Using the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller for Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria V and Cyclone V Devices
|
|
|
- Catherine Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller for Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria V and Cyclone V Devices Subscribe Feedback The Altera Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller dynamically reconfigures the transceiver PHY in Arria V and Cyclone V devices. You can use the dynamic reconfiguration features to reconfigure the transceiver channels to support multiple or different data rates and physical medium attachment (PMA) settings without interrupting adjacent transceiver channels or powering down the transceiver channels. The reconfiguration methods are similar between Arria V, Cyclone V, and Stratix V devices. The features supported in Arria V and Cyclone V devices are a subset of those supported in Stratix V devices. Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide Reconfiguration Methods You can dynamically change the transceiver setting using either register-based or streamer-based reconfiguration. Both methods use a sequence of Avalon -MM writes and reads to update the transceiver settings. Refer to the read and write transfer timing diagrams in the Avalon Interface Specifications Register-Based Reconfiguration Register-based reconfiguration does not require any MIF files during the reconfiguration process. It uses a set of dedicated reconfiguration addresses to carry out a specific reconfiguration function. You use a specific flow to carry out this reconfiguration. The design example in this application note demonstrates the following: The analog (PMA) reconfiguration update on the VOD settings The method to trigger the duty cycle distortion (DCD) calibration Arria V GX Dynamic Reconfiguration Design Example on page 3 Refer to the Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide for the register-based reconfiguration read and write flow. Streamer-Based Reconfiguration The streamer-based reconfiguration mode supports the reconfiguration features that are not achievable with the register-based method All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are trademarks of and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. ISO 900:2008 Registered 0 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 9534
2 2 There are two supported modes: MIF Streaming and Direct Write. Both modes use the streamer module in the Reconfiguration Controller. The streamer module uses the same address to carry out reconfiguration. However, the data values are different and you must specify that to the Reconfiguration Controller. MIF Streaming mode (Mode 0): Streams the entire content of a MIF Uses the streamer module The advantage of this mode is you only need to use one command to execute the write process of the entire MIF. You do not need to manually control the write process to dedicated reconfiguration addresses such as PMA settings, reference clock selection, and PLL selection. The design example demonstrates the streamer-based reconfiguration mode when switching the TX PLL connected to the transceiver channel. Direct Write mode (Mode ): No MIF streaming is required You need to selectively write the reconfiguration data May require multiple writes and reads The advantage of this mode is to access the reconfiguration address that is not supported by the register-based method. Arria V GX Dynamic Reconfiguration Design Example on page 3 Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide Transceiver Calibration Function The Reconfiguration Controller supports two calibration functions: offset cancellation and duty cycle distortion (DCD) calibration. The design example shows how to execute the DCD calibration from the Reconfiguration Controller. Arria V GX Dynamic Reconfiguration Design Example on page 3 Duty Cycle Distortion Calibration on page 6 Duty Cycle Distortion (DCD) calibration is used to calibrate the TX duty cycle to compensate for the skew introduced by different clock networks. Unsupported Reconfiguration Modes The Reconfiguration Controller in Arria V and Cyclone V devices does not support the following modes: Switching between a receiver-only channel and a transmitter-only channel Switching between one PHY IP to another PHY IP (for example, switching from a deterministic latency PHY IP to a custom PHY IP) Switching between PMA Direct mode to non-pma Direct mode Bonded mode configuration TX PLL reconfiguration if the TX PLL is connected to bonded channels
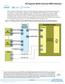
3 3 Arria V GX Dynamic Reconfiguration Design Example The design example uses the Reconfiguration Controller to dynamically reconfigure a Native PHY IP to support multiple data rates of 2500 Mbps and 5000 Mbps by switching the external PLL connected to the transceiver channel. The design example uses a 5AGXFB3H4F35C5 device and is compiled with the Quartus II 2.sp software. The reconfiguration commands are controlled through the System Console tool that ships with the Quartus II software. This design example demonstrates the following reconfiguration methods: Streamer-based reconfiguration The MIF streaming reconfiguration is used to switch the TX PLLs that are connected to the transceiver channel. Register-based reconfiguration Changing VOD setting Triggering DCD calibration manually The design example consists of the following modules. The numbers refer to the position of the modules in the following figure. The system-level diagram shows how the different modules interact in the reconfiguration design example.. Arria V GX Transceiver Native PHY IP 2. Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller 3. Qsys system 4. PHY Reset Controller 5. CMU PLL Transceiver PLL 6. Fractional PLL (fpll) Altera fpll 7. ROM containing the MIF for reconfiguration 8. In-System Sources and Probes (ISSP) The design example also contains a PRBS data generator and checker. The data generator generates a PRBS5 data pattern. The data checker verifies the PRBS5 data received.
4 4 Figure : System Diagram Creating the Qsys System The reconfiguration design example uses a simple Qsys system that consists of three components: the JTAG to Avalon Master Bridge, the External Slave Interface, and the PIO. Follow the steps below to examine the Qsys system:. Launch the Quartus II software 2. On the File menu, click Open 3. Browse and select the console_interface.qsys file located in the original_design/ directory 4. Click Open
5 The Qsys System Components The Qsys tool launches and shows all components used. The Qsys system contains the following components: The JTAG to Avalon Master Bridge component acts as the master in the design example and is the main communication channel between the System Console tool and the external slave interface in the design. The System Console tool issues Avalon reads and writes to the Reconfiguration Controller to carry out reconfiguration of the PHY IP. The External Slave Interface component exports all required Avalon signals to the top-level design. With the Avalon signals exported, the Qsys system can interface with any Avalon-compliant component that resides outside of the Qsys component library. The Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller is an Avalon-compliant component. Therefore, the External Slave Interface component must be connected to the JTAG to Avalon Master Bridge. The PIO component uses external input as control bits in the system. In this design example, the PIO is connected to the rate_select port, which is used to trigger the rate change of the channel from 2500 Mbps to 5000 Mbps. The PIO connects to the JTAG to Avalon Master Bridge. You can also connect any PIO to status bits to be monitored externally. Note: The Arria V and Cyclone V PHY IP components are not supported in the Qsys tool in the Quartus II software. To interface with an Arria V or Cyclone V PHY IP in a Qsys system, you must use an external slave interface. Figure 2: Component Map of the Qsys System 5 Table : Memory Map of the Qsys System Name Component Name Base Address Description reconfig External Slave Interface 0x000 Exports Avalon signals to interface with the Reconfiguration Controller pio_0 PIO (Parallel I/O) 0x800 Export the rate_select port for TX PLL selection Qsys System Integration Tool Support
6 6 Creating the Transceiver Native PHY IP The design example uses the Arria V Native PHY IP as a single duplex transceiver channel. Unlike other PHY IP, the Native PHY IP does not include the Avalon-MM interface. Instead, it exposes all signals directly as ports. In this design example, the Native PHY IP interfaces with the Reset Controller, Reconfiguration Controller, and the ISSP. The Native PHY is created such that two transmit PLLs are used to clock the data channels. Both transmit PLLs are instantiated using external transceiver PLLs. The CMU PLL and fpll are selected as the external transceiver PLLs. Follow the steps in the following figures to set up the parameters required by the Native PHY to switch between the two external transceiver PLLs. Figure 3: Datapath Options, TX PMA, and TX PLL0 Settings in Native PHY IP. Check this option to use the external TX PLL 2. Use 2 external PLLs 3. Indicate that TX PLL 0 is following the PLL setting in the PMA tab 4. TX PLL 0 is set to 2500 Mbps
7 Figure 4: TX PLL and RX PMA settings in Native PHY IP 7. This option remains checked 2. You can change the TX PLL setting in this field. In this example, you set it to 5,000 Mbps 3. Check this option to change the CDR setting dynamically to support a different data rate Turn on the Enable CDR dynamic reconfiguration option to allow the data rate change of the CDR during streamer-based reconfiguration. With the Reconfiguration Controller connected, you can selectively determine which transmit PLL is used. Refer to the gxb_duplex.v file in the design example for the standard PCS settings. Refer to the Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide for more information on how to instantiate the Native PHY IP Datapath, Standard PCS, and RX PMA options. Creating the Reconfiguration Controller The Reconfiguration Controller controls the dynamic reconfiguration of Arria V and Cyclone V PHY IPs. The following steps describe how to set up the Reconfiguration Controller to dynamically control the PMA settings, change the PLL selection by stream a MIF file, and trigger DCD calibration manually. The Native PHY IP created in the previous section requires two reconfiguration interfaces, one for the REGULAR RX/TX Channel and one for the CDR TX PLL, as shown in the following figure. You can verify the logical interface information in the Transceiver Reconfiguration Report.
8 8 Figure 5: Transceiver Reconfiguration Report The Transceiver Reconfiguration Report is located under Fitter Report > GXB Report. Refer to the parameters setting in the figure below to set up the Interface Bundles, Transceiver Calibration functions, Analog Features, and Reconfiguration Features functions. Figure 6: Arria V Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller. Select 2 - one for the RX/TX channel interface and one for the CDR TX PLL interface 2. The first interface bundle is connected to the Native PHY IP and the second is connected to the transceiver PLL (CMU PLL / fpll) 3. Check this option to perform manual DCD calibration 4. Do not enable this option. Running the channel at 2,500 Mbps does not require DCD calibration during power-up 6. Check this option to allow streamer-based (MIF) reconfiguration 5. Check this option to allow VOD setting reconfiguration The Interface Bundles section specifies two interface bundles. The first interface is connected to the RX/TX channels as shown in Figure 5. The second interface is connected to the CMU PLL. The following table shows the Interface Bundles connection in the top-level design file a5_top.v. Table 2: Interface Bundles Parameters Reconfiguration Ports [69:0] ch0_0_to_xcvr [45:0] ch0_0_from_xcvr Native PHY/ CMU PLL Ports [69:0] reconfig_to_xcvr [45:0] reconfig_from_xcvr Connected to Connected to RX/TX channel
9 9 Reconfiguration Ports [69:0] ch to_xcvr [45:0] ch from_xcvr Native PHY/ CMU PLL Ports [69:0] reconfig_to_cmu [45:0] reconfig_from_cmu Connected to Connected to CMU PLL In the Transceiver Calibration Functions section, turn on the Enable duty cycle calibration option. In the Analog Features section, turn on the Enable Analog controls option to enable VOD setting reconfiguration. In the Reconfiguration Features section, turn on the Enable channel/pll reconfiguration option to allow the streamer-based reconfiguration process. This reconfiguration mode reconfigures the TX/RX data path, CDR settings, and TX PLL selection. After all parameters have been specified, you can generate the Reconfiguration Controller. Duty Cycle Distortion Calibration on page 6 Duty Cycle Distortion (DCD) calibration is used to calibrate the TX duty cycle to compensate for the skew introduced by different clock networks. Creating the CMU PLL Using an Arria V Transceiver PLL The design example uses the Arria V Transceiver PLL to clock the transceiver channel at 5000 Mbps. When you turn on the Use external TX PLL option in the Native PHY IP, you can connect to this external transceiver PLL. This transceiver PLL is referring to the CMU PLL as illustrated in the System Diagram. You can instantiate this IP in the MegaWizard Plug-in Manager > Interface > Transceiver PHY > Arria V Transceiver PLL v2.. Refer to the following figure to set the parameters for the CMU PLL. Figure 7: Arria V Transceiver PLL Parameters Setting When Configured as CMU PLL Select the CMU PLL type Set the data rate to 5000 Mbps You do not have to turn on the Enable PLL reconfiguration option if you are not dynamically reconfiguring the PLL parameter settings. This option allows you to change the PLL settings to support different data rates. Note: If you are using an fpll in your design, if you want to switch the fpll with another CMU PLL, you must instantiate the CMU PLL using the Arria V Transceiver PLL IP. Turn on the option Use external TX PLL in the Native PHY IP to instantiate a CMU PLL.
10 0 Creating a Fractional PLL (fpll) using Altera PLL The design example uses the Altera PLL v2. to configure an fpll to clock the transceiver channel at 2500 Mbps. To connect the Native PHY IP to the fpll, you must turn on the Use external TX PLL option in the Native PHY IP. You can instantiate this IP in the MegaWizard Plug-in Manager > IO > Altera PLL v2. Refer to the figure below to set the parameters in the fpll. Figure 8: Altera PLL Parameters Setting when Configured as an fpll Enable the PLL locked signal Set the desired frequency to 250 MHz because the VCO in the PLL is running at half the serial data rate of 2500 Mbps Creating the Transceiver PHY Reset Controller The design example uses the Transceiver PHY Reset Controller to control the reset sequence of the transceiver channel. As shown in the figure below, set the Number of TX PLLs field to 2. In this design example, you switch the TX PLL between the CMU PLL and fpll. Therefore, you must connect both PLL locked signals, pll_locked[:0], to the reset controller to indicate the release of tx_digitalreset. The reset controller releases tx_digitalreset whenever there is an assertion on either of the pll_locked[:0] signals. Leave the remaining settings in the PHY Reset Controller to their default values.
11 Figure 9: Transceiver Reset Controller Parameter Settings Set this option to 2. There will be indexing on the pll_locked[:0] port. Connect the locked signal from the fpll and CMU PLL to this port. Creating a ROM that Contains the MIF for Reconfiguration Dynamic reconfiguration of the Native PHY can be performed using one of two methods: register-based and streamer-based. The register-based reconfiguration is carried out by writing to a specific set of memory-mapped registers in the transceiver channel. The streamer-based reconfiguration is carried out by streaming a MIF that contains the reconfiguration data to the Reconfiguration Controller. The steps below describe how to generate the MIF for reconfiguration for the design example. Note: Two different design directories should be used to compile the original design and the MIF design. This practice prevents inadvertently deleting or modifying the design files. The MIF design is the original design with different settings specified for the Native PHY IP. In the original design, the initial data rate is set to 2500 Mbps. Change the Native PHY IP settings so that after MIF reconfiguration the data rate is 5000 Mbps. To generate the MIF files, use the table below for the settings in the Native PHY IP. Only the settings in the TX PMA tab change.
12 2 Table 3: MIF Files Generation in Reference with Native PHY IP Settings PHY IP settings not listed in the table remain the same throughout all MIF files generation. MIF # MIF files (Mbps) Data Rate (Mbps) PMA TX Local Clock Division Factor TX PLL Base Data Rate (Mbps) Use external TX PLL TX PMA Number of TX PLLs Main TX PLL Logical Index PLL Base Data Rate (Mbps) TX PLL 0 Selected Clock Network PLL Base Data Rate (Mbps) TX PLL Selected Clock Network nonbonded nonbonded nonbonded nonbonded 5000 Compiling the Design Example The compilation process generates an.sof programming file for the Arria V device. At this point in the procedure two designs exist: the original design and the MIF design. The MIF design is compiled first because the MIF generated will be used by the original design. Specifically, the MIF generated by the MIF design is used in the original design to configure from one data rate to another. Follow the steps below to compile a design.. Open the MIF project in the Quartus II software 2. On the Processing menu, click Start Compilation After a successful compilation, a reconfig_mif directory is created in the MIF design s project directory. The following MIF files are used for each data rate: 2500 Mbps mif_2500.mif 5000 Mbps mif_5000.mif The original design is compiled after the MIF design. However, before the original design is compiled you must specify the MIF created by the MIF design. The module mif_rom is used to store the MIF. Follow the steps below to specify the MIF file.. Open the original project in the Quartus II software 2. Launch the MegaWizard Plug-In Manager from the Tools menu 3. From the MegaWizard, browse to the original_design/ directory and select mif_rom.v 4. All parameters are the same except that you must specify the MIF file. Specify the mif_design/reconfig_mif/mif_2500.mif file by browsing to the MIF 5. Click Finish to generate the new mif_rom module 6. Repeat these steps for the ROM to store the MIF for 5000 Mbps. After the MIF has been specified, the original design is ready for compilation. Follow the steps below to perform a design compilation.. Open the original project in the Quartus II software 2. On the Processing menu, click Start Compilation After a successful compilation, an a5_top.sof file will exist in the original/output_files/ directory. This SOF will be used to program the Arria V GX device.
13 Creating In-System Sources and Probes (ISSP) The ISSP is instantiated to control the PHY reset, enable serial loopback, and align word boundaries on received data. The Qsys system communicates with the ISSP to control the Native PHY. Table 4: ISSP and Its Control in the Design Example 3 Bit [2] [] [0] ISSP rx_std_wa_patternalign rx_seriallpbken hssi_reset Description Aligns the word boundaries in manual alignment mode Enables the serial loopback of the transceiver channel Used as a system reset Performing Reconfiguration with the System Console Tool With the Avalon to JTAG Master Bridge, reconfiguration commands are directly streamed to the Reconfiguration Controller through the JTAG port. The System Console tool issues commands to initiate dynamic reconfiguration of the Native PHY IP. This design example uses a Tcl script called main.tcl that consists of several different procedures with different functionality. Note: Program the Arria V GX device with the SOF generated in the previous section before launching the System Console. Having both the programmer and System Console open simultaneously can cause programming errors. Before any reconfiguration can take place, you must first launch the System Console tool. To launch the System Console, perform the following steps:. Program the Arria V Device with the SOF generated from the original design 2. Launch the Quartus II software 3. From the Quartus II software, on the Tools menu, click Qsys 4. From the Qsys tool, on the Tools menu, click System Console 5. Ensure that the present working directory contains main.tcl The following table lists the procedures in main.tcl. You can type in a procedure name and its value to execute the reconfiguration process. Verify your results with the signal tap file (stp.stp) by looking at the signals listed in the following table. Table 5: Description of Procedures in main.tcl Command Name txpll_register <Value> <Value> 0 Description Select logical TX PLL 0 as TX PLL (fpll). Only the tx_std_clkout frequency is updated. Select logical TX PLL as TX PLL (CMU PLL). Only the tx_std_clkout frequency is updated.
14 4 Command Name txpll_mif <Value> reset sloopback <Value> read_vod write_vod <Value> patternalign <Value> <Value> N/A 0 N/A Description Select logical TX PLL 0 as TX PLL (fpll). Both the tx_std_clkout and rx_std_clkout frequencies are updated. Select logical TX PLL as TX PLL (CMU PLL). Both the tx_std_clkout and rx_std_clkout frequencies are updated. System Reset Enable serial loopback. Verify with the rx_seriallpbken port in the signal tap file Disable serial loopback. Verify with the rx_seriallpbken port in the signal tap file Read back VOD value (read back data in hexadecimal value) Writing VOD value with valid settings of 0-63 Enable pattern alignment detection. To resynchronize to the new word boundary after each MIF based reconfiguration, use this command to create a 0-to- transition to the rx_std_wa_patternalign signal. Disable pattern alignment detection. Set this signal to 0 to re-assert the rx_std_wa_patternalign signal. To reconfigure the transceiver channel, type the reconfiguration commands as shown below in the Tcl Console. For example: source main.tcl sloopback >> Enable serial loopback txpll_mif 2500 >> TX PLL switch to fpll. Data channel at 2500 Mbps reset >> Reset the transceiver channel after each streamer-based >> reconfiguration txpll_mif 5000 >> TX PLL switch to CMU PLL. Data channel at 5000 Mbps reset >> Reset the transceiver channel after each streamer-based >> reconfiguration These commands allow the System Console to communicate directly with the Avalon to JTAG Bridge Master, which in turn communicates with the Reconfiguration Controller.
15 Analyzing and Debugging Designs with the System Console Refer to the Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide for more information on the specific address map associated with the Reconfiguration Controller 5 Streaming a MIF to Perform Channel Reconfiguration Switch the TX PLL to change the transceiver channel from 2500 Mbps to 5000 Mbps. You can switch the PLL by streaming a MIF. Table 6: Steps for Using the Streamer-Based Reconfiguration Mode Step Reconfiguration Step Memory Map Address Value Written Description Write to the logical channel register 0x38 0h Logical channel 0 selected (Physical ch0) 2 Write MIF mode 0 to the control and status register 0x3A 0h Streamer mode selected 3 Write to the "feature offset register 0x3B 0h Select MIF base address 4 Write to the data offset register 0x3C 8000h Specify base address at 8000h 5 Write to the write bit of the control and status register 0x3A h Trigger "write" operation 6 Write to the "feature offset register to start the mif operation 0x3B h Select Start MIF Stream 7 Write to the data offset register to trigger the mif write process 0x3C h Set to trigger the MIF streaming 8 Write to the write bit of the control and status register 0x3A h Trigger "write" operation Refer to the Streamer-based reconfiguration section in the Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide for a description of the Streamer module. Manual Trigger for DCD Calibration IP via Register-based Reconfiguration You can trigger the DCD calibration IP manually. The following table lists the steps to access the reconfiguration address reserved for DCD calibration IP. You must trigger the DCD calibration IP when you switch from 2500 Mbps to 5000 Mbps because it switches the clock network and the channel data rate is >495.2 Mbps. In the design example, the DCD calibration is triggered when the data channel is running at 5000 Mbps and after TX PLL switching happens. You can refer to the txpll_mif procedure in main.tcl for more details. You can select any base address except the Reconfiguration Controller and Avalon-MM master base address
16 6 Table 7: Using the Register-Based Reconfiguration Method to Trigger DCD Calibration Step Reconfiguration Step Memory Map Address Value Written Description Write to the logical channel register 0x48 0h Logical channel 0 selected (Physical ch0) 2 Write to the data offset register 0x4B 0h Select DCD calibration mode 3 Write to manually trigger ON DCD calibration IP 0x4C h Manually turn ON DCD calibration IP 4 Check reconfig_busy signals Port N/A reconfig_busy signal stays asserted as long as the DCD IP is calibrating the TX buffer. 5 Write to manually trigger OFF DCD calibration IP 0x4C 0h Manually turn OFF DCD calibration IP Note: Reset your channel after each manual DCD calibration. Performing VOD Reconfiguration via Register-Based Reconfiguration You can reconfigure the transceiver channel to change the VOD settings. To verify the new settings, perform a write to the channel and read back the VOD setting. Table 8: Using the Register-Based Reconfiguration Method to Reconfigure VOD Settings Step Reconfiguration Step Memory Map Address Value Written Description Write to the logical channel register 0x08 0h Logical channel 0 selected (Physical ch0) 2 Write to the PMA offset register 0x0B 0h Select VOD settings 3 Write VOD valid settings 0x0C 0-63 Set the VOD settings with entered valid settings 4 Write to the write bit of the control and status register 0x4A h Trigger "write" operation For more information on the register address and the relevant bits to access for read and write processes, refer to the "Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller IP Core" chapter in the Altera Transceiver PHY IP Core User Guide Duty Cycle Distortion Calibration Duty Cycle Distortion (DCD) calibration is used to calibrate the TX duty cycle to compensate for the skew introduced by different clock networks. You must turn on the DCD calibration IP when you switch from 2500 Mbps to 5000 Mbps, because TX PLL switching causes a different clock network to be used.
17 Enable the DCD calibration IP for Arria V and Cyclone V devices if either of the following conditions is applicable: Data rate is Mbps Clock network switching (TX PLL switching) and the data rate is Mbps The DCD calibration features and options are summarized in the following table. Refer to the usage condition to enable the DCD Calibration IP. 7 Table 9: DCD Calibration Features and Their Options Transceiver Calibration Function Option Description Usage Condition Enable duty cycle calibration Use DCD calibration IP either during power up or user mode Data rate Mbps Clock network switching (TX PLL switching) and the data rate is Mbps Disabled Disabled DCD calibration features Data rate < Mbps DCD calibration IP process at power up mode and during user mode (manual DCD calibration) Data rate Mbps Calibrate duty cycle during power up Disabled DCD calibration IP will not start at power up mode, but can still be triggered during user mode if the Enable duty cycle calibration option is enabled Data rate change from < Mbps to Mbps Clock network switching (TX PLL switching) and the data rate is Mbps Create optional calibration status ports N/A tx_cal_busy, rx_cal_busy, cal_busy_in ports exposed tx_cal_busy should be connected to cal_busy_in port if you are using more than one Reconfiguration Controller per side of the device Note: Do not enable DCD calibration for applications running at < Mbps. The following table lists the data rate usage conditions and when to enable the power up and manual DCD calibration IP. Table 0: DCD Calibration Usage Data Rate (Mbps) Usage Conditions Case From To Data Rate Switch < < < < DCD Calibration Power Up Manual x x x x N/A N/A
18 8 Data Rate (Mbps) Usage Conditions Case From To Example Example Clock Network Switch (TX PLL Switching) < < < < DCD Calibration Power Up Manual x x x x x If your design is using more than one Reconfiguration Controller (per side of the device) and the data channels are running Mbps, you must chain the Reconfiguration Controller. The following figure shows the chaining method. The chaining is required from the first Reconfiguration Controller until the last Reconfiguration Controller (per side of the device), as long as the DCD calibration IP is enabled. The purpose of chaining the Reconfiguration Controller is to allow the DCD calibration process to execute sequentially. For example, in the following figure, by chaining the tx_cal_busy signal in the upstream Reconfiguration Controller to the cal_busy_in port of the downstream Reconfiguration Controller, the DCD is calibrated for the transceiver channels connected to the upstream controller before the transceiver channels connected to the downstream controller. The cal_busy_in port will reset the downstream Reconfiguration Controller when the upstream Reconfiguration Controller is busy with the DCD calibration. The cal_busy_in port of the upstream Reconfiguration Controller is connected to ground. The tx_cal_busy port of the downstream Reconfiguration Controller can be left unconnected. Note: If you are using only one Reconfiguration Controller with DCD calibration enabled, the cal_busy_in port must be tied to ground. This process is handled by the Reconfiguration Controller internally. You only need to connect the ports as described for proper functionality. Figure 0: Chaining the Reconfiguration Controller
19 As this design example demonstrates, the Reconfiguration Controller provides an easy and efficient method to dynamically change the Arria V GX Native PHY IP's settings, including TX PLL switching, VOD setting updates, and triggering the DCD calibration process during user mode. 9 Document Revision History Table : Document Revision History Date March 203 Version Initial release. Changes
Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices
 Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices AN-645-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the transceiver reconfiguration controller to dynamically reconfigure
Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices AN-645-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the transceiver reconfiguration controller to dynamically reconfigure
Implementing 9.8G CPRI in Arria V GT and ST FPGAs
 03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices
 July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
July 2014 SIV53004-2014.07.09 3. ALTGX_RECONFIG IP Core User Guide for Stratix IV Devices SIV53004-2014.07.09 This document describes how to define and instantiate the ALTGX_RECONFIG IP core using the
Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide
 Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide Subscribe UG-A10XCVR 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide Contents Arria 10 Transceiver PHY Overview...1-1
Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide Subscribe UG-A10XCVR 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide Contents Arria 10 Transceiver PHY Overview...1-1
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices
 AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.1 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.1 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices
 AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.8 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 558: Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Arria II Devices AN-558-3.8 Application Note This application note describes how to use the dynamic reconfiguration feature and why you may want use this
AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices
 AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices July 2010 AN-610-1.0 This application note describes how to implement deterministic latency for Common Public Radio
AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices July 2010 AN-610-1.0 This application note describes how to implement deterministic latency for Common Public Radio
Debugging Transceiver Links
 Debugging s 11 QII53029 Subscribe This chapter describes using the Transceiver Toolkit to optimize high-speed serial links in your board design. The Transceiver Toolkit provides real-time control, monitoring,
Debugging s 11 QII53029 Subscribe This chapter describes using the Transceiver Toolkit to optimize high-speed serial links in your board design. The Transceiver Toolkit provides real-time control, monitoring,
PCI Express Multi-Channel DMA Interface
 2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Quick Start Guide...
Intel Stratix 10 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Quick Start Guide...
Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide
 Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide Subscribe UG-20025 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Quick Start Guide...1-1 Directory Structure... 1-2 Design Components...
Low Latency 40G Ethernet Example Design User Guide Subscribe UG-20025 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Quick Start Guide...1-1 Directory Structure... 1-2 Design Components...
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide
 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe UG-028 05.06.203 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC-2 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Contents About This MegaCore
00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe UG-028 05.06.203 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC-2 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Contents About This MegaCore
2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design
 2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design AN-642-1.0 Application Note The Altera 2.5G Reed-Solomon (RS) II MegaCore function reference design demonstrates a basic application of the Reed-Solomon
2.5G Reed-Solomon II MegaCore Function Reference Design AN-642-1.0 Application Note The Altera 2.5G Reed-Solomon (RS) II MegaCore function reference design demonstrates a basic application of the Reed-Solomon
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices
 SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Stratix 10 ES Editions Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Stratix 10 ES Editions Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document
25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. 25G
25G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. 25G
Altera JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9680 Hardware Checkout Report
 2015.05.11 Altera JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9680 Hardware Checkout Report AN-710 Subscribe The Altera JESD204B IP core is a high-speed point-to-point serial interface intellectual property (IP). The JESD204B
2015.05.11 Altera JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9680 Hardware Checkout Report AN-710 Subscribe The Altera JESD204B IP core is a high-speed point-to-point serial interface intellectual property (IP). The JESD204B
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide...
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide...
SerialLite III Streaming IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices
 IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start
IP Core Design Example User Guide for Intel Arria 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Quick Start
System Debugging Tools Overview
 9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide
 2015.05.04 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 Subscribe The Altera IOPLL megafunction IP core allows you to configure the settings of Arria 10 I/O PLL. Altera IOPLL
2015.05.04 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 Subscribe The Altera IOPLL megafunction IP core allows you to configure the settings of Arria 10 I/O PLL. Altera IOPLL
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design
 AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Low Latency 100G Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Nios II Performance Benchmarks
 Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
Subscribe Performance Benchmarks Overview This datasheet lists the performance and logic element (LE) usage for the Nios II Classic and Nios II Gen2 soft processor, and peripherals. Nios II is configurable
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design
 AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference
AN 830: Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel FPGA Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference
AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface
 AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon -ST Pass-Through
AN 836: RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 RapidIO II Reference Design for Avalon -ST Pass-Through
Recommended Protocol Configurations for Stratix IV GX FPGAs
 Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Intel Stratix 10 Clocking and PLL User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 Clocking and PLL User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 Clocking
Intel Stratix 10 Clocking and PLL User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 Clocking
10. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
10. Introduction to Uni IP November 2012 EMI_RM_008-2.1 EMI_RM_008-2.1 The Altera,, and LP SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, RLDRAM II controller with Uni, and RLDRAM
H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Intel Stratix 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide
 Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide UG-20051 2017.09.19 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1 Directory Structure... 4 1.2 Design Components...
Interlaken IP Core (2nd Generation) Design Example User Guide UG-20051 2017.09.19 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Quick Start Guide... 3 1.1 Directory Structure... 4 1.2 Design Components...
AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report
 AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and AD9691 Hardware
AN 779: Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and ADI AD9691 Hardware Checkout Report Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA JESD204B IP Core and AD9691 Hardware
Building Interfaces with Arria 10 High-Speed Transceivers
 Building Interfaces with Arria 10 High-Speed Transceivers Course Description In this course, you will learn how you can build high-speed, gigabit interfaces using the 20- nm embedded transceivers found
Building Interfaces with Arria 10 High-Speed Transceivers Course Description In this course, you will learn how you can build high-speed, gigabit interfaces using the 20- nm embedded transceivers found
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-M10UFM 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 User Flash Memory
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide
 100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function Contents
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function Contents
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction User Guide
 ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction ALTDQ_DQS2 Megafunction 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01089-2.2 Feedback Subscribe 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
9. Functional Description Example Designs
 November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
November 2012 EMI_RM_007-1.3 9. Functional Description Example Designs EMI_RM_007-1.3 This chapter describes the example designs and the traffic generator. Two independent example designs are created during
8. Introduction to UniPHY IP
 8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
8. Introduction to Uni IP November 2011 EMI_RM_008-1.1 EMI_RM_008-1.1 The Altera and SDRAM controllers with Uni, QDR II and QDR II+ SRAM controllers with Uni, and RLDRAM II controller with Uni provide
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide
 DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Operations Part Number Compiler Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Operations Part Number Compiler Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices
 Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices ES-01027-2.3 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on known device issues affecting Cyclone IV devices. Table 1 lists specific Cyclone IV issues,
Errata Sheet for Cyclone IV Devices ES-01027-2.3 Errata Sheet This errata sheet provides updated information on known device issues affecting Cyclone IV devices. Table 1 lists specific Cyclone IV issues,
Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices
 Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices ES-1035-2.5 Errata Sheet Table 1. Device Issues (Part 1 of 2) This errata sheet provides information about known issues affecting Cyclone V devices. Table 1 lists the
Errata Sheet for Cyclone V Devices ES-1035-2.5 Errata Sheet Table 1. Device Issues (Part 1 of 2) This errata sheet provides information about known issues affecting Cyclone V devices. Table 1 lists the
Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 H-tile Hard IP for Ethernet Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 Transceiver Usage
 Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Transceiver Layout... 3 1.1 L-Tile and H-Tile Overview...4 1.1.1 PLLs...4
Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Transceiver Layout... 3 1.1 L-Tile and H-Tile Overview...4 1.1.1 PLLs...4
Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1
 Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1 High Speed Design Team, San Diego Thursday, July 23, 2009 1 2009 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions
Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1 High Speed Design Team, San Diego Thursday, July 23, 2009 1 2009 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions
4K Format Conversion Reference Design
 4K Format Conversion Reference Design AN-646 Application Note This application note describes a 4K format conversion reference design. 4K resolution is the next major enhancement in video because of the
4K Format Conversion Reference Design AN-646 Application Note This application note describes a 4K format conversion reference design. 4K resolution is the next major enhancement in video because of the
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide
 Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 2017.06.16 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents...3 Device Family Support...
Altera I/O Phase-Locked Loop (Altera IOPLL) IP Core User Guide UG-01155 2017.06.16 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents...3 Device Family Support...
Design Guidelines for Intel FPGA DisplayPort Interface
 2018-01-22 Design Guidelines for Intel FPGA DisplayPort Interface AN-745 Subscribe The design guidelines help you implement the Intel FPGA DisplayPort IP core using Intel FPGA devices. These guidelines
2018-01-22 Design Guidelines for Intel FPGA DisplayPort Interface AN-745 Subscribe The design guidelines help you implement the Intel FPGA DisplayPort IP core using Intel FPGA devices. These guidelines
Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide
 Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01172 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01172 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
50G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide
 50G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01140 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function
50G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01140 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function
Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v3.0 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices
 Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v3.0 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Send Feedback Contents Contents 1. Overview of the Ethernet Link Inspector for Intel Stratix 10 Devices... 3 1.1. Features...3 1.1.1.
Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v3.0 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Send Feedback Contents Contents 1. Overview of the Ethernet Link Inspector for Intel Stratix 10 Devices... 3 1.1. Features...3 1.1.1.
NIOS II Processor Booting Methods In MAX 10 Devices
 2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
2015.01.23 AN-730 Subscribe MAX 10 device is the first MAX device series which supports Nios II processor. Overview MAX 10 devices contain on-chip flash which segmented to two types: Configuration Flash
Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support
 Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support RN-01057 Release Notes This document provides late-breaking information about device support in the 10.0 SP1 version of the Altera Quartus II software.
Quartus II Software Version 10.0 SP1 Device Support RN-01057 Release Notes This document provides late-breaking information about device support in the 10.0 SP1 version of the Altera Quartus II software.
Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction
 Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction UG-032405-6.0 User Guide This user guide describes the features and behavior of the ALTPLL_RECONFIG megafunction that you can configure
Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction UG-032405-6.0 User Guide This user guide describes the features and behavior of the ALTPLL_RECONFIG megafunction that you can configure
AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines
 AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines AN-756 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Implementing the Altera PHYLite Design... 3 1.1.1 Parameter
AN 756: Altera GPIO to Altera PHYLite Design Implementation Guidelines AN-756 2017.05.08 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1...3 1.1 Implementing the Altera PHYLite Design... 3 1.1.1 Parameter
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide
 100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01128 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01128 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 About This MegaCore Function
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. High Bandwidth
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM2) Interface Intel FPGA IP Design Example Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. High Bandwidth
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit)
 Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
Board Update Portal based on Nios II Processor with EPCQ (Arria 10 GX FPGA Development Kit) Date: 1 December 2016 Revision:1.0 2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY,
Simulating the ASMI Block in Your Design
 2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
2015.08.03 AN-720 Subscribe Supported Devices Overview You can simulate the ASMI block in your design for the following devices: Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10 Cyclone V Stratix V In the Quartus II software,
JESD204B IP Core. User Guide. 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 14.
 JESD04B IP Core User Guide Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 4.0 Subscribe UG-04 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC- JESD04B IP Core User Guide Contents JESD04B IP Core
JESD04B IP Core User Guide Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 4.0 Subscribe UG-04 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC- JESD04B IP Core User Guide Contents JESD04B IP Core
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Building Gigabit Interfaces in Altera Transceiver Devices
 Building Gigabit Interfaces in Altera Transceiver Devices Course Description In this course, you will learn how you can build high-speed, gigabit interfaces using the 28- nm embedded transceivers found
Building Gigabit Interfaces in Altera Transceiver Devices Course Description In this course, you will learn how you can build high-speed, gigabit interfaces using the 28- nm embedded transceivers found
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
 DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v4.1 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices
 Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v4.1 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Contents Contents 1. Overview of Ethernet Link Inspector for Intel Stratix 10 Devices... 3 1.1. Features...3 1.1.1. Link Monitor...3
Ethernet Link Inspector User Guide v4.1 for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Contents Contents 1. Overview of Ethernet Link Inspector for Intel Stratix 10 Devices... 3 1.1. Features...3 1.1.1. Link Monitor...3
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
Arria 10 JESD204B IP Core Design Example User Guide
 Arria 10 JESD204B IP Core Design Example User Guide UG-DEX-A10-JESD204B 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Arria 10 JESD204B
Arria 10 JESD204B IP Core Design Example User Guide UG-DEX-A10-JESD204B 2017.05.08 Last updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents 1 Arria 10 JESD204B
AN 833: Intel Stratix 10 GX 16- Lane RX JESD204B-ADC12DJ3200 Interoperability Reference Design
 AN 833: Intel Stratix 10 GX 16- Lane RX JESD204B-ADC12DJ3200 Interoperability Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Intel Stratix 10 GX 16-Lane
AN 833: Intel Stratix 10 GX 16- Lane RX JESD204B-ADC12DJ3200 Interoperability Reference Design Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Intel Stratix 10 GX 16-Lane
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide
 Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Generic Serial Flash Interface Intel FPGA IP Core User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Generic
Intel FPGA Low Latency Ethernet 10G MAC Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices
 Intel FPGA Low Latency Ethernet 10G MAC Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
Intel FPGA Low Latency Ethernet 10G MAC Design Example User Guide for Intel Stratix 10 Devices Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF
Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide
 Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Cyclone 10 External Memory Interfaces IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
Intel Stratix 10 L- and H-Tile Transceiver PHY User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 L- and H-Tile Transceiver PHY User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Overview... 7 1.1. L-Tile/H-Tile Layout in Intel Stratix 10 Device
Intel Stratix 10 L- and H-Tile Transceiver PHY User Guide Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Overview... 7 1.1. L-Tile/H-Tile Layout in Intel Stratix 10 Device
AN 803: Implementing Analog-to- Digital Converter Multi-Link Designs with Intel Arria 10 JESD204B RX IP Core
 AN 803: Implementing Analog-to- Digital Converter Multi-Link Designs with Intel Arria 10 JESD204B RX IP Core Subscribe S Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Implementing Analog-to-Digital
AN 803: Implementing Analog-to- Digital Converter Multi-Link Designs with Intel Arria 10 JESD204B RX IP Core Subscribe S Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Implementing Analog-to-Digital
Nios II Embedded Design Suite 6.1 Release Notes
 December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide
 Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Customizable Flash Programmer Overview... 3 1.1. Device Family Support...3 1.2. Software Support...
Customizable Flash Programmer User Guide Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Customizable Flash Programmer Overview... 3 1.1. Device Family Support...3 1.2. Software Support...
External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
External Memory Interfaces Intel Arria 10 FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents
16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes
 June 2012 QII53021-12.0.0 16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes QII53021-12.0.0 This chapter provides detailed instructions about how to use the In-System Sources and Probes Editor and
June 2012 QII53021-12.0.0 16. Design Debugging Using In-System Sources and Probes QII53021-12.0.0 This chapter provides detailed instructions about how to use the In-System Sources and Probes Editor and
Intel Cyclone 10 GX Transceiver PHY User Guide
 Intel Cyclone 10 GX Transceiver PHY User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Cyclone 10 GX Transceiver PHY
Intel Cyclone 10 GX Transceiver PHY User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.1 Subscribe Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Cyclone 10 GX Transceiver PHY
Arria 10 Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions
 Arria 10 Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 14.0 Arria 10 Edition Subscribe UG-01145_avmm_dma 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Arria 10 Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 14.0 Arria 10 Edition Subscribe UG-01145_avmm_dma 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices
 January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata
 Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata Updated for Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs: 1.0 Production Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web:
Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs 1.0 Errata Updated for Intel Acceleration Stack for Intel Xeon CPU with FPGAs: 1.0 Production Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web:
JESD204B Intel Cyclone 10 GX FPGA IP Design Example User Guide
 JESD204B Intel Cyclone 10 GX FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. JESD204B
JESD204B Intel Cyclone 10 GX FPGA IP Design Example User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. JESD204B
EFEC20 IP Core. Features
 EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
EFEC20 IP Core DS-1034-1.2 Data Sheet The Altera 20% Enhanced Forward Error Correction (EFEC20) IP core includes a highperformance encoder and decoder for Optical Transport Network (OTN) FEC applications.
AN 690: PCI Express DMA Reference Design for Stratix V Devices
 AN 690: PCI Express DMA Reference Design for Stratix V Devices an690-1.0 Subscribe The PCI Express Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA Reference Design highlights the performance of the Avalon-MM 256-Bit
AN 690: PCI Express DMA Reference Design for Stratix V Devices an690-1.0 Subscribe The PCI Express Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA Reference Design highlights the performance of the Avalon-MM 256-Bit
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.0. Errata are functional defects
March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.0. Errata are functional defects
Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software
 Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software AN-370-3.2 Application Note Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution for
Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software AN-370-3.2 Application Note Introduction Using the interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the first in-system programming solution for
Upgrading to UniPHY-based Controllers from ALTMEMPHY-based Controllers
 Upgrading to UniPHY-based Controllers from ALTMEMPHY-based Controllers 14 emi_rm_012 Subscribe The following topics describe the process of upgrading to UniPHY from DDR2 or DDR3 SDRAM High-Performance
Upgrading to UniPHY-based Controllers from ALTMEMPHY-based Controllers 14 emi_rm_012 Subscribe The following topics describe the process of upgrading to UniPHY from DDR2 or DDR3 SDRAM High-Performance
3. Stratix II GX Dynamic Reconfiguration
 3. Stratix II GX Dynamic Reconfiguration SIIGX52007-1.1 Introduction The Stratix II GX gigabit transceiver block gives you a simplified means to dynamically reconfigure: Transmit and receive analog settings
3. Stratix II GX Dynamic Reconfiguration SIIGX52007-1.1 Introduction The Stratix II GX gigabit transceiver block gives you a simplified means to dynamically reconfigure: Transmit and receive analog settings
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide Subscribe UG-01101 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation
DSP Builder. DSP Builder v6.1 Issues. Error When Directory Pathname is a Network UNC Path
 March 2007, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for DSP Builder version 6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors which may cause DSP Builder to deviate
March 2007, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for DSP Builder version 6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors which may cause DSP Builder to deviate
Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide
 Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01172 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
Low Latency 40- and 100-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe Last updated for Quartus Prime Design Suite: 16.0 UG-01172 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com
FFT MegaCore Function User Guide
 FFT MegaCore Function User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com MegaCore Version: 11.0 Document Date: May 2011 Copyright 2011 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The
FFT MegaCore Function User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com MegaCore Version: 11.0 Document Date: May 2011 Copyright 2011 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The
Video and Image Processing Suite
 Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel MAX 10 User Flash Memory
Single-Port Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design
 Single-Port Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design AN-647-1.2 Application Note This application note deibes Single-Port Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip reference designs
Single-Port Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip Reference Design AN-647-1.2 Application Note This application note deibes Single-Port Triple-Speed Ethernet and On-Board PHY Chip reference designs
13. HardCopy Design Migration Guidelines
 November 2012 EMI_DG_012-2.2 13. HardCopy Design Migration Guidelines EMI_DG_012-2.2 This chapter discusses HardCopy migration guidelines or UniPHY-based designs. I you want to migrate your ALTMEMPHY-based
November 2012 EMI_DG_012-2.2 13. HardCopy Design Migration Guidelines EMI_DG_012-2.2 This chapter discusses HardCopy migration guidelines or UniPHY-based designs. I you want to migrate your ALTMEMPHY-based
High-Performance FPGA PLL Analysis with TimeQuest
 High-Performance FPGA PLL Analysis with TimeQuest August 2007, ver. 1.0 Application Note 471 Introduction f Phase-locked loops (PLLs) provide robust clock management and clock synthesis capabilities for
High-Performance FPGA PLL Analysis with TimeQuest August 2007, ver. 1.0 Application Note 471 Introduction f Phase-locked loops (PLLs) provide robust clock management and clock synthesis capabilities for
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices
 9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
9. SEU Mitigation in Cyclone IV Devices May 2013 CYIV-51009-1.3 CYIV-51009-1.3 This chapter describes the cyclical redundancy check (CRC) error detection feature in user mode and how to recover from soft
