All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
|
|
|
- Shon Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Add a Switch to the VTP Domain Verify Troubleshoot Related Information Introduction This document provides a sample configuration on how to migrate a campus network of all VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) Transparent mode switches to a network with VTP server(s) and clients. This document can also be used to restructure the VTP domains that exist. Prerequisites Requirements Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration: Basic knowledge of Catalyst Switch Administration Knowledge of VTP Components Used The information in this document is based on Software Release 12.2(25)SEC2, and (CatOS) version 8.1(2). The information in this document is applicable to all Cisco devices that support VLAN Trunk Protocol version 2. The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command. Conventions Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
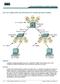
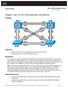
2 Background Information VTP reduces administration in a switched network. When you configure a new VLAN on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that is available on most of the Cisco Catalyst series products. Note: This document does not cover VTP version 3. VTP version 3 differs from VTP version 1 (v1) and version 2 (v2). It is only available on CatOS 8.1(1) or later. VTP version 3 incorporates many changes from VTP v1 and v2. Make certain that you understand the differences between VTP version 3 and earlier versions before you alter your network configuration. Refer to one of these sections from Configuring VTP for more information: Understanding How VTP Version 3 Works Interaction with VTP Version 1 and VTP Version 2 Configure In this section, you are presented with the information to migrate your campus network from all VTP transparent configuration to VTP server client configuration. This section also provides the quick steps used to introduce a new switch to the VTP domain that exists. Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to find more information on the commands used in this document. Network Diagram This document uses this network setup:
3 The network includes: Two distribution layer switchesdistributiona and DistributionB that both run Software. Two access layer switchesaccessa runs Software and AccessB runs CatOS Software. The initial VLAN database has these Ethernet VLANs: DistributionAVLANs 1, 10, and 11 DistributionBVLANs 1, 20, and 21 AccessAVLANs 1, 30, and 31 AccessBVLANs 1, 40, and 41 Configurations This section consists of three sub sections: Pre Migration Checks Migration Planning Migration Procedure Pre Migration Checks This section provides the checklist to make sure the network is ready for the migration process. In order to receive the current status of the VTP configuration in the switch, issue the show vtp status command for, and the show vtp domain command for CatOS.
4 1. DistributionA#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 7 VTP Operating Mode : Transparent VTP Domain Name : migration VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest : 0xE5 0x9F 0x80 0x70 0x73 0x62 0xC0 0x54 Configuration last modified by at :23:21 DistributionA# AccessB> (enable) show vtp domain Version : running VTP1 (VTP3 capable) Domain Name : migration Password : not configured Notifications: disabled Updater ID: Feature Mode Revision VLAN Client 0 Pruning : disabled VLANs prune eligible: AccessB> (enable) Check if all switches are in VTP Transparent mode. Issue these commands in order to change the VTP mode: AccessA#conf t AccessA(config)#vtp mode transparent Setting device to VTP TRANSPARENT mode AccessA(config)#exit AccessA# AccessB> (enable) set vtp mode transparent Changing VTP mode for all features VTP domain migration modified AccessB> (enable) 2. Check if all switches have the same VTP domain name. Issue these commands in order to change the VTP domain name: DistributionB(config)#vtp domain migration Changing VTP domain name from aaaa to migration DistributionB(config)# AccessB> (enable) set vtp domain migration
5 3. VTP domain migration modified AccessB> (enable) Check if all switches run the same VTP version. Issue these commands in order to change the VTP version: or vtp version 2 set vtp v2 enable set vtp version 2 4. Check if all switches run the same VTP password (if any configured). Issue these commands in order to change the VTP password: vtp password vtp_password AccessB> (enable) set vtp passwd? <passwd> Password (0 to clear) AccessB> (enable) set vtp passwd vtp_password Generating the secret associated to the password. VTP domain migration modified 5. Check if all switches are connected by trunk links. DistributionA#show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Gi2/0/1 auto n isl trunking 1 Gi2/0/5 auto n 802.1q trunking 1 Gi2/0/9 desirable n isl trunking 1 Gi2/0/10 desirable n isl trunking 1 Port Gi2/0/1 Gi2/0/5 Gi2/0/9 Gi2/0/10 Vlans allowed on trunk Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Gi2/0/1 1,10 11 Gi2/0/5 1,10 11 Gi2/0/9 1,10 11 Gi2/0/10 1,10 11 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi2/0/1 1,10 11 Gi2/0/5 1,10 11 Gi2/0/9 1,10 11
6 AccessB> (enable) show trunk * indicates vtp domain mismatch # indicates dot1q all tagged enabled on the port Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan 3/25 desirable n isl trunking 1 3/26 desirable n isl trunking 1 6/1 nonegotiate dot1q trunking 1 6/2 nonegotiate dot1q trunking 1 6/3 nonegotiate dot1q trunking 1 6/4 nonegotiate dot1q trunking 1 16/1 nonegotiate isl trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk 3/ , / , /1 6/2 6/3 6/4 16/ , Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Migration Planning Determine the number of VLANs required for the network. The maximum number of active VLANs supported by Catalyst switches varies with models. AccessA#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 250 Number of existing VLANs : 7 VTP Operating Mode : Transparent VTP Domain Name : migration VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest Configuration last modified by at :23:21 AccessA# : 0xC8 0xB7 0x36 0xC3 0xBD 0xC6 0x56 0xB2 Determine the switches, such as DistributionA and DistributionB, which will be the VTP servers. One or more switches can be VTP servers in a domain. Choose one switch, such as DistributionA, in order to start the migration. Migration Procedure Complete these steps in order to configure the campus network with VTP mode server and client: 1. Change the VTP mode of the DistributionA to Server.
7 DistributionA#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DistributionA(config)#vtp mode server Setting device to VTP SERVER mode DistributionA(config)#exit DistributionA# 2. Create the VLANs that are required in the domain.! Before creating VLANs DistributionA#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Gi2/0/2, Gi2/0/3, Gi2/0/4 Gi2/0/6, Gi2/0/7, Gi2/0/8 Gi2/0/11, Gi2/0/12, Gi2/0/13 Gi2/0/14, Gi2/0/15, Gi2/0/16 Gi2/0/17, Gi2/0/18, Gi2/0/19 Gi2/0/20, Gi2/0/21, Gi2/0/22 10 VLAN0010 active Gi2/0/23 11 VLAN0011 active Gi2/0/ fddi default act/unsup 1003 token ring default act/unsup 1004 fddinet default act/unsup 1005 trnet default act/unsup VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 1 enet enet enet fddi tr srb 0 0! Creating required VLANs DistributionA#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DistributionA(config)#vlan 20 21,30 31,40 41 DistributionA(config vlan)#exit DistributionA(config)#exit DistributionA#! After creating VLANs DistributionA#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Gi2/0/2, Gi2/0/3, Gi2/0/4 Gi2/0/6, Gi2/0/7, Gi2/0/8 Gi2/0/11, Gi2/0/12, Gi2/0/13 Gi2/0/14, Gi2/0/15, Gi2/0/16 Gi2/0/17, Gi2/0/18, Gi2/0/19 Gi2/0/20, Gi2/0/21, Gi2/0/22 10 VLAN0010 active Gi2/0/23 11 VLAN0011 active Gi2/0/24
8 20 VLAN0020 active 21 VLAN0021 active 30 VLAN0030 active 31 VLAN0031 active 40 VLAN0040 active 41 VLAN0041 active 1002 fddi default act/unsup 1003 token ring default act/unsup 1004 fddinet default act/unsup 1005 trnet default act/unsup VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 3. If no new VLANs are to be configured, create a dummy VLAN. This increases the Configuration Revision to '1', which enables the VLAN database to propagate throughout the network. DistributionA#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DistributionA(config)#vlan 100 DistributionA(config vlan)#name dummy DistributionA(config vlan)#exit DistributionA(config)#exit DistributionA# Change the VTP mode of DistributionB to Client, followed by AccessA and AccessB. DistributionB#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DistributionB(config)#vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode. DistributionB(config)#exit DistributionB# DistributionB#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 13 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : migration VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest : 0xBD 0xA4 0x94 0xE6 0xE3 0xC7 0xA7 0x86 Configuration last modified by at :23:21 AccessB> (enable) set vtp mode client Changing VTP mode for all features VTP domain migration modified 4. Verify if all VLANs are propagated across the domain.
9 DistributionB#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Fa1/0/1, Fa1/0/3, Fa1/0/4 Fa1/0/5, Fa1/0/7, Fa1/0/8 Fa1/0/11, Fa1/0/12, Fa1/0/13 Fa1/0/14, Fa1/0/15, Fa1/0/16 Fa1/0/17, Fa1/0/18, Fa1/0/19 Fa1/0/20, Fa1/0/21, Fa1/0/22 Fa1/0/23, Fa1/0/24 10 VLAN0010 active 11 VLAN0011 active 20 VLAN0020 active Gi1/0/1 21 VLAN0021 active Gi1/0/2 30 VLAN0030 active 31 VLAN0031 active 40 VLAN0040 active 41 VLAN0041 active 1002 fddi default act/unsup 1003 token ring default act/unsup 1004 fddinet default act/unsup 1005 trnet default act/unsup AccessB> (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans 1 default active 64 2/1 2 3/1 24,3/ / VLAN0010 active VLAN0011 active VLAN0020 active VLAN0021 active VLAN0030 active VLAN0031 active VLAN0040 active 111 3/47 41 VLAN0041 active 112 3/ fddi default active token ring default active fddinet default active trnet default active 67 VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans fddi trcrf Check if any switchport is in the Inactive state. A switchport can go to Inactive state if the VLAN configured for that switchport does not exist in the switch. Create appropriate VLAN(s), as required, in the VTP server switch.
10 From the output of the show interfaces switchport command, you can determine if a switchport is in Inactive mode if it has the Inactive keyword for the Access Mode VLAN attribute. DistributionB#show interfaces switchport Name: Fa1/0/1 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL! Part of output elided. Name: Fa1/0/24 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 50 (Inactive) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL Protected: false Unknown unicast blocked: disabled Create the VLAN 50 in the VTP server switch (DistributionA). DistributionA#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DistributionA(config)#vlan 50
11 DistributionA(config vlan)#name Vlan50 DistributionA(config vlan)#end DistributionA#! Verify the switchport status in the DistributionB switch. DistributionB#show interfaces fa1/0/24 switchport Name: Fa1/0/24 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 50 (Vlan50) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL 6. Change the VTP mode of the DistributionB switch to Server. The VTP server switch(es) must have the same configuration revision number, and must be the highest in the VTP domain. Add a Switch to the VTP Domain A recently added switch can cause problems in the network. It can be a switch that was previously used in the lab, and a good VTP domain name was entered. The switch was configured as a VTP client and was connected to the rest of the network. Then, you brought the trunk link up to the rest of the network. In just a few seconds, the whole network can go down. If the configuration revision number of the switch that you inserted is higher than the configuration revision number of the VTP domain, it propagates its VLAN database through the VTP domain. This occurs whether the switch is a VTP client or a VTP server. A VTP client can erase VLAN information on a VTP server. You can tell this has occurred when many of the ports in your network go into the Inactive state but continue to assign to a nonexistent VLAN. Note: Refer to Flash Animation: VTP for a demonstration of this problem. Complete these steps in order to avoid this issue when you add a switch to the network:
12 1. Before you connect the new switch to the network, change the VTP mode of the switch to Transparent. This resets the Configuration Revision number to zero ('0'). 2. Connect the switch to the network and configure the appropriate trunk links. 3. Configure the VTP attributes: a. Configure the VTP domain name to match the VTP domain name of the network. b. Configure the VTP version and password (if any required). 4. Change the VTP mode to Client. The Configuration Revision number is still zero ('0'). VLANs start to propagate from the VTP server(s) that exists in the network. 5. Verify if all required VLANs are available in the new switch and in the VTP servers of the network. 6. If any VLAN is missing, a quick workaround is to add it from one of the VTP servers. Refer to How a Recently Inserted Switch Can Cause Network Problems for more information. Verify There is no separate verification procedure available for this configuration. Use the verification steps provided as part of the configuration example. The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output. show vtp status []Displays the current status of the VTP domain. show vtp domain []Displays the current status of the VTP domain. show vlandisplays the VLAN information. Troubleshoot There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration. Refer to VTP Troubleshooting and Caveats for information on common issues with VTP. Related Information Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) LAN Product Support LAN Switching Technology Support Technical Support & Documentation Cisco Systems Contacts & Feedback Help Site Map Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions Privacy Statement Cookie Policy Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. Updated: Feb 02, 2007 Document ID: 81682
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98155 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP Configure VTP VTP Troubleshooting and Caveats Unable
Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98155 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP Configure VTP VTP Troubleshooting and Caveats Unable
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLAN Commands. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.x (Catalyst 3650 Switches) 1
 client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
VLAN. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 3850 Switches) 1
 clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98154 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP VTP Configuration Guidelines VTP Configuration on Catalyst
Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98154 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP VTP Configuration Guidelines VTP Configuration on Catalyst
Table of Contents. Cisco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Document ID: 10558...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 This document contains
Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Document ID: 10558...1 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device...1 This document contains
ISP /24. Fas0/0. Fas1/0/1. Fas1/0/22 NYCORE1. Cisco PS. Fas0/1. Lab Nic /24
 Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches
 Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches Document ID: 118736 Contributed by Meghana Tandon, Sumanth Srinath, and Vishnu Asok, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 06, 2015 Contents Introduction
Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches Document ID: 118736 Contributed by Meghana Tandon, Sumanth Srinath, and Vishnu Asok, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 06, 2015 Contents Introduction
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V
 isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Understanding VTP...2 VTP Domain Name...2
isco Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (V Table of Contents Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)...1 Contents...1 Introduction...1 Understanding VTP...2 VTP Domain Name...2
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012
 Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers.
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
Understanding and Configuring VTP
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Works CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
RealCiscoLAB.com. Multiple Spanning Tree. Topology. Objective. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH. Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST).
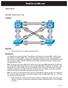 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
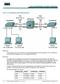 Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
CCNP Bootcamp. Introduction
 0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
PT Activity 4.3.3: Configure VTP
 Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Investigate the current configuration. Configure S1 as VTP server. Configure S2 and S3 as VTP clients. Configure VLANs on S1. Configure trunks on S1, S2, and S3. Verify
Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Investigate the current configuration. Configure S1 as VTP server. Configure S2 and S3 as VTP clients. Configure VLANs on S1. Configure trunks on S1, S2, and S3. Verify
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones
 Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Switches running the LAN Base feature set support only static routing on SVIs.
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
 24 CHAPTER Prerequisites for VTP, page 24-1 Restrictions for VTP, page 24-1 Information About VTP, page 24-2 Default Settings for VTP, page 24-9 How to Configure VTP, page 24-10 For complete syntax and
24 CHAPTER Prerequisites for VTP, page 24-1 Restrictions for VTP, page 24-1 Information About VTP, page 24-2 Default Settings for VTP, page 24-9 How to Configure VTP, page 24-10 For complete syntax and
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1
 Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Version 1 and Version 2 Work CHAPTER
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to
 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Scenario 3 3: VTP Pruning
 Scenario 3 3: VTP Pruning In the previous scenario, the list of allowed VLANs is configured manually. This configuration is static, which means that if you need to enable a previously disallowed VLAN on
Scenario 3 3: VTP Pruning In the previous scenario, the list of allowed VLANs is configured manually. This configuration is static, which means that if you need to enable a previously disallowed VLAN on
VLANs. CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter Sep-13
 VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
Using VLAN & Bridge APPENDIX
 APPENDIX I Using VLAN & Bridge The VLAN & Bridge application allows you to configure groups of ports independent of their physical location as a virtual LAN. This arrangement is called a logical grouping
APPENDIX I Using VLAN & Bridge The VLAN & Bridge application allows you to configure groups of ports independent of their physical location as a virtual LAN. This arrangement is called a logical grouping
Implement VTP. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008
 Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
VLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 VLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 29, 2013 Last Modified: June 26, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San
VLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 29, 2013 Last Modified: June 26, 2014 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 18 RAPID SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (RSTP) Objective: To configure & Verify Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) successfully
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 18 RAPID SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (RSTP) Objective: To configure & Verify Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) successfully
Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Additional Scenarios A P P E N D I X
 A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.)
 CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
CCIE Foundation. WorkBooks.com. Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP. 3550/3560 Switching. Answers
 CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
Catalyst 1900 Series and Catalyst 2820 Series Enterprise Edition Software Configuration Guide
 INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
Cisco Switch VLAN Setup (IOS)
 Summary WirelessTrakker requires that the switch ports involved for connecting the components for WirelessTrakker be 802.1q VLAN tagged / trunked ports. These directions tell you how to do that. Note:
Summary WirelessTrakker requires that the switch ports involved for connecting the components for WirelessTrakker be 802.1q VLAN tagged / trunked ports. These directions tell you how to do that. Note:
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
CHAPTER 1 LAN Design
 CHAPTER 1 LAN Design As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to scale. A network that
CHAPTER 1 LAN Design As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to scale. A network that
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches
 Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security
 Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II VTP VLAN Trucking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates
Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II VTP VLAN Trucking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates
Lab Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch
 Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
