Using VLAN & Bridge APPENDIX
|
|
|
- Harvey Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPENDIX I Using VLAN & Bridge The VLAN & Bridge application allows you to configure groups of ports independent of their physical location as a virtual LAN. This arrangement is called a logical grouping the logical group is called a virtual LAN (VLAN). Ports or groups of ports in a VLAN are called VLAN members. VLANs prevent traffic, including broadcasts and multicasts, from being propagated to members of other VLANs. Switches are interconnected by the Inter-Switch Link (ISL) port so that VLAN traffic can cross multiple switches. A Layer-2 switch is basically a bridge. Both switches and bridges allow multiple ports to be active simultaneously. Every VLAN has an equivalent bridge. Most of the configuration required for bridging is related to the spanning-tree algorithm, which allows the connected network topology to contain multiple physical paths between two stations but constrains the active topology to a single-span tree. If a port on one bridge fails, the other bridges can reconfigure the topology and switch traffic to new paths. A VLAN, therefore, can be considered equivalent to a bridged LAN. Note If the spanning-tree algorithm is not enabled, no backup path exists to maintain bridge connectivity. To start the VLAN & Bridge application from CiscoView, select Configure>device>VLAN & Bridge. Using VLAN & Bridge I-1
2 VLAN and Bridge VLAN and Bridge The main window for VLAN and bridging configuration is the VLAN & Bridge window. The VLAN & Bridge window contains information about the currently configured VLANs in the device Timesaver You can drag-and drop a port directly into a VLAN. Click on the port in the device display, drag it onto the opened VLAN & Bridge Table, then drop in into one of the VLAN fields. The system automatically assigns the port to the designated VLAN. Hints for Configuring VLAN and Bridge Information for the Device. VLANs can be of 5 types: Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring, FDDI Net, and TRNet. Use the action buttons in the VLAN & Bridge window as follows: The View Ports section contains the following action buttons: VLAN Members Highlights in red the ports on the switch that belong to the selected VLAN. Inter Switch Highlights in blue the ports on the switch that are running in ISL mode. To highlight the ports in a VLAN that are running in ISL mode in blue, select a VLAN, and click Inter Switch. Clear Ports Clears the highlights in the device display. To clear the highlights in the device display, click Clear Ports. VLAN Non-Trunk Members Displays a summary of ports that are non-trunk members of a selected VLAN. The Bridges section contains the following action buttons: Note The buttons in the Bridges section depend on whether you select a TrVlan or a TrNetVlan entry from the VLAN table: If you select a TrVLAN entry, only Configure... and Forwarding... are displayed. If you select a TrNet VLAN entry, only Configure... is displayed. I-2 Getting Started with Ciscoview
3 Configure... Opens the Configure Bridge window and displays Bridge MIB variable information. See VLAN Bridge Configuration for more information. Forwarding... Displays the bridge forwarding information for the selected device. See Bridge Forwarding for more information. Static... Displays manually configured forwarding information about the bridge; this information is displayed in table form. See Bridging Statics (Applicable to TR Ports only) for more information. The VTP-VLAN section contains the following action buttons: Local Mgmt Domain Displays the VTP Local Management Domain window. This is the domain from which all VLANs on the module can communicate with each other and with other ports on other Catalyst 5000 series modules. See Local Management Domain for more information. Create VLAN... Displays the Create VLAN window. See Create VLAN for more information. Delete VLAN... Deletes the selected VLAN. See Delete VLAN for more information. Modify VLAN... Opens the Modify VLAN window. See Modify VLAN for more information. Procedures This section contains procedures for using the VTP-VLAN section tools. Local Management Domain The Local Management Domain window allows you to create a new VTP management domain and define the boundary of a defined VLAN or to modify or display the existing domain information. Note You must provide a domain name to each VLAN to ensure the VLAN functions properly. Using VLAN & Bridge I-3
4 To create, modify, or display a management domain, perform the following steps: Step 1 Step 2 From the VLAN & Bridge, click Local Mgmt Domain. The VTP management Domain window opens. Enter information into (or review values in) the following fields: Note A domain name must be entered. If a domain name is not specified, ports cannot be assigned to any VLAN, regardless of the access level. Domain Index. Domain Name. Domain Local Mode (select either VTP client mode, VTP server mode, or transparent mode). Transparent mode is a non-client-server mode. Note The Domain Local Mode must be set to server mode to create, modify, or delete a VLAN. When selected, server mode sets the switch to act as a server from which other servers will receive VLAN information. Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Domain Config Revision Number. This number is used for synchronization. Domain last Updater s IP. For example, this number is the server s IP address when VTP server mode is selected. Domain lastchange. This entry should display a date. Domain PruningState: Select either the enabled or disabled state. Click Modify to save the input and refresh the VLAN & Bridge window. If the device returns any errors during this operation, CiscoView displays the information. Repeat Steps 1 through 3 for each domain as required. Click Cancel to exit the window. I-4 Getting Started with Ciscoview
5 Create VLAN The Create VLAN window allows you to create a new VLAN. For additional information regarding the fields within the windows, click Help to access the online help. To create a VLAN, perform the following steps: Step 1 From the VLAN & Bridge table, click Create VLAN. The Create VLAN dialog box opens. Note Although all the fields are shown in the dialog box, any field not appropriate for the VLAN type is grayed out. Step 2 Enter values into the following fields: VLAN Number. For VLANs of Ethernet type, enter any existing VLAN number from the preceding VLAN & Bridge table. For VLANs of (Token Ring) trcrf type, use a number that is not already assigned from the preceding VLAN & Bridge table. VLAN State (operational is the default setting; the other option is suspended). VLAN Type (default is ethernet; other options are fddi, trcrf, fddinet, or trbrf.) For VLANs of type trbrf, you must create a net first, then use the Create VLAN window and select VLAN Type trcrf to create Token Ring VLANs inside the net. See Note below for more information. Note The trcrf VLAN type is used for Token Ring VLANs made up of (at most) one transparently bridged LAN segment. The trbrf type is used for VLANs that represent the scope of many trcrf VLANs connected via a source routing bridge. The Token Ring trbrf type can be said to represent the bridged broadcast domain. Using VLAN & Bridge I-5
6 Step 3 Enter values into the following optional fields or leave the fields blank: VLAN Name. Enter any name, if desired. This name is used as the ELAN name for the ATM LAN Emulation segment of this VLAN. VLAN MTU Size. The range is 1500 through for all VLAN types. The MTU size is defined as the largest MAC-layer of the data frame that can be transmitted on the VLAN. For Token Ring VLANs, the default is VLAN SAID Field (Integer). This is the value of the SAID field for the VLAN. For VLANs of Ethernet type, enter a unique number; no range is established but enter a number starting with 100,000 plus (+) the VLAN number, for example, This field is disabled for other VLAN types. This field is disabled for Token Ring VLANs. VLAN Ring Number. The range is 0x1 through 0xfff. This field is available for VLANs of type FDDI or Token Ring. Note: Source Routing (srb) must be configured for use on this VLAN. For Token Ring VLANs, use the Token Ring number here; or give any number within the sepcified range that is not duplicated in any other VLAN. VLAN Bridge Number. This is the bridge number of thevtp-capable switches for this VLAN. This field is disabled for VLANs of Ethernet and Token Ring types but enabled for VLAN types. This object is available only for VLANs that are involved with emulating token ring segments. VLAN STP Type. The type of the spanning-tree-protocol running on this VLAN. This field is disabled for VLANs of Ethernet and Token Ring types, but enabled for VLAN types. Parent VLAN ID. The parent VLAN for this VLAN, available only for VLANs of type FDDI or Token Ring when source-route bridging (SRB) is configured for use on this VLAN. This field is disabled for VLANs of Ethernet type. For Token Ring VLANs, enter the trbrf VLAN number here. Translational VLAN1 Number. A VLAN to which this VLAN is being translationally bridged. For VLANs of Ethernet type, enter any existing VLAN number from the original VLAN & Bridge window s table. This field is disabled for Token Ring VLANs. I-6 Getting Started with Ciscoview
7 Translational VLAN2 Number. Another VLAN to which this VLAN is being translationally bridged. This field is disabled for Token Ring VLANs. VLAN Bridge Type. The type of the bridging mode in use on this VLAN. Choose either srt for source-route transparent bridging or srb for source-route bridging. VLAN ARE Hop Count (1...14). The maximum number of bridge hops in All Routes Explorer frames on this VLAN. This field is applicable to FDDI and Token Ring VLANs. VLAN STE Hop Count (1...14). The maximum number of bridge hops allowed in Spanning Tree Explorer frames on this VLAN. This field is applicable to FDDI and Token Ring VLANs. Backup CRF. Choose On if this VLAN is of type trcrf and also is acting as a backup trcrf for the ISL-distributed BRF. Note If your system is a Catalyst 5000 series switch, skip Steps 4 and 5 and proceed to Step 6. If your system is a Catalyst 3000 series switch, proceed to Step 4. Perform Steps 4 and 5 only on Catalyst 3000 series switches loaded with Software Release 2.2(2) or later. Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 Step 8 Step 9 From the VLAN & Bridge table, select the newly created VLAN and click Modify VLAN. Change the Preferred VLAN value to yes and click Apply. Use the drag and drop technique to assign the ports to the VLAN. Click Apply to save the input and refresh the VLAN & Bridge table. If the device returns any errors during this operation, CiscoView displays the information. Repeat Steps 1 through 3 and Steps 6 and 7 for each new VLAN on the Catalyst 5000 series switch, and Steps 1 through 7 for each new VLAN on the Catalyst 3000 series switch. Click Cancel to exit the window. Using VLAN & Bridge I-7
8 Delete VLAN To delete a VLAN, perform the following steps: Step 1 From the VLAN & Bridge table, select a VLAN, and click Delete. A confirmation window opens. Note Removal of a VLAN deactivates all the ports in the VLAN. Step 2 Step 3 Click Apply to confirm the deletion of the VLAN or Cancel to exit the window. If deleted, the VLAN is removed from the device VLAN table. Click Cancel to exit the window. Modify VLAN To modify a VLAN, select a VLAN from the VLAN table and click Modify VLAN. A dialog box similar to the one for creating a VLAN appears. For additional information on the fields in the windows, click Help to access the online help. To modify a VLAN, perform the following steps: Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 From the VLAN & Bridge table, select a VLAN and click Modify VLAN. A dialog box similar to the one for creating VLAN appears. Change the value(s) as appropriate and click Apply. If the device returns any errors during this operation, CiscoView displays the information. Click Cancel to exit the window. I-8 Getting Started with Ciscoview
Configuring the Catalyst 3920
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Catalyst 3920 You might not have to configure the Catalyst 3920 for it to work in your network; it is shipped with default configuration parameters and can function with these
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Catalyst 3920 You might not have to configure the Catalyst 3920 for it to work in your network; it is shipped with default configuration parameters and can function with these
This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers.
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
Configuring VLAN CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 LMS collects data about devices so that you can configure and manage Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) in your network. You must set up your LMS server properly to ensure that Data Collection
CHAPTER 10 LMS collects data about devices so that you can configure and manage Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) in your network. You must set up your LMS server properly to ensure that Data Collection
Understanding and Configuring VTP
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac
![2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac 2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac](/thumbs/72/68003916.jpg) 2] Chapter 2 traceroute mac traceroute mac Use the traceroute mac privileged EXEC command on the switch stack or on a standalone switch to display the Layer 2 path taken by the packets from the specified
2] Chapter 2 traceroute mac traceroute mac Use the traceroute mac privileged EXEC command on the switch stack or on a standalone switch to display the Layer 2 path taken by the packets from the specified
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
 Configuring Inter-Switch Link This chapter explains how to configure Inter-Switch Link (TRISL) on Cisco routers. The chapter describes TRISL in the context of the Inter-Switch Link (ISL) protocol and the
Configuring Inter-Switch Link This chapter explains how to configure Inter-Switch Link (TRISL) on Cisco routers. The chapter describes TRISL in the context of the Inter-Switch Link (ISL) protocol and the
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
Catalyst 1900 Series and Catalyst 2820 Series Enterprise Edition Software Configuration Guide
 INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Managing Physical and Logical Network Services with Topology Services
 CHAPTER 2 Managing Physical and Logical Network Services with Topology Services Topology Services is an application that enables you to view, monitor, and configure the physical and logical services on
CHAPTER 2 Managing Physical and Logical Network Services with Topology Services Topology Services is an application that enables you to view, monitor, and configure the physical and logical services on
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Works CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
2rd2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Cisco 7600 Series Router verify. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]} {/ios flash-filesystem}
![2rd2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Cisco 7600 Series Router verify. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]} {/ios flash-filesystem} 2rd2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Cisco 7600 Series Router verify. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]} {/ios flash-filesystem}](/thumbs/72/67723196.jpg) Chapter 2 2rd2 verify verify To verify the checksum of a file on a Flash memory file system or compute an MD5 signature for a file, use the verify command. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]}
Chapter 2 2rd2 verify verify To verify the checksum of a file on a Flash memory file system or compute an MD5 signature for a file, use the verify command. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]}
Switches running the LAN Base feature set support only static routing on SVIs.
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
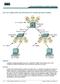 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
VLAN Commands. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.x (Catalyst 3650 Switches) 1
 client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
Cisco IOS Commands for the Catalyst 6500 Series Switches with the Supervisor Engine 32 PISA verify
 Chapter 2 verify verify To verify the checksum of a file on a flash memory file system or compute an MD5 signature for a file, use the verify command. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]}
Chapter 2 verify verify To verify the checksum of a file on a flash memory file system or compute an MD5 signature for a file, use the verify command. verify {{{/md5 flash-filesystem} [expected-md5-signature]}
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Version 1 and Version 2 Work CHAPTER
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
no udld {aggressive enable message time seconds}
 udld udld To enable aggressive or normal mode in UniDirectional Link Detection protocol (UDLD) and set the configurable message time, use the udld command in global configuration mode. To disable aggressive
udld udld To enable aggressive or normal mode in UniDirectional Link Detection protocol (UDLD) and set the configurable message time, use the udld command in global configuration mode. To disable aggressive
Configuring Spanning Tree
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
CHAPTER 8 Configuring Spanning Tree This chapter describes how to configure spanning tree on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For information on configuring the PortFast, UplinkFast, and BackboneFast
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
 24 CHAPTER Prerequisites for VTP, page 24-1 Restrictions for VTP, page 24-1 Information About VTP, page 24-2 Default Settings for VTP, page 24-9 How to Configure VTP, page 24-10 For complete syntax and
24 CHAPTER Prerequisites for VTP, page 24-1 Restrictions for VTP, page 24-1 Information About VTP, page 24-2 Default Settings for VTP, page 24-9 How to Configure VTP, page 24-10 For complete syntax and
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Overview. About the Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 Switches CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
VLAN. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 3850 Switches) 1
 clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Overview of Bridging
 Overview of Bridging The Bridging section of this guide discusses the following software components for bridging and routing protocols in Cisco routers: Transparent and Source-Route Transparent (SRT) Bridging,
Overview of Bridging The Bridging section of this guide discusses the following software components for bridging and routing protocols in Cisco routers: Transparent and Source-Route Transparent (SRT) Bridging,
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring Token Ring LAN Emulation
 This chapter describes how to configure Token Ring LAN emulation (LANE) on the Catalyst 5000 platform. This feature is supported on the following Catalyst 5000 series ATM modules: ATM Dual PHY OC-12 modules
This chapter describes how to configure Token Ring LAN emulation (LANE) on the Catalyst 5000 platform. This feature is supported on the following Catalyst 5000 series ATM modules: ATM Dual PHY OC-12 modules
Source-Route Bridging
 25 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Describe when to use source-route bridging. Understand the difference between SRB and transparent bridging. Know the mechanism that end stations use to specify a source-route.
25 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Describe when to use source-route bridging. Understand the difference between SRB and transparent bridging. Know the mechanism that end stations use to specify a source-route.
Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis
 CHAPTER 4 Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis Path Analysis is an operations and diagnostic application that traces the connectivity between two specified points on your network and the physical and
CHAPTER 4 Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis Path Analysis is an operations and diagnostic application that traces the connectivity between two specified points on your network and the physical and
Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98154 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP VTP Configuration Guidelines VTP Configuration on Catalyst
Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98154 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP VTP Configuration Guidelines VTP Configuration on Catalyst
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1
 Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Routing Between VLANs Overview
 Routing Between VLANs Overview This chapter provides an overview of VLANs. It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information about designing VLANs.
Routing Between VLANs Overview This chapter provides an overview of VLANs. It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information about designing VLANs.
Routing Between VLANs Overview
 Routing Between VLANs Overview This chapter provides an overview of VLANs. It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information about designing VLANs.
Routing Between VLANs Overview This chapter provides an overview of VLANs. It describes the encapsulation protocols used for routing between VLANs and provides some basic information about designing VLANs.
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Implement VTP. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008
 Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to
 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
RealCiscoLAB.com. Multiple Spanning Tree. Topology. Objective. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH. Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST).
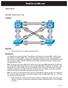 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
EtherChannel, Neighbor View, and Trap Receiver Table
 CHAPTER 9 EtherChannel, Neighbor View, and Trap Receiver Table This chapter descibes the configuration procedures for the EtherChannel, Neighbor View, and Trap Receiver Table applications. To start the
CHAPTER 9 EtherChannel, Neighbor View, and Trap Receiver Table This chapter descibes the configuration procedures for the EtherChannel, Neighbor View, and Trap Receiver Table applications. To start the
Cisco Catalyst 4xxx Supports Management Module SM-CAT1006
 Cisco Catalyst 4xxx Titlepae Supports Management Module SM-CAT1006 Device Management Copyright Notice Document 9033538-01. Copyright October 2001 Aprisma Management Technologies, Inc., 121 Technology Drive,
Cisco Catalyst 4xxx Titlepae Supports Management Module SM-CAT1006 Device Management Copyright Notice Document 9033538-01. Copyright October 2001 Aprisma Management Technologies, Inc., 121 Technology Drive,
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lab Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch
 Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Table of Contents. Cisco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Document ID: 10558...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 This document contains
Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Document ID: 10558...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 This document contains
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/300-115 Question: 323 An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition
Managing Network Spanning Trees
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
Configuring VTP V3. Configuring VTP V3. VTP V3 Overview. Guidelines and Limitation. This chapter contains the following sections:
 This chapter contains the following sections:, page 1 From Cisco NX-OS Release 7.2(0)N1(1), VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) V3 supports PVLAN integration, 4K VLAN integration, generic database transport mechanism,
This chapter contains the following sections:, page 1 From Cisco NX-OS Release 7.2(0)N1(1), VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) V3 supports PVLAN integration, 4K VLAN integration, generic database transport mechanism,
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
This guide outlines the tasks involved in installing and configuring the Oracle Communications IP Service Activator Cisco CatOS cartridge.
 Oracle Communications IP Service Activator Cisco CatOS Cartridge Guide Release 7.2 E47723-01 October 2013 This guide outlines the tasks involved in installing and configuring the Oracle Communications
Oracle Communications IP Service Activator Cisco CatOS Cartridge Guide Release 7.2 E47723-01 October 2013 This guide outlines the tasks involved in installing and configuring the Oracle Communications
Cisco CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test. Version
 Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V
 isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Understanding VTP...2 VTP Domain Name...2
isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Understanding VTP...2 VTP Domain Name...2
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
the larger the number of users and devices, the more broadcasts and packets each switch must handle.
 VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
ISP /24. Fas0/0. Fas1/0/1. Fas1/0/22 NYCORE1. Cisco PS. Fas0/1. Lab Nic /24
 Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008
 Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis
 CHAPTER 5 Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis Path Analysis is an operations and diagnostic application that traces the connectivity between two specified points on your network, including the physical
CHAPTER 5 Tracking Packet Flow Using Path Analysis Path Analysis is an operations and diagnostic application that traces the connectivity between two specified points on your network, including the physical
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
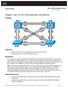 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 3750-X or 3560-X switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a Catalyst
CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 3750-X or 3560-X switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a Catalyst
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Enchilada Solutions
 Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
3. What could you use if you wanted to reduce unnecessary broadcast, multicast, and flooded unicast packets?
 Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Introduction to the Catalyst 3920
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to the Catalyst 3920 This chapter contains the following information about the Catalyst 3920: Product Overview Physical Characteristics of the Catalyst 3920 System Architecture Product
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to the Catalyst 3920 This chapter contains the following information about the Catalyst 3920: Product Overview Physical Characteristics of the Catalyst 3920 System Architecture Product
The Year of the Virtual LAN
 1995 - The Year of the Virtual LAN IEEE Conference, Maui, July 1995 mmcnealis@cisco.com Agenda Where are we today? Virtual LAN Technologies IEEE 802.10 Virtual LANs vlans and IEEE 802.1d Conclusion Date
1995 - The Year of the Virtual LAN IEEE Conference, Maui, July 1995 mmcnealis@cisco.com Agenda Where are we today? Virtual LAN Technologies IEEE 802.10 Virtual LANs vlans and IEEE 802.1d Conclusion Date
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
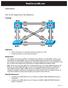 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
OmniMSS Powerful, high-performance LAN-to-ATM internetworking services
 OmniMSS Powerful, high-performance LAN-to-ATM internetworking services LAN emulation (LANE) and Multi-Protocol over ATM (MPOA) are two of the services that make ATM networks valuable in the enterprise.
OmniMSS Powerful, high-performance LAN-to-ATM internetworking services LAN emulation (LANE) and Multi-Protocol over ATM (MPOA) are two of the services that make ATM networks valuable in the enterprise.
