Bits, Bytes, and Precision
|
|
|
- Toby Parker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bits, Bytes, and Precision Bit: Smallest amount of information in a computer. Binary: A bit holds either a 0 or 1. Series of bits make up a number. Byte: 8 bits. Single precision variable: 4 bytes (32 bits) Essentially 10 significant digits. Double precision variable: 8 bytes (64 bits) Essentially19 significant digits
2 Example: Quality controlling hourly station reports on a local mesonet (25 stations) Read in temperatures and dew points from a file. Find the average temperature and dew point Print stations that have temperature and/or dew points greater than ±5 ºF from the mean, sorted so that stations with the largest deviation are printed first How do I accomplish this task? You could try and read and re-read the file over and over, but this is inefficient. What do you do?
3 FORTRAN 90: Arrays Meteorology 227 Fall 2017
4 Data Structures Data structure to store and organize the collection of temperatures and dew points. Structure should allow data storage and retrieval. Data should be stored in main memory. 1-D array: Stores a fixed number of data values, all of the same type.
5 1-D Arrays In FORTRAN 90, the type statement would look like: REAL, DIMENSION(25) :: TEMP REAL, DIMENSION(25) :: DEW REAL, DIMENSION(25) :: TEMP, DEW Creates two arrays named TEMP and DEW consisting of 25 memory locations for each in which reals can be stored.
6 Accessing an Array Two methods of accessing an array Use array-variable (TEMP, DEW) to refer to the entire array. TEMP = 0 Use a subscripting variable and an index to refer to an individual element TEMP(5), DEW(6) is the 5 th temperature and the 6 th dew point. Each subscript variable refers to a memory location. By default, FORTRAN indexing starts at 1 unless otherwise stated. TEMP(1) is the first element, TEMP(2) is the second, etc.
7 Examples TEMP(5) = 68 DEW(5) = 66 DEPRESSION(5) = TEMP(5) DEW(5) PRINT *, Dew Point Depression =, DEPRESSION(5) READ(10,*) TEMP(N), DEW(N) How might this be used? DO N=1, 25 READ(10,*) TEMP(N), DEW(N) END DO Mean-time to failure program in book.
8 Implied DO loops Can be used to simplify input and output Useful, but does sacrifice readability. (list-of-variables, control-var = init-value, limit, step) READ(10,*) (TEMP(N), DEW(N), N=1,25) This is equivalent to the loop on the previous slide.
9 Compile time and Allocatable Arrays What do we currently know? Size of arrays are fixed at compile time. Small dataset: wasted memory Large dataset: Too large to store and process correctly.
10 Compile time arrays type, DIMENSION(l:u) :: list-of-array-names type :: list-of-array specifiers array-name(l:u) FORTRAN does allow a subscript to be any integer value, positive, negative, or zero Must not fall outside of the range specified. INTEGER, PARAMETER ::LowerLimit_1= -1, UpperLimit_1 = 3, & LowerLimit_2 = 0, UpperLimit_2 = 5 INTEGER, DIMENSION(LowerLimit_1 : UpperLimit_1) :: Alpha REAL, DIMENSION(LowerLimit_2 : UpperLimit_2) :: Beta
11 Run-time or Allocatable arrays ALLOCATE attribute REAL, DIMENSION(:), ALLOCATABLE :: list-of-array-names REAL, DIMENSION(:), ALLOCATABLE :: A, B Later in program.. ALLOCATE(list, STAT = status-variable) List is a list of array specifications of the form array-name(l:u) Status-variable is an integer variable that: 0 is allocation of array is successful. Non-zero if an error occurred. Even later in the program DEALLOCATE(list, STAT=status-variable) Status-variable is identical to ALLOCATE statement except for deallocating the array.
12 Array Constants Arrays may be filled by a list of values enclosed between (/ and /) A = (/ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 /) This may be simplified with an implied do loop A = (/ (2*N, N = 1, 10) /) A = (/ 2, 4, (N, N = 6, 18, 2), 20 /) How do we use this? INTEGER, DIMENSION(10) :: A A = (/ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 /) A = (/ (2*N, N = 1, 10) /) A = (/ 2, 4, (N, N = 6, 18, 2), 20 /) Each of these are the same as: DO N = 1, 10 A(N) = 2*N END DO
13 Quick Digression: Modulus MOD(A,P) = A INT(A/P) * P Returns the remainder when A is divided by P. Examples Z = MOD(9,3) Z = MOD(10,3) Z = MOD(Hours_into_model_run,24) Arguments can be integer or real.
14 Array Expressions Operators and functions normally applied to simple expressions may also be applied to arrays having the same number of elements. Operations are carried out element by element. INTEGER, DIMENSION(4) :: A, B INTEGER, DIMENSION(0:3) :: C INTEGER, DIMENSION(6:9) :: D LOGICAL, DIMENSION(4) :: P A = (/ 1, 2, 3, 4 /) B = (/ 5, 6, 7, 8 /) C = (/ -1, 3, -5, 7 /) A = A+B D = 2 * ABS(C) + 1 P = (C > 0).AND. (MOD(B,3) == 0) What are A, D, and P? A = 6, 8, 10, 12 D = 3, 7, 11, 15 P =.false.,.true.,.false.,.false.
15 Array Assignment Array-variable = expression The value of expression assigned to an array variable must be either: An array of the same size as the array variable, or A simple value. In the second case, the value is broadcast to all members of the array.
16 Array Sections and Subarrays Allows you to construct new arrays by selecting elements from another array Array-name(subscript-triplet) Array-name(vector-subscript) Subscript triplet: lower : upper : stride If lower (upper) is omitted, the lower (upper) bound in the array declaration is used. INTEGER, DIMENSION(10) :: A INTEGER, DIMENSION(5) :: B, I A = (/ 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 110 /) B = A(2 : 10 : 2) What is B?
17 Array sections cont.: Vector-subscripts A = (/ 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 110 /) N = (/ 6, 5, 3, 9, 1 /) B = A(N) Assigns to B the element locations from array A listed by N. Values in N become indices. B = 66, 55, 33, 99, 11 B = A(( /5, 3,3,4, 3 /))? A(1 : 10 : 2) = (/ N**2, N = 1, 5 /)?
18 Subarrays cont.: Input/Output DO N = 1, NumTemps READ(10,*) Temp(N) END DO READ(10,*) (Temp(N), N = 1, NumTemps) READ(10, *) Temp(1:NumTemps) PRINT *, Temp(1:NumTemps)
19 WHERE construct Used to assign values to arrays depending on the value of a logical array expression WHERE (logical-array-expr) array-var = array-expr. ELSEWHERE array-var = array-expr END WHERE Logical expression is evaluated element by element. INTEGER, DIMENSION(5) :: A = (/ 0, 2, 5, 0, 10 /) REAL, DIMENSION(5) :: B WHERE (A > 0) B = 1.0/ REAL(A) ELSEWHERE B = -1.0 END WHERE What is B? B = -1.0, 0.5, 0.2, -1.0, 0.1
20 Arrays as Arguments Several intrinsic functions exist for arrays ALLOCATED(A) Returns true if memory has been allocated to the allocatable array A and false otherwise MAXVAL(A) Returns the maximum value of A MINVAL(A) Returns the minimum value of A MAXLOC(A) Returns a one-dimensional array containing on element whose value is the position of the first occurrence of the maximum value in A. MINLOC(A) DOT_PRODUCT(A,B) Returns the dot product of arrays A and B. SUM(A) Returns the sum of the elements in A. PRODUCT(A) Returns the product of the elements in A. SIZE(A) Returns the number of elements in A. Others can be found in appendix A.
21 Multi-Dimensional Arrays Many applications Data naturally fits into a table. Times series of temperature measurements from multiple stations. Data is on a grid. Example: Hourly data from Flory micronet. 50 stations reporting hourly output. Construct table/form array to hold data. REAL, DIMENSION(24,50) :: Temperature Indices are arranged as (hour, station) REAL, DIMENSION(1:24,1:50) :: Temperature Question: What is Temperature(12,12)?
22 Multi-Dimensional Arrays cont. This array only holds data for one day, what if I want multiple days? REAL, DIMENSION(365,24,50) :: Temperature Indices are arranged as (day, hour, station). What is Temperature(180,12,20)? Temperature from the 20 th station on the 180 th day of year at the 12 th hour.
23 Declarations Compile time type, DIMENSION(L 1 :U 1,L 2 :U 2,.,L k :U k ) :: list type, list-of-array-specifiers Number of dimensions, k, is called the rank of the array. REAL, DIMENSION(1:2,-1:3) :: Alpha REAL, DIMENSION(0:2,0:3,1:2) :: Beta List all of the valid references to each array?
24 Declarations - Allocatable type, DIMENSION(:, :, :,..., :), ALLOCATABLE :: list REAL, DIMENSION (:, :, :), ALLOCATABLE :: Beta REAL, DIMENSION (:, :), ALLOCATABLE :: Alpha ALLOCATE(Beta(0:2,0:3,1:2), Alpha(1:2,-1:3), & STAT = AllocateStatus) Example: Table of temperatures.
25 Sorting and Searching Section 8.4 Sorting: Arranging items in a list so that they are in ascending or descending order. Selection sort, quick sort, bubble sort Searching: Finding a specified item and retrieving information associated with that item. Linear search, binary search
26 Selection Sort Traverse the list, or part of the list, several times, each time selecting one item to be correctly positioned. Method (ascending order): 1. Find smallest item and move it to the first position by exchanging it with that number. 2. Scan the rest of the list starting from position #2 and repeat. 3. Continue in this manner until the list is sorted rd element in the list to the end of the list, etc. Let s practice.
27 Quick Sort (Recursive sorting) More efficient than a selection sort. One of the fastest sorting methods. Method: Select pivot element (typically first element). Perform exchanges so that all elements on left of pivot are less than the pivot and all elements on the right are greater than the pivot. Correctly positions the pivot element. Divides the list into two sub-lists. Sort sub-lists independently in the same way. Divide and conquer approach. 50, 30, 20, 80, 90, 70, 95, 85, 10, 15, 75, 25
28 Searching Linear Search Begin with first item in list and search sequentially until desired item is found or end of list is reached. Binary Search If a list has been sorted, a binary search can be used more efficiently. Method Examine middle element in the list. Is it the desired element? If not, determine if desired item in the first or second half of list. Search that half of the list using the same approach.
Searching, Sorting. Arizona State University 1
 Searching, Sorting CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 9 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State
Searching, Sorting CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 9 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State
High Institute of Computer Science & Information Technology Term : 1 st. El-Shorouk Academy Acad. Year : 2013 / Year : 2 nd
 El-Shorouk Academy Acad. Year : 2013 / 2014 High Institute of Computer Science & Information Technology Term : 1 st Year : 2 nd Computer Science Department Object Oriented Programming Section (1) Arrays
El-Shorouk Academy Acad. Year : 2013 / 2014 High Institute of Computer Science & Information Technology Term : 1 st Year : 2 nd Computer Science Department Object Oriented Programming Section (1) Arrays
Lecture 2 Arrays, Searching and Sorting (Arrays, multi-dimensional Arrays)
 Lecture 2 Arrays, Searching and Sorting (Arrays, multi-dimensional Arrays) In this lecture, you will: Learn about arrays Explore how to declare and manipulate data into arrays Understand the meaning of
Lecture 2 Arrays, Searching and Sorting (Arrays, multi-dimensional Arrays) In this lecture, you will: Learn about arrays Explore how to declare and manipulate data into arrays Understand the meaning of
Chapter 4. Fortran Arrays
 Chapter 4. Fortran Arrays Fortran arrays are any object with the dimension attribute. In Fortran 90/95, and in HPF, arrays may be very different from arrays in older versions of Fortran. Arrays can have
Chapter 4. Fortran Arrays Fortran arrays are any object with the dimension attribute. In Fortran 90/95, and in HPF, arrays may be very different from arrays in older versions of Fortran. Arrays can have
CSC 307 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHM ANALYSIS IN C++ SPRING 2011
 CSC 307 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHM ANALYSIS IN C++ SPRING 2011 Date: 01/18/2011 (Due date: 01/20/2011) Name and ID (print): CHAPTER 6 USER-DEFINED FUNCTIONS I 1. The C++ function pow has parameters.
CSC 307 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHM ANALYSIS IN C++ SPRING 2011 Date: 01/18/2011 (Due date: 01/20/2011) Name and ID (print): CHAPTER 6 USER-DEFINED FUNCTIONS I 1. The C++ function pow has parameters.
8.1. Chapter 8: Introduction to Search Algorithms. Linear Search. Linear Search. Linear Search - Example 8/23/2014. Introduction to Search Algorithms
 Chapter 8: Searching and Sorting Arrays 8.1 Introduction to Search Algorithms Introduction to Search Algorithms Search: locate an item in a list of information Two algorithms we will examine: Linear search
Chapter 8: Searching and Sorting Arrays 8.1 Introduction to Search Algorithms Introduction to Search Algorithms Search: locate an item in a list of information Two algorithms we will examine: Linear search
We can use a max-heap to sort data.
 Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching
 Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching Sorting takes an unordered collection and makes it an ordered one. 1 2 3 4 5 6 77 42 35 12 101 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 5 12 35 42 77 101 There are many algorithms for sorting a list
Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching Sorting takes an unordered collection and makes it an ordered one. 1 2 3 4 5 6 77 42 35 12 101 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 5 12 35 42 77 101 There are many algorithms for sorting a list
190 Lecture 14 Arrays, allocation
 190 Lecture 14 Arrays, allocation Reading assignment: chapters. 8, 9, 10, 11, VECTORS AND ARRAYS real::v(4) means v = v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4 real::v(1:4)same thing v = v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4 real::v(0:3)means
190 Lecture 14 Arrays, allocation Reading assignment: chapters. 8, 9, 10, 11, VECTORS AND ARRAYS real::v(4) means v = v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4 real::v(1:4)same thing v = v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4 real::v(0:3)means
ARRAYS COMPUTER PROGRAMMING. By Zerihun Alemayehu
 ARRAYS COMPUTER PROGRAMMING By Zerihun Alemayehu AAiT.CED Rm. E119B BASIC RULES AND NOTATION An array is a group of variables or constants, all of the same type, that are referred to by a single name.
ARRAYS COMPUTER PROGRAMMING By Zerihun Alemayehu AAiT.CED Rm. E119B BASIC RULES AND NOTATION An array is a group of variables or constants, all of the same type, that are referred to by a single name.
Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings. Objectives. Objectives (cont d.) Introduction. Arrays 12/23/2016. In this chapter, you will:
 Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about arrays Declare and manipulate data into arrays Learn about array index out of bounds Learn about the restrictions on array
Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about arrays Declare and manipulate data into arrays Learn about array index out of bounds Learn about the restrictions on array
Java How to Program, 9/e. Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Copyright 1992-2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Searching data involves determining whether a value (referred to as the search key) is present in the data
Java How to Program, 9/e Copyright 1992-2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Searching data involves determining whether a value (referred to as the search key) is present in the data
LECTURE 08 SEARCHING AND SORTING ARRAYS
 PowerPoint Slides adapted from *Starting Out with C++: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E* by *Tony Gaddis* Copyright 2012 Pearson Education Inc. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LECTURE 08 SEARCHING AND
PowerPoint Slides adapted from *Starting Out with C++: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E* by *Tony Gaddis* Copyright 2012 Pearson Education Inc. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LECTURE 08 SEARCHING AND
Allocating Storage for 1-Dimensional Arrays
 Allocating Storage for 1-Dimensional Arrays Recall that if we know beforehand what size we want an array to be, then we allocate storage in the declaration statement, e.g., real, dimension (100 ) :: temperatures
Allocating Storage for 1-Dimensional Arrays Recall that if we know beforehand what size we want an array to be, then we allocate storage in the declaration statement, e.g., real, dimension (100 ) :: temperatures
Sorting. Task Description. Selection Sort. Should we worry about speed?
 Sorting Should we worry about speed? Task Description We have an array of n values in any order We need to have the array sorted in ascending or descending order of values 2 Selection Sort Select the smallest
Sorting Should we worry about speed? Task Description We have an array of n values in any order We need to have the array sorted in ascending or descending order of values 2 Selection Sort Select the smallest
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 6. Sorting Algorithms
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 6 6.0 Introduction Sorting algorithms used in computer science are often classified by: Computational complexity (worst, average and best behavior) of element
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 6 6.0 Introduction Sorting algorithms used in computer science are often classified by: Computational complexity (worst, average and best behavior) of element
Test Bank Ver. 5.0: Data Abstraction and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, 5 th edition, Frank M. Carrano
 Chapter 2 Recursion: The Mirrors Multiple Choice Questions 1. In a recursive solution, the terminates the recursive processing. a) local environment b) pivot item c) base case d) recurrence relation 2.
Chapter 2 Recursion: The Mirrors Multiple Choice Questions 1. In a recursive solution, the terminates the recursive processing. a) local environment b) pivot item c) base case d) recurrence relation 2.
Data Abstraction & Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors 6th Edition Carrano, Henry Test Bank
 Data Abstraction & Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors 6th Edition Carrano, Henry Test Bank Download link: https://solutionsmanualbank.com/download/test-bank-for-data-abstractionproblem-solving-with-c-walls-and-mirrors-6-e-carrano-henry/
Data Abstraction & Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors 6th Edition Carrano, Henry Test Bank Download link: https://solutionsmanualbank.com/download/test-bank-for-data-abstractionproblem-solving-with-c-walls-and-mirrors-6-e-carrano-henry/
8/2/10. Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE. Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE
 Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE Searching algorithms Linear search Complexity Sorting algorithms
Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE Searching algorithms Linear search Complexity Sorting algorithms
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
Overview of Sorting Algorithms
 Unit 7 Sorting s Simple Sorting algorithms Quicksort Improving Quicksort Overview of Sorting s Given a collection of items we want to arrange them in an increasing or decreasing order. You probably have
Unit 7 Sorting s Simple Sorting algorithms Quicksort Improving Quicksort Overview of Sorting s Given a collection of items we want to arrange them in an increasing or decreasing order. You probably have
C Language Part 2 Digital Computer Concept and Practice Copyright 2012 by Jaejin Lee
 C Language Part 2 (Minor modifications by the instructor) 1 Scope Rules A variable declared inside a function is a local variable Each local variable in a function comes into existence when the function
C Language Part 2 (Minor modifications by the instructor) 1 Scope Rules A variable declared inside a function is a local variable Each local variable in a function comes into existence when the function
CS 445: Data Structures Final Examination: Study Guide
 CS 445: Data Structures Final Examination: Study Guide Java prerequisites Classes, objects, and references Access modifiers Arguments and parameters Garbage collection Self-test questions: Appendix C Designing
CS 445: Data Structures Final Examination: Study Guide Java prerequisites Classes, objects, and references Access modifiers Arguments and parameters Garbage collection Self-test questions: Appendix C Designing
Introduction to Fortran95 Programming Part II. By Deniz Savas, CiCS, Shef. Univ., 2018
 Introduction to Fortran95 Programming Part II By Deniz Savas, CiCS, Shef. Univ., 2018 Summary of topics covered Logical Expressions, IF and CASE statements Data Declarations and Specifications ARRAYS and
Introduction to Fortran95 Programming Part II By Deniz Savas, CiCS, Shef. Univ., 2018 Summary of topics covered Logical Expressions, IF and CASE statements Data Declarations and Specifications ARRAYS and
Subject: Computer Science
 Subject: Computer Science Topic: Data Types, Variables & Operators 1 Write a program to print HELLO WORLD on screen. 2 Write a program to display output using a single cout statement. 3 Write a program
Subject: Computer Science Topic: Data Types, Variables & Operators 1 Write a program to print HELLO WORLD on screen. 2 Write a program to display output using a single cout statement. 3 Write a program
Objectives. Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings. Objectives (cont d.) Introduction 12/14/2014. In this chapter, you will:
 Objectives Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings In this chapter, you will: Learn about arrays Declare and manipulate data into arrays Learn about array index out of bounds Learn about the restrictions on array
Objectives Chapter 8 Arrays and Strings In this chapter, you will: Learn about arrays Declare and manipulate data into arrays Learn about array index out of bounds Learn about the restrictions on array
Today. CISC101 Reminders & Notes. Searching in Python - Cont. Searching in Python. From last time
 CISC101 Reminders & Notes Test 3 this week in tutorial USATs at the beginning of next lecture Please attend and fill out an evaluation School of Computing First Year Information Session Thursday, March
CISC101 Reminders & Notes Test 3 this week in tutorial USATs at the beginning of next lecture Please attend and fill out an evaluation School of Computing First Year Information Session Thursday, March
Principles of Programming. Chapter 6: Arrays
 Chapter 6: Arrays In this chapter, you will learn about Introduction to Array Array declaration Array initialization Assigning values to array elements Reading values from array elements Simple Searching
Chapter 6: Arrays In this chapter, you will learn about Introduction to Array Array declaration Array initialization Assigning values to array elements Reading values from array elements Simple Searching
Goals for This Lecture:
 Goals for This Lecture: Understand what function subprograms are Understand how to use function subprograms Understand the various kinds of REAL types Understand how to select precision in a processor
Goals for This Lecture: Understand what function subprograms are Understand how to use function subprograms Understand the various kinds of REAL types Understand how to select precision in a processor
PERFORMANCE OF VARIOUS SORTING AND SEARCHING ALGORITHMS Aarushi Madan Aarusi Tuteja Bharti
 PERFORMANCE OF VARIOUS SORTING AND SEARCHING ALGORITHMS Aarushi Madan Aarusi Tuteja Bharti memory. So for the better performance of an algorithm, time complexity and space complexity has been considered.
PERFORMANCE OF VARIOUS SORTING AND SEARCHING ALGORITHMS Aarushi Madan Aarusi Tuteja Bharti memory. So for the better performance of an algorithm, time complexity and space complexity has been considered.
Cpt S 122 Data Structures. Sorting
 Cpt S 122 Data Structures Sorting Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Sorting Process of re-arranging data in ascending or descending order Given
Cpt S 122 Data Structures Sorting Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Sorting Process of re-arranging data in ascending or descending order Given
Quick-Sort fi fi fi 7 9. Quick-Sort Goodrich, Tamassia
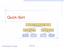 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Prof. Sushant S Sundikar 1
 UNIT 5 The related activities of sorting, searching and merging are central to many computer applications. Sorting and merging provide us with a means of organizing information take advantage of the organization
UNIT 5 The related activities of sorting, searching and merging are central to many computer applications. Sorting and merging provide us with a means of organizing information take advantage of the organization
Sorting Algorithms. Array Data is being arranged in ascending order using the bubble sort algorithm. #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7
 Sorting Algorithms One of the fundamental problems of computer science is ordering a list of items. There s a plethora of solutions to this problem, known as sorting algorithms. Some sorting algorithms
Sorting Algorithms One of the fundamental problems of computer science is ordering a list of items. There s a plethora of solutions to this problem, known as sorting algorithms. Some sorting algorithms
Chapter 3. Fortran Statements
 Chapter 3 Fortran Statements This chapter describes each of the Fortran statements supported by the PGI Fortran compilers Each description includes a brief summary of the statement, a syntax description,
Chapter 3 Fortran Statements This chapter describes each of the Fortran statements supported by the PGI Fortran compilers Each description includes a brief summary of the statement, a syntax description,
Chapter 8 Search and Sort
 Chapter 8 Search and Sort Goals This chapter begins by showing two algorithms used with arrays: selection sort and binary search. After studying this chapter, you will be able to understand how binary
Chapter 8 Search and Sort Goals This chapter begins by showing two algorithms used with arrays: selection sort and binary search. After studying this chapter, you will be able to understand how binary
Computer System and programming in C
 1 Basic Data Types Integral Types Integers are stored in various sizes. They can be signed or unsigned. Example Suppose an integer is represented by a byte (8 bits). Leftmost bit is sign bit. If the sign
1 Basic Data Types Integral Types Integers are stored in various sizes. They can be signed or unsigned. Example Suppose an integer is represented by a byte (8 bits). Leftmost bit is sign bit. If the sign
Practical Exercise 1 Question 1: The Hello World Program Write a Fortran 95 program to write out Hello World on the screen.
 Practical Exercise Question : The Hello World Program Write a Fortran 95 program to write out Hello World on the screen. Question : Some Division One Results A particular number can be expressed as the
Practical Exercise Question : The Hello World Program Write a Fortran 95 program to write out Hello World on the screen. Question : Some Division One Results A particular number can be expressed as the
L14 Quicksort and Performance Optimization
 L14 Quicksort and Performance Optimization Alice E. Fischer Fall 2018 Alice E. Fischer L4 Quicksort... 1/12 Fall 2018 1 / 12 Outline 1 The Quicksort Strategy 2 Diagrams 3 Code Alice E. Fischer L4 Quicksort...
L14 Quicksort and Performance Optimization Alice E. Fischer Fall 2018 Alice E. Fischer L4 Quicksort... 1/12 Fall 2018 1 / 12 Outline 1 The Quicksort Strategy 2 Diagrams 3 Code Alice E. Fischer L4 Quicksort...
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010106 Set No. 1 1. (a) Draw a Flowchart for the following The average score for 3 tests has to be greater than 80 for a candidate to qualify for the interview. Representing the conditional
Code No: R05010106 Set No. 1 1. (a) Draw a Flowchart for the following The average score for 3 tests has to be greater than 80 for a candidate to qualify for the interview. Representing the conditional
Binary Search and Worst-Case Analysis
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong A significant part of computer science is devoted to understanding the power of the RAM model in solving specific problems.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong A significant part of computer science is devoted to understanding the power of the RAM model in solving specific problems.
INTRODUCTION TO FORTRAN PART II
 INTRODUCTION TO FORTRAN PART II Prasenjit Ghosh An example: The Fibonacci Sequence The Fibonacci sequence consists of an infinite set of integer nos. which satisfy the following recurrence relation x n
INTRODUCTION TO FORTRAN PART II Prasenjit Ghosh An example: The Fibonacci Sequence The Fibonacci sequence consists of an infinite set of integer nos. which satisfy the following recurrence relation x n
An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type.
 Data Structures Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous
Data Structures Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous
Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 3 Fall, Points
 Introduction to Computer Science Fall, 2001 100 Points Notes 1. Tear off this sheet and use it to keep your answers covered at all times. 2. Turn the exam over and write your name next to the staple. Do
Introduction to Computer Science Fall, 2001 100 Points Notes 1. Tear off this sheet and use it to keep your answers covered at all times. 2. Turn the exam over and write your name next to the staple. Do
Pseudo code of algorithms are to be read by.
 Cs502 Quiz No1 Complete Solved File Pseudo code of algorithms are to be read by. People RAM Computer Compiler Approach of solving geometric problems by sweeping a line across the plane is called sweep.
Cs502 Quiz No1 Complete Solved File Pseudo code of algorithms are to be read by. People RAM Computer Compiler Approach of solving geometric problems by sweeping a line across the plane is called sweep.
Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach. By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran
 Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran The Problem Given an array X, having some labelled items.
Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran The Problem Given an array X, having some labelled items.
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixedsize sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection
 Morteza Noferesti Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixedsize sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful
Morteza Noferesti Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixedsize sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful
Component 02. Algorithms and programming. Sorting Algorithms and Searching Algorithms. Matthew Robinson
 Component 02 Algorithms and programming Sorting Algorithms and Searching Algorithms 1 BUBBLE SORT Bubble sort is a brute force and iterative sorting algorithm where each adjacent item in the array is compared.
Component 02 Algorithms and programming Sorting Algorithms and Searching Algorithms 1 BUBBLE SORT Bubble sort is a brute force and iterative sorting algorithm where each adjacent item in the array is compared.
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS. Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 7. 1-D & 2-D Arrays
 CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 7. 1-D & 2-D Arrays Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 1 Arrays Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 1-D Arrays Data Structures The Array Data Type How to Declare
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 7. 1-D & 2-D Arrays Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 1 Arrays Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 1-D Arrays Data Structures The Array Data Type How to Declare
V2 3/5/2012. Programming in C. Introduction to Arrays. 111 Ch 07 A 1. Introduction to Arrays
 Programming in C 1 Introduction to Arrays A collection of variable data Same name Same type Contiguous block of memory Can manipulate or use Individual variables or List as one entity 2 Celsius temperatures:
Programming in C 1 Introduction to Arrays A collection of variable data Same name Same type Contiguous block of memory Can manipulate or use Individual variables or List as one entity 2 Celsius temperatures:
Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers
 Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 06 - Stephen Scott Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke 1 / 30 Fall 2009 Chapter 8 8.1 Declaring and 8.2 Array Subscripts 8.3 Using
Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 06 - Stephen Scott Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke 1 / 30 Fall 2009 Chapter 8 8.1 Declaring and 8.2 Array Subscripts 8.3 Using
Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs
 Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs I. The student will analyze the different systems, and languages of the computer. (SM 1.4, 3.1, 3.4, 3.6) II. The student will write, compile, link and run a simple C++
Computer Programming C++ (wg) CCOs I. The student will analyze the different systems, and languages of the computer. (SM 1.4, 3.1, 3.4, 3.6) II. The student will write, compile, link and run a simple C++
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++
 CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 3 Monday, April 17, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 11 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 3 Monday, April 17, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 11 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++
 CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 3 Monday, April 17, 2017 Total - 100 Points A Instructions: Total of 11 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 3 Monday, April 17, 2017 Total - 100 Points A Instructions: Total of 11 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; :
![Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; : Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; :](/thumbs/74/69682489.jpg) Runtime Environment Relationship between names and data objects (of target machine) Allocation & de-allocation is managed by run time support package Each execution of a procedure is an activation of the
Runtime Environment Relationship between names and data objects (of target machine) Allocation & de-allocation is managed by run time support package Each execution of a procedure is an activation of the
Quadratic: the time that it takes to sort an array is proportional to the. square of the number of elements.
 ITEC 136 Business Programming Concepts Week 12, Part 01 Overview 1 Week 12 Overview Week 11 review Associative Arrays Common Array Operations Inserting shifting elements right Removing shifting elements
ITEC 136 Business Programming Concepts Week 12, Part 01 Overview 1 Week 12 Overview Week 11 review Associative Arrays Common Array Operations Inserting shifting elements right Removing shifting elements
These are reserved words of the C language. For example int, float, if, else, for, while etc.
 Tokens in C Keywords These are reserved words of the C language. For example int, float, if, else, for, while etc. Identifiers An Identifier is a sequence of letters and digits, but must start with a letter.
Tokens in C Keywords These are reserved words of the C language. For example int, float, if, else, for, while etc. Identifiers An Identifier is a sequence of letters and digits, but must start with a letter.
C/C++ Programming Lecture 18 Name:
 . The following is the textbook's code for a linear search on an unsorted array. //***************************************************************** // The searchlist function performs a linear search
. The following is the textbook's code for a linear search on an unsorted array. //***************************************************************** // The searchlist function performs a linear search
COMP Data Structures
 COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 5 - Sorting University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 55 Overview Review: Insertion Sort Merge Sort Quicksort
COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 5 - Sorting University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 55 Overview Review: Insertion Sort Merge Sort Quicksort
A Brief Introduction to Fortran of 15
 A Brief Introduction to Fortran 90 1 of 15 Data Types and Kinds Data types Intrisic data types (INTEGER, REAL,LOGICAL) derived data types ( structures or records in other languages) kind parameter (or
A Brief Introduction to Fortran 90 1 of 15 Data Types and Kinds Data types Intrisic data types (INTEGER, REAL,LOGICAL) derived data types ( structures or records in other languages) kind parameter (or
Chapter 10. Sorting and Searching Algorithms. Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1. Sorting. Given a set (container) of n elements
 Chapter Sorting and Searching Algorithms Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1 Sorting Given a set (container) of n elements Eg array, set of words, etc Suppose there is an order relation that can be set across
Chapter Sorting and Searching Algorithms Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1 Sorting Given a set (container) of n elements Eg array, set of words, etc Suppose there is an order relation that can be set across
Sorting. Sorting in Arrays. SelectionSort. SelectionSort. Binary search works great, but how do we create a sorted array in the first place?
 Sorting Binary search works great, but how do we create a sorted array in the first place? Sorting in Arrays Sorting algorithms: Selection sort: O(n 2 ) time Merge sort: O(nlog 2 (n)) time Quicksort: O(n
Sorting Binary search works great, but how do we create a sorted array in the first place? Sorting in Arrays Sorting algorithms: Selection sort: O(n 2 ) time Merge sort: O(nlog 2 (n)) time Quicksort: O(n
Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting. Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms
 Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms Overview Writing programs to solve problem consists of a large number of decisions how to represent
Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms Overview Writing programs to solve problem consists of a large number of decisions how to represent
FORTRAN - ARRAYS. For example, to declare a one-dimensional array named number, of real numbers containing 5 elements, you write,
 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/fortran/fortran_arrays.htm FORTRAN - ARRAYS Copyright tutorialspoint.com Arrays can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/fortran/fortran_arrays.htm FORTRAN - ARRAYS Copyright tutorialspoint.com Arrays can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used
Sorting. Data structures and Algorithms
 Sorting Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and Mount (Wiley, 2004) Outline Bubble
Sorting Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and Mount (Wiley, 2004) Outline Bubble
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology. Unit 4.2
 MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 4.2 Quiz 1 results (out of 25) Mean: 19.9, (standard deviation = 3.9) Equivalent to 79.1% (SD = 15.6) Median: 21.5 High score: 24 Low score: 13 Pointer
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 4.2 Quiz 1 results (out of 25) Mean: 19.9, (standard deviation = 3.9) Equivalent to 79.1% (SD = 15.6) Median: 21.5 High score: 24 Low score: 13 Pointer
For searching and sorting algorithms, this is particularly dependent on the number of data elements.
 Looking up a phone number, accessing a website and checking the definition of a word in a dictionary all involve searching large amounts of data. Searching algorithms all accomplish the same goal finding
Looking up a phone number, accessing a website and checking the definition of a word in a dictionary all involve searching large amounts of data. Searching algorithms all accomplish the same goal finding
Sorting/Searching and File I/O. Sorting Searching Reading for this lecture: L&L
 Sorting/Searching and File I/O Sorting Searching Reading for this lecture: L&L 10.4-10.5 1 Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items in a particular order The sorting process is based
Sorting/Searching and File I/O Sorting Searching Reading for this lecture: L&L 10.4-10.5 1 Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items in a particular order The sorting process is based
Sorting Goodrich, Tamassia Sorting 1
 Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
How to declare an array in C?
 Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous values.
Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous values.
COSC2430: Programming and Data Structures Sparse Matrix Multiplication: Search and Sorting Algorithms
 COSC2430: Programming and Data Structures Sparse Matrix Multiplication: Search and Sorting Algorithms 1 Introduction You will create a C++ program to multiply two sparse matrices as efficiently as possible
COSC2430: Programming and Data Structures Sparse Matrix Multiplication: Search and Sorting Algorithms 1 Introduction You will create a C++ program to multiply two sparse matrices as efficiently as possible
AP Computer Science. Arrays. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
 AP Computer Science Arrays Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp: 44 Day 3's high temp: 39
AP Computer Science Arrays Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp: 44 Day 3's high temp: 39
Sorting and Searching
 Sorting and Searching Sorting o Simple: Selection Sort and Insertion Sort o Efficient: Quick Sort and Merge Sort Searching o Linear o Binary Reading for this lecture: http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/python/42sort/
Sorting and Searching Sorting o Simple: Selection Sort and Insertion Sort o Efficient: Quick Sort and Merge Sort Searching o Linear o Binary Reading for this lecture: http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/python/42sort/
Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2010 Handout Decaf Language Tuesday, Feb 2 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2010 Handout Decaf Language Tuesday, Feb 2 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Review More Arrays Modules Final Review
 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 MORE ARRAYS Using Arrays Why do we need dynamic arrays? Using Dynamic Arrays 3 MODULES Global Variables Interface Blocks Modular Programming 4 FINAL REVIEW THE STORY SO FAR... Create
OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 MORE ARRAYS Using Arrays Why do we need dynamic arrays? Using Dynamic Arrays 3 MODULES Global Variables Interface Blocks Modular Programming 4 FINAL REVIEW THE STORY SO FAR... Create
UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SCHOOL OF INFORMATICS INFR08013 INFORMATICS 1 - FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
 UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SCHOOL OF INFORMATICS INFR08013 INFORMATICS 1 - FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING Monday 15 th December 2014 14:30 to 16:30 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1.
UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SCHOOL OF INFORMATICS INFR08013 INFORMATICS 1 - FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING Monday 15 th December 2014 14:30 to 16:30 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1.
C How to Program, 7/e by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 C How to Program, 7/e This chapter serves as an introduction to data structures. Arrays are data structures consisting of related data items of the same type. In Chapter 10, we discuss C s notion of
C How to Program, 7/e This chapter serves as an introduction to data structures. Arrays are data structures consisting of related data items of the same type. In Chapter 10, we discuss C s notion of
CS1500 Algorithms and Data Structures for Engineering, FALL Virgil Pavlu, Jose Annunziato,
 CS1500 Algorithms and Data Structures for Engineering, FALL 2012 Virgil Pavlu, vip@ccs.neu.edu Jose Annunziato, jannunzi@gmail.com Rohan Garg Morteza Dilgir Huadong Li cs1500hw@gmail.com http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/vip/teach/cpp_eng/
CS1500 Algorithms and Data Structures for Engineering, FALL 2012 Virgil Pavlu, vip@ccs.neu.edu Jose Annunziato, jannunzi@gmail.com Rohan Garg Morteza Dilgir Huadong Li cs1500hw@gmail.com http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/vip/teach/cpp_eng/
Sorting and Selection
 Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
Introduction to Programming with Fortran 90
 Introduction to Programming with Fortran 90 p. 1/?? Introduction to Programming with Fortran 90 Array Concepts Nick Maclaren Computing Service nmm1@cam.ac.uk, ext. 34761 November 2007 Introduction to Programming
Introduction to Programming with Fortran 90 p. 1/?? Introduction to Programming with Fortran 90 Array Concepts Nick Maclaren Computing Service nmm1@cam.ac.uk, ext. 34761 November 2007 Introduction to Programming
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON
 DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Sorting, Searching Algorithm and Regular Expression Peter Lo Sorting Algorithms Put Elements of List in Certain Order 2 Bubble Sort The bubble sort makes multiple
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Sorting, Searching Algorithm and Regular Expression Peter Lo Sorting Algorithms Put Elements of List in Certain Order 2 Bubble Sort The bubble sort makes multiple
Table ADT and Sorting. Algorithm topics continuing (or reviewing?) CS 24 curriculum
 Table ADT and Sorting Algorithm topics continuing (or reviewing?) CS 24 curriculum A table ADT (a.k.a. Dictionary, Map) Table public interface: // Put information in the table, and a unique key to identify
Table ADT and Sorting Algorithm topics continuing (or reviewing?) CS 24 curriculum A table ADT (a.k.a. Dictionary, Map) Table public interface: // Put information in the table, and a unique key to identify
Analysis of Algorithms. Unit 4 - Analysis of well known Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Unit 4 - Analysis of well known Algorithms 1 Analysis of well known Algorithms Brute Force Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Divide and Conquer Algorithms Decrease and Conquer Algorithms
Analysis of Algorithms Unit 4 - Analysis of well known Algorithms 1 Analysis of well known Algorithms Brute Force Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Divide and Conquer Algorithms Decrease and Conquer Algorithms
Arrays. Arizona State University 1
 Arrays CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 8 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Arrays CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 8 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 7/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 7/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Merge sort Quick sort Radix sort Summary We will see more complex techniques
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 7/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Merge sort Quick sort Radix sort Summary We will see more complex techniques
Chapter 6. A Brief Introduction to Fortran David A. Padua
 Chapter 6. A Brief Introduction to Fortran 90 1998 David A. Padua 1 of 15 6.1 Data Types and Kinds Data types Intrisic data types (INTEGER, REAL,LOGICAL) derived data types ( structures or records in other
Chapter 6. A Brief Introduction to Fortran 90 1998 David A. Padua 1 of 15 6.1 Data Types and Kinds Data types Intrisic data types (INTEGER, REAL,LOGICAL) derived data types ( structures or records in other
Bubble sort is so named because the numbers are said to bubble into their correct positions! Bubble Sort
 Sorting Sorting is the process of placing elements from a collection in some kind of order. For example, a list of words could be sorted alphabetically or by length. A list of cities could be sorted by
Sorting Sorting is the process of placing elements from a collection in some kind of order. For example, a list of words could be sorted alphabetically or by length. A list of cities could be sorted by
1 a = [ 5, 1, 6, 2, 4, 3 ] 4 f o r j i n r a n g e ( i + 1, l e n ( a ) 1) : 3 min = i
![1 a = [ 5, 1, 6, 2, 4, 3 ] 4 f o r j i n r a n g e ( i + 1, l e n ( a ) 1) : 3 min = i 1 a = [ 5, 1, 6, 2, 4, 3 ] 4 f o r j i n r a n g e ( i + 1, l e n ( a ) 1) : 3 min = i](/thumbs/88/116649184.jpg) Selection Sort Algorithm Principles of Computer Science II Sorting Algorithms This algorithm first finds the smallest element in the array and exchanges it with the element in the first position, then
Selection Sort Algorithm Principles of Computer Science II Sorting Algorithms This algorithm first finds the smallest element in the array and exchanges it with the element in the first position, then
School of Computer Science Introduction to Algorithms and Programming Winter Midterm Examination # 1 Wednesday, February 11, 2015
 Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-141-01 Introduction to Algorithms and Programming Winter 2015 Midterm Examination # 1 Wednesday, February 11, 2015 Marking Exemplar Duration of examination: 75
Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-141-01 Introduction to Algorithms and Programming Winter 2015 Midterm Examination # 1 Wednesday, February 11, 2015 Marking Exemplar Duration of examination: 75
Algorithms and Applications
 Algorithms and Applications 1 Areas done in textbook: Sorting Algorithms Numerical Algorithms Image Processing Searching and Optimization 2 Chapter 10 Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers
Algorithms and Applications 1 Areas done in textbook: Sorting Algorithms Numerical Algorithms Image Processing Searching and Optimization 2 Chapter 10 Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers
Divide-and-Conquer. The most-well known algorithm design strategy: smaller instances. combining these solutions
 Divide-and-Conquer The most-well known algorithm design strategy: 1. Divide instance of problem into two or more smaller instances 2. Solve smaller instances recursively 3. Obtain solution to original
Divide-and-Conquer The most-well known algorithm design strategy: 1. Divide instance of problem into two or more smaller instances 2. Solve smaller instances recursively 3. Obtain solution to original
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang
 Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
CS 3360 Design and Implementation of Programming Languages. Exam 1
 1 Spring 2016 (Monday, March 21) Name: CS 3360 Design and Implementation of Programming Languages Exam 1 This test has 18 questions and pages numbered 1 through 6. Reminders This test is closed-notes and
1 Spring 2016 (Monday, March 21) Name: CS 3360 Design and Implementation of Programming Languages Exam 1 This test has 18 questions and pages numbered 1 through 6. Reminders This test is closed-notes and
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Acknowledgement. Outline
 Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
C++ Programming. Arrays and Vectors. Chapter 6. Objectives. Chiou. This chapter introduces the important topic of data structures collections
 C++ Programming Chapter 6 Arrays and Vectors Yih-Peng Chiou Room 617, BL Building (02) 3366-3603 3603 ypchiou@cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw Photonic Modeling and Design Lab. Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics
C++ Programming Chapter 6 Arrays and Vectors Yih-Peng Chiou Room 617, BL Building (02) 3366-3603 3603 ypchiou@cc.ee.ntu.edu.tw Photonic Modeling and Design Lab. Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics
Chapter 8 Algorithms 1
 Chapter 8 Algorithms 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
Chapter 8 Algorithms 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
Computer Science 4U Unit 1. Programming Concepts and Skills Algorithms
 Computer Science 4U Unit 1 Programming Concepts and Skills Algorithms Algorithm In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculations. Algorithms are used for calculation,
Computer Science 4U Unit 1 Programming Concepts and Skills Algorithms Algorithm In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculations. Algorithms are used for calculation,
1 Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Fundamental mathematical techniques reviewed: Mathematical induction Recursion. Typically taught in courses such as Calculus and Discrete Mathematics.
 Fundamental mathematical techniques reviewed: Mathematical induction Recursion Typically taught in courses such as Calculus and Discrete Mathematics. Techniques introduced: Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms
Fundamental mathematical techniques reviewed: Mathematical induction Recursion Typically taught in courses such as Calculus and Discrete Mathematics. Techniques introduced: Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms
