Hytera DMR Conventional Series
|
|
|
- Walter Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Hytera DMR Conventional Series IP Multi-site Connect Application Notes Version 1.0 Date: January 28, 2011 Web: 2
3 Revision History Version Date Description Remarks R Initial release 3
4 Contents 1. Overview Definition Application Principle Version Restraint Requirements Requirements on Devices Requirements on Network References Network Architecture Four Basic Schemes Heavy Overlapping Coverage Non-overlapping Coverage Minimal Overlapping Coverage Multiple Overlapping Coverage Network Topology of IP Multi-site Connect Local Area Network Wide Area Network WAN and LAN Broadband Wireless Access Point-to-Point (PTP) and Ethernet Cable Point-to-Point (PTP) and Local Area Network (LAN) Point-to-Point (PTP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) Point-to-Point (PTP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Wide Area Network (WAN) Equipment Connection and Configuration Parameter Configurations Ethernet Cable Connection Method Configuring a Terminal
5 5.2.3 Configuring a Repeater Local Area Network (LAN) Connection Method Configuring a Terminal Configuring a Repeater LAN Configuration LAN DHCP Server Configuring the Exchange Device Wide Area Network (WAN) Connection Method Configuring a Terminal Configuring a Repeater Configuring the Exchange Device Configuring the Routing Device Broadband Wireless Access Connection Method Configuring a Terminal Configuring a Repeater Broadband Wireless Access Devices Digital Functions Supported in IP Multi-site Connect Mode FAQ
6 1. Overview 1.1 Definition IP Multi-site Connect is a function, which enables repeaters in different areas to exchange data, voice and packets over a TCP/IP-based network. 1.2 Application IP Multi-site Connect can bring users these typical benefits: 1) To connect two or more conventional communication systems in different areas. For example, you can use this function to connect two repeaters over a large geographic area. 2) To construct a more effective communication area with wider coverage For example, you can deploy multiple repeaters in a large building to ensure seamless communication. This can help fight the problems from unfavorable terrains. 3) To broadcast a message to all connected repeaters For example, the dispatcher can send an instruction to all repeaters in IP Multi-site Connect mode in case of an emergency. 4) To connect repeaters working with varied frequency bands For example, UHF repeaters and VHF repeaters can be connected so that data and voice can be exchanged among them. 5) To use multiple IP-based applications For example, when IP Multi-site Connect is enabled, you can use multiple IP-based software (such as Dispatcher) as well as API-based software developed by any third party to realize more functions. * Consult your dealer for more information on supported software. * Consult your dealer for more information on development of API-based software. 6
7 1.3 Principle 1) IP Multi-site Connect IP Multi-site Connect is designed to extend the communication coverage by connecting multiple repeaters in dispersed locations over a TCP/IP-based network. In IP Multi-site Connect mode, DMR protocol is transported by TCP/IP protocol and a Hytera-owned protocol at Application Layer. Accordingly, it is reasonable to conclude that this mode only changes the DMR transmission media without affecting the services of DMR terminals. N Sites One Repeater - Coverage IP Multi-site Connect - Coverage Figure Wider Coverage in IP Multi-site Connect Mode 2) TCP/IP Model The figure below describes how IP Multi-site Connect works: Application layer Transport layer Network layer Physical layer Hytera-owned transmission protocol TCP UDP IP ICMP Subject to specific requirements Figure TCP/IP Model Physical layer: the lowest layer of TCP/IP. Network layer: also called IP layer. It is responsible for routing IP packets. Transport layer: to set up a session between the source host and 7
8 the destination host. It consists of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Application layer: to combine and realize the function of Session Layer and Presentation Layer. It provides application-specific protocols. As can be seen from the above figure, our IP Multi-site Connect function uses UDP at Transport Layer and self-owned transmission protocol at Application Layer. At Network Layer and Physical Layer, different protocols and devices may apply depending on actual requirements. 1.4 Version 1) R3.0: to release IP Multi-site Connect for the first time; 2) R3.5: to improve IP Multi-site Connect; to release the function "Roaming" and the application "Repeater Diagnostic and Control" (RDAC); * R1.0 is designed to give a rough introduction to IP Multi-site Connect, and more information will be available after R3.5. * Consult your dealer for more information on DMR conventional series software. 1.5 Restraint The use of IP Multi-site Connect may be subject to the following conditions: 1) The repeater must operate in Digital mode; 2) The repeater configurations; 3) The network type and the configurations of network devices. 8
9 2. Requirements 2.1 Requirements on Devices 1) Repeaters (see Hytera device list for details) 2) Terminals (see Hytera device list for details) 3) Exchange devices (consult your supplier for details) 4) Routing devices (consult your supplier for details) 5) Broadband wireless access devices (consult your supplier for details) 6) Network cables 2.2 Requirements on Network 1) The IP network can either be a dedicated network or an internet provided by Internet Service Provider (ISP). 2) A number of technologies are supported by the ISPs, including dial-up, xdsl, cable modem, broadband wireless access, canopy, ISDN, satellite internet access, and so on. Currently, the IP network is not applicable to dial-up connection due to narrow bandwidth or satellite internet access due to large delay. 3) Sufficient bandwidth is required for IP network. 4) In IP network, there must be a static IP address and UDP port for Master repeater and Slave repeater. For the latter, it is unnecessary to fix its IP address and UDP port. 5) The repeater can locate behind the firewall, router or NAT. 6) IP address instead of proxy server shall be used to access the WAN. 9
10 3. References N/A 10
11 4. Network Architecture 4.1 Four Basic Schemes Heavy Overlapping Coverage In the overlapping areas, different frequencies are used, while in the non-overlapping areas, the same frequency is employed but different color codes are required for roaming service. In this scenario, a user may be in the coverage involving 3 to 4 sites at the same time, and it takes about 10 minutes to move from one site to another. TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=1 TX=F3 RX=F4 CC=3 TX=F5 RX=F6 CC=2 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=4 Figure Heavy Overlapping Coverage Non-overlapping Coverage This scheme is designed for countryside or part of a small city. It involves multiple separate sites and no overlapping coverage is present. In the non-overlapping areas, the same frequency is used while different color codes are required for roaming service. In this scenario, a user can only enjoy the coverage 11
12 from one site at the same time, and it takes several hours to move from one site to another. TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=1 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=2 TX=F3 RX=F4 CC=3 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=4 Figure Non-overlapping Coverage Minimal Overlapping Coverage This scheme is designed for communication services along the road, railway, river or coastline. It involves multiple sites and minimal overlapping coverage. The overlapped areas share a single frequency, but different color codes are required for roaming service. In this scenario, a user can enjoy the coverage involving one or two sites at the same time, and it takes about an hour to move from one site to another. 12
13 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=4 TX=F3 RX=F4 CC=3 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=2 TX=F5 RX=F6 CC=1 Figure Minimal Overlapping Coverage Multiple Overlapping Coverage This scheme is designed for a high-rise building or a deep well. It involves multiple sites standing close from each other and multiple overlapping coverage. Since the coverage of each site is limited due to adverse geology conditions, frequency reuse is seldom available, and quick signal attenuation occurs frequently. In this scenario, a user can enjoy the coverage from one or two sites at the same time, and it takes about 1 minute to move from one site to another. 13
14 TX=F1 RX=F2 CC=1 TX=F3 RX=F4 CC=2 TX=F5 RX=F6 CC=3 TX=F7 RX=F8 CC=4 Figure Multiple Overlapping Coverage 4.2 Network Topology of IP Multi-site Connect The network topology of IP Multi-site Connect can operate with many networks or can connect all Wide Area Channels (WACH) via a physical network, depending upon the repeater location and the network connection. Typically, there are two kinds of network topologies: Local area network (LAN) Wide area network (WAN) In most cases, LAN and WAN together constitute the network topology. In the following sections, details on LAN and WAN will be given respectively. * The same network configurations may apply to analog/digital repeaters, enabled/disabled repeaters, wide area/local repeaters or any device developed by a third party based on IP Multi-site Connect protocols. 14
15 4.2.1 Local Area Network In IP Multi-site Connect mode, these networks are supported: Dedicated LAN A company s LAN Dedicated radio communication system Despite variable LAN configurations, the IP Multi-site Connect network system can work properly once all devices are in the same LAN or connected to some other networks via a router or NAT. In order for the system to operate at its best, however, the technicians must have a good knowledge of bandwidth required by related devices. Additionally, only the Master repeater needs a static IPv4 address, which the other network devices can use to connect the wide area system. The following figure shows an example of IP Multi-site Connect operating with LAN. Note that the network devices may belong to different wide area systems, for example, there are multiple dispatching centers. 15
16 IP Multi-site Connect Device Network IP Multi-site Connect Device IP Multi-site Connect Device LAN IP Multi-site Connect Device IP Multi-site Connect Device IP Multi-site Connect Device Figure IP Multi-site Connect Network Operating with LAN Wide Area Network The biggest advantage of IP Multi-site Connect lies in that it can connect dispersed sites quickly through the internet provided by an ISP, which provides a range of technologies for IP Multi-site Connect: Dedicated T1 DSL (typically ADSL) Cable modem Broadband wireless access such as Canopy ISDN Frame relay others At present, the IP network is not applicable to dial-up connection due to narrow 16
17 bandwidth or satellite internet access due to large delay. In order for the system to operate at its best, the system engineering personnel must have a good knowledge of bandwidth and time delay required by related devices. In addition, a sound understanding of bandwidth and time delay between two sites is also required, especially between two distant sites. In general, the time delay of satellite access across 5 continents is unacceptable, whereas this problem does not exist with cable communication. It is necessary to note that a repeater's communication request will be sent to all other repeaters in the same system. In other words, the bandwidth required by a site correlates with the sum of repeaters in the system. When a new repeater is added, all other repeaters would require extra bandwidth. The IP Multi-site Connect network can work with many routers, NAT and firewalls. It is recommended to install the repeater behind these devices. Most routers have a useful function -- secure VPN (Virtual Private Network). The VPN will not pose a burden on the bandwidth but may result in time delay. To receive unrequested messages from other repeaters, the Master repeater needs a static IPv4 address, which the other network devices can use to connect the wide area system. Additionally, the router, NAT or firewall connecting Master repeater must be configured properly as well. The following figure shows an example of IP Multi-site Connect operating with WAN. Note that the network devices may belong to different wide area systems, for example, there are multiple dispatching centers. 17
18 IP Multi-site Connect Device Network Router IP Multi-site Connect Device Router Router IP Multi-site Connect Device WAN IP Multi-site Connect Device Router Router IP Multi-site Connect Device Router IP Multi-site Connect Device Figure IP Multi-site Connect Network Operating with WAN WAN and LAN Generally, WAN and LAN together constitute the network topology, for example, multiple remote sites or the LAN of two sites can be connected via an ISP. For WAN, its required bandwidth is related to the number of network devices in IP Multi-site Connect system, that is, the value shall be the sum of required bandwidth of each network device; for a site, since the communication request of a repeater will be sent to all other repeaters in the same system, the ISP bandwidth required for a site is the sum of all other sites bandwidth. When a new repeater is added, all other repeaters would require extra bandwidth. Similar to WAN, to receive messages from other repeaters, the Master repeater needs a static IPv4 address, which the other network devices can use to connect the wide area system. In a LAN, the repeater containing a static IP address is 18
19 deemed as the Master repeater by default. Likewise, the router, NAT or firewall connecting Master repeater must be configured properly to receive unrequested messages from other repeaters. For the IP Multi-site Connect network to work over IPv4, the routers in wide area network must support HairPinning a function that will send the source address a message indicating how to reach the destination. The following figure shows an example of IP Multi-site Connect operating with WAN and LAN. Note that the network devices may belong to different wide area systems, for example, there are multiple dispatching centers. IP Multi-site Connect Device Network Router IP Multi-site Connect Device IP Multi-site Connect Device LAN 广域网 WAN LAN Router Router IP Multi-site Connect Device IP Multi-site Connect Device Router IP Multi-site Connect Device Figure IP Multi-site Connect Network System Operating with WAN and LAN WAN. Note: the number of IP devices has an impact on the bandwidth requirement of 19
20 4.3 Broadband Wireless Access IP Multi-site Connect provides a number of schemes for broadband wireless access to meet your actual needs. The typical schemes are illustrated as below. * You can contact your dealer for more information on how to use broadband wireless access devices (PTP, PMP SM, PMP AP, etc) Point-to-Point (PTP) and Ethernet Cable Figure By Point-to-Point (PTP) and Ethernet Cable Point-to-Point (PTP) and Local Area Network (LAN) 20
21 Figure By Point-to-Point (PTP) and Local Area Network (LAN) Point-to-Point (PTP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) Figure By Point-to-Point (PTP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) 21
22 4.3.4 Point-to-Point (PTP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) LAN2 WAN LAN1 Figure By Point-to-Point (PTP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) IP Invalid API SW 1 Slave Repeater2 PMP AP Device DHCP Service DHCP Service WACH1 WACH2 Tx Rx LAN2 WAN LAN1 PMP SM Device PMP SM Device Router Router API SW 2 Tx WACH1 Tx WACH1 Rx WACH2 Rx WACH2 Master Repeater Slave Repeater1 Figure By Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) and Wide Area Network (WAN) 22
23 4.3.6 Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) IP Valid IP Valid PMP AP Device PMP AP Device PMP SM Device PMP SM Device PMP SM Device PMP SM Device API SW 1 Tx Rx WACH1 WACH2 API SW 2 Tx Rx WACH1 WACH2 Master Repeater Slave Repeater Figure Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Local Area Network (LAN) Point-to-Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Wide Area Network (WAN) LAN2 LAN1 WAN Figure Point-to- Multipoint (PMP) Cluster and Wide Area Network (WAN) 23
24 5. Equipment Connection and Configuration 5.1 Parameter Configurations The appropriate configuration scheme shall be selected on the basis of network topology and the actual application. In general, the involved parameters include: 1) Terminal parameters 2) Repeater parameters 3) Routing parameters 4) Broadband wireless access parameters * Routing devices contain firewall, NAT, router and etc. You can contact your dealer for their specific configurations. * Broadband wireless access devices include Canopy and etc. You can contact your dealer for their specific configurations. 5.2 Ethernet Cable Connection Method An Ethernet cable is required to connect two repeaters in this scheme. The disadvantage of the scheme lies in poor expandability. 24
25 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal B Terminal A IP Multi-site Connect Rpt IP Multi-site Connect Rpt Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Repeater Repeater Ethernet Cable Figure Ethernet Cable Connection Configuring a Terminal A terminal may be a portable radio or mobile radio. Please refer to Hytera DMR Conventional Series Terminal List. You can contact your dealer for details. As the terminal works the same way in both IP Multi-site Connect mode and single repeater mode, you can refer to the parameter settings in the single repeater mode to configure it. To configure a terminal, do as follows: 1) Configure the settings applicable to single repeater mode. 2) Do define the Slot Operation option; otherwise, the terminal only operates in DM mode. For the terminal and repeater, ensure that the same slot must be selected in the configuration. For example: 2.1) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 2 for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.2) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 or Slot 2 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to None for the repeater, the 25
26 terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.3) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 1 or Slot1&Slot2 for the repeater, the terminal can operate in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 3) The Color Code for the terminal must be consistent with the current repeater. Otherwise, the terminal can not work in the system. Figure Time Slot and Color Code Configuration Configuring a Repeater The simplest IP Multi-site Connect network can be established by connecting two repeaters back to back. In other words, you can use an Ethernet cable to connect two repeaters directly. Generally, this scheme is used for cross-band communication or network service demonstration. To configure a Master repeater, do as follows: 1) Run the CPS and read the existing configuration data. 26
27 Figure Setting ID for the Master Repeater 2) Go to General Setting->IP Multi-site Network, and set the Repeater Type option to IP Multi-site Master.(See Figure ) 3) Leave the Authentication Key field at its default values. 4) Be sure that the DHCP option is not selected. Input static values for the Ethernet IP, Gateway IP, and Netmask. As for all repeaters in the system, the Ethernet IP and gateway IP shall share the same network address ( ). (See Figure ) Ethernet IP ( ): The Master repeater s static address must be unique in the system. Gateway IP ( ): this defines an abstract gateway address. There is no gateway for this configuration, but it is necessary to define an abstract address. The address must be unique and it is highly recommended that the last digit should not be set to 0. Netmask: it defines the IP addresses range x (x=0-255). 27
28 Figure Setting IP Multi-site Network Parameters for the Master Repeater 5) Leave the IP Multi-site UDP Port and P2P Firewall Open Timer (sec) at their default values. 6) Go to Channel->Digital Channel->CH D1->IP Multi-site Connect, and choose the desired slot from the dropdown list. Then, the corresponding slot works as a wide area channel. Fig Setting IP Multi-site Connect for the Master Repeater 7) Finally write the new configuration data into the Master repeater via CPS. To configure a Slave repeater, do as follows: 1) Run the CPS and read the existing configuration data. 28
29 Figure Setting ID for the Slave Repeater 2) Go to General Setting->IP Multi-site Network, and set the Repeater Type option to IP Multi-site Slave.(See Figure ) 3) Leave the Authentication Key field at its default values. 4) Configure the Master IP, Master UDP port and Ethernet IP address in accord with the Master repeater. 5) Be sure that the DHCP option is not selected. 6) The proper static values must be entered for the Ethernet IP, Gateway IP and Netmask, making it possible to share the same subnet with Master repeater. (See Figure ) Ethernet IP ( ): The Slave repeater s static address must be unique in the system. Gateway IP ( ): Configured in accordance with the Master repeater. Netmask: Configured in accordance with the Master repeater. 7) Leave the IP Site UDP Port and P2P Firewall Open Timer (sec) at their default values. 8) Leave the Jitter Buffer Length at the default value. Its definition is given in the help file of CPS supplied by Hytera. Only qualified technicians are allowed to change this parameter. 29
30 Fig Setting IP Multi-site Network Parameters for the Slave Repeater 9) Go to Channel->Digital Channel->CH D1->IP Multi-site Connect, and choose the desired slot from the dropdown list. Then, the corresponding slot works as a wide area channel. Figure Setting IP Multi-site Connect for the Slave Repeater 10) Finally write the new configuration data into the Slave repeater via CPS. 5.3 Local Area Network (LAN) Connection Method This scheme is used to connect a switch or multiple switches within the LAN, achieving seamless communication in the same area. 30
31 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal B Repeater Terminal A Repeater IP Multi-site Con. Rpt Switch Switch IP Multi-site Con. Rpt Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Cable Repeater Cable Cable Repeater Slot Operation Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal C Terminal D Figure Local Area Network Connection Configuring a Terminal A terminal means a portable radio or mobile radio. Please refer to Hytera DMR Conventional Series Terminal List. You can contact your dealer for details. As the terminal works the same way in both IP Multi-site Connect mode and single repeater mode, you can refer to the parameter settings in single repeater mode to configure it. To configure a terminal, do as follows: 1) Configure the settings applicable to single repeater mode. 2) Do define the Slot Operation option; otherwise, the terminal only works in DM mode. For the terminal and repeater, ensure that the same slot must be selected in the configuration. For example: 2.1) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 2 for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 31
32 2.2) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 or Slot 2 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to None for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.3) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 1 or Slot1&Slot2 for the repeater, the terminal can operate in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 3) The Color Code for the terminal must be consistent with the current repeater. Otherwise, the terminal can not work in the system. Figure Setting Slot Operation and Color Code Configuring a Repeater LAN Configuration Adopting the Back to Back configuration, IP Multi-site Connect in the LAN can be achieved by a switch. The advantage of this scheme is that more IP access devices, Repeater Diagnostic and Control (RDAC) applications and PC applications can be added to the system. In addition, it is useful for explaining network topologies. There is no DHCP server and Gateway for this LAN configuration. Thus the configuration is consistent with that of Ethernet Cable. However, the following points should be taken into account. 32
33 1) The same Authentication Key must be specified for all repeaters and RDAC applications in the system. Note: RDAC will be released in R3.5. You can contact your dealer for more information. 2) Go to General Setting->IP Multi-site Network, and input the same value in the Authentication Key field for the Master repeater and the Salve repeater. Figure Setting Authentication Key 3) If a repeater is to be added to an existing LAN, its Ethernet IP, Gateway IP and netmask must work with all devices in LAN properly. Refer to for more details about how to create a new LAN or private network. 4) Refer to for more details about how to configure IP Multi-site Connect LAN DHCP Server A DHCP server is introduced to the IP Multi-site Connect system within the LAN. The configuration is consistent with that of LAN Configuration ; however the following points should be taken into account. 1) A static IP address shall be assigned to the Master repeater in the system, while the IP addresses for other Slave repeaters and RDAC applications shall be allocated by the DHCP server dynamically. 2) Any static IP address assigned to an IP site must be outside the range of dynamic IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server, but within the range of IP address for the subnet. 33
34 3) The IP address for the Slave repeater shall be assigned dynamically as shown in figure Figure Setting DHCP Configuring the Exchange Device The configuration depends on the type of exchange devices. Please consult your dealer for more information on their configurations! 5.4 Wide Area Network (WAN) Connection Method This scheme is used to connect multiple sites across different areas. The key to this scheme is the routing device, which can link with multiple repeaters in different locations to achieve IP Multi-site Connect in the WAN. * Routing devices include firewall, NAT, router and etc. 34
35 LAN1 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal B Repeater Cable Switch Router LAN2 Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal A Repeater Cable IP Multi-site Con. Rpt WAN IP Multi-site Con. Rpt Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Cable Router Repeater Cable Repeater Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal C Switch Figure WAN Connection Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal D Configuring a Terminal * A terminal means a portable radio or mobile radio. Please refer to Hytera DMR Conventional Series Terminal List. You can contact your dealer for details. As the terminal works the same way in both IP Multi-site Connect mode and single repeater mode, you can refer to the parameter settings in single repeater mode to configure it. To configure a terminal, do as follows: 1) Configure the settings applicable to single repeater mode. 2) Do define the Slot Operation option; otherwise, the terminal only works in DM mode. For the terminal and repeater, ensure that the same slot must be selected in the configuration. For example: 2.1) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 2 for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.2) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 or Slot 2 for the 35
36 terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to None for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.3) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 1 or Slot1&Slot2 for the repeater, the terminal can operate in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 3) The Color Code for the terminal must be consistent with the current repeater. Otherwise, the terminal can not work in the system. Figure Setting Slot Operation and Color Code Configuring a Repeater As usual, the IP Multi-site Connect system contains many Wide Area Networks and Local Area Networks linked by routers. The public network is a typical example, which is capable of connecting many LANs to the WAN by ADSL. In the above system, the IP address for the Master repeater is assigned to LAN1 statically, as the following figure shows. 36
37 Figure Setting IP Address for the Master Repeater The Ethernet IP (e.g. the Master repeater s IP address) is beyond the range of IP addresses assigned by the DHCP Server, but still within the range of IP addresses for the subnet (as specified by the Gateway Netmask for the devices on the LAN). Thus the Gateway IP address shall conform to the LAN1 IP address of the router. As a result, all Slave repeater and RDAC applications shall get the IP address assigned by their respective LAN DHCP servers. Figure Assigning IP Address by the DHCP Server The WAN address used by the Master repeater must be shared by all Slave repeaters and RDAC applications. Figure Setting the WAN Address for the Slave Repeater When configuring the Slave repeaters and RDAC application, the WAN address of router in LAN 1 shall be applied to the IP address field of Master repeater, because the IP addresses of all devices are configured within the router netmask, so they can not be identified in the WAN. Thus, Port Forwarding must be 37
38 configured for all LAN1 routers, forwarding the incoming packet from the defined port of the WAN to the Master repeater. In the current configuration, the UDP port in the WAN is the same as in the Master repeater. In reality, different UDP ports can be defined to the WAN and the Master repeater, as long as all Slave repeaters and RDAC applications share the same port in the WAN. The following points should be taken into account in this configuration: 1)Do not configure "Port Forwarding" for the Slave repeater and RDAC applications, since their routers can perform it automatically. 2) The public IP addresses for all Slave repeaters and RDAC applications are notified by the Master repeater upon connecting the Slave repeaters. 3) The Slave repeaters on a certain LAN do not need to be configured with same UDP port, as the router will distribute a unique port during forwarding. 4) The public IP address and port assigned by the router to a given Slave repeater will be taken back if they are not in use within a pre-defined time limit. In this case, all Slave repeaters and RDAC applications must transmit Keep Alive message regularly. The frequency for transmitting such messages can be set in the P2P Firewall Open Timer (sec) field. Make sure that the value of this field is less than the duration which the router keeps alive. Figure Setting P2P Firewall Open Timer (sec) 5) The IP address of the Master repeater must be configured into the WAN address rather than the LAN address, as for all Slave repeaters and RDAC applications on the Master repeater s LAN. Otherwise, repeaters from other LANs can not link with RDAC applications. 6) The LAN 1 and LAN 2 routers must support HairPinning, which ensures that the WAN address can not be replaced by the subnet address. 7) Some routers that support partial HairPinning may not support all repeaters and RDAC applications on the Master repeater s LAN. But they can still support other repeaters and RDAC applications, which are not in the same LAN as 38
39 the Master repeater 8) The Delay will be introduced by the IP network. 9) The detailed configuration of IP Multi-site Connect is shown in Figure Note: not all routers are able to support Port Forwarding. Figure Setting IP Multi-site Network 10) Some private network (e.g. Intranets) is capable of addressing all devices by their IP addresses. When a device is connected to this network, the DHCP server will assign the IP address to it and adjust the router to map the packet to the appropriate Master repeater. Meanwhile, a static IP address is required for the Master repeater Configuring the Exchange Device The configuration varies greatly according to different exchange devices. Please consult your dealer for more information on configurations! Configuring the Routing Device The configuration varies greatly according to different routing devices. Please consult your dealer for more information on the specific configuration! 39
40 5.5 Broadband Wireless Access Connection Method This scheme is used to link multiple sites across areas. The key to this solution is that broadband wireless access devices and Canopy are employed to facilitate the communication of multiple repeaters in dispersed locations. For instance, communication can be achieved by means of the wireless link including microwave, WiFi, 3G and 4G. It is an ideal solution for emergency communication. Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal B BWA Device Repeater Slot Operation Slot1 or Slot2 Terminal A IP Multi-site Con. Rpt IP Multi-site Con. Rpt Cable Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config Slot1(and/or)Slot2 Config BWA Device Cable Repeater Figure Broadband Wireless Access Configuring a Terminal A terminal means a portable radio or mobile radio. Please refer to Hytera DMR Conventional Series Terminal List. You can contact your dealer for details. As the terminal works the same way in both IP Multi-site Connect mode and single repeater mode, you can refer to the parameter settings in single repeater mode to configure it. To configure a terminal, do as follows: 1) Configure the settings applicable to single repeater mode. 2) Do define the Slot Operation option; otherwise, the terminal only 40
41 works in DM mode. Ensure that the same slot must be specified for the terminal and repeater in the system. For example: 2.1) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 2 for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.2) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 or Slot 2 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to None for the repeater, the terminal only operates in single repeater mode rather than in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 2.3) If the Slot Operation option is set to Slot 1 for the terminal and IP Multi-site Connect to Slot 1 or Slot1&Slot2 for the repeater, the terminal can operate in IP Multi-site Connect mode. 3) The Color Code for the terminal must be consistent with the current repeater. Otherwise, the terminal can not work in the system. Figure Slot Operation and Color Code Configuring a Repeater The repeater is configured as per the specific network used in broadband wireless access mode. For further details, refer to Ethernet Cable, Local Area Network and Wide Area Network. If you have any question, please contact your dealer. 41
42 5.5.4 Broadband Wireless Access Devices The configuration varies greatly according to different broadband wireless access devices. Please consult your dealer for more information on configurations! 42
43 6. Digital Functions Supported in IP Multi-site Connect Mode Terminals (portable radio and mobile radio) are capable of providing a set of digital services (R3.0) in IP Multi-site Connect mode, as the following table shows. Functions Voice Service Supplementary Service Data Service Emergency Service Other Functions Private Call PTT ID and Alias Message Emergency Alarm Dual WACH (Slot1 & Slot 2) Group Call Radio Enable/ Radio Disable *GPS Emergency Call WACH and LACH All Call Remote Monitor *API Radio Check Emergency Alarm w/call Revert Channel Basic and Full Encryption Pseudo Trunking Alert Call Lone Worker Time-out Timer (TOT) Man Down *Scan The specific function is subject to the software version. * : indicates that the function is partially available at present. For more information, please consult your dealer. Table 6-1 Digital Functions Supported in IP Multi-site Connect Mode 43
44 7. FAQ 7.1 How is the system capacity in IP Multi-site Connect network? At present, the IP Multi-site Connect network supports up to 15 repeaters. If you want to add more repeaters to this network, it is required to improve the hardware performance of the operational devices. Otherwise, the data can not be transmitted to all repeaters within the defined time. Since the number of terminals available in IP Multi-site Connect mode and single repeater mode is the same, the former only extends the coverage but does not increase the call capacity. 7.2 Can other repeaters work normally when one of the repeaters fails? Yes. The entire network is similar to a peer-to-peer network. The Master repeater is used for registration and broadcasting address. If a Slave repeater disconnects, the Master repeater can detect and broadcast it to other Slave repeaters; if the Master repeater disconnects, all Slave repeaters still can work. However, new address can not be added and the status of other repeaters can not be acquired until the Master repeater restores to normal operation. 7.3 How to select frequency and color code in IP Multi-site Connect network? You can select the proper networking scheme as per your actual needs, as stated in section 4.1. In the overlapping area, it is recommended that the frequency of the repeater be different, but the color code can be the same or varied. For adjacent repeaters sharing the same frequency, it is better to use different color code to avoid probable interference. 44
45 7.4 What is the difference between IP Multi-site Connect network system and simulcast system? 1) In a simulcast system, the exchange center or server is a must, which is used to receive and transmit data and time sequence. And the repeater acts as a transceiver. Therefore, the exchange center or server shall be available at any time, and a hot backup is required If necessary. For IP Multi-site Connect network, there is no independent exchange center or server. One repeater operates as the master one and other repeaters as the slave ones. Each works independently. 2) The simulcast system is capable of time sequence synchronization, enabling the transceiver to use the same frequency in overlapping area, but in IP Multi-site Connect network, different repeaters shall use different frequencies to achieve quality communication. 3) At present, the IP Multi-site Connect network supports 15 repeaters at most, while the simulcast system has no limit on the number of repeaters. 7.5 How to upgrade a single repeater system to IP Multi-site Connect network system? Terminals (portable radio and mobile radio) in single site mode can communicate with those in IP Multi-site Connect mode. If you want to upgrade the single repeater system, you just need to upgrade the existing software and configure all parameters again for the repeater and terminal. The API application configured for the terminal in single repeater system can work normally in IP Multi-site Network without update. 7.6 What factors shall be considered when establishing an IP Multi-site Connect network? The network establishment and configuration are determined by the devices 45
46 and IP network. You d better get help from the network administrator due to the complicate networking environments. Some common factors are listed below: 1) Ensure that there is no conflicting IP address, which can break off communication. If the DHCP option is selected, the static IP address might as well be outside the range of the addresses which are available to be allocated. It can avoid the conflicting address assigned by the DHCP server. 2) The Quality of Service (QoS) can be introduced to the router in the Ethernet network to assure you quality communication, provided that there are other networking devices acting as IP networking ones in IP Multi-site Connect network. In addition, it is necessary to enhance the communication priority and reserve adequate bandwidth. 3) Be sure that the UDP port is free from restriction of the firewall. Otherwise, it can block the IP address or the UDP port operated in IP network. For more information, please consult the local network administrator or ISP. 4) It is better to choose an ISP who can provide unlimited traffic services, because the voice transmission over internet may lead to heavy traffic. For an IP Multi-site Connect network containing 5/15 repeaters, 20/65 GB traffic is required per month. 46
DMR Conventional Radio. SIP Phone Application Notes
 DMR Conventional Radio SIP Phone Application Notes Copyright Information Hytera is the trademark or registered trademark of Hytera Communications Corporation Limited (the Company) in PRC and/or other countries
DMR Conventional Radio SIP Phone Application Notes Copyright Information Hytera is the trademark or registered trademark of Hytera Communications Corporation Limited (the Company) in PRC and/or other countries
Q-Balancer Range FAQ The Q-Balance LB Series General Sales FAQ
 Q-Balancer Range FAQ The Q-Balance LB Series The Q-Balance Balance Series is designed for Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to provide cost-effective solutions for link resilience and load balancing
Q-Balancer Range FAQ The Q-Balance LB Series The Q-Balance Balance Series is designed for Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to provide cost-effective solutions for link resilience and load balancing
Hytera DMR Conventional Series
 Hytera DMR Conventional Series Repeater Diagnostics And Control Application Notes Version 1.0 Date: June 15, 2011 Web: http://www.hytera.com Copyright Information Hytera is the trademark or registered
Hytera DMR Conventional Series Repeater Diagnostics And Control Application Notes Version 1.0 Date: June 15, 2011 Web: http://www.hytera.com Copyright Information Hytera is the trademark or registered
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Chapter 7 LAN Configuration
 Chapter 7 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Wireless ADSL Modem VPN Firewall Router. These features can be found by selecting Network Configuration
Chapter 7 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Wireless ADSL Modem VPN Firewall Router. These features can be found by selecting Network Configuration
31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers
 31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers CONTENTS Focus Questions... 2 Chapter 1: Explore the Network... 2 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System... 5 Chapter 3: Network
31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers CONTENTS Focus Questions... 2 Chapter 1: Explore the Network... 2 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System... 5 Chapter 3: Network
Microsoft Exam
 Volume: 176 Questions Question No: 1 One advantage of dynamic routing is that it: A. Automatically maintains routing tables. B. Limits traffic derived from routing protocols. C. Reduces broadcast traffic.
Volume: 176 Questions Question No: 1 One advantage of dynamic routing is that it: A. Automatically maintains routing tables. B. Limits traffic derived from routing protocols. C. Reduces broadcast traffic.
DRG-Series. Digital Radio Gateway. Hytera DMR IP (Tier-2) Digital Radio Supplement
 DRG-Series Digital Radio Gateway Hytera DMR IP (Tier-2) Digital Radio Supplement DRG-Series Digital Radio Gateway Hytera DMR IP (Tier-2) Digital Radio Supplement 2017 Omnitronics Pty Ltd. All rights reserved.
DRG-Series Digital Radio Gateway Hytera DMR IP (Tier-2) Digital Radio Supplement DRG-Series Digital Radio Gateway Hytera DMR IP (Tier-2) Digital Radio Supplement 2017 Omnitronics Pty Ltd. All rights reserved.
Barracuda Link Balancer
 Barracuda Networks Technical Documentation Barracuda Link Balancer Administrator s Guide Version 2.3 RECLAIM YOUR NETWORK Copyright Notice Copyright 2004-2011, Barracuda Networks www.barracuda.com v2.3-111215-01-1215
Barracuda Networks Technical Documentation Barracuda Link Balancer Administrator s Guide Version 2.3 RECLAIM YOUR NETWORK Copyright Notice Copyright 2004-2011, Barracuda Networks www.barracuda.com v2.3-111215-01-1215
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration
 Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure LAN Setup, LAN Groups and Routing (Static IP) features of your ProSafe VPN Firewall 50. These features can be found under the Network
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure LAN Setup, LAN Groups and Routing (Static IP) features of your ProSafe VPN Firewall 50. These features can be found under the Network
UIP1869V User Interface Guide
 UIP1869V User Interface Guide (Firmware version 0.1.8 and later) Table of Contents Opening the UIP1869V's Configuration Utility... 3 Connecting to Your Broadband Modem... 5 Setting up with DHCP... 5 Updating
UIP1869V User Interface Guide (Firmware version 0.1.8 and later) Table of Contents Opening the UIP1869V's Configuration Utility... 3 Connecting to Your Broadband Modem... 5 Setting up with DHCP... 5 Updating
User Guide TL-R470T+/TL-R480T REV9.0.2
 User Guide TL-R470T+/TL-R480T+ 1910012468 REV9.0.2 September 2018 CONTENTS About This Guide Intended Readers... 1 Conventions... 1 More Information... 1 Accessing the Router Overview... 3 Web Interface
User Guide TL-R470T+/TL-R480T+ 1910012468 REV9.0.2 September 2018 CONTENTS About This Guide Intended Readers... 1 Conventions... 1 More Information... 1 Accessing the Router Overview... 3 Web Interface
DPX8000 Series Deep Service Switching Gateway User Configuration Guide BRAS Service Board Module v1.0
 DPX8000 Series Deep Service Switching Gateway User Configuration Guide BRAS Service Board Module v1.0 i Hangzhou DPtech Technologies Co., Ltd. provides full- range technical support. If you need any help,
DPX8000 Series Deep Service Switching Gateway User Configuration Guide BRAS Service Board Module v1.0 i Hangzhou DPtech Technologies Co., Ltd. provides full- range technical support. If you need any help,
FAQ Guide. i-mo 310 & 540 Series Bonding Routers. FAQ Guide. for the i-mo 310 & 540 Series Appliances
 FAQ Guide i-mo 310 & 540 Series Bonding Routers FAQ Guide for the i-mo 310 & 540 Series Appliances Content Content... 2 i-mo OptiBond - answers to frequently asked questions.... 4 How many cellular links
FAQ Guide i-mo 310 & 540 Series Bonding Routers FAQ Guide for the i-mo 310 & 540 Series Appliances Content Content... 2 i-mo OptiBond - answers to frequently asked questions.... 4 How many cellular links
Configuration Guide TL-ER5120/TL-ER6020/TL-ER REV3.0.0
 Configuration Guide TL-ER5120/TL-ER6020/TL-ER6120 1910012186 REV3.0.0 June 2017 CONTENTS About This Guide Intended Readers... 1 Conventions... 1 More Information... 1 Viewing Status Information... 2 System
Configuration Guide TL-ER5120/TL-ER6020/TL-ER6120 1910012186 REV3.0.0 June 2017 CONTENTS About This Guide Intended Readers... 1 Conventions... 1 More Information... 1 Viewing Status Information... 2 System
MTA_98-366_Vindicator930
 MTA_98-366_Vindicator930 Number: 98-366 Passing Score: 700 Time Limit: 45 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft Technology Associate Networking Fundamentals MTA 98-366 Exam A QUESTION
MTA_98-366_Vindicator930 Number: 98-366 Passing Score: 700 Time Limit: 45 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft Technology Associate Networking Fundamentals MTA 98-366 Exam A QUESTION
MRD-310 MRD G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide. Web configuration reference guide
 Web configuration reference guide 6623-3201 MRD-310 MRD-330 Westermo Teleindustri AB 2008 3G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide www.westermo.com Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration...
Web configuration reference guide 6623-3201 MRD-310 MRD-330 Westermo Teleindustri AB 2008 3G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide www.westermo.com Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration...
Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID:
 69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
User Manual. SSV Remote Access Gateway. Web ConfigTool
 SSV Remote Access Gateway Web ConfigTool User Manual SSV Software Systems GmbH Dünenweg 5 D-30419 Hannover Phone: +49 (0)511/40 000-0 Fax: +49 (0)511/40 000-40 E-mail: sales@ssv-embedded.de Document Revision:
SSV Remote Access Gateway Web ConfigTool User Manual SSV Software Systems GmbH Dünenweg 5 D-30419 Hannover Phone: +49 (0)511/40 000-0 Fax: +49 (0)511/40 000-40 E-mail: sales@ssv-embedded.de Document Revision:
WiNG 5.x How-To Guide
 WiNG 5.x How-To Guide Tunneling Remote Traffic using L2TPv3 Part No. TME-08-2012-01 Rev. A MOTOROLA, MOTO, MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS and the Stylized M Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Motorola
WiNG 5.x How-To Guide Tunneling Remote Traffic using L2TPv3 Part No. TME-08-2012-01 Rev. A MOTOROLA, MOTO, MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS and the Stylized M Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Motorola
Internet BroadBand Router
 Internet BroadBand Router 4 Port / 7 Port / 8 Port User Guide Doc. No.: 032102-01 Table of Content INTRODUCTION... 1 APPLICATIONS:... 1 HARDWARE INSTALLATION... 2 HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:... 2 PARTS NAMES
Internet BroadBand Router 4 Port / 7 Port / 8 Port User Guide Doc. No.: 032102-01 Table of Content INTRODUCTION... 1 APPLICATIONS:... 1 HARDWARE INSTALLATION... 2 HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:... 2 PARTS NAMES
Requirements and best practices for enabling Enhanced PTT over Wi-Fi networks
 Requirements and best practices for enabling Enhanced PTT over Wi-Fi networks The following guide is intended for users of Enhanced PTT to ensure that their Wi-Fi networks meet minimum requirements for
Requirements and best practices for enabling Enhanced PTT over Wi-Fi networks The following guide is intended for users of Enhanced PTT to ensure that their Wi-Fi networks meet minimum requirements for
DMR Conventional Series, Release Note R5.5
 DMR Conventional Series, Release Note R5.5 Sofware Version 5.05 Document Version 5.05.14 Software Release Date: 15-10-2013 Release Note 5-5_ENG V1.04 2013 Hytera Mobilfunk GmbH 31848 Bad Münder, Germany
DMR Conventional Series, Release Note R5.5 Sofware Version 5.05 Document Version 5.05.14 Software Release Date: 15-10-2013 Release Note 5-5_ENG V1.04 2013 Hytera Mobilfunk GmbH 31848 Bad Münder, Germany
Huawei GB Design Enterprise-level Networks. Download Full Version :
 Huawei GB0-360 Design Enterprise-level Networks Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/gb0-360 QUESTION: 387 The cable for cabled TV signals can be used to provide high bandwidth
Huawei GB0-360 Design Enterprise-level Networks Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/gb0-360 QUESTION: 387 The cable for cabled TV signals can be used to provide high bandwidth
Wireless Router at Home
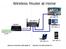 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless a CPE User Manual
 NOTICE Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user's authority to operate the equipment. Company has an on-going policy
NOTICE Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user's authority to operate the equipment. Company has an on-going policy
1100 Dexter Avenue N Seattle, WA NetMotion Mobility Architecture A Look Under the Hood
 TM 1100 Dexter Avenue N Seattle, WA 98109 206.691.5555 www.netmotionwireless.com NetMotion Mobility Architecture A Look Under the Hood NetMotion Mobility Architecture A Look Under the Hood Wireless networking
TM 1100 Dexter Avenue N Seattle, WA 98109 206.691.5555 www.netmotionwireless.com NetMotion Mobility Architecture A Look Under the Hood NetMotion Mobility Architecture A Look Under the Hood Wireless networking
Network Configuration Guide
 Cloud VoIP Network Configuration PURPOSE This document outlines the recommended VoIP configuration settings for customer provided Firewalls and internet bandwidth requirements to support Mitel phones.
Cloud VoIP Network Configuration PURPOSE This document outlines the recommended VoIP configuration settings for customer provided Firewalls and internet bandwidth requirements to support Mitel phones.
TRBOnet Enterprise. MOTOTRBO Link. Deployment Guide. Internet. US Office Neocom Software Jog Road, Suite 202 Delray Beach, FL 33446, USA
 TRBOnet Enterprise MOTOTRBO Link Deployment Guide World HQ Neocom Software 8th Line 29, Vasilyevsky Island St. Petersburg, 199004, Russia US Office Neocom Software 15200 Jog Road, Suite 202 Delray Beach,
TRBOnet Enterprise MOTOTRBO Link Deployment Guide World HQ Neocom Software 8th Line 29, Vasilyevsky Island St. Petersburg, 199004, Russia US Office Neocom Software 15200 Jog Road, Suite 202 Delray Beach,
Vigor2910 Dual-WAN Security Router User s Guide
 Vigor2910 Dual-WAN Security Router User s Guide Version: 2.1 Date: 2006/8/15 Copyright 2006 All rights reserved. This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No part may be reproduced,
Vigor2910 Dual-WAN Security Router User s Guide Version: 2.1 Date: 2006/8/15 Copyright 2006 All rights reserved. This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No part may be reproduced,
INTRODUCTION. What You Need to Read. What this LANbook Covers
 Qwest DSLSM LANbook INTRODUCTION What You Need to Read If you are self-installing Qwest DSL on a local area network in your home or business, start with Chapter 1: Welcome to the Qwest DSL LANbook on page
Qwest DSLSM LANbook INTRODUCTION What You Need to Read If you are self-installing Qwest DSL on a local area network in your home or business, start with Chapter 1: Welcome to the Qwest DSL LANbook on page
Light Mesh AP. User s Guide. 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft
 Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Configuring High Availability (HA)
 4 CHAPTER This chapter covers the following topics: Adding High Availability Cisco NAC Appliance To Your Network, page 4-1 Installing a Clean Access Manager High Availability Pair, page 4-3 Installing
4 CHAPTER This chapter covers the following topics: Adding High Availability Cisco NAC Appliance To Your Network, page 4-1 Installing a Clean Access Manager High Availability Pair, page 4-3 Installing
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005
 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
 CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
Standalone DVR User s Manual. Figure 4-81
 Figure 4-81 4.11.2 Network 4.11.2.1 TCP/IP The single network adapter interface is shown as in Figure 4-82 and the dual network adapters interface is shown as in Figure 4-83 Network Mode : Includes multiple
Figure 4-81 4.11.2 Network 4.11.2.1 TCP/IP The single network adapter interface is shown as in Figure 4-82 and the dual network adapters interface is shown as in Figure 4-83 Network Mode : Includes multiple
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Chapter 5 Advanced Configuration
 Chapter 5 Advanced Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. Configuring Advanced Security The modem router
Chapter 5 Advanced Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. Configuring Advanced Security The modem router
Truffle Broadband Bonding Network Appliance
 Truffle Broadband Bonding Network Appliance Reliable high throughput data connections with low-cost & diverse transport technologies PART I Truffle in standalone installation for a single office. Executive
Truffle Broadband Bonding Network Appliance Reliable high throughput data connections with low-cost & diverse transport technologies PART I Truffle in standalone installation for a single office. Executive
Getting Started. 16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card. Model No. KX-TDA0490
 16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card Getting Started Model No. KX-TDA0490 Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic 16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card. Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save
16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card Getting Started Model No. KX-TDA0490 Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic 16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card. Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save
Calix T07xG HGU ONT Operation and Maintenance Guide
 Calix T07xG HGU ONT Operation and Maintenance Guide July 2013 #220-00589, Rev 10 Contents About This Document... 5 Revision History... 6 Product Introduction... 7 Chapter 1: ONT Configuration... 11 Web
Calix T07xG HGU ONT Operation and Maintenance Guide July 2013 #220-00589, Rev 10 Contents About This Document... 5 Revision History... 6 Product Introduction... 7 Chapter 1: ONT Configuration... 11 Web
MUM Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam April Sao Thiên Vương - 1
 MUM Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam April 2017 Sao Thiên Vương - http://switch-router.com 1 My name: Binh Nguyen Dang Thai Email: binhndt@uranus.com.vn Cellphone: +84 909006026 Website: http://uranus.com.vn Support
MUM Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam April 2017 Sao Thiên Vương - http://switch-router.com 1 My name: Binh Nguyen Dang Thai Email: binhndt@uranus.com.vn Cellphone: +84 909006026 Website: http://uranus.com.vn Support
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
Allstream NGNSIP Security Recommendations
 Allstream NGN SIP Trunking Quick Start Guide We are confident that our service will help increase your organization s performance and productivity while keeping a cap on your costs. Summarized below is
Allstream NGN SIP Trunking Quick Start Guide We are confident that our service will help increase your organization s performance and productivity while keeping a cap on your costs. Summarized below is
16/06/56. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks
 Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
The Administration Tab - Diagnostics
 The Administration Tab - Diagnostics The diagnostic tests (Ping and Traceroute) allow you to check the connections of your network components. Ping Test. The Ping test will check the status of a connection.
The Administration Tab - Diagnostics The diagnostic tests (Ping and Traceroute) allow you to check the connections of your network components. Ping Test. The Ping test will check the status of a connection.
Contents. 2 NB750 Load Balancing Router User Guide YML817 Rev1
 Contents CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.2 Hardware... 6 1.2.1 Front Panel View... 6 1.2.2 Rear Panel View... 7 1.2.3 Hardware Load Default... 7 1.3 Features... 8 1.3.1 Software Feature...
Contents CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.2 Hardware... 6 1.2.1 Front Panel View... 6 1.2.2 Rear Panel View... 7 1.2.3 Hardware Load Default... 7 1.3 Features... 8 1.3.1 Software Feature...
Communications and Networks The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
BGS2 GPRS Modem ER75i Router ETM450 Router
 . GSM Modem Manual BGS2 GPRS Modem ER75i Router ETM450 Router 2016-05-04 ClimaCheck Sweden AB, Box 46, SE-131 06 Nacka, Sweden Visiting/delivery address: Gamla Värmdövägen 6, SE-131 37 Nacka Sweden Tel.:
. GSM Modem Manual BGS2 GPRS Modem ER75i Router ETM450 Router 2016-05-04 ClimaCheck Sweden AB, Box 46, SE-131 06 Nacka, Sweden Visiting/delivery address: Gamla Värmdövägen 6, SE-131 37 Nacka Sweden Tel.:
ON-LINE EXPERT SUPPORT THROUGH VPN ACCESS
 ON-LINE EXPERT SUPPORT THROUGH VPN ACCESS P. Fidry, V. Rakotomanana, C. Ausanneau Pierre.fidry@alcatel-lucent.fr Alcatel-Lucent, Centre de Villarceaux, 91620, Nozay, France Abstract: As a consequence of
ON-LINE EXPERT SUPPORT THROUGH VPN ACCESS P. Fidry, V. Rakotomanana, C. Ausanneau Pierre.fidry@alcatel-lucent.fr Alcatel-Lucent, Centre de Villarceaux, 91620, Nozay, France Abstract: As a consequence of
IT Essentials (ITE v5.0 & v5.02) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 100% 2016
 IT Essentials (ITE v5.0 & v5.02) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 100% 2016 1. Which network device makes forwarding decisions based on the destination MAC address that is contained in the frame? Repeater hub switch*
IT Essentials (ITE v5.0 & v5.02) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 100% 2016 1. Which network device makes forwarding decisions based on the destination MAC address that is contained in the frame? Repeater hub switch*
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Con t e n t s. Chapter 1 Introduction to Networking 1. Chapter 2 Overview of Networking Components 21.
 Con t e n t s Introduction xix Chapter 1 Introduction to Networking 1 Comparing Logical and Physical Networks.... 1 Networking Home Computers........................................... 2 Networking Small
Con t e n t s Introduction xix Chapter 1 Introduction to Networking 1 Comparing Logical and Physical Networks.... 1 Networking Home Computers........................................... 2 Networking Small
NZQA unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 6. Demonstrate basic knowledge of telecommunications concepts
 Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate basic knowledge of telecommunications concepts Level 2 Credits 10 Purpose This unit standard covers basic telecommunications principles and is intended for telecommunications
Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate basic knowledge of telecommunications concepts Level 2 Credits 10 Purpose This unit standard covers basic telecommunications principles and is intended for telecommunications
CHAPTER 7 ADVANCED ADMINISTRATION PC
 ii Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Broadband ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 3 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION... 6 Requirements... 6 Procedure... 6 CHAPTER 3 SETUP...
ii Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Broadband ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 3 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION... 6 Requirements... 6 Procedure... 6 CHAPTER 3 SETUP...
Huawei Emergency Command Network Solution Brochure-Detailed
 Doc. Code Huawei Emergency Command Solution Brochure-Detailed Issue V1.0 Date 2012-09-21 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Huawei Emergency Command Solution 1 Background Emergency command is used to control
Doc. Code Huawei Emergency Command Solution Brochure-Detailed Issue V1.0 Date 2012-09-21 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Huawei Emergency Command Solution 1 Background Emergency command is used to control
CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014
 CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014 1 Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router: R1# copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host [ ]? When the
CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014 1 Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router: R1# copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host [ ]? When the
UNIT II NETWORKING
 UNIT II INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS NETWORKING Wireless Network The cellular telephone system is responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular area known as coverage region or market The interconnection
UNIT II INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS NETWORKING Wireless Network The cellular telephone system is responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular area known as coverage region or market The interconnection
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Page 2 Skype Connect Requirements Guide
 Thinking about implementing Skype Connect? Read this guide first. Skype Connect provides connectivity between your business and the Skype community. By adding Skype Connect to your existing SIP-enabled
Thinking about implementing Skype Connect? Read this guide first. Skype Connect provides connectivity between your business and the Skype community. By adding Skype Connect to your existing SIP-enabled
Wireless-G Router User s Guide
 Wireless-G Router User s Guide 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction Installing Your Router System Requirements Installation Instructions Chapter 2: Preparing Your Network Preparing Your Network
Wireless-G Router User s Guide 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction Installing Your Router System Requirements Installation Instructions Chapter 2: Preparing Your Network Preparing Your Network
User Manual. Model: 4GoIP. Version 1.0
 User Manual Four Channel s GSM VoIP Gateway Model: 4GoIP Version 1.0 Contents 1 Product Introduction... 3 1.1 General Information...3 1.2 Protocol...3 1.3 Hardware Specification...4 1.4 Software Specification...4
User Manual Four Channel s GSM VoIP Gateway Model: 4GoIP Version 1.0 Contents 1 Product Introduction... 3 1.1 General Information...3 1.2 Protocol...3 1.3 Hardware Specification...4 1.4 Software Specification...4
Broadvox Fusion SIP Trunks Configuration Guide PBX Platform: KX-TDA50
 Broadvox Fusion SIP Trunks Configuration Guide PBX Platform: KX-TDA50 3/20/2013 1 Overview This document describes the configuration procedures required for the KX-TDA50 to make full use of the capabilities
Broadvox Fusion SIP Trunks Configuration Guide PBX Platform: KX-TDA50 3/20/2013 1 Overview This document describes the configuration procedures required for the KX-TDA50 to make full use of the capabilities
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration
 Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. This chapter contains the following sections
Chapter 3 LAN Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the advanced LAN features of your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. This chapter contains the following sections
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
Fundamental Issues. System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3. System Models. Architectural Model. Middleware. Bina Ramamurthy
 System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3 Bina Ramamurthy Fundamental Issues There is no global time. All communications are by means of messages. Message communication may be affected by network delays
System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3 Bina Ramamurthy Fundamental Issues There is no global time. All communications are by means of messages. Message communication may be affected by network delays
WL5041 Router User Manual
 TECOM WL5041 Router User Manual TECOM CO., LTD. March 2003 2003 by TECOM CO., LTD. All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan Table of contents Package Contents--------------------------------------- 2 Installing
TECOM WL5041 Router User Manual TECOM CO., LTD. March 2003 2003 by TECOM CO., LTD. All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan Table of contents Package Contents--------------------------------------- 2 Installing
It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
 1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
QUICK START GUIDE. Pepwave Express. Quick Start Guide. Pepwave Express. Nov Pepwave
 Quick Start Guide Nov-12 http://www.pepwave.com 1 Copyright @ 2012 Pepwave First Time Setup 1. Default Configuration IP: 192.168.0.1 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 2. Network Configuration acts as a CPE bridge
Quick Start Guide Nov-12 http://www.pepwave.com 1 Copyright @ 2012 Pepwave First Time Setup 1. Default Configuration IP: 192.168.0.1 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 2. Network Configuration acts as a CPE bridge
TEW-211BRP. Wireless AP Router. User s Manual
 TEW-211BRP Wireless AP Router User s Manual Version 1.4 - Jan 2002 CONTENTS Introduction...3 Hardware Installation...5 General Wireless AP Router System Connection...6 Wireless AP Router Default Settings
TEW-211BRP Wireless AP Router User s Manual Version 1.4 - Jan 2002 CONTENTS Introduction...3 Hardware Installation...5 General Wireless AP Router System Connection...6 Wireless AP Router Default Settings
Application Note Asterisk BE with SIP Trunking - Configuration Guide
 Application Note Asterisk BE with SIP Trunking - Configuration Guide 23 January 2009 Asterisk BE SIP Trunking Table of Contents 1 ASTERISK BUSINESS EDITION AND INGATE... 1 1.1 SIP TRUNKING SUPPORT... 2
Application Note Asterisk BE with SIP Trunking - Configuration Guide 23 January 2009 Asterisk BE SIP Trunking Table of Contents 1 ASTERISK BUSINESS EDITION AND INGATE... 1 1.1 SIP TRUNKING SUPPORT... 2
2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork. 3. Each machine is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
 نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
This course prepares candidates for the CompTIA Network+ examination (2018 Objectives) N
 CompTIA Network+ (Exam N10-007) Course Description: CompTIA Network+ is the first certification IT professionals specializing in network administration and support should earn. Network+ is aimed at IT
CompTIA Network+ (Exam N10-007) Course Description: CompTIA Network+ is the first certification IT professionals specializing in network administration and support should earn. Network+ is aimed at IT
Recommended Network Configurations
 Recommended Network Configurations The following configurations are the supported types of connections from the customer s site to Mitel s hosted data center. It is important that the WAN connectivity
Recommended Network Configurations The following configurations are the supported types of connections from the customer s site to Mitel s hosted data center. It is important that the WAN connectivity
Special expressions, phrases, abbreviations and terms of Computer Networks
 access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
Table of Contents. CRA-200 Analog Telephone Adapter 2 x Ethernet Port + 2 x VoIP Line. Quick Installation Guide. CRA-200 Quick Installation Guide
 CRA-200 Analog Telephone Adapter 2 x Ethernet Port + 2 x VoIP Line Quick Installation Guide Table of Contents VoIP ATA Package Contents... 2 Checklist... 2 IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 3 Connecting
CRA-200 Analog Telephone Adapter 2 x Ethernet Port + 2 x VoIP Line Quick Installation Guide Table of Contents VoIP ATA Package Contents... 2 Checklist... 2 IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 3 Connecting
DrayTek Vigor Technical Specifications. PPPoE, PPTP, DHCP client, static IP, L2TP*, Ipv6. Redundancy. By WAN interfaces traffic volume
 DrayTek Vigor 3900 Technical Specifications WAN Protocol Ethernet PPPoE, PPTP, DHCP client, static IP, L2TP*, Ipv6 Multi WAN Outbound policy based load balance Allow your local network to access Internet
DrayTek Vigor 3900 Technical Specifications WAN Protocol Ethernet PPPoE, PPTP, DHCP client, static IP, L2TP*, Ipv6 Multi WAN Outbound policy based load balance Allow your local network to access Internet
Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN
 Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN 麟瑞科技台南辦事處技術經理張晃崚 WLAN & VPN FAQ What is WLAN?802.11a?802.11b?802.11g? Which standard (product) should we use? How to deploy WLAN? How to block intruders? How to authenticate
Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN 麟瑞科技台南辦事處技術經理張晃崚 WLAN & VPN FAQ What is WLAN?802.11a?802.11b?802.11g? Which standard (product) should we use? How to deploy WLAN? How to block intruders? How to authenticate
IP806GA/GB Wireless ADSL Router
 IP806GA/GB Wireless ADSL Router 802.11g/802.11b Wireless Access Point ADSL Modem NAT Router 4-Port Switching Hub User's Guide Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless ADSL Router Features...
IP806GA/GB Wireless ADSL Router 802.11g/802.11b Wireless Access Point ADSL Modem NAT Router 4-Port Switching Hub User's Guide Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless ADSL Router Features...
Application Note Asterisk BE with Remote Phones - Configuration Guide
 Application Note Asterisk BE with Remote Phones - Configuration Guide 15 January 2009 Asterisk BE - Remote SIP Phones Table of Contents 1 ASTERISK BUSINESS EDITION AND INGATE... 1 1.1 REMOTE SIP PHONE
Application Note Asterisk BE with Remote Phones - Configuration Guide 15 January 2009 Asterisk BE - Remote SIP Phones Table of Contents 1 ASTERISK BUSINESS EDITION AND INGATE... 1 1.1 REMOTE SIP PHONE
Content 1 OVERVIEW HARDWARE DESCRIPTION HARDWARE INSTALLATION PC CONFIGURATION GUIDE... 5 WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT GUIDE...
 Content 1 OVERVIEW...1 1.1FEATURES...1 1.2 PACKETCONTENTS...3 1.3 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 1.4 FACTORY DEFAULTS...4 1.5 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS...4 2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION... 6 3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION...8 4
Content 1 OVERVIEW...1 1.1FEATURES...1 1.2 PACKETCONTENTS...3 1.3 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 1.4 FACTORY DEFAULTS...4 1.5 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS...4 2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION... 6 3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION...8 4
2Wire IG 2700 ADSL Router. RJ45 connecting cable
 Technical Support Information Case 6. BT 2Wire 2700 ADSL Router (BT Business Hub) configuration to allow a BT Versatility Broadband Module (BBM) IP Gateway connection for VoIP (IP Trunks and IP Extensions)
Technical Support Information Case 6. BT 2Wire 2700 ADSL Router (BT Business Hub) configuration to allow a BT Versatility Broadband Module (BBM) IP Gateway connection for VoIP (IP Trunks and IP Extensions)
Facilitator. Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers. Class Logistics
 Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers APPA Institute for Facilities Management Dallas, TX January 16, 2017 Facilitator J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Chief Information Officer Community
Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers APPA Institute for Facilities Management Dallas, TX January 16, 2017 Facilitator J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Chief Information Officer Community
APPLICATION NOTES. M1 Audio Control. Basic control of distributed audio Systems using the M1 Control
 PRODUCT APPLICATION NOTES M1 Audio Control Basic control of distributed audio Systems using the M1 Control COMPATIBLE AUDIO DISTRIBUTION CONTROLLERS Russound - CAM & CAV series only (RNET) Proficient -
PRODUCT APPLICATION NOTES M1 Audio Control Basic control of distributed audio Systems using the M1 Control COMPATIBLE AUDIO DISTRIBUTION CONTROLLERS Russound - CAM & CAV series only (RNET) Proficient -
Router Router Microprocessor controlled traffic direction home router DSL modem Computer Enterprise routers Core routers
 Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition. N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition
 N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D500 N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D1500 User Manual May 2018 202-11390-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support
N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D500 N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D1500 User Manual May 2018 202-11390-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support
Section 3 - Configuration. Enable Auto Channel Scan:
 Enable Auto Channel Scan: Wireless Channel: The Auto Channel Scan setting can be selected to allow the DGL-4500 to choose the channel with the least amount of interference. Indicates the channel setting
Enable Auto Channel Scan: Wireless Channel: The Auto Channel Scan setting can be selected to allow the DGL-4500 to choose the channel with the least amount of interference. Indicates the channel setting
MODERNIZATION OF AUTOMATIC SURFACE WEATHER OBSERVING SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS TO UTILIZE TCP/IP TECHNOLOGY
 MODERNIZATION OF AUTOMATIC SURFACE WEATHER OBSERVING SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS TO UTILIZE TCP/IP TECHNOLOGY Olli Ojanperä, Hannu Heikkinen and Hannu M. Heikkinen Vaisala Oyj, P.O.Box 26, FIN-00421 Helsinki,
MODERNIZATION OF AUTOMATIC SURFACE WEATHER OBSERVING SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS TO UTILIZE TCP/IP TECHNOLOGY Olli Ojanperä, Hannu Heikkinen and Hannu M. Heikkinen Vaisala Oyj, P.O.Box 26, FIN-00421 Helsinki,
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide
 Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features
 Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
The Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Range Forward
 The Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Range Forward The Applications and Gaming Tab allows you to set up public services on your network, such as web servers, ftp servers, e-mail servers, or other specialized
The Applications and Gaming Tab - Port Range Forward The Applications and Gaming Tab allows you to set up public services on your network, such as web servers, ftp servers, e-mail servers, or other specialized
07/ CONFIGURING SECURITY SETTINGS
 SECURITY LOG Malformed packet: Failed parsing a packed has been blocked because it is malformed. Maximum security enabled service a packet has been accepted because it belongs to a permitted service in
SECURITY LOG Malformed packet: Failed parsing a packed has been blocked because it is malformed. Maximum security enabled service a packet has been accepted because it belongs to a permitted service in
RP-FSO522 2-Line FXO, 2-Line FXS SIP IP Gateway. Feature
 RP-FSO522 2-Line FXO, 2-Line FXS SIP IP Gateway RP-FSO522 is an 2-Line FXO plus 2-Line FXS gateway with SIP protocol IP device which allows to connect 2 Lines of analog PSTN telephone line and connect
RP-FSO522 2-Line FXO, 2-Line FXS SIP IP Gateway RP-FSO522 is an 2-Line FXO plus 2-Line FXS gateway with SIP protocol IP device which allows to connect 2 Lines of analog PSTN telephone line and connect
Hybrid IP-PBX Information about IP Proprietary Telephones KX-TDA200. Panasonic KX-TDA100 Panasonic KX-TDA200. Phone:
 Panasonic KX-TDA100 Panasonic KX-TDA200 www.voicesonic.com Phone: 877-289-2829 Hybrid IP-PBX Information about IP Proprietary Telephones Model KX-TDA100 KX-TDA200 Panasonic KX-TDA100, KXTDA100, TDA100,
Panasonic KX-TDA100 Panasonic KX-TDA200 www.voicesonic.com Phone: 877-289-2829 Hybrid IP-PBX Information about IP Proprietary Telephones Model KX-TDA100 KX-TDA200 Panasonic KX-TDA100, KXTDA100, TDA100,
IT114 NETWORK+ Learning Unit 1 Objectives: 1, 2 Time In-Class Time Out-Of-Class Hours 2-3. Lectures: Course Introduction and Overview
 IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
MiPDF.COM. 1. Convert the decimal number 231 into its binary equivalent. Select the correct answer from the list below.
 CCNA1 v6.0 Pretest Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. Convert the decimal number 231 into its binary equivalent. Select the correct answer from the list below. 11110010 11011011 11110110 11100111* 11100101
CCNA1 v6.0 Pretest Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. Convert the decimal number 231 into its binary equivalent. Select the correct answer from the list below. 11110010 11011011 11110110 11100111* 11100101
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Module 11. OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards
 Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
WISNETWORKS. WisOS 11ac V /3/21. Software version WisOS 11ac
 WISNETWORKS User Manual V1.1 2016/3/21 Software version 1.0.0021 Table of contents 1. Setup& WMI... 3 1.1 Hardware Setup... 3 1.2 Web Management Interface... 3 2. Status... 4 2.1 Overview... 4 2.1.1 System...
WISNETWORKS User Manual V1.1 2016/3/21 Software version 1.0.0021 Table of contents 1. Setup& WMI... 3 1.1 Hardware Setup... 3 1.2 Web Management Interface... 3 2. Status... 4 2.1 Overview... 4 2.1.1 System...
Chapter Topics Part 1. Network Definitions. Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security
 Chapter Topics Part 1 Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security CS10001 Computer Literacy Business Networks Network Advantages Client/Server Networks Network Classifications Servers Toplogies Chapter
Chapter Topics Part 1 Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security CS10001 Computer Literacy Business Networks Network Advantages Client/Server Networks Network Classifications Servers Toplogies Chapter
