Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
|
|
|
- Annice Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Spring 2003 Yale Patt, Instructor Hyesoon Kim, Onur Mutlu, Moinuddin Qureshi, Santhosh Srinath, TAs Exam 2, April 14, 2003 Name: Problem 1 (30 points): Problem 2 (20 points): Problem 3 (20 points): Problem 4 (15 points): Problem 5 (15 points): tal (100 points): Note: Please be sure that your answers to all questions (and all supporting work that is required) are contained in the space provided. Note: Please be sure your name is recorded on each sheet of the exam. GOOD LUCK!
2 Problem 1 (30 points): Part a (5 points): A bus has Data, Address, and Control lines. MSYN and SSYN are has these lines are (circle one) synch/asynch. Why is that the case? lines. A bus that Part b (5 points): We wish to perform residue arithmetic using moduli 4, 7, 9. How many numbers can we represent uniquely in the residue domain? What is the value of the decimal number 249 in the residue domain? Part c (5 points): Single decimal digit, saturating arithmetic = 3-5 = Part d (5 points): Pipelining increases the performance of a processor if the pipeline can be kept full with useful instructions. Two reasons that often prevent the pipeline from staying full with useful instructions are (in two words each): 2
3 Problem 1 continued: Part e (5 points): for (i=1; i 500; i++) A[i] = (B[i] + A[i-1])/4; Is the loop vectorizable? Circle one: yes/no. Explain why/why not (10 words should be enough). Part f (5 points): We wish to represent the decimal value 27 with an 8-bit floating point number, having a sign bit, 4 bits of excess-7 exponent and three bits of fraction. The exact representation is which will not fit in the available bits. So, we do some rounding. In the IEEE Floating Point standard, there are four rounding modes. Assuming the above format is legitimate, what exact decimal value would I get using the unbiased nearest rounding mode? Show the representation. Decimal Value 8 bit representation 3
4 Problem 2 (20 points): Part a. A five instruction sequence executes according to masulo s algorithm. Each instruction is of the form ADD D,S1,S2 or MUL D,S1,S2. ADDs are pipelined and take 9 cycles (F-D-E1-E2-E3-E4-E5-E6-WB). MULs are also pipelined and take 11 cycles (two extra execute stages). The microengine must wait until a result is in a register before it sources it (reads it as a source operand). The register file before and after the sequence are shown below (tags for After are ignored). Before After V tag value V tag value 0 1 z z z z z z z z Complete the five instruction sequence in program order in the space below. Note that we have helped you by giving you the opcode and two source operand addresses for instruction 4. (The program sequence is unique.) MUL, 6, 6 Part b. In cycle 1 instruction 1 is fetched. In cycle 2, instruction 1 is decoded and instruction 2 is fetched. In cycle 3, instruction 1 starts execution, instruction 2 is decoded, and instruction 3 is fetched. Assume the reservation stations are all initially empty. Put each instruction into the next available reservation station. For example, the first ADD goes into a. The first MUL goes into x. Instructions remain in the reservation stations until they are completed.show the state of the reservation stations at the end of cycle 8. Note: make it easier for the grader, when allocating source registers to reservation stations, please always have the higher numbered register be assigned to S2. a b c x y z + X 4
5 Problem 2 continued: Part c. Show the state of the egister Alias Table (V, tag, Value) at the end of cycle V tag value 5
6 Problem 3 (20 points): A processor with 32 MB byte-addressable physical memory has a virtually-indexed, physically-tagged write-back cache. The cache is 4-way set associative and 2 bits are used for each block to implement a victim/next-victim pseudo-lu replacement policy. The size of the tag store of the cache is 9216 bits. The cache can store 512 blocks of 128 bytes of data. Based on this information, answer the following questions: Part a. How many frames are there in physical memory? Part b. What is the page size? Part c. How many bits of the cache index come from the virtual page number? Part d. What is the size of the data store in bits? 6
7 Problem 4 (15 points): Suppose we have a 13-bit floating point format in which 54.5 is represented as Part a. What is the precision of this format? Part b. What is the range of normalized positive numbers? Part c. What is the smallest positive subnormal number representable in this format? 7
8 Problem 5 (15 points): In Lab Assignment 3 we augmented the datapath, the state machine and the microsequencer in order to handle interrupts, page faults and access control violations. In this problem, we are interested in extending your machine to take an exception in case a TAP instruction produces an illegal starting address. If the address obtained from the trap vector table is odd or it maps to page 0 (address range [0:511]), your machine should take an exception. We will call this exception an illegal service routine address exception and assign it an exception vector 4. Shown below is a typical state machine from Lab 3. It has states for the TI instruction, the TAP instruction and the micro subroutine for exception handling. MA< PC PC< PC+1 MA< TI MD< M 35 I< MD BEN< I<11> N + I<10> Z + I<9> P [I[15:12]] micro subroutine for exceptions MD < PS PS[15] < 0 Saved_USP < 6 6 < Saved_SSP MD< M 38 PC< MD 39 MA, 6< MD< M 42 PS< MD TAP MA< LSHF(ZEXT(I[7:0]),1) MD< M 7< PC PC< MD MA, 6< 6 2 Write 41 MD < PC 2 MA, 6< < Write 50 MA< Vector Saved_SSP< 6 6< Saved_USP MD< M 54 PC< MD 8
9 Problem 5 continued: Part a. Specify the logic function to test an illegal service routine address. Part b. Modify the given state machine to test the illegal service routine address exception. Specify clearly the operations performed in each state. Show clearly how the control is transferred to the micro subroutine in case of an exception. Your solution should cause only such changes to the datapath as are absolutely necessary. You may not need to use all the states provided below. BEN < I[11]&N + I[10]&Z + I[9]&P [ I[15:12] ] TAP A B C D E F 49 9
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 460N Fall 2018 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Chirag Sakhuja, John MacKay, Aniket Deshmukh, Mohammad Behnia, TAs Final Exam
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 460N Fall 2018 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Chirag Sakhuja, John MacKay, Aniket Deshmukh, Mohammad Behnia, TAs Final Exam
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Spring 2003 Yale Patt, Instructor Hyesoon Kim, Onur Mutlu, Moinuddin Qureshi, Santhosh Srinath, TAs Exam 1,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Spring 2003 Yale Patt, Instructor Hyesoon Kim, Onur Mutlu, Moinuddin Qureshi, Santhosh Srinath, TAs Exam 1,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 60N, Fall 00 Yale Patt, Instructor Santhosh Srinath, Danny Lynch, TAs Exam, November 9, 00 Name: Problem (0 points):
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 60N, Fall 00 Yale Patt, Instructor Santhosh Srinath, Danny Lynch, TAs Exam, November 9, 00 Name: Problem (0 points):
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Fall 2005 Yale Patt, Instructor Aater Suleman, Linda Bigelow, Jose Joao, Veynu Narasiman, TAs Final Exam, December,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Fall 2005 Yale Patt, Instructor Aater Suleman, Linda Bigelow, Jose Joao, Veynu Narasiman, TAs Final Exam, December,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Fall 003 Yale Patt, Instructor Santhosh Srinath, Danny Lynch, TAs Exam 1, October 0, 003 Name: Problem 1 (0
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 360N, Fall 003 Yale Patt, Instructor Santhosh Srinath, Danny Lynch, TAs Exam 1, October 0, 003 Name: Problem 1 (0
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises II - Solutions
 ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises II - Solutions Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises II - Solutions Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 0N, Fall 005 Yale Patt, Instructor Aater Suleman, Linda Bigelow, Jose Joao, Veynu Narasiman, TAs Exam, November, 005
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 0N, Fall 005 Yale Patt, Instructor Aater Suleman, Linda Bigelow, Jose Joao, Veynu Narasiman, TAs Exam, November, 005
NAME: Problem Points Score. 7 (bonus) 15. Total
 Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 NAME: Problem Points Score 1 40
Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 NAME: Problem Points Score 1 40
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE N Spring 7 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Chirag Sakhuja, Sarbartha Banerjee, Jonathan Dahm, Arjun Teh, TAs Exam March, 7
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE N Spring 7 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Chirag Sakhuja, Sarbartha Banerjee, Jonathan Dahm, Arjun Teh, TAs Exam March, 7
1 Tomasulo s Algorithm
 Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L), Spring 2018 Optional HW 4: Out-of-Order Execution, Dataflow, Branch Prediction, VLIW, and Fine-Grained Multithreading uctor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Juan Gomez
Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L), Spring 2018 Optional HW 4: Out-of-Order Execution, Dataflow, Branch Prediction, VLIW, and Fine-Grained Multithreading uctor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Juan Gomez
Design of Digital Circuits ( L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017
 Name: Student ID: Final Examination Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017 Professors Onur Mutlu and Srdjan Capkun Problem 1 (70 Points): Problem 2 (50 Points): Problem 3 (40
Name: Student ID: Final Examination Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017 Professors Onur Mutlu and Srdjan Capkun Problem 1 (70 Points): Problem 2 (50 Points): Problem 3 (40
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 46N Fall Y. N. Patt, Instructor Siavash Zangeneh, Ali Fakhrzadehgan, Steven Flolid, Matthew Normyle TAs Exam 1 October
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 46N Fall Y. N. Patt, Instructor Siavash Zangeneh, Ali Fakhrzadehgan, Steven Flolid, Matthew Normyle TAs Exam 1 October
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I
 ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois
EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS. Midterm Exam. ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring Instructor: Onur Mutlu
 Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem Points
Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem Points
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 2011 Yale Patt, Instructor Faruk Guvenilir, Milad Hashemi, Jennifer Davis, Garrett Galow, Ben Lin, Taylor
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 2011 Yale Patt, Instructor Faruk Guvenilir, Milad Hashemi, Jennifer Davis, Garrett Galow, Ben Lin, Taylor
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I - SOLUTIONS
 ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I - SOLUTIONS Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu,
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Review Session Questions I - SOLUTIONS Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu,
SOLUTION. Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name:
 SOLUTION Notes: CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS 252 Graduate Computer Architecture Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: I am taking CS152 / CS252 This is a closed
SOLUTION Notes: CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS 252 Graduate Computer Architecture Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: I am taking CS152 / CS252 This is a closed
ECE 154A Introduction to. Fall 2012
 ECE 154A Introduction to Computer Architecture Fall 2012 Dmitri Strukov Lecture 10 Floating point review Pipelined design IEEE Floating Point Format single: 8 bits double: 11 bits single: 23 bits double:
ECE 154A Introduction to Computer Architecture Fall 2012 Dmitri Strukov Lecture 10 Floating point review Pipelined design IEEE Floating Point Format single: 8 bits double: 11 bits single: 23 bits double:
1 Tomasulo s Algorithm
 Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L), Spring 2018 Optional HW 4: Out-of-Order Execution, Dataflow, Branch Prediction, VLIW, and Fine-Grained Multithreading SOLUTIONS uctor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Juan
Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L), Spring 2018 Optional HW 4: Out-of-Order Execution, Dataflow, Branch Prediction, VLIW, and Fine-Grained Multithreading SOLUTIONS uctor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Juan
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 2011 Yale Patt, Instructor Faruk Guvenilir, Milad Hashemi, Jennifer Davis, Garrett Galow, Ben Lin, Taylor
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 2011 Yale Patt, Instructor Faruk Guvenilir, Milad Hashemi, Jennifer Davis, Garrett Galow, Ben Lin, Taylor
Sunday, April 25, 2010
 Sunday, April 25, 2010 BSNL TTA EXAM MICRO PROCESSER BSNL TTA EXAM MICRO PROCESSER 1. A 32-bit processor has (a) 32 registers (b) 32 I/O devices (c) 32 Mb of RAM (d) a 32-bit bus or 32-bit registers 2.
Sunday, April 25, 2010 BSNL TTA EXAM MICRO PROCESSER BSNL TTA EXAM MICRO PROCESSER 1. A 32-bit processor has (a) 32 registers (b) 32 I/O devices (c) 32 Mb of RAM (d) a 32-bit bus or 32-bit registers 2.
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
Fill in your name, section, and username. DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
 NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
15-740/ Computer Architecture, Fall 2011 Midterm Exam II
 15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture, Fall 2011 Midterm Exam II Instructor: Onur Mutlu Teaching Assistants: Justin Meza, Yoongu Kim Date: December 2, 2011 Name: Instructions: Problem I (69 points) : Problem
15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture, Fall 2011 Midterm Exam II Instructor: Onur Mutlu Teaching Assistants: Justin Meza, Yoongu Kim Date: December 2, 2011 Name: Instructions: Problem I (69 points) : Problem
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin. Problem 1 (12 points): Problem 2 (12 points):
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 382N, Spring 2012 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Veynu Narasiman and Carlos Villavieja, TAs Exam 1, March 28, 2012 Name :
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 382N, Spring 2012 Y. N. Patt, Instructor Veynu Narasiman and Carlos Villavieja, TAs Exam 1, March 28, 2012 Name :
DC57 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION JUNE 2013
 Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012
 CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 s Lecture 2: 1 Announcements HW7 will be posted tonight Lab sessions resume next week Lecture 2: 2 Course Content Binary numbers and logic gates
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 s Lecture 2: 1 Announcements HW7 will be posted tonight Lab sessions resume next week Lecture 2: 2 Course Content Binary numbers and logic gates
Introduction to C. Why C? Difference between Python and C C compiler stages Basic syntax in C
 Final Review CS304 Introduction to C Why C? Difference between Python and C C compiler stages Basic syntax in C Pointers What is a pointer? declaration, &, dereference... Pointer & dynamic memory allocation
Final Review CS304 Introduction to C Why C? Difference between Python and C C compiler stages Basic syntax in C Pointers What is a pointer? declaration, &, dereference... Pointer & dynamic memory allocation
15-740/ Computer Architecture Lecture 10: Out-of-Order Execution. Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Fall 2011, 10/3/2011
 5-740/8-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 0: Out-of-Order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Fall 20, 0/3/20 Review: Solutions to Enable Precise Exceptions Reorder buffer History buffer
5-740/8-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 0: Out-of-Order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Fall 20, 0/3/20 Review: Solutions to Enable Precise Exceptions Reorder buffer History buffer
Blog -
 . Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
. Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
Computer System Architecture Midterm Examination Spring 2002
 Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
ISA Instruction Operation
 This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
Computer Architecture EE 4720 Midterm Examination
 Name Solution Computer Architecture EE 4720 Midterm Examination 22 March 2000, 13:40 14:30 CST Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Exam Total (35 pts) (20 pts) (45 pts) (100 pts) Good Luck! Problem 1:
Name Solution Computer Architecture EE 4720 Midterm Examination 22 March 2000, 13:40 14:30 CST Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Exam Total (35 pts) (20 pts) (45 pts) (100 pts) Good Luck! Problem 1:
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam
 Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
Lecture 10 Exceptions and Interrupts. How are exceptions generated?
 Lecture 10 Exceptions and Interrupts The ARM processor can work in one of many operating modes. So far we have only considered user mode, which is the "normal" mode of operation. The processor can also
Lecture 10 Exceptions and Interrupts The ARM processor can work in one of many operating modes. So far we have only considered user mode, which is the "normal" mode of operation. The processor can also
Computer Architecture Lecture 12: Out-of-Order Execution (Dynamic Instruction Scheduling)
 18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 12: Out-of-Order Execution (Dynamic Instruction Scheduling) Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2015, 2/13/2015 Agenda for Today & Next Few Lectures
18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 12: Out-of-Order Execution (Dynamic Instruction Scheduling) Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2015, 2/13/2015 Agenda for Today & Next Few Lectures
CMSC411 Fall 2013 Midterm 1
 CMSC411 Fall 2013 Midterm 1 Name: Instructions You have 75 minutes to take this exam. There are 100 points in this exam, so spend about 45 seconds per point. You do not need to provide a number if you
CMSC411 Fall 2013 Midterm 1 Name: Instructions You have 75 minutes to take this exam. There are 100 points in this exam, so spend about 45 seconds per point. You do not need to provide a number if you
COMP 4211 Seminar Presentation
 COMP Seminar Presentation Based On: Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach by Hennessey and Patterson Presenter : Feri Danes Outline Exceptions Handling Floating Points Operations Case Study: MIPS
COMP Seminar Presentation Based On: Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach by Hennessey and Patterson Presenter : Feri Danes Outline Exceptions Handling Floating Points Operations Case Study: MIPS
ECE 2020B Fundamentals of Digital Design Spring problems, 6 pages Exam Two 26 February 2014
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Computer Architecture Lecture 14: Out-of-Order Execution. Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/18/2013
 18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 14: Out-of-Order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/18/2013 Reminder: Homework 3 Homework 3 Due Feb 25 REP MOVS in Microprogrammed
18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 14: Out-of-Order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/18/2013 Reminder: Homework 3 Homework 3 Due Feb 25 REP MOVS in Microprogrammed
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises III
 ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises III Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois Serre,
ETH, Design of Digital Circuits, SS17 Practice Exercises III Instructors: Prof. Onur Mutlu, Prof. Srdjan Capkun TAs: Jeremie Kim, Minesh Patel, Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Der-Yeuan Yu, Francois Serre,
ECE 2030D Computer Engineering Spring problems, 5 pages Exam Two 8 March 2012
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Computer System Architecture Final Examination Spring 2002
 Computer System Architecture 6.823 Final Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 180 Minutes 22 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer System Architecture 6.823 Final Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 180 Minutes 22 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.
![PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers. PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.](/thumbs/96/128058841.jpg) Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
ELCT 707 Micro Computer Applications Final-term Exam, Winter 2009
 German University in Cairo Jan 16 th 2010 Information Engineering and Technology Dept. Dr. Gamal Fahmy Bar Code ELCT 707 Micro Computer Applications Final-term Exam, Winter 2009 Exam Duration: Three hours
German University in Cairo Jan 16 th 2010 Information Engineering and Technology Dept. Dr. Gamal Fahmy Bar Code ELCT 707 Micro Computer Applications Final-term Exam, Winter 2009 Exam Duration: Three hours
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
CS Computer Architecture
 CS 35101 Computer Architecture Section 600 Dr. Angela Guercio Fall 2010 Computer Systems Organization The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of the computer. Fetches instructions from main memory.
CS 35101 Computer Architecture Section 600 Dr. Angela Guercio Fall 2010 Computer Systems Organization The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of the computer. Fetches instructions from main memory.
Pipelining. CSC Friday, November 6, 2015
 Pipelining CSC 211.01 Friday, November 6, 2015 Performance Issues Longest delay determines clock period Critical path: load instruction Instruction memory register file ALU data memory register file Not
Pipelining CSC 211.01 Friday, November 6, 2015 Performance Issues Longest delay determines clock period Critical path: load instruction Instruction memory register file ALU data memory register file Not
Do not open this exam until instructed to do so. CS/ECE 354 Final Exam May 19, CS Login: QUESTION MAXIMUM SCORE TOTAL 115
 Name: Solution Signature: Student ID#: Section #: CS Login: Section 2: Section 3: 11:00am (Wood) 1:00pm (Castano) CS/ECE 354 Final Exam May 19, 2000 1. This exam is open book/notes. 2. No calculators.
Name: Solution Signature: Student ID#: Section #: CS Login: Section 2: Section 3: 11:00am (Wood) 1:00pm (Castano) CS/ECE 354 Final Exam May 19, 2000 1. This exam is open book/notes. 2. No calculators.
SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 YEAR: 10 Computing Time: 1½ Hr. Name: Class: Instructions: 1. Answer all the questions in the space provided on this paper. 2. Calculators
SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 YEAR: 10 Computing Time: 1½ Hr. Name: Class: Instructions: 1. Answer all the questions in the space provided on this paper. 2. Calculators
Computer Architecture Sample Test 1
 Computer Architecture Sample Test 1 Question 1. Suppose we have 32-bit memory addresses, a byte-addressable memory, and a 512 KB (2 19 bytes) cache with 32 (2 5 ) bytes per block. a) How many total lines
Computer Architecture Sample Test 1 Question 1. Suppose we have 32-bit memory addresses, a byte-addressable memory, and a 512 KB (2 19 bytes) cache with 32 (2 5 ) bytes per block. a) How many total lines
Wrong Path Events and Their Application to Early Misprediction Detection and Recovery
 Wrong Path Events and Their Application to Early Misprediction Detection and Recovery David N. Armstrong Hyesoon Kim Onur Mutlu Yale N. Patt University of Texas at Austin Motivation Branch predictors are
Wrong Path Events and Their Application to Early Misprediction Detection and Recovery David N. Armstrong Hyesoon Kim Onur Mutlu Yale N. Patt University of Texas at Austin Motivation Branch predictors are
Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination
 Name Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination Primary: 6 December 1999, Alternate: 7 December 1999, 10:00 12:00 CST 15:00 17:00 CST Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Exam Total (25 pts)
Name Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination Primary: 6 December 1999, Alternate: 7 December 1999, 10:00 12:00 CST 15:00 17:00 CST Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Exam Total (25 pts)
Computer Architecture Lecture 13: State Maintenance and Recovery. Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/15/2013
 18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 13: State Maintenance and Recovery Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/15/2013 Reminder: Homework 3 Homework 3 Due Feb 25 REP MOVS in Microprogrammed
18-447 Computer Architecture Lecture 13: State Maintenance and Recovery Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Spring 2013, 2/15/2013 Reminder: Homework 3 Homework 3 Due Feb 25 REP MOVS in Microprogrammed
ECE 411 Exam 1. Name:
 This exam has 5 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have 3 hours to complete this exam.
This exam has 5 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have 3 hours to complete this exam.
CS433 Midterm. Prof Josep Torrellas. October 16, Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes
 CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
c. What are the machine cycle times (in nanoseconds) of the non-pipelined and the pipelined implementations?
 Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Final Exam Fall 2007
 ICS 233 - Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Final Exam Fall 2007 Wednesday, January 23, 2007 7:30 am 10:00 am Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd
ICS 233 - Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Final Exam Fall 2007 Wednesday, January 23, 2007 7:30 am 10:00 am Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd
Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE. Spring April 3, 2006
 Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Spring 2006 April 3, 2006 ID Number 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 Total /75 Problem 1. ( 15 points) Logic Design: A three-input switching function is expressed as f(a,
Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Spring 2006 April 3, 2006 ID Number 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 Total /75 Problem 1. ( 15 points) Logic Design: A three-input switching function is expressed as f(a,
cs470 - Computer Architecture 1 Spring 2002 Final Exam open books, open notes
 1 of 7 ay 13, 2002 v2 Spring 2002 Final Exam open books, open notes Starts: 7:30 pm Ends: 9:30 pm Name: (please print) ID: Problem ax points Your mark Comments 1 10 5+5 2 40 10+5+5+10+10 3 15 5+10 4 10
1 of 7 ay 13, 2002 v2 Spring 2002 Final Exam open books, open notes Starts: 7:30 pm Ends: 9:30 pm Name: (please print) ID: Problem ax points Your mark Comments 1 10 5+5 2 40 10+5+5+10+10 3 15 5+10 4 10
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : 2BS_CS_C_Computer Orgnisation_248 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28- COMPUTER SCIENCE &
Serial : 2BS_CS_C_Computer Orgnisation_248 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28- COMPUTER SCIENCE &
ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013
 ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013 Professor: Sherief Reda School of Engineering, Brown University 1. [from Debois et al. 30 points] Consider the non-pipelined implementation of
ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013 Professor: Sherief Reda School of Engineering, Brown University 1. [from Debois et al. 30 points] Consider the non-pipelined implementation of
Computer Architecture V Fall Practice Exam Questions
 Computer Architecture V22.0436 Fall 2002 Practice Exam Questions These are practice exam questions for the material covered since the mid-term exam. Please note that the final exam is cumulative. See the
Computer Architecture V22.0436 Fall 2002 Practice Exam Questions These are practice exam questions for the material covered since the mid-term exam. Please note that the final exam is cumulative. See the
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
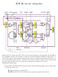 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
BEng (Hons.) Telecommunications. BSc (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security
 BEng (Hons.) Telecommunications BSc (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security Cohorts: BTEL/15B/FT BCNS/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 2 Resit Examinations for BTEL/13B/FT & BTEL/15B/FT
BEng (Hons.) Telecommunications BSc (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security Cohorts: BTEL/15B/FT BCNS/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 2 Resit Examinations for BTEL/13B/FT & BTEL/15B/FT
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 25 Instructors: Krste sanović, Vladimir Stojanovic 25-4-9 L J fter the exam,
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 25 Instructors: Krste sanović, Vladimir Stojanovic 25-4-9 L J fter the exam,
NAME: 1a. (10 pts.) Describe the characteristics of numbers for which this floating-point data type is well-suited. Give an example.
 MSU CSC 285 Spring, 2007 Exam 2 (5 pgs.) NAME: 1. Suppose that a eight-bit floating-point data type is defined with the eight bits divided into fields as follows, where the bits are numbered with zero
MSU CSC 285 Spring, 2007 Exam 2 (5 pgs.) NAME: 1. Suppose that a eight-bit floating-point data type is defined with the eight bits divided into fields as follows, where the bits are numbered with zero
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 13, 2000
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering
 Print: First Name:............ Solutions............ Last Name:............................. Student Number:............................................... University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science
Print: First Name:............ Solutions............ Last Name:............................. Student Number:............................................... University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science
CENG 3531 Computer Architecture Spring a. T / F A processor can have different CPIs for different programs.
 Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2017 Instructors: Randy Katz, Krste Asanovic CS61C MIDTERM 2
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2017 Instructors: Randy Katz, Krste Asanovic 2017 10 31 CS61C MIDTERM 2 After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2017 Instructors: Randy Katz, Krste Asanovic 2017 10 31 CS61C MIDTERM 2 After the
unused unused unused unused unused unused
 BCD numbers. In some applications, such as in the financial industry, the errors that can creep in due to converting numbers back and forth between decimal and binary is unacceptable. For these applications
BCD numbers. In some applications, such as in the financial industry, the errors that can creep in due to converting numbers back and forth between decimal and binary is unacceptable. For these applications
CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS
 CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS UNIT-I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. What are the eight great ideas in computer architecture? The eight
CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS UNIT-I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. What are the eight great ideas in computer architecture? The eight
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
University of Florida EEL 4744 Spring 2011 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering 31 March Apr-11 1:29 PM
 University of Florida EE 4744 Spring 2011 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Page 1/15 Exam 2 Go Gators! Instructions: Turn off cell phones beepers and other noise making devices. Show all work on the front of the test
University of Florida EE 4744 Spring 2011 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Page 1/15 Exam 2 Go Gators! Instructions: Turn off cell phones beepers and other noise making devices. Show all work on the front of the test
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #1 February 14th, 2011 Professor Krste Asanović
 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #1 February 14th, 2011 Professor Krste Asanović Name: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 15 Pages Notes: Not all questions
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #1 February 14th, 2011 Professor Krste Asanović Name: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 15 Pages Notes: Not all questions
CS433 Homework 2 (Chapter 3)
 CS Homework 2 (Chapter ) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration..
CS Homework 2 (Chapter ) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration..
CMU Introduction to Computer Architecture, Spring Midterm Exam 1. Date: Wed., 3/6. Legibility & Name (5 Points): Problem 1 (65 Points):
 Name: CMU 18-447 Introduction to Computer Architecture, Spring 2013 Midterm Exam 1 Instructions: Date: Wed., 3/6 Legibility & Name (5 Points): Problem 1 (65 Points): Problem 2 (25 Points): Problem 3 (20
Name: CMU 18-447 Introduction to Computer Architecture, Spring 2013 Midterm Exam 1 Instructions: Date: Wed., 3/6 Legibility & Name (5 Points): Problem 1 (65 Points): Problem 2 (25 Points): Problem 3 (20
CIS 371 Spring 2015 Computer Organization and Design 7 May 2015 Final Exam
 CIS 371 Spring 2015 Computer Organization and Design 7 May 2015 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
CIS 371 Spring 2015 Computer Organization and Design 7 May 2015 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 013 Yale Patt, Instructor Ben Lin, Mochamad Asri, Ameya Chaudhari, Nikhil Garg, Lauren Guckert, Jack Koenig,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 013 Yale Patt, Instructor Ben Lin, Mochamad Asri, Ameya Chaudhari, Nikhil Garg, Lauren Guckert, Jack Koenig,
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 1 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 1 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic: 754
 IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic: 754 G.E. Antoniou G.E. Antoniou () IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic: 754 1 / 34 Floating Point Standard: IEEE 754 1985/2008 Established in 1985 (2008)
IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic: 754 G.E. Antoniou G.E. Antoniou () IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic: 754 1 / 34 Floating Point Standard: IEEE 754 1985/2008 Established in 1985 (2008)
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 25 Instructors: Krste sanović, Vladimir Stojanovic 25-4-9 L J fter the exam,
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 25 Instructors: Krste sanović, Vladimir Stojanovic 25-4-9 L J fter the exam,
EE 457 Unit 8. Exceptions What Happens When Things Go Wrong
 1 EE 457 Unit 8 Exceptions What Happens When Things Go Wrong 2 What are Exceptions? Exceptions are rare events triggered by the hardware and forcing the processor to execute a software handler HW Interrupts
1 EE 457 Unit 8 Exceptions What Happens When Things Go Wrong 2 What are Exceptions? Exceptions are rare events triggered by the hardware and forcing the processor to execute a software handler HW Interrupts
CS61C Midterm 2 Review Session. Problems + Solutions
 CS61C Midterm 2 Review Session Problems + Solutions Floating Point Big Ideas in Number Rep Represent a large range of values by trading off precision. Store a number of fixed size (significand) and float
CS61C Midterm 2 Review Session Problems + Solutions Floating Point Big Ideas in Number Rep Represent a large range of values by trading off precision. Store a number of fixed size (significand) and float
CS433 Homework 2 (Chapter 3)
 CS433 Homework 2 (Chapter 3) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies
CS433 Homework 2 (Chapter 3) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies
Good luck and have fun!
 Midterm Exam October 13, 2014 Name: Problem 1 2 3 4 total Points Exam rules: Time: 90 minutes. Individual test: No team work! Open book, open notes. No electronic devices, except an unprogrammed calculator.
Midterm Exam October 13, 2014 Name: Problem 1 2 3 4 total Points Exam rules: Time: 90 minutes. Individual test: No team work! Open book, open notes. No electronic devices, except an unprogrammed calculator.
Co-processor Math Processor. Richa Upadhyay Prabhu. NMIMS s MPSTME February 9, 2016
 8087 Math Processor Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu February 9, 2016 Introduction Need of Math Processor: In application where fast calculation is required Also where there
8087 Math Processor Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu February 9, 2016 Introduction Need of Math Processor: In application where fast calculation is required Also where there
Exam-2 Scope. 3. Shared memory architecture, distributed memory architecture, SMP, Distributed Shared Memory and Directory based coherence
 Exam-2 Scope 1. Memory Hierarchy Design (Cache, Virtual memory) Chapter-2 slides memory-basics.ppt Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory technology and optimizations Virtual memory 2. SIMD, MIMD, Vector,
Exam-2 Scope 1. Memory Hierarchy Design (Cache, Virtual memory) Chapter-2 slides memory-basics.ppt Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory technology and optimizations Virtual memory 2. SIMD, MIMD, Vector,
Chapter 3 Instruction-Level Parallelism and its Exploitation (Part 1)
 Chapter 3 Instruction-Level Parallelism and its Exploitation (Part 1) ILP vs. Parallel Computers Dynamic Scheduling (Section 3.4, 3.5) Dynamic Branch Prediction (Section 3.3) Hardware Speculation and Precise
Chapter 3 Instruction-Level Parallelism and its Exploitation (Part 1) ILP vs. Parallel Computers Dynamic Scheduling (Section 3.4, 3.5) Dynamic Branch Prediction (Section 3.3) Hardware Speculation and Precise
Very short answer questions. You must use 10 or fewer words. "True" and "False" are considered very short answers.
 Very short answer questions. You must use 10 or fewer words. "True" and "False" are considered very short answers. [1] Which is on average more effective, dynamic or static branch prediction? [1] Does
Very short answer questions. You must use 10 or fewer words. "True" and "False" are considered very short answers. [1] Which is on average more effective, dynamic or static branch prediction? [1] Does
Computer Organisation CS303
 Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 5: Processors Our goal: understand basics of processors and CPU understand the architecture of MARIE, a model computer a close look at the instruction
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 5: Processors Our goal: understand basics of processors and CPU understand the architecture of MARIE, a model computer a close look at the instruction
VIII. DSP Processors. Digital Signal Processing 8 December 24, 2009
 Digital Signal Processing 8 December 24, 2009 VIII. DSP Processors 2007 Syllabus: Introduction to programmable DSPs: Multiplier and Multiplier-Accumulator (MAC), Modified bus structures and memory access
Digital Signal Processing 8 December 24, 2009 VIII. DSP Processors 2007 Syllabus: Introduction to programmable DSPs: Multiplier and Multiplier-Accumulator (MAC), Modified bus structures and memory access
Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!)
 The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS370 Introduction to Computer Organization Midterm Exam 1 October 22, 2009 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!) Open book,
The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS370 Introduction to Computer Organization Midterm Exam 1 October 22, 2009 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!) Open book,
CS 230 Practice Final Exam & Actual Take-home Question. Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts)
 Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination
 THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
Design of Digital Circuits Lecture 21: GPUs. Prof. Onur Mutlu ETH Zurich Spring May 2017
 Design of Digital Circuits Lecture 21: GPUs Prof. Onur Mutlu ETH Zurich Spring 2017 12 May 2017 Agenda for Today & Next Few Lectures Single-cycle Microarchitectures Multi-cycle and Microprogrammed Microarchitectures
Design of Digital Circuits Lecture 21: GPUs Prof. Onur Mutlu ETH Zurich Spring 2017 12 May 2017 Agenda for Today & Next Few Lectures Single-cycle Microarchitectures Multi-cycle and Microprogrammed Microarchitectures
15-740/ Computer Architecture Lecture 8: Issues in Out-of-order Execution. Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University
 15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 8: Issues in Out-of-order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Readings General introduction and basic concepts Smith and Sohi, The Microarchitecture
15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 8: Issues in Out-of-order Execution Prof. Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Readings General introduction and basic concepts Smith and Sohi, The Microarchitecture
