the IEEE 802.11 Protocol By Pablo Brenner online:
Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 9: MAC Protocols for WLANs Instructor: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) 1 Reference 1. A Technical Tutorial on the IEEE 802.11 Protocol By Pablo Brenner online:
Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks
 Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks The Wireless Medium is a scarce precious resource. Furthermore, the access medium is broadcast in nature. It is necessary to share this resource efficiently and
Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks The Wireless Medium is a scarce precious resource. Furthermore, the access medium is broadcast in nature. It is necessary to share this resource efficiently and
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Metronome: Spectrum Sharing in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks. Ramki Gummadi (MIT)
 Metronome: Spectrum Sharing in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Ramki Gummadi (MIT) Joint work with Hari Balakrishnan (MIT) Srinivasan Seshan (CMU) COMSNETS 2009 1 Motivation Heterogeneous wireless n/w
Metronome: Spectrum Sharing in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Ramki Gummadi (MIT) Joint work with Hari Balakrishnan (MIT) Srinivasan Seshan (CMU) COMSNETS 2009 1 Motivation Heterogeneous wireless n/w
Wireless Router at Home
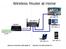 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
