CS 268: Computer Networking
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 268: Computer Networking L-10 Wireless in the Real World Wireless in the Real World Real world deployment patterns Mesh networks and deployments Assigned reading Modeling Wireless Links Architecture and Evaluation of an Unplanned b Mesh Network 2
2 Wireless Challenges Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather than wire Don t know what hosts are involved Host may not be using same link technology Mobility Other characteristics of wireless Noisy lots of losses Slow Interaction of multiple transmitters at receiver Collisions, capture, interference Multipath interference 3 Overview Deployment patterns Reaction to interference Interference mitigation Mesh networks Architecture Measurements 4
3 Characterizing Current Deployments Datasets Place Lab: 28,000 APs MAC, ESSID, GPS Selected US cities Wifimaps: 300,000 APs MAC, ESSID, Channel, GPS (derived) wifimaps.com Pittsburgh Wardrive: 667 APs MAC, ESSID, Channel, Supported Rates, GPS 5 AP Stats, Degrees: Placelab (Placelab: APs, MAC, ESSID, GPS) #APs Max. degree 50 m Portland San Diego San Francisco Boston
4 Degree Distribution: Place Lab 7 Unmanaged Devices WifiMaps.com (300,000 APs, MAC, ESSID, Channel) Channel %age Most users don t change default channel Channel selection must be automated 8
5 Growing Interference in Unlicensed Bands Anecdotal evidence of problems, but how severe? Characterize how operates under interference in practice Other What do we expect? Throughput to decrease linearly with interference There to be lots of options for devices to tolerate interference Bit-rate adaptation Power control FEC Packet size variation Spread-spectrum processing Transmission and reception diversity Throughput (linear) Theory Interferer power (log-scale) 10
6 Key Questions How damaging can a low-power and/or narrow-band interferer be? How can today s hardware tolerate interference well? What options work well, and why? 11 What we see Effects of interference more severe in practice Caused by hardware limitations of commodity cards, which theory doesn t model Throughput (linear) Theory Practice Interferer power (log-scale) 12
7 Experimental Setup Access Point UDP flow Client Interferer Receiver Path RF Analog Signal signal Amplifier To RF Amplifiers control ADC 6-bit samples Timing Recovery PHY AGC Barker Correlator Demodulator Descrambler Preamble Detector/ Header CRC-16 Checker PHY MAC Data (includes beacons) Receiver SFD CRC Payload PHY header Extend SINR model to capture these vulnerabilities Interested in worst-case natural or adversarial interference Have developed range of attacks that trigger these vulnerabilities 14
8 Timing Recovery Interference Interferer sends continuous SYNC pattern Interferes with packet acquisition (PHY reception errors) Weak interferer Moderate interferer Log-scale 15 Interference Management Interference will get worse Density/device diversity is increasing Unlicensed spectrum is not keeping up Spectrum management Channel hopping effective at mitigating some performance problems [Sigcomm07] Coordinated spectrum use based on RF sensor network Transmission power control Enable spatial reuse of spectrum by controlling transmit power Must also adapt carrier sense behavior to take advantage 16
9 Impact of frequency separation Even small frequency separation (i.e., adjacent channel) helps 5MHz separation (good performance) 17 Transmission Power Control Choose transmit power levels to maximize physical spatial reuse Tune MAC to ensure nodes transmit simultaneously when possible Spatial reuse = network capacity / link capacity Client 2 AP 1 AP 2 Concurrent transmissions increase spatial reuse Client 2 AP 2 Client 1 AP 1 Client 1 Spatial Reuse, 1 Spatial Reuse, 2 18
10 Transmission Power Control in Practice For simple scenario easy to compute optimal transmit power May or may not enable simultaneous transmit Protocol builds on iterative pair-wise optimization AP 1 d 12 AP 2 d 11 d 22 Adjusting transmit power requires adjusting carrier sense thresholds Echos, Alpha or eliminate carrier sense Altrusitic Echos eliminates starvation in Echos d 21 Client 1 Client 2 19 Details of Power Control Hard to do per-packet with many NICs Some even might have to re-init (many ms) May have to balance power with rate Reasonable goal: lowest power for max rate But finding ths empirically is hard! Many {power, rate} combinations, and not always easy to predict how each will perform Alternate goal: lowest power for max needed rate But this interacts with other people because you use more channel time to send the same data. Uh-oh. Nice example of the difficulty of local vs. global optimization 20
11 Rate Adaptation General idea: Observe channel conditions like SNR (signalto-noise ratio), bit errors, packet errors Pick a transmission rate that will get best goodput There are channel conditions when reducing the bitrate can greatly increase throughput e.g., if a ½ decrease in bitrate gets you from 90% loss to 10% loss. 21 Simple rate adaptation scheme Watch packet error rate over window (K packets or T seconds) If loss rate > thresh high (or SNR <, etc) Reduce Tx rate If loss rate < thresh low Increase Tx rate Most devices support a discrete set of rates , 2, 5.5, 11, etc. 22
12 Challenges in rate adaptation Channel conditions change over time Loss rates must be measured over a window SNR estimates from the hardware are coarse, and don t always predict loss rate May be some overhead (time, transient interruptions, etc.) to changing rates 23 Power and Rate Selection Algorithms Rate Selection Auto Rate Fallback: ARF Estimated Rate Fallback: ERF Goal: Transmit at minimum necessary power to reach receiver Minimizes interference with other nodes Paper: Can double or more capacity, if done right. Joint Power and Rate Selection Power Auto Rate Fallback: PARF Power Estimated Rate Fallback: PERF Conservative Algorithms Always attempt to achieve highest possible modulation rate 24
13 Power Control/Rate Control summary Complex interactions. More power: Higher received signal strength May enable faster rate (more S in S/N) May mean you occupy media for less time Interferes with more people Less power Interfere with fewer people Less power + less rate Fewer people but for a longer time Gets even harder once you consider Carrier sense Calibration and measurement error Mobility 25 Overview Deployment patterns Reaction to interference Interference mitigation Mesh networks Architecture Measurements 26
14 Community Wireless Network Share a few wired Internet connections Construction of community networks Multi-hop network Nodes in chosen locations Directional antennas Require well-coordination Access point Clients directly connect Access points operates independently Do not require much coordination 27 Roofnet Goals Operate without extensive planning or central management Provide wide coverage and acceptable performance Design decisions Unconstrained node placement Omni-directional antennas Multi-hop routing Optimization of routing for throughput in a slowly changing network 28
15 Roofnet Design Deployment Over an area of about four square kilometers in Cambridge, Messachusetts Most nodes are located in buildings 3~4 story apartment buildings 8 nodes are in taller buildings Each Rooftnet node is hosted by a volunteer user Hardware PC, omni-directional antenna, hard drive b card RTS/CTS disabled Share the same b channel Non-standard pseudo-ibss mode Similar to standard b IBSS (ad hoc) Omit beacon and BSSID (network ID) 29 Roofnet Node Map 1 kilometer 30
16 Roofnet 31 Typical Rooftop View 32
17 A Roofnet Self-Installation Kit Antenna ($65) 8dBi, 20 degree vertical 50 ft. Cable ($40) Low loss (3dB/100ft) Computer ($340) 533 MHz PC, hard disk, CDROM b card ($155) Engenius Prism 2.5, 200mW Miscellaneous ($75) Chimney Mount, Lightning Arrestor, etc. Software ( free ) Our networking software based on Click Total: $685 Takes a user about 45 minutes to install on a flat roof 33 Software and Auto-Configuration Linux, routing software, DHCP server, web server Automatically solve a number of problems Allocating addresses Finding a gateway between Roofnet and the Internet Choosing a good multi-hop route to that gateway Addressing Roofnet carries IP packets inside its own header format and routing protocol Assign addresses automatically Only meaningful inside Roofnet, not globally routable The address of Roofnet nodes Low 24 bits are the low 24 bits of the node s Ethernet address High 8 bits are an unused class-a IP address block The address of hosts Allocate x via DHCP and use NAT between the Ethernet and Roofnet 34
18 Software and Auto-Configuration Gateway and Internet Access A small fraction of Roofnet users will share their wired Internet access links Nodes which can reach the Internet Advertise itself to Roofnet as an Internet gateway Acts as a NAT for connection from Roofnet to the Internet Other nodes Select the gateway which has the best route metric Roofnet currently has four Internet gateways 35 Evaluation Method Multi-hop TCP 15 second one-way bulk TCP transfer between each pair of Roofnet nodes Single-hop TCP The direct radio link between each pair of routes Loss matrix The loss rate between each pair of nodes using byte broadcasts Multi-hop density TCP throughput between a fixed set of four nodes Varying the number of Roofnet nodes that are participating in routing 36
19 Evaluation Basic Performance (Multi-hop TCP) The routes with low hop-count have much higher throughput Multi-hop routes suffer from inter-hop collisions 37 Evaluation Basic Performance (Multi-hop TCP) TCP throughput to each node from its chosen gateway Round-trip latencies for 84-byte ping packets to estimate interactive delay 38
20 Evaluation Link Quality and Distance (Single-hop TCP, Multi-hop TCP) Most available links are between 500m and 1300m and 500 kbits/s Srcr Use almost all of the links faster than 2 Mbits/s and ignore majority of the links which are slower than that Fast short hops are the best policy 39 Evaluation Link Quality and Distance (Multi-hop TCP, Loss matrix) Median delivery probability is 0.8 1/4 links have loss rates of 50% or more detects the losses with its ACK mechanism and resends the packets 40
21 Evaluation Architectural Alternatives Maximize the number of additional nodes with non-zero throughput to some gateway Ties are broken by average throughput 41 Evaluation Inter-hop Interference (Multi-hop TCP, Single-hop TCP) Concurrent transmissions on different hops of a route collide and cause packet loss 42
22 Roofnet Summary The network s architectures favors Ease of deployment Omni-directional antennas Self-configuring software Link-quality-aware multi-hop routing Evaluation of network performance Average throughput between nodes is 627kbits/s Well served by just a few gateways whose position is determined by convenience Multi-hop mesh increases both connectivity and throughput 43 Roofnet Link Level Measurements Analyze cause of packet loss Neighbor Abstraction Ability to hear control packets or No Interference Strong correlation between BER and S/N RoofNet pairs communicate At intermediate loss rates Temporal Variation Spatial Variation 44
23 Lossy Links are Common 45 Delivery Probabilities are Uniformly Distributed 46
24 Delivery vs. SNR SNR not a good predictor 47 Is it Bursty Interference? May interfere but not impact SNR measurement 48
25 Two Different Roofnet Links Top is typical of bursty interference, bottom is not Most links are like the bottom 49 Is it Multipath Interference? Simulate with channel emulator 50
26 A Plausible Explanation Multi-path can produce intermediate loss rates Appropriate multi-path delay is possible due to long-links 51 Key Implications Lack of a link abstraction! Links aren t on or off sometimes in-between Protocols must take advantage of these intermediate quality links to perform well How unique is this to Roofnet? Cards designed for indoor environments used outdoors 52
27 Roofnet Design - Routing Protocol Srcr Find the highest throughput route between any pair of Roofnet nodes Source-routes data packets like DSR Maintains a partial database of link metrics Learning fresh link metrics Forward a packet Flood to find a route Overhear queries and responses Finding a route to a gateway Each Roofnet gateway periodically floods a dummy query When a node receives a new query, it adds the link metric information The node computes the best route The node re-broadcasts the query Send a notification to a failed packet s source if the link condition is changed 53 Roofnet Design Routing Metric ETT (Estimated Transmission Time) metric Srcr chooses routes with ETT Predict the total amount of time it would take to send a data packet Take into account link s highest-throughput transmit bit-rate and delivery probability Each Roofnet node sends periodic 1500-byte broadcasts Bit-rate Selection b transmit bit-rates 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbits/s SampleRate Judge which bit-rate will provide the highest throughput Base decisions on actual data transmission Periodically sends a packet at some other bit-rate 54
Wireless in the Real World : Computer Networking. Wireless Challenges. Overview
 Wireless in the Real World 15-744: Computer Networking L-9 Wireless in the Real World Real world deployment patterns Mesh networks and deployments Assigned reading White Space Networking with Wi-Fi like
Wireless in the Real World 15-744: Computer Networking L-9 Wireless in the Real World Real world deployment patterns Mesh networks and deployments Assigned reading White Space Networking with Wi-Fi like
Architecture and Evaluation of an Unplanned b Mesh Network
 Architecture and Evaluation of an Unplanned 802.11b Mesh Network John Bicket, Daniel Aguayo, Sanjit Biswas, and Robert Morris MIT CSAIL (MobiCom 05) slides by Jong-Kwon Lee, presented by Fallon Chen May
Architecture and Evaluation of an Unplanned 802.11b Mesh Network John Bicket, Daniel Aguayo, Sanjit Biswas, and Robert Morris MIT CSAIL (MobiCom 05) slides by Jong-Kwon Lee, presented by Fallon Chen May
Wireless Mesh Networks
 Wireless Mesh Networks COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 6 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from I. F. Akyildiz, B. Karp] Wireless Mesh Networks Describes wireless networks in which each node can communicate
Wireless Mesh Networks COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 6 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from I. F. Akyildiz, B. Karp] Wireless Mesh Networks Describes wireless networks in which each node can communicate
Typical rooftop view
 Roofnet map Typical rooftop view Roofnet Goals and Design Ideas Goals Operate without extensive planning or central management Provide wide coverage and acceptable performance Design decisions Unconstrained
Roofnet map Typical rooftop view Roofnet Goals and Design Ideas Goals Operate without extensive planning or central management Provide wide coverage and acceptable performance Design decisions Unconstrained
Wireless and Mobile Communications
 Wireless and Mobile Communications Outline Overview MAC Routing Wireless in real world Leverage broadcasting nature Wireless security 2 From Wired to Wireless The Difference: # 1 The Difference #2 Unicast
Wireless and Mobile Communications Outline Overview MAC Routing Wireless in real world Leverage broadcasting nature Wireless security 2 From Wired to Wireless The Difference: # 1 The Difference #2 Unicast
Wireless and Mobile Communications
 Wireless and Mobile Communications Outline Overview MAC Routing Wireless in real world Leverage broadcasting nature Wireless security 2 From Wired to Wireless The Difference: # 1 The Difference #2 Unicast
Wireless and Mobile Communications Outline Overview MAC Routing Wireless in real world Leverage broadcasting nature Wireless security 2 From Wired to Wireless The Difference: # 1 The Difference #2 Unicast
Outline. Lecture 16: Wireless Networking. Physical Layer (Layer 1) Ethernet: Wireless is Different. Attenuation Over Space
 Outline Lecture 16: Wireless Networking Wireless physical layer challenges - Signal, noise, modulation - A little bit of EE goes a long way Wireless link layers - Hidden terminals, exposed terminals -
Outline Lecture 16: Wireless Networking Wireless physical layer challenges - Signal, noise, modulation - A little bit of EE goes a long way Wireless link layers - Hidden terminals, exposed terminals -
Wireless Internet Routing. Learning from Deployments Link Metrics
 Wireless Internet Routing Learning from Deployments Link Metrics 1 Learning From Deployments Early worked focused traditional routing issues o Control plane: topology management, neighbor discovery o Data
Wireless Internet Routing Learning from Deployments Link Metrics 1 Learning From Deployments Early worked focused traditional routing issues o Control plane: topology management, neighbor discovery o Data
Bridging Link Power Asymmetry in Mobile Whitespace Networks Sanjib Sur and Xinyu Zhang
 Bridging Link Power Asymmetry in Mobile Whitespace Networks Sanjib Sur and Xinyu Zhang University of Wisconsin - Madison 1 Wireless Access in Vehicles Wireless network in public vehicles use existing infrastructure
Bridging Link Power Asymmetry in Mobile Whitespace Networks Sanjib Sur and Xinyu Zhang University of Wisconsin - Madison 1 Wireless Access in Vehicles Wireless network in public vehicles use existing infrastructure
Wireless MACs: MACAW/802.11
 Wireless MACs: MACAW/802.11 Mark Handley UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Fundamentals: Spectrum and Capacity A particular radio transmits over some range of frequencies; its bandwidth, in the physical
Wireless MACs: MACAW/802.11 Mark Handley UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Fundamentals: Spectrum and Capacity A particular radio transmits over some range of frequencies; its bandwidth, in the physical
15-441: Computer Networking. Wireless Networking
 15-441: Computer Networking Wireless Networking Outline Wireless Challenges 802.11 Overview Link Layer Ad-hoc Networks 2 Assumptions made in Internet Host are (mostly) stationary Address assignment, routing
15-441: Computer Networking Wireless Networking Outline Wireless Challenges 802.11 Overview Link Layer Ad-hoc Networks 2 Assumptions made in Internet Host are (mostly) stationary Address assignment, routing
Wireless Challenges : Computer Networking. Overview. Routing to Mobile Nodes. Lecture 25: Wireless Networking
 Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 25: Wireless Networking Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather than wire Don t know what hosts are involved Host may
Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 25: Wireless Networking Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather than wire Don t know what hosts are involved Host may
Link Estimation and Tree Routing
 Network Embedded Systems Sensor Networks Link Estimation and Tree Routing 1 Marcus Chang, mchang@cs.jhu.edu Slides: Andreas Terzis Outline Link quality estimation Examples of link metrics Four-Bit Wireless
Network Embedded Systems Sensor Networks Link Estimation and Tree Routing 1 Marcus Chang, mchang@cs.jhu.edu Slides: Andreas Terzis Outline Link quality estimation Examples of link metrics Four-Bit Wireless
Mobile Routing : Computer Networking. Overview. How to Handle Mobile Nodes? Mobile IP Ad-hoc network routing Assigned reading
 Mobile Routing 15-744: Computer Networking L-10 Ad Hoc Networks Mobile IP Ad-hoc network routing Assigned reading Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Routing Protocols A High Throughput
Mobile Routing 15-744: Computer Networking L-10 Ad Hoc Networks Mobile IP Ad-hoc network routing Assigned reading Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Routing Protocols A High Throughput
Lecture 16: Wireless Networking
 Lecture 16: Wireless Networking Outline Wireless physical layer challenges - Signal, noise, modulation - A little bit of EE goes a long way Wireless link layers - Hidden terminals, exposed terminals -
Lecture 16: Wireless Networking Outline Wireless physical layer challenges - Signal, noise, modulation - A little bit of EE goes a long way Wireless link layers - Hidden terminals, exposed terminals -
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 10: Rate Adaptation Frequency-Aware Rate Adaptation (MobiCom 09) Lecturer: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Motivation The bandwidth supported in 802.11 is getting
Wireless Communication Systems @CS.NCTU Lecture 10: Rate Adaptation Frequency-Aware Rate Adaptation (MobiCom 09) Lecturer: Kate Ching-Ju Lin ( 林靖茹 ) Motivation The bandwidth supported in 802.11 is getting
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Christos Papadopoulos
 CS557: Measurements Christos Papadopoulos Adapted by Lorenzo De Carli Outline End-to-End Packet Dynamics - Paxon99b Wireless measurements - Aguayo04a Note: both these studies are old, so the results have
CS557: Measurements Christos Papadopoulos Adapted by Lorenzo De Carli Outline End-to-End Packet Dynamics - Paxon99b Wireless measurements - Aguayo04a Note: both these studies are old, so the results have
Wireless Challenges : Computer Networking. Overview. Routing to Mobile Nodes. Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless
 Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless Peter Steenkiste Fall 2010 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f10 Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather
Wireless Challenges 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Mobile and Wireless Peter Steenkiste Fall 2010 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f10 Force us to rethink many assumptions Need to share airwaves rather
ECE 598HH: Special Topics in Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
 ECE 598HH: Special Topics in Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 21: Opportunistic Routing Haitham Hassanieh *These slides are courtesy of Dina Katabi 1 Lecture Outline Single Path Routing Opportunistic
ECE 598HH: Special Topics in Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 21: Opportunistic Routing Haitham Hassanieh *These slides are courtesy of Dina Katabi 1 Lecture Outline Single Path Routing Opportunistic
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer
 Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Link Layer II: MACA and MACAW
 Link Layer II: MACA and MACAW COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 5 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from J. Kurose, K. Ross, D. Holmar] Medium access: Timeline Packet radio Wireless LAN Wired LAN ALOHAnet
Link Layer II: MACA and MACAW COS 463: Wireless Networks Lecture 5 Kyle Jamieson [Parts adapted from J. Kurose, K. Ross, D. Holmar] Medium access: Timeline Packet radio Wireless LAN Wired LAN ALOHAnet
CS 268: Computer Networking. Taking Advantage of Broadcast
 CS 268: Computer Networking L-12 Wireless Broadcast Taking Advantage of Broadcast Opportunistic forwarding Network coding Assigned reading XORs In The Air: Practical Wireless Network Coding ExOR: Opportunistic
CS 268: Computer Networking L-12 Wireless Broadcast Taking Advantage of Broadcast Opportunistic forwarding Network coding Assigned reading XORs In The Air: Practical Wireless Network Coding ExOR: Opportunistic
15-441: Computer Networking. Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks
 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
A Measurement Study of Multiplicative Overhead Effects in Wireless Networks
 A Measurement Study of Multiplicative Overhead Effects in Wireless Joseph Camp, Vincenzo Mancuso, Omer Gurewitz, and Edward W. Knightly INFOCOM 2008 http://networks.rice.edu System: Large-scale, Multi-tier
A Measurement Study of Multiplicative Overhead Effects in Wireless Joseph Camp, Vincenzo Mancuso, Omer Gurewitz, and Edward W. Knightly INFOCOM 2008 http://networks.rice.edu System: Large-scale, Multi-tier
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols. Broch et al Presented by Brian Card
 A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols Broch et al Presented by Brian Card 1 Outline Introduction NS enhancements Protocols: DSDV TORA DRS AODV Evaluation Conclusions
A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols Broch et al Presented by Brian Card 1 Outline Introduction NS enhancements Protocols: DSDV TORA DRS AODV Evaluation Conclusions
Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité )
 Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité ) Prof. J.-P. Hubaux February 12, 2004 Duration: 2 hours, all documents allowed Please write your answers on these sheets, at the
Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité ) Prof. J.-P. Hubaux February 12, 2004 Duration: 2 hours, all documents allowed Please write your answers on these sheets, at the
L3: SampleRate (Chapter 3)
 COS-598A, Spring 2017, Kyle Jamieson L3: SampleRate (Chapter 3) Indoor Network Measurements 45-node indoor wireless testbed Mesh topology Linux Soekris router with Atheros 802.11a/b/g card RTS/CTS protocol
COS-598A, Spring 2017, Kyle Jamieson L3: SampleRate (Chapter 3) Indoor Network Measurements 45-node indoor wireless testbed Mesh topology Linux Soekris router with Atheros 802.11a/b/g card RTS/CTS protocol
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Granting Silence to Avoid Wireless Collisions
 Granting Silence to Avoid Wireless Collisions Jung Il Choi, Mayank Jain, Maria A. Kazandjieva, and Philip Levis October 6, 2010 ICNP 2010 Wireless Mesh and CSMA One UDP flow along a static 4-hop route
Granting Silence to Avoid Wireless Collisions Jung Il Choi, Mayank Jain, Maria A. Kazandjieva, and Philip Levis October 6, 2010 ICNP 2010 Wireless Mesh and CSMA One UDP flow along a static 4-hop route
Multicasting in ad hoc networks: Energy efficient
 Multicasting in ad hoc networks: Energy efficient Blerta Bishaj Helsinki University of Technology 1. Introduction...2 2. Sources of power consumption... 3 3. Directional antennas... 3 4. TCP... 3 5. Energy-efficient
Multicasting in ad hoc networks: Energy efficient Blerta Bishaj Helsinki University of Technology 1. Introduction...2 2. Sources of power consumption... 3 3. Directional antennas... 3 4. TCP... 3 5. Energy-efficient
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols
 A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols By Josh Broch, David A. Maltz, David B. Johnson, Yih- Chun Hu, Jorjeta Jetcheva Presentation by: Michael Molignano Jacob
A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc Network Routing Protocols By Josh Broch, David A. Maltz, David B. Johnson, Yih- Chun Hu, Jorjeta Jetcheva Presentation by: Michael Molignano Jacob
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Links, clocks, optics and radios
 Links, clocks, optics and radios end IP addresses Source Destination Data 171.64.74.55 176.22.45.66 176 10110000 start Example of On-Off Keying +5V 0V Volts 1 0 time Data 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
Links, clocks, optics and radios end IP addresses Source Destination Data 171.64.74.55 176.22.45.66 176 10110000 start Example of On-Off Keying +5V 0V Volts 1 0 time Data 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
Rate Adaptation in
 Rate Adaptation in 802.11 SAMMY KUPFER Outline Introduction Intuition Basic techniques Techniques General Designs Robust Rate Adaptation for 802.11 (2006) Efficient Channel aware Rate Adaptation in Dynamic
Rate Adaptation in 802.11 SAMMY KUPFER Outline Introduction Intuition Basic techniques Techniques General Designs Robust Rate Adaptation for 802.11 (2006) Efficient Channel aware Rate Adaptation in Dynamic
CHAPTER 7 SIMULATION OBSERVATIONS
 CHAPTER 7 CHAPTER 7 SIMULATION OBSERVATIONS Over a randomly distributed wireless network system with the specification is modeled with the suggested algorithms for communication from a selected source
CHAPTER 7 CHAPTER 7 SIMULATION OBSERVATIONS Over a randomly distributed wireless network system with the specification is modeled with the suggested algorithms for communication from a selected source
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Network Simulators, Emulators and Testbeds
 Outline Network Simulators, Emulators and Testbeds By: George Nychis Gaurang Sardesai Motivation for Research Different Techniques Simulators Assumptions/Axioms Methods and Results Testbeds Architecture
Outline Network Simulators, Emulators and Testbeds By: George Nychis Gaurang Sardesai Motivation for Research Different Techniques Simulators Assumptions/Axioms Methods and Results Testbeds Architecture
Hands-On Exercises: IEEE Standard
 Hands-On Exercises: IEEE 802.11 Standard Mohammad Hossein Manshaei and Jean-Pierre Hubaux {hossein.manshaei,jean-pierre.hubaux}@epfl.ch Laboratory for Computer Communications and Applications (LCA) March
Hands-On Exercises: IEEE 802.11 Standard Mohammad Hossein Manshaei and Jean-Pierre Hubaux {hossein.manshaei,jean-pierre.hubaux}@epfl.ch Laboratory for Computer Communications and Applications (LCA) March
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Configuring the Radio Network
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes the procedures for configuring the bridge s radio network. Here s what you ll find in this chapter: Using the Configuration Radio Menu, page 4-2 Establishing an SSID (Ssid),
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes the procedures for configuring the bridge s radio network. Here s what you ll find in this chapter: Using the Configuration Radio Menu, page 4-2 Establishing an SSID (Ssid),
Omni Center Predictive Wi-Fi Assessment
 Omni Center Predictive Wi-Fi Assessment Name: Omni Center Predictive Wi-Fi Assessment Location: Onalaska, WI 1 Network capacity configuration 2.4 GHz 5 GHz Minimum Data Rate 12 Mbits/s 12 Mbits/s Band
Omni Center Predictive Wi-Fi Assessment Name: Omni Center Predictive Wi-Fi Assessment Location: Onalaska, WI 1 Network capacity configuration 2.4 GHz 5 GHz Minimum Data Rate 12 Mbits/s 12 Mbits/s Band
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Outline. A Professional Company in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Copyright , EstiNet Technologies Inc. All Rights Reserved..
 Physical Layer Outline Signal Propagation Media The Calculation of Signal Delivery Time The Evaluation of End-to-end Delay Signal Encoding and Modulation Wired Signal s Encoding, Decoding and Decoding
Physical Layer Outline Signal Propagation Media The Calculation of Signal Delivery Time The Evaluation of End-to-end Delay Signal Encoding and Modulation Wired Signal s Encoding, Decoding and Decoding
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1
 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
Packet-Level Diversity From Theory to Practice: An based Experimental Investigation
 Packet-Level Diversity From Theory to Practice: An 802.11- based Experimental Investigation E. Vergetis, E. Pierce, M. Blanco and R. Guérin University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical & Systems
Packet-Level Diversity From Theory to Practice: An 802.11- based Experimental Investigation E. Vergetis, E. Pierce, M. Blanco and R. Guérin University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical & Systems
CS551 Ad-hoc Routing
 CS551 Ad-hoc Routing Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs551-f12 1 Mobile Routing Alternatives Why not just assume a base station? good for many cases, but not some (military, disaster recovery, sensor
CS551 Ad-hoc Routing Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs551-f12 1 Mobile Routing Alternatives Why not just assume a base station? good for many cases, but not some (military, disaster recovery, sensor
Making Friends with Broadcast. Administrivia
 Making Friends with Broadcast CMU 15-744 David Andersen Administrivia Midterm Mean 66.5, Median 70, Stddev 13.7 Histo: 35-39 37 38 40-44 45-49 50-54 54 54 54 55-59 56 57 60-64 61 64 64 65-69 69 70-74 71
Making Friends with Broadcast CMU 15-744 David Andersen Administrivia Midterm Mean 66.5, Median 70, Stddev 13.7 Histo: 35-39 37 38 40-44 45-49 50-54 54 54 54 55-59 56 57 60-64 61 64 64 65-69 69 70-74 71
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY
 98 CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY Underwater wireless sensor networks deployed of sensor nodes with sensing, forwarding and processing abilities that operate in underwater. In this environment brought challenges,
98 CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY Underwater wireless sensor networks deployed of sensor nodes with sensing, forwarding and processing abilities that operate in underwater. In this environment brought challenges,
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety
 WHITE PAPER Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety Relating Technical Capabilities to User Experience Executive Summary Government and public safety organizations are watching the fast pace of technological
WHITE PAPER Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety Relating Technical Capabilities to User Experience Executive Summary Government and public safety organizations are watching the fast pace of technological
Announcements / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Wireless. Regular Ethernet CSMA/CD.
 Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Outline. Multi-Channel Reliability and Spectrum Usage in Real Homes Empirical Studies for Home-Area Sensor Networks. Smart Grid
 Multi-Channel Reliability and Spectrum Usage in Real Homes Empirical Studies for Home-Area Sensor Networks Experimental methodology Empirical study in homes Spectrum study of existing wireless signals
Multi-Channel Reliability and Spectrum Usage in Real Homes Empirical Studies for Home-Area Sensor Networks Experimental methodology Empirical study in homes Spectrum study of existing wireless signals
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Link Layer: Retransmissions
 Link Layer: Retransmissions Context on Reliability Where in the stack should we place reliability functions? Application Transport Network Link Physical CSE 461 University of Washington 2 Context on Reliability
Link Layer: Retransmissions Context on Reliability Where in the stack should we place reliability functions? Application Transport Network Link Physical CSE 461 University of Washington 2 Context on Reliability
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Links Reading: Chapter 2. Goals of Todayʼs Lecture. Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame
 Links Reading: Chapter 2 CS 375: Computer Networks Thomas Bressoud 1 Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared
Links Reading: Chapter 2 CS 375: Computer Networks Thomas Bressoud 1 Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
standard. Acknowledgement: Slides borrowed from Richard Y. Yale
 802.11 standard Acknowledgement: Slides borrowed from Richard Y. Yang @ Yale IEEE 802.11 Requirements Design for small coverage (e.g. office, home) Low/no mobility High data rate applications Ability to
802.11 standard Acknowledgement: Slides borrowed from Richard Y. Yang @ Yale IEEE 802.11 Requirements Design for small coverage (e.g. office, home) Low/no mobility High data rate applications Ability to
Links. CS125 - mylinks 1 1/22/14
 Links 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared media Channel partitioning Taking turns Random access Shared
Links 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared media Channel partitioning Taking turns Random access Shared
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
A Directional MAC Protocol with the DATA-frame Fragmentation and Short Busy Advertisement Signal for Mitigating the Directional Hidden Node Problem
 2012 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications - (PIMRC) A Directional MAC Protocol with the DATA-frame Fragmentation and Short Busy Advertisement Signal for
2012 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications - (PIMRC) A Directional MAC Protocol with the DATA-frame Fragmentation and Short Busy Advertisement Signal for
Implementation and use of Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology for Public Safety, Traffic applications, and Highway Engineering
 Implementation and use of Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology for Public Safety, Traffic applications, and Highway Engineering Topics of discussion * Section 1. Wireless vs. Wired. Advantages and disadvantages
Implementation and use of Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology for Public Safety, Traffic applications, and Highway Engineering Topics of discussion * Section 1. Wireless vs. Wired. Advantages and disadvantages
ARUBA OS ARUBA CONTROLLER FEATURES USED TO OPTIMIZE PERFORMANCE
 ARUBA OS ARUBA CONTROLLER FEATURES USED TO OPTIMIZE PERFORMANCE Technical Climb Webinar 10:00 GMT 11:00 CET 13:00 GST Oct 26th, 2016 Presenter: Barath Srinivasan barath.srinivasan@hpe.com Welcome to the
ARUBA OS ARUBA CONTROLLER FEATURES USED TO OPTIMIZE PERFORMANCE Technical Climb Webinar 10:00 GMT 11:00 CET 13:00 GST Oct 26th, 2016 Presenter: Barath Srinivasan barath.srinivasan@hpe.com Welcome to the
PHY Link Channel Resource Allocation, Overhead, Impact on Procedures. Nicola Varanese (Qualcomm)
 PHY Link Channel Resource Allocation, Overhead, Impact on Procedures Nicola Varanese (Qualcomm) 1 Summary A PHY Control Channel (PLC) is needed for Aiding PHY initialization and CNU bring-up Broadcasting
PHY Link Channel Resource Allocation, Overhead, Impact on Procedures Nicola Varanese (Qualcomm) 1 Summary A PHY Control Channel (PLC) is needed for Aiding PHY initialization and CNU bring-up Broadcasting
IEEE Wireless LAN draft Standard
 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN draft Standard Keith B. Amundsen Wireless Solutions 508-470-9483 keith_b_amundsen@raytheon.com October 24, 1996 Worcester Polytechnic Institute Introduction IEEE 802.11 Draft 5.0
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN draft Standard Keith B. Amundsen Wireless Solutions 508-470-9483 keith_b_amundsen@raytheon.com October 24, 1996 Worcester Polytechnic Institute Introduction IEEE 802.11 Draft 5.0
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg
 Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
OSBRiDGE 24XL(i) Configuration Manual. Firmware 2.05b9
 OSBRiDGE 24XL(i) Configuration Manual Firmware 2.05b9 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 24XL devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP: 192.168.1.250
OSBRiDGE 24XL(i) Configuration Manual Firmware 2.05b9 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 24XL devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP: 192.168.1.250
A High-Throughput Path Metric for Multi-Hop Wireless Routing
 Wireless Networks, 49 434, 25 C 25 Springer Science + Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A High-Throughput Path Metric for Multi-Hop Wireless Routing DOUGLAS S. J. DE COUTO, DANIEL AGUAYO,
Wireless Networks, 49 434, 25 C 25 Springer Science + Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A High-Throughput Path Metric for Multi-Hop Wireless Routing DOUGLAS S. J. DE COUTO, DANIEL AGUAYO,
CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications. Link Layer
 CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications Link Layer Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs455-s13 1 Link Layer
CS 455/555 Intro to Networks and Communications Link Layer Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs455-s13 1 Link Layer
Outdoor High Power b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0
 Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Wireless Router at Home
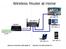 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Reminder: Datalink Functions Computer Networking. Datalink Architectures
 Reminder: Datalink Functions 15-441 15 441 15-641 Computer Networking Lecture 5 Media Access Control Peter Steenkiste Fall 2015 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f15 Framing: encapsulating a network layer datagram
Reminder: Datalink Functions 15-441 15 441 15-641 Computer Networking Lecture 5 Media Access Control Peter Steenkiste Fall 2015 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f15 Framing: encapsulating a network layer datagram
Throughput Considerations for Wireless Networks
 Wi4Net White Paper: Throughput Considerations for Wireless Networks About us CelPlan Technologies has been a worldwide leading provider of wireless network design, optimization and performance evaluation
Wi4Net White Paper: Throughput Considerations for Wireless Networks About us CelPlan Technologies has been a worldwide leading provider of wireless network design, optimization and performance evaluation
Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in : Collision or Weak Signal?
 Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in 802.11: Collision or Weak Signal? Shravan Rayanchu Arunesh Mishra Dheeraj Agrawal Sharad Saha Suman Banerjee Wisconsin Wireless and NetworkinG Systems (WiNGS) Lab University
Diagnosing Wireless Packet Losses in 802.11: Collision or Weak Signal? Shravan Rayanchu Arunesh Mishra Dheeraj Agrawal Sharad Saha Suman Banerjee Wisconsin Wireless and NetworkinG Systems (WiNGS) Lab University
Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks
 fast efficient and robust networking FERN Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks Ian Chakeres Chivukula Koundinya Pankaj Aggarwal Outline IEEE 802.11s mesh multicast FERM algorithms
fast efficient and robust networking FERN Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks Ian Chakeres Chivukula Koundinya Pankaj Aggarwal Outline IEEE 802.11s mesh multicast FERM algorithms
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Topics. Link Layer Services (more) Link Layer Services LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS. flow control: error detection:
 1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
The Transition from Unsynchronized to GPS Synchronized Networks Finally Explained
 The Transition from Unsynchronized to GPS Synchronized Networks Finally Explained TABLE OF CONTENTS Abstract....................... 3 Single Sector Solution.................. 3 Multi-Sector Solution 3
The Transition from Unsynchronized to GPS Synchronized Networks Finally Explained TABLE OF CONTENTS Abstract....................... 3 Single Sector Solution.................. 3 Multi-Sector Solution 3
Wireless Challenges and Resolutions
 Wireless Challenges and Resolutions 1 Steven Shelton Senior Network Engineer Oak Ridge National Laboratory Oak Ridge, Tennessee ows@ornl.gov 2 Wireless Challenges and Resolutions Sections Common Problems
Wireless Challenges and Resolutions 1 Steven Shelton Senior Network Engineer Oak Ridge National Laboratory Oak Ridge, Tennessee ows@ornl.gov 2 Wireless Challenges and Resolutions Sections Common Problems
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
Sanjit Zubin Biswas. Master of Science. at the. March Certified by... Robert Morris Associate Professor Thesis Supervisor
 Opportunistic Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Networks by Sanjit Zubin Biswas B.S., Stanford University (2002) Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in partial fulfillment
Opportunistic Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Networks by Sanjit Zubin Biswas B.S., Stanford University (2002) Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in partial fulfillment
Presented by: Murad Kaplan
 Presented by: Murad Kaplan Introduction. Design of SCP-MAC. Lower Bound of Energy Performance with Periodic Traffic. Protocol Implementation. Experimental Evaluation. Related Work. 2 Energy is a critical
Presented by: Murad Kaplan Introduction. Design of SCP-MAC. Lower Bound of Energy Performance with Periodic Traffic. Protocol Implementation. Experimental Evaluation. Related Work. 2 Energy is a critical
Solving High Density WiFi
 Edgewater Wireless July 2015 Solving High Density WiFi Does High Throughput 802.11ac hold up in high density applications? The answer might surprise you. While everyone is trying to design networks using
Edgewater Wireless July 2015 Solving High Density WiFi Does High Throughput 802.11ac hold up in high density applications? The answer might surprise you. While everyone is trying to design networks using
CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice
 CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice IEEE 802.11 (WLAN/WiFi) Bhaskaran Raman, Department of CSE, IIT Kanpur http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/braman/courses/wless-spring2007/ IEEE 802.11 (WiFi)
CS698T Wireless Networks: Principles and Practice IEEE 802.11 (WLAN/WiFi) Bhaskaran Raman, Department of CSE, IIT Kanpur http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/braman/courses/wless-spring2007/ IEEE 802.11 (WiFi)
Practical Lazy Scheduling in Wireless Sensor Networks. Ramana Rao Kompella and Alex C. Snoeren
 Practical Lazy Scheduling in Wireless Sensor Networks Ramana Rao Kompella and Alex C. Snoeren Distributed Rate Adaptation Problem: In wireless networks (e.g., sensor nets, 802.11) radios consume significant
Practical Lazy Scheduling in Wireless Sensor Networks Ramana Rao Kompella and Alex C. Snoeren Distributed Rate Adaptation Problem: In wireless networks (e.g., sensor nets, 802.11) radios consume significant
Shared Access Networks Wireless. 1/27/14 CS mywireless 1
 Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Interference avoidance in wireless multi-hop networks 1
 Interference avoidance in wireless multi-hop networks 1 Youwei Zhang EE228A Project Report, Spring 2006 1 Motivation Wireless networks share the same unlicensed parts of the radio spectrum with devices
Interference avoidance in wireless multi-hop networks 1 Youwei Zhang EE228A Project Report, Spring 2006 1 Motivation Wireless networks share the same unlicensed parts of the radio spectrum with devices
3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols
 33 3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols 3.1 Introduction Construction of best possible multicast trees and maintaining the group connections in sequence is challenging even in
33 3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols 3.1 Introduction Construction of best possible multicast trees and maintaining the group connections in sequence is challenging even in
Research Directions in Low-Power Wireless Networks
 Research Directions in Low-Power Wireless Networks Behnam Dezfouli [ dezfouli@ieee.org ] November 2014 1 q OBSERVING AND CHARACTERIZING THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENT ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS For example,
Research Directions in Low-Power Wireless Networks Behnam Dezfouli [ dezfouli@ieee.org ] November 2014 1 q OBSERVING AND CHARACTERIZING THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENT ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS For example,
