A Comparative Analysis of Packet Fragmentation with MPLS Unicast IP Routing and OSPF in an IPbased
|
|
|
- Dina Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Comparative Analysis of Packet Fragmentation with MPLS Unicast IP Routing and OSPF in an IPbased Network Harja Mat Ikram Yusof, Suraya Zainuddin, Murizah Kassim and Ruhani Ab Rahman Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam Selangor, Malaysia. Abstract Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is acknowledged and widely used to overcome drawbacks in traditional Internet Protocol (IP) routing. This paper presents network performance on the effect of packet fragmentation over IP and MPLS networks. Performance analysis on Windows XP is evaluated which tested in an environment using GNS3 which emulates on real environment telecommunication network. Network performance observed on Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) with and without MPLS label implementation accompanied by combination of different data sizes and different Maximum Transfer Units (MTUs). Round-Trip-Time (RTT) is calculated on throughput and packet loss. Results present an analysis performance on different protocols, data sizes and produced MTUs. OSPF provides better RTT and throughput compared to MPLS with default MTU setting. Better RTT and calculated throughput performance is obtained by increasing the MTU for interface, IP and MPLS. RTT for MPLS is slightly higher due to the introduction of label to each packet send. Packet loss behavior is similar in both OSPF and MPLS which more visible when fragmentation happened. This study concludes that upon packet fragmentation, performances are degraded. Index Terms Packet Fragmentation; MPLS; Unicast IP Routing; OSPF. I. INTRODUCTION Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standard architecture proposed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that integrates label swapping forwarding with network layer routing. Various research on MPLS network are analyzed and the technology become more important in providing best performance on its technology used [1], [2], [3]. MPLS is a promising effort in order to deliver traffic management and connection-oriented Quality of Service (QoS) support which speed up the packet-forwarding process, while retaining the flexibility of an IP-based network approach. It also reduces the amount of per-packet processing required at each router in an IP-based network and enhanced router performance. MPLS provides new capabilities in four areas that have ensured its popularity which are QoS support, traffic engineering (TE), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and multiprotocol support. Multiple studies had been done on the performance analysis between MPLS protocol over conventional network and proved it is better [4]. MPLS provides better performance and easier traffic engineering (TE) compare to OSPF that has been simulated using SSF-Net [5] and NS2 [6]. Packet drop behavior in MPLS is almost negligible amount compared to traditional IP network. However, QoS-aware multi-plane routing method for OSPF-based IP access networks has been done and present that some enhanced performance with new algorithms are presented [7]. Some tools are offered in the market for modeling and simulating MPLS networks such as GNS3, OpenSim MPLS and Opnet [8]. A study on measured MPLS also has been done using Linux platform where results presented higher MPLS RTT compare to conventional IP [9]. Most of the research on comparing OSPF and MPLS focus on the traffic engineering and virtual private network, which are the core applications in MPLS implementation [10]. Limited article is written on the MPLS unicast IP routing performance which is the basic to other well-known MPLS application such as MPLS VPN and TE [11]. This paper presented on the assessment and analysis performance of MPLS Unicast IP Routing. Test bed setup in GNS3 is emulated on real network of telecommunications site. The performance is observed on how the fragmentation effects RTT, throughput and packet drops over OSPF and MPLS unicast IP forwarding. This study covers on the design, optimization and simulations with test bed data on Windows XP operating system. Results present an analysis performance on different protocols, data sizes and produced MTUs. Analysis shows OSPF provides better RTT and throughput compared to MPLS with default MTU setting. Better RTT and calculated throughput performance can be obtained by increasing the MTU for interface, IP and MPLS. It is concluded that with packet fragmentation, throughput performances are degraded. II. MPLS UNICAST IP ROUTING The MPLS is used for simple unicast packet forwarding logic based on labels. During the selection of packet forwarding, MPLS considers only available routes in the unicast IP routing table which also used on OSPF routing. MPLS is similar to OSPF which have similar path forwarding where all other factors remain unchanged [11]. MPLS unicast IP forwarding does not offer any significant advantages by ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3 95
2 Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering itself, however it is useful with other application such as MPLS-TE and MPLS-VPN that use MPLS unicast IP forwarding as one part of their MPLS network[9]. Unicast IP routing is the most common application for MPLS. A study presented two mechanisms required on the control plane which are IP routing protocol and label distribution protocol. In this particular study, OSPF is chosen for IP routing protocol to carry the information regarding the reachability of networks while Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is selected for label binding over network learned via the routing protocol. A label is assigned to every destination network in the IP forwarding table and stack bit is set to 1 due to a single label with 32 bits inserted between Layer 2 and 3 indicates the MPLS frame mode. Figure 1 illustrates simplified model of routing and forwarding mapping: Figure 1: Mapping between Routing and Forwarding B. Test Environment Setup In order to study on the behavior and performance of the network, topology for the simulation should be representative of typical topology. Thus, test bed is setup based on the simplify network of existing telecommunication site. However, a few assumptions are made in order to ease the study and observation which are: All routers used in the topologies are Cisco C3640. All interfaces used in the topologies are serials with similar cost. One subnet (which consists of multiple routers (hops) in actual network) is represented by one router (one hop in test bed network). IP assignment is self-defined due to security purposes (not similar IP range as implemented in actual network). Figure 2 illustrates the existing network topology for the site and Table 2 indicates the hardware technical configuration used for the test bed environment. Host 1 is connected to Router M1 and Host 2 is connected to Router M9. Host 1 is connected to the physical network card on the host machine that run GNS3 while Host 2 is connected to virtual machine that run on the similar machine. Each host is furnished with Wireshark, a network protocol analyzer. III. METHODOLOGY MPLS IP routing and OSPF set up is established and simulated in order to analyzed both performance. The OSPF and MPLS topologies set up have used three simulation tools which are Graphical Network Simulator (GNS3), VMWare Player and Wireshark. A. Simulations Tools i. GNS3 GNS3 is a freeware graphical network simulator that allows users to design and deploy simulation for complex network topologies. It is a complementary tool to real lab [12]. GNS3 encompasses package which are valuable and combination of these emulators provide complete and accurate simulation of real network [13]. In this study, network topologies are created using software like Dynamips, VirtualBox that run desktop and server operating systems, Qemu as a generic open source machine emulator, Wireshark as a packet capture freeware and connection to virtual network or host and real device. ii. VMware Player VMware player is virtualization software which can run existing virtual appliances and create its own virtual machines. It is a free desktop application that allow user to run a virtual machine on a Windows or Linux PC [14]. This application combines powerful virtualization features into the player which allows Virtual machine isolation, Access to host PC devices, Adjustable memory for optimal performance, Powerful networking capabilities and configurable shutdown iii. Wireshark It is a free and open-source packet analyzer. Wireshark is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communication protocol development, and education. This freeware capable to understand the structure (encapsulation) of different networking protocols [15]. Figure 2: Actual Network Topology for the Selected Site The test environment comprises 21 routers inclusive of 4 Customer Edge (CE) routers, 4 Provider Edge (PE) routers and 13 Provider (P). Cisco C3640 routers are tuned to the optimized idle PC value in order to obtained a stable network topology on GNS3. ICMP network protocol packets are sent from Host 1 to Host 2 via command prompt on the host machine to observe the network performance. OSPF routing configured on all routers in order to setup OSPF routing based network. Figure 3 shows samples of command for OSPF routing configuration. MTU size set to to cater additional 3 labels of 4 byte for MPLS labels. Basic configuration is configured on the router s interfaces to allow MPLS MTU size to be changes as required value. router ospf [process-id] network [ip address] [mask] area [area-id] MPLS is enabled on the router s interfaces to establish MPLS unicast IP forwarding as following: interface [type-number] mpls ip mpls label protocol ldp Change router s interfaces and IP MTU : interface [type-number] mtu [value] ip mtu [value] interface [type-number] mpls mtu [value] Figure 3: OSPF Routing Command 96 ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3
3 A Comparative Analysis of Packet Fragmentation with MPLS Unicast IP Routing and OSPF in an IP-based Network Table 1 Major themes and sub-themes on the topic of virtual university No Hardware Configurations 1. Host 1 2. Host 2 3. Router M1 to M21 4. Channel Capacity Processor: Intel Core 2 Duo CPU RAM: 128 MB Operating System: Microsoft Windows XP NIC: VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter Monitoring Tools: Wireshark Network Protocol Analyzer Version Processor: Intel Core 2 Duo CPU RAM: 2.5 GB Operating System: Microsoft Windows XP NIC: Broadcom Netlink Fast Ethernet Monitoring Tools: Wireshark Network Protocol Analyzer Version Model: Cisco 3640 IOS: 3600 Software (C3640-JS-M), Version 12.4 (23) Fast Ethernet Interface: NM 1FE-TX Serial Interface: NM-4T Idle PC Value: 0x604d9334 Fast Ethernet: 100 Mbps T1 Serial: Mbps C. System Flow Figure 4 shows the entire test and experiment which is done systematically to ensure the stable data readings. Host is setup and connected to the identified network topology. Started packet captured trap is retrieved. ICMP packets are send and tested of all condition is retrieved again if routed are successful. Figure 5: MPLS Labels and Stack Bit All logs and data are saved for analysis. If data is not sufficient and all condition is not well, repeated loop for capture packet and start hosts are done. Above all mentioned command, ip cef needs to be enabled. Traceroute command is used to check on the path established for packet travelling from Host 1 to Host 2. Test has analyzed a traceroute from Host 1 with OSPF routing established and MPLS labels can be seen on the forwarding path once MPLS was enabled by issuing traceroute at the router. MPLS labels and stacking bit are observed from the experiment at every hop in the packet s routing path from Host 1 to Host 2 using Wireshark and Cisco commands. Figure 5 depicts the label swapping flow and stack bit monitored for MPLS unicast IP forwarding during the experiment. IV. ANALYSIS AND RESULT Analysis presents the observation results acquired from the conduct research. An ICMP packet was issued using Ping command to obtain RTT between 2 hosts. Throughput is calculated based on the RTT and packet loss was observed. A. Variation of Packet Size in OSPF and MPLS Topologies Figure 6 and Figure 7 show average RTT for both OSPF and MPLS unicast IP forwarding without DF Bit Set with default MTU of. ICMP packets size are varied to 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, and 2000 bytes. Table 2 presents RTT that shows nearly similar readings for OSPF and MPLS with DF bit sets. Unfortunately, at and 2000 bytes size sent, host received ICMP error of Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set for both topologies. Figure 6: OSPF RTT Performance Figure 4: Test Flow ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3 97
4 Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering Figure 7: MPLS RTT Performance Table 2 Maximum Theoretical TCP Throughput on Windows XP Test Condition Packet Size < bytes Packet Size byes Packet Size < bytes Packet Size < bytes DF Set Average RTT (ms) OSPF Throughput (Kbps) Yes No Yes Packet needs to be fragmented MPLS No Yes No Yes Packet needs to be fragmented Figure 8 shows the packet drop behavior in OSPF network without DF bit set. Occurrence of packet drop is more frequent for packet size larger or equal to bytes. Figure 9 presents the packet drop in OSPF network for DF bit set. Packet drop is almost negligible. Number of packet drop in MPLS topology without DF set is pictured as per Figure 10. Similar as per OSPF, packet loss is frequent for packet size larger or equal to bytes However, no packet drop is observed when DF was set. Figure 10: MPLS without DF Bit Set Data is observed and analyzed from the perspective of ICMP RTT, calculated throughput and packet loss. Data presents that incremental in packet size don t have significant impact on the RTT and throughput. As long as packet size is smaller than the MTU and no fragmentation occurs in both topologies. Packet drop is negligible. However, once the packet size increases more than the MTU, fragmentation happened. RTT increases and it decreases the calculated throughput. Occurrence of packet drop is frequent. Half or more of the data captured from the runs perceive to have packet loss around %. B. Variation of MTU in OSPF and MPLS Topologies Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is measured as one of the performance for the analyzed comparison. In this study, network interface and IP MTU are varied from default of to and for OSPF as similar for MPLS topology, interface, IP and MPLS MTU without DF (W-DF). Changes in MTUs are done to the PE and P routers. Figure 11 shows average RTT when ICMP packets send with fragmentation allowed for default MTU =. Figure 12 shows average RTT when ICMP packets send with fragmentation allowed for default MTU =. Figure 8: Packet Drop for OSPF without DF Bit Set Figure 11: Average RTT w-df Bit Set, MTU = Figure 9: Packet Drop for OSPF with DF Bit Set Figure 12: Average RTT w- DF, MTU = TU = Figure 13 indicates average RTT when ICMP packets send with fragmentation allowed for default MTU =. Figure 98 ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3
5 A Comparative Analysis of Packet Fragmentation with MPLS Unicast IP Routing and OSPF in an IP-based Network 14 illustrates the average RTT for both OSPF and MPLS networks when DF bit is set. When packets sent with DF, no fragmentation was allowed. Figure 13: Average RTT w-df Bit Set (MTU = ) Table 3 Maximum Theoretical TCP Throughput on Windows XP on OSPF TEST CONDITION OSPF Fragment Don't Fragment MTU ICMP Size > 1472 Byte Average RTT (ms) Throughput (Kbps) Yes No Yes Yes Table 4 Maximum Theoretical TCP Throughput on Windows XP on MPLS Figure 14: Average RTT with DF Bit Set Table 3 and Table 4 presents MTU, ICMP size, average RTT and throughput for both OSPF and MPLS networks when DF bit is set. When packets sent with DF, no fragmentation was allowed. Maximum theoretical TCP throughput is calculated and results are tabulated as in the table. Analyzed presents that similar RTT response for both topologies noticed when packet send without fragmentation allowed (DF is set) using default MTU. However, once the packet size reached 1473 for OSPF, it is dropped. This is due to ICMP packet send with the addition of 28 bytes of IP header resulted size more than which is default MTU value. Similar response also discovered when MPLS unicast IP packet achieved 1469 bytes. In the MPLS network, 4 bytes lesser of ICMP packet size can be sent compare to OSPF caused by the allocation for 32 bits MPLS shim. Data also presents stable data readings for OSPF when MTU was changed from to and. However, different RTT performance observed for MPLS. When MTU is change from to to, there is a remarkable improvement in the RTT performance which relates back to the calculated throughput. This is due to packet was not fragmented when MTU increased to. During MTU set to default, ICMP Packet of 1473 is split into 2 which are 1472 bytes and 1 byte. Overall, OSPF performance is better than MPLS with unicast IP routing in term of RTT and throughput. RTT for MPLS seems to be slightly higher due to the introduction of label to each packet send. In this case, 4 bytes label is appended to each packet send out with MPLS applied. Packet loss behavior is similar in both network which more visible when fragmentation happened. TEST CONDITION MPLS Fragment Don't Fragment MTU ICMP Size > 1472 Byte Average RTT (ms) Throughput (Kbps) No Yes No Yes No Yes No Packet needs to be fragmented No No V. CONCLUSION This paper presents the experiment done on OSPF and MPLS unicast IP routing topologies by looking into packet fragmentation impact to their performance. Packet size and MTU are set as variable in this study. Tests were established on Cisco C3640 routers with Windows XP environment hosts. Results were analyzed and compared in term of RTT, calculated throughput and packet loss. Obviously, OSPF has better performance compare to MPLS either packet is fragmented or vice versa. As earlier iterated, MPLS unicast IP forwarding itself does not offer any benefit. However, when it comes to MPLS competent applications such as TE and VPN, MPLS unicast IP routing is a compulsory. Thus, research propose for case of MPLS unicast IP routing is better to run by itself without other applications, OSPF is suggested and preferred by taking into consideration on the RTT and throughput performance. However, this study does not look into detail on how MPLS unicast IP routing provides advantage in term of IP looping prevention. This is capability that can be further analyzed for performance degradation compare to OSPF. Future study on Transport Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) throughput observation together with IP looping prevention also can be done looking on performance issue. ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3 99
6 Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering REFERENCES [1] Charles N. A Comparative Simulation Study of IP, MPLS, MPLS-TE for Latency and Packet Loss Reduction over a WAN, International Journal of Networks and Communications, vol. 6, no.1, pp.1-7, [2] Ab Rahman R, Alias FA, Kassim M, Yusof MI, Hashim H., Implementation of high availability concept based on traffic segregation over MPLS-TE, ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, vol. 10, no. 3, pp , [3] Ab Rahman R, Kassim M, Ariffin N. Performance Analysis on Wan Optimizations: Bandwidth Management in Multi Protocol Level Switching (MPLS) VirtualPrivate Network (VPN), 2011 International Conference on Future Information Technology, IPCSIT,vol.13, [4] Barakovic J, Bajric H, Husic, A. Multimedia Traffic Analysis of MPLS and non-mpls Network,, Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Proceedings ELMAR, [5] Köhler S, Binzenhöfer, A. MPLS traffic engineering in OSPF networks- A combined approach,, Teletraffic Science and Engineering: Elsevier BV, pp , [6] Rahman MA, Hassan Z, Kabir AH, Lutfullah KAM, Amin MR. Performance Analysis of MPLS Protocols over conventional Network,, 2008 China-Japan Joint Microwave Conference. Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE), [7] Jaron A, Mihailovic A, Aghvami A., QoS-Aware Multi-Plane Routing Method For OSPF-based IP Access Networks,, Computer Networks, [8] Sllame AM. Modeling and simulating MPLS networks, The 2014 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications. Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE), [9] Nadeau TD. The MPLS Traffic Engineering MIB (MPLS-TE MIB), MPLS Network Management: Elsevier BV. pp , [10] Porwal MK, Yadav A, Charhate SV., Traffic Analysis of MPLS and Non MPLS Network including MPLS Signaling Protocols and Traffic Distribution in OSPF and MPLS, 2008 First International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology: Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE), [11] Systems C. Implementing AAA Authentication, Securing and Controlling Cisco Routers: Informa UK Limited, [12] WANG Y, WANG J. Use gns3 to simulate network laboratory, Computer Programming Skills & Maintenance, pp.12:046, [13] Faxun L. The Application of GNS3 in Network Experiments, Computer & Telecommunication, pp.10:032, [14] Ruest N, Ruest D. Virtualization, A Beginner's Guide, McGraw-Hill, Inc., [15] Shimonski R., The Wireshark Field Guide: Analyzing and Troubleshooting Network Traffic: Newnes, ISSN: e-issn: Vol. 8 No. 3
Improving the usage of Network Resources using MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Improving
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Improving
Virtual Routing and Forwarding-lite Traffic Management over Multi-protocol Layer Switching- Virtual Private Network
 Virtual Routing and Forwarding-lite Traffic Management over Multi-protocol Layer Switching- Virtual Private Network Ruhani Ab Rahman, Nur Asikin Zahari, Murizah Kassim, Mat Ikram Yusof Faculty of Electrical
Virtual Routing and Forwarding-lite Traffic Management over Multi-protocol Layer Switching- Virtual Private Network Ruhani Ab Rahman, Nur Asikin Zahari, Murizah Kassim, Mat Ikram Yusof Faculty of Electrical
Implementing MPLS Forwarding
 All Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) features require a core set of MPLS label management and forwarding services; the MPLS Forwarding Infrastructure (MFI) supplies these services. Feature History
All Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) features require a core set of MPLS label management and forwarding services; the MPLS Forwarding Infrastructure (MFI) supplies these services. Feature History
Lecture 3. The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Measuring MPLS overhead
 Measuring MPLS overhead A. Pescapè +*, S. P. Romano +, M. Esposito +*, S. Avallone +, G. Ventre +* * ITEM - Laboratorio Nazionale CINI per l Informatica e la Telematica Multimediali Via Diocleziano, 328
Measuring MPLS overhead A. Pescapè +*, S. P. Romano +, M. Esposito +*, S. Avallone +, G. Ventre +* * ITEM - Laboratorio Nazionale CINI per l Informatica e la Telematica Multimediali Via Diocleziano, 328
Configuring MLPPP. Finding Feature Information
 The Multilink Point-to-Point (MLPPP) feature provides load balancing functionality over multiple WAN links, while providing multivendor interoperability, packet fragmentation and proper sequencing, and
The Multilink Point-to-Point (MLPPP) feature provides load balancing functionality over multiple WAN links, while providing multivendor interoperability, packet fragmentation and proper sequencing, and
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
Performance Evaluation of IPv4 and IPv6 over MPLS using OPNET
 Performance Evaluation of IPv4 and IPv6 over MPLS using OPNET Suhail Ahmad Wajid Ali Hamdani Mohsin Hassan Magray ABSTRACT Over the last two decades, we have witnessed a rapid deployment of real-time applications
Performance Evaluation of IPv4 and IPv6 over MPLS using OPNET Suhail Ahmad Wajid Ali Hamdani Mohsin Hassan Magray ABSTRACT Over the last two decades, we have witnessed a rapid deployment of real-time applications
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Improve the QoS by Applying Differentiated Service over MPLS Network
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 9, September 2015,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 9, September 2015,
Introduction to MPLS APNIC
 Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Networking for Data Acquisition Systems. Fabrice Le Goff - 14/02/ ISOTDAQ
 Networking for Data Acquisition Systems Fabrice Le Goff - 14/02/2018 - ISOTDAQ Outline Generalities The OSI Model Ethernet and Local Area Networks IP and Routing TCP, UDP and Transport Efficiency Networking
Networking for Data Acquisition Systems Fabrice Le Goff - 14/02/2018 - ISOTDAQ Outline Generalities The OSI Model Ethernet and Local Area Networks IP and Routing TCP, UDP and Transport Efficiency Networking
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool
 IP Telephony Contact Centers Mobility Services WHITE PAPER Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool April 2005 avaya.com Table of Contents Overview... 1 Network Impact... 2 Network Paths... 2 Path Generation...
IP Telephony Contact Centers Mobility Services WHITE PAPER Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool April 2005 avaya.com Table of Contents Overview... 1 Network Impact... 2 Network Paths... 2 Path Generation...
Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:
![Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision: Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:](/thumbs/79/79964001.jpg) Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
Cisco. Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM)
 Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
HP Routing Switch Series
 HP 12500 Routing Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3414 Software version: 12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
HP 12500 Routing Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3414 Software version: 12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
MPLS Intro. Cosmin Dumitru March 14, University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group ...
 MPLS Intro Cosmin Dumitru c.dumitru@uva.nl University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group March 14, 2011 Disclaimer Information presented in these slides may be slightly biased towards
MPLS Intro Cosmin Dumitru c.dumitru@uva.nl University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group March 14, 2011 Disclaimer Information presented in these slides may be slightly biased towards
Lab 6.7.1: Ping and Traceroute
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1-ISP R2-Central Eagle Server S0/0/0 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252 N/A Fa0/0 192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1-ISP R2-Central Eagle Server S0/0/0 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252 N/A Fa0/0 192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0
IP SLAs Overview. Finding Feature Information. Information About IP SLAs. IP SLAs Technology Overview
 This module describes IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs). IP SLAs allows Cisco customers to analyze IP service levels for IP applications and services, to increase productivity, to lower operational costs,
This module describes IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs). IP SLAs allows Cisco customers to analyze IP service levels for IP applications and services, to increase productivity, to lower operational costs,
Hands-On Troubleshooting IPTV with WireShark
 Hands-On Course Description This Hands-On course will enable attendees to upgrade their knowledge about how Video and Television is carried over IP in state-of-the art systems. At the end of the course
Hands-On Course Description This Hands-On course will enable attendees to upgrade their knowledge about how Video and Television is carried over IP in state-of-the art systems. At the end of the course
MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU. Multiprotocol Label Switching
 MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU Multiprotocol Label Switching Basic Concepts of MPLS 2 Contents Drawbacks of Traditional IP Forwarding Basic MPLS Concepts MPLS versus IP over ATM Traffic Engineering with
MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU Multiprotocol Label Switching Basic Concepts of MPLS 2 Contents Drawbacks of Traditional IP Forwarding Basic MPLS Concepts MPLS versus IP over ATM Traffic Engineering with
MPLS VPN. 5 ian 2010
 MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
The Interconnection Structure of. The Internet. EECC694 - Shaaban
 The Internet Evolved from the ARPANET (the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), a project funded by The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) in 1969. ARPANET's purpose was to provide the U.S. Defense
The Internet Evolved from the ARPANET (the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), a project funded by The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) in 1969. ARPANET's purpose was to provide the U.S. Defense
Manually Configured IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels
 This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
 CHAPTER 39 This chapter describes how to use Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) on the switch. Cisco IP SLAs is a part of Cisco IOS software that allows Cisco customers to analyze IP service
CHAPTER 39 This chapter describes how to use Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) on the switch. Cisco IP SLAs is a part of Cisco IOS software that allows Cisco customers to analyze IP service
Foreword xxiii Preface xxvii IPv6 Rationale and Features
 Contents Foreword Preface xxiii xxvii 1 IPv6 Rationale and Features 1 1.1 Internet Growth 1 1.1.1 IPv4 Addressing 1 1.1.2 IPv4 Address Space Utilization 3 1.1.3 Network Address Translation 5 1.1.4 HTTP
Contents Foreword Preface xxiii xxvii 1 IPv6 Rationale and Features 1 1.1 Internet Growth 1 1.1.1 IPv4 Addressing 1 1.1.2 IPv4 Address Space Utilization 3 1.1.3 Network Address Translation 5 1.1.4 HTTP
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp
 MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 15 20 15 MPLS and NGN Networks: The Future Aspects for Railways Communication System Alok Pandey E,
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 15 20 15 MPLS and NGN Networks: The Future Aspects for Railways Communication System Alok Pandey E,
Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze
 Picture 15 13 Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
Picture 15 13 Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia. Guy Leduc. Chapter 2 MPLS networks. Chapter 2: MPLS
 Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
TCP/IP Networking. Training Details. About Training. About Training. What You'll Learn. Training Time : 9 Hours. Capacity : 12
 TCP/IP Networking Training Details Training Time : 9 Hours Capacity : 12 Prerequisites : There are no prerequisites for this course. About Training About Training TCP/IP is the globally accepted group
TCP/IP Networking Training Details Training Time : 9 Hours Capacity : 12 Prerequisites : There are no prerequisites for this course. About Training About Training TCP/IP is the globally accepted group
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series
 HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4676a Software version: Release 23xx Document version: 6W101-20150320 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4676a Software version: Release 23xx Document version: 6W101-20150320 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
Send documentation comments to You must enable FCIP before attempting to configure it on the switch.
 CHAPTER 9 (Fibre Channel over IP) is an IETF standards based protocol for connecting Fibre Channel SANs over IP based networks. encapsulates the FCP frames in a TCP/IP packet which is then sent across
CHAPTER 9 (Fibre Channel over IP) is an IETF standards based protocol for connecting Fibre Channel SANs over IP based networks. encapsulates the FCP frames in a TCP/IP packet which is then sent across
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
II. Principles of Computer Communications Network and Transport Layer
 II. Principles of Computer Communications Network and Transport Layer A. Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Header An IP datagram consists of a header part and a text part. The header has a 20-byte fixed part
II. Principles of Computer Communications Network and Transport Layer A. Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Header An IP datagram consists of a header part and a text part. The header has a 20-byte fixed part
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)
 MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) First Published: January 1, 1999 Last Updated: May 1, 2008 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) enables peer label switch routers
MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) First Published: January 1, 1999 Last Updated: May 1, 2008 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) enables peer label switch routers
McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000
 !! McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 "#$% & '$# )1 ) ) )6 ) )* )- ). )0 )1! )11 )1 )1 )16 )1 3'' 4", ( ( $ ( $ $$+, $$, /+ & 23,4 )/+ &4 $ 53" Network Layer Position of network layer Figure
!! McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 "#$% & '$# )1 ) ) )6 ) )* )- ). )0 )1! )11 )1 )1 )16 )1 3'' 4", ( ( $ ( $ $$+, $$, /+ & 23,4 )/+ &4 $ 53" Network Layer Position of network layer Figure
Implementing IP in IP Tunnel
 This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for IP in IP tunnels on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Note For a complete description of the IP in IP tunnel commands listed in this
This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for IP in IP tunnels on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Note For a complete description of the IP in IP tunnel commands listed in this
Why Your Application only Uses 10Mbps Even the Link is 1Gbps?
 Why Your Application only Uses 10Mbps Even the Link is 1Gbps? Contents Introduction Background Information Overview of the Issue Bandwidth-Delay Product Verify Solution How to Tell Round Trip Time (RTT)
Why Your Application only Uses 10Mbps Even the Link is 1Gbps? Contents Introduction Background Information Overview of the Issue Bandwidth-Delay Product Verify Solution How to Tell Round Trip Time (RTT)
The Traceroute Command in MPLS
 The Traceroute Command in MPLS Document ID: 26585 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Normal traceroute Command MPLS traceroute Command no mpls ip propagate ttl
The Traceroute Command in MPLS Document ID: 26585 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Normal traceroute Command MPLS traceroute Command no mpls ip propagate ttl
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV
 MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV First Published: January 26, 2004 Last Updated: February 27, 2009 The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps
MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV First Published: January 26, 2004 Last Updated: February 27, 2009 The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals. Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4
 CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4 Updated: 20/05/2008 1 6.0.1 Introduction Addressing is a key function of Network layer protocols that enables data communication
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4 Updated: 20/05/2008 1 6.0.1 Introduction Addressing is a key function of Network layer protocols that enables data communication
Cisco IP Fragmentation and PMTUD
 Table of Contents IP Fragmentation and PMTUD...1 Introduction...1 IP Fragmentation and Reassembly...1 Issues with IP Fragmentation...3 Avoiding IP Fragmentation: What TCP MSS Does and How It Works...4
Table of Contents IP Fragmentation and PMTUD...1 Introduction...1 IP Fragmentation and Reassembly...1 Issues with IP Fragmentation...3 Avoiding IP Fragmentation: What TCP MSS Does and How It Works...4
MPLS over GRE. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN L3VPN over GRE
 The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
Implementation of Multicast Routing on IPv4 and IPv6 Networks
 Implementation of Multicast Routing on IPv4 and IPv6 Networks Dr.Sridevi, Assistant Professor, Dept of Computer Science, Karnatak University, Dharwad. Abstract: Fast developing world of technology, multimedia
Implementation of Multicast Routing on IPv4 and IPv6 Networks Dr.Sridevi, Assistant Professor, Dept of Computer Science, Karnatak University, Dharwad. Abstract: Fast developing world of technology, multimedia
Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process
 Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process Document ID: 107615 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Understanding BGP Processes
Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process Document ID: 107615 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Understanding BGP Processes
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV
 MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
Centralization of Network using Openflow Protocol
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(S2), 165 170, January 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 DOI : 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8iS2/61217 Centralization of Network using Openflow
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(S2), 165 170, January 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 DOI : 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8iS2/61217 Centralization of Network using Openflow
Table of Contents. Cisco MPLS FAQ For Beginners
 Table of Contents MPLS FAQ For Beginners...1 Document ID: 4649...1 Questions...1 Introduction...1 Q. What is Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)?...1 Q. What is a label? What is the structure of the
Table of Contents MPLS FAQ For Beginners...1 Document ID: 4649...1 Questions...1 Introduction...1 Q. What is Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)?...1 Q. What is a label? What is the structure of the
Computer Networks: Lab 3 Traceroute and IP Luca Bedogni
 Computer Networks: Lab 3 Traceroute and IP Luca Bedogni Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Bologna A brief introduction We will leverage the traceroute utility It traces the route
Computer Networks: Lab 3 Traceroute and IP Luca Bedogni Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Bologna A brief introduction We will leverage the traceroute utility It traces the route
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals
 CCNA Exploration 4.0 1. Network Fundamentals The goal of this course is to introduce you to fundamental networking concepts and technologies. These online course materials will assist you in developing
CCNA Exploration 4.0 1. Network Fundamentals The goal of this course is to introduce you to fundamental networking concepts and technologies. These online course materials will assist you in developing
Configuring MPLS and EoMPLS
 37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. MPLS is a packet-switching technology that integrates
37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. MPLS is a packet-switching technology that integrates
Lecture 8. Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
Question 7: What are Asynchronous links?
 Question 1:.What is three types of LAN traffic? Unicasts - intended for one host. Broadcasts - intended for everyone. Multicasts - intended for an only a subset or group within an entire network. Question2:
Question 1:.What is three types of LAN traffic? Unicasts - intended for one host. Broadcasts - intended for everyone. Multicasts - intended for an only a subset or group within an entire network. Question2:
MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE
 MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE 1 SHEETAL BORSE, 2 MRUDUL DIXIT 1,2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Cummins College of Engineering
MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE 1 SHEETAL BORSE, 2 MRUDUL DIXIT 1,2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Cummins College of Engineering
Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN
 Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network
 Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Mobile
 Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Mobile Product Overview Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Mobile extends Cisco WAAS Software application acceleration benefits to mobile employees
Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Mobile Product Overview Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Mobile extends Cisco WAAS Software application acceleration benefits to mobile employees
INTE-C5O44 - Internet
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 340 - EPSEVG - Vilanova i la Geltrú School of Engineering 744 - ENTEL - Department of Network Engineering BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 340 - EPSEVG - Vilanova i la Geltrú School of Engineering 744 - ENTEL - Department of Network Engineering BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN
A MPLS Simulation for Use in Design Networking for Multi Site Businesses
 A MPLS Simulation for Use in Design Networking for Multi Site Businesses Petac Eugen Ovidius University of Constanța, Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science epetac@univ-ovidius.ro Abstract The ease
A MPLS Simulation for Use in Design Networking for Multi Site Businesses Petac Eugen Ovidius University of Constanța, Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science epetac@univ-ovidius.ro Abstract The ease
Goals and topics. Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Network Media T Circuit switching networks. Topics. Packet-switching networks
 Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Media T-110.250 19.2.2002 Antti Ylä-Jääski 19.2.2002 / AYJ lide 1 Goals and topics protocols Discuss how packet-switching networks differ from circuit switching networks.
Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Media T-110.250 19.2.2002 Antti Ylä-Jääski 19.2.2002 / AYJ lide 1 Goals and topics protocols Discuss how packet-switching networks differ from circuit switching networks.
Chapter 7 CONCLUSION
 97 Chapter 7 CONCLUSION 7.1. Introduction A Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) could be considered as network of mobile nodes which communicate with each other without any fixed infrastructure. The nodes in
97 Chapter 7 CONCLUSION 7.1. Introduction A Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) could be considered as network of mobile nodes which communicate with each other without any fixed infrastructure. The nodes in
Performance Evaluation of MPLS TE Signal Protocols with Different Audio Codecs for Voice Application
 Performance Evaluation of MPLS TE Signal Protocols with Different Audio Codecs for Voice Application Sarmad K. Ibrahim Computer Engineering Department, Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mahmoud M. AL-Quzwini
Performance Evaluation of MPLS TE Signal Protocols with Different Audio Codecs for Voice Application Sarmad K. Ibrahim Computer Engineering Department, Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mahmoud M. AL-Quzwini
Internetworking/Internetteknik, Examination 2G1305 Date: August 18 th 2004 at 9:00 13:00 SOLUTIONS
 Internetworking/Internetteknik, Examination 2G1305 Date: August 18 th 2004 at 9:00 13:00 SOLUTIONS 1. General (5p) a) The so-called hourglass model (sometimes referred to as a wine-glass ) has been used
Internetworking/Internetteknik, Examination 2G1305 Date: August 18 th 2004 at 9:00 13:00 SOLUTIONS 1. General (5p) a) The so-called hourglass model (sometimes referred to as a wine-glass ) has been used
MPLS/Tag Switching. Background. Chapter Goals CHAPTER
 28 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the advantages of MPLS. Learn the components of an MPLS system. Compare and contrast MPLS and hop-by-hop routing. Describe the two methods of label distribution. Explain
28 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the advantages of MPLS. Learn the components of an MPLS system. Compare and contrast MPLS and hop-by-hop routing. Describe the two methods of label distribution. Explain
Performance Evaluation of NEMO Basic Support Implementations
 Performance Evaluation of NEMO Basic Support Implementations Romain Kuntz, Koshiro Mitsuya, Ryuji Wakikawa Keio University, Japan E-mail: {kuntz,mitsuya,ryuji}@sfc.wide.ad.jp Abstract. The NEMO Basic Support
Performance Evaluation of NEMO Basic Support Implementations Romain Kuntz, Koshiro Mitsuya, Ryuji Wakikawa Keio University, Japan E-mail: {kuntz,mitsuya,ryuji}@sfc.wide.ad.jp Abstract. The NEMO Basic Support
Computer Networks Security: intro. CS Computer Systems Security
 Computer Networks Security: intro CS 166 - Computer Systems Security A very easy network 3/14/16 Computer Networks: Intro 2 Two philosophers example Translator Language Translator Engineer Communication
Computer Networks Security: intro CS 166 - Computer Systems Security A very easy network 3/14/16 Computer Networks: Intro 2 Two philosophers example Translator Language Translator Engineer Communication
Hands-On TCP/IP Networking
 Hands-On Course Description In this Hands-On TCP/IP course, the student will work on a live TCP/IP network, reinforcing the discussed subject material. TCP/IP is the communications protocol suite on which
Hands-On Course Description In this Hands-On TCP/IP course, the student will work on a live TCP/IP network, reinforcing the discussed subject material. TCP/IP is the communications protocol suite on which
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
Implementing QOS Policy in MPLS Network
 Implementing QOS Policy in MPLS Network Vishal H. Shukla ME Student DJSCOE Vile Parle (west), Mumbai-56 Sanjay B. Deshmukh Asst. Professor DJSCOE Vile Parle (west), Mumbai-56 ABSTRACT Quality of Service
Implementing QOS Policy in MPLS Network Vishal H. Shukla ME Student DJSCOE Vile Parle (west), Mumbai-56 Sanjay B. Deshmukh Asst. Professor DJSCOE Vile Parle (west), Mumbai-56 ABSTRACT Quality of Service
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 10 Virtual Networks and Remote Access Objectives 1. Explain virtualization and identify characteristics of virtual network components 2. Create and configure
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 10 Virtual Networks and Remote Access Objectives 1. Explain virtualization and identify characteristics of virtual network components 2. Create and configure
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
Access Switch VLAN Y Y.1 /24
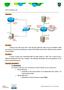 Topology: Fa 0/1 VNC Server Fa 0/0 Port B Access Router Trunk VLAN X Access Switch VLAN Y Backbone Router 141.85.Y.1 /24 28.0.0.42 OSPF X.0.0.0/8 Port A 27.45.67.89 Work Station DHCP Server The Goal: Connect
Topology: Fa 0/1 VNC Server Fa 0/0 Port B Access Router Trunk VLAN X Access Switch VLAN Y Backbone Router 141.85.Y.1 /24 28.0.0.42 OSPF X.0.0.0/8 Port A 27.45.67.89 Work Station DHCP Server The Goal: Connect
Introduction to Segment Routing
 Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Router Architecture Overview
 Chapter 4: r Introduction (forwarding and routing) r Review of queueing theory r Router design and operation r IP: Internet Protocol m IPv4 (datagram format, addressing, ICMP, NAT) m Ipv6 r Generalized
Chapter 4: r Introduction (forwarding and routing) r Review of queueing theory r Router design and operation r IP: Internet Protocol m IPv4 (datagram format, addressing, ICMP, NAT) m Ipv6 r Generalized
Network Test and Monitoring Tools
 ajgillette.com Technical Note Network Test and Monitoring Tools Author: A.J.Gillette Date: December 6, 2012 Revision: 1.3 Table of Contents Network Test and Monitoring Tools...1 Introduction...3 Link Characterization...4
ajgillette.com Technical Note Network Test and Monitoring Tools Author: A.J.Gillette Date: December 6, 2012 Revision: 1.3 Table of Contents Network Test and Monitoring Tools...1 Introduction...3 Link Characterization...4
Lab - Using Wireshark to Examine a UDP DNS Capture
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Record a PC s IP Configuration Information Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture DNS Queries and Responses Part 3: Analyze Captured DNS or UDP Packets Background / Scenario If you
Topology Objectives Part 1: Record a PC s IP Configuration Information Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture DNS Queries and Responses Part 3: Analyze Captured DNS or UDP Packets Background / Scenario If you
ATM in TCP/IP environment: Adaptations and Effectiveness
 Bremen Institute of Industrial Technology and Applied Work Science ATM in TCP/IP environment: Adaptations and Effectiveness Dipl.-Ing. Kai-Oliver Detken, BIBA ATM Traffic Symposium, Mykonos, Greece, September
Bremen Institute of Industrial Technology and Applied Work Science ATM in TCP/IP environment: Adaptations and Effectiveness Dipl.-Ing. Kai-Oliver Detken, BIBA ATM Traffic Symposium, Mykonos, Greece, September
Multiprotocol Label Switching Overview
 This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
TS Open Day Data Center Fibre Channel over IP
 TS Open Day Data Center Fibre Channel over IP Presented by: Rong Cheng- TAC LAN & DCN China Jan 30 th, 2015 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 FCIP Introduction FCIP Configuration
TS Open Day Data Center Fibre Channel over IP Presented by: Rong Cheng- TAC LAN & DCN China Jan 30 th, 2015 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 FCIP Introduction FCIP Configuration
Configuring MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting and Analysis
 Configuring MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting and Analysis This module contains information about and instructions for configuring the MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting feature. The MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting
Configuring MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting and Analysis This module contains information about and instructions for configuring the MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting feature. The MPLS Egress NetFlow Accounting
CPSC 826 Internetworking. The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline. The Network Layer
 1 CPSC 826 Intering The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline The Network Layer Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu November 10, 2004 Network layer
1 CPSC 826 Intering The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline The Network Layer Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu November 10, 2004 Network layer
Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6
 Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6 Mrs. Sheetal Mali Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Parvatibai Genba Sopanrao Moze College of Engineering Wagholi,
Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6 Mrs. Sheetal Mali Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Parvatibai Genba Sopanrao Moze College of Engineering Wagholi,
Table of Contents Chapter 1 MPLS Basics Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Basic Concepts of MPLS... 1-2 1.1.2 Architecture of MPLS... 1-5 1.1.3 MPLS and Routing Protocols... 1-7 1.1.4 Applications of MPLS...
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Basic Concepts of MPLS... 1-2 1.1.2 Architecture of MPLS... 1-5 1.1.3 MPLS and Routing Protocols... 1-7 1.1.4 Applications of MPLS...
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP. BGP IPv4 Label Session
 MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF
 Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF Document ID: 13736 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Mechanism Configure Network Diagram Quick Configuration Guide Configurations
Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF Document ID: 13736 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Mechanism Configure Network Diagram Quick Configuration Guide Configurations
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Tunneling Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to Tunneling... 1-1 1.1.1 IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel... 1-2 1.1.2 IPv4 over IPv4 Tunnel... 1-7 1.2 Tunneling Configuration Task List... 1-8 1.3 Configuring
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to Tunneling... 1-1 1.1.1 IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel... 1-2 1.1.2 IPv4 over IPv4 Tunnel... 1-7 1.2 Tunneling Configuration Task List... 1-8 1.3 Configuring
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching
 COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
CS-435 spring semester Network Technology & Programming Laboratory. Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis
 CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture #4 preview ICMP ARP DHCP NAT
CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture #4 preview ICMP ARP DHCP NAT
Multiprotocol Label Switching
 This module describes and how to configure it on Cisco switches. Restrictions for, page 1 Information about, page 1 How to Configure, page 3 Verifying Configuration, page 6 Restrictions for (MPLS) fragmentation
This module describes and how to configure it on Cisco switches. Restrictions for, page 1 Information about, page 1 How to Configure, page 3 Verifying Configuration, page 6 Restrictions for (MPLS) fragmentation
