CS 3330 Exam 1 Fall 2017 Computing ID:
|
|
|
- Amanda Higgins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 1 of 8 mail I: S 3330 xam 1 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if we are unsure of what you wrote you will get a zero on that problem. ubble and Pledge the exam or you will lose points. ssume unless otherwise specified: little-endian 64-bit architecture %rsp points to the most recently pushed value, not to the next unused stack address. questions are single-selection unless identified as select-all Variable Weight: point values per question are marked in square brackets. Mark clarifications: If you need to clarify an answer, do so, and also add a * to the top right corner of your answer box Question 1 [2 pt]: ach of the following statements about Y86 is true. Which of them is typical of instruction sets that are called RIS-like? Write in the box next to each property that is typical of a RIS-like instruction set. Leave other boxes blank. the mrmovq only has one way to specify a memory location a single instruction can change the stack pointer and read or write from the stack instructions have different lengths, depending on how many operands they have the addq instruction does not support a memory operand Question 2 [2 pt]: onsider the circuit above, where,, and are 64-bit registers, and is a block of combinatorial logic which takes two 64-bit inputs and produces the 64-bit sum of its inputs. ach of the registers is connected to an (undrawn) common clock signal. If initially outputs 1, initilly outputs 2, and initially outputs 3, what is the value output by after 2 rising edges of the clock signal? Write your answer as a decimal number.
2 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 2 of 8 mail I: Question 3 [2 pt]: onsider the following x86 assembly code: shrq is a logical right shift, and andq is bitwise and. foo: andq $0xFF00, %rdi shrq $4, %rdi movq %rdi, %rax retq If this function is executed and %rdi (first argument) is 0x12345, what the value of %rax when it returns? Write your answer as a hexadecimal number. Information for questions 4 6 In the single-cycle processor discussed in the book and lecture, the register file has two write register number inputs and two corresponding register value inputs; and two read register number inputs and two corresponding register value outputs. The questions below ask about pairs of register file inputs; each possible answer specifies two values, one for each of the two inputs. Question 4 [2 pt]: (see above) While the processor is executing a call instruction, what should the two write register number inputs be equal to? F two parts of the instruction memory output 0xF ( no register ) (for both inputs) part of the program counter output and the register number for %rsp part of register number for %rsp and 0xF ( no register ) part of the LU output and the register number for %rsp part of the instruction memory output and the register number for %rsp Question 5 [2 pt]: (see above) While the processor is executing a pushq instruction, what should the two read register number inputs be equal to? F two parts of the instruction memory output part of the LU output and the register number for %rsp part of the program counter output and the register number for %rsp part of the instruction memory output and the register number for %rsp it doesn t matter; this instruction doesn t read registers the register number for %rsp for one input; and the other doesn t matter Question 6 [2 pt]: (see above) While the processor is executing a subq instruction, what should the two read register number inputs be equal to? part of register number for %rsp for one input; and the other doesn t matter it doesn t matter; this instruction doesn t read registers part of the LU output and the register number for %rsp part of the instruction memory output and the register number for %rsp two parts of the instruction memory output F part of the program counter output and the register number for %rsp
3 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 3 of 8 mail I: Question 7 [2 pt]: Suppose we wanted to add a cmpje r, r, ST instruction to the Y86 single cycle processor design discussed in class and the textbook. This instruction would test if the value stored in the register r was equal to the value stored in the register r. If so, it would jump to ST. Which of the following would be true about adding this instruction to the processor design? Write in each box which is true. Leave other boxes blank. it would require an extra input to the MUX controlling the program counter input it would be the only instruction that performs an LU operation without setting the condition codes it would require adding an additional read port to the register file it would require reading more than 10 bytes from the instruction memory at a time Question 8 [2 pt]: onsider the incomplete Y86 assembly function absolute_value below which takes a single 64-bit integer argument in %rdi and returns a value in %rax: absolute_value: irmovq $0, %rax subq %rdi, %rax %rdi, %rax ret In order for this function to return the absolute value of its argument, what should be placed in the blank? subq cmovg rrmovq cmove cmovl F none of the above Question 9 [2 pt]: What are the values of the condition codes ZF and SF after running the following Y86 assembly snippet: subq %rax, %rax irmovq $-10, %rax ZF = 0, SF = 0 ZF = 0, SF = 1 ZF = 1, SF = 1 ZF = 1, SF = 0 not enough information is provided Question 10 [2 pt]: Using the abbreviations K, M, G, T, etc. (representing powers of two, not ten), what is 2 17?
4 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 4 of 8 mail I: Question 11 [2 pt]: Which of the following are present in object files? Select all that apply. the memory addresses of labels the initial values of global variables the names of labels machine code Question 12 [2 pt]: onsider the following code: while (b > c) { b += c; } If b is stored in %rbx and c is stored in %rcx, which of the following is a correct translation of this loop to assembly code? (Recall that cmpq, performs the computation -.) Write in the box next to each correct translation. Leave other boxes blank. jmp middle addq %rbx, %rcx middle: cmpq %rcx, %rbx jl start end: cmpq %rcx, %rbx jle end addq %rcx, %rbx cmpq %rbx, %rcx jl start end: addq %rcx, %rbx cmpq %rcx, %rbx jg start cmpq %rcx, %rbx jle end addq %rcx, %rbx jmp start end:
5 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 5 of 8 mail I: Information for questions onsider the following Y86-64 assembly and its corresponding encoding. The numbers before the :s represents a memory address and the sequence of hexadecimal values after it represent the bytes of the instructions in order from lowest to highest address. For example 0x234: would mean that address 0x234 contains the byte 0x56 and address 0x235 contains the byte 0x78. 0x000: 30 f irmovq $1, %rcx 0x00a: 30 f irmovq $2, %rdx 0x014: andq %rcx, %rdx 0x016: mrmovq 8(%rcx), %rax Question 13 [2 pt]: (see above) What is the value of %rax after this snippet executes? 0 1 0x30 0x2f230 0x2f23000 F 0x30f202 G 0x30f (ends with 6 zeroes) H there is not enough information to determine this I none of the above Question 14 [2 pt]: (see above) What is the value of %rdx after this snippet executes? F there is not enough information to determine this. G none of the above Question 15 [2 pt]: Suppose a long *x is stored in the register %rax and a long y is stored in the register %rbx. Which of the following x86 assembly snippets is equivalent to the code x += y? (lea stands for load effective address.) F addq %rbx, %rax addq (%rbx, 8), %rax leaq (%rax, %rbx, 8), %rax movq (%rax, %rbx, 8), %rax leaq (%rbx, 8), %rax none of the above
6 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 6 of 8 mail I: Question 16 [2 pt]: The processor design in our book can send part of the output of the instruction memory directly to one of the LU inputs. Which of these Y86 instructions is this useful for? Place in each box corresponding to a true answer. Leave other boxes blank. mrmovq addq call pushq Information for questions Suppose we wanted to add an instruction iaddq to the Y86 instruciton set. This instruction would add a constant to an register. For example, iaddq $100, %rax would add 100 to the value stored in %rax. Question 17 [2 pt]: the same layout as: irmovq mrmovq addq call none of the above (see above) This instruction could have an encoding in machine code with Question 18 [2 pt]: (see above) When this instruction executes in the single-cycle design discussed in lecture and our textbook, one of the value to write inputs to the register file will not be used, and the other should be equal to: the register file output the address of the next instruction the LU output the data memory output none of the above
7 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 7 of 8 mail I: Question 19 [2 pt]: onsider the following Y86 assembly code: addq %rax, %rax rrmovq %rax, %r8 subq %rbx, %r8 jle start If %rax corresponds to the variable a and %rbx corresponds to the variable b, which of the following snippets is equivalent to this code? (You may assume integer overflow does not occur and that all variables are 8-byte signed long ints.) do { a += a; } while (b <= a); do { a += a; } while (b > a); do { a += a; a -= b; } while (b <= a); do { a += a; a -= b; } while (b <= 0); none of the above Question 20 [6 pt]: If x and y are nonnegative unsigned integers between 0 and , which of the following expressions are always true? Write in the box next to each expression which is always true. Leave other boxes blank. ((x >> 1) (y >> 1) 1) > (x + y + 1) ((x & 0xFF) >> 1) > (x & 0xFF) (x ^ y) <= (x y) ((x >> 7) (y >> 7)) == ((x y) >> 7) ((x & 0xFF) (x >> 8)) <= 0xFF F (x & y) <= (x ^ y)
8 S 3330 Fall 2017 xam 1 Variant page 8 of 8 mail I: Information for questions onsider the following code: int array[5] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}; int *x = array + 3; Question 21 [2 pt]: *(x + 1)? (see above) Immediately after the above code runs, what is the value of unknown; this is expression is undefined behavior and/or may crash 4 F 6 G none of the above Question 22 [2 pt]: of array be? (see above) fter x -= 1; *x -= 1; x -= 1;, what would the value unknown; the code is undefined behavior and/or may crash {2, 3, 6, 8, 10} {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} {2, 4, 5, 8, 10} {2, 4, 6, 7, 10} F {2, 4, 5, 7, 10} G none of the above Pledge: On my honor as a student, I have neither given nor received aid on this exam. Your signature here
CS 3330 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Computing ID:
 S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 3 Variant E page 1 of 16 Email I: S 3330 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if
S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 3 Variant E page 1 of 16 Email I: S 3330 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if
CS 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Computing ID:
 S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Variant page 1 of 8 Email I: S 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if we
S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Variant page 1 of 8 Email I: S 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if we
CS 3330 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Name: EXAM KEY Computing ID: KEY
 S 3330 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Variant E page 1 of 6 Email I: KEY S 3330 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Name: EXM KEY omputing I: KEY Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write
S 3330 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Variant E page 1 of 6 Email I: KEY S 3330 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Name: EXM KEY omputing I: KEY Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write
Intel x86-64 and Y86-64 Instruction Set Architecture
 CSE 2421: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Intel x86-64 and Y86-64 Instruction Set Architecture Presentation J Read/Study: Bryant 3.1 3.5, 4.1 Gojko Babić 03-07-2018 Intel x86
CSE 2421: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Intel x86-64 and Y86-64 Instruction Set Architecture Presentation J Read/Study: Bryant 3.1 3.5, 4.1 Gojko Babić 03-07-2018 Intel x86
CS 3330 Exam 2 Spring 2016 Name: EXAM KEY Computing ID: KEY
 S 3330 Spring 2016 xam 2 Variant U page 1 of 6 mail I: KY S 3330 xam 2 Spring 2016 Name: XM KY omputing I: KY Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters
S 3330 Spring 2016 xam 2 Variant U page 1 of 6 mail I: KY S 3330 xam 2 Spring 2016 Name: XM KY omputing I: KY Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters
Computer Organization: A Programmer's Perspective
 A Programmer's Perspective Instruction Set Architecture Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il Outline: CPU Design Background Instruction sets Logic design Sequential Implementation A simple, but not very fast
A Programmer's Perspective Instruction Set Architecture Gal A. Kaminka galk@cs.biu.ac.il Outline: CPU Design Background Instruction sets Logic design Sequential Implementation A simple, but not very fast
Computer Architecture I: Outline and Instruction Set Architecture. CENG331 - Computer Organization. Murat Manguoglu
 Computer Architecture I: Outline and Instruction Set Architecture CENG331 - Computer Organization Murat Manguoglu Adapted from slides of the textbook: http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/ Outline Background Instruction
Computer Architecture I: Outline and Instruction Set Architecture CENG331 - Computer Organization Murat Manguoglu Adapted from slides of the textbook: http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/ Outline Background Instruction
cmovxx ra, rb 2 fn ra rb irmovq V, rb 3 0 F rb V rmmovq ra, D(rB) 4 0 ra rb mrmovq D(rB), ra 5 0 ra rb OPq ra, rb 6 fn ra rb jxx Dest 7 fn Dest
 Instruction Set Architecture Computer Architecture: Instruction Set Architecture CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization Lecture #16, February 24th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Based
Instruction Set Architecture Computer Architecture: Instruction Set Architecture CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization Lecture #16, February 24th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Based
CS 3330 Final Exam Spring 2016 Computing ID:
 S 3330 Spring 2016 Final xam Variant O page 1 of 10 mail I: S 3330 Final xam Spring 2016 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly:
S 3330 Spring 2016 Final xam Variant O page 1 of 10 mail I: S 3330 Final xam Spring 2016 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly:
CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018
 CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018 Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your left: Name of person to your right: Signature indicating:
CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018 Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your left: Name of person to your right: Signature indicating:
x86 Programming II CSE 351 Winter
 x86 Programming II CSE 351 Winter 2017 http://xkcd.com/1652/ Administrivia 2 Address Computation Instruction v leaq src, dst lea stands for load effective address src is address expression (any of the
x86 Programming II CSE 351 Winter 2017 http://xkcd.com/1652/ Administrivia 2 Address Computation Instruction v leaq src, dst lea stands for load effective address src is address expression (any of the
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: October 11, 2017 at 17:42 CS429 Slideset 6: 1 Topics of this Slideset
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: October 11, 2017 at 17:42 CS429 Slideset 6: 1 Topics of this Slideset
Instruc(on Set Architecture. Computer Architecture Instruc(on Set Architecture Y86. Y86-64 Processor State. Assembly Programmer s View
 Instruc(on Set Architecture Computer Architecture Instruc(on Set Architecture Y86 CSCI 2021: Machine Architecture and Organiza(on Pen- Chung Yew Department Computer Science and Engineering University of
Instruc(on Set Architecture Computer Architecture Instruc(on Set Architecture Y86 CSCI 2021: Machine Architecture and Organiza(on Pen- Chung Yew Department Computer Science and Engineering University of
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11
 CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 3 is due March 2, midnight Announcement Programming
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 3 is due March 2, midnight Announcement Programming
Topics of this Slideset. CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture. Instruction Set Architecture. Why Y86? Instruction Set Architecture
 Topics of this Slideset CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Intro to Assembly language Programmer visible state Y86
Topics of this Slideset CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Intro to Assembly language Programmer visible state Y86
x86 64 Programming II
 x86 64 Programming II CSE 351 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Akshat Aggarwal An Wang Andrew Hu Brian Dai Britt Henderson James Shin Kevin Bi Kory Watson Riley Germundson Sophie
x86 64 Programming II CSE 351 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Akshat Aggarwal An Wang Andrew Hu Brian Dai Britt Henderson James Shin Kevin Bi Kory Watson Riley Germundson Sophie
x86-64 Programming II
 x86-64 Programming II CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/409/ Administrative Homework
x86-64 Programming II CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/409/ Administrative Homework
CS 3330: SEQ part September 2016
 1 CS 3330: SEQ part 2 15 September 2016 Recall: Timing 2 compute new values between rising edges compute compute compute compute clock signal registers, memories change at rising edges next value register
1 CS 3330: SEQ part 2 15 September 2016 Recall: Timing 2 compute new values between rising edges compute compute compute compute clock signal registers, memories change at rising edges next value register
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions
 CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate
Machine-Level Programming (2)
 Machine-Level Programming (2) Yanqiao ZHU Introduction to Computer Systems Project Future (Fall 2017) Google Camp, Tongji University Outline Control Condition Codes Conditional Branches and Conditional
Machine-Level Programming (2) Yanqiao ZHU Introduction to Computer Systems Project Future (Fall 2017) Google Camp, Tongji University Outline Control Condition Codes Conditional Branches and Conditional
CS 107. Lecture 13: Assembly Part III. Friday, November 10, Stack "bottom".. Earlier Frames. Frame for calling function P. Increasing address
 CS 107 Stack "bottom" Earlier Frames Lecture 13: Assembly Part III Argument n Friday, November 10, 2017 Computer Systems Increasing address Argument 7 Frame for calling function P Fall 2017 Stanford University
CS 107 Stack "bottom" Earlier Frames Lecture 13: Assembly Part III Argument n Friday, November 10, 2017 Computer Systems Increasing address Argument 7 Frame for calling function P Fall 2017 Stanford University
Areas for growth: I love feedback
 Assembly part 2 1 Areas for growth: I love feedback Speed, I will go slower. Clarity. I will take time to explain everything on the slides. Feedback. I give more Kahoot questions and explain each answer.
Assembly part 2 1 Areas for growth: I love feedback Speed, I will go slower. Clarity. I will take time to explain everything on the slides. Feedback. I give more Kahoot questions and explain each answer.
L09: Assembly Programming III. Assembly Programming III. CSE 351 Spring Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia. Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Assembly Programming III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis
Assembly Programming III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis
Assembly Programming III
 Assembly Programming III CSE 410 Winter 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Kathryn Chan, Kevin Bi, Ryan Wong, Waylon Huang, Xinyu Sui Facebook Stories puts a Snapchat clone above the News
Assembly Programming III CSE 410 Winter 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Kathryn Chan, Kevin Bi, Ryan Wong, Waylon Huang, Xinyu Sui Facebook Stories puts a Snapchat clone above the News
CS3330 Exam 1 Spring Name: CS3330 Spring 2015 Exam 1 Page 1 of 6 ID: KEY
 S3330 Spring 2015 xam 1 Page 1 of 6 mail I: KY S3330 xam 1 Spring 2015 Name: irections: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Write clearly: if we are unsure what you
S3330 Spring 2015 xam 1 Page 1 of 6 mail I: KY S3330 xam 1 Spring 2015 Name: irections: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Write clearly: if we are unsure what you
last time Assembly part 2 / C part 1 condition codes reminder: quiz
 last time Assembly part 2 / C part 1 linking extras: different kinds of relocations addresses versus offset to addresses dynamic linking (briefly) AT&T syntax destination last O(B, I, S) B + I S + O jmp
last time Assembly part 2 / C part 1 linking extras: different kinds of relocations addresses versus offset to addresses dynamic linking (briefly) AT&T syntax destination last O(B, I, S) B + I S + O jmp
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2017
 CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2017 February 08, 2017 Please read through the entire examination first, and make sure you write your name and NetID on all pages! We designed this exam so that it can be completed
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2017 February 08, 2017 Please read through the entire examination first, and make sure you write your name and NetID on all pages! We designed this exam so that it can be completed
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: February 26, 2018 at 12:02 CS429 Slideset 8: 1 Controlling Program
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: February 26, 2018 at 12:02 CS429 Slideset 8: 1 Controlling Program
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 6
 CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 6 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 2 is out Announcement Programming Assignment
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 6 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 2 is out Announcement Programming Assignment
Question Points Score Total: 100
 Computer Science 2021 Spring 2016 Midterm Exam 1 February 29th, 2016 Time Limit: 50 minutes, 3:35pm-4:25pm This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Once we tell you to start,
Computer Science 2021 Spring 2016 Midterm Exam 1 February 29th, 2016 Time Limit: 50 minutes, 3:35pm-4:25pm This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Once we tell you to start,
x64 Cheat Sheet Fall 2014
 CS 33 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner x64 Cheat Sheet Fall 2014 1 x64 Registers x64 assembly code uses sixteen 64-bit registers. Additionally, the lower bytes of some of these registers may be accessed
CS 33 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner x64 Cheat Sheet Fall 2014 1 x64 Registers x64 assembly code uses sixteen 64-bit registers. Additionally, the lower bytes of some of these registers may be accessed
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015
 CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate will prove
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate will prove
CSE 351 Midterm Exam
 University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse February 5, 2018 CSE 351 Midterm Exam Last Name: First Name: SOLUTIONS UW Student ID Number: UW NetID (username):
University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse February 5, 2018 CSE 351 Midterm Exam Last Name: First Name: SOLUTIONS UW Student ID Number: UW NetID (username):
last time Exam Review on the homework on office hour locations hardware description language programming language that compiles to circuits
 last time Exam Review hardware description language programming language that compiles to circuits stages as conceptual division not the order things happen easier to figure out wiring stage-by-stage?
last time Exam Review hardware description language programming language that compiles to circuits stages as conceptual division not the order things happen easier to figure out wiring stage-by-stage?
Machine Language CS 3330 Samira Khan
 Machine Language CS 3330 Samira Khan University of Virginia Feb 2, 2017 AGENDA Logistics Review of Abstractions Machine Language 2 Logistics Feedback Not clear Hard to hear Use microphone Good feedback
Machine Language CS 3330 Samira Khan University of Virginia Feb 2, 2017 AGENDA Logistics Review of Abstractions Machine Language 2 Logistics Feedback Not clear Hard to hear Use microphone Good feedback
CSE 351 Midterm Exam Spring 2016 May 2, 2015
 Name: CSE 351 Midterm Exam Spring 2016 May 2, 2015 UWNetID: Solution Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes (no calculators, no mobile phones, no laptops,
Name: CSE 351 Midterm Exam Spring 2016 May 2, 2015 UWNetID: Solution Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes (no calculators, no mobile phones, no laptops,
Lecture 3 CIS 341: COMPILERS
 Lecture 3 CIS 341: COMPILERS HW01: Hellocaml! Announcements is due tomorrow tonight at 11:59:59pm. HW02: X86lite Will be available soon look for an announcement on Piazza Pair-programming project Simulator
Lecture 3 CIS 341: COMPILERS HW01: Hellocaml! Announcements is due tomorrow tonight at 11:59:59pm. HW02: X86lite Will be available soon look for an announcement on Piazza Pair-programming project Simulator
Machine Level Programming: Control
 Machine Level Programming: Control Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed
Machine Level Programming: Control Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed
Do not turn the page until 5:10.
 University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2018-10-29 Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your Left Right All work is my own. I
University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2018-10-29 Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your Left Right All work is my own. I
Control flow (1) Condition codes Conditional and unconditional jumps Loops Conditional moves Switch statements
 Control flow (1) Condition codes Conditional and unconditional jumps Loops Conditional moves Switch statements 1 Conditionals and Control Flow Two key pieces 1. Comparisons and tests: check conditions
Control flow (1) Condition codes Conditional and unconditional jumps Loops Conditional moves Switch statements 1 Conditionals and Control Flow Two key pieces 1. Comparisons and tests: check conditions
Machine-Level Programming II: Control
 Machine-Level Programming II: Control CSE 238/2038/2138: Systems Programming Instructor: Fatma CORUT ERGİN Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides 1 Today Control: Condition codes Conditional
Machine-Level Programming II: Control CSE 238/2038/2138: Systems Programming Instructor: Fatma CORUT ERGİN Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides 1 Today Control: Condition codes Conditional
Machine-Level Programming II: Control
 Mellon Machine-Level Programming II: Control CS140 Computer Organization and Assembly Slides Courtesy of: Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron 1 First https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ivuu8jobb1q 2
Mellon Machine-Level Programming II: Control CS140 Computer Organization and Assembly Slides Courtesy of: Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron 1 First https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ivuu8jobb1q 2
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. x86-64 Control Flow
 CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor x86-64 Control Flow Topics Condition codes Jumps Conditional moves Jump tables Motivation We cannot translate the following C function to assembly, using only data
CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor x86-64 Control Flow Topics Condition codes Jumps Conditional moves Jump tables Motivation We cannot translate the following C function to assembly, using only data
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: February 28, 2018 at 06:32 CS429 Slideset 9: 1 Mechanisms in Procedures
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: February 28, 2018 at 06:32 CS429 Slideset 9: 1 Mechanisms in Procedures
CSCI 2021: x86-64 Control Flow
 CSCI 2021: x86-64 Control Flow Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Mon Mar 11 11:54:06 CDT 2019 1 Logistics Reading Bryant/O Hallaron Ch 3.6: Control Flow Ch 3.7: Procedure calls Goals Jumps and Control flow
CSCI 2021: x86-64 Control Flow Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Mon Mar 11 11:54:06 CDT 2019 1 Logistics Reading Bryant/O Hallaron Ch 3.6: Control Flow Ch 3.7: Procedure calls Goals Jumps and Control flow
Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition. Carnegie Mellon
 Carnegie Mellon Machine-Level Programming III: Procedures 15-213/18-213/14-513/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, September 18, 2018 Today Procedures Mechanisms Stack Structure Calling
Carnegie Mellon Machine-Level Programming III: Procedures 15-213/18-213/14-513/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, September 18, 2018 Today Procedures Mechanisms Stack Structure Calling
Assembly III: Procedures. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Assembly III: Procedures Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control To beginning of procedure code
Assembly III: Procedures Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control To beginning of procedure code
Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) Bits and bitwise operations. Outline. Unsigned and signed integers. Floating point numbers. Number representation
 Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) CSci 2021: Review Lecture 1 Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Number representation Bits and bitwise operators Unsigned and signed
Midterm 1 topics (in one slide) CSci 2021: Review Lecture 1 Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Number representation Bits and bitwise operators Unsigned and signed
Machine- Level Representa2on: Procedure
 Machine- Level Representa2on: Procedure CSCI 2021: Machine Architecture and Organiza2on Pen- Chung Yew Department Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota With Slides from Bryant, O Hallaron
Machine- Level Representa2on: Procedure CSCI 2021: Machine Architecture and Organiza2on Pen- Chung Yew Department Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota With Slides from Bryant, O Hallaron
Assembly II: Control Flow. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Assembly II: Control Flow Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Processor State (x86-64) RAX 63 31 EAX 0 RBX EBX RCX RDX ECX EDX General-purpose
Assembly II: Control Flow Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Processor State (x86-64) RAX 63 31 EAX 0 RBX EBX RCX RDX ECX EDX General-purpose
Machine-Level Programming III: Procedures
 Machine-Level Programming III: Procedures CSE 238/2038/2138: Systems Programming Instructor: Fatma CORUT ERGİN Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control
Machine-Level Programming III: Procedures CSE 238/2038/2138: Systems Programming Instructor: Fatma CORUT ERGİN Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control
Unit 8: Programming Languages CS 101, Fall 2018
 Unit 8: Programming Languages CS 101, Fall 2018 Learning Objectives After completing this unit, you should be able to: Explain the difference between an assembler, compiler, and interpreter. Name and describe
Unit 8: Programming Languages CS 101, Fall 2018 Learning Objectives After completing this unit, you should be able to: Explain the difference between an assembler, compiler, and interpreter. Name and describe
Assembly Language: Function Calls
 Assembly Language: Function Calls 1 Goals of this Lecture Help you learn: Function call problems x86-64 solutions Pertinent instructions and conventions 2 Function Call Problems (1) Calling and returning
Assembly Language: Function Calls 1 Goals of this Lecture Help you learn: Function call problems x86-64 solutions Pertinent instructions and conventions 2 Function Call Problems (1) Calling and returning
Changelog. Assembly (part 1) logistics note: lab due times. last time: C hodgepodge
 Changelog Assembly (part 1) Corrections made in this version not seen in first lecture: 31 August 2017: slide 34: split out from previous slide; clarify zero/positive/negative 31 August 2017: slide 26:
Changelog Assembly (part 1) Corrections made in this version not seen in first lecture: 31 August 2017: slide 34: split out from previous slide; clarify zero/positive/negative 31 August 2017: slide 26:
Assembly II: Control Flow
 Assembly II: Control Flow Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
Assembly II: Control Flow Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
Corrections made in this version not seen in first lecture:
 Assembly (part 1) 1 Changelog 1 Corrections made in this version not seen in first lecture: 31 August 2017: slide 34: split out from previous slide; clarify zero/positive/negative 31 August 2017: slide
Assembly (part 1) 1 Changelog 1 Corrections made in this version not seen in first lecture: 31 August 2017: slide 34: split out from previous slide; clarify zero/positive/negative 31 August 2017: slide
MACHINE LEVEL PROGRAMMING 1: BASICS
 MACHINE LEVEL PROGRAMMING 1: BASICS CS 045 Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. Donald J. Patterson Adapted from Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition
MACHINE LEVEL PROGRAMMING 1: BASICS CS 045 Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. Donald J. Patterson Adapted from Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition
Machine-level Programs Procedure
 Computer Systems Machine-level Programs Procedure Han, Hwansoo Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control To beginning of procedure code Back to return point Passing data Procedure arguments Return value
Computer Systems Machine-level Programs Procedure Han, Hwansoo Mechanisms in Procedures Passing control To beginning of procedure code Back to return point Passing data Procedure arguments Return value
Do not turn the page until 5:10.
 University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2017-10-30 Last Name: First Name: Perfect Perry Student ID Number: 1234567 Name of person to your Left Right
University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2017-10-30 Last Name: First Name: Perfect Perry Student ID Number: 1234567 Name of person to your Left Right
Princeton University Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems. Assembly Language: Function Calls
 Princeton University Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems Assembly Language: Function Calls 1 Goals of this Lecture Help you learn: Function call problems x86-64 solutions Pertinent
Princeton University Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems Assembly Language: Function Calls 1 Goals of this Lecture Help you learn: Function call problems x86-64 solutions Pertinent
CS367. Program Control
 CS367 Program Control outline program control condition codes branching looping conditional moves switches (special case of branching) Condition Codes Processor State (x86-64, Partial) Info about currently
CS367 Program Control outline program control condition codes branching looping conditional moves switches (special case of branching) Condition Codes Processor State (x86-64, Partial) Info about currently
CS 261 Fall Machine and Assembly Code. Data Movement and Arithmetic. Mike Lam, Professor
 CS 261 Fall 2018 0000000100000f50 55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 10 48 8d 3d 3b 00 00 00 c7 0000000100000f60 45 fc 00 00 00 00 b0 00 e8 0d 00 00 00 31 c9 89 0000000100000f70 45 f8 89 c8 48 83 c4 10 5d c3 Mike Lam,
CS 261 Fall 2018 0000000100000f50 55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 10 48 8d 3d 3b 00 00 00 c7 0000000100000f60 45 fc 00 00 00 00 b0 00 e8 0d 00 00 00 31 c9 89 0000000100000f70 45 f8 89 c8 48 83 c4 10 5d c3 Mike Lam,
bitwise (finish) / SEQ part 1
 bitwise (finish) / SEQ part 1 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 14 September 2017: slide 16-17: the x86 arithmetic shift instruction is sar, not sra last time 2 bitwise
bitwise (finish) / SEQ part 1 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 14 September 2017: slide 16-17: the x86 arithmetic shift instruction is sar, not sra last time 2 bitwise
CSE 401/M501 Compilers
 CSE 401/M501 Compilers x86-64 Lite for Compiler Writers A quick (a) introduction or (b) review [pick one] Hal Perkins Autumn 2018 UW CSE 401/M501 Autumn 2018 J-1 Administrivia HW3 due tonight At most 1
CSE 401/M501 Compilers x86-64 Lite for Compiler Writers A quick (a) introduction or (b) review [pick one] Hal Perkins Autumn 2018 UW CSE 401/M501 Autumn 2018 J-1 Administrivia HW3 due tonight At most 1
CS3330 Exam 3 Spring 2015
 S3330 Spring 2015 xam 3 variant Page 1 of 12 S3330 xam 3 Spring 2015 Name: ompi: Letters: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Single-select: ll multiple-select questions
S3330 Spring 2015 xam 3 variant Page 1 of 12 S3330 xam 3 Spring 2015 Name: ompi: Letters: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Single-select: ll multiple-select questions
Question Points Score Total: 100
 CSci 2021 Section 010 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam 2 (solutions) November 16th, 2018 Time Limit: 50 minutes, 3:35pm-4:25pm This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 4 questions. Once we tell
CSci 2021 Section 010 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam 2 (solutions) November 16th, 2018 Time Limit: 50 minutes, 3:35pm-4:25pm This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 4 questions. Once we tell
L08: Assembly Programming II. Assembly Programming II. CSE 351 Spring Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia. Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Assembly Programming II CSE 351 Spring 2017 Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis
Assembly Programming II CSE 351 Spring 2017 Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis
Procedures and the Call Stack
 Procedures and the Call Stack Topics Procedures Call stack Procedure/stack instructions Calling conventions Register-saving conventions Why Procedures? Why functions? Why methods? int contains_char(char*
Procedures and the Call Stack Topics Procedures Call stack Procedure/stack instructions Calling conventions Register-saving conventions Why Procedures? Why functions? Why methods? int contains_char(char*
Do not turn the page until 5:10.
 University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2017-10-30 Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your Left Right All work is my own. I
University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2017-10-30 Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your Left Right All work is my own. I
Machine Program: Procedure. Zhaoguo Wang
 Machine Program: Procedure Zhaoguo Wang Requirements of procedure calls? P() { y = Q(x); y++; 1. Passing control int Q(int i) { int t, z; return z; Requirements of procedure calls? P() { y = Q(x); y++;
Machine Program: Procedure Zhaoguo Wang Requirements of procedure calls? P() { y = Q(x); y++; 1. Passing control int Q(int i) { int t, z; return z; Requirements of procedure calls? P() { y = Q(x); y++;
Foundations of Computer Systems
 18-600 Foundations of Computer Systems Lecture 7: Processor Architecture & Design John P. Shen & Gregory Kesden September 20, 2017 Lecture #7 Processor Architecture & Design Lecture #8 Pipelined Processor
18-600 Foundations of Computer Systems Lecture 7: Processor Architecture & Design John P. Shen & Gregory Kesden September 20, 2017 Lecture #7 Processor Architecture & Design Lecture #8 Pipelined Processor
Do not turn the page until 5:10.
 University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2018-10-29 Last Name: First Name: Perfect Perry Student ID Number: 1234567 Name of person to your Left Right
University of Washington Computer Science & Engineering Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia 2018-10-29 Last Name: First Name: Perfect Perry Student ID Number: 1234567 Name of person to your Left Right
Brief Assembly Refresher
 Brief Assembly Refresher 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 23 Jan 2018: if-to-assembly if (...) goto needed b < 42 23 Jan 2018: caller/callee-saved: correct comment
Brief Assembly Refresher 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 23 Jan 2018: if-to-assembly if (...) goto needed b < 42 23 Jan 2018: caller/callee-saved: correct comment
CSE351 Autumn 2014 Midterm Exam (29 October 2014)
 CSE351 Autumn 2014 Midterm Exam (29 October 2014) Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate will prove
CSE351 Autumn 2014 Midterm Exam (29 October 2014) Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate will prove
SEQ part 3 / HCLRS 1
 SEQ part 3 / HCLRS 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 September 2017: data memory value MUX input for call is PC + 10, not PC 21 September 2017: slide 23: add input
SEQ part 3 / HCLRS 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 September 2017: data memory value MUX input for call is PC + 10, not PC 21 September 2017: slide 23: add input
CSE2421 FINAL EXAM SPRING Name KEY. Instructions: Signature
 CSE2421 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2013 Name KEY Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes, closed-neighbor exam. Only a writing utensil is needed for this exam. No calculators allowed. If you need to go
CSE2421 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2013 Name KEY Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes, closed-neighbor exam. Only a writing utensil is needed for this exam. No calculators allowed. If you need to go
Where We Are. Optimizations. Assembly code. generation. Lexical, Syntax, and Semantic Analysis IR Generation. Low-level IR code.
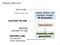 Where We Are Source code if (b == 0) a = b; Low-level IR code Optimized Low-level IR code Assembly code cmp $0,%rcx cmovz %rax,%rdx Lexical, Syntax, and Semantic Analysis IR Generation Optimizations Assembly
Where We Are Source code if (b == 0) a = b; Low-level IR code Optimized Low-level IR code Assembly code cmp $0,%rcx cmovz %rax,%rdx Lexical, Syntax, and Semantic Analysis IR Generation Optimizations Assembly
15-213/18-243, Fall 2010 Exam 1 - Version A
 Andrew login ID: Full Name: Section: 15-213/18-243, Fall 2010 Exam 1 - Version A Tuesday, September 28, 2010 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your Andrew login
Andrew login ID: Full Name: Section: 15-213/18-243, Fall 2010 Exam 1 - Version A Tuesday, September 28, 2010 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your Andrew login
Carnegie Mellon. Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition
 1 Machine-Level Programming II: Control 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 6 th Lecture, Sept. 13, 2018 2 Today Control: Condition codes Conditional branches Loops Switch Statements 3 Recall: ISA
1 Machine-Level Programming II: Control 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 6 th Lecture, Sept. 13, 2018 2 Today Control: Condition codes Conditional branches Loops Switch Statements 3 Recall: ISA
Machine Level Programming: Basics
 Machine Level Programming: Basics Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 2 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed
Machine Level Programming: Basics Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 2 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed
Changelog. Brief Assembly Refresher. a logistics note. last time
 Changelog Brief Assembly Refresher Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 23 Jan 2018: if-to-assembly if (...) goto needed b < 42 23 Jan 2018: caller/callee-saved: correct comment about
Changelog Brief Assembly Refresher Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 23 Jan 2018: if-to-assembly if (...) goto needed b < 42 23 Jan 2018: caller/callee-saved: correct comment about
Machine/Assembler Language Putting It All Together
 COMP 40: Machine Structure and Assembly Language Programming Fall 2015 Machine/Assembler Language Putting It All Together Noah Mendelsohn Tufts University Email: noah@cs.tufts.edu Web: http://www.cs.tufts.edu/~noah
COMP 40: Machine Structure and Assembly Language Programming Fall 2015 Machine/Assembler Language Putting It All Together Noah Mendelsohn Tufts University Email: noah@cs.tufts.edu Web: http://www.cs.tufts.edu/~noah
How Software Executes
 How Software Executes CS-576 Systems Security Instructor: Georgios Portokalidis Overview Introduction Anatomy of a program Basic assembly Anatomy of function calls (and returns) Memory Safety Intel x86
How Software Executes CS-576 Systems Security Instructor: Georgios Portokalidis Overview Introduction Anatomy of a program Basic assembly Anatomy of function calls (and returns) Memory Safety Intel x86
1 Number Representation(10 points)
 Name: Sp15 Midterm Q1 1 Number Representation(10 points) 1 NUMBER REPRESENTATION(10 POINTS) Let x=0xe and y=0x7 be integers stored on a machine with a word size of 4bits. Show your work with the following
Name: Sp15 Midterm Q1 1 Number Representation(10 points) 1 NUMBER REPRESENTATION(10 POINTS) Let x=0xe and y=0x7 be integers stored on a machine with a word size of 4bits. Show your work with the following
CS201- Lecture 7 IA32 Data Access and Operations Part II
 CS201- Lecture 7 IA32 Data Access and Operations Part II RAOUL RIVAS PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY Announcements 2 Address Computation Examples %rdx %rcx 0xf000 0x0100 movq 8(%rdx),%rax movq (%rdx,%rcx),%rax
CS201- Lecture 7 IA32 Data Access and Operations Part II RAOUL RIVAS PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY Announcements 2 Address Computation Examples %rdx %rcx 0xf000 0x0100 movq 8(%rdx),%rax movq (%rdx,%rcx),%rax
Stack Frame Components. Using the Stack (4) Stack Structure. Updated Stack Structure. Caller Frame Arguments 7+ Return Addr Old %rbp
 Stack Frame Components Frame pointer %rbp Stack pointer Caller Frame rguments 7+ Return ddr Old %rbp Saved Registers + Local Variables rgument Build 1 Using the Stack (4) Stack Structure long call_incr()
Stack Frame Components Frame pointer %rbp Stack pointer Caller Frame rguments 7+ Return ddr Old %rbp Saved Registers + Local Variables rgument Build 1 Using the Stack (4) Stack Structure long call_incr()
Instructions and Instruction Set Architecture
 Chapter 2 Instructions and Instruction Set Architecture In this lecture, we study computer instructions and instruction set architecture by using assembly language programming. We will study x86-64 architecture
Chapter 2 Instructions and Instruction Set Architecture In this lecture, we study computer instructions and instruction set architecture by using assembly language programming. We will study x86-64 architecture
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. x86-64 Control Flow
 CS 261 Fall 2016 Mike Lam, Professor x86-64 Control Flow Topics Condition codes Jumps Conditional moves Jump tables Motivation Can we translate the following C function to assembly, using only data movement
CS 261 Fall 2016 Mike Lam, Professor x86-64 Control Flow Topics Condition codes Jumps Conditional moves Jump tables Motivation Can we translate the following C function to assembly, using only data movement
x86 Programming I CSE 351 Winter
 x86 Programming I CSE 351 Winter 2017 http://xkcd.com/409/ Administrivia Lab 2 released! Da bomb! Go to section! No Luis OH Later this week 2 Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals
x86 Programming I CSE 351 Winter 2017 http://xkcd.com/409/ Administrivia Lab 2 released! Da bomb! Go to section! No Luis OH Later this week 2 Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals
Assembly Language II: Addressing Modes & Control Flow
 Assembly Language II: Addressing Modes & Control Flow Learning Objectives Interpret different modes of addressing in x86 assembly Move data seamlessly between registers and memory Map data structures in
Assembly Language II: Addressing Modes & Control Flow Learning Objectives Interpret different modes of addressing in x86 assembly Move data seamlessly between registers and memory Map data structures in
x86 64 Programming I CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia
 x86 64 Programming I CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan Administrivia
x86 64 Programming I CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan Administrivia
x86-64 Programming III & The Stack
 x86-64 Programming III & The Stack CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/1652/ Administrative
x86-64 Programming III & The Stack CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/1652/ Administrative
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2017 Lecture 12
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 12 CS24 MIDTERM Midterm format: 6 hour overall time limit, multiple sittings (If you are focused on midterm, clock should be running.) Open book
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 12 CS24 MIDTERM Midterm format: 6 hour overall time limit, multiple sittings (If you are focused on midterm, clock should be running.) Open book
Changelog. Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 13 Feb 2018: add slide on constants and width
 HCL 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 13 Feb 2018: add slide on constants and width simple ISA 4: mov-to-register 2 irmovq $constant, %ryy rrmovq %rxx, %ryy mrmovq 10(%rXX),
HCL 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 13 Feb 2018: add slide on constants and width simple ISA 4: mov-to-register 2 irmovq $constant, %ryy rrmovq %rxx, %ryy mrmovq 10(%rXX),
The Stack & Procedures
 The Stack & Procedures CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/648/
The Stack & Procedures CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/648/
%r8 %r8d. %r9 %r9d. %r10 %r10d. %r11 %r11d. %r12 %r12d. %r13 %r13d. %r14 %r14d %rbp. %r15 %r15d. Sean Barker
 Procedure Call Registers Return %rax %eax %r8 %r8d Arg 5 %rbx %ebx %r9 %r9d Arg 6 Arg 4 %rcx %ecx %r10 %r10d Arg 3 %rdx %edx %r11 %r11d Arg 2 %rsi %esi %r12 %r12d Arg 1 %rdi %edi %r13 %r13d ptr %esp %r14
Procedure Call Registers Return %rax %eax %r8 %r8d Arg 5 %rbx %ebx %r9 %r9d Arg 6 Arg 4 %rcx %ecx %r10 %r10d Arg 3 %rdx %edx %r11 %r11d Arg 2 %rsi %esi %r12 %r12d Arg 1 %rdi %edi %r13 %r13d ptr %esp %r14
CS , Fall 2007 Exam 1
 Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2007 Exam 1 Wednesday October 17, 2007 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the
Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2007 Exam 1 Wednesday October 17, 2007 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CPSC 261: MIDTERM 1 February 14, 2017
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CPSC 261: MIDTERM 1 February 14, 2017 Last Name: First Name: Signature: UBC Student #: Important notes about this examination 1. You have 70 minutes to write the 6 questions
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CPSC 261: MIDTERM 1 February 14, 2017 Last Name: First Name: Signature: UBC Student #: Important notes about this examination 1. You have 70 minutes to write the 6 questions
Compiling C Programs Into X86-64 Assembly Programs
 CSE 2421: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Compiling C Programs Into X86-64 Assembly Programs Part B: If Else, Loops, Recursion & Switch Presentation L Read/Study: Bryant 3.6 Gojko
CSE 2421: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Compiling C Programs Into X86-64 Assembly Programs Part B: If Else, Loops, Recursion & Switch Presentation L Read/Study: Bryant 3.6 Gojko
Test I Solutions MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Fall Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer cience MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.035 Fall 2017 Test I olutions Mean 83.63 Median 86 td. dev 12.03 1 I Regular Expressions and Finite-tate Automata
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer cience MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.035 Fall 2017 Test I olutions Mean 83.63 Median 86 td. dev 12.03 1 I Regular Expressions and Finite-tate Automata
