Using the Nios Development Board Configuration Controller Reference Designs
|
|
|
- Chrystal Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs July ver 1.1 Application Note 346 Introduction Many modern embedded systems utilize flash memory to store processor configuration information and program data for the system processor. Increasingly, flash memory is also being used to store hardware configuration data for field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) located in the embedded system. The use of flash memory for both processor memory and FPGA configuration data typically requires an intelligent configuration controller, particularly for systems with soft embedded processors such as the Altera Nios II processor solution. Altera s Nios II development boards, Stratix II and Cyclone II editions, contain a programmable configuration controller that provides a stable platform for managing system configuration and reset in embedded systems. The Nios II development board configuration controller is implemented in an Altera EPM7256AE non-volatile MAX 7000 device. The controller platform provides instant-on configuration control enabling systems to be configured, or reconfigured, in a minimal amount of time. This application note: Describes how to use configuration controller reference designs for systems containing Altera Stratix II or Cyclone II devices Provides the steps to port reference designs to your board Provides suggestions for modifying the reference designs to support more complex systems f f For more information about the Nios II embedded processor see: The Nios II Processor Reference Handbook and the Nios II Software Developer s Handbook. For more information about the Nios II development boards, see the: Nios Development Board Cyclone II Edition, Reference Manual and the Nios Development Board Stratix II Edition, Reference Manual. Controller Overview The configuration controller on the Nios development boards is designed to: Intelligently configure FPGAs from a flash memory device on system power-up Altera Corporation 1 AN
2 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Utilize a single flash memory device to store hardware configuration data as well as embedded software instructions and data Provide flash partitions for multiple hardware images Provide a mechanism for users to reset the board to a known working hardware image Provide an interface to a Nios II processor residing on an FPGA so that the processor can issue a reconfiguration request to the configuration controller; facilitating in-the-field upgrades This section discusses: Flash images on the Nios development board, Stratix II & Cyclone II editions controller boot sequences for Stratix II & Cyclone II editions controller hardware for Stratix II & Cyclone II editions controller reference designs for Stratix II & Cyclone II editions Flash Images on the Nios Development Board, Stratix II Edition The Nios development board, Stratix II edition includes an Altera EPCS64 serial configuration device as well as an 8-bit wide Common Flash Interface (CFI) flash. The CFI flash image on the Nios development board, Stratix II edition is partitioned into three sections, see Figure 1 on page 3. In the CFI flash: The first section is used for general programming or data storage. The other two sections user and safe image are used to store FPGA hardware configurations The user image typically contains a hardware design that is under development or testing The safe (factory programmed) image is assumed to contain a known working or default hardware image The EPCS64 is divided into two sections with a floating section boundary. The section boundary between the User Hardware and User Software/Data sections is determined by the size of the User Hardware section. 2 Altera Corporation
3 Controller Overview It is the configuration controller s responsibility to load the EPCS user, CFI user or the CFI safe image into the Stratix II device. By observing the behavior illustrated in the Figure 2 flowchart, the configuration controller determines which image to load. Figure 1. Nios Development Board Flash Partition Address (hex) 0x x x x x x x x CFI Flash User Software or Data (6 MB) User Hardware Image (1MB) Safe Hardware Image (1MB) Factory programmed-do not erase Available for user-data Flash Allocation EPCS Flash User Hardware Image User Software or Data Controller Boot Sequence for Stratix II Devices When the Nios development board, Stratix II edition initially powers-on, the configuration controller is idle until it detects the power-on reset. Upon detecting power-on reset, the controller attempts to load the EPCS user image into the FPGA. If configuration of the EPCS user flash image is successful, the controller will continually flash the User LED, tri-state all of its flash interface pins, and remain idle until a reset, reconfiguration, or safe image request is detected. If configuration of the user flash image fails, the controller will attempt to program the safe flash image into the Stratix II device. If the controller can successfully program the safe flash image into the Stratix II device, it will illuminate the Safe LED. The controller remains idle until a reset, reconfiguration, or safe image request is detected. If an error occurs while programming the safe image to the device, the controller will illuminate the Error LED and remain in an error state. The controller will only exit the error state when a reset or power-on reset request is detected. Altera Corporation 3
4 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Figure 2 shows the configuration controller boot sequence flowchart for Stratix II devices. Figure 2. Controller Boot Sequence Flowchart Power on state Power on reset detected Load user image from serial configuration device to FPGA Reset or reconfig request successful? No Yes Blink User LED Safe config request Reset or reconfig request Light user LED Yes Load user image from parallel flash to FPGA successful? Safe config request No Load safe image from parallel flash to FPGA successful? Yes Safe config request Light safe LED Reset or reconfig request No reset Light error LED f For more information on the configuration process and the flash structure of the Nios development board, Stratix II edition, refer to: Nios Development Board Stratix II Edition, Reference Manual. 4 Altera Corporation
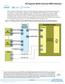
5 Controller Overview Controller Hardware for Stratix II Devices Stratix II FPGAs can be programmed in a number of different modes; however, when programming a Stratix II device via an external configuration controller, it is recommended to program the device in fast passive parallel (FPP) mode. When in FPP mode, the external configuration controller generates a configuration clock for the Stratix II device and presents an 8-bit configuration data word to the Stratix II device on each configuration clock cycle. f For more information on the FPP configuration capabilities of Stratix II devices refer to the Stratix II Device Handbook, Chapter 13: Configuring Stratix II & Stratix II GX Devices. The configuration controller reference design included with the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) uses an EPM7256AE device to generate the configuration clock for the Stratix II device as well as generate the address and control signals necessary to pull configuration data out of flash memory. Figure 3 shows the development board configuration controller block diagram for Stratix II devices. Altera Corporation 5
6 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Figure 3. Development Board Controller for Stratix II Devices A[23..0] D[7..0] CONTROL MAX EPM7256AE Controller External Flash Drive A[23..0] D[7..0] CONTROL reset_n Flash Address and Control-Logic Generator Clock Generator Reset Distribution Logic Control Logic Status Monitor DATA[0] Device DCLK CONF_DONE STATUS_n CONFIG_n Reconfig_request CS_n ASDO Stratix II EP2S60 ENET RST PROTO1 RST PROTO2 RST Status LEDs Figure 3 illustrates that the configuration controller can be conceptually viewed as five sub-blocks, which are described in this section. Flash Address & Control Logic Generator The flash address and control logic block generates the address signals to send to the CFI flash device. The logic will initiate configuration from either the user or factory image based on inputs from the control logic, and then increment the CFI flash address bus until the appropriate number of configuration bytes have been transferred, or an error is detected. After a successful configuration, the CFI flash address and control pins of the EPM7256AE device are tri-stated so that the flash can be accessed by the Nios II embedded processor running in the Stratix II device. 6 Altera Corporation
7 Controller Overview Clock Generator The configuration clock generator drives the DCLK input signal of the Stratix II device. The clock is derived from the 50 MHz oscillator on the Stratix II development board. The reference design divides the oscillator by 16 to create a 3.125MHz configuration clock. The clock is also used to time the address and control signals of the CFI flash device. Reset Distribution Logic The configuration controller is also used to deliver resets to other devices on the development board. A board level reset is issued to the Ethernet device, the flash device, and the two, board-prototype headers when: A power-on reset occurs. A reconfiguration request from the processor arrives. The force safe button is pressed. Control Logic To control the configuration flow, the configuration control logic monitors the various board reset sources as well as the Stratix II device configuration status signals. This logic block drives the MSEL pins on the Stratix II device to set the configuration mode based on the flow chart shown in Figure 2 on page 4. The logic manages the loading of the user or factory images based on the status of the Stratix II devices STATUS_n and CONF_DONE signals. The configuration control logic is also responsible for initiating a new configuration if a reset_n is detected, the board s Force Safe button has been pressed, or the Nios II processor residing in the Stratix II device issues a Reconfiguration_request. Status Monitor The Nios development board, Stratix II edition contains four LEDs used to indicate the configuration status of the processor. LEDs are illuminated depending on which image is loaded into the Stratix II device or if an error has occurred during configuration. Controller Reference Designs for Stratix II Devices The Nios II EDS provides configuration controller reference design for the EP2S60 device. If you have installed the Nios II EDS, you will find the source code and Quartus II project files for the reference design at: \kits\nios2_60\examples\config_controller\niosii_stratixii_ 2s60_rohs Altera Corporation 7
8 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Table 1 provide a description of each of the source files used in the configuration controller design. Table 1. Stratix II Controller Files File Name config_controller.tdf address_counter.tdf dclk_divider.tdf reset_counter.tdf Description Top-level design. Contains control logic and instantiations of the lower-level files, i.e., address_counter.tdf, dclk_divider.tdf, reset_counter.tdf. Counter used to generate address bus for flash device access. Clock divider used to generate DCLK from the board oscillator. Used to debounce reset switch inputs. Flash Image on the Nios Development Board, Cyclone II Edition The flash image on the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition also contains a user and safe (factory programmed) image in CFI flash as well as a user hardware image in an EPCS64 serial configuration device. Controller Boot Sequence for Cyclone II Devices When the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition initially powerson, the configuration controller is idle until it detects the power-on reset. Upon detecting power-on reset, the controller attempts to load the image stored in serial flash into the FPGA. If configuration of the serial flash image is successful the controller continuously blinks the User LED on the development board, tri-states all of its flash interface pins, and remains idle until a reset or reconfiguration request is detected. If configuration of the serial flash image fails, the controller will attempt to program the user image from the 8-bit flash into the Cyclone II device. In this case, the User LED will illuminate if the controller can successfully program the user image into the Cyclone II device and the controller will remain idle until a reset, reconfiguration request, or safe image reset is detected. If configuration of the user image fails, the controller will attempt to load the safe image from the 8-bit flash into the Cyclone II device. The Safe LED is illuminated when the safe image is properly loaded. If an error 8 Altera Corporation
9 Controller Overview occurs while programming the safe image to the device, the controller will illuminate the Error LED and remain in an error state. The controller will only exit the error state when a reset or power-on reset is issued. The configuration controller boot sequence flowchart for the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition is shown in Figure 2 on page 4. f For more information on the configuration process and the flash structure of the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition, refer to: Nios Development Board Reference Manual, Cyclone II Edition. Controller Hardware for Cyclone II Devices Cyclone II FPGAs are programmed serially via either a download cable, a serial configuration device, or in passive serial (PS) mode using an external configuration controller. The configuration controller reference design demonstrates the flexibility of using a CPLD as a configuration controller in that the same CPLD can be used as a configuration controller for two different Altera device families. In the case of the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition, the configuration controller has been modified to enable programming the Cyclone II device in PS mode using an 8-bit flash as the configuration source as well as from an Altera serial configuration device. f For more information on the configuration capabilities of Cyclone II devices refer to the Cyclone II Device Handbook, Chapter 13: Configuring Cyclone II FPGAs. The configuration controller reference design included with the Nios development board, Cyclone II edition, uses a MAX 7256AE device to generate the configuration clock for the Cyclone II device as well as generate the address and control signals necessary to pull configuration data out of flash memory and convert it to serial data for the Cyclone II device. Figure 4 illustrates a block diagram of the configuration controller reference design for Cyclone II devices. Altera Corporation 9
10 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Figure 4. Development Board Controller for Cyclone II Devices A[23..0] DATA[7..0] CONTROL External Flash Drive A[23..0] DATA[7..0] CONTROL MAX EPM7256AE Controller Flash Address and Control-Logic Generator Flash Parallel to Serial Data Converter Device CSn ASD0 reset_n Clock Generator Reset Distribution Logic Control Logic Status Monitor DATA0 DCLK MSEL[1..0] CONF_DONE STATUS_n CONFIG_n Reconfig_Request Cyclone II EP2C35 ENET RST PROTO1 RST PROTO2 RST Status LEDs The main differences between the Cyclone II edition development board s configuration controllers and the Stratix II edition development board s configuration controllers are that the Cyclone II edition includes: A parallel to serial converter block Control logic block modifications The parallel to serial block reads an 8-bit word from the flash image every 8 DCLK cycles and shifts the word out to the DATA0 input of the Cyclone II device on every DCLK cycle. 10 Altera Corporation
11 Porting the Controller Reference Designs to Other Boards Controller Reference Designs for Cyclone II Devices The Nios Development Kit, Cyclone II Edition provides configuration controller reference design for the Cyclone II EP2C35 device. If you have installed the Nios Development Kit, you will find the source code and Quartus II project files for the reference designs at: \kits\nios2_60\examples\config_controller\niosii_cycloneii_2c35 Table 2 provides a description of each of the source files used in the configuration controller design. Table 2. Cyclone II Controller Files File Name config_controller.tdf address_counter.tdf dclk_divider.tdf reset_counter.tdf data_bit_counter.tdf shift_register.tdf Description Top-level design. Contains control logic and instantiations of the lower-level files, i.e., address_counter.tdf, dclk_divider.tdf, reset_counter.tdf, data_bit_counter.tdf, shift_register.tdf. Counter used to generate address bus for flash access. Clock divider used to generate DCLK from the board oscillator. Used to debounce reset switch inputs. Used to determine when a word should be loaded into the shift register. Shifts a configuration bit out to the DATA0 line each DCLK cycle. Porting the Controller Reference Designs to Other Boards The configuration controller reference design included with Nios development kits can easily be adapted to work on other boards that contain a CPLD and an Altera FPGA. In general, the only required modification is to match the Nios development board configuration controller to the type of flash image present on the board to which you are porting. The flash image contained on the Nios development board is an 8-bitwide, 16-MByte flash, which requires 24 address lines. Other size flashes may require a different number of address bits. If this is the case, you need to modify the configuration controller source code such that the address bus width matches the address width of your flash. Altera Corporation 11
12 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs If you are using a different size flash, it will also be necessary to modify the location of the user and safe images within the configuration controller. The configuration controller for the Stratix II development board wires the upper two address bits (i.e., bits 23 and 22) to the 16- MByte flash and to 1 (or V CC ), and uses address bit 21 to select between the user and safe images. See Figure 5. Figure 5. 8-Bit Wide, Uniform Sector Flash Connection MAX Controller 16-MByte Uniform Sector Flash A23 A22 A21 A[20..0] V CC Control Logic Address Counter Note: (1) Figure 5 assumes that the configuration target is an EP2C35 device. Other size devices may have different configuration file sizes requiring different address mapping. If you are using a 4-MByte flash, change the address bus width from [23..0] to [21..0] and wire address bit 21 of the configuration controller address bus to 1 (or V CC ); then continue to use bit 20 to select between the user and safe image as indicated in Figure Altera Corporation
13 Porting the Controller Reference Designs to Other Boards Figure 6. 8-Bit Wide, Uniform Sector Flash Connection A21 MAX Controller V CC 4-MByte Uniform Sector Flash A20 A[19..0] Control Logic Address Counter Note: (1) Figure 6 assumes that the configuration target is an EP2C35 device. Other size devices may have different configuration file sizes requiring different address mapping. If you are using a top boot sector flash, you will also need to make modifications to the source code. The flash used in the Nios development kits is a uniform sector flash; therefore, it is generally advisable to leave the lower sections of a uniform sector flash for the host processor and the upper sections for data storage. However, a top boot sector flash will generally reserve the upper sections as processor boot code. In this case, it is better to store the hardware configuration data in a lower section of the flash. This type of flash requires that the upper address bit (bit 21) of the flash be tied to 0 (or GND), and bit 20 be used to select the user or safe image (see Figure 7). Figure 7. 8-Bit-Wide, Top Boot Sector Flash Connections MAX Controller A21 4-MByte Top Boot Flash A20 A[19..0] Control Logic Address Counter GND Note: (1) Figure 7 assumes that the configuration target is an EP2C35 device. Other size devices may have different configuration file sizes requiring different address mapping. Altera Corporation 13
14 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Modifying the Reference Design to Support a Variety of Systems & Requirements In addition to accommodating different flash types, the configuration controller reference design can be modified to support many different types of systems and configuration requirements. For example a MAX device can be used to create configuration controllers that can: Select from multiple flash images Provide support for Ethernet upgrades Configure multiple devices Selecting from Multiple Flash Images The reference design that ships with Nios development kits is designed to first attempt to program the user image into the targeted FPGA. If the user image configuration attempt fails, the reference design will then attempt to program the safe image. The concept of a priority image-selection design can easily be extended to include a number of user images that can be chosen to program the FPGA. Figure 8 shows an example configuration controller that is designed for priority image selection. The Figure 8 controller design is virtually identical to the Figure 3 controller design. However, the Figure 8 controller has a 2-bit image_select[1..0] bus that is used to select one of four user images stored in flash. The 2-bit image_select[1..0]bus is driven by an external source such as a Nios embedded processor running in the targeted device. To load a new image into the targeted device, the Nios processor (or external source) writes out the desired configuration image number to the image_select[1..0] bus and issues a reconfiguration request. An alternative solution is to reserve a flash memory location that contains a hardware image number. In this scenario, the processor writes to the desired flash configuration number. When a reset or reconfiguration request is issued, the configuration controller reads the image number location from flash and proceeds to load the indicated image into the targeted device. 14 Altera Corporation
15 Modifying the Reference Design to Support a Variety of Systems & Requirements Figure 8. Image Select Capability Safe Image Image 1 Image 2 Image 3 Program MEMORY DATA[7..0] A[22..0] CS_n OE_n RW_n reset_n MAX EPM7256AE Controller Flash Address and Control-Logic Generator Clock Generator Reset Distribution Logic Control Logic Status Monitor DCLK CONF_DONE STATUS_n CONFIG_n image_select[1..0] Reconfig_request Stratix Device Nios CPU ENET RST PROTO1 RST PROTO2 RST Status LEDs Upgrade Hardware Image via an Ethernet Link The configuration controller that ships with Nios development kits supports upgrading the hardware image over an Ethernet link. The Ethernet upgrade can be achieved when a Nios embedded processor equipped with a transmission control protocol (TCP) stack is running in the targeted FPGA. In this scenario, the Nios processor can receive a programming file via an Ethernet link, and then burn the programming file into flash. After the flash file has been upgraded, the Nios processor issues a reconfiguration request, which downloads the new hardware image into the targeted device. Figure 9 shows an example system that can automatically be reconfigured via an Ethernet link. Altera Corporation 15
16 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Figure 9. Ethernet Reconfigurable System Safe Image Image 1 Image 2 DATA[7..0] A[22..0] CS_n OE_n RW_n MAX EPM7256AE Controller Flash Address and Control-Logic Generator Image 3 Program Memory reset_n Clock Generator Reset Distribution Logic Control Logic Status Monitor DCLK CONF_DONE STATUS_n CONFIG_n image_select[1..0] Reconfig_request Stratix Device Nios CPU TCP Stack ENET RST PROTO1 RST PROTO2 RST Status LEDs Multiple Device Multiple FPGAs on-board configuration is another application that demonstrates the flexibility of a CPLD-based configuration controller. There are a number of different configuration scenarios that exist when multiple FPGAs reside on the same board, including: Multiple identical FPGAs Multiple FPGAs from the same vendor with different hardware images Multiple FPGAs from different vendors Figure 10 illustrates a configuration controller that could be used to configure multiple FPGAs where each FPGA requires a different configuration file. The Figure 10 controller can program different device family devices from either the same vendor or different vendors. In this 16 Altera Corporation
17 Conclusion scenario, the flash memory contains two configuration images for two targeted FPGAs. The Figure 10 controller logic is designed to program one device at a time. Figure 10. Multiple Device FPGA 1 Image FPGA 2 Image DATA[7..0] A[22..0] CS_n OE_n RW_n reset_n MAX EPM7256AE Controller Flash Address and Control-Logic Generator Clock Generator Control Logic DATA[7..0] Config signals Reconfig_request DATA[7..0] Device 1 Config signals Device 2 Reset Distribution Logic Status Monitor Reconfig_request ENET RST PROTO1 RST PROTO2 RST Status LEDs Conclusion The use of flash memory to store hardware configuration data for FPGAs located in an embedded system typically requires an intelligent configuration controller. Altera s Nios development boards, Stratix II and Cyclone II editions, contain a programmable configuration controller that provides a stable platform for managing system configuration and reset in embedded systems. With the Nios development board configuration controller reference designs included with the Nios development kits, you can: Port reference designs to other boards Modify the reference designs to support more complex systems and configuration requirements Altera Corporation 17
18 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs Because the Altera MAX family of CPLDs are ideally suited for use as board-level configuration controllers, the Nios development board s configuration controller utilizes an Altera MAX CPLD. The programmable nature of MAX CPLDs allows the same device to be used in a variety of different systems. Because the MAX device can support both local and remote configuration updates, a MAX-based configuration controller is particularly useful in systems with embedded processors such as the Nios embedded processor. 18 Altera Corporation
19 Conclusion 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA (408) Applications Hotline: (800) 800-EPLD Literature Services: Copyright 2004 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions Company, the stylized Altera logo, specific device designations, and all other words and logos that are identified as trademarks and/or service marks are, unless noted otherwise, the trademarks and service marks of Altera Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. All other product or service names are the property of their respective holders. Altera products are protected under numerous U.S. and foreign patents and pending applications, maskwork rights, and copyrights. Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera Corporation. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. Printed on recycled paper Altera Corporation 19
20 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs 20 Altera Corporation
21 Conclusion Altera Corporation 21
Using the Nios II Configuration Controller Reference Designs
 Using the Nios II Controller Reerence Designs AN-346-1.2 March 2009 Introduction This application note describes coniguration controller reerence designs or Nios II systems using Altera Stratix II, Cyclone
Using the Nios II Controller Reerence Designs AN-346-1.2 March 2009 Introduction This application note describes coniguration controller reerence designs or Nios II systems using Altera Stratix II, Cyclone
Nios II Embedded Design Suite 6.1 Release Notes
 December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
 DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current
 AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable
 ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable December 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Features Allows PC users to perform the following functions: Program MAX 9000, MAX 7000S, MAX 7000AE, MAX 7000B, MAX 3000A,
ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable December 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Features Allows PC users to perform the following functions: Program MAX 9000, MAX 7000S, MAX 7000AE, MAX 7000B, MAX 3000A,
Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander
 Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander March 2004, ver 2.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontroller and microprocessors
Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander March 2004, ver 2.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontroller and microprocessors
Active Serial Memory Interface
 Active Serial Memory Interface October 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Altera Cyclone TM devices can be configured in active serial configuration mode. This mode reads a configuration bitstream
Active Serial Memory Interface October 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Altera Cyclone TM devices can be configured in active serial configuration mode. This mode reads a configuration bitstream
Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander
 Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander August 2003, Ver 1.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontrollers and microprocessors limit I/O
Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander August 2003, Ver 1.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontrollers and microprocessors limit I/O
ByteBlaster II Download Cable User Guide
 ByteBlaster II Download Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com UG-BBII81204-1.1 P25-10324-00 Document Version: 1.1 Document Date: December 2004 Copyright
ByteBlaster II Download Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com UG-BBII81204-1.1 P25-10324-00 Document Version: 1.1 Document Date: December 2004 Copyright
Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software
 Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software July 2006, ver. 3.0 Application Note 370 Introduction Using the Joint Test Action Group () interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the
Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software July 2006, ver. 3.0 Application Note 370 Introduction Using the Joint Test Action Group () interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the
Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor
 Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features... Preliminary Information Part of Altera s Excalibur TM embedded processor solutions, the Nios TM soft core embedded processor is
Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features... Preliminary Information Part of Altera s Excalibur TM embedded processor solutions, the Nios TM soft core embedded processor is
USB BitJetLite Download Cable
 USB BitJetLite Download Cable User Guide, Inc. (USA) 14100 Murphy Avenue San Martin, CA 95046 (408) 852-0067 http://www.slscorp.com Product Version: 1.0 Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: Copyright 2010,.All
USB BitJetLite Download Cable User Guide, Inc. (USA) 14100 Murphy Avenue San Martin, CA 95046 (408) 852-0067 http://www.slscorp.com Product Version: 1.0 Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: Copyright 2010,.All
Stratix FPGA Family. Table 1 shows these issues and which Stratix devices each issue affects. Table 1. Stratix Family Issues (Part 1 of 2)
 January 2007, ver. 3.1 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix devices. This document addresses known issues and includes methods to work around the issues. Table 1 shows
January 2007, ver. 3.1 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix devices. This document addresses known issues and includes methods to work around the issues. Table 1 shows
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design
 Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
Enhanced Configuration Devices
 Enhanced Configuration Devices October 2007, Version 1.2 Errata Sheet Introduction Intel-Flash- Based EPC Device Protection f This errata sheet provides updated information on enhanced configuration devices
Enhanced Configuration Devices October 2007, Version 1.2 Errata Sheet Introduction Intel-Flash- Based EPC Device Protection f This errata sheet provides updated information on enhanced configuration devices
Enhanced Configuration Devices
 Enhanced Configuration Devices July 2008, Version 1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction Intel-Flash- Based EPC Device Protection f This errata sheet provides updated information on enhanced configuration devices
Enhanced Configuration Devices July 2008, Version 1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction Intel-Flash- Based EPC Device Protection f This errata sheet provides updated information on enhanced configuration devices
Implementing LED Drivers in MAX Devices
 Implementing LE rivers in MAX evices ecember 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 286 Introduction Commercial LE river Chips iscrete light-emitting diode (LE) driver chips are common on many system boards.
Implementing LE rivers in MAX evices ecember 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 286 Introduction Commercial LE river Chips iscrete light-emitting diode (LE) driver chips are common on many system boards.
9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Arria II Devices
 July 2012 AIIGX51009-4.3 9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Arria II Devices AIIGX51009-4.3 This chapter describes the supported configuration schemes for Arria II devices,
July 2012 AIIGX51009-4.3 9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Arria II Devices AIIGX51009-4.3 This chapter describes the supported configuration schemes for Arria II devices,
White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver
 White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver is designed to configure Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) through the ByteBlasterMV
White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver is designed to configure Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) through the ByteBlasterMV
FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions
 FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions Razak Mohammedali Product Marketing Engineer Altera Corporation DSP processors are widely used for implementing many DSP applications. Although DSP processors
FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions Razak Mohammedali Product Marketing Engineer Altera Corporation DSP processors are widely used for implementing many DSP applications. Although DSP processors
Cyclone II FPGA Family
 ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface
 White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
10. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix IV Devices
 September 2012 SIV51010-3.5 10. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix IV Devices SIV51010-3.5 This chapter describes the configuration, design security, and remote system
September 2012 SIV51010-3.5 10. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix IV Devices SIV51010-3.5 This chapter describes the configuration, design security, and remote system
Simulating the ASMI Block in Your Design
 2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide
 Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Remote Update Intel FPGA IP User Guide... 3
Simple Excalibur System
 Excalibur Solutions Simple Excalibur System August 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 242 Introduction This application note describes a simple Excalibur system design that consists of software running on
Excalibur Solutions Simple Excalibur System August 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 242 Introduction This application note describes a simple Excalibur system design that consists of software running on
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function
 POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function November 2004, MegaCore Version 2.2.2 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version v2.2.2 of the POS-PHY Level
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function November 2004, MegaCore Version 2.2.2 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version v2.2.2 of the POS-PHY Level
Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface
 Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface January 2003, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction PTF Assignments SDRAM is commonly used in cost-sensitive applications requiring large amounts of memory.
Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface January 2003, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction PTF Assignments SDRAM is commonly used in cost-sensitive applications requiring large amounts of memory.
MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide
 MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: July 2004 P25-10322-00 Copyright
MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Document Version: 1.0 Document Date: July 2004 P25-10322-00 Copyright
FPGA Design Security Solution Using MAX II Devices
 White Paper FPGA Solution Using MAX II Devices Introduction SRAM-based FPGAs are volatile devices. They require external memory to store the configuration data that is sent to them at power up. It is possible
White Paper FPGA Solution Using MAX II Devices Introduction SRAM-based FPGAs are volatile devices. They require external memory to store the configuration data that is sent to them at power up. It is possible
Nios II Embedded Design Suite 7.1 Release Notes
 Nios II Embedded Design Suite 7.1 Release Notes May 2007, Version 7.1 Release Notes This document contains release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 7.1. Table of Contents: New
Nios II Embedded Design Suite 7.1 Release Notes May 2007, Version 7.1 Release Notes This document contains release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 7.1. Table of Contents: New
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance
 Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance in Altera Devices September 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 178 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor, includes
Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance in Altera Devices September 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 178 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor, includes
Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim
 Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim Ray Duran Staff Design Specialist FAE, Altera Corporation 408-544-7937
Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim Ray Duran Staff Design Specialist FAE, Altera Corporation 408-544-7937
AIRbus Interface. Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width. Functional Description. General Arrangement
 AIRbus Interface December 22, 2000; ver. 1.00 Functional Specification 9 Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width of the data bus) Read and write access Four-way
AIRbus Interface December 22, 2000; ver. 1.00 Functional Specification 9 Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width of the data bus) Read and write access Four-way
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit)
 Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix V Devices
 January 2011 SV51010-1.2 9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix V Devices SV51010-1.2 This chapter contains information about the Stratix V supported configuration schemes,
January 2011 SV51010-1.2 9. Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in Stratix V Devices SV51010-1.2 This chapter contains information about the Stratix V supported configuration schemes,
Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices
 Crosspoint Switch Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices March 200, ver. 2.0 Application Note 29 Introduction With a high level of flexibility, performance, and programmability, you can use crosspoint
Crosspoint Switch Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices March 200, ver. 2.0 Application Note 29 Introduction With a high level of flexibility, performance, and programmability, you can use crosspoint
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
December 2002, ver. 1.3 Application Note 191. Six individual interrupts Six-bit priority scheme Five-bit priority scheme plus one individual interrupt
 Excalibur Solutions Using the Interrupt Controller December 22, ver..3 Application Note 9 Introduction This document describes the operation of the interrupt controller for the Excalibur devices, particularly
Excalibur Solutions Using the Interrupt Controller December 22, ver..3 Application Note 9 Introduction This document describes the operation of the interrupt controller for the Excalibur devices, particularly
Introduction. Design Hierarchy. FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow
 FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow February 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 171 Introduction To maximize the benefits of the LogicLock TM block-based design methodology in the
FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow February 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 171 Introduction To maximize the benefits of the LogicLock TM block-based design methodology in the
PCI Express Multi-Channel DMA Interface
 2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
Implementing LED Drivers in MAX and MAX II Devices. Introduction. Commercial LED Driver Chips
 Implementing LE rivers in MAX and MAX II evices October 2008 AN-286-2.3 Introduction iscrete LE driver chips are common on many system boards. Altera MAX II, MAX 7000B, MAX 7000A, MAX 3000A, and MAX 7000S
Implementing LE rivers in MAX and MAX II evices October 2008 AN-286-2.3 Introduction iscrete LE driver chips are common on many system boards. Altera MAX II, MAX 7000B, MAX 7000A, MAX 3000A, and MAX 7000S
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design
 ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
Using MicroC/OS-II RTOS with the Nios II Processor Tutorial Preliminary Information
 Using MicroC/OS-II RTOS with the Nios II Processor Tutorial Preliminary Information 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Copyright 2004 Altera Corporation. All rights
Using MicroC/OS-II RTOS with the Nios II Processor Tutorial Preliminary Information 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Copyright 2004 Altera Corporation. All rights
Stratix II FPGA Family
 October 2008, ver. 2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the
October 2008, ver. 2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Stratix II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the
RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function
 RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function April 2005, MegaCore version 2.2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.2.1 of the RapidIO Physical
RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function April 2005, MegaCore version 2.2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.2.1 of the RapidIO Physical
AN423: Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver
 AN423: Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver June 2008, version 1.1 Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver configures Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) in passive
AN423: Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver June 2008, version 1.1 Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver configures Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) in passive
Recommended Protocol Configurations for Stratix IV GX FPGAs
 Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices
 Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
Quad-Serial Configuration (EPCQ) Devices Datasheet
 2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
2016.05.30 CF52012 Subscribe This datasheet describes quad-serial configuration (EPCQ) devices. EPCQ is an in-system programmable NOR flash memory. Supported Devices Table 1: Supported Altera EPCQ Devices
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller December 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller December 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller October 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.0 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.0 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller October 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.0 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.0 contain the following information: System
PCI Express Compiler. System Requirements. New Features & Enhancements
 April 2006, Compiler Version 2.1.0 Release Notes These release notes for the PCI Express Compiler version 2.1.0 contain the following information: System Requirements New Features & Enhancements Errata
April 2006, Compiler Version 2.1.0 Release Notes These release notes for the PCI Express Compiler version 2.1.0 contain the following information: System Requirements New Features & Enhancements Errata
RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function
 RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function November 2006, MegaCore Version 1.0.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore function version
RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function November 2006, MegaCore Version 1.0.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore function version
Simultaneous Multi-Mastering with the Avalon Bus
 Simultaneous Multi-Mastering with the Avalon Bus April 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 184 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor version 2.1 supports an enhanced
Simultaneous Multi-Mastering with the Avalon Bus April 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 184 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor version 2.1 supports an enhanced
UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function
 UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function October 2005, Version 2.5.0 Release Notes These release notes for the UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore function contain the following information: System Requirements
UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function October 2005, Version 2.5.0 Release Notes These release notes for the UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore function contain the following information: System Requirements
Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded
 Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded Logic Analyzer January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 280 Introduction The SignalTap II embedded logic analyzer, available exclusively in the Altera
Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded Logic Analyzer January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 280 Introduction The SignalTap II embedded logic analyzer, available exclusively in the Altera
Nios II Performance Benchmarks
 Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface. Introduction. EBI Characteristics
 Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface October 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 143 Introduction In the Excalibur family of devices, an ARM922T processor, memory and peripherals are embedded
Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface October 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 143 Introduction In the Excalibur family of devices, an ARM922T processor, memory and peripherals are embedded
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software
 Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software AN-370-3.2 Application Note Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution for
Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software AN-370-3.2 Application Note Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution for
White Paper AHB to Avalon & Avalon to AHB Bridges
 White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
Video and Image Processing Suite
 Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices
 Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices ES-1035-2.5 Errata Sheet Table 1. Device Issues (Part 1 of 2) This errata sheet provides information about known issues affecting Cyclone V devices. Table 1 lists the
Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices ES-1035-2.5 Errata Sheet Table 1. Device Issues (Part 1 of 2) This errata sheet provides information about known issues affecting Cyclone V devices. Table 1 lists the
8. Remote System Upgrades with Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices
 8. Remote System Upgrades with Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52008-4.5 Introduction System designers today face difficult challenges such as shortened design cycles, evolving standards, and system
8. Remote System Upgrades with Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52008-4.5 Introduction System designers today face difficult challenges such as shortened design cycles, evolving standards, and system
El Camino Training - Engineering - Consultancy
 El Camino Training - Engineering - Consultancy SD/MMC Loader FPGA Configuration IP General Description As Altera introduces higher-density programmable logic devices (PLDs) to the market, the size of the
El Camino Training - Engineering - Consultancy SD/MMC Loader FPGA Configuration IP General Description As Altera introduces higher-density programmable logic devices (PLDs) to the market, the size of the
CORDIC Reference Design. Introduction. Background
 CORDIC Reference Design June 2005, ver. 1.4 Application Note 263 Introduction The co-ordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) reference design implements the CORDIC algorithm, which converts cartesian
CORDIC Reference Design June 2005, ver. 1.4 Application Note 263 Introduction The co-ordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) reference design implements the CORDIC algorithm, which converts cartesian
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in V-series FPGA Devices User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in V-series FPGA Devices User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 CvP Overview Contents Overview... 1-1
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in V-series FPGA Devices User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 CvP Overview Contents Overview... 1-1
3. Serial Configuration Devices (EPCS1, EPCS4, EPCS16, EPCS64, and EPCS128) Data Sheet
 June 2011 C51014-3.4 3. Serial Configuration Devices (EPCS1, EPCS4, EPCS16, EPCS64, and EPCS128) Data Sheet C51014-3.4 Features The serial configuration devices provide the following features: 1-, 4-,
June 2011 C51014-3.4 3. Serial Configuration Devices (EPCS1, EPCS4, EPCS16, EPCS64, and EPCS128) Data Sheet C51014-3.4 Features The serial configuration devices provide the following features: 1-, 4-,
SONET/SDH Compiler. Introduction. SONET/SDH Compiler v2.3.0 Issues
 January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
AN 370: Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software
 AN 370: Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software April 2009 AN-370-3.1 Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution
AN 370: Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software April 2009 AN-370-3.1 Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution
Implementing the Top Five Control-Path Applications with Low-Cost, Low-Power CPLDs
 Implementing the Top Five Control-Path Applications with Low-Cost, Low-Power CPLDs WP-01146-1.2 White Paper Since their introduction in the mid-1980s and across all end markets, CPLDs have been design
Implementing the Top Five Control-Path Applications with Low-Cost, Low-Power CPLDs WP-01146-1.2 White Paper Since their introduction in the mid-1980s and across all end markets, CPLDs have been design
Video Input Daughter Card Reference Manual
 Video Input Daughter Card Reference Manual 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Document Version 1.0 Document Date November 2006 Copyright 2006 Altera Corporation.
Video Input Daughter Card Reference Manual 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 http://www.altera.com Document Version 1.0 Document Date November 2006 Copyright 2006 Altera Corporation.
Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs
 Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs December 2000, ver. 1 Application Note Introduction The Excalibur embedded processor devices achieve a new level of system integration from the inclusion
Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs December 2000, ver. 1 Application Note Introduction The Excalibur embedded processor devices achieve a new level of system integration from the inclusion
HPS SoC Boot Guide - Cyclone V SoC Development Kit
 2014.07.03 AN-709 Subscribe Introduction This document describes the available boot stages and source modes for both the HPS and FPGA fabric. The boot sequence is a multi-stage process, where each stage
2014.07.03 AN-709 Subscribe Introduction This document describes the available boot stages and source modes for both the HPS and FPGA fabric. The boot sequence is a multi-stage process, where each stage
Nios Embedded Processor Development Board
 Nios Embedded Processor Development Board July 2003, ver. 2.2 Data Sheet Introduction Development Board Features Functional Overview This data sheet describes the features and functionality of the Nios
Nios Embedded Processor Development Board July 2003, ver. 2.2 Data Sheet Introduction Development Board Features Functional Overview This data sheet describes the features and functionality of the Nios
NIOS II Processor Booting Methods In MAX 10 Devices
 2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
Using the Parallel Flash Loader with the Quartus II Software
 Using the Parallel Flash Loader with the Quartus II Software May 2008, ver. 4.1 Application Note 386 Introduction With the density of FPGAs increasing, the need for larger configuration storage is also
Using the Parallel Flash Loader with the Quartus II Software May 2008, ver. 4.1 Application Note 386 Introduction With the density of FPGAs increasing, the need for larger configuration storage is also
Intel Cyclone 10 LP Device Family Pin Connection Guidelines
 Intel Cyclone 10 LP Device Family Pin Connection Guidelines Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Intel Cyclone 10 LP Pin Connection Guidelines...4 Clock and
Intel Cyclone 10 LP Device Family Pin Connection Guidelines Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Intel Cyclone 10 LP Pin Connection Guidelines...4 Clock and
Nios DMA. General Description. Functional Description
 Nios DMA January 2003, Version 1.1 Data Sheet General Functional The Nios DMA module is an Altera SOPC Builder library component included in the Nios development kit. The DMA module allows for efficient
Nios DMA January 2003, Version 1.1 Data Sheet General Functional The Nios DMA module is an Altera SOPC Builder library component included in the Nios development kit. The DMA module allows for efficient
Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral
 Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral March 2001, ver. 1.1 Data Sheet General Description The Nios universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter UART implements simple RS-232 asynchronous transmit and
Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral March 2001, ver. 1.1 Data Sheet General Description The Nios universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter UART implements simple RS-232 asynchronous transmit and
Arria II GX FPGA Development Board
 Arria II GX FPGA Development Board DDR2 SODIMM Interface 2011 Help Document DDR2 SODIMM Interface Measurements were made on the DDR2 SODIMM interface using the Board Test System user interface. The Address,
Arria II GX FPGA Development Board DDR2 SODIMM Interface 2011 Help Document DDR2 SODIMM Interface Measurements were made on the DDR2 SODIMM interface using the Board Test System user interface. The Address,
White Paper Performing Equivalent Timing Analysis Between Altera Classic Timing Analyzer and Xilinx Trace
 Introduction White Paper Between Altera Classic Timing Analyzer and Xilinx Trace Most hardware designers who are qualifying FPGA performance normally run bake-off -style software benchmark comparisons
Introduction White Paper Between Altera Classic Timing Analyzer and Xilinx Trace Most hardware designers who are qualifying FPGA performance normally run bake-off -style software benchmark comparisons
Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide
 Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version 8. Document Version: 2. Document Date: June 28
Error Correction Code (ALTECC_ENCODER and ALTECC_DECODER) Megafunctions User Guide 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version 8. Document Version: 2. Document Date: June 28
MILITARY ANTI-TAMPERING SOLUTIONS USING PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC
 MILITARY ANTI-TAMPERING SOLUTIONS USING PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC Charlie Jenkins (Altera, San Jose, California, chjenkin@altera.com) Christian Plante (Altera, San Jose, California, cplante@altera.com) ABSTRACT
MILITARY ANTI-TAMPERING SOLUTIONS USING PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC Charlie Jenkins (Altera, San Jose, California, chjenkin@altera.com) Christian Plante (Altera, San Jose, California, cplante@altera.com) ABSTRACT
Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs
 Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs AN-630-1.0 Application Note This application note describes the real-time in-system programmability (ISP) and ISP Clamp programming modes and their usage in
Real-Time ISP and ISP Clamp for Altera CPLDs AN-630-1.0 Application Note This application note describes the real-time in-system programmability (ISP) and ISP Clamp programming modes and their usage in
AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Serial Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software
 AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader IP Core
AN 370: Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader with the Intel Quartus Prime Software Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Using the Intel FPGA Flash Loader IP Core
9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices
 February 2011 SIV51009-3.2 9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices SIV51009-3.2 This chapter describes hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their implementation
February 2011 SIV51009-3.2 9. Hot Socketing and Power-On Reset in Stratix IV Devices SIV51009-3.2 This chapter describes hot-socketing specifications, power-on reset (POR) requirements, and their implementation
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models
 Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models August 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models August 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
ASMI Parallel II Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1.... 3 1.1. Ports...4 1.2.
Section 3. System Integration
 Section 3. System Integration This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 9, Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in the Cyclone III Device Family Chapter 10, Hot-Socketing
Section 3. System Integration This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 9, Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in the Cyclone III Device Family Chapter 10, Hot-Socketing
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide
 Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Altera ASMI Parallel II IP Core User Guide UG-20068 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1... 3 1.1 Ports...4 1.2 Parameters... 5
Table 1 shows the issues that affect the FIR Compiler v7.1.
 May 2007, Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera, v7.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera MegaCore function
May 2007, Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera, v7.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera MegaCore function
