public class MaxSeq { public static Node maxs (int[] table){ int count = 0; Node[] nodes = new Node[table.length]; Node n = new Node(table[0],1,1);
|
|
|
- Chloe Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 public class MaxSeq { public static Node maxs (int[] table){ int count = 0; Node[] nodes = new Node[table.length]; Node n = new Node(table[0],1,1); for (int i = 1; i < table.length; i++){ if (table[i] == n.getelem()) n.inclen(); else {count = insertnode(nodes,n,count); n = new Node(table[i],1,1); count = insertnode(nodes,n,count); return maxnode(nodes, count); public static int insertnode(node[]ns, Node n, int count){ boolean found = false; for (int i = 0; i < count &&!found; i++){ if (ns[i].getelem() == n.getelem() && ns[i].getlen() == n.getlen()){ found = true; ns[i].incoccur(); if (!found) {ns[count] = n; count++; return count; public static Node maxnode(node[]ns, int count){ display(ns, count); int n = 0; for (int i = 1; i < count; i++){ if (ns[i].getlen() > ns[n].getlen()) n = i; 1
2 return ns[n]; public static void display(node[] ns, int count){ System.out.print("\n\nThe subsequences are:\n"); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){ System.out.print("\n" + ns[i]); System.out.print("\n"); /* public static int Nseqs (Node[] ns, int count, int L){ int N = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) if (ns[i].getlen() == L) N = N + ns[i].getoccurs(); return N; */ public static void main(string[] args){ int[] table = new int[args.length]; for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) table[i] = Integer.parseInt(args[i]); Node n = maxs(table); System.out.print("\n\nThus the first subsequence of max length is:\n" + n + "\n\n"); 2
3 public class Fstatistics { public static void putchar (char c){system.out.print(c); public static void draw_line (int label, char form, int len){ putchar('\n'); System.out.printf("%3d", label); putchar(' '); while (len > 0) {putchar(form); len--; public static void display_day_statistics(int day, int men, int women, int children){ draw_line(day, 'M', (men + 5)/10); draw_line(day, 'W', (women + 5)/10); draw_line(day, 'C', (children + 5)/10); draw_line(day, 'T', (men+women+children+5)/10); public static void main(string[] args){ int Day = 1, Men, Women, Children; int MaxM = 0, MaxW = 0, MaxC = 0, MaxT = 0, DM = 0, DW = 0, DC = 0, DT = 0; while(!stdin.isempty()){ Men = StdIn.readInt(); Women = StdIn.readInt(); Children = StdIn.readInt(); display_day_statistics(day, Men, Women, Children); if (Men > MaxM) {MaxM = Men; DM = Day; if (Women > MaxW) {MaxW = Women; DW = Day; if (Children > MaxC) {MaxC = Children; DC = Day; if (Men + Women + Children > MaxT) {MaxT = Men + Women + Children; DT = Day; Day++; System.out.printf("\n\nMax no of men was %4d on day %3d", MaxM, DM); System.out.printf("\nMax no of women was %4d on day %3d", MaxW, DW); System.out.printf("\nMax no of children was %4d on day %3d", MaxC, DC); System.out.printf("\nMax no of total passengers was %4d on day %3d\n\n", MaxT, DT); 3
4 public class Caps { public static char capl (char c) { if ('a' <= c && c <= 'z') return (char) ((int) c - (int) 'a' + (int) 'A'); else return c; public static void main (String [] args) { while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { char c = StdIn.readChar(); System.out.print(capL(c)); public class LineN{ public static void main (String[] args){ int count=1; System.out.printf("%3d: ", count); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()){ char c = StdIn.readChar(); System.out.print(c); if (c=='\n') {count++; System.out.printf("%3d: ", count); 4
5 public class WCount { public static boolean white_space (char c) { return c == ' ' c == '\n' c == '\t'; public static void main (String[] args) { char c = ' '; boolean wflag = false; int words=0, lines=0, chars=0; while(!stdin.isempty()) { c = StdIn.readChar(); chars++; if (c == '\n') lines++; if (white_space(c) && wflag) wflag = false; else if (!white_space(c) &&!wflag) {words++; wflag=true; if (c!= '\n') lines++; System.out.printf("chars = %d, words = %d, lines = %d", chars, words, lines); 5
6 public class XmasFigs { public static void snowmanrow (int row){ switch (row){ case 1: System.out.printf(" "); break; case 2: System.out.printf(" / \\ "); break; case 3: System.out.printf(" x x "); break; case 4: System.out.printf(" O "); break; case 5: System.out.printf(" _ \\ --- / _ "); break; case 6: System.out.printf(" \\ / "); break; case 7: System.out.printf(" \\/ \\/ "); break; case 8: System.out.printf(" o "); break; case 9: System.out.printf(" "); break; case 10: System.out.printf(" o "); break; case 11: System.out.printf(" "); break; case 12: System.out.printf(" \\ / "); break; case 13: System.out.printf(" * MERRY XMAS * "); public static void starrow (int row){ switch (row){ case 1: System.out.print(" * "); break; case 2: System.out.print(" *** "); break; case 3: System.out.print(" ********* "); break; case 4: System.out.print(" ******* "); break; case 5: System.out.print(" ********* "); break; case 6: System.out.print(" *** "); break; case 7: System.out.print(" * "); public static void xmasrow (int row){ switch (row){ case 1: System.out.print(" case 2: System.out.print(" "); break; "); break; 6
7 case 3: System.out.print(" MERRY "); break; case 4: System.out.print(" X M A S "); break; case 5: System.out.print(" ********* "); break; case 6: System.out.print(" "); break; case 7: System.out.print(" "); public static void blankrow(){ System.out.print(" "); public static boolean[][] instantiate (int size){ boolean[][] t = new boolean[size][size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) t[i][j] = StdIn.readBoolean(); return t; public static void drawstars(boolean[] bs, boolean mid){ int count = bs.length/2; for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++){ System.out.println(); for (int j = 0; j < bs.length; j++) if (mid && j == count) xmasrow(i); else if (bs[j]) starrow(i); else blankrow(); public static void main (String[] args){ int choice = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); if (choice == 1){ int count = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 7
8 for (int i = 1; i <=13; i++){ System.out.println(); for (int j = 1; j <= count; j++) snowmanrow(i); System.out.println(); else {int size = StdIn.readInt(); int mid = size / 2; boolean[][] blanks = instantiate(size); for (int row = 0; row < blanks.length; row++){ if (row == mid) drawstars(blanks[row], true); else drawstars(blanks[row], false); public class CreatePattern { public static void main (String[] args){ int size = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); System.out.print(size + "\n"); boolean[][]t = new boolean[size][size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) t[i][i] = true; for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) t[i][size-1-i] = true; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) if(t[i][j]) System.out.print("true\t"); else System.out.print("false\t"); System.out.print("\n"); 8
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
Java Loop Control. Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
 Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
CS141 Programming Assignment #6
 CS141 Programming Assignment #6 Due Sunday, Nov 18th. 1) Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2 1
CS141 Programming Assignment #6 Due Sunday, Nov 18th. 1) Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2 1
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Code Analysis Sample Questions
 Code Analysis Sample Questions Because the event rules may vary from year to year, these sample questions may address topics not included in the current year's rules. 1. What is the printed output of the
Code Analysis Sample Questions Because the event rules may vary from year to year, these sample questions may address topics not included in the current year's rules. 1. What is the printed output of the
Spring University of New Mexico CS152 Midterm Exam. Print Your Name
 Print Your Name You may use one page of hand written notes (both sides) and a dictionary. No i-phones, calculators or any other type of non-organic computer. Do not take this exam if you are sick. Once
Print Your Name You may use one page of hand written notes (both sides) and a dictionary. No i-phones, calculators or any other type of non-organic computer. Do not take this exam if you are sick. Once
1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[])
![1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[]) 1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[])](/thumbs/75/72215142.jpg) 1. Find the output of following java program. public static void main(string arg[]) int arr[][]=4,3,2,1; int i,j; for(i=1;i>-1;i--) for(j=1;j>-1;j--) System.out.print(arr[i][j]); 1234 The above java program
1. Find the output of following java program. public static void main(string arg[]) int arr[][]=4,3,2,1; int i,j; for(i=1;i>-1;i--) for(j=1;j>-1;j--) System.out.print(arr[i][j]); 1234 The above java program
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving. Quiz 1 March 7, 2003
 1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises
 AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises 1. What is displayed? int [] a = new int[ 3 ]; System.out.println(a.length ); 2. What is displayed? int [] sting = { 34, 23, 67, 89, 12 ; System.out.println( sting[ 1 ] );
AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises 1. What is displayed? int [] a = new int[ 3 ]; System.out.println(a.length ); 2. What is displayed? int [] sting = { 34, 23, 67, 89, 12 ; System.out.println( sting[ 1 ] );
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
(A) 99 ** (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
6 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
 6 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING ITERATION STATEMENT CONTENTS WHILE DO~WHILE FOR statement 2 Iteration Statement provides While / do-while / For statements for supporting an iteration logic function that the logic
6 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING ITERATION STATEMENT CONTENTS WHILE DO~WHILE FOR statement 2 Iteration Statement provides While / do-while / For statements for supporting an iteration logic function that the logic
Recitation: Loop Jul 7, 2008
 Nested Loop Recitation: Loop Jul 7, 2008 1. What is the output of the following program? Use pen and paper only. The output is: ****** ***** **** *** ** * 2. Test this program in your computer 3. Use "for
Nested Loop Recitation: Loop Jul 7, 2008 1. What is the output of the following program? Use pen and paper only. The output is: ****** ***** **** *** ** * 2. Test this program in your computer 3. Use "for
public class ThreeDigits {
 public class ThreeDigits { public static boolean palindrome(int i){ if (i >= 0 && i = 10 && i
public class ThreeDigits { public static boolean palindrome(int i){ if (i >= 0 && i = 10 && i
CIS Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1
 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
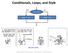 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
CS 1083 Introduction to Programming I for Computer Scientists Sample Final Questions
 CS 1083 Introduction to Programming I for Computer Scientists Sample Final Questions 1. What is printed by the following program? Show all your work for partial credit. public class SampleFinalq1 { public
CS 1083 Introduction to Programming I for Computer Scientists Sample Final Questions 1. What is printed by the following program? Show all your work for partial credit. public class SampleFinalq1 { public
Computação I. Exercises. Leonardo Vanneschi NOVA IMS, Universidade Nova de Lisboa. Leonardo Vanneschi Computação I NOVA IMS
 Computação I Exercises Leonardo Vanneschi NOVA IMS, Universidade Nova de Lisboa 1 Exercise 1 Write a Java program composed by: a. A method called myaverage that has the following parameters: an array A
Computação I Exercises Leonardo Vanneschi NOVA IMS, Universidade Nova de Lisboa 1 Exercise 1 Write a Java program composed by: a. A method called myaverage that has the following parameters: an array A
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups:
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
(A) 99 (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
CS 170 Section 3, Spring 2015 Programming in Java Midterm Exam 1. Name (print):
 Name (print): INSTRUCTIONS: o Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. o Do NOT communicate with anyone other than the professor/proctor for ANY reason
Name (print): INSTRUCTIONS: o Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. o Do NOT communicate with anyone other than the professor/proctor for ANY reason
Lab Assignment Three
 Lab Assignment Three C212/A592 Fall Semester 2010 Due in OnCourse by Friday, September 17, 11:55pm (Dropbox will stay open until Saturday, September 18, 11:55pm) Abstract Read and solve the problems below.
Lab Assignment Three C212/A592 Fall Semester 2010 Due in OnCourse by Friday, September 17, 11:55pm (Dropbox will stay open until Saturday, September 18, 11:55pm) Abstract Read and solve the problems below.
CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008
 CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A
 AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011
 CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Exam 2. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Timing ListOperations
 Timing ListOperations Michael Brockway November 13, 2017 These slides are to give you a quick start with timing operations in Java and with making sensible use of the command-line. Java on a command-line
Timing ListOperations Michael Brockway November 13, 2017 These slides are to give you a quick start with timing operations in Java and with making sensible use of the command-line. Java on a command-line
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1
 FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1 ACADEMIC SESSION 2014; SEMESTER 3 PRG102D: BASIC PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS Section A Compulsory section Question
FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1 ACADEMIC SESSION 2014; SEMESTER 3 PRG102D: BASIC PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS Section A Compulsory section Question
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
AP Programming - Chapter 6 Lecture
 page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
Conditionals, Loops, and Style. Control flow thus far. if statement. Control flow. Common branching statement Evaluate a boolean expression
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 12, Name
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
true false Imperative Programming III, sections , 3.0, 3.9 Introductory Programming Control flow of programs While loops: generally Loops
 Introductory Programming Imperative Programming III, sections 3.6-3.8, 3.0, 3.9 Anne Haxthausen a IMM, DTU 1. Loops (while, do, for) (sections 3.6 3.8) 2. Overview of Java s (learnt so far) 3. Program
Introductory Programming Imperative Programming III, sections 3.6-3.8, 3.0, 3.9 Anne Haxthausen a IMM, DTU 1. Loops (while, do, for) (sections 3.6 3.8) 2. Overview of Java s (learnt so far) 3. Program
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ Test 2. Question Max Mark Internal External
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Test 2 Question Max Mark Internal
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Test 2 Question Max Mark Internal
Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test Mar 2018
 Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test 2.1 22 Mar 2018 Student Name Student Number Answer ALL Questions 1. What output is produced when the following Java program fragment
Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test 2.1 22 Mar 2018 Student Name Student Number Answer ALL Questions 1. What output is produced when the following Java program fragment
Tools : The Java Compiler. The Java Interpreter. The Java Debugger
 Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 2, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
For that purpose, java provides control structures that serve to specify what has to be done by our program, when and under which circumstances.
 Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose, java provides control structures
Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose, java provides control structures
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
 Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
The data in the table are arranged into 12 rows and 12 columns. The process of printing them out can be expressed in a pseudocode algorithm as
 Control structures in Java are statements that contain statements. In particular, control structures can contain control structures. You've already seen several examples of if statements inside loops,
Control structures in Java are statements that contain statements. In particular, control structures can contain control structures. You've already seen several examples of if statements inside loops,
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following:
 PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
Flow Control. Key Notion. Statement Categories. 28-Oct-10
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
ESC101 : Fundamental of Computing
 ESC101 : Fundamental of Computing End Semester Exam 19 November 2008 Name : Roll No. : Section : Note : Read the instructions carefully 1. You will lose 3 marks if you forget to write your name, roll number,
ESC101 : Fundamental of Computing End Semester Exam 19 November 2008 Name : Roll No. : Section : Note : Read the instructions carefully 1. You will lose 3 marks if you forget to write your name, roll number,
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
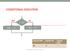 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Exercise (Revisited)
 Exercise (Revisited) Redo the cashier problem by using an infinite loop with a break statement. 1... 2 while (true) { 3 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 4 price = input.nextint(); 5 if (price
Exercise (Revisited) Redo the cashier problem by using an infinite loop with a break statement. 1... 2 while (true) { 3 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 4 price = input.nextint(); 5 if (price
Combined Assignment Operators. Flow of Control. Increment Decrement Operators. Operators Precedence (Highest to Lowest) Slide Set 05: Java Loops
 Flow of control Flow of Control Program instruction execution sequence Sequential Control Structure Selection (Branching) Control Structure Repetition (Loop) Control Structure Operator Usage Relational
Flow of control Flow of Control Program instruction execution sequence Sequential Control Structure Selection (Branching) Control Structure Repetition (Loop) Control Structure Operator Usage Relational
Recursion. Overview. Mathematical induction. Hello recursion. Recursion. Example applications. Goal: Compute factorial N! = 1 * 2 * 3...
 Recursion Recursion Overview A method calling itself A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming paradigm Related to mathematical induction Example applications Factorial
Recursion Recursion Overview A method calling itself A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming paradigm Related to mathematical induction Example applications Factorial
Flow Control. Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester IDC Herzliya
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
BIT Java Programming. Sem 1 Session 2011/12. Chapter 2 JAVA. basic
 BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
INDEX. A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line. The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line
 A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line INDEX The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line COMMENTS Single Line Comment Multiline Comment Documentation Comment TYPE CASTING Implicit Type
A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line INDEX The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line COMMENTS Single Line Comment Multiline Comment Documentation Comment TYPE CASTING Implicit Type
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011
 Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013 qüáë= íéëí= Ü~ë= U= èìéëíáçåëi= ïéáöüíéç= ~ë= áåçáå~íéçk= qüé= Éñ~ã= áë= ÅäçëÉÇ= ÄççâI=ÉñÅÉéí=íÜ~í= óçì= ~êé= ~ääçïéç= íç= ìëé= ~= çåé=
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013 qüáë= íéëí= Ü~ë= U= èìéëíáçåëi= ïéáöüíéç= ~ë= áåçáå~íéçk= qüé= Éñ~ã= áë= ÅäçëÉÇ= ÄççâI=ÉñÅÉéí=íÜ~í= óçì= ~êé= ~ääçïéç= íç= ìëé= ~= çåé=
CS 102/107 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #2 - Prof. Reed Spring 2011
 CS 102/107 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #2 - Prof. Reed Spring 2011 What is your name?: This test has the following sections: I. True/False... 60 points; (30 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS 102/107 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #2 - Prof. Reed Spring 2011 What is your name?: This test has the following sections: I. True/False... 60 points; (30 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS180. Exam 1 Review
 CS180 Exam 1 Review What is the output to the following code? System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + (2 + 2)); System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + 2 + 2); What is the output to the following code? System.out.println(String.valueOf(15+20));
CS180 Exam 1 Review What is the output to the following code? System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + (2 + 2)); System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + 2 + 2); What is the output to the following code? System.out.println(String.valueOf(15+20));
1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method.
 Name: Write all of your responses on these exam pages. 1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method. 2. Java is a platform-independent
Name: Write all of your responses on these exam pages. 1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method. 2. Java is a platform-independent
public class CMemory {
 public class CMemory { private int size; private char[] content; private boolean[] status; // allocation status private int[][] holes; private int numholes; public CMemory (int s){ size = s; content =
public class CMemory { private int size; private char[] content; private boolean[] status; // allocation status private int[][] holes; private int numholes; public CMemory (int s){ size = s; content =
CSE 8A Lecture 12. Reading for next class: : Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey!
 CSE 8A Lecture 12 Reading for next class: 8.1-8.3: Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey! A vote for CSE 8A Yen Chuan (Allen) Liu and Pin (Arthur) Chu 1) Solo: (30 sec)
CSE 8A Lecture 12 Reading for next class: 8.1-8.3: Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey! A vote for CSE 8A Yen Chuan (Allen) Liu and Pin (Arthur) Chu 1) Solo: (30 sec)
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 topics: introduction to java, part 1
 topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 12, Name: KEY. Question Value Score
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays
 AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays Arrays. An array is an object that consists of an of similar items. An array has a single name and the items in an array are referred to in terms of their
AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays Arrays. An array is an object that consists of an of similar items. An array has a single name and the items in an array are referred to in terms of their
Write a program which converts all lowercase letter in a sentence to uppercase.
 Write a program which converts all lowercase letter in a sentence to uppercase. For Example: 1) Consider a sentence "welcome to Java Programming!" its uppercase conversion is " WELCOME TO JAVA PROGRAMMING!"
Write a program which converts all lowercase letter in a sentence to uppercase. For Example: 1) Consider a sentence "welcome to Java Programming!" its uppercase conversion is " WELCOME TO JAVA PROGRAMMING!"
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Programming in the Small II: Control
 Programming in the Small II: Control 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University Agenda Selection
Programming in the Small II: Control 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University Agenda Selection
CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I. Copyright 2016 by Smart Coding School
 CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I Primitive Data Type Primitive Data Type 8-bit signed Two s complement Integer -128 ~ 127 Primitive Data Type 16-bit signed Two s complement Integer -32768 ~ 32767 Primitive Data
CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I Primitive Data Type Primitive Data Type 8-bit signed Two s complement Integer -128 ~ 127 Primitive Data Type 16-bit signed Two s complement Integer -32768 ~ 32767 Primitive Data
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011
 CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5)
 Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
Midterm Practice Problems - answer key Answers appear in boldface.
 Part 1. (a) Consider the following code segment: int p = 30; int b; Midterm Practice Problems - answer key Answers appear in boldface. System.out.print( Please enter an integer ); b = kb.nextint(); if
Part 1. (a) Consider the following code segment: int p = 30; int b; Midterm Practice Problems - answer key Answers appear in boldface. System.out.print( Please enter an integer ); b = kb.nextint(); if
Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011
 Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE : FUNDAMENTALS OF SOFTWARE DESIGEN AND DEVELOPMENT COURSE CODE : PROG1003 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE
Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE : FUNDAMENTALS OF SOFTWARE DESIGEN AND DEVELOPMENT COURSE CODE : PROG1003 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 2, Name: Question Value Score
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Last Class CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Last Class CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013
 CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
COS 126 Exam Review. Exams overview Example programming exam Example written exam questions (part 1)
 COS 126 Exam Review Exams overview Example programming exam Example written exam questions (part 1) Exams overview (revisited) We have exams in the fall Two written exams. Two programming exams. Prep sessions
COS 126 Exam Review Exams overview Example programming exam Example written exam questions (part 1) Exams overview (revisited) We have exams in the fall Two written exams. Two programming exams. Prep sessions
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
Chapter 4: Control structures. Repetition
 Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps
 COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
Manipulating One-dimensional Arrays
 Manipulating One-dimensional Arrays Mitsu Ogihara Department of Computer Science University of Miami 1 / 30 Table of Contents 1 For each 2 Exchanging Values 3 Reversing 2 / 30 For-each iteration For enumerating
Manipulating One-dimensional Arrays Mitsu Ogihara Department of Computer Science University of Miami 1 / 30 Table of Contents 1 For each 2 Exchanging Values 3 Reversing 2 / 30 For-each iteration For enumerating
Warm up question. 2)Which of the following operators are defined on a half integer? Which of the following would it be useful to write as behaviors?
 Warm up question Suppose we have defined a class called half-integer The point of the class is to be able to store regular integers and also half integers (i.e. 3.5) 1)What would be a good way to represent
Warm up question Suppose we have defined a class called half-integer The point of the class is to be able to store regular integers and also half integers (i.e. 3.5) 1)What would be a good way to represent
Variables and data types
 Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
2. What are the two main components to the CPU and what do each of them do? 3. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter?
 COSC 117 Final Exam Spring 2011 Name: Part 1: Definitions & Short Answer (3 Points Each) 1. What do CPU and ALU stand for? 2. What are the two main components to the CPU and what do each of them do? 3.
COSC 117 Final Exam Spring 2011 Name: Part 1: Definitions & Short Answer (3 Points Each) 1. What do CPU and ALU stand for? 2. What are the two main components to the CPU and what do each of them do? 3.
CS Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009
 CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 72 points; ( 36 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 72 points; ( 36 questions, 2 points each) II.
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Written Exam 1
 COS 26 General Computer Science Fall 27 Written Exam This exam has 7 questions (including question ) worth a total of 7 points. You have 5 minutes. Write all answers inside the designated spaces. Policies.
COS 26 General Computer Science Fall 27 Written Exam This exam has 7 questions (including question ) worth a total of 7 points. You have 5 minutes. Write all answers inside the designated spaces. Policies.
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key
 Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key 1. [Question:] (15 points) Consider the code fragment below. Mark each location where an automatic cast will occur. Also find
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key 1. [Question:] (15 points) Consider the code fragment below. Mark each location where an automatic cast will occur. Also find
