Architecture, Programming and Performance of MIC Phi Coprocessor
|
|
|
- Ezra Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Architecture, Programming and Performance of MIC Phi Coprocessor JanuszKowalik, Piotr Arłukowicz Professor (ret), The Boeing Company, Washington, USA Assistant professor, Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, University of Gdańsk, Poland ABSTRACT: The article is showing the advantage of using Xeon PHI processors along with well-established technologies like MPI and OpenMP over newer but more troublesome OpenCL and GPGPU approach. The state-of-the art Xeon PHI technology is presented and brief summary about the architecture and performance is discussed. KEYWORDS: Xeon Phi, Performance, MPI, Saxpy, Vectorization I. INTRODUCTION Typical solution algorithm for scientific and technical problem is a mix of highly parallel, lowly parallel and sequential components. This led computer designers to the idea of heterogeneous computing technologies where architecturally different processors execute parts of algorithms. Two distinct heterogeneous architectures appeared between 1990 and Table 1 summarizes key features of the General Purpose Graphics Processing Units (GPGPU) and the Many Integrated Core (MIC). Table. 1. Summary of the GPGPU and the MIC technologies. Two heterogeneous computer technologies GPGPU and MIC 1990s GPGPU General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit highly parallel ACCELERATOR Devices slaves to CPU Require new programming tools: CUDA, OpenCL Intel MIC technology Many Integrated Core Xeon PHI COPROCESSOR Peer to host CPU Uses well established software development languages and tools: C, C++, Fortran, OpenMP, MPI Both technologies objective is speeding up computation but their architecture, software and program execution modes are significantly different. GPGPU highly parallel devices are accelerators whose relationship to CPU can be called the master-slave relation. On the other hand (MIC) Phi coprocessor is a peer partner of CPU that can either collaborate with CPU or execute algorithms independently alone. Intel Phi architecture is a part of the announced in 2016 new HPC initiative called the Scalable System Framework. Intel expects this framework to be a steptowards exascale computing. Copyright to IJARSET
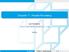
2 II. ARCHITECTURE Fig. 2. Phi coprocessor architecture The simplest architectural description of Phi coprocessor is the Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP) on a chip [1]. A slightly more precise definition is the Cache Coherent Uniform MemoryAccess (ccuma) processor. The cores are connected by a bidirectional bus shown in Fig.2. Phi clock frequency is lower than the state of the art Intel CPU and the memory size is smaller. The impressive performance of Phi comes not from clock frequency but its many core parallelism. Each core has two processing units: the scalar processing Unit (SPU) and the vector processing unit (VPU). Instruction is fetched, decoded and then executed either by SPU or VPU. Both SPU and VPU have access to scalar and vector registers, data and instruction L1 cache memories and L2 cache. The simplest heterogeneous platform with Phi contains one or two CPU processors and one Phi coprocessor. It is important to note that these processors do not share memory. They communicate via Peripheral Communication Interface express bus (PCI). This bus is relatively slow and may become a bottleneck if improperly used. Phi coprocessor is one of the most successful building blocks of large supercomputers. In November 2015 TOP-500 list contained 35 supercomputers using Phi coprocessors. Among them was the champion Tianhe-2 supercomputer in China and Stampede in the Texas Advanced Application Computing Center. Phi can be regarded as a Linux s cluster network node. This and the Phi peerage relative to host CPU justify the name coprocessor rather than accelerator although PHI can accelerate computation. Further arguments supporting the Phi status as coprocessor will be explained in the next section on Software and Programming. III. SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING The key software observation is that software stack architecture of CPU and of Phi are almost identical. This allows user to choose from several options for executing program. We discuss these options later in this section. One of the very pregnant in consequences decision made by Intel was not designing new parallel languages for Phi. Instead Intel extended existing familiar languages and accepted by the HPC community standard programming tools. The languages include: C, C++, Fortran and OpenCL [5]. Software development tools include: OpenMP [2], MPI [3], Cilk Plus [4], Thread Building Blocks (TBB) and Intel Mathematical Kernel Library (MKL). This decision positively influenced porting existing software to platforms withphi coprocessors.fig.3 illustrates porting advantage for coprocessor PHI. Copyright to IJARSET
3 Fig.3. Phi porting advantage. For the sake of fairness it should be added that GPUs have proved to be successful in application areas dealing with graphics and visualization and may be the preferred technology for corresponding users. On the other hand it might be hard for GPU to compete with the MIC technology in the application areas where OpenMP and MPI already have been used as standard tools for parallel software. Initial feedback from users who ported their OpenMP and MPI programs to computers with Phi indicates that porting has been easy and economically attractive. MIC hardware and software architectures allow users of platforms with Phi three option of using Phi coprocessor shown in Fig.4. Symmetric. Fig.4 Three options for executing programs. Here workload is divided and one part is executed on CPU and the second part on Phi. This option uses the entire platform power. An example could be an MPI application where some processes are running on CPU and other on Phi. In this case the programmer should ensure well balanced workloads keeping in mind the CPU and Phi performance differences. Offload. In This option the code is compiled and executed on CPU but some highly parallel parts of the algorithm are offloaded to the Phi coprocessor. Offload is somewhat similar to the GPU style of computing. Copyright to IJARSET
4 Native. Phi coprocessor working alone. The code is compiled and executed on Phi coprocessor. This option is very fast for codes that are uniformly highly parallel. The offload option has two cases: firstly non-shared memory case for applications with bitwise capable data such as arrays and scalars and secondly virtual shared memory case for problems with complex data structures using pointers such as trees and linked lists. Two cases are shown in Fig. 5. Fig. 5. Two offload cases. Most common data types in scientific and technical application are scalars and arrays so we can use the non-shared memory case. In non-shared memory case the data are transferred between CPU and Phi via PCI. To minimize the communication penalty we minimize the ratio of transferred data size to the amount of computation. An example of favorable ratio is, if transferring n data items to Phi is followed by executing n-square operations. Consider for instance computation of matrix/vector product. If matrix A is stored in Phi then transferring vector v from CPU to Phi and computing the Av product would satisfy the desired property of minimizing ratio of transfer to computation. VI. PERFORMANCE A helpful hint how we should use a heterogeneous platform. With Phi is provided by Fig.6 showing performance of CPU and Phi as functions of used threads. Fig.6. CPU (blue) and Phi (red) performance The central idea of using heterogeneous computer is assigning parts of code to processors that execute them best. In this spirit I/O, sequential and lowly parallel tasks should be assigned to CPU. Phi coprocessor is best for highly parallel tasks. Obvious assignment cases include: a) run uniformly highly parallel code on Phi coprocessor alone. b) small problems that do not scale up to using about cores should use CPU c) for problems that have well defined highly parallel components consider offload. For some algorithms choosing offload versus native execution option requires a trade-off consideration. Offload needs data transfer reducing performance but each device is working optimally. On the other hand the native option Copyright to IJARSET
5 eliminates data transfer but some scalar or lowly parallel tasks have to be executed by Phi coprocessor that performs best for highly parallel tasks. In general it is recommended to involve all cores with each core running at least two threads. This advice boils down to using at least 100 threads total. Published results of benchmark testing and real applications fully support this recommendation. This rule has been termed the scaling rule by Intel researchers [1]. They demonstrated that scaling is not sufficient for achieving optimal Phi performance of 1 TeraFlops for double precision. The second required key performance factor is vectorization. V. VECTORIZATION Vectorization is a group of data of the same type than is processed by a single operation. Vectorization is also called the Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD). In Phi coprocessor vectorization is using the data parallel engines VPU that perform SIMD operations. The Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors vector engine VPU supports 512-bit vector width. The vector instructions mean performing 16 single precision or 8 double precision arithmetic operations simultaneously. The performance boost that vectorization offers is a key to the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor speed. Intel research documents suggest that if the application is not bandwidth limited, the best use of Intel Xeon Phi is when most operations are vector instructions. Very fortunately many algorithms for solving scientific and engineering problems use extensively linear algebra containing vector operations. Several examples of linear algebra SIMD operations are listed below 1. Sum of two vectors z[i]=x[i]+y[i] 2. Vector triad d[i]=a[i]+b[i]*c[i] 3. Saxpy y[i]=a*x[i]+y[i] 4. Dot product is SIMD followed by reduction a[1]*b[1] +a[2]*b[2] Euclidean norm 1 2 = i v 6. Matrix/vector product has two loops. The external loop can be parallelized. The internal loop is vectorizable. 7. Matrix/matrix product. 8. Matrix LU decomposition for solving general linear equations. 9. The Conjugate Gradient Method (CGM) The Conjugate Gradient Method for solving linear equations with positive definite matrices is fully vectorizable. Every iteration of CGM contains one matrix/vector product, two vector dot products and three Saxpy operations. All these operations are vectorizable using SIMD instructions.there are several requirements for vectorizing a loop: 1. The number of loop iterations is countable 2. The loop consists of a single block without jumps or branches 3. The Block has single entry and exit 4. There are no function calls inside the block except the vectorized common mathematical functions such as sin, cos, sqrt etc. Copyright to IJARSET
6 A block satisfying these requirements is regarded as a single instruction and it is executed in parallel as SIMD. Below is an example of SIMD block. void example(double*a, double*b, double*c, double*d, int n){ int i; #pragmasimd for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { a[i] = c[i] * d[i]; b[i] = c[i] d[i]; } } Obstacles to vectorization include: noncontiguous data access in memory, indirect addressing, and data dependency. REFERENCES. [1]J.Jeffers and J.Reinders Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor High Performance Programming Elsevier and Morgan Kaufmann [2]B.Chapman, G. Jost and R. van der Pas, Using OpenMP, The MIT Press [3]W.Gropp, E.Lusk and A.Skjellum, Using MPI, The MIT Press [4]A.D.Robinson Parallel Programming with CilkPlus Intel document [5]J.Kowalik and T.Puzniakowski Using OpenCL IOS Press, Copyright to IJARSET
Introduction to Xeon Phi. Bill Barth January 11, 2013
 Introduction to Xeon Phi Bill Barth January 11, 2013 What is it? Co-processor PCI Express card Stripped down Linux operating system Dense, simplified processor Many power-hungry operations removed Wider
Introduction to Xeon Phi Bill Barth January 11, 2013 What is it? Co-processor PCI Express card Stripped down Linux operating system Dense, simplified processor Many power-hungry operations removed Wider
Overview of Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor
 Overview of Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor Sept 20, 2013 Ritu Arora Texas Advanced Computing Center Email: rauta@tacc.utexas.edu This talk is only a trailer A comprehensive training on running and optimizing
Overview of Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor Sept 20, 2013 Ritu Arora Texas Advanced Computing Center Email: rauta@tacc.utexas.edu This talk is only a trailer A comprehensive training on running and optimizing
The Stampede is Coming: A New Petascale Resource for the Open Science Community
 The Stampede is Coming: A New Petascale Resource for the Open Science Community Jay Boisseau Texas Advanced Computing Center boisseau@tacc.utexas.edu Stampede: Solicitation US National Science Foundation
The Stampede is Coming: A New Petascale Resource for the Open Science Community Jay Boisseau Texas Advanced Computing Center boisseau@tacc.utexas.edu Stampede: Solicitation US National Science Foundation
Parallel Programming on Ranger and Stampede
 Parallel Programming on Ranger and Stampede Steve Lantz Senior Research Associate Cornell CAC Parallel Computing at TACC: Ranger to Stampede Transition December 11, 2012 What is Stampede? NSF-funded XSEDE
Parallel Programming on Ranger and Stampede Steve Lantz Senior Research Associate Cornell CAC Parallel Computing at TACC: Ranger to Stampede Transition December 11, 2012 What is Stampede? NSF-funded XSEDE
Performance of deal.ii on a node
 Performance of deal.ii on a node Bruno Turcksin Texas A&M University, Dept. of Mathematics Bruno Turcksin Deal.II on a node 1/37 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Architecture 3 Paralution 4 Other Libraries 5 Conclusions
Performance of deal.ii on a node Bruno Turcksin Texas A&M University, Dept. of Mathematics Bruno Turcksin Deal.II on a node 1/37 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Architecture 3 Paralution 4 Other Libraries 5 Conclusions
PORTING CP2K TO THE INTEL XEON PHI. ARCHER Technical Forum, Wed 30 th July Iain Bethune
 PORTING CP2K TO THE INTEL XEON PHI ARCHER Technical Forum, Wed 30 th July Iain Bethune (ibethune@epcc.ed.ac.uk) Outline Xeon Phi Overview Porting CP2K to Xeon Phi Performance Results Lessons Learned Further
PORTING CP2K TO THE INTEL XEON PHI ARCHER Technical Forum, Wed 30 th July Iain Bethune (ibethune@epcc.ed.ac.uk) Outline Xeon Phi Overview Porting CP2K to Xeon Phi Performance Results Lessons Learned Further
The Era of Heterogeneous Computing
 The Era of Heterogeneous Computing EU-US Summer School on High Performance Computing New York, NY, USA June 28, 2013 Lars Koesterke: Research Staff @ TACC Nomenclature Architecture Model -------------------------------------------------------
The Era of Heterogeneous Computing EU-US Summer School on High Performance Computing New York, NY, USA June 28, 2013 Lars Koesterke: Research Staff @ TACC Nomenclature Architecture Model -------------------------------------------------------
Investigation of Intel MIC for implementation of Fast Fourier Transform
 Investigation of Intel MIC for implementation of Fast Fourier Transform Soren Goyal Department of Physics IIT Kanpur e-mail address: soren@iitk.ac.in The objective of the project was to run the code for
Investigation of Intel MIC for implementation of Fast Fourier Transform Soren Goyal Department of Physics IIT Kanpur e-mail address: soren@iitk.ac.in The objective of the project was to run the code for
Programming Models for Multi- Threading. Brian Marshall, Advanced Research Computing
 Programming Models for Multi- Threading Brian Marshall, Advanced Research Computing Why Do Parallel Computing? Limits of single CPU computing performance available memory I/O rates Parallel computing allows
Programming Models for Multi- Threading Brian Marshall, Advanced Research Computing Why Do Parallel Computing? Limits of single CPU computing performance available memory I/O rates Parallel computing allows
Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Matt Kelly & Ryan Rawlins
 Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Matt Kelly & Ryan Rawlins Outline History & Motivation Architecture Core architecture Network Topology Memory hierarchy Brief comparison to GPU & Tilera Programming Applications
Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Matt Kelly & Ryan Rawlins Outline History & Motivation Architecture Core architecture Network Topology Memory hierarchy Brief comparison to GPU & Tilera Programming Applications
Accelerator Programming Lecture 1
 Accelerator Programming Lecture 1 Manfred Liebmann Technische Universität München Chair of Optimal Control Center for Mathematical Sciences, M17 manfred.liebmann@tum.de January 11, 2016 Accelerator Programming
Accelerator Programming Lecture 1 Manfred Liebmann Technische Universität München Chair of Optimal Control Center for Mathematical Sciences, M17 manfred.liebmann@tum.de January 11, 2016 Accelerator Programming
Tutorial. Preparing for Stampede: Programming Heterogeneous Many-Core Supercomputers
 Tutorial Preparing for Stampede: Programming Heterogeneous Many-Core Supercomputers Dan Stanzione, Lars Koesterke, Bill Barth, Kent Milfeld dan/lars/bbarth/milfeld@tacc.utexas.edu XSEDE 12 July 16, 2012
Tutorial Preparing for Stampede: Programming Heterogeneous Many-Core Supercomputers Dan Stanzione, Lars Koesterke, Bill Barth, Kent Milfeld dan/lars/bbarth/milfeld@tacc.utexas.edu XSEDE 12 July 16, 2012
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors
 Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors Reference: Parallel Programming and Optimization with Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors, by A. Vladimirov and V. Karpusenko, 2013 Ring Bus on Intel Xeon Phi Example with 8 cores Xeon
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors Reference: Parallel Programming and Optimization with Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors, by A. Vladimirov and V. Karpusenko, 2013 Ring Bus on Intel Xeon Phi Example with 8 cores Xeon
Trends in HPC (hardware complexity and software challenges)
 Trends in HPC (hardware complexity and software challenges) Mike Giles Oxford e-research Centre Mathematical Institute MIT seminar March 13th, 2013 Mike Giles (Oxford) HPC Trends March 13th, 2013 1 / 18
Trends in HPC (hardware complexity and software challenges) Mike Giles Oxford e-research Centre Mathematical Institute MIT seminar March 13th, 2013 Mike Giles (Oxford) HPC Trends March 13th, 2013 1 / 18
Preparing for Highly Parallel, Heterogeneous Coprocessing
 Preparing for Highly Parallel, Heterogeneous Coprocessing Steve Lantz Senior Research Associate Cornell CAC Workshop: Parallel Computing on Ranger and Lonestar May 17, 2012 What Are We Talking About Here?
Preparing for Highly Parallel, Heterogeneous Coprocessing Steve Lantz Senior Research Associate Cornell CAC Workshop: Parallel Computing on Ranger and Lonestar May 17, 2012 What Are We Talking About Here?
Overview of research activities Toward portability of performance
 Overview of research activities Toward portability of performance Do dynamically what can t be done statically Understand evolution of architectures Enable new programming models Put intelligence into
Overview of research activities Toward portability of performance Do dynamically what can t be done statically Understand evolution of architectures Enable new programming models Put intelligence into
the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor
 the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor 1 Introduction about the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor comparing Phi with CUDA the Intel Many Integrated Core architecture 2 Programming the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor with
the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor 1 Introduction about the Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor comparing Phi with CUDA the Intel Many Integrated Core architecture 2 Programming the Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor with
GPU Architecture. Alan Gray EPCC The University of Edinburgh
 GPU Architecture Alan Gray EPCC The University of Edinburgh Outline Why do we want/need accelerators such as GPUs? Architectural reasons for accelerator performance advantages Latest GPU Products From
GPU Architecture Alan Gray EPCC The University of Edinburgh Outline Why do we want/need accelerators such as GPUs? Architectural reasons for accelerator performance advantages Latest GPU Products From
Parallel Processors. The dream of computer architects since 1950s: replicate processors to add performance vs. design a faster processor
 Multiprocessing Parallel Computers Definition: A parallel computer is a collection of processing elements that cooperate and communicate to solve large problems fast. Almasi and Gottlieb, Highly Parallel
Multiprocessing Parallel Computers Definition: A parallel computer is a collection of processing elements that cooperate and communicate to solve large problems fast. Almasi and Gottlieb, Highly Parallel
How to perform HPL on CPU&GPU clusters. Dr.sc. Draško Tomić
 How to perform HPL on CPU&GPU clusters Dr.sc. Draško Tomić email: drasko.tomic@hp.com Forecasting is not so easy, HPL benchmarking could be even more difficult Agenda TOP500 GPU trends Some basics about
How to perform HPL on CPU&GPU clusters Dr.sc. Draško Tomić email: drasko.tomic@hp.com Forecasting is not so easy, HPL benchmarking could be even more difficult Agenda TOP500 GPU trends Some basics about
Introduc)on to Xeon Phi
 Introduc)on to Xeon Phi ACES Aus)n, TX Dec. 04 2013 Kent Milfeld, Luke Wilson, John McCalpin, Lars Koesterke TACC What is it? Co- processor PCI Express card Stripped down Linux opera)ng system Dense, simplified
Introduc)on to Xeon Phi ACES Aus)n, TX Dec. 04 2013 Kent Milfeld, Luke Wilson, John McCalpin, Lars Koesterke TACC What is it? Co- processor PCI Express card Stripped down Linux opera)ng system Dense, simplified
Parallel Programming. Exploring local computational resources OpenMP Parallel programming for multiprocessors for loops
 Parallel Programming Exploring local computational resources OpenMP Parallel programming for multiprocessors for loops Single computers nowadays Several CPUs (cores) 4 to 8 cores on a single chip Hyper-threading
Parallel Programming Exploring local computational resources OpenMP Parallel programming for multiprocessors for loops Single computers nowadays Several CPUs (cores) 4 to 8 cores on a single chip Hyper-threading
Big Data Analytics Performance for Large Out-Of- Core Matrix Solvers on Advanced Hybrid Architectures
 Procedia Computer Science Volume 51, 2015, Pages 2774 2778 ICCS 2015 International Conference On Computational Science Big Data Analytics Performance for Large Out-Of- Core Matrix Solvers on Advanced Hybrid
Procedia Computer Science Volume 51, 2015, Pages 2774 2778 ICCS 2015 International Conference On Computational Science Big Data Analytics Performance for Large Out-Of- Core Matrix Solvers on Advanced Hybrid
Intel Performance Libraries
 Intel Performance Libraries Powerful Mathematical Library Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL) Energy Science & Research Engineering Design Financial Analytics Signal Processing Digital Content Creation
Intel Performance Libraries Powerful Mathematical Library Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL) Energy Science & Research Engineering Design Financial Analytics Signal Processing Digital Content Creation
CS 470 Spring Other Architectures. Mike Lam, Professor. (with an aside on linear algebra)
 CS 470 Spring 2016 Mike Lam, Professor Other Architectures (with an aside on linear algebra) Parallel Systems Shared memory (uniform global address space) Primary story: make faster computers Programming
CS 470 Spring 2016 Mike Lam, Professor Other Architectures (with an aside on linear algebra) Parallel Systems Shared memory (uniform global address space) Primary story: make faster computers Programming
Resources Current and Future Systems. Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D.
 Resources Current and Future Systems Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D. tkaiser@mines.edu 1 Most likely talk to be out of date History of Top 500 Issues with building bigger machines Current and near future academic
Resources Current and Future Systems Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D. tkaiser@mines.edu 1 Most likely talk to be out of date History of Top 500 Issues with building bigger machines Current and near future academic
Optimizing Data Locality for Iterative Matrix Solvers on CUDA
 Optimizing Data Locality for Iterative Matrix Solvers on CUDA Raymond Flagg, Jason Monk, Yifeng Zhu PhD., Bruce Segee PhD. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maine, Orono,
Optimizing Data Locality for Iterative Matrix Solvers on CUDA Raymond Flagg, Jason Monk, Yifeng Zhu PhD., Bruce Segee PhD. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maine, Orono,
Intel MIC Programming Workshop, Hardware Overview & Native Execution LRZ,
 Intel MIC Programming Workshop, Hardware Overview & Native Execution LRZ, 27.6.- 29.6.2016 1 Agenda Intro @ accelerators on HPC Architecture overview of the Intel Xeon Phi Products Programming models Native
Intel MIC Programming Workshop, Hardware Overview & Native Execution LRZ, 27.6.- 29.6.2016 1 Agenda Intro @ accelerators on HPC Architecture overview of the Intel Xeon Phi Products Programming models Native
Serial. Parallel. CIT 668: System Architecture 2/14/2011. Topics. Serial and Parallel Computation. Parallel Computing
 CIT 668: System Architecture Parallel Computing Topics 1. What is Parallel Computing? 2. Why use Parallel Computing? 3. Types of Parallelism 4. Amdahl s Law 5. Flynn s Taxonomy of Parallel Computers 6.
CIT 668: System Architecture Parallel Computing Topics 1. What is Parallel Computing? 2. Why use Parallel Computing? 3. Types of Parallelism 4. Amdahl s Law 5. Flynn s Taxonomy of Parallel Computers 6.
An Introduction to the Intel Xeon Phi. Si Liu Feb 6, 2015
 Training Agenda Session 1: Introduction 8:00 9:45 Session 2: Native: MIC stand-alone 10:00-11:45 Lunch break Session 3: Offload: MIC as coprocessor 1:00 2:45 Session 4: Symmetric: MPI 3:00 4:45 1 Last
Training Agenda Session 1: Introduction 8:00 9:45 Session 2: Native: MIC stand-alone 10:00-11:45 Lunch break Session 3: Offload: MIC as coprocessor 1:00 2:45 Session 4: Symmetric: MPI 3:00 4:45 1 Last
Performance Analysis of Memory Transfers and GEMM Subroutines on NVIDIA TESLA GPU Cluster
 Performance Analysis of Memory Transfers and GEMM Subroutines on NVIDIA TESLA GPU Cluster Veerendra Allada, Troy Benjegerdes Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ames Laboratory Iowa State University &
Performance Analysis of Memory Transfers and GEMM Subroutines on NVIDIA TESLA GPU Cluster Veerendra Allada, Troy Benjegerdes Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ames Laboratory Iowa State University &
Intel C++ Compiler User's Guide With Support For The Streaming Simd Extensions 2
 Intel C++ Compiler User's Guide With Support For The Streaming Simd Extensions 2 This release of the Intel C++ Compiler 16.0 product is a Pre-Release, and as such is 64 architecture processor supporting
Intel C++ Compiler User's Guide With Support For The Streaming Simd Extensions 2 This release of the Intel C++ Compiler 16.0 product is a Pre-Release, and as such is 64 architecture processor supporting
Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Architecture
 Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Architecture Karl Solchenbach Director European Exascale Labs BMW2011, November 3, 2011 1 Notice and Disclaimers Notice: This document contains information on products
Intel Many Integrated Core (MIC) Architecture Karl Solchenbach Director European Exascale Labs BMW2011, November 3, 2011 1 Notice and Disclaimers Notice: This document contains information on products
Chapter 17 - Parallel Processing
 Chapter 17 - Parallel Processing Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ Luis Tarrataca Chapter 17 - Parallel Processing 1 / 71 Table of Contents I 1 Motivation 2 Parallel Processing Categories
Chapter 17 - Parallel Processing Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ Luis Tarrataca Chapter 17 - Parallel Processing 1 / 71 Table of Contents I 1 Motivation 2 Parallel Processing Categories
Introduction to the Xeon Phi programming model. Fabio AFFINITO, CINECA
 Introduction to the Xeon Phi programming model Fabio AFFINITO, CINECA What is a Xeon Phi? MIC = Many Integrated Core architecture by Intel Other names: KNF, KNC, Xeon Phi... Not a CPU (but somewhat similar
Introduction to the Xeon Phi programming model Fabio AFFINITO, CINECA What is a Xeon Phi? MIC = Many Integrated Core architecture by Intel Other names: KNF, KNC, Xeon Phi... Not a CPU (but somewhat similar
General Purpose GPU Programming (1) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 14
 General Purpose GPU Programming (1) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 14 Lecture Outline Heterogenous multi-core systems and general purpose GPU programming Programming models Heterogenous multi-kernels
General Purpose GPU Programming (1) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 14 Lecture Outline Heterogenous multi-core systems and general purpose GPU programming Programming models Heterogenous multi-kernels
Advanced OpenMP Features
 Christian Terboven, Dirk Schmidl IT Center, RWTH Aachen University Member of the HPC Group {terboven,schmidl@itc.rwth-aachen.de IT Center der RWTH Aachen University Vectorization 2 Vectorization SIMD =
Christian Terboven, Dirk Schmidl IT Center, RWTH Aachen University Member of the HPC Group {terboven,schmidl@itc.rwth-aachen.de IT Center der RWTH Aachen University Vectorization 2 Vectorization SIMD =
GPUs and Emerging Architectures
 GPUs and Emerging Architectures Mike Giles mike.giles@maths.ox.ac.uk Mathematical Institute, Oxford University e-infrastructure South Consortium Oxford e-research Centre Emerging Architectures p. 1 CPUs
GPUs and Emerging Architectures Mike Giles mike.giles@maths.ox.ac.uk Mathematical Institute, Oxford University e-infrastructure South Consortium Oxford e-research Centre Emerging Architectures p. 1 CPUs
Vincent C. Betro, R. Glenn Brook, & Ryan C. Hulguin XSEDE Xtreme Scaling Workshop Chicago, IL July 15-16, 2012
 Vincent C. Betro, R. Glenn Brook, & Ryan C. Hulguin XSEDE Xtreme Scaling Workshop Chicago, IL July 15-16, 2012 Outline NICS and AACE Architecture Overview Resources Native Mode Boltzmann BGK Solver Native/Offload
Vincent C. Betro, R. Glenn Brook, & Ryan C. Hulguin XSEDE Xtreme Scaling Workshop Chicago, IL July 15-16, 2012 Outline NICS and AACE Architecture Overview Resources Native Mode Boltzmann BGK Solver Native/Offload
Intel MIC Programming Workshop, Hardware Overview & Native Execution. IT4Innovations, Ostrava,
 , Hardware Overview & Native Execution IT4Innovations, Ostrava, 3.2.- 4.2.2016 1 Agenda Intro @ accelerators on HPC Architecture overview of the Intel Xeon Phi (MIC) Programming models Native mode programming
, Hardware Overview & Native Execution IT4Innovations, Ostrava, 3.2.- 4.2.2016 1 Agenda Intro @ accelerators on HPC Architecture overview of the Intel Xeon Phi (MIC) Programming models Native mode programming
Introduction to the Intel Xeon Phi on Stampede
 June 10, 2014 Introduction to the Intel Xeon Phi on Stampede John Cazes Texas Advanced Computing Center Stampede - High Level Overview Base Cluster (Dell/Intel/Mellanox): Intel Sandy Bridge processors
June 10, 2014 Introduction to the Intel Xeon Phi on Stampede John Cazes Texas Advanced Computing Center Stampede - High Level Overview Base Cluster (Dell/Intel/Mellanox): Intel Sandy Bridge processors
Particle-in-Cell Simulations on Modern Computing Platforms. Viktor K. Decyk and Tajendra V. Singh UCLA
 Particle-in-Cell Simulations on Modern Computing Platforms Viktor K. Decyk and Tajendra V. Singh UCLA Outline of Presentation Abstraction of future computer hardware PIC on GPUs OpenCL and Cuda Fortran
Particle-in-Cell Simulations on Modern Computing Platforms Viktor K. Decyk and Tajendra V. Singh UCLA Outline of Presentation Abstraction of future computer hardware PIC on GPUs OpenCL and Cuda Fortran
Introduction: Modern computer architecture. The stored program computer and its inherent bottlenecks Multi- and manycore chips and nodes
 Introduction: Modern computer architecture The stored program computer and its inherent bottlenecks Multi- and manycore chips and nodes Motivation: Multi-Cores where and why Introduction: Moore s law Intel
Introduction: Modern computer architecture The stored program computer and its inherent bottlenecks Multi- and manycore chips and nodes Motivation: Multi-Cores where and why Introduction: Moore s law Intel
NVIDIA GTX200: TeraFLOPS Visual Computing. August 26, 2008 John Tynefield
 NVIDIA GTX200: TeraFLOPS Visual Computing August 26, 2008 John Tynefield 2 Outline Execution Model Architecture Demo 3 Execution Model 4 Software Architecture Applications DX10 OpenGL OpenCL CUDA C Host
NVIDIA GTX200: TeraFLOPS Visual Computing August 26, 2008 John Tynefield 2 Outline Execution Model Architecture Demo 3 Execution Model 4 Software Architecture Applications DX10 OpenGL OpenCL CUDA C Host
PROGRAMOVÁNÍ V C++ CVIČENÍ. Michal Brabec
 PROGRAMOVÁNÍ V C++ CVIČENÍ Michal Brabec PARALLELISM CATEGORIES CPU? SSE Multiprocessor SIMT - GPU 2 / 17 PARALLELISM V C++ Weak support in the language itself, powerful libraries Many different parallelization
PROGRAMOVÁNÍ V C++ CVIČENÍ Michal Brabec PARALLELISM CATEGORIES CPU? SSE Multiprocessor SIMT - GPU 2 / 17 PARALLELISM V C++ Weak support in the language itself, powerful libraries Many different parallelization
OpenACC 2.6 Proposed Features
 OpenACC 2.6 Proposed Features OpenACC.org June, 2017 1 Introduction This document summarizes features and changes being proposed for the next version of the OpenACC Application Programming Interface, tentatively
OpenACC 2.6 Proposed Features OpenACC.org June, 2017 1 Introduction This document summarizes features and changes being proposed for the next version of the OpenACC Application Programming Interface, tentatively
Parallel Systems. Project topics
 Parallel Systems Project topics 2016-2017 1. Scheduling Scheduling is a common problem which however is NP-complete, so that we are never sure about the optimality of the solution. Parallelisation is a
Parallel Systems Project topics 2016-2017 1. Scheduling Scheduling is a common problem which however is NP-complete, so that we are never sure about the optimality of the solution. Parallelisation is a
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. Parallel Processors (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI.
 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Parallel Processors (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI 6.6 - End Today s Contents GPU Cluster and its network topology The Roofline performance
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Parallel Processors (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI 6.6 - End Today s Contents GPU Cluster and its network topology The Roofline performance
Scalasca support for Intel Xeon Phi. Brian Wylie & Wolfgang Frings Jülich Supercomputing Centre Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany
 Scalasca support for Intel Xeon Phi Brian Wylie & Wolfgang Frings Jülich Supercomputing Centre Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany Overview Scalasca performance analysis toolset support for MPI & OpenMP
Scalasca support for Intel Xeon Phi Brian Wylie & Wolfgang Frings Jülich Supercomputing Centre Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany Overview Scalasca performance analysis toolset support for MPI & OpenMP
Energy Efficient K-Means Clustering for an Intel Hybrid Multi-Chip Package
 High Performance Machine Learning Workshop Energy Efficient K-Means Clustering for an Intel Hybrid Multi-Chip Package Matheus Souza, Lucas Maciel, Pedro Penna, Henrique Freitas 24/09/2018 Agenda Introduction
High Performance Machine Learning Workshop Energy Efficient K-Means Clustering for an Intel Hybrid Multi-Chip Package Matheus Souza, Lucas Maciel, Pedro Penna, Henrique Freitas 24/09/2018 Agenda Introduction
Performance of Multicore LUP Decomposition
 Performance of Multicore LUP Decomposition Nathan Beckmann Silas Boyd-Wickizer May 3, 00 ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the performance of four parallel LUP decomposition implementations. The implementations
Performance of Multicore LUP Decomposition Nathan Beckmann Silas Boyd-Wickizer May 3, 00 ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the performance of four parallel LUP decomposition implementations. The implementations
All routines were built with VS2010 compiler, OpenMP 2.0 and TBB 3.0 libraries were used to implement parallel versions of programs.
 technologies for multi-core numeric computation In order to compare ConcRT, OpenMP and TBB technologies, we implemented a few algorithms from different areas of numeric computation and compared their performance
technologies for multi-core numeric computation In order to compare ConcRT, OpenMP and TBB technologies, we implemented a few algorithms from different areas of numeric computation and compared their performance
Resources Current and Future Systems. Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D.
 Resources Current and Future Systems Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D. tkaiser@mines.edu 1 Most likely talk to be out of date History of Top 500 Issues with building bigger machines Current and near future academic
Resources Current and Future Systems Timothy H. Kaiser, Ph.D. tkaiser@mines.edu 1 Most likely talk to be out of date History of Top 500 Issues with building bigger machines Current and near future academic
Double Rewards of Porting Scientific Applications to the Intel MIC Architecture
 Double Rewards of Porting Scientific Applications to the Intel MIC Architecture Troy A. Porter Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Stanford
Double Rewards of Porting Scientific Applications to the Intel MIC Architecture Troy A. Porter Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory and Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Stanford
Multi-Processors and GPU
 Multi-Processors and GPU Philipp Koehn 7 December 2016 Predicted CPU Clock Speed 1 Clock speed 1971: 740 khz, 2016: 28.7 GHz Source: Horowitz "The Singularity is Near" (2005) Actual CPU Clock Speed 2 Clock
Multi-Processors and GPU Philipp Koehn 7 December 2016 Predicted CPU Clock Speed 1 Clock speed 1971: 740 khz, 2016: 28.7 GHz Source: Horowitz "The Singularity is Near" (2005) Actual CPU Clock Speed 2 Clock
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 1 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 1 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 1 Dec 2017](/thumbs/77/76587427.jpg) arxiv:1712.00143v1 [hep-lat] 1 Dec 2017 MILC Code Performance on High End CPU and GPU Supercomputer Clusters Carleton DeTar 1, Steven Gottlieb 2,, Ruizi Li 2,, and Doug Toussaint 3 1 Department of Physics
arxiv:1712.00143v1 [hep-lat] 1 Dec 2017 MILC Code Performance on High End CPU and GPU Supercomputer Clusters Carleton DeTar 1, Steven Gottlieb 2,, Ruizi Li 2,, and Doug Toussaint 3 1 Department of Physics
MAGMA. Matrix Algebra on GPU and Multicore Architectures
 MAGMA Matrix Algebra on GPU and Multicore Architectures Innovative Computing Laboratory Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee Piotr Luszczek (presenter) web.eecs.utk.edu/~luszczek/conf/
MAGMA Matrix Algebra on GPU and Multicore Architectures Innovative Computing Laboratory Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee Piotr Luszczek (presenter) web.eecs.utk.edu/~luszczek/conf/
Accelerator cards are typically PCIx cards that supplement a host processor, which they require to operate Today, the most common accelerators include
 3.1 Overview Accelerator cards are typically PCIx cards that supplement a host processor, which they require to operate Today, the most common accelerators include GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) AMD/ATI
3.1 Overview Accelerator cards are typically PCIx cards that supplement a host processor, which they require to operate Today, the most common accelerators include GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) AMD/ATI
Parallel Programming Libraries and implementations
 Parallel Programming Libraries and implementations Partners Funding Reusing this material This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Parallel Programming Libraries and implementations Partners Funding Reusing this material This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Towards a codelet-based runtime for exascale computing. Chris Lauderdale ET International, Inc.
 Towards a codelet-based runtime for exascale computing Chris Lauderdale ET International, Inc. What will be covered Slide 2 of 24 Problems & motivation Codelet runtime overview Codelets & complexes Dealing
Towards a codelet-based runtime for exascale computing Chris Lauderdale ET International, Inc. What will be covered Slide 2 of 24 Problems & motivation Codelet runtime overview Codelets & complexes Dealing
G P G P U : H I G H - P E R F O R M A N C E C O M P U T I N G
 Joined Advanced Student School (JASS) 2009 March 29 - April 7, 2009 St. Petersburg, Russia G P G P U : H I G H - P E R F O R M A N C E C O M P U T I N G Dmitry Puzyrev St. Petersburg State University Faculty
Joined Advanced Student School (JASS) 2009 March 29 - April 7, 2009 St. Petersburg, Russia G P G P U : H I G H - P E R F O R M A N C E C O M P U T I N G Dmitry Puzyrev St. Petersburg State University Faculty
GPU ACCELERATED DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
 CIS 601 - Graduate Seminar Presentation 1 GPU ACCELERATED DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS PRESENTED BY HARINATH AMASA CSU ID: 2697292 What we will talk about.. Current problems GPU What are GPU Databases GPU
CIS 601 - Graduate Seminar Presentation 1 GPU ACCELERATED DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS PRESENTED BY HARINATH AMASA CSU ID: 2697292 What we will talk about.. Current problems GPU What are GPU Databases GPU
General introduction: GPUs and the realm of parallel architectures
 General introduction: GPUs and the realm of parallel architectures GPU Computing Training August 17-19 th 2015 Jan Lemeire (jan.lemeire@vub.ac.be) Graduated as Engineer in 1994 at VUB Worked for 4 years
General introduction: GPUs and the realm of parallel architectures GPU Computing Training August 17-19 th 2015 Jan Lemeire (jan.lemeire@vub.ac.be) Graduated as Engineer in 1994 at VUB Worked for 4 years
Designing Optimized MPI Broadcast and Allreduce for Many Integrated Core (MIC) InfiniBand Clusters
 Designing Optimized MPI Broadcast and Allreduce for Many Integrated Core (MIC) InfiniBand Clusters K. Kandalla, A. Venkatesh, K. Hamidouche, S. Potluri, D. Bureddy and D. K. Panda Presented by Dr. Xiaoyi
Designing Optimized MPI Broadcast and Allreduce for Many Integrated Core (MIC) InfiniBand Clusters K. Kandalla, A. Venkatesh, K. Hamidouche, S. Potluri, D. Bureddy and D. K. Panda Presented by Dr. Xiaoyi
Heterogeneous Computing and OpenCL
 Heterogeneous Computing and OpenCL Hongsuk Yi (hsyi@kisti.re.kr) (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information) Contents Overview of the Heterogeneous Computing Introduction to Intel Xeon Phi
Heterogeneous Computing and OpenCL Hongsuk Yi (hsyi@kisti.re.kr) (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information) Contents Overview of the Heterogeneous Computing Introduction to Intel Xeon Phi
Di Zhao Ohio State University MVAPICH User Group (MUG) Meeting, August , Columbus Ohio
 Di Zhao zhao.1029@osu.edu Ohio State University MVAPICH User Group (MUG) Meeting, August 26-27 2013, Columbus Ohio Nvidia Kepler K20X Intel Xeon Phi 7120 Launch Date November 2012 Q2 2013 Processor Per-processor
Di Zhao zhao.1029@osu.edu Ohio State University MVAPICH User Group (MUG) Meeting, August 26-27 2013, Columbus Ohio Nvidia Kepler K20X Intel Xeon Phi 7120 Launch Date November 2012 Q2 2013 Processor Per-processor
Computer Architecture and Structured Parallel Programming James Reinders, Intel
 Computer Architecture and Structured Parallel Programming James Reinders, Intel Parallel Computing CIS 410/510 Department of Computer and Information Science Lecture 17 Manycore Computing and GPUs Computer
Computer Architecture and Structured Parallel Programming James Reinders, Intel Parallel Computing CIS 410/510 Department of Computer and Information Science Lecture 17 Manycore Computing and GPUs Computer
Intel Software Development Products for High Performance Computing and Parallel Programming
 Intel Software Development Products for High Performance Computing and Parallel Programming Multicore development tools with extensions to many-core Notices INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN
Intel Software Development Products for High Performance Computing and Parallel Programming Multicore development tools with extensions to many-core Notices INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN
Don t reinvent the wheel. BLAS LAPACK Intel Math Kernel Library
 Libraries Don t reinvent the wheel. Specialized math libraries are likely faster. BLAS: Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms LAPACK: Linear Algebra Package (uses BLAS) http://www.netlib.org/lapack/ to download
Libraries Don t reinvent the wheel. Specialized math libraries are likely faster. BLAS: Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms LAPACK: Linear Algebra Package (uses BLAS) http://www.netlib.org/lapack/ to download
Introduction to Runtime Systems
 Introduction to Runtime Systems Towards Portability of Performance ST RM Static Optimizations Runtime Methods Team Storm Olivier Aumage Inria LaBRI, in cooperation with La Maison de la Simulation Contents
Introduction to Runtime Systems Towards Portability of Performance ST RM Static Optimizations Runtime Methods Team Storm Olivier Aumage Inria LaBRI, in cooperation with La Maison de la Simulation Contents
OpenMP 4.0 (and now 5.0)
 OpenMP 4.0 (and now 5.0) John Urbanic Parallel Computing Scientist Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center Copyright 2018 Classic OpenMP OpenMP was designed to replace low-level and tedious solutions like POSIX
OpenMP 4.0 (and now 5.0) John Urbanic Parallel Computing Scientist Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center Copyright 2018 Classic OpenMP OpenMP was designed to replace low-level and tedious solutions like POSIX
Offload acceleration of scientific calculations within.net assemblies
 Offload acceleration of scientific calculations within.net assemblies Lebedev A. 1, Khachumov V. 2 1 Rybinsk State Aviation Technical University, Rybinsk, Russia 2 Institute for Systems Analysis of Russian
Offload acceleration of scientific calculations within.net assemblies Lebedev A. 1, Khachumov V. 2 1 Rybinsk State Aviation Technical University, Rybinsk, Russia 2 Institute for Systems Analysis of Russian
INTRODUCTION TO OPENACC. Analyzing and Parallelizing with OpenACC, Feb 22, 2017
 INTRODUCTION TO OPENACC Analyzing and Parallelizing with OpenACC, Feb 22, 2017 Objective: Enable you to to accelerate your applications with OpenACC. 2 Today s Objectives Understand what OpenACC is and
INTRODUCTION TO OPENACC Analyzing and Parallelizing with OpenACC, Feb 22, 2017 Objective: Enable you to to accelerate your applications with OpenACC. 2 Today s Objectives Understand what OpenACC is and
BlueGene/L (No. 4 in the Latest Top500 List)
 BlueGene/L (No. 4 in the Latest Top500 List) first supercomputer in the Blue Gene project architecture. Individual PowerPC 440 processors at 700Mhz Two processors reside in a single chip. Two chips reside
BlueGene/L (No. 4 in the Latest Top500 List) first supercomputer in the Blue Gene project architecture. Individual PowerPC 440 processors at 700Mhz Two processors reside in a single chip. Two chips reside
The Heterogeneous Programming Jungle. Service d Expérimentation et de développement Centre Inria Bordeaux Sud-Ouest
 The Heterogeneous Programming Jungle Service d Expérimentation et de développement Centre Inria Bordeaux Sud-Ouest June 19, 2012 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Heterogeneous System Zoo 3. Similarities 4. Programming
The Heterogeneous Programming Jungle Service d Expérimentation et de développement Centre Inria Bordeaux Sud-Ouest June 19, 2012 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Heterogeneous System Zoo 3. Similarities 4. Programming
IN FINITE element simulations usually two computation
 Proceedings of the International Multiconference on Computer Science and Information Technology pp. 337 342 Higher order FEM numerical integration on GPUs with OpenCL 1 Przemysław Płaszewski, 12 Krzysztof
Proceedings of the International Multiconference on Computer Science and Information Technology pp. 337 342 Higher order FEM numerical integration on GPUs with OpenCL 1 Przemysław Płaszewski, 12 Krzysztof
Programming for the Intel Many Integrated Core Architecture By James Reinders. The Architecture for Discovery. PowerPoint Title
 Programming for the Intel Many Integrated Core Architecture By James Reinders The Architecture for Discovery PowerPoint Title Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor 1. Designed for Highly Parallel workloads 2. and
Programming for the Intel Many Integrated Core Architecture By James Reinders The Architecture for Discovery PowerPoint Title Intel Xeon Phi coprocessor 1. Designed for Highly Parallel workloads 2. and
Intra-MIC MPI Communication using MVAPICH2: Early Experience
 Intra-MIC MPI Communication using MVAPICH: Early Experience Sreeram Potluri, Karen Tomko, Devendar Bureddy, and Dhabaleswar K. Panda Department of Computer Science and Engineering Ohio State University
Intra-MIC MPI Communication using MVAPICH: Early Experience Sreeram Potluri, Karen Tomko, Devendar Bureddy, and Dhabaleswar K. Panda Department of Computer Science and Engineering Ohio State University
CPU-GPU Heterogeneous Computing
 CPU-GPU Heterogeneous Computing Advanced Seminar "Computer Engineering Winter-Term 2015/16 Steffen Lammel 1 Content Introduction Motivation Characteristics of CPUs and GPUs Heterogeneous Computing Systems
CPU-GPU Heterogeneous Computing Advanced Seminar "Computer Engineering Winter-Term 2015/16 Steffen Lammel 1 Content Introduction Motivation Characteristics of CPUs and GPUs Heterogeneous Computing Systems
 For your convenience Apress has placed some of the front matter material after the index. Please use the Bookmarks and Contents at a Glance links to access them. Contents at a Glance About the Author...
For your convenience Apress has placed some of the front matter material after the index. Please use the Bookmarks and Contents at a Glance links to access them. Contents at a Glance About the Author...
represent parallel computers, so distributed systems such as Does not consider storage or I/O issues
 Top500 Supercomputer list represent parallel computers, so distributed systems such as SETI@Home are not considered Does not consider storage or I/O issues Both custom designed machines and commodity machines
Top500 Supercomputer list represent parallel computers, so distributed systems such as SETI@Home are not considered Does not consider storage or I/O issues Both custom designed machines and commodity machines
On Level Scheduling for Incomplete LU Factorization Preconditioners on Accelerators
 On Level Scheduling for Incomplete LU Factorization Preconditioners on Accelerators Karl Rupp, Barry Smith rupp@mcs.anl.gov Mathematics and Computer Science Division Argonne National Laboratory FEMTEC
On Level Scheduling for Incomplete LU Factorization Preconditioners on Accelerators Karl Rupp, Barry Smith rupp@mcs.anl.gov Mathematics and Computer Science Division Argonne National Laboratory FEMTEC
Introduction to parallel computers and parallel programming. Introduction to parallel computersand parallel programming p. 1
 Introduction to parallel computers and parallel programming Introduction to parallel computersand parallel programming p. 1 Content A quick overview of morden parallel hardware Parallelism within a chip
Introduction to parallel computers and parallel programming Introduction to parallel computersand parallel programming p. 1 Content A quick overview of morden parallel hardware Parallelism within a chip
Parallel Computing. Hwansoo Han (SKKU)
 Parallel Computing Hwansoo Han (SKKU) Unicore Limitations Performance scaling stopped due to Power consumption Wire delay DRAM latency Limitation in ILP 10000 SPEC CINT2000 2 cores/chip Xeon 3.0GHz Core2duo
Parallel Computing Hwansoo Han (SKKU) Unicore Limitations Performance scaling stopped due to Power consumption Wire delay DRAM latency Limitation in ILP 10000 SPEC CINT2000 2 cores/chip Xeon 3.0GHz Core2duo
HPC trends (Myths about) accelerator cards & more. June 24, Martin Schreiber,
 HPC trends (Myths about) accelerator cards & more June 24, 2015 - Martin Schreiber, M.Schreiber@exeter.ac.uk Outline HPC & current architectures Performance: Programming models: OpenCL & OpenMP Some applications:
HPC trends (Myths about) accelerator cards & more June 24, 2015 - Martin Schreiber, M.Schreiber@exeter.ac.uk Outline HPC & current architectures Performance: Programming models: OpenCL & OpenMP Some applications:
Performance Evaluation of BLAS on a Cluster of Multi-Core Intel Processors
 Performance Evaluation of BLAS on a Cluster of Multi-Core Intel Processors Mostafa I. Soliman and Fatma S. Ahmed Computers and Systems Section, Electrical Engineering Department Aswan Faculty of Engineering,
Performance Evaluation of BLAS on a Cluster of Multi-Core Intel Processors Mostafa I. Soliman and Fatma S. Ahmed Computers and Systems Section, Electrical Engineering Department Aswan Faculty of Engineering,
Solving Dense Linear Systems on Platforms with Multiple Hardware Accelerators
 Solving Dense Linear Systems on Platforms with Multiple Hardware Accelerators Francisco D. Igual Enrique S. Quintana-Ortí Gregorio Quintana-Ortí Universidad Jaime I de Castellón (Spain) Robert A. van de
Solving Dense Linear Systems on Platforms with Multiple Hardware Accelerators Francisco D. Igual Enrique S. Quintana-Ortí Gregorio Quintana-Ortí Universidad Jaime I de Castellón (Spain) Robert A. van de
CS 470 Spring Other Architectures. Mike Lam, Professor. (with an aside on linear algebra)
 CS 470 Spring 2018 Mike Lam, Professor Other Architectures (with an aside on linear algebra) Aside (P3 related): linear algebra Many scientific phenomena can be modeled as matrix operations Differential
CS 470 Spring 2018 Mike Lam, Professor Other Architectures (with an aside on linear algebra) Aside (P3 related): linear algebra Many scientific phenomena can be modeled as matrix operations Differential
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor
 Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor http://tinyurl.com/inteljames twitter @jamesreinders James Reinders it s all about parallel programming Source Multicore CPU Compilers Libraries, Parallel Models Multicore CPU
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor http://tinyurl.com/inteljames twitter @jamesreinders James Reinders it s all about parallel programming Source Multicore CPU Compilers Libraries, Parallel Models Multicore CPU
Reusing this material
 XEON PHI BASICS Reusing this material This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.en_us
XEON PHI BASICS Reusing this material This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.en_us
Modelling and implementation of algorithms in applied mathematics using MPI
 Modelling and implementation of algorithms in applied mathematics using MPI Lecture 1: Basics of Parallel Computing G. Rapin Brazil March 2011 Outline 1 Structure of Lecture 2 Introduction 3 Parallel Performance
Modelling and implementation of algorithms in applied mathematics using MPI Lecture 1: Basics of Parallel Computing G. Rapin Brazil March 2011 Outline 1 Structure of Lecture 2 Introduction 3 Parallel Performance
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor
 Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor A guide to using it on the Cray XC40 Terminology Warning: may also be referred to as MIC or KNC in what follows! What are Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors? Hardware designed to accelerate
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor A guide to using it on the Cray XC40 Terminology Warning: may also be referred to as MIC or KNC in what follows! What are Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors? Hardware designed to accelerate
COMPUTING ELEMENT EVOLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON SIMULATION CODES
 COMPUTING ELEMENT EVOLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON SIMULATION CODES P(ND) 2-2 2014 Guillaume Colin de Verdière OCTOBER 14TH, 2014 P(ND)^2-2 PAGE 1 CEA, DAM, DIF, F-91297 Arpajon, France October 14th, 2014 Abstract:
COMPUTING ELEMENT EVOLUTION AND ITS IMPACT ON SIMULATION CODES P(ND) 2-2 2014 Guillaume Colin de Verdière OCTOBER 14TH, 2014 P(ND)^2-2 PAGE 1 CEA, DAM, DIF, F-91297 Arpajon, France October 14th, 2014 Abstract:
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor
 Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 1 Agenda Introduction Intel Xeon Phi Architecture Programming Models Outlook Summary 2 Intel Multicore Architecture Intel Many Integrated Core Architecture (Intel MIC) Foundation
Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessor 1 Agenda Introduction Intel Xeon Phi Architecture Programming Models Outlook Summary 2 Intel Multicore Architecture Intel Many Integrated Core Architecture (Intel MIC) Foundation
Introduction to Intel Xeon Phi programming techniques. Fabio Affinito Vittorio Ruggiero
 Introduction to Intel Xeon Phi programming techniques Fabio Affinito Vittorio Ruggiero Outline High level overview of the Intel Xeon Phi hardware and software stack Intel Xeon Phi programming paradigms:
Introduction to Intel Xeon Phi programming techniques Fabio Affinito Vittorio Ruggiero Outline High level overview of the Intel Xeon Phi hardware and software stack Intel Xeon Phi programming paradigms:
OpenCL Vectorising Features. Andreas Beckmann
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft OpenCL Vectorising Features Andreas Beckmann Levels of Vectorisation vector units, SIMD devices width, instructions SMX, SP cores Cus, PEs vector operations within kernels
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft OpenCL Vectorising Features Andreas Beckmann Levels of Vectorisation vector units, SIMD devices width, instructions SMX, SP cores Cus, PEs vector operations within kernels
Technology for a better society. hetcomp.com
 Technology for a better society hetcomp.com 1 J. Seland, C. Dyken, T. R. Hagen, A. R. Brodtkorb, J. Hjelmervik,E Bjønnes GPU Computing USIT Course Week 16th November 2011 hetcomp.com 2 9:30 10:15 Introduction
Technology for a better society hetcomp.com 1 J. Seland, C. Dyken, T. R. Hagen, A. R. Brodtkorb, J. Hjelmervik,E Bjønnes GPU Computing USIT Course Week 16th November 2011 hetcomp.com 2 9:30 10:15 Introduction
Parallel Computing: Parallel Architectures Jin, Hai
 Parallel Computing: Parallel Architectures Jin, Hai School of Computer Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer
Parallel Computing: Parallel Architectures Jin, Hai School of Computer Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer
GPU Programming Using NVIDIA CUDA
 GPU Programming Using NVIDIA CUDA Siddhante Nangla 1, Professor Chetna Achar 2 1, 2 MET s Institute of Computer Science, Bandra Mumbai University Abstract: GPGPU or General-Purpose Computing on Graphics
GPU Programming Using NVIDIA CUDA Siddhante Nangla 1, Professor Chetna Achar 2 1, 2 MET s Institute of Computer Science, Bandra Mumbai University Abstract: GPGPU or General-Purpose Computing on Graphics
arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Nov 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Nov 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Nov 2013](/thumbs/74/70979601.jpg) arxiv:1311.0590v1 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Nov 2013 Performance of Kepler GTX Titan GPUs and Xeon Phi System, Weonjong Lee, and Jeonghwan Pak Lattice Gauge Theory Research Center, CTP, and FPRD, Department
arxiv:1311.0590v1 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Nov 2013 Performance of Kepler GTX Titan GPUs and Xeon Phi System, Weonjong Lee, and Jeonghwan Pak Lattice Gauge Theory Research Center, CTP, and FPRD, Department
