Verification and Validation
|
|
|
- Lawrence Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 COMP 201 web-page: Verification and Validation 1
2 Verification and Validation Ensuring that a software system meets a user's needs 2
3 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V & V To explain static analysis as a verification technique To describe the Cleanroom software development process 3
4 Verification vs Validation Verification: "Are we building the product right" The software should conform to its specification Validation: "Are we building the right product" The software should do what the user really requires 4
5 Verification vs Validation Verification should check the program meets its specification as written in the requirements document for example. This may involve checking that it meets it functional and non-functional requirements Validation ensures that the product meets the customers expectations This goes beyond checking it meets its specification; as we have seen, system specifications don t always accurately reflect the real needs of users 5
6 The Verification & Validation Process As a whole life-cycle process - V & V must be applied at each stage in the software process. Has two principal objectives The discovery of defects in a system The assessment of whether or not the system is usable in an operational situation. 6
7 Static and Dynamic Verification Software inspections Concerned with analysis of the static system representation to discover problems (static verification) May be supplement by tool-based document and code analysis Software testing Concerned with exercising and observing product behaviour (dynamic verification) The system is executed with test data and its operational behaviour is observed 7
8 An Example of Bad Code public class Temperature { // constructor public Temperature(double inittemp) { x = inittemp; } // calctgrd function to calc. the value of a T gradiant public double calctgrd(float ZVAL) { float a = x * x; a = a * ZVAL * ; return a; } public double x; } 8
9 Static and Dynamic Verification System testing is only possible when an executable version of the program is available This is therefore an advantage of incremental development since a testable version of the system is available at a fairly early stage New functionality can be checked as it is added to the system and we can perform regression testing (we will talk about this in a few slides time) Real data can be used as input to the system and we try to observe any anomalies in the output 9
10 Static and Dynamic V&V Static verification Requirements specification High-level design Formal specification Detailed design Program Prototype Dynamic validation 10
11 Program Testing Can reveal the presence of errors NOT their absence!!! A successful test is a test which discovers one or more errors Program testing is the only validation technique for non-functional requirements Should be used in conjunction with static verification to provide full V&V coverage 11
12 Types of Testing Defect testing Tests designed to discover system defects. A successful defect test is one which reveals the presence of defects in a system. Statistical testing Tests designed to reflect the frequency of user inputs. Used for reliability estimation. 12
13 Verification & Validation Goals Verification and validation should establish a degree of confidence that the software is fit for purpose This does NOT mean completely free of defects The degree of confidence required depends upon several different factors as we see on the next slide 13
14 Verification & Validation Goals Software function A much higher level of confidence that the system is fit for purpose is required for safety critical systems that for prototype systems for example User expectations Users sometimes have a low expectation of software and are willing to tolerate some system failures (although this is decreasing) Marketing environment Competing programs must be taken into account and the required schedule for introducing the product to market. Cheaper products may be expected to have more faults. 14
15 Testing and Debugging Defect testing and debugging are distinct processes (!) Verification and validation is concerned with establishing the existence of defects in a program Debugging is concerned with (!!) Debugging involves - locating and - repairing these errors formulating a hypothesis about program behaviour then testing these hypotheses to find the system error 15
16 Testing and Debugging There is no simple process for debugging and it often involves looking for patterns in test outputs with defects and using a programmers skill to locate the error Question: Recall the programs you have written in Java for example so far. Were there errors in early versions? How did you discover them and fix them? Were they syntactic or semantic errors? Interactive debuggers provide a special run-time environment with access to the symbol table and program variables to aid error location. You can also step-through the program line by line 16
17 More Incorrect Code! public class Temperature { // calctgrd function to calc. the value of a T gradient public double calctgrd(float ZVAL) { } int a = (int) x * x if(a = 1) x = ZVAL * ; return a; } public double x; Syntax error (missing semicolon) Semantic error (should use double equals) 17
18 Syntax and Semantic Errors A syntax error should be caught by the compiler which will (usually) indicate the location the error occurred in and the type of error. A semantic error (also called a logical error) can occur in a program which compiles and runs, but produces incorrect output on some (or all) input (e.g. An incorrect algorithm or mistake in a formulae etc.) Semantic errors are often harder to detect since the compiler may not be able to indicate where/what the problem is. 18
19 Testing and Debugging Once errors are located, it is necessary to correct the program code and re-test the program Regression testing after fixing a defect, it is advisable to retest the program with all previous test data to make sure the fix has not introduced new problems This is not always feasible due to costs Experience has shown that a large proportion of fault repairs introduce new errors or are incomplete 19
20 The Debugging Process Test results Specification Test cases Locate error Design error repair Repair error Re-test program 20
21 V & V Planning Careful planning is required to get the most out of testing and inspection processes Planning should start early in the development process The plan should identify the balance between static verification and testing Test planning is about defining standards for the testing process rather than describing product tests 21
22 The V-model of Development Requir ements specification System specification System design Detailed design Acceptance test plan System integration test plan Sub-system integration test plan Module and unit code and tess Service Acceptance test System integration test Sub-system integration test This diagram shows how test plans should be derived from the system specification and design. 22
23 The Structure of a Software Test Plan The testing process - a description of the major phases of the testing process Requirements traceability testing should ensure that all requirements are individually tested Tested items Specify the products of the software process to be tested Testing schedule An overall schedule for the testing of the software is required and resources (time and personnel) must be allocated as part of the general project schedule 23
24 The Structure of a Software Test Plan Test recording procedures The results of tests must be systematically recorded, it is not enough to simply run the tests. This allows an audit of the testing process to check it has been carried out correctly (imagine a safety critical system; procedures for auditing the tests are often necessary) Hardware and software requirements This part of the document sets out a list of software tools required and the estimated hardware utilisation Constraints Any constraints affecting the testing process should be anticipated in this section 24
25 Software Inspections Involve people examining the source representation with the aim of discovering anomalies and defects Does not require execution of a system so it may be used before the implementation phase May be applied to any representation of the system (requirements, design, test data, etc.) Very effective technique for discovering errors 25
26 Software Inspections Incomplete versions of the system can be inspected without additional costs specialised test harnesses that work on only a part of the program are not required As well as program defects, inspections can consider broader quality attributes such as compliance with standards, portability and maintainability Poor programming style and inefficiencies can be found which could make the system difficult to maintain and update 26
27 Inspection Success Many different defects may be discovered in a single inspection, there is no interaction between errors to be concerned with. In testing, one defect, may mask another, so several executions are required They reuse domain and programming knowledge so reviewers are likely to have seen the types of error that commonly arise 27
28 Inspections and Testing Inspections and testing are complementary and not opposing verification techniques Both should be used during the V & V process Inspections can check conformance with a specification but not conformance with the customer s real requirements Also inspections cannot check non-functional characteristics such as performance, usability, etc. (Emergent properties). 28
29 Lecture Key Points Verification and validation are not the same thing. Verification shows conformance with specification; Validation shows that the program meets the customer s needs Test plans should be drawn up to guide the testing process. Program inspections are very effective in discovering errors Different types of systems and software development processes require different levels of verification and validation 29
Verification and Validation. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1
 Verification and Validation 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V & V To
Verification and Validation 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V & V To
Verification and Validation. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1
 Verification and Validation Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1 Verification vs validation Verification: "Are we building the product right?. The software should
Verification and Validation Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1 Verification vs validation Verification: "Are we building the product right?. The software should
Part 5. Verification and Validation
 Software Engineering Part 5. Verification and Validation - Verification and Validation - Software Testing Ver. 1.7 This lecture note is based on materials from Ian Sommerville 2006. Anyone can use this
Software Engineering Part 5. Verification and Validation - Verification and Validation - Software Testing Ver. 1.7 This lecture note is based on materials from Ian Sommerville 2006. Anyone can use this
Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1
 Verification and Validation Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V
Verification and Validation Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V
Verification and Validation
 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 19 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification
Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 19 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification
ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού
 ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2008 ΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 18-19: Έλεγχος και Πιστοποίηση Λειτουργίας ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙ ΗΣ Λέκτορας ΗΜΜΥ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) [Προσαρμογή από Ian Sommerville, Software
ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2008 ΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 18-19: Έλεγχος και Πιστοποίηση Λειτουργίας ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙ ΗΣ Λέκτορας ΗΜΜΥ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) [Προσαρμογή από Ian Sommerville, Software
Objectives. Chapter 19. Verification vs. validation. Topics covered. Static and dynamic verification. The V&V process
 Objectives Chapter 19 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s need are to introduce software verification and validation (V&V) and to discuss the distinction between
Objectives Chapter 19 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s need are to introduce software verification and validation (V&V) and to discuss the distinction between
Ingegneria del Software II academic year: Course Web-site: [www.di.univaq.it/ingegneria2/]
![Ingegneria del Software II academic year: Course Web-site: [www.di.univaq.it/ingegneria2/] Ingegneria del Software II academic year: Course Web-site: [www.di.univaq.it/ingegneria2/]](/thumbs/72/67051960.jpg) Course: Ingegneria del Software II academic year: 2004-2005 Course Web-site: [www.di.univaq.it/ingegneria2/] Verification and Validation Lecturer: Henry Muccini and Vittorio Cortellessa Computer Science
Course: Ingegneria del Software II academic year: 2004-2005 Course Web-site: [www.di.univaq.it/ingegneria2/] Verification and Validation Lecturer: Henry Muccini and Vittorio Cortellessa Computer Science
Verification and Validation. Assuring that a software system meets a user s needs. Verification vs Validation. The V & V Process
 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s needs Ian Sommerville 1995/2000 (Modified by Spiros Mancoridis 1999) Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapters 19,20 Slide 1
Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s needs Ian Sommerville 1995/2000 (Modified by Spiros Mancoridis 1999) Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapters 19,20 Slide 1
Lecture 15 Software Testing
 Lecture 15 Software Testing Includes slides from the companion website for Sommerville, Software Engineering, 10/e. Pearson Higher Education, 2016. All rights reserved. Used with permission. Topics covered
Lecture 15 Software Testing Includes slides from the companion website for Sommerville, Software Engineering, 10/e. Pearson Higher Education, 2016. All rights reserved. Used with permission. Topics covered
Aerospace Software Engineering
 16.35 Aerospace Software Engineering Verification & Validation Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Would You...... trust a completely-automated nuclear power plant?... trust a completely-automated
16.35 Aerospace Software Engineering Verification & Validation Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Would You...... trust a completely-automated nuclear power plant?... trust a completely-automated
Verification and Validation
 Steven Zeil February 13, 2013 Contents 1 The Process 3 1 2 Non-Testing V&V 7 2.1 Code Review....... 8 2.2 Mathematically-based verification......................... 19 2.3 Static analysis tools... 23 2.4
Steven Zeil February 13, 2013 Contents 1 The Process 3 1 2 Non-Testing V&V 7 2.1 Code Review....... 8 2.2 Mathematically-based verification......................... 19 2.3 Static analysis tools... 23 2.4
Verification and Validation
 Steven Zeil February 13, 2013 Contents 1 The Process 2 2 Non-Testing V&V 3 2.1 Code Review........... 4 2.2 Mathematically-based verification.................................. 8 2.3 Static analysis tools.......
Steven Zeil February 13, 2013 Contents 1 The Process 2 2 Non-Testing V&V 3 2.1 Code Review........... 4 2.2 Mathematically-based verification.................................. 8 2.3 Static analysis tools.......
Software Testing. Software Testing
 Software Testing Software Testing Error: mistake made by the programmer/ developer Fault: a incorrect piece of code/document (i.e., bug) Failure: result of a fault Goal of software testing: Cause failures
Software Testing Software Testing Error: mistake made by the programmer/ developer Fault: a incorrect piece of code/document (i.e., bug) Failure: result of a fault Goal of software testing: Cause failures
Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering. Faculty of Computing Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
 Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering Faculty of Computing Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 2016 Software Engineering 2 Recap on SDLC Phases & Artefacts Domain Analysis
Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering Faculty of Computing Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 2016 Software Engineering 2 Recap on SDLC Phases & Artefacts Domain Analysis
Verification and Validation. Verification and validation
 Verification and Validation Verification and validation Verification and Validation (V&V) is a whole life-cycle process. V&V has two objectives: Discovery of defects, Assessment of whether or not the system
Verification and Validation Verification and validation Verification and Validation (V&V) is a whole life-cycle process. V&V has two objectives: Discovery of defects, Assessment of whether or not the system
Chapter 8. Achmad Benny Mutiara
 Chapter 8 SOFTWARE-TESTING STRATEGIES Achmad Benny Mutiara amutiara@staff.gunadarma.ac.id 8.1 STATIC-TESTING STRATEGIES Static testing is the systematic examination of a program structure for the purpose
Chapter 8 SOFTWARE-TESTING STRATEGIES Achmad Benny Mutiara amutiara@staff.gunadarma.ac.id 8.1 STATIC-TESTING STRATEGIES Static testing is the systematic examination of a program structure for the purpose
Chapter 8 Software Testing. Chapter 8 Software testing
 Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered Introduction to testing Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing Test-driven development as interleave approach.
Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered Introduction to testing Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing Test-driven development as interleave approach.
Software Testing. Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18
 Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Software Testing 1 Defect Testing Defect testing involves
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Software Testing 1 Defect Testing Defect testing involves
In this Lecture you will Learn: Testing in Software Development Process. What is Software Testing. Static Testing vs.
 In this Lecture you will Learn: Testing in Software Development Process Examine the verification and validation activities in software development process stage by stage Introduce some basic concepts of
In this Lecture you will Learn: Testing in Software Development Process Examine the verification and validation activities in software development process stage by stage Introduce some basic concepts of
The requirements engineering process
 3 rd Stage Lecture time: 8:30-12:30 AM Instructor: Ali Kadhum AL-Quraby Lecture No. : 5 Subject: Software Engineering Class room no.: Department of computer science Process activities The four basic process
3 rd Stage Lecture time: 8:30-12:30 AM Instructor: Ali Kadhum AL-Quraby Lecture No. : 5 Subject: Software Engineering Class room no.: Department of computer science Process activities The four basic process
Topics in Software Testing
 Dependable Software Systems Topics in Software Testing Material drawn from [Beizer, Sommerville] Software Testing Software testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and represents the
Dependable Software Systems Topics in Software Testing Material drawn from [Beizer, Sommerville] Software Testing Software testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and represents the
Software Quality. Richard Harris
 Software Quality Richard Harris Part 1 Software Quality 143.465 Software Quality 2 Presentation Outline Defining Software Quality Improving source code quality More on reliability Software testing Software
Software Quality Richard Harris Part 1 Software Quality 143.465 Software Quality 2 Presentation Outline Defining Software Quality Improving source code quality More on reliability Software testing Software
Lecture 26: Testing. Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall Dr. Jamie Payton
 Lecture 26: Testing Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Dec. 9, 2008 Verification vs validation Verification:
Lecture 26: Testing Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Dec. 9, 2008 Verification vs validation Verification:
Advanced Software Engineering: Software Testing
 Advanced Software Engineering: Software Testing COMP 3705(L4) Sada Narayanappa Anneliese Andrews Thomas Thelin Carina Andersson Web: http://www.megadatasys.com Assisted with templates News & Project News
Advanced Software Engineering: Software Testing COMP 3705(L4) Sada Narayanappa Anneliese Andrews Thomas Thelin Carina Andersson Web: http://www.megadatasys.com Assisted with templates News & Project News
Software Engineering 2 A practical course in software engineering. Ekkart Kindler
 Software Engineering 2 A practical course in software engineering Quality Management Main Message Planning phase Definition phase Design phase Implem. phase Acceptance phase Mainten. phase 3 1. Overview
Software Engineering 2 A practical course in software engineering Quality Management Main Message Planning phase Definition phase Design phase Implem. phase Acceptance phase Mainten. phase 3 1. Overview
Three General Principles of QA. COMP 4004 Fall Notes Adapted from Dr. A. Williams
 Three General Principles of QA COMP 4004 Fall 2008 Notes Adapted from Dr. A. Williams Software Quality Assurance Lec2 1 Three General Principles of QA Know what you are doing. Know what you should be doing.
Three General Principles of QA COMP 4004 Fall 2008 Notes Adapted from Dr. A. Williams Software Quality Assurance Lec2 1 Three General Principles of QA Know what you are doing. Know what you should be doing.
MONIKA HEINER.
 LESSON 1 testing, intro 1 / 25 SOFTWARE TESTING - STATE OF THE ART, METHODS, AND LIMITATIONS MONIKA HEINER monika.heiner@b-tu.de http://www.informatik.tu-cottbus.de PRELIMINARIES testing, intro 2 / 25
LESSON 1 testing, intro 1 / 25 SOFTWARE TESTING - STATE OF THE ART, METHODS, AND LIMITATIONS MONIKA HEINER monika.heiner@b-tu.de http://www.informatik.tu-cottbus.de PRELIMINARIES testing, intro 2 / 25
Software Testing. Software Testing. in the textbook. Chapter 8. Verification and Validation. Verification and Validation: Goals
 Software Testing in the textbook Software Testing Chapter 8 Introduction (Verification and Validation) 8.1 Development testing 8.2 Test-driven development 8.3 Release testing 8.4 User testing 1 2 Verification
Software Testing in the textbook Software Testing Chapter 8 Introduction (Verification and Validation) 8.1 Development testing 8.2 Test-driven development 8.3 Release testing 8.4 User testing 1 2 Verification
Chapter 8 Software Testing. Chapter 8 So-ware tes0ng
 Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered ² Introduction to testing ² Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing ² Test-driven development as interleave
Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered ² Introduction to testing ² Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing ² Test-driven development as interleave
An Introduction to Systematic Software Testing. Robert France CSU
 An Introduction to Systematic Software Testing Robert France CSU Why do we need to systematically test software? Poor quality products can Inconvenience direct and indirect users Result in severe financial
An Introduction to Systematic Software Testing Robert France CSU Why do we need to systematically test software? Poor quality products can Inconvenience direct and indirect users Result in severe financial
Software Quality Assurance. David Janzen
 Software Quality Assurance David Janzen What is quality? Crosby: Conformance to requirements Issues: who establishes requirements? implicit requirements Juran: Fitness for intended use Issues: Who defines
Software Quality Assurance David Janzen What is quality? Crosby: Conformance to requirements Issues: who establishes requirements? implicit requirements Juran: Fitness for intended use Issues: Who defines
Software testing. Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1
 Software testing Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1 Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles
Software testing Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1 Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles
Learning outcomes. Systems Engineering. Debugging Process. Debugging Process. Review
 Systems Engineering Lecture 9 System Verification II Dr. Joanna Bryson Dr. Leon Watts University of Bath Department of Computer Science 1 Learning outcomes After both lectures and doing the reading, you
Systems Engineering Lecture 9 System Verification II Dr. Joanna Bryson Dr. Leon Watts University of Bath Department of Computer Science 1 Learning outcomes After both lectures and doing the reading, you
INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Introduction to Software Testing d_sinnig@cs.concordia.ca Department for Computer Science and Software Engineering What is software testing? Software testing consists
INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Introduction to Software Testing d_sinnig@cs.concordia.ca Department for Computer Science and Software Engineering What is software testing? Software testing consists
Chapter 8 Software Testing
 Chapter 8 Software Testing Chapter 8 Software Testing Slide 1 Topics covered Validation vs. defect testing Inspections and testing Development testing Unit testing Component testing System testing Test-driven
Chapter 8 Software Testing Chapter 8 Software Testing Slide 1 Topics covered Validation vs. defect testing Inspections and testing Development testing Unit testing Component testing System testing Test-driven
Static and dynamic Testing
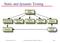 Static and dynamic Testing Static testing Requirements specification High-level design Formal specification Detailed design Program Prototype Dynamic testing Ian Sommerville 1995 Software Engineering,
Static and dynamic Testing Static testing Requirements specification High-level design Formal specification Detailed design Program Prototype Dynamic testing Ian Sommerville 1995 Software Engineering,
Chapter 11, Testing. Using UML, Patterns, and Java. Object-Oriented Software Engineering
 Chapter 11, Testing Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object-Oriented Software Engineering Outline Terminology Types of errors Dealing with errors Quality assurance vs Testing Component Testing! Unit testing!
Chapter 11, Testing Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object-Oriented Software Engineering Outline Terminology Types of errors Dealing with errors Quality assurance vs Testing Component Testing! Unit testing!
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION. Saulius Ragaišis.
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt CSC2008 SE Software Verification and Validation Learning Objectives: Distinguish between program validation
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt CSC2008 SE Software Verification and Validation Learning Objectives: Distinguish between program validation
Requirements Engineering: Specification & Validation. Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 18
 Requirements Engineering: Specification & Validation Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 18 The Problems of Requirements What goal(s) are we trying to satisfy? How do we identify the scope
Requirements Engineering: Specification & Validation Software Requirements and Design CITS 4401 Lecture 18 The Problems of Requirements What goal(s) are we trying to satisfy? How do we identify the scope
Software Engineering Lifecycles. Controlling Complexity
 Software Engineering Lifecycles Class url:http://laser.cs.umass.edu/courses/cs320.spring11/ Controlling Complexity Separation of Concerns Planning Ahead Do a little work now to make later work easier The
Software Engineering Lifecycles Class url:http://laser.cs.umass.edu/courses/cs320.spring11/ Controlling Complexity Separation of Concerns Planning Ahead Do a little work now to make later work easier The
Chapter 9. Software Testing
 Chapter 9. Software Testing Table of Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction to software testing... 1 The testers... 2 The developers... 2 An independent testing team... 2 The customer... 2 Principles of
Chapter 9. Software Testing Table of Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction to software testing... 1 The testers... 2 The developers... 2 An independent testing team... 2 The customer... 2 Principles of
Overview. State-of-the-Art. Relative cost of error correction. CS 619 Introduction to OO Design and Development. Testing.
 Overview CS 619 Introduction to OO Design and Development ing! Preliminaries! All sorts of test techniques! Comparison of test techniques! Software reliability Fall 2012! Main issues: There are a great
Overview CS 619 Introduction to OO Design and Development ing! Preliminaries! All sorts of test techniques! Comparison of test techniques! Software reliability Fall 2012! Main issues: There are a great
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 9-Software Testing, Verification and Validation
 Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 9-Software Testing, Verification and Validation Yan Shi SE 2730 Lecture Notes Verification and Validation Verification: Are
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 9-Software Testing, Verification and Validation Yan Shi SE 2730 Lecture Notes Verification and Validation Verification: Are
Lecture 9. Verification and Validation. Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs. Tutorial Questions. Verification and Validation
 ICT 381 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Lance Fung School of Information Technology Lecture 9 Verification and Validation Ref: Sommerville I., Software Engineering, 6th Edition, Chapter 19 Slide 1 Slide 2 Tutorial
ICT 381 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Lance Fung School of Information Technology Lecture 9 Verification and Validation Ref: Sommerville I., Software Engineering, 6th Edition, Chapter 19 Slide 1 Slide 2 Tutorial
Software Processes. Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1
 Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
Software Processes Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 4 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software process models To describe three generic process models and when they may be
Verification and Validation
 Verification and Validation Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics Covered 1. Verification and Validation 2. Software Inspections 3. Automated Static Analysis 4. Verification and Formal Methods 2 2 1. Verification
Verification and Validation Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics Covered 1. Verification and Validation 2. Software Inspections 3. Automated Static Analysis 4. Verification and Formal Methods 2 2 1. Verification
Introduction to Software Engineering
 Introduction to Software Engineering Gérald Monard Ecole GDR CORREL - April 16, 2013 www.monard.info Bibliography Software Engineering, 9th ed. (I. Sommerville, 2010, Pearson) Conduite de projets informatiques,
Introduction to Software Engineering Gérald Monard Ecole GDR CORREL - April 16, 2013 www.monard.info Bibliography Software Engineering, 9th ed. (I. Sommerville, 2010, Pearson) Conduite de projets informatiques,
Software Engineering
 Software Engineering Lecture 13: Testing and Debugging Testing Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2014 Recap Recap Testing detect the presence of bugs by observing failures Recap Testing
Software Engineering Lecture 13: Testing and Debugging Testing Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2014 Recap Recap Testing detect the presence of bugs by observing failures Recap Testing
CMSC 435: Software Engineering Section 0201
 CMSC 435: Software Engineering Section 0201 Atif M. Memon (atif@cs.umd.edu) 4115 A.V.Williams building Phone: 301-405-3071 Office hours Tu.Th. (11:00am-1:00pm) Don t wait, don t hesitate, do communicate!!
CMSC 435: Software Engineering Section 0201 Atif M. Memon (atif@cs.umd.edu) 4115 A.V.Williams building Phone: 301-405-3071 Office hours Tu.Th. (11:00am-1:00pm) Don t wait, don t hesitate, do communicate!!
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies
 CODING Good software development organizations normally require their programmers to follow some welldefined and standard style of coding called coding standards. Most software development organizations
CODING Good software development organizations normally require their programmers to follow some welldefined and standard style of coding called coding standards. Most software development organizations
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. Software Specification Software Design and Implementation Software Validation. Peter Mileff PhD
 Peter Mileff PhD SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Software Specification Software Design and Implementation Software Validation University of Miskolc Department of Information Technology Software Specification...
Peter Mileff PhD SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Software Specification Software Design and Implementation Software Validation University of Miskolc Department of Information Technology Software Specification...
Examination Questions Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes
 Swedish Software Testing Board (SSTB) International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) Foundation Certificate in Software Testing Practice Exam Examination Questions 2011-10-10 Time allowed:
Swedish Software Testing Board (SSTB) International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) Foundation Certificate in Software Testing Practice Exam Examination Questions 2011-10-10 Time allowed:
Bridge Course On Software Testing
 G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
Sample Question Paper. Software Testing (ETIT 414)
 Sample Question Paper Software Testing (ETIT 414) Q 1 i) What is functional testing? This type of testing ignores the internal parts and focus on the output is as per requirement or not. Black-box type
Sample Question Paper Software Testing (ETIT 414) Q 1 i) What is functional testing? This type of testing ignores the internal parts and focus on the output is as per requirement or not. Black-box type
CS 307: Software Engineering. Lecture 10: Software Design and Architecture
 CS 307: Software Engineering Lecture 10: Software Design and Architecture Prof. Jeff Turkstra 2017 Dr. Jeffrey A. Turkstra 1 Announcements Discuss your product backlog in person or via email by Today Office
CS 307: Software Engineering Lecture 10: Software Design and Architecture Prof. Jeff Turkstra 2017 Dr. Jeffrey A. Turkstra 1 Announcements Discuss your product backlog in person or via email by Today Office
COMP220: SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT TOOLS COMP285: COMPUTER AIDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
 COMP220: SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT TOOLS COMP285: COMPUTER AIDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Sebastian Coope coopes@liverpool.ac.uk www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp220/ www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp285/ COMP 285/220
COMP220: SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT TOOLS COMP285: COMPUTER AIDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Sebastian Coope coopes@liverpool.ac.uk www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp220/ www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp285/ COMP 285/220
Recap on SDLC Phases & Artefacts. Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering
 Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering Faculty of Computing UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia Recap on SDLC Phases & Artefacts Domain Analysis @ Business Process Requirement
Topic: Software Verification, Validation and Testing Software Engineering Faculty of Computing UniversitiTeknologi Malaysia Recap on SDLC Phases & Artefacts Domain Analysis @ Business Process Requirement
Chapter 15 Debugging
 Chapter 15 Debugging Known, but unfixed errors Just ignore errors at this point. There is nothing we can do except to try to keep going. -A comment in XFS (xfs_vnodeops.c, line 1785) Error, skip block
Chapter 15 Debugging Known, but unfixed errors Just ignore errors at this point. There is nothing we can do except to try to keep going. -A comment in XFS (xfs_vnodeops.c, line 1785) Error, skip block
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
Verification and Validation
 Chapter 5 Verification and Validation Chapter Revision History Revision 0 Revision 1 Revision 2 Revision 3 Revision 4 original 94/03/23 by Fred Popowich modified 94/11/09 by Fred Popowich reorganization
Chapter 5 Verification and Validation Chapter Revision History Revision 0 Revision 1 Revision 2 Revision 3 Revision 4 original 94/03/23 by Fred Popowich modified 94/11/09 by Fred Popowich reorganization
Introduction To Software Testing. Brian Nielsen. Center of Embedded Software Systems Aalborg University, Denmark CSS
 Introduction To Software Testing Brian Nielsen bnielsen@cs.aau.dk Center of Embedded Software Systems Aalborg University, Denmark CSS 1010111011010101 1011010101110111 What is testing? Testing Testing:
Introduction To Software Testing Brian Nielsen bnielsen@cs.aau.dk Center of Embedded Software Systems Aalborg University, Denmark CSS 1010111011010101 1011010101110111 What is testing? Testing Testing:
Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming in Python.
 Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming in Python http://cis-linux1.temple.edu/~tuf80213/courses/temple/cis1051/ Overview Types of errors Testing methods Debugging in Python 2 Errors An error in
Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming in Python http://cis-linux1.temple.edu/~tuf80213/courses/temple/cis1051/ Overview Types of errors Testing methods Debugging in Python 2 Errors An error in
All the subjective part of 2011 papers solved complete reference numbers
 1 All current papers 2011 Solved papers (eagle_eye) CS504 Current data final term paper 15 FEB All the subjective part of 2011 papers solved complete reference numbers 1) Describe the the concept of cyclomatic
1 All current papers 2011 Solved papers (eagle_eye) CS504 Current data final term paper 15 FEB All the subjective part of 2011 papers solved complete reference numbers 1) Describe the the concept of cyclomatic
Sample Exam Syllabus
 ISTQB Foundation Level 2011 Syllabus Version 2.9 Release Date: December 16th, 2017. Version.2.9 Page 1 of 46 Dec 16th, 2017 Copyright 2017 (hereinafter called ISTQB ). All rights reserved. The authors
ISTQB Foundation Level 2011 Syllabus Version 2.9 Release Date: December 16th, 2017. Version.2.9 Page 1 of 46 Dec 16th, 2017 Copyright 2017 (hereinafter called ISTQB ). All rights reserved. The authors
CS 424 Software Quality Assurance & Testing LECTURE 3 BASIC CONCEPTS OF SOFTWARE TESTING - I
 LECTURE 3 BASIC CONCEPTS OF SOFTWARE TESTING - I WHAT IS SOFTWARE TESTING? Testing can find faults in the software but cannot prove that the software is error-free. OBJECTIVES OF SOFTWARE TESTING To test
LECTURE 3 BASIC CONCEPTS OF SOFTWARE TESTING - I WHAT IS SOFTWARE TESTING? Testing can find faults in the software but cannot prove that the software is error-free. OBJECTIVES OF SOFTWARE TESTING To test
Software testing. Objectives. Contents
 8 Software testing Objectives The objective of this chapter is to introduce software testing and software testing processes. When you have read the chapter, you will: understand the stages of testing from
8 Software testing Objectives The objective of this chapter is to introduce software testing and software testing processes. When you have read the chapter, you will: understand the stages of testing from
Testing. ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design. Why is testing so hard? Why do testing?
 Testing ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 24: Introduction to Software Testing and Verification What is software testing? Running a program in order to find bugs (faults,
Testing ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 24: Introduction to Software Testing and Verification What is software testing? Running a program in order to find bugs (faults,
QA Best Practices: A training that cultivates skills for delivering quality systems
 QA Best Practices: A training that cultivates skills for delivering quality systems Dixie Neilson QA Supervisor Lynn Worm QA Supervisor Maheen Imam QA Analyst Information Technology for Minnesota Government
QA Best Practices: A training that cultivates skills for delivering quality systems Dixie Neilson QA Supervisor Lynn Worm QA Supervisor Maheen Imam QA Analyst Information Technology for Minnesota Government
Main concepts to be covered. Testing and Debugging. Code snippet of the day. Results. Testing Debugging Test automation Writing for maintainability
 Main concepts to be covered Testing and Debugging Testing Debugging Test automation Writing for maintainability 4.0 Code snippet of the day public void test() { int sum = 1; for (int i = 0; i
Main concepts to be covered Testing and Debugging Testing Debugging Test automation Writing for maintainability 4.0 Code snippet of the day public void test() { int sum = 1; for (int i = 0; i
SE 2730 Final Review
 SE 2730 Final Review 1. Introduction 1) What is software: programs, associated documentations and data 2) Three types of software products: generic, custom, semi-custom Why is semi-custom product more
SE 2730 Final Review 1. Introduction 1) What is software: programs, associated documentations and data 2) Three types of software products: generic, custom, semi-custom Why is semi-custom product more
Program Correctness and Efficiency. Chapter 2
 Program Correctness and Efficiency Chapter 2 Chapter Objectives To understand the differences between the three categories of program errors To understand the effect of an uncaught exception and why you
Program Correctness and Efficiency Chapter 2 Chapter Objectives To understand the differences between the three categories of program errors To understand the effect of an uncaught exception and why you
IT323 - Software Engineering 2 1
 IT323 - Software Engineering 2 1 Explain how standards may be used to capture organizational wisdom about effective methods of software development. Suggest four types of knowledge that might be captured
IT323 - Software Engineering 2 1 Explain how standards may be used to capture organizational wisdom about effective methods of software development. Suggest four types of knowledge that might be captured
The testing process. Component testing. System testing
 Software testing Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles of system and component testing To describe strategies for generating system
Software testing Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles of system and component testing To describe strategies for generating system
XVIII. Software Testing. Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Ingegneria del Software I A.A. 2006/2007 Andrea Polini
 XVIII. Software Testing Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Objective General discussion on Testing Testing Phases Approaches to testing Structural testing Functional testing Testing non functional
XVIII. Software Testing Laurea Triennale in Informatica Corso di Objective General discussion on Testing Testing Phases Approaches to testing Structural testing Functional testing Testing non functional
Evaluation in Information Visualization. An Introduction to Information Visualization Techniques for Exploring Large Database. Jing Yang Fall 2005
 An Introduction to Information Visualization Techniques for Exploring Large Database Jing Yang Fall 2005 1 Evaluation in Information Visualization Class 3 2 1 Motivation What are the advantages and limitations
An Introduction to Information Visualization Techniques for Exploring Large Database Jing Yang Fall 2005 1 Evaluation in Information Visualization Class 3 2 1 Motivation What are the advantages and limitations
Verification and Test with Model-Based Design
 Verification and Test with Model-Based Design Flight Software Workshop 2015 Jay Abraham 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The software development process Develop, iterate and specify requirements Create high
Verification and Test with Model-Based Design Flight Software Workshop 2015 Jay Abraham 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The software development process Develop, iterate and specify requirements Create high
W.C.Uduwela. Dept. of Mathematics & Computer Science
 Software Testing W.C.Uduwela Dept. of Mathematics & Computer Science The image cann ot be displayed. Your compu ter may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been cor rup ted.
Software Testing W.C.Uduwela Dept. of Mathematics & Computer Science The image cann ot be displayed. Your compu ter may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been cor rup ted.
Software Engineering and Scientific Computing
 Software Engineering and Scientific Computing Barbara Paech, Hanna Remmel Institute of Computer Science Im Neuenheimer Feld 326 69120 Heidelberg, Germany http://se.ifi.uni-heidelberg.de paech@informatik.uni-heidelberg.de
Software Engineering and Scientific Computing Barbara Paech, Hanna Remmel Institute of Computer Science Im Neuenheimer Feld 326 69120 Heidelberg, Germany http://se.ifi.uni-heidelberg.de paech@informatik.uni-heidelberg.de
10. Software Testing Fundamental Concepts
 10. Software Testing Fundamental Concepts Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2016 Testing in Object-Oriented Point of View Error Correction Cost
10. Software Testing Fundamental Concepts Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2016 Testing in Object-Oriented Point of View Error Correction Cost
Quote by Bruce Sterling, from: A Software Testing Primer, Nick Jenkins
 Software Testing Why Test? Quote by Bruce Sterling, from: A Software Testing Primer, Nick Jenkins https://www.typemock.com/software-bugs-infographic A bug found at design time costs ten times less to fix
Software Testing Why Test? Quote by Bruce Sterling, from: A Software Testing Primer, Nick Jenkins https://www.typemock.com/software-bugs-infographic A bug found at design time costs ten times less to fix
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools. Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 15 Testing
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 15 Testing Where we are Some very basic software engineering topics in the midst of tools Today: testing (how, why, some terms) Later:
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 15 Testing Where we are Some very basic software engineering topics in the midst of tools Today: testing (how, why, some terms) Later:
Techniques for the unambiguous specification of software
 Formal Techniques for the unambiguous of software Objectives To explain why formal techniques help discover problems in system requirements To describe the use of algebraic techniques for interface To
Formal Techniques for the unambiguous of software Objectives To explain why formal techniques help discover problems in system requirements To describe the use of algebraic techniques for interface To
Architectural Design
 Architectural Design Topics i. Architectural design decisions ii. Architectural views iii. Architectural patterns iv. Application architectures Chapter 6 Architectural design 2 PART 1 ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
Architectural Design Topics i. Architectural design decisions ii. Architectural views iii. Architectural patterns iv. Application architectures Chapter 6 Architectural design 2 PART 1 ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) Software Quality Assurance
 Software Quality Assurance (SQA) Software Quality Assurance Use of analysis to validate artifacts requirements analysis design analysis code analysis and testing Technical/Document reviews Control of changes
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) Software Quality Assurance Use of analysis to validate artifacts requirements analysis design analysis code analysis and testing Technical/Document reviews Control of changes
Higher-order Testing. Stuart Anderson. Stuart Anderson Higher-order Testing c 2011
 Higher-order Testing Stuart Anderson Defining Higher Order Tests 1 The V-Model V-Model Stages Meyers version of the V-model has a number of stages that relate to distinct testing phases all of which are
Higher-order Testing Stuart Anderson Defining Higher Order Tests 1 The V-Model V-Model Stages Meyers version of the V-model has a number of stages that relate to distinct testing phases all of which are
Program Analysis And Its Support in Software Development
 Program Analysis And Its Support in Software Development Qing Yi class web site: www.cs.utsa.edu/~qingyi/cs6463 cs6463 1 A little about myself Qing Yi B.S. Shandong University, China. Ph.D. Rice University,
Program Analysis And Its Support in Software Development Qing Yi class web site: www.cs.utsa.edu/~qingyi/cs6463 cs6463 1 A little about myself Qing Yi B.S. Shandong University, China. Ph.D. Rice University,
Testing! Prof. Leon Osterweil! CS 520/620! Spring 2013!
 Testing Prof. Leon Osterweil CS 520/620 Spring 2013 Relations and Analysis A software product consists of A collection of (types of) artifacts Related to each other by myriad Relations The relations are
Testing Prof. Leon Osterweil CS 520/620 Spring 2013 Relations and Analysis A software product consists of A collection of (types of) artifacts Related to each other by myriad Relations The relations are
Regression testing. Whenever you find a bug. Why is this a good idea?
 Regression testing Whenever you find a bug Reproduce it (before you fix it!) Store input that elicited that bug Store correct output Put into test suite Then, fix it and verify the fix Why is this a good
Regression testing Whenever you find a bug Reproduce it (before you fix it!) Store input that elicited that bug Store correct output Put into test suite Then, fix it and verify the fix Why is this a good
Chapter 9 Quality and Change Management
 MACIASZEK, L.A. (2007): Requirements Analysis and System Design, 3 rd ed. Addison Wesley, Harlow England ISBN 978-0-321-44036-5 Chapter 9 Quality and Change Management Pearson Education Limited 2007 Topics
MACIASZEK, L.A. (2007): Requirements Analysis and System Design, 3 rd ed. Addison Wesley, Harlow England ISBN 978-0-321-44036-5 Chapter 9 Quality and Change Management Pearson Education Limited 2007 Topics
Lecture 15 Distributed System Architectures
 Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Lecture 15 Distributed System Architectures Architectural
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Lecture 15 Distributed System Architectures Architectural
Pearson Education 2007 Chapter 9 (RASD 3/e)
 MACIASZEK, L.A. (2007): Requirements Analysis and System Design, 3 rd ed. Addison Wesley, Harlow England ISBN 978-0-321-44036-5 Chapter 9 Quality and Change Management Pearson Education Limited 2007 Topics
MACIASZEK, L.A. (2007): Requirements Analysis and System Design, 3 rd ed. Addison Wesley, Harlow England ISBN 978-0-321-44036-5 Chapter 9 Quality and Change Management Pearson Education Limited 2007 Topics
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 COMP 201 web-page:
 Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Lecture 19 Essentials of Class Models 1 On Naming classes
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 Lecture 19 Essentials of Class Models 1 On Naming classes
Chap 2. Introduction to Software Testing
 Chap 2. Introduction to Software Testing 2.1 Software Testing Concepts and Processes 2.2 Test Management 1 2.1 Software Testing Concepts and Processes 1. Introduction 2. Testing Dimensions 3. Test Concepts
Chap 2. Introduction to Software Testing 2.1 Software Testing Concepts and Processes 2.2 Test Management 1 2.1 Software Testing Concepts and Processes 1. Introduction 2. Testing Dimensions 3. Test Concepts
Subject : Computer Science. Paper : Software Quality Management. Module : CASE Tools
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper : Software Quality Management Module : CASE Tools Module No: Quadrant 1: CS/SQM/26 e-text An increasing variety of specialized computerized tools (actually
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper : Software Quality Management Module : CASE Tools Module No: Quadrant 1: CS/SQM/26 e-text An increasing variety of specialized computerized tools (actually
CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT
 CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT AUTOMATED SOURCE CODE ANALYSIS TO MAINTAIN COMPLIANCE SIMPLIFY AND STREAMLINE CERT C++ COMPLIANCE The CERT C++ compliance module reports on dataflow problems, software defects,
CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT AUTOMATED SOURCE CODE ANALYSIS TO MAINTAIN COMPLIANCE SIMPLIFY AND STREAMLINE CERT C++ COMPLIANCE The CERT C++ compliance module reports on dataflow problems, software defects,
Model-Based Design for High Integrity Software Development Mike Anthony Senior Application Engineer The MathWorks, Inc.
 Model-Based Design for High Integrity Software Development Mike Anthony Senior Application Engineer The MathWorks, Inc. Tucson, AZ USA 2009 The MathWorks, Inc. Model-Based Design for High Integrity Software
Model-Based Design for High Integrity Software Development Mike Anthony Senior Application Engineer The MathWorks, Inc. Tucson, AZ USA 2009 The MathWorks, Inc. Model-Based Design for High Integrity Software
18-642: Software Development Processes
 18-642: Software Development Processes 9/6/2017 Coding Is Essentially 0% of Creating Software http://e.ubmelectronics.com/2013embeddedstudy/index.html 2 Old-School Waterfall Development Cycle Bugs SPECIFY
18-642: Software Development Processes 9/6/2017 Coding Is Essentially 0% of Creating Software http://e.ubmelectronics.com/2013embeddedstudy/index.html 2 Old-School Waterfall Development Cycle Bugs SPECIFY
Test design techniques
 INF3121 : Software Testing 12. 02. 2015 Lecture 4 Test design techniques Lecturer: Raluca Florea INF3121/ 12.02.2015 / Raluca Florea 1 Overview 1. The test development process 2. Categories of test design
INF3121 : Software Testing 12. 02. 2015 Lecture 4 Test design techniques Lecturer: Raluca Florea INF3121/ 12.02.2015 / Raluca Florea 1 Overview 1. The test development process 2. Categories of test design
Why testing and analysis. Software Testing. A framework for software testing. Outline. Software Qualities. Dependability Properties
 Why testing and analysis Software Testing Adapted from FSE 98 Tutorial by Michal Young and Mauro Pezze Software is never correct no matter what developing testing technique is used All software must be
Why testing and analysis Software Testing Adapted from FSE 98 Tutorial by Michal Young and Mauro Pezze Software is never correct no matter what developing testing technique is used All software must be
