TMCM-142. TMCL TM Firmware Manual Version: JUN-24
|
|
|
- Maximilian Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual Version: JUN-24 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Waterloohain 5 D Hamburg, Germany
2 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 2 Table of contents 1 Life support policy Features Order codes Overview Putting the TMCM-142 into operation Starting up Testing with a simple TMCL TM program Operating the module in direct mode TMCL TM and TMCL-IDE Binary command format Reply format Status codes Stand-alone applications TMCL TM command overview Motion commands Parameter commands I/O port commands Control commands Calculation commands TMCL TM commands The ASCII interface Format of the command line Format of a reply Commands that can be used in ASCII mode Configuring the ASCII interface Commands ROR (rotate right) ROL (rotate left) MST (motor stop) MVP (move to position) SAP (set axis parameter) GAP (get axis parameter) STAP (store axis parameter) RSAP (restore axis parameter) SGP (set global parameter) GGP (get global parameter) STGP (store global parameter) RSGP (restore global parameter) RFS (reference search) SIO (set output) GIO (get input/output) CALC (calculate) COMP (compare) JC (jump conditional) JA (jump always) CSUB (call subroutine) RSUB (return from subroutine) WAIT (wait for an event to occur) STOP (stop TMCL TM program execution) SCO (set coordinate) GCO (get coordinate) CCO (capture coordinate) ACO (accu to coordinate) CALCX (calculate using the X register) AAP (accumulator to axis parameter)... 79
3 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) AGP (accumulator to global parameter) CLE (clear error flags) Customer specific TMCL TM command extension (UF0 UF7/user function) Request target position reached event BIN (return to binary mode) TMCL Control Functions Axis parameters Real world units vs. units of the TMC Global parameters Bank Bank Bank Hints and tips PID controller of the TMC457 - easypid TM Reference search Fixing microstep errors Using the RS485 interface Revision history Firmware revision Document Revision References
4 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 4 1 Life support policy TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG does not authorize or warrant any of its products for use in life support systems, without the specific written consent of TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG. Life support systems are equipment intended to support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when properly used in accordance with instructions provided, can be reasonably expected to result in personal injury or death. TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG 2009 Information given in this data sheet is believed to be accurate and reliable. However neither responsibility is assumed for the consequences of its use nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties, which may result from its use. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
5 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 5 2 Features The TMCM-142 is a high-performance single axis stepper motor controller/driver with encoder feedback. The integrated TMC457 motion controller provides superior performance with regard to microstep resolution (up to 1024), maximum velocity (integrated chopsync ), ramp calculation (S-shaped ramps, calculated in realtime) and encoder feedback support (closing the loop in hardware with PID regulator). The driver stage supports motors with up to 5A RMS coil current and offers exceptional low power dissipation. Together with the TMCM-IF standard add-on interface/adapter board a large number of interface options is available. Applications Compact high-resolution/high-performance stepper motor controller/driver solutions Smooth movements with high microstep resolution and S-shaped ramps High precision and high repeatability with encoder feedback and PID position regulator Electrical data Supply voltage: +18V +78.5V DC Motor current: up to 7A peak / 5A RMS (programmable) Supported motors Two phase bipolar motors with 1A to 5A RMS coil current Incremental encoder (a/b + optional index channel, differential, open-collector or single ended signals) Interfaces Optically isolated inputs for home and stop switches general purpose analogue and digital inputs and outputs RS422, RS232, CAN and USB serial interfaces available RS422, RS485, RS232, CAN or USB serial interfaces available on standard add-on interface board TMCM-IF Features 1024 times micro stepping Automatic ramp generation (trapezoid and S-shaped) in real-time in hardware On the fly alteration of motion parameters (e.g. position, velocity, acceleration) Uses TMC457 high performance controller Chopsync for high speed High-efficient operation, low power dissipation Integrated protection: overtemperature/undervoltage Software Stand-alone operation using TMCL TM or remote controlled operation Memory for 2048 TMCL TM commands PC-based application development software TMCL-IDE included CANopen ready
6 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 6 3 Order codes The TMCM-142 is currently available with the standard adapter/interface add-on board TMCM-IF: Order code Description Dimensions [mm 3 ] TMCM-142-IF Single axis stepper motor controller/driver, 76x70x33 5A RMS, 75V, with encoder feedback and the standard adapter/interface board TMCM-IF Related motors QSH mm/NEMA23, 1.8 step angle 57.2 x 57.2 x 41/55/ 78.5 mm QSH mm/NEMA24, 1.8 step angle 60.5 x 60.5 x 45/56/ 65/86 mm Table 3.1: Order codes Versions without the standard adapter/interface board TMCM-IF (just the baseboard) or custom interface boards are available on request.
7 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 7 4 Overview As with most TRINAMIC modules the software running on the microprocessor of the TMCM-142 consists of two parts, a boot loader and the firmware itself. Whereas the boot loader is installed during production and testing at TRINAMIC and remains normally untouched throughout the whole lifetime, the firmware can be updated by the user. New versions can be downloaded free of charge from the TRINAMIC website ( The firmware shipped with this module is related to the standard TMCL TM firmware shipped with most of TRINAMIC modules with regard to protocol and commands. Corresponding, this module is based on the TMC457 motion controller for stepper motors and the TMC239 power driver and supports the standard TMCL TM with a special range of values. All commands and parameters available with this unit are explained on the following pages.
8 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 8 5 Putting the TMCM-142 into operation Here you can find basic information for putting your module into operation. Further text contains a simple example for a TMCL TM program and a short description of operating the module in direct mode. The things you need: TMCM-142-IF, consisting of TMCM-142 base and standard TMCM-IF adapter/interface add-on board. Interface (RS232, RS485, USB or CAN) suitable to your TMCM-142-IF with cables Nominal supply voltage +24V DC ( V DC) for your module A stepper motor which fit to your module, for example QSH-5718 or QSH TMCL-IDE program and PC Encoder optional Precautions: Do not connect or disconnect the TMCM-142 and the TMCM-IF while powered! Do not connect or disconnect the motor while powered! Do not mix up connections or short-circuit pins. Avoid bounding I/O wires with motor power wires as this may cause noise picked up from the motor supply. Do not exceed the maximum power supply of 78.5V DC. Start with power supply OFF!
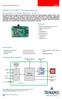
9 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Starting up 1. Connect the TMCM-142 and the TMCM-IF Usually TRINAMIC delivers the base board and the add-on board connected. If not for any reason, this figure will show you how to do this. Connector 2 Pin 1 Connector 3 Base Connector 3 Pin 1 Connector 2 Pin 1 Adapter USB Connector 1 Connector 4 Pin Terminal1 Connector 1 Terminal1 Connector 3 Connector 2 USB Connector 1 Connector 4 D-SUB Side View Figure 5.1: Connectors of the TMCM-142 and the TMCM-IF 2. Connect the motor and the power supply Connect the motor and the power supply with connector 1 of the TMCM-142: 1 8 Pin Label Description 1 NC Not connected 2 NC Not connected 3 GND Supply ground 4 +V Supply Voltage 5 B 2 Motor connection, Coil B 6 B 1 Motor connection, Coil B 7 A 2 Motor connection, Coil A 8 A 1 Motor connection, Coil A Table 5.1: Base connector 1-1x8 pin, 5mm pitch screw connector Attention: Do not exceed the maximum power supply of 78.5V DC.
10 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Connect the interface In this case we choose the USB interface for serial communication. USB is one out of five different interfaces available for communication with the TMCM-142-IF. You can refer to the hardware manuals of the TMCM-142 and the TMCM-IF for further information about the pinning of other interfaces. Connect the USB interface: Choose the USB port of the TMCM-IF and connect the interface with a USB cable. Accordingly, adjust the DIP switches. ON ON ON Switch Switch Switch 100 Switch 101 and 102 select the different interfaces (RS422 or RS232, CAN, RS485 and USB). DIP switch 100 adjusts the address of the CAN and RS-422 interfaces Figure 5.2: Overview of DIP switches For selecting the USB interface, configure the DIP switches 101 and 102 as shown below: ON ON Switch Switch 101 Figure 5.3: Configuration of DIP switches for USB
11 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Connect the encoder Differential and single ended incremental encoders with/without zero/index channel are supported. If you want to use an encoder to meet your needs, you can connect as follows: Single ended encoder: GND to pin 20 +5V to pin 16 A to pin 34 N to pin 29 B to pin 33 Differential encoder: GND to pin 20 +5V to pin 16 A+ to pin 34, A- to pin 12 N+ to pin 29, N- to pin 18 B+ to pin 33, B- to pin 14 Pin Name Function PIN Name Function 1 TX- RS422 Transmit (data out RS422 Transmit + (data out from 2 TX+ from indexer) indexer) 3 RX- RS422 Receive (data into RS422 Receive + (data out from 4 RX+ indexer) indexer) 5 Internally pulled down via 2k7 Analog user controlled input #0. resistor. Not supported by 6 IN0_A/D No internal resistors. TMCL. 7 REF R Optically isolated, active low STEP_ Step clock output from indexer 8 limit switch input Right OUT/RXD RS232 option: RS232 receive 9 OUT_1 User controlled output #1. No Direction output from indexer. 10 DIR_OUT/TXD internal resistors. RS232 option: RS232 transmit 11 IN7 Digital user controlled input #7. Differential encoder: Channel A- Optically isolated, active low 12 ENC_Ainput (optional) (needs power supply on pin 15) 13 IN2_A/D Analog user controlled input #2. Differential encoder: Channel B- 14 ENC_B- No internal resistors. input (optional) 15 +5V DC bias for input opto couplers 16 +5VDC Logic supply out for encoder 17 OUT_0 User controlled output #0. No Differential encoder: Channel N- 18 ENC_Ninternal resistors. input (optional) 19 REF L Optically isolated, active low limit switch input Left 20 GND Logic supply ground connection 21 IN3 Digital user controlled input #3. User controlled output #2. No 22 OUT_2 No internal resistors. (TTL) internal resistors. Digital user controlled input #8. 23 IN8 Optically isolated, active low (needs power supply on pin 15) 24 Not supported by TMCL. 25 IN5 Digital user controlled input #5. Analog user controlled input #1. 26 IN1_A/D No internal resistors. (TTL) No internal resistors. High voltage open collector 27 ALARM output indicating driver fault condition. 28 Not supported by TMCL. 29 ENC_N+ Encoder option: Digital user controlled input #6. Single ended: Channel N input 30 IN6 No internal resistors. (TTL) Differential: Channel N+ input 31 FS Active for one clock pulse at each on-pole fullstep position. 32 IN4 Digital user controlled input #4. No internal resistors. (TTL)
12 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 12 Pin Name Function PIN Name Function 33 ENC_B+ Encoder option: Single ended: Channel B input Differential: Channel B+ input 34 ENC_A+ Table 5.2: TMCM-IF connector 3 and TMCM-142 connector 3 Encoder option: Single ended: Channel A input Differential: Channel A+ input 5. Switch power supply ON The LED for power should glow now. This indicates that the on-board +5V supply is available. If this does not occur, switch power OFF and check your connections as well as the power supply. 6. Start the TMCL-IDE software development environment The TMCL-IDE is on hand on the TechLibCD and on Installing the TMCL-IDE: Make sure the COM port you intend to use is not blocked by another program. Open TMCL-IDE by clicking TMCL.exe. Choose Setup and Options and thereafter the Connection tab. Choose COM port and type with the parameters shown below (baud rate 9600). Click OK.
13 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Testing with a simple TMCL TM program Open the file test2.tmc. The following source code appears on the screen: A description for the TMCL commands can be found in Appendix A. //A simple example for using TMCL and TMCL-IDE ROL 0, //Rotate motor 0 with speed WAIT TICKS, 0, 500 MST 0 ROR 0, //Rotate motor 1 with WAIT TICKS, 0, 500 MST 0 SAP 4, 0, //Set max. Velocity SAP 5, 0, //Set max. Acceleration Loop: MVP ABS, 0, //Move to Position WAIT POS, 0, 0 //Wait until position reached MVP ABS, 0, //Move to Position WAIT POS, 0, 0 //Wait until position reached JA Loop //Infinite Loop Assemble Stop Download Run 7. Click on Icon Assemble to convert the TMCL into machine code. 8. Then download the program to the TMCM-142 module via the icon Download. 9. Press icon Run. The desired program will be executed. 10. Click Stop button to stop the program.
14 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Operating the module in direct mode 1. Start TMCL Direct Mode. Direct Mode 2. If the communication is established the TMCM-142-IF is automatically detected. If the module is not detected, please check all points above (cables, interface, power supply, COM port, baud rate). 3. Issue a command by choosing instruction, type (if necessary), motor, and value and click Execute to send it to the module. Examples: ROR rotate right, motor 0, value 500 -> Click Execute. The first motor is rotating now. MST motor stop, motor 0 -> Click Execute. The first motor stops now. You will find a description of all TMCL TM commands in the following chapters.
15 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 15 6 TMCL TM and TMCL-IDE The TMCM-142 supports TMCL TM direct mode (binary commands or ASCII interface) and stand-alone TMCL TM program execution. You can store up to 2048 TMCL TM instructions on it. In direct mode and most cases the TMCL TM communication over RS485, RS232, RS422, USB or CAN follows a strict master/slave relationship. That is, a host computer (e.g. PC/PLC) acting as the interface bus master will send a command to the TMCM-142. The TMCL TM interpreter on the module will then interpret this command, do the initialization of the motion controller, read inputs and write outputs or whatever is necessary according to the specified command. As soon as this step has been done, the module will send a reply back over RS485/RS232/RS422/USB/CAN to the bus master. Only then should the master transfer the next command. Normally, the module will just switch to transmission and occupy the bus for a reply, otherwise it will stay in receive mode. It will not send any data over the interface without receiving a command first. This way, any collision on the bus will be avoided when there are more than two nodes connected to a single bus. The Trinamic Motion Control Language (TMCL TM ) provides a set of structured motion control commands. Every motion control command can be given by a host computer or can be stored in an EEPROM on the TMCM TM module to form programs that run stand-alone on the module. For this purpose there are not only motion control commands but also commands to control the program structure (like conditional jumps, compare and calculating). Every command has a binary representation and a mnemonic. The binary format is used to send commands from the host to a module in direct mode, whereas the mnemonic format is used for easy usage of the commands when developing stand-alone TMCL TM applications using the TMCL-IDE (Integrated Development Environment). There is also a set of configuration variables for the axis and for global parameters which allow individual configuration of nearly every function of a module. This manual gives a detailed description of all TMCL TM commands and their usage. 6.1 Binary command format Every command has a mnemonic and a binary representation. When commands are sent from a host to a module, the binary format has to be used. Every command consists of a one-byte command field, a one-byte type field, a one-byte motor/bank field and a four-byte value field. So the binary representation of a command always has seven bytes. When a command is to be sent via RS232, RS422, RS485 or USB interface, it has to be enclosed by an address byte at the beginning and a checksum byte at the end. In this case it consists of nine bytes. This is different when communicating is via the CAN bus. Address and checksum are included in the CAN standard and do not have to be supplied by the user. The binary command format for RS232/RS422/RS485/USB is as follows: Bytes Meaning 1 Module address 1 Command number 1 Type number 1 Motor or Bank number 4 Value (MSB first!) 1 Checksum The checksum is calculated by adding up all the other bytes using an 8-bit addition. When using CAN bus, just leave out the first byte (module address) and the last byte (checksum).
16 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 16 Checksum calculation As mentioned above, the checksum is calculated by adding up all bytes (including the module address byte) using 8-bit addition. Here are two examples to show how to do this: in C: unsigned char i, Checksum; unsigned char Command[9]; //Set the Command array to the desired command Checksum = Command[0]; for(i=1; i<8; i++) Checksum+=Command[i]; Command[8]=Checksum; //insert checksum as last byte of the command //Now, send it to the module in Delphi: var i, Checksum: byte; Command: array[0...8] of byte; //Set the Command array to the desired command //Calculate the Checksum: Checksum:=Command[0]; for i:=1 to 7 do Checksum:=Checksum+Command[i]; Command[8]:=Checksum; //Now, send the Command array (9 bytes) to the module 6.2 Reply format Every time a command has been sent to a module, the module sends a reply. The reply format for RS485/RS422/RS232/USB is as follows: Bytes Meaning 1 Reply address 1 Module address 1 Status (e.g. 100 means no error) 1 Command number 4 Value (MSB first!) 1 Checksum The checksum is also calculated by adding up all the other bytes using an 8-bit addition. When using CAN bus, the first byte (reply address) and the last byte (checksum) are left out. Do not send the next command before you have received the reply!
17 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Status codes The reply contains a status code. The status code can have one of the following values: Code Meaning 100 Successfully executed, no error 101 Command loaded into TMCL TM program EEPROM 1 Wrong checksum 2 Invalid command 3 Wrong type 4 Invalid value 5 Configuration EEPROM locked 6 Command not available 6.3 Stand-alone applications The module is equipped with an EEPROM for storing TMCL TM applications. You can use TMCL-IDE for developing stand-alone TMCL TM applications. You can load them down into the EEPROM and then it will run on the module. The TMCL-IDE contains an editor and a TMCL TM assembler where the commands can be entered using their mnemonic format. They will be assembled automatically into their binary representations. Afterwards this code can be downloaded into the module to be executed there. 6.4 TMCL TM command overview In this section a short overview of the TMCL TM commands is given Motion commands These commands control the motion of the motor. They are the most important commands and can be used in direct mode or in stand-alone mode. Mnemonic Command number Meaning ROL 2 Rotate left ROR 1 Rotate right MVP 4 Move to position MST 3 Motor stop RFS 13 Reference search SCO 30 Store coordinate CCO 32 Capture coordinate GCO 31 Get coordinate
18 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Parameter commands These commands are used to set, read and store axis parameters or global parameters. Axis parameters can be set independently for the axis, whereas global parameters control the behavior of the module itself. These commands can also be used in direct mode and in stand-alone mode. Mnemonic Command number Meaning SAP 5 Set axis parameter GAP 6 Get axis parameter STAP 7 Store axis parameter into EEPROM RSAP 8 Restore axis parameter from EEPROM SGP 9 Set global parameter GGP 10 Get global parameter STGP 11 Store global parameter into EEPROM RSGP 12 Restore global parameter from EEPROM I/O port commands These commands control the external I/O ports and can be used in direct mode and in stand-alone mode. Mnemonic Command number Meaning SIO 14 Set output GIO 15 Get input Control commands These commands are used to control the program flow (loops, conditions, jumps etc.). It does not make sense to use them in direct mode. They are intended for stand-alone mode only. Mnemonic Command number Meaning JA 22 Jump always JC 21 Jump conditional COMP 20 Compare accumulator with constant value CLE 36 Clear error flags CSUB 23 Call subroutine RSUB 24 Return from subroutine WAIT 27 Wait for a specified event STOP 28 End of a TMCL TM program
19 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Calculation commands These commands are intended to be used for calculations within TMCL TM applications. Although they could also be used in direct mode it does not make much sense to do so. Mnemonic Command Meaning number CALC 19 Calculate using the accumulator and a constant value CALCX 33 Calculate using the accumulator and the X register AAP 34 Copy accumulator to an axis parameter AGP 35 Copy accumulator to a global parameter ACO 39 Copy accu to coordinate For calculating purposes there is an accumulator (or accu or A register) and an X register. When executed in a TMCL TM program (in stand-alone mode), all TMCL TM commands that read a value store the result in the accumulator. The X register can be used as an additional memory when doing calculations. It can be loaded from the accumulator. When a command that reads a value is executed in direct mode the accumulator will not be affected. This means that while a TMCL TM program is running on the module (stand-alone mode), a host can still send commands like GAP, GGP or GIO to the module (e.g. to query the actual position of the motor) without affecting the flow of the TMCL TM program running on the module.
20 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) TMCL TM commands The following TMCL TM commands are currently supported: Command Number Parameter Description ROR 1 <motor number>, <velocity> Rotate right with specified velocity ROL 2 <motor number>, <velocity> Rotate left with specified velocity MST 3 <motor number> Stop motor movement MVP 4 ABS REL COORD, <motor number>, <position offset> SAP 5 <parameter>, <motor number>, <value> Move to position (absolute or relative) Set axis parameter (motion control specific settings) GAP 6 <parameter>, <motor number> Get axis parameter (read out motion control specific settings) STAP 7 <parameter>, <motor number> Store axis parameter permanently (non volatile) RSAP 8 <parameter>; <motor number> Restore axis parameter SGP 9 <parameter>, <bank number>, <value> Set global parameter (module specific settings, e.g. communication settings, or TMCL user variables) GGP 10 <parameter>, <bank number> Get global parameter (read out module specific settings e.g. communication settings, or TMCL user variables) STGP 11 <parameter>, <bank number> Store global parameter (TMCL user variables only) RSGP 12 <parameter>, <bank> Restore global parameter (TMCL user variables only) RFS 13 START STOP STATUS, <motor number> SIO 14 <port number>, <bank number>, <value> Reference search Set digital output to specified value GIO 15 <port number>, <bank number> Get value of analogue/digital input CALC 19 <operation>, <value> Process accumulator & value COMP 20 <value> Compare accumulator <-> value JC 21 <condition>, <jump address> Jump conditional JA 22 <jump address> Jump absolute CSUB 23 <subroutine address> Call subroutine RSUB 24 Return from subroutine WAIT 27 <condition>, <motor number>, <ticks> Wait with further program execution STOP 28 Stop program execution SCO 30 <coordinate number>, <motor number>, <position> Set coordinate
21 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 21 Command Number Parameter Description GCO 31 <coordinate number>, <motor number> CCO 32 <coordinate number>, <motor number> TMCL control commands: Instruction Description Type Mot/Bank Value 128 stop application a running TMCL standalone application is stopped 129 run application TMCL execution is started (or continued) 130 step application only the next command of a TMCL application is executed 131 reset application the program counter is set to zero, and the standalone application is stopped (when running or stepped) 132 start download mode 133 quit download mode 134 read TMCL memory 135 get application status 136 get firmware version 137 restore factory settings target command execution is stopped and all following commands are transferred to the TMCL memory target command execution is resumed the specified program memory location is read one of these values is returned: 0 stop 1 run 2 step 3 reset return the module type and firmware revision either as a string or in binary format reset all settings stored in the EEPROM to their factory defaults This command does not send back a reply. (don't care) 0 - run from current address 1 - run from specified address (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) starting address (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) starting address of the application (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) 0 string 1 binary Get coordinate Capture coordinate CALCX 33 <operation> Process accumulator & X-register AAP 34 <parameter>, <motor number> Accumulator to axis parameter AGP 35 <parameter>, <bank> Accumulator to global parameter ACO 39 <coordinate number, <motor number> Accu to coordinate (don't care) (don't care) (don't care) <memory address> (don't care) (don't care) (don t care) (don t care) (don t care) (don t care) must be 1234
22 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) The ASCII interface Since TMCL TM V3.21 there is also an ASCII interface that can be used to communicate with the module and to send some commands as text strings. The ASCII command line interface is entered by sending the binary command 139 (enter ASCII mode). Afterwards the commands are entered as in the TMCL-IDE. Please note that only those commands, which can be used in direct mode, also can be entered in ASCII mode. For leaving the ASCII mode and re-enter the binary mode enter the command BIN Format of the command line As the first character, the address character has to be sent. The address character is A when the module address is 1, B for modules with address 2 and so on. After the address character there may be spaces (but this is not necessary). Then, send the command with its parameters. At the end of a command line a <CR> character has to be sent. Here are some examples for valid command lines: AMVP ABS, 1, A MVP ABS, 1, AROL 2, 500 A MST 1 ABIN These command lines would address the module with address 1. To address e.g. module 3, use address character C instead of A. The last command line shown above will make the module return to binary mode Format of a reply After executing the command the module sends back a reply in ASCII format. This reply consists of: the address character of the host (host address that can be set in the module) the address character of the module the status code as a decimal number the return value of the command as a decimal number a <CR> character So, after sending AGAP 0, 1 the reply would be BA if the actual position of axis 1 is 5000, the host address is set to 2 and the module address is 1. The value 100 is the status code 100 that means command successfully executed Commands that can be used in ASCII mode The following commands can be used in ASCII mode: ROL, ROR, MST, MVP, SAP, GAP, STAP, RSAP, SGP, GGP, STGP, RSGP, RFS, SIO, GIO, SAC, SCO, GCO, CCO, UF0, UF1, UF2, UF3, UF4, UF5, UF6, and UF7. There are also special commands that are only available in ASCII mode: BIN: This command quits ASCII mode and returns to binary TMCL TM mode. RUN: This command can be used to start a TMCL TM program in memory. STOP: Stops a running TMCL TM application Configuring the ASCII interface The module can be configured so that it starts up either in binary mode or in ASCII mode. Global parameter 67 is used for this purpose (please see also chapter 8.1). Bit 0 determines the startup mode: If this bit is set, the module starts up in ASCII mode, else it will start up in binary mode (default). Bit 4 and Bit 5 determine how the characters that are entered are echoed back. Normally, both bits are set to zero. In this case every character that is entered is echoed back when the module is addressed. A Character can also
23 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 23 be erased using the backspace character (press the backspace key in a terminal program). When bit 4 is set and bit 5 is clear the characters that are entered are not echoed back immediately but the entire line will be echoed back after the <CR> character has been sent. When bit 5 is set and bit 4 is clear there will be no echo, only the reply will be sent. This may be useful in RS485 systems.
24 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) Commands The module specific commands are explained in more detail on the following pages. They are listed according to their command number ROR (rotate right) With this command the motor will be instructed to rotate with a specified velocity in right direction (increasing the position counter). Internal function: First, velocity mode is selected. Then, the velocity value is transferred to axis parameter #0 (target velocity). The module is based on the TMC457 motor controller and the TMC239 power driver. This makes possible choosing a velocity between 0 and When axis parameter #255 (unit conversion mode) is set to 1 the speed must be given as microsteps per second. In this case the range for the speed is microsteps/second. Related commands: ROL, MST, SAP, GAP Mnemonic: ROR 0, <velocity> Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 1 (don't care) 0* <velocity> *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Example: Rotate right, motor #0, velocity = 350 Mnemonic: ROR 0, 350 Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $01 $00 $02 $00 $00 $01 $5e $62
25 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) ROL (rotate left) With this command the motor will be instructed to rotate with a specified velocity (opposite direction compared to ROR, decreasing the position counter). Internal function: First, velocity mode is selected. Then, the velocity value is transferred to axis parameter #0 (target velocity). The module is based on the TMC457 motor controller and the TMC239 power driver. This makes possible choosing a velocity between 0 and When axis parameter #255 (unit conversion mode) is set to 1 the speed must be given as microsteps per second. In this case the range for the speed is microsteps/second. Related commands: ROR, MST, SAP, GAP Mnemonic: ROL 0, <velocity> Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 2 (don't care) 0* <velocity> *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Example: Rotate left, motor #0, velocity = 1200 Mnemonic: ROL 0, 1200 Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $02 $00 $00 $00 $00 $04 $b0 $b8
26 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) MST (motor stop) With this command the motor will be instructed to stop either with deceleration ramp (soft stop) or without (hard stop). Please note: Depending on motor speed a hard stop might lead to step losses. Internal function: The axis parameter target velocity is set to zero. Related commands: ROL, ROR, SAP, GAP Mnemonic: MST 0 Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 3 (don't care) 0* (don't care) *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS Example: Stop motor Mnemonic: MST 0 VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $03 $00 $00 $00 $00 $00 $00 $05
27 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) MVP (move to position) With this command the motor will be instructed to move to a specified relative or absolute position or a pre-programmed coordinate. It will use the acceleration/deceleration ramp and the positioning speed programmed into the unit. This command is non-blocking that is, a reply will be sent immediately after command interpretation and initialization of the motion controller. Further commands may follow without waiting for the motor reaching its end position. The maximum velocity and acceleration are defined by axis parameters #4 and #5. Three operation types are available: Moving to an absolute position in the range from Starting a relative movement by means of an offset to the actual position. In this case, the new resulting position value must not exceed the above mentioned limits, too. Moving the motor to a (previously stored) coordinate (refer to SCO for details). Internal function: A new position value is transferred to the axis parameter #2 target position. Related commands: SAP, GAP, SCO, CCO, GCO, MST Mnemonic: MVP <ABS REL COORD>, 0, <position offset coordinate number> Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 4 0 ABS absolute 0* <position> 2 COORD coordinate *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS 1 REL relative 0* <offset> VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Example: Move motor to (absolute) position Mnemonic: MVP ABS, 0, * <coordinate number (0...20) Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $04 $00 $00 $00 $01 $5f $90 $f6 Example: Move motor from current position 1000 steps backward (move relative 1000) Mnemonic: MVP REL, 0, Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $04 $01 $00 $ff $ff $fc $18 $18
28 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 28 Example: Move motor to previously stored coordinate #8 Mnemonic: MVP COORD, 0, 8 Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $04 $02 $00 $00 $00 $00 $08 $11 When moving to a coordinate, the coordinate has to be set properly in advance with the help of the SCO, CCO or ACO command.
29 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) SAP (set axis parameter) With this command most of the motion control parameters of the module can be specified. The settings will be stored in SRAM and therefore are volatile. That is, information will be lost after power off. Please use command STAP (store axis parameter) in order to store any setting permanently. Internal function: The parameter format is converted ignoring leading zeros (or ones for negative values). The parameter is transferred to the correct position in the appropriate device. Related commands: GAP, STAP, RSAP, AAP Mnemonic: SAP <parameter number>, 0, <value> Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 5 <parameter number> *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Axis parameters, which can be used for SAP: 0* <value> Please note, that for the binary representation <parameter number> has to be filled with the number and the <value> has to be filled with a value from range. Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 0 Target position [µsteps] 1 Actual position [µsteps] 2 Target speed [µsteps/t] 3 Actual speed [µsteps/t] 4 Max. positioning speed Speed used for positioning (MVP commands) [µsteps/t] 5 Max. acceleration and deceleration Sets acceleration and deceleration to the same value [µsteps/t 2 ] 6 Max. current Current when motor is running means 0%, 15 means 100% of the maximum possible current. 7 Standby current Current when motor is standing means 0%, 15 means 100% of the maximum possible current. 12 Right limit switch disable Deactivates the function of the 0/1 right limit switch when set to Left limit switch disable Deactivates the function of the left limit switch when set to 1. 0/1
30 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 30 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 14 Switch mode Bit 2: left stop switch polarity Bit 3: right stop switch polarity Bit 4: swap left and right stop switch Bit 5: enable soft stop Bit 8: latch position on left stop switch going active Bit 9: latch position on left stop switch going inactive Bit 10: latch position on right stop switch going active Bit 11: latch position on right stop switch going inactive Bit 12: latch encoder position on stop switch event 15 Stop deceleration Deceleration when touching a stop switch [µsteps/t 2 ] 16 Max. acceleration Acceleration [µsteps/t 2 ] 17 Max. deceleration Deceleration [µsteps/t 2 ] 18 Bow 0 trapezoidal ramps, corresponds to an infinite bow value 1 18 S-shaped ramps in logarithmic representation. bow_value = 2^(bow_index-1) bow_index = 1, 2, 3 18 bow_value = 1, 2, The resulting bow_value must not exceed A_MAX or D_MAX setting. Otherwise oscillations may result. 19 Shaft Reverses the motor direction when set to Standby delay Time after the motor has stopped until the current is changed to standby current. 21 Mixed decay run 0: no mixed decay when running 1: use mixed decay when running 22 Mixed decay standby 0: no mixed decay when standing 1: use mixed decay when standing 23 Chopper clock divider Chopper clock frequency divider. Do not change! Chopper clock = 16MHz/value Default = [µsteps/t 3 ] 0/ [1/f CLK / 2 16 ] 0/1 0/
31 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 31 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 27 Microstep resolution micro steps micro steps micro steps micro steps micro steps 5 64 micro steps 6 32 micro steps 7 16 micro steps 8 8 micro steps 9 4 micro steps 10 2 micro steps 11 1 full step 28 PID tolerance Tolerance for PID regulation If the absolute value of the error pid_e is below pid_tolerance after an exact hit, then the pid_error_in becomes 0 and pid_i_sum is set to zero, until the tolerance zone is left again [µsteps] 29 Sine wave offset The sine wave offset can be adapted for optimum microstep performance on zero crossing of the coil currents. A too low offset leads to the motor turning too slow during zero transition, a too high offset leads to a larger step. This parameter can be optimized for the motor type. It mainly depends on motor inductivity and coil resistance. 30 PID p factor P parameter (unsigned) update frequency f CLK /128; Result: pid_e*pid_p/256 (becomes clipped to +/-2^31) 31 PID i factor I parameter (unsigned) Result: (pid_isum/256)*pid_i/256 (becomes clipped to +/-2^31) 32 PID d factor D parameter (unsigned), pid_e is sampled with a frequency of (f CLK [Hz]/128/pid_d_clkdiv). Result: (pid_e_last pid_e_now) * pid_d (The delta-error (pid_e_last pid_e_now) becomes clipped to +/- 127) 33 PID i clipping Clipping parameter for pid_isum Clipping of (pid_isum*2^16*pid_iclip) 35 PID d clock divider Clock divider for D part calculation D-part is calculated with a frequency of: f CLK / (pid_d_clkdiv*128) (attention: pid_d_clkdiv=0 results in 256) [1/1024 of sine wave amplitude]
32 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 32 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 37 PID dv clipping Clipping parameter for PID calculation result pid_v_actual [µsteps/t] pid_v_actual = v_actual + clip(pid_result, pid_dv_clip) 40 PID mode 0: do not use PID 1: use PID 0/1 42 Encoder constant With every pulse this constant is added to or subtracted from the encoder position register. This constant is given in units of 1/65536 when bit 13 in param. 43 is not set or in 1/10000 when bit 13 in param. 43 is set [µsteps/216] or decimal: Bits 31-16: [µsteps] Bits 15-0: [1/1000 µsteps] 43 Encoder mode Bit 0: polarity of channel A when null channel is active Bit 1: polarity of channel B when null channel is active Bit 2: polarity of null channel Bit 3: ignore polarity of A and B channel when null channel is active Bit 4: continuous clear while null channel is active Bit 5: clear once at next null channel event. Bit 6: null channel is positive edge triggered Bit 7: null channel is negative edge triggered Bit 8: clear encoder position on null event (otherwise it is latched only) Bit 13: Encoder divisor selection (0=encoder constant/65535, 1=encoder constant/10000). 47 Encoder warn distance Maximum deviation between motor [µsteps] and encoder. 48 Compare position Tbd [µsteps] 50 Right position limit Position limit when moving in positive direction. 51 Left position limit Position limit when moving in negative direction. 52 Right position limit enable The motor cannot drive beyond the right position limit when set to Left position limit enable The motor cannot drive beyond the left position limit when set to Microstep table position Position of the microstep table pointer. 64 Step pulse length Length of the step pulses on the step/direction output [µsteps] [µsteps] 0/1 0/ [1/16 MHz]
33 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 33 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 128 Ramp mode Normally set automatically by the ROL, ROR, MVP and MST commands. 0: positioning mode 1: reserved 2: velocity mode 3: hold mode 193 Reference search mode 1 Only the left reference switch 1/2/3 is searched. 2 The right switch is searched and afterwards the left switch is searched. 3 Three-switch-mode: the right switch is searched first and afterwards the reference switch will be searched. Please see 9.2 for details on reference search 194 Reference search speed Specifies the reference search speed [µsteps/t] 195 Reference switch speed Specifies the speed for the exact reference switch calibration. 212 Maximum encoder deviation When the actual position (param. 1) and the encoder position (param [µsteps] 41) differ more than the value set here, the motor will be stopped. Setting this parameter to 0 disables this function. 255 Unit conversion mode Units to use for velocity and acceleration: 0: use TMC457 units 1: use PPS units 0/1 Please use the TMC457 calculations data file ( for getting best values. Please refer to 7.1 for information about real world units vs. units of the TMC457. Example: Set the absolute maximum current of motor to 200mA Mnemonic: SAP 6, 0, 200 Binary: Byte Index Function Target- Instruction Type Motor/ Operand Operand Operand Operand Checksum address Number Bank Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0 Value (hex) $01 $05 $06 $00 $00 $00 $00 $c8 $d5
34 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) GAP (get axis parameter) Most parameters of the TMCM-142 can be adjusted individually for the axis. With this parameter they can be read out. In stand-alone mode the requested value is also transferred to the accumulator register for further processing purposes (such as conditioned jumps). In direct mode the value read is only output in the value field of the reply (without affecting the accumulator). Internal function: The parameter is read out of the correct position in the appropriate device. The parameter format is converted adding leading zeros (or ones for negative values). Related commands: SAP, STAP, AAP, RSAP Mnemonic: GAP <parameter number>, 0 Binary representation: INSTRUCTION NO. TYPE MOT/BANK VALUE 6 <parameter number> 0* (don't care) *motor number is always O as only one motor is involved Reply in direct mode: STATUS VALUE 100 OK (don't care) Axis parameters, which can be used for GAP: Please note, that for the binary representation <parameter number> has to be filled with the number and the <value> has to be filled with a value from range. Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 0 Target position [µsteps] 1 Actual position [µsteps] 2 Target speed [µsteps/t] 3 Actual speed [µsteps/t] 4 Max. positioning speed Speed used for positioning (MVP commands) [µsteps/t] 5 Max. acceleration and deceleration Sets acceleration and deceleration to the same value [µsteps/t 2 ] 6 Max. current Current when motor is running means 0%, 15 means 100% of the maximum possible current. 7 Standby current Current when motor is standing means 0%, 15 means 100% of the maximum possible current. 8 Position reached 1 when the target position and the actual position are equal. 0/1
35 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 35 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 9 Switch status Bit 0: left limit switch status (same as par. 11) Bit 1: right limit switch status (same as par. 12) Bit 2: latch left ready (cleared when read) Bit 3: latch right ready (cleared when read) Bit 4: stop left condition due to stop switch Bit 5: stop right condition due to stop switch 10 Right limit switch status Logic state of the right switch. 0/1 11 Left limit switch status Logic state of the left switch. 0/1 12 Right limit switch disable Deactivates the function of the 0/1 right limit switch when set to Left limit switch disable Deactivates the function of the left limit switch when set to 1. 0/1 14 Switch mode Bit 2: left stop switch polarity Bit 3: right stop switch polarity Bit 4: swap left and right stop switch Bit 5: enable soft stop Bit 8: latch position on left stop switch going active Bit 9: latch position on left stop switch going inactive Bit 10: latch position on right stop switch going active Bit 11: latch position on right stop switch going inactive Bit 12: latch encoder position on stop switch event 15 Stop deceleration Deceleration when touching a stop switch [µsteps/t 2 ] 16 Max. acceleration Acceleration [µsteps/t 2 ] 17 Max. deceleration Deceleration [µsteps/t 2 ] 18 Bow 0 trapezoidal ramps, corresponds to an infinite bow value 1 18 S-shaped ramps in logarithmic representation. bow_value = 2^(bow_index-1) bow_index = 1, 2, 3 18 bow_value = 1, 2, The resulting bow_value must not exceed A_MAX or D_MAX setting. Otherwise oscillations may result. 19 Shaft Reverses the motor direction when set to Standby delay Time after the motor has stopped until the current is changed to standby current [µsteps/t 3 ] 0/ [1/f CLK / 2 16 ]
36 TMCM-142 TMCL TM Firmware Manual (V1.06 / 2014-JUN-24) 36 Number Axis parameter Description Range [Unit] 21 Mixed decay run 0: no mixed decay when running 0/1 1: use mixed decay when running 22 Mixed decay standby 0: no mixed decay when standing 0/1 1: use mixed decay when standing 23 Chopper clock divider Chopper clock frequency divider. Do not change! Chopper clock = 16MHz/value Default = Actual load value The actual load value = low load 0 = high load 26 Driver status Bit 0: driver error Bit 1: over temperature pre-warning 27 Microstep resolution micro steps micro steps micro steps micro steps micro steps 5 64 micro steps 6 32 micro steps 7 16 micro steps 8 8 micro steps 9 4 micro steps 10 2 micro steps 11 1 full step 28 PID tolerance Tolerance for PID regulation If the absolute value of the error pid_e is below pid_tolerance after an exact hit, then the pid_error_in becomes 0 and pid_i_sum is set to zero, until the tolerance zone is left again [µsteps] 29 Sine wave offset The sine wave offset can be adapted for optimum microstep performance on zero crossing of the coil currents. A too low offset leads to the motor turning too slow during zero transition, a too high offset leads to a larger step. This parameter can be optimized for the motor type. It mainly depends on motor inductivity and coil resistance. 30 PID p factor P parameter (unsigned) update frequency f CLK /128; Result: pid_e*pid_p/256 (becomes clipped to +/-2^31) 31 PID i factor I parameter (unsigned) Result: (pid_isum/256)*pid_i/256 (becomes clipped to +/-2^31) [1/1024 of sine wave amplitude]
PDx SE TMCM SE
 PDx-140-42-SE TMCM-140-42-SE TMCL Firmware Manual Version: 1.07 2014-JUN-24 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Waterloohain 5 22769 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51 48 06-60 http://www.trinamic.com
PDx-140-42-SE TMCM-140-42-SE TMCL Firmware Manual Version: 1.07 2014-JUN-24 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Waterloohain 5 22769 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51 48 06-60 http://www.trinamic.com
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V4.45 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-351 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 24 V SPI, RS232, RS485, CAN, and USB Encoder Interface + + TMCM-351
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V4.45 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-351 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 24 V SPI, RS232, RS485, CAN, and USB Encoder Interface + + TMCM-351
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.29 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24V DC up-to 0.7A RMS / 1.4A RMS RS485 Interface sensostep Encoder + + UNIQUE
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.29 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24V DC up-to 0.7A RMS / 1.4A RMS RS485 Interface sensostep Encoder + + UNIQUE
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.19 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-6110 6 axes stepper controller / driver up to 1.1A RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS485 [or RS232] + + TRINAMIC Motion Control
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.19 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-6110 6 axes stepper controller / driver up to 1.1A RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS485 [or RS232] + + TRINAMIC Motion Control
Firmware TMCL MCST Instruction Manual W E CREATE MOTION
 Firmware TMCL MCST 3601 Instruction Manual EN W E CREATE MOTION Imprint Version: 1st edition, 01.10.2014 Copyright by FAULHABER PRECISTEP SA Rue des Gentianes 53 2300 La Chaux-de-Fonds Switzerland All
Firmware TMCL MCST 3601 Instruction Manual EN W E CREATE MOTION Imprint Version: 1st edition, 01.10.2014 Copyright by FAULHABER PRECISTEP SA Rue des Gentianes 53 2300 La Chaux-de-Fonds Switzerland All
TMCM-1110 TMCL Firmware Manual
 Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1110 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.08 Document Revision V1.01 2017-OCT-10 The TMCM-1110 is a single axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1110 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.08 Document Revision V1.01 2017-OCT-10 The TMCM-1110 is a single axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.27 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1141 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24 V DC up-to 1.1 A / 2A RMS USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.27 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1141 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24 V DC up-to 1.1 A / 2A RMS USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.06 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-3110 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 48 V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Encoder Interface + + TRINAMIC
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.06 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-3110 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 48 V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Encoder Interface + + TRINAMIC
TMCM-3110 TMCL Firmware Manual
 Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-3110 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.11 Document Revision V1.05 2017-JAN-24 The TMCM-3110 is a triple axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-3110 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.11 Document Revision V1.05 2017-JAN-24 The TMCM-3110 is a triple axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Update V1.03 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + 1-axis stepper controller / driver module 1A RMS / 2.8A RMS 24V DC USB, RS485 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Update V1.03 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + 1-axis stepper controller / driver module 1A RMS / 2.8A RMS 24V DC USB, RS485 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control
PD TMCL Firmware Manual
 PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD28-1021 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.42 Document Revision V1.05 2018-JAN-09 The PD28-1021 is a full mechatronic solution, made up of a TMCM-1021 stepper
PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD28-1021 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.42 Document Revision V1.05 2018-JAN-09 The PD28-1021 is a full mechatronic solution, made up of a TMCM-1021 stepper
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Firmware Version V1.19 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + PD-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.06-0.12Nm / 24V sensostep Encoder RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Firmware Version V1.19 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + PD-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.06-0.12Nm / 24V sensostep Encoder RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE
TMCM-1111 TMCL Firmware Manual
 Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1111 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.05 Document Revision V1.00 2016-OCT-20 The TMCM-1111 is a single axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1111 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.05 Document Revision V1.00 2016-OCT-20 The TMCM-1111 is a single axis controller/driver module for 2-phase bipolar stepper
TMCM Firmware Version V1.27 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.27 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1140 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2 A / 24 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.27 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1140 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2 A / 24 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.31 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-6110 6 Axes Stepper Controller / Driver 1.1A RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS485 [or RS232] + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V1.31 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-6110 6 Axes Stepper Controller / Driver 1.1A RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS485 [or RS232] + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Firmware Version V4.42 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1180 PD86-1180 1-axis stepper controller / driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN +
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Firmware Version V4.42 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1180 PD86-1180 1-axis stepper controller / driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN +
TMCM-142-IF. Hardware Manual
 TMCM-142-IF Hardware Manual Version: 1.01 2009-JUL-31 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com TMCM-142-IF Manual (V1.01/2009-JUL-31) 2 Table
TMCM-142-IF Hardware Manual Version: 1.01 2009-JUL-31 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com TMCM-142-IF Manual (V1.01/2009-JUL-31) 2 Table
PD TMCL Firmware Manual
 PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD42-1270 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.0 2017-Mar-02 The PD42-1270 is an easy to use, single axis controller/driver PANdrive for
PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD42-1270 TMCL Firmware Manual Firmware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.0 2017-Mar-02 The PD42-1270 is an easy to use, single axis controller/driver PANdrive for
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.08 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Module 5A / 24 V Hall Sensor Interface Encoder Interface RS485 and USB Interface
MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.08 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Module 5A / 24 V Hall Sensor Interface Encoder Interface RS485 and USB Interface
TMCC160 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 motioncookie SYSTEM IN A PACKAGE motioncookie TMCC160 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL TMCC160 TMCL Firmware Version 2.09 2015-NOV-25 Document Revision 1.0 2015-DEC-04 The TMCL Firmware is used in combination with
motioncookie SYSTEM IN A PACKAGE motioncookie TMCC160 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL TMCC160 TMCL Firmware Version 2.09 2015-NOV-25 Document Revision 1.0 2015-DEC-04 The TMCL Firmware is used in combination with
Firmware Version V2.09 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.09 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Module 5A / 24 V Hall Sensor Interface Encoder Interface RS485 and USB Interface
MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.09 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Module 5A / 24 V Hall Sensor Interface Encoder Interface RS485 and USB Interface
TMCM-1613 FIRMWARE MANUAL
 Module for BLDC Motors Modules TMCM-1613 FIRMWARE MANUAL TMCM-1613 Firmware Version 1.00 2016-MAR-28 Document Revision 1.00 2016-MAR-28 SHORT SPEC The TMCM-1613 firmware performs hall sensor-based block
Module for BLDC Motors Modules TMCM-1613 FIRMWARE MANUAL TMCM-1613 Firmware Version 1.00 2016-MAR-28 Document Revision 1.00 2016-MAR-28 SHORT SPEC The TMCM-1613 firmware performs hall sensor-based block
TMCM-171 module Hardware Manual
 TMCM-171 module Hardware Manual BLDC servo motor controller 20A/48V with RS485 and CAN interface Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG TMCM-171 Manual (V0.92 / Nov 7th, 2007) 2 Contents 1 Features...4
TMCM-171 module Hardware Manual BLDC servo motor controller 20A/48V with RS485 and CAN interface Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG TMCM-171 Manual (V0.92 / Nov 7th, 2007) 2 Contents 1 Features...4
TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL
 MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.05 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver 10A / 48V RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Firmware Version V2.05 TMCL FIRMWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver 10A / 48V RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
TMCL/PC Quick Start. Version: 1.00 December 19 th, 2005
 TMCL/PC Quick Start Version: 1.00 December 19 th, 2005 2 TMCL/PC Quick Start Version Version Date Author Comment 1.00 19-Dec-2005 OK Initial version Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Differences between TMCL/PC
TMCL/PC Quick Start Version: 1.00 December 19 th, 2005 2 TMCL/PC Quick Start Version Version Date Author Comment 1.00 19-Dec-2005 OK Initial version Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Differences between TMCL/PC
TMCM-310 Stepper Motor Motion Control Module
 TMCM-310 Stepper Motor Motion Control Module Documentation Version: 1.00 Date: June, 13 th, 003 /15 TMCM-310 Documentation v1.00 Life support policy TRINAMIC Microchips GmbH does not authorize or warrant
TMCM-310 Stepper Motor Motion Control Module Documentation Version: 1.00 Date: June, 13 th, 003 /15 TMCM-310 Documentation v1.00 Life support policy TRINAMIC Microchips GmbH does not authorize or warrant
BB-303 Manual Baseboard for TMCM-303
 BB-303 Manual Baseboard for TMCM-303 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Sternstraße 67 D 20357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com BB-303 Manual (V1.04 / Jul 9th, 2007) 2 Contents 1 Features...
BB-303 Manual Baseboard for TMCM-303 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Sternstraße 67 D 20357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com BB-303 Manual (V1.04 / Jul 9th, 2007) 2 Contents 1 Features...
TMCM-090. Version JAN-27. Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Waterloohain 5 D Hamburg, Germany
 TMCM-090 Version 1.04 2011-JAN-27 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Waterloohain 5 D 22769 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com TMCM-090 Manual (V1.04 /2011-JAN-27) 2 Table of contents 1 Features...
TMCM-090 Version 1.04 2011-JAN-27 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Waterloohain 5 D 22769 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com TMCM-090 Manual (V1.04 /2011-JAN-27) 2 Table of contents 1 Features...
TMCM Axis Encoder Interface Module. Manual. Version: 1.12 November 29 th, 2006
 TMCM-323 3- Axis Encoder Interface Module Manual Version: 1.12 November 29 th, 2006 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51
TMCM-323 3- Axis Encoder Interface Module Manual Version: 1.12 November 29 th, 2006 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51
TMCM-102. High Performance Stepper Motor Module with Encoder Interface. Version: 1.02 June 24 th, 2009
 TMCM-102 High Performance Stepper Motor Module with Encoder Interface Version: 1.02 June 24 th, 2009 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com
TMCM-102 High Performance Stepper Motor Module with Encoder Interface Version: 1.02 June 24 th, 2009 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany http://www.trinamic.com
TMCM-610. Hardware Manual. Version: APR-30
 TMCM-610 Hardware Manual Version: 1.14 2010-APR-30 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51 48 06-60 http://www.trinamic.com
TMCM-610 Hardware Manual Version: 1.14 2010-APR-30 Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG Sternstraße 67 D - 20 357 Hamburg, Germany Phone +49-40-51 48 06-0 FAX: +49-40-51 48 06-60 http://www.trinamic.com
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.2 UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.7A RMS / 24V DC RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.7A RMS / 24V DC RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-6110 V TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany. MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-60 6-axes stepper controller / driver up to.a RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS48 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-60 6-axes stepper controller / driver up to.a RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS48 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version 1.0 MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS
 MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-640 + + -axis BLDC controller / driver 5A / 24V DC RS485 + USB interface hall sensor interface encoder interface TRINAMIC Motion
MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-640 + + -axis BLDC controller / driver 5A / 24V DC RS485 + USB interface hall sensor interface encoder interface TRINAMIC Motion
CANopen MANUAL. TMCM axis stepper controller/driver board 2.8A RMS / 24V DC Encoder interface
 CANopen MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES CANopen Firmware Version V3.18 CANopen MANUAL TMCM-351 3-axis stepper controller/driver board 2.8A RMS / 24V DC Encoder interface TMCM-341 3-axis controller board
CANopen MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES CANopen Firmware Version V3.18 CANopen MANUAL TMCM-351 3-axis stepper controller/driver board 2.8A RMS / 24V DC Encoder interface TMCM-341 3-axis controller board
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V 1.1 MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS
 MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V 1.1 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver plug-in module 10A / 48V DC RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH
MODULE FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V 1.1 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver plug-in module 10A / 48V DC RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.0 UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1161 1-axis Stepper Controller / Driver up to 2.8 RMS / 24V DC USB, RS485, and RS232 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1161 1-axis Stepper Controller / Driver up to 2.8 RMS / 24V DC USB, RS485, and RS232 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion
Hardware MCST Technical Manual W E CREATE MOTION
 Hardware MCST 3601 Technical Manual EN W E CREATE MOTION Imprint Version: 1st edition, 01.10.2014 Copyright by FAULHABER PRECISTEP SA Rue des Gentianes 53 2300 La Chaux-de-Fonds Switzerland All rights
Hardware MCST 3601 Technical Manual EN W E CREATE MOTION Imprint Version: 1st edition, 01.10.2014 Copyright by FAULHABER PRECISTEP SA Rue des Gentianes 53 2300 La Chaux-de-Fonds Switzerland All rights
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-1613 TMCM-1613-REC. Hardware Version V TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V 1.10 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1613 + + Single Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Block-commutation Hall-sensor based Analog+digital inputs / outputs Up-to
MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V 1.10 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1613 + + Single Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Block-commutation Hall-sensor based Analog+digital inputs / outputs Up-to
The TMCL Wrapper DLL (USB version)
 The TMCL Wrapper DLL (USB version) Version: 0.02 October 1 st, 2004 D - 20357 Hamburg, Germany 2 The TMCL Wrapper DLL (USB) Version Version Date Author Comment 0.01 28-May-04 OK Initial version 0.02 1-Oct-04
The TMCL Wrapper DLL (USB version) Version: 0.02 October 1 st, 2004 D - 20357 Hamburg, Germany 2 The TMCL Wrapper DLL (USB) Version Version Date Author Comment 0.01 28-May-04 OK Initial version 0.02 1-Oct-04
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1161 Stepper motor with controller/driver 0.55 3.1Nm / 24V DC sensostep encoder USB, RS485, and RS232 + + UNIQUE
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1161 Stepper motor with controller/driver 0.55 3.1Nm / 24V DC sensostep encoder USB, RS485, and RS232 + + UNIQUE
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-1613 TMCM-1613-REC. Hardware Version V TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V 1.10 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1613 + + Single Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Block-commutation Hall-sensor based Analog+digital inputs / outputs Up-to
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V 1.10 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1613 + + Single Axis BLDC Controller / Driver Block-commutation Hall-sensor based Analog+digital inputs / outputs Up-to
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-1640 V 1.04 MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS
 MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES V 1.04 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-axis BLDC controller / driver 5A / 24V DC RS485 + USB interface hall sensor interface hallfx encoder interface + + TRINAMIC Motion
MODULES FOR BLDC MOTORS MODULES V 1.04 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1640 1-axis BLDC controller / driver 5A / 24V DC RS485 + USB interface hall sensor interface hallfx encoder interface + + TRINAMIC Motion
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrives V 1.52 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-113-60-SE controller / driver up to 2.8A RMS / 24V RS232 or RS485 integrated sensostep encoder chopsync stallguard PD-113-57/60-SE
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrives V 1.52 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-113-60-SE controller / driver up to 2.8A RMS / 24V RS232 or RS485 integrated sensostep encoder chopsync stallguard PD-113-57/60-SE
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.2. TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany. MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1310 1-Axis Stepper Closed Loop Controller / Driver 3 A RMS / 48 V ABN and SSI Encoder Input 18 GPIOs USB, EtherCAT + + TRINAMIC
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1310 1-Axis Stepper Closed Loop Controller / Driver 3 A RMS / 48 V ABN and SSI Encoder Input 18 GPIOs USB, EtherCAT + + TRINAMIC
PD42-x-1370 Hardware Manual
 PANdrive for Stepper PANDRIVE PD42-x-1370 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.10 2018-AUG-18 The PANdrive PD42-1-1370, PD42-2-1370, PD42-3-1370 amd PD42-4-1370 are small and compact
PANdrive for Stepper PANDRIVE PD42-x-1370 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.10 2018-AUG-18 The PANdrive PD42-1-1370, PD42-2-1370, PD42-3-1370 amd PD42-4-1370 are small and compact
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.06-0.12Nm / 24V sensostep Encoder RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1021 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.06-0.12Nm / 24V sensostep Encoder RS485 Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
TMCM Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL. TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 Hardware Version V.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-3 -Axis Stepper Closed Loop Controller/Driver 3.0 A / 48 V Encoder Input 8 GPIOs USB, CAN, RS485 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany
Hardware Version V.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-3 -Axis Stepper Closed Loop Controller/Driver 3.0 A / 48 V Encoder Input 8 GPIOs USB, CAN, RS485 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany
Bootloader Firmware Update Protocol and Procedure
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS Bootloader Firmware Update Protocol and Procedure Valid for TMCM-1110 steprocker This application note will give a brief overview of the firmware update procedure and the communication
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS Bootloader Firmware Update Protocol and Procedure Valid for TMCM-1110 steprocker This application note will give a brief overview of the firmware update procedure and the communication
HARDWARE MANUAL V 1.04 TMCM-1110 V1.1 UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.04 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-0 V. -axis stepper controller / driver A RMS / 2.8A RMS 24V DC USB, RS485 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.04 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-0 V. -axis stepper controller / driver A RMS / 2.8A RMS 24V DC USB, RS485 + + UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.4 UNIQUE FEATURES: TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.4 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24V DC up-to 0.7A RMS / 1.4A RMS RS485 Interface sensostep Encoder + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE Hardware Version V1.4 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1021 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24V DC up-to 0.7A RMS / 1.4A RMS RS485 Interface sensostep Encoder + + UNIQUE FEATURES:
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.3 UNIQUE FEATURES. TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V1.3 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1141 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24 V DC up-to 1.1 A / 2A RMS USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V1.3 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1141 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 24 V DC up-to 1.1 A / 2A RMS USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES
TMCM-3230 Hardware Manual
 MODULE Module for Stepper Motors TMCM-3230 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.30 Document Revision V0.91 2017-JUL-12 The TMCM-3230 is a compact and easy to use 3-axes stepper motor controller and driver
MODULE Module for Stepper Motors TMCM-3230 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.30 Document Revision V0.91 2017-JUL-12 The TMCM-3230 is a compact and easy to use 3-axes stepper motor controller and driver
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-60 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.55-3. Nm / 48 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-60 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.55-3. Nm / 48 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-1630 V 1.03 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS. 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver plug-in module 10A / 48V DC RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB
 MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE V 1.03 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver plug-in module 10A / 48V DC RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
MODULE FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULE V 1.03 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1630 1-Axis BLDC Controller / Driver plug-in module 10A / 48V DC RS232 / CAN or RS485 / USB + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg,
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.1 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1160 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.55-3.1 Nm / 48 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.1 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1160 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.55-3.1 Nm / 48 V sensostep Encoder USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrives V 1.01 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1180 PD86-1180 1-axis stepper controller / driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN + + TRINAMIC Motion Control
MECHATRONIC DRIVES WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrives V 1.01 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1180 PD86-1180 1-axis stepper controller / driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN + + TRINAMIC Motion Control
TMCM-1240 Hardware Manual
 Module for Stepper MODULE TMCM-1240 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.20 Document Revision V1.2 2018-DEC-05 The TMCM-1240 is a single axis motor controller/driver board for 2-phase bipolar stepper motors
Module for Stepper MODULE TMCM-1240 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.20 Document Revision V1.2 2018-DEC-05 The TMCM-1240 is a single axis motor controller/driver board for 2-phase bipolar stepper motors
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM Hardware Version V1.1. TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany. MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-30 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 48 V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Encoder Interface + + TRINAMIC
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-30 3-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8 A / 48 V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Encoder Interface + + TRINAMIC
R325P Single Axis Driver
 R325P Single Axis Driver User Manual And Commands Guide Version 1.3 Thank you for purchasing the R325P Single-Axis Step & Direction Driver. This product is warranted to be free of manufacturing defects
R325P Single Axis Driver User Manual And Commands Guide Version 1.3 Thank you for purchasing the R325P Single-Axis Step & Direction Driver. This product is warranted to be free of manufacturing defects
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1141 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.27-0.49 Nm / 24 V DC USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.2 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD-1141 Stepper Motor with Controller / Driver 0.27-0.49 Nm / 24 V DC USB, RS485, and S/D Interface + + UNIQUE FEATURES
Application note AN020: Connecting modules with RS485 interface Preliminary
 Application note AN020: connecting modules with RS485 interface (V1.10 / 2018-JUL-05) 1 Application note AN020: Connecting modules with RS485 interface Preliminary TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Application note AN020: connecting modules with RS485 interface (V1.10 / 2018-JUL-05) 1 Application note AN020: Connecting modules with RS485 interface Preliminary TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
TMCM-1260 Hardware Manual
 Module for Stepper MODULE TMCM-1260 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.20 2018-05-17 The TMCM-1260 is a single axis motor controller/driver board for 2-phase bipolar stepper motors
Module for Stepper MODULE TMCM-1260 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.20 2018-05-17 The TMCM-1260 is a single axis motor controller/driver board for 2-phase bipolar stepper motors
TMC428 Evaluation Kit V2.0 Manual English
 TMC428 Evaluation Kit V2.0 Manual English Version: 2.01 July 30 th, 2002 2 TMC428 Evaluation Kit V2.01 Version Version Date Author Remarks 2.00 2002-07-29 OK Created from version 1.02 2.01 2002-07-30 OK
TMC428 Evaluation Kit V2.0 Manual English Version: 2.01 July 30 th, 2002 2 TMC428 Evaluation Kit V2.01 Version Version Date Author Remarks 2.00 2002-07-29 OK Created from version 1.02 2.01 2002-07-30 OK
HARDWARE MANUAL TMCM-6110 V TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany. MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS
 MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-60 6-axes stepper controller / driver up to.a RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS48 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com
MODULES FOR STEPPER MOTORS MODULES V.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-60 6-axes stepper controller / driver up to.a RMS / 24V DC USB, CAN, RS48 + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com
EVAL BOARD MANUAL. TMC429+TMC24x-EVAL V TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany.
 EVALUATION FOR ICs EVALUATION BOARDS V 1.00 EVAL BOARD MANUAL + + TMC429+TMC24x-EVAL Evaluation kit for TMC429 and TMC24x + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com TMC429+TMC24x-EVAL
EVALUATION FOR ICs EVALUATION BOARDS V 1.00 EVAL BOARD MANUAL + + TMC429+TMC24x-EVAL Evaluation kit for TMC429 and TMC24x + + TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, Germany www.trinamic.com TMC429+TMC24x-EVAL
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-80 PD86-80 -Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN + + TRINAMIC Motion
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V. HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-80 PD86-80 -Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 5.5A RMS/ 24 or 48V DC USB, RS232, RS485, and CAN + + TRINAMIC Motion
TMCM-1633 Hardware Manual
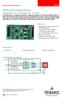 Module for BLDC/PMSM Motors MODULE TMCM-1633 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.01 2017-Sept-07 The TMCM-1633 is a single axis controller module for brushless DC (BLDC) and PMSM
Module for BLDC/PMSM Motors MODULE TMCM-1633 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.01 2017-Sept-07 The TMCM-1633 is a single axis controller module for brushless DC (BLDC) and PMSM
A Issue A Original. Instruction Manual. nxds Serial Comms Interface
 Instruction Manual A735-01-860 Issue A Original nxds Serial Comms Interface Description nxds6i nxds10i nxds15i nxds20i Item Number A735-01-983 A736-01-983 A737-01-983 A738-01-983 nxds6ic nxds10ic nxds15ic
Instruction Manual A735-01-860 Issue A Original nxds Serial Comms Interface Description nxds6i nxds10i nxds15i nxds20i Item Number A735-01-983 A736-01-983 A737-01-983 A738-01-983 nxds6ic nxds10ic nxds15ic
PD57/60-x-1260 Hardware Manual
 PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD57/60-x-1260 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.00 2018-03-29 The PANdrive PD57-1-1260, PD57-2-1260, PD60-3-1260 amd PD60-4-1260 are powerful
PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD57/60-x-1260 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.10 Document Revision V1.00 2018-03-29 The PANdrive PD57-1-1260, PD57-2-1260, PD60-3-1260 amd PD60-4-1260 are powerful
TMC429+TMC26x-EVAL. Firmware Version V2.04 TMC429+TMC26x EVALUATION BOARD MANUAL UNIQUE FEATURES
 EVALUATION FOR ICs EVALUATION BOARD Firmware Version V2.04 TMC429+TMC26x EVALUATION BOARD MANUAL + + TMC429+TMC26x-EVAL + + Evaluation Board for TMC429 Motion Controller and TMC262, TMC261, and TMC260
EVALUATION FOR ICs EVALUATION BOARD Firmware Version V2.04 TMC429+TMC26x EVALUATION BOARD MANUAL + + TMC429+TMC26x-EVAL + + Evaluation Board for TMC429 Motion Controller and TMC262, TMC261, and TMC260
TMCM-302 Stepper Motor Motion Control Module
 DATA SHEET (V0.8 / October st, 2002) PRELIMINARY Stepper Motor Motion Control Module PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET TRINAMIC Microchips GmbH Deelbögenkamp 4C D 22297 Hamburg GERMANY T +49 - (0) 40-5 48 06-0 F
DATA SHEET (V0.8 / October st, 2002) PRELIMINARY Stepper Motor Motion Control Module PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET TRINAMIC Microchips GmbH Deelbögenkamp 4C D 22297 Hamburg GERMANY T +49 - (0) 40-5 48 06-0 F
TMC262-EVAL MANUAL (V. 1.0 / 2011-Sep-07) 1
 TMC262-EVAL MANUAL (V. 1.0 / 2011-Sep-07) 1 TMC262 EVAL manual Evaluation board for the TMC262 stepper motor driver IC with coolstep TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, GERMANY www.trinamic.com
TMC262-EVAL MANUAL (V. 1.0 / 2011-Sep-07) 1 TMC262 EVAL manual Evaluation board for the TMC262 stepper motor driver IC with coolstep TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG Hamburg, GERMANY www.trinamic.com
TECHNICAL REFERENCE BSD V-3A Bipolar Stepper Driver
 TECHNICAL REFERENCE BSD 3630 36V-3A Bipolar Stepper Driver Contents Chapter 1 Safety Precautions.. 3 Chapter 2 Drive Overview...4 2.1 Key Features...4 2.2 Drive Description...4 2.3 Applications. 4 Chapter
TECHNICAL REFERENCE BSD 3630 36V-3A Bipolar Stepper Driver Contents Chapter 1 Safety Precautions.. 3 Chapter 2 Drive Overview...4 2.1 Key Features...4 2.2 Drive Description...4 2.3 Applications. 4 Chapter
LNX Series Motor and Drives
 LNX Series Motor and Drives Operator's Manual PN 04-01808 x PRECISION MOTION CONTROLS 2530 Berryessa Rd. #209 San Jose, CA 95132 1 2 Table of Contents Page Introduction 1. Description 3 2. Warranty 4 Installation
LNX Series Motor and Drives Operator's Manual PN 04-01808 x PRECISION MOTION CONTROLS 2530 Berryessa Rd. #209 San Jose, CA 95132 1 2 Table of Contents Page Introduction 1. Description 3 2. Warranty 4 Installation
Motion Controller. MXC Series Multi-Axis Motion Controller Compact Motion Controller with up to 6 Axes of Control
 MXC Series Multi-Axis Motion Controller Compact Motion Controller with up to 6 Axes of Control Allied Motion s MXC motion controller is a very compact, multi-axis servo and/or step motor motion controller,
MXC Series Multi-Axis Motion Controller Compact Motion Controller with up to 6 Axes of Control Allied Motion s MXC motion controller is a very compact, multi-axis servo and/or step motor motion controller,
motioncookie SYSTEM IN A PACKAGE
 motioncookie SYSTEM IN A PACKAGE motioncookie TMCC160-EVAL MANUAL TMCC160 TMCL Hardware Version 1.1 Document Revision 1.0 2015-AUG-16 The TMCC160-EVAL is designed for evaluating all features of the TMCC160-LC
motioncookie SYSTEM IN A PACKAGE motioncookie TMCC160-EVAL MANUAL TMCC160 TMCL Hardware Version 1.1 Document Revision 1.0 2015-AUG-16 The TMCC160-EVAL is designed for evaluating all features of the TMCC160-LC
TMCM-1111 Hardware Manual
 Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1111 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V0.90 2017-July-11 The TMCM-1111 steprocker servo is a single axis motor controller/driver board for
Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1111 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V0.90 2017-July-11 The TMCM-1111 steprocker servo is a single axis motor controller/driver board for
R325 Single Axis Controller/Driver
 R325 Single Axis Controller/Driver User Manual And Commands Guide Version 1.02 RMS Technologies 2533 N. Carson St. #4698, Carson City, NV 89706-0147 1-877-301-3609 www.rmsmotion.com sales@rmsmotion.com
R325 Single Axis Controller/Driver User Manual And Commands Guide Version 1.02 RMS Technologies 2533 N. Carson St. #4698, Carson City, NV 89706-0147 1-877-301-3609 www.rmsmotion.com sales@rmsmotion.com
TMCM-1270 Hardware Manual
 Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1270 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.10 2017-Mar-05 TMCM-1270 is an easy to use smart stepper motor driver module. The module is controlled
Module for Stepper Motors MODULE TMCM-1270 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.10 2017-Mar-05 TMCM-1270 is an easy to use smart stepper motor driver module. The module is controlled
D115 The Fast Optimal Servo Amplifier For Brush, Brushless, Voice Coil Servo Motors
 D115 The Fast Optimal Servo Amplifier For Brush, Brushless, Voice Coil Servo Motors Ron Boe 5/15/2014 This user guide details the servo drives capabilities and physical interfaces. Users will be able to
D115 The Fast Optimal Servo Amplifier For Brush, Brushless, Voice Coil Servo Motors Ron Boe 5/15/2014 This user guide details the servo drives capabilities and physical interfaces. Users will be able to
MBC25SI1TB. Programmable Simple Indexer/Driver. User s Guide E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA
 MBC25SI1TB Programmable Simple Indexer/Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471
MBC25SI1TB Programmable Simple Indexer/Driver User s Guide A N A H E I M A U T O M A T I O N 4985 E. Landon Drive Anaheim, CA 92807 e-mail: info@anaheimautomation.com (714) 992-6990 fax: (714) 992-0471
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR MOTION CONTROL PRODUCT GUIDE 2013
 SMART SOLUTIONS FOR MOTION CONTROL PRODUCT GUIDE 2013 TR INAMIC SMART SOLUT IONS FOR MOT ION CONTROL TRINAMIC is a fabless semiconductor company and serves the market with self developed integrated circuits
SMART SOLUTIONS FOR MOTION CONTROL PRODUCT GUIDE 2013 TR INAMIC SMART SOLUT IONS FOR MOT ION CONTROL TRINAMIC is a fabless semiconductor company and serves the market with self developed integrated circuits
Stepper motor driver HEM-545 last change:
 Documentation for Stepper motor driver HEM-545 last change: 16.03.2011 Functional description HEM-545 is a one channel motor driver for 2-phase stepping motors with pulse and direction interface. Motor
Documentation for Stepper motor driver HEM-545 last change: 16.03.2011 Functional description HEM-545 is a one channel motor driver for 2-phase stepping motors with pulse and direction interface. Motor
ST400C-NT USER S GUIDE. Table of Contents
 ST400C-NT USER S GUIDE Table of Contents Board Overview Block Diagram Disclaimer Introduction Features 1 Quick Start 2 Function Description Host Interface and Communication with PC's 3 Networking Operation
ST400C-NT USER S GUIDE Table of Contents Board Overview Block Diagram Disclaimer Introduction Features 1 Quick Start 2 Function Description Host Interface and Communication with PC's 3 Networking Operation
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1060 PD-1060 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8A / 48V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Integrated
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.0 HARDWARE MANUAL + + TMCM-1060 PD-1060 1-Axis Stepper Controller / Driver 2.8A / 48V USB, RS485, and CAN Step/Dir Interface Integrated
Hybrid AC Driver [GCNC-1110]
![Hybrid AC Driver [GCNC-1110] Hybrid AC Driver [GCNC-1110]](/thumbs/86/94474371.jpg) Page 1 Installation Manual and Datasheet Page 2 Key Features Smooth and quiet operation at all speeds and extremely low motor heating Industrial grade performance for an alternating current servo motor
Page 1 Installation Manual and Datasheet Page 2 Key Features Smooth and quiet operation at all speeds and extremely low motor heating Industrial grade performance for an alternating current servo motor
Decades of experience embodied in dependable building blocks.
 About Us Decades of experience embodied in dependable building blocks. Trinamic is the global leader in embedded motor and motion control. Our ICs and microsystems connect the digital and physical worlds.
About Us Decades of experience embodied in dependable building blocks. Trinamic is the global leader in embedded motor and motion control. Our ICs and microsystems connect the digital and physical worlds.
KOLLMORGEN. SERVOSTAR CD. SERCOS IDN Manual M-SS rev. F. Solutions by D A N A H E R M O T I O N
 KOLLMORGEN www.danahermotion.com SERVOSTAR CD Solutions by D A N A H E R M O T I O N SERCOS IDN Manual M-SS-017-05 rev. F Revision History Revision Edition Date Reason for Revision 1 05/01/1999 Initial
KOLLMORGEN www.danahermotion.com SERVOSTAR CD Solutions by D A N A H E R M O T I O N SERCOS IDN Manual M-SS-017-05 rev. F Revision History Revision Edition Date Reason for Revision 1 05/01/1999 Initial
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR
 MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.4 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD28-1-1021 PD28-3-1021 + + Stepper Motor NEMA11 / 28mm 0.06-0.12Nm with Controller / Driver up-to 0.7A RMS / 24V
MECHATRONIC DRIVE WITH STEPPER MOTOR PANdrive Hardware Version V1.4 HARDWARE MANUAL + + PD28-1-1021 PD28-3-1021 + + Stepper Motor NEMA11 / 28mm 0.06-0.12Nm with Controller / Driver up-to 0.7A RMS / 24V
User s Manual. Extremely Low Noise 3-phase Microstepping Driver. For 3L583M. Version All Rights Reserved
 User s Manual For Extremely Low Noise 3-phase Microstepping Driver Version 1.0 2008 All Rights Reserved Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! The content in this manual
User s Manual For Extremely Low Noise 3-phase Microstepping Driver Version 1.0 2008 All Rights Reserved Attention: Please read this manual carefully before using the driver! The content in this manual
AG300 Family CTL01-3A-03, AMP01-2A-02
 AG300 Family CTL01-3A-03, AMP01-2A-02 Hardware User's Manual Page 1 Revision control table Version Description Date 1.0 Initial (based on Hardware Manual of previous hardware versions) April 27, 2016 1.1
AG300 Family CTL01-3A-03, AMP01-2A-02 Hardware User's Manual Page 1 Revision control table Version Description Date 1.0 Initial (based on Hardware Manual of previous hardware versions) April 27, 2016 1.1
AN022: The Bootloader Protocol
 APPLICATION NOTE AN022: The Bootloader Protocol Document Revision V2.00 2018-APR-04 This application note describes the protocol used to update the firmware of a Trinamic module or a Trinamic evaluation
APPLICATION NOTE AN022: The Bootloader Protocol Document Revision V2.00 2018-APR-04 This application note describes the protocol used to update the firmware of a Trinamic module or a Trinamic evaluation
Device manual Profibus encoder. RM30xx RN30xx /00 06/2013
 Device manual Profibus encoder RM30xx RN30xx 706355/00 06/2013 Contents 1 Preliminary note................................................. 4 1.1 Symbols used...............................................
Device manual Profibus encoder RM30xx RN30xx 706355/00 06/2013 Contents 1 Preliminary note................................................. 4 1.1 Symbols used...............................................
Stepper Motor. Vcc 3.3~5V User MCU Direc on Pulse Enable. Vcc DIR STP
 Miniature size 2.mm x 2.mm x 1.5mm Integral design to fit motors, work standalone as well Wide range input voltage 10-0 0-2A / 1.5 - A / - 8A adjustable phase current 1 to 16th micro stepping Automatic
Miniature size 2.mm x 2.mm x 1.5mm Integral design to fit motors, work standalone as well Wide range input voltage 10-0 0-2A / 1.5 - A / - 8A adjustable phase current 1 to 16th micro stepping Automatic
User Manual For DM332T. 2-Phase Digital Stepper Drive. Designed by StepperOnline. Manufactured by Leadshine
 User Manual For DM332T 2-Phase Digital Stepper Drive Designed by StepperOnline Manufactured by Leadshine #7 Zhongke Road, Jiangning, Nanjing, China T: 0086-2587156578 Web site: www.omc-stepperonline.com
User Manual For DM332T 2-Phase Digital Stepper Drive Designed by StepperOnline Manufactured by Leadshine #7 Zhongke Road, Jiangning, Nanjing, China T: 0086-2587156578 Web site: www.omc-stepperonline.com
PD Hardware Manual
 PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD42-1070 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.00 2016-Aug-04 PD42-1070 is an easy to use PANdrive smart stepper motor. The module is controlled
PANdrive for Stepper Motors PANDRIVE PD42-1070 Hardware Manual Hardware Version V1.00 Document Revision V1.00 2016-Aug-04 PD42-1070 is an easy to use PANdrive smart stepper motor. The module is controlled
LN3X Series Motor and Drives
 LN3X Series Motor and Drives Operator's Manual PN 04-01920 C PRECISION MOTION CONTROLS 2175 De La Cruz Blvd., #1 Santa Clara, CA 95050 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 Description... 3 Features... 3 Warranty...
LN3X Series Motor and Drives Operator's Manual PN 04-01920 C PRECISION MOTION CONTROLS 2175 De La Cruz Blvd., #1 Santa Clara, CA 95050 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 Description... 3 Features... 3 Warranty...
TMC 423 Datasheet Serial Triple Incremental Encoder Interface
 TMC43 Data Sheet (V. / March 9 th, 7) / TMC 43 Datasheet Serial Triple Incremental Encoder Interface TCK SDO SDI SCK NSCS SDO48 NSCS48 NINT PRA/IO VCCA NC CLK EXT_RES VCCI TDI ENC_A ENC_B COLUMN_PIN()
TMC43 Data Sheet (V. / March 9 th, 7) / TMC 43 Datasheet Serial Triple Incremental Encoder Interface TCK SDO SDI SCK NSCS SDO48 NSCS48 NINT PRA/IO VCCA NC CLK EXT_RES VCCI TDI ENC_A ENC_B COLUMN_PIN()
SD17098IX Specifications Networked Stepper Driver & Indexer Revision 0.0
 The SD17098IX is a 170V 9.8amp stepper driver and indexer combination that communicates on a Network. The available networks, along with the corresponding AMCI part numbers, are shown in the following
The SD17098IX is a 170V 9.8amp stepper driver and indexer combination that communicates on a Network. The available networks, along with the corresponding AMCI part numbers, are shown in the following
