Lecture 15: Virtual Memory
|
|
|
- Asher Garrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 15: Virtual Memory Last Time: Cache wrap-up Virtual memory motivation Today Virtual memory implementations Lecture 15 1
2 Physical Memory Addressing LW R1,0(R2) CPU Cache DRAM 256MB address 32 bits tag ind off 32 bits 28 bits Lecture 15 2
3 Webster s definition of virtual Pronunciation: 'v&r-ch&-w&l, -ch&l; 'v&rch-w&l Function: adjective Etymology: Middle English, possessed of certain physical virtues, from Medieval Latin virtualis, from Latin virtus strength, virtue 1:being such in essence or effect though not formally recognized or admitted <a virtual dictator> 2:of, relating to, or using virtual memory 3:of, relating to, or being a hypothetical particle whose existence is inferred from indirect evidence <virtual photons> Lecture 15 3
4 The goal of virtual memory Make it appear as if each process has: It s own private memory The memory is nearly infinite in size The challenge... Physical memory is: Limited in size Shared by all of the processes running on the machine The job of the virtual memory system is to maintain the illusion we want, given the physical limitations. Lecture 15 4
5 What if? A program is loaded into different places in memory each time it runs? Relocation A program wants to use more memory than physically exists? Page to disk We want to switch between multiple programs that use different data? Protection Lecture 15 5
6 Simple View of Memory PC R1... R31 Code Data Stack Single program runs at a time Code and static data are at fixed locations code starts at fixed location, e.g., 0x100 subroutines may be at fixed locations (absolute jumps) data locations may be wired into code Stack accesses relative to stack pointer. Lecture 15 6
7 Running Two Programs (Relocation) No Protection PC R1... R31 PC R1... R31 Code Data Stack Code Data Stack Need to relocate logical addresses to physical locations Stack is already relocatable all accesses relative to SP Code can be made relocatable allow only relative jumps all accesses relative to PC Data segment can calculate all addresses relative to a DP expensive faster with hardware support base register Lecture 15 7
8 Base-Register Addressing Logical Address Logical Address Base (DP) Add a single base register, BR, to hardware Base register loaded with data pointer (DP) for current program All data addresses added to base before accessing memory Can relocate code too Often implemented with a three-input adder Need to bypass base register to access system tables for program switching a place to stand Lecture 15 8
9 Base Register Addressing Sys Code Sys Table Base 0 Base 1 Code Data Stack Code Data System code handles switching between programs System table contains: - Base address of each program - Saved state of non-running programs Stack Lecture 15 9
10 Providing Protection Between Programs (Length Registers) Sys Code Sys Table Base 0 Length 0 + Base 1 Length 1 + Code Data Stack Code Data Stack Add a Length Register LR to the hardware A program is only allowed to access memory from BR to BR+Length-1 A program cannot set BR or LR they are privileged registers But how do we switch programs? Lecture 15 10
11 Base + Length Addressing Privileged Registers Logical Address Base Length < Logical Address Allowed Lecture 15 11
12 What a mess! Is there a better way that: Simplifies protection Enables relocation Extends the physical memory capacity Lecture 15 12
13 A Load to Virtual Memory LW R1,0(R2) CPU Virtual Addr. 32 bits Translate Cache Physical Addr. 26 bits DRAM 64MB 21 bits Translate from virtual space to physical space VA PA May need to go to disk Lecture 15 13
14 A Load to Virtual Memory LW R1,0(R2) Process 1 CPU Virtual Addr. 32 bits Translate Cache Physical Addr. 26 bits DRAM 64MB Process 2 21 bits Both programs can use the same set of addresses! Change translation tables to point same VA to different PA for different programs Lecture 15 14
15 Paging and Protection How to ensure that processes can t access each other s data Put them in separate virtual address spaces Control the mappings of VA to PA for each process Separate page tables How can you share data between processes Give them each a VA mapping to the same PA Similar entry in each process page table Lecture 15 15
16 Virtual Address Translation Virtual Page Number (VPN) Page Offset Translation Table Physical Page Number (PPN) Page Offset Main Memory = 64MB Page Size = 4KB VPN = 20 bits PPN = 14 bits Translation table aka Page Table Lecture 15 16
17 Page Table Construction Page Table Register valid Physical Page Number + VPN offset PPN offset Page table size (14 + 1) * 2 20 = 4MB Where to put the page table? Lecture 15 17
18 Paging: Main Memory as a Cache for Disk data page (4-256KB) Demand Paging 32 bit addresses = 4GB, Main Memory = 64MB Dynamically adjust what data stays in main memory Page similar to cache block Note: file system >> 4GB, managed by O/S Lecture 15 18
19 Virtual Addresses Span Memory+Disk Virtual Addresses Physical Addresses Disk Mappings changed dynamically by O/S In response to users data accesses OS triggered by hardware Lecture 15 19
20 What if Data is Not in DRAM? 1) Examine page table 2) Discover that no mapping exists 3) Select page to evict, store back to disk 4) Bring in new page from disk 5) Update page table Lecture 15 20
21 Page Fault User Program Runs Page fault OS requests page OS Installs page User program resumes Disk read 2nd User Program Runs Disk interrupt Lecture 15 21
22 VM Requires Restartable (or resumable) instructions must be able to resume program after recovering from a page fault Ability to mark a page not present and raise a page fault when referencing such a page (Optional) Maintain status bits per page R - referenced - for use by replacement algorithm M -modified-to determine when page is dirty Lecture 15 22
23 Page Frame Management Free Proc 1 Link R M State Page Frame Table OS maintains page table for each user process page frame table free page list pages evicted when number of free pages falls below a low water mark. pages evicted using a replacement policy random, FIFO, LRU, clock if M-bit is clear, need not copy the page back to disk Lecture 15 23
24 Page Management and Thrashing W X Y Z X Y Z W Reference four pages in sequence, mapped to three page frames Y Z W X Need to keep a process working set in memory or thrashing will occur Find working set size by increasing page frame allocation until PF/s falls below limit Swap out whole process if insufficient page frames for working set Lecture 15 24
25 Page Table Organization PTP 2 n-o Flat page table has size proportional to size of virtual address space can be very large for a machine with 64-bit addresses and several processes Three solutions page the page table (fixed mapping) what really needs to be locked down? multi-level page table (lower levels paged - Tree) inverted page table (hash table) Lecture 15 25
26 Multi-Level Page Table Dir1 Dir2 Page offset PTP Directory Directory e.g., 42-bit VA with 12-bit offset 10-bits for each of three fields byte entries in each table (one page) Page Directory Page Table Lecture 15 26
27 Inverted Page Tables Virtual Address Page Offset Hash Page Frame S Store only PTEs for pages in physical memory Miss in page table implies page is on disk Need KP entries for P page frames (usually K > 2) = OK Frame Offset Lecture 15 27
28 Summary Virtual memory provides Illusion of private memory system for each process Protection Relocation in memory system Demand paging But page tables can be large Motivates: paging page tables, multi-level tables, inverted page tables Next time Integration of virtual memory into cache hierarchy DRAM memory organization Lecture 15 28
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: an Introduction to Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: an Introduction to Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications
Chapter 8. Virtual Memory
 Operating System Chapter 8. Virtual Memory Lynn Choi School of Electrical Engineering Motivated by Memory Hierarchy Principles of Locality Speed vs. size vs. cost tradeoff Locality principle Spatial Locality:
Operating System Chapter 8. Virtual Memory Lynn Choi School of Electrical Engineering Motivated by Memory Hierarchy Principles of Locality Speed vs. size vs. cost tradeoff Locality principle Spatial Locality:
Computer Science 146. Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and Virtual Memory
 HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS May 16, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory 1 / 36 DRAM Fundamentals Random-access
HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS May 16, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory 1 / 36 DRAM Fundamentals Random-access
Virtual Memory. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. November 15, MIT Fall 2018 L20-1
 Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L20-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L20-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Another View of the Memory Hierarchy. Lecture #25 Virtual Memory I Memory Hierarchy Requirements. Memory Hierarchy Requirements
 CS61C L25 Virtual I (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #25 Virtual I 27-8-7 Scott Beamer, Instructor Another View of the Hierarchy Thus far{ Next: Virtual { Regs Instr.
CS61C L25 Virtual I (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #25 Virtual I 27-8-7 Scott Beamer, Instructor Another View of the Hierarchy Thus far{ Next: Virtual { Regs Instr.
Virtual Memory. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 12, 2018 L16-1
 Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Computer Systems. Virtual Memory. Han, Hwansoo
 Computer Systems Virtual Memory Han, Hwansoo A System Using Physical Addressing CPU Physical address (PA) 4 Main memory : : 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8:... M-: Data word Used in simple systems like embedded microcontrollers
Computer Systems Virtual Memory Han, Hwansoo A System Using Physical Addressing CPU Physical address (PA) 4 Main memory : : 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8:... M-: Data word Used in simple systems like embedded microcontrollers
198:231 Intro to Computer Organization. 198:231 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 14
 98:23 Intro to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Virtual Memory 98:23 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Instructor: Nicole Hynes nicole.hynes@rutgers.edu Credits: Several slides courtesy of
98:23 Intro to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Virtual Memory 98:23 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Instructor: Nicole Hynes nicole.hynes@rutgers.edu Credits: Several slides courtesy of
Memory Hierarchy Requirements. Three Advantages of Virtual Memory
 CS61C L12 Virtual (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #12 Virtual 2009-08-03 Jeremy Huddleston Review!! Cache design choices: "! Size of cache: speed v. capacity "! size (i.e., cache aspect ratio)
CS61C L12 Virtual (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #12 Virtual 2009-08-03 Jeremy Huddleston Review!! Cache design choices: "! Size of cache: speed v. capacity "! size (i.e., cache aspect ratio)
Carnegie Mellon. Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition
 Carnegie Mellon Virtual Memory: Concepts 5-23: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, October 24, 27 Instructor: Randy Bryant 2 Hmmm, How Does This Work?! Process Process 2 Process n Solution:
Carnegie Mellon Virtual Memory: Concepts 5-23: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, October 24, 27 Instructor: Randy Bryant 2 Hmmm, How Does This Work?! Process Process 2 Process n Solution:
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory. Robert Wagner
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
VIRTUAL MEMORY II. Jo, Heeseung
 VIRTUAL MEMORY II Jo, Heeseung TODAY'S TOPICS How to reduce the size of page tables? How to reduce the time for address translation? 2 PAGE TABLES Space overhead of page tables The size of the page table
VIRTUAL MEMORY II Jo, Heeseung TODAY'S TOPICS How to reduce the size of page tables? How to reduce the time for address translation? 2 PAGE TABLES Space overhead of page tables The size of the page table
Virtual Memory. Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1
 Virtual Memory Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1 Virtual Memory Use main memory as a cache for secondary (disk) storage Managed jointly by CPU hardware and the operating system (OS) Programs
Virtual Memory Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1 Virtual Memory Use main memory as a cache for secondary (disk) storage Managed jointly by CPU hardware and the operating system (OS) Programs
Address Translation. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Address Translation Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics How to reduce the size of page tables? How to reduce the time for
Address Translation Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics How to reduce the size of page tables? How to reduce the time for
Computer Architecture. Lecture 8: Virtual Memory
 Computer Architecture Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Dr. Ahmed Sallam Suez Canal University Spring 2015 Based on original slides by Prof. Onur Mutlu Memory (Programmer s View) 2 Ideal Memory Zero access time
Computer Architecture Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Dr. Ahmed Sallam Suez Canal University Spring 2015 Based on original slides by Prof. Onur Mutlu Memory (Programmer s View) 2 Ideal Memory Zero access time
Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts
 Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS 37 8 th February 28 (lecture notes derived from material from Phil Gibbons, Dave O Hallaron, and Randy Bryant) Today Processes Virtual
Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS 37 8 th February 28 (lecture notes derived from material from Phil Gibbons, Dave O Hallaron, and Randy Bryant) Today Processes Virtual
Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging
 Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 12, 2014
Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 12, 2014
Virtual Memory. Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs
 Virtual Memory Today Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs Fabián Chris E. Bustamante, Riesbeck, Fall Spring 2007 2007 A system with physical memory only Addresses generated
Virtual Memory Today Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs Fabián Chris E. Bustamante, Riesbeck, Fall Spring 2007 2007 A system with physical memory only Addresses generated
Lecture 19: Virtual Memory: Concepts
 CSCI-UA.2-3 Computer Systems Organization Lecture 9: Virtual Memory: Concepts Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Some slides adapted (and slightly modified) from: Clark Barrett
CSCI-UA.2-3 Computer Systems Organization Lecture 9: Virtual Memory: Concepts Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Some slides adapted (and slightly modified) from: Clark Barrett
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Memory
 CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
Virtual Memory. Reading. Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 (2) Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili
 Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Memory Hierarchy. Mehran Rezaei
 Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su06 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #23: VM I 2006-08-08 CS 61C L23 VM I (1) Andy Carle Outline Cache Review Virtual Memory CS 61C L23 VM I (2) Improving Miss Penalty
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su06 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #23: VM I 2006-08-08 CS 61C L23 VM I (1) Andy Carle Outline Cache Review Virtual Memory CS 61C L23 VM I (2) Improving Miss Penalty
Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging
 Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 9, 2015
Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 9, 2015
virtual memory. March 23, Levels in Memory Hierarchy. DRAM vs. SRAM as a Cache. Page 1. Motivation #1: DRAM a Cache for Disk
 5-23 March 23, 2 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating address translation with TLBs Pentium II/III system Motivation #: DRAM a Cache for The full address space is quite large: 32-bit
5-23 March 23, 2 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating address translation with TLBs Pentium II/III system Motivation #: DRAM a Cache for The full address space is quite large: 32-bit
1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory
 Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Virtual Memory. Samira Khan Apr 27, 2017
 Virtual Memory Samira Khan Apr 27, 27 Virtual Memory Idea: Give the programmer the illusion of a large address space while having a small physical memory So that the programmer does not worry about managing
Virtual Memory Samira Khan Apr 27, 27 Virtual Memory Idea: Give the programmer the illusion of a large address space while having a small physical memory So that the programmer does not worry about managing
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 11 - Virtual Memory and Caches
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 11 - Virtual Memory and Caches Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 11 - Virtual Memory and Caches Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture!
 Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Why it works: locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware and
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Why it works: locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware and
Modern Virtual Memory Systems. Modern Virtual Memory Systems
 6.823, L12--1 Modern Virtual Systems Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 6.823, L12--2 Modern Virtual Systems illusion of a large, private, uniform store Protection
6.823, L12--1 Modern Virtual Systems Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 6.823, L12--2 Modern Virtual Systems illusion of a large, private, uniform store Protection
Virtual Memory. Motivation:
 Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
CS252 S05. Main memory management. Memory hardware. The scale of things. Memory hardware (cont.) Bottleneck
 Main memory management CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 16 Memory Hierarchy 3 (Main Memory & Memory) Questions: How big should main memory be? How to handle reads and writes? How to find
Main memory management CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 16 Memory Hierarchy 3 (Main Memory & Memory) Questions: How big should main memory be? How to handle reads and writes? How to find
Memory management. Requirements. Relocation: program loading. Terms. Relocation. Protection. Sharing. Logical organization. Physical organization
 Requirements Relocation Memory management ability to change process image position Protection ability to avoid unwanted memory accesses Sharing ability to share memory portions among processes Logical
Requirements Relocation Memory management ability to change process image position Protection ability to avoid unwanted memory accesses Sharing ability to share memory portions among processes Logical
CSE 153 Design of Operating Systems
 CSE 53 Design of Operating Systems Winter 28 Lecture 6: Paging/Virtual Memory () Some slides modified from originals by Dave O hallaron Today Address spaces VM as a tool for caching VM as a tool for memory
CSE 53 Design of Operating Systems Winter 28 Lecture 6: Paging/Virtual Memory () Some slides modified from originals by Dave O hallaron Today Address spaces VM as a tool for caching VM as a tool for memory
Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 2002
 5-23 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 22 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs class9.ppt Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical
5-23 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 22 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs class9.ppt Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Virtual Memory
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Virtual Memory Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/30/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #24 1 Review of Last Lecture (1/2) Multiple instruction issue increases max speedup, but
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Virtual Memory Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/30/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #24 1 Review of Last Lecture (1/2) Multiple instruction issue increases max speedup, but
14 May 2012 Virtual Memory. Definition: A process is an instance of a running program
 Virtual Memory (VM) Overview and motivation VM as tool for caching VM as tool for memory management VM as tool for memory protection Address translation 4 May 22 Virtual Memory Processes Definition: A
Virtual Memory (VM) Overview and motivation VM as tool for caching VM as tool for memory management VM as tool for memory protection Address translation 4 May 22 Virtual Memory Processes Definition: A
MEMORY: SWAPPING. Shivaram Venkataraman CS 537, Spring 2019
 MEMORY: SWAPPING Shivaram Venkataraman CS 537, Spring 2019 ADMINISTRIVIA - Project 2b is out. Due Feb 27 th, 11:59 - Project 1b grades are out Lessons from p2a? 1. Start early! 2. Sketch out a design?
MEMORY: SWAPPING Shivaram Venkataraman CS 537, Spring 2019 ADMINISTRIVIA - Project 2b is out. Due Feb 27 th, 11:59 - Project 1b grades are out Lessons from p2a? 1. Start early! 2. Sketch out a design?
ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems. Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I)
 ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I) 1 Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
ECE7995 Caching and Prefetching Techniques in Computer Systems Lecture 8: Buffer Cache in Main Memory (I) 1 Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
This Unit: Main Memory. Virtual Memory. Virtual Memory. Other Uses of Virtual Memory
 This Unit: Virtual Application OS Compiler Firmware I/O Digital Circuits Gates & Transistors hierarchy review DRAM technology A few more transistors Organization: two level addressing Building a memory
This Unit: Virtual Application OS Compiler Firmware I/O Digital Circuits Gates & Transistors hierarchy review DRAM technology A few more transistors Organization: two level addressing Building a memory
Chapter 5B. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Memory Management! How the hardware and OS give application pgms:" The illusion of a large contiguous address space" Protection against each other"
 Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Spatial and temporal locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Spatial and temporal locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware
Chapter 6: Demand Paging
 ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER ( 5-006-00 ) Networks and Operating Systems Chapter 6: Demand Paging Source: http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor If you miss a key
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER ( 5-006-00 ) Networks and Operating Systems Chapter 6: Demand Paging Source: http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor If you miss a key
a process may be swapped in and out of main memory such that it occupies different regions
 Virtual Memory Characteristics of Paging and Segmentation A process may be broken up into pieces (pages or segments) that do not need to be located contiguously in main memory Memory references are dynamically
Virtual Memory Characteristics of Paging and Segmentation A process may be broken up into pieces (pages or segments) that do not need to be located contiguously in main memory Memory references are dynamically
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Virtual Memory Nov 9, 2009"
 Virtual Memory Nov 9, 2009" Administrivia" 2! 3! Motivations for Virtual Memory" Motivation #1: DRAM a Cache for Disk" SRAM" DRAM" Disk" 4! Levels in Memory Hierarchy" cache! virtual memory! CPU" regs"
Virtual Memory Nov 9, 2009" Administrivia" 2! 3! Motivations for Virtual Memory" Motivation #1: DRAM a Cache for Disk" SRAM" DRAM" Disk" 4! Levels in Memory Hierarchy" cache! virtual memory! CPU" regs"
Virtual Memory. Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University
 Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
Virtual Memory. CS 351: Systems Programming Michael Saelee
 Virtual Memory CS 351: Systems Programming Michael Saelee registers cache (SRAM) main memory (DRAM) local hard disk drive (HDD/SSD) remote storage (networked drive / cloud) previously: SRAM
Virtual Memory CS 351: Systems Programming Michael Saelee registers cache (SRAM) main memory (DRAM) local hard disk drive (HDD/SSD) remote storage (networked drive / cloud) previously: SRAM
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Lecture 23: Virtual Memory. Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 23: Virtual Memory Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Virtual Memory Paged Physical Memory Swap Space Page Faults
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 23: Virtual Memory Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Virtual Memory Paged Physical Memory Swap Space Page Faults
Memory Management. Goals of this Lecture. Motivation for Memory Hierarchy
 Memory Management Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: The memory hierarchy Spatial and temporal locality of reference Caching, at multiple levels Virtual memory and thereby How the hardware and
Memory Management Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: The memory hierarchy Spatial and temporal locality of reference Caching, at multiple levels Virtual memory and thereby How the hardware and
Lec 13: Linking and Memory. Kavita Bala CS 3410, Fall 2008 Computer Science Cornell University. Announcements
 Lec 13: Linking and Memory Kavita Bala CS 3410, Fall 2008 Computer Science Cornell University PA 2 is out Due on Oct 22 nd Announcements Prelim Oct 23 rd, 7:30-9:30/10:00 All content up to Lecture on Oct
Lec 13: Linking and Memory Kavita Bala CS 3410, Fall 2008 Computer Science Cornell University PA 2 is out Due on Oct 22 nd Announcements Prelim Oct 23 rd, 7:30-9:30/10:00 All content up to Lecture on Oct
Virtual Memory I. CSE 351 Spring Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Virtual Memory I CSE 35 Spring 27 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Midterms Graded If you did
Virtual Memory I CSE 35 Spring 27 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Midterms Graded If you did
Memory. Principle of Locality. It is impossible to have memory that is both. We create an illusion for the programmer. Employ memory hierarchy
 Datorarkitektur och operativsystem Lecture 7 Memory It is impossible to have memory that is both Unlimited (large in capacity) And fast 5.1 Intr roduction We create an illusion for the programmer Before
Datorarkitektur och operativsystem Lecture 7 Memory It is impossible to have memory that is both Unlimited (large in capacity) And fast 5.1 Intr roduction We create an illusion for the programmer Before
Memory Management. Chapter 4 Memory Management. Multiprogramming with Fixed Partitions. Ideally programmers want memory that is.
 Chapter 4 Memory Management Ideally programmers want memory that is Memory Management large fast non volatile 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms
Chapter 4 Memory Management Ideally programmers want memory that is Memory Management large fast non volatile 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms
Memory hier ar hier ch ar y ch rev re i v e i w e ECE 154B Dmitri Struko Struk v o
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
Virtual Memory. Physical Addressing. Problem 2: Capacity. Problem 1: Memory Management 11/20/15
 Memory Addressing Motivation: why not direct physical memory access? Address translation with pages Optimizing translation: translation lookaside buffer Extra benefits: sharing and protection Memory as
Memory Addressing Motivation: why not direct physical memory access? Address translation with pages Optimizing translation: translation lookaside buffer Extra benefits: sharing and protection Memory as
V. Primary & Secondary Memory!
 V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
CSE 120. Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware. July 18, Day 5 Memory. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Software TLB Management
 CSE 120 July 18, 2006 Day 5 Memory Instructor: Neil Rhodes Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware Cache to map virtual page numbers to page frame Associative memory: HW looks up in
CSE 120 July 18, 2006 Day 5 Memory Instructor: Neil Rhodes Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Implemented in Hardware Cache to map virtual page numbers to page frame Associative memory: HW looks up in
Multi-level Translation. CS 537 Lecture 9 Paging. Example two-level page table. Multi-level Translation Analysis
 Multi-level Translation CS 57 Lecture 9 Paging Michael Swift Problem: what if you have a sparse address space e.g. out of GB, you use MB spread out need one PTE per page in virtual address space bit AS
Multi-level Translation CS 57 Lecture 9 Paging Michael Swift Problem: what if you have a sparse address space e.g. out of GB, you use MB spread out need one PTE per page in virtual address space bit AS
CSE 351. Virtual Memory
 CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging. Cache Performance
 6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter Page Table Management, TLBs and Other Pragmatics. Gary Kimura
 CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2013 Page Table Management, TLBs and Other Pragmatics Gary Kimura Moving now from Hardware to how the OS manages memory Two main areas to discuss Page table management,
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2013 Page Table Management, TLBs and Other Pragmatics Gary Kimura Moving now from Hardware to how the OS manages memory Two main areas to discuss Page table management,
@2010 Badri Computer Architecture Assembly II. Virtual Memory. Topics (Chapter 9) Motivations for VM Address translation
 Virtual Memory Topics (Chapter 9) Motivations for VM Address translation 1 Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical DRAM as a Cache for the Disk Address space of a process can exceed physical memory
Virtual Memory Topics (Chapter 9) Motivations for VM Address translation 1 Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical DRAM as a Cache for the Disk Address space of a process can exceed physical memory
Memory hierarchy review. ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
Chapter 5 (Part II) Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Module 9: Virtual Memory
 Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmenation 9.1 Background
Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmenation 9.1 Background
Virtual Memory. CS61, Lecture 15. Prof. Stephen Chong October 20, 2011
 Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 20. Virtual Memory
 COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 20. Virtual Memory Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Virtual Memory Topics Reducing Cache Miss Penalty (#2) Use
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 20. Virtual Memory Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Virtual Memory Topics Reducing Cache Miss Penalty (#2) Use
Virtual Memory. Stefanos Kaxiras. Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources.
 Virtual Memory Stefanos Kaxiras Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources. Caches Review & Intro Intended to make the slow main memory look fast by
Virtual Memory Stefanos Kaxiras Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources. Caches Review & Intro Intended to make the slow main memory look fast by
Agenda. CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Virtual Memory II. Goals of Virtual Memory. Memory Hierarchy Requirements
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Virtual II Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Agenda Review of Last Lecture Goals of Virtual Page Tables Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Administrivia VM Performance
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Virtual II Guest Lecturer: Justin Hsia Agenda Review of Last Lecture Goals of Virtual Page Tables Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Administrivia VM Performance
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems ( ) Chapter 6: Demand Paging
 ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems (5-006-00) Chapter 6: Demand Paging http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor (0) # Inverted page table One
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems (5-006-00) Chapter 6: Demand Paging http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor (0) # Inverted page table One
Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging. Highly-Associative Caches
 Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging 6.823, L8--1 Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Highly-Associative
Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging 6.823, L8--1 Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Highly-Associative
Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) Main Memory
 Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) CPU CPU CPU Cache Multiplexor Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory bank 0 Memory bank 1 Memory bank 2 Memory bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization
Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) CPU CPU CPU Cache Multiplexor Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory bank 0 Memory bank 1 Memory bank 2 Memory bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization
Recall from Tuesday. Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS.
 Paging 11/10/16 Recall from Tuesday Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS Process 3 Process 3 OS: Place Process 3 Process 1 Process
Paging 11/10/16 Recall from Tuesday Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS Process 3 Process 3 OS: Place Process 3 Process 1 Process
CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems
 CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2018 Lecture 10: Virtual Memory II Ryan Huang Slides adapted from Geoff Voelker s lectures Administrivia Next Tuesday project hacking day No class My office
CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2018 Lecture 10: Virtual Memory II Ryan Huang Slides adapted from Geoff Voelker s lectures Administrivia Next Tuesday project hacking day No class My office
Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden of managing overlays.
 CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
Memory - Paging. Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1
 Memory - Paging Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Physical Frame Allocation How do we allocate physical memory across multiple processes? What if Process A needs to evict a page from Process
Memory - Paging Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Physical Frame Allocation How do we allocate physical memory across multiple processes? What if Process A needs to evict a page from Process
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
Lecture #15: Translation, protection, sharing
 Lecture #15: Translation, protection, sharing Review -- 1 min Goals of virtual memory: protection relocation sharing illusion of infinite memory minimal overhead o space o time Last time: we ended with
Lecture #15: Translation, protection, sharing Review -- 1 min Goals of virtual memory: protection relocation sharing illusion of infinite memory minimal overhead o space o time Last time: we ended with
UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Virtual Memory II 2007-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Hardware repair?! This technology allows
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Virtual Memory II 2007-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Hardware repair?! This technology allows
The Virtual Memory Abstraction. Memory Management. Address spaces: Physical and Virtual. Address Translation
 The Virtual Memory Abstraction Memory Management Physical Memory Unprotected address space Limited size Shared physical frames Easy to share data Virtual Memory Programs are isolated Arbitrary size All
The Virtual Memory Abstraction Memory Management Physical Memory Unprotected address space Limited size Shared physical frames Easy to share data Virtual Memory Programs are isolated Arbitrary size All
Move back and forth between memory and disk. Memory Hierarchy. Two Classes. Don t
 Memory Management Ch. 3 Memory Hierarchy Cache RAM Disk Compromise between speed and cost. Hardware manages the cache. OS has to manage disk. Memory Manager Memory Hierarchy Cache CPU Main Swap Area Memory
Memory Management Ch. 3 Memory Hierarchy Cache RAM Disk Compromise between speed and cost. Hardware manages the cache. OS has to manage disk. Memory Manager Memory Hierarchy Cache CPU Main Swap Area Memory
Memory Management Ch. 3
 Memory Management Ch. 3 Ë ¾¾ Ì Ï ÒÒØ Å ÔÔ ÓÐÐ 1 Memory Hierarchy Cache RAM Disk Compromise between speed and cost. Hardware manages the cache. OS has to manage disk. Memory Manager Ë ¾¾ Ì Ï ÒÒØ Å ÔÔ ÓÐÐ
Memory Management Ch. 3 Ë ¾¾ Ì Ï ÒÒØ Å ÔÔ ÓÐÐ 1 Memory Hierarchy Cache RAM Disk Compromise between speed and cost. Hardware manages the cache. OS has to manage disk. Memory Manager Ë ¾¾ Ì Ï ÒÒØ Å ÔÔ ÓÐÐ
Motivation. Memory Management. Memory Management. Computer Hardware Review
 Memory Management Motivation Vera Goebel Department of Informatics, University of Oslo with slides from: C. Griwodz (Ifi/UiO), P. Halvorsen (Ifi/UiO), K. Li (Princeton), A. Tanenbaum (VU Amsterdam), and
Memory Management Motivation Vera Goebel Department of Informatics, University of Oslo with slides from: C. Griwodz (Ifi/UiO), P. Halvorsen (Ifi/UiO), K. Li (Princeton), A. Tanenbaum (VU Amsterdam), and
Virtual Memory - Objectives
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 16: Virtual Memory Chapter 7 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy Virtual Memory - Objectives
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 16: Virtual Memory Chapter 7 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy Virtual Memory - Objectives
Operating Systems Lecture 6: Memory Management II
 CSCI-GA.2250-001 Operating Systems Lecture 6: Memory Management II Hubertus Franke frankeh@cims.nyu.edu What is the problem? Not enough memory Have enough memory is not possible with current technology
CSCI-GA.2250-001 Operating Systems Lecture 6: Memory Management II Hubertus Franke frankeh@cims.nyu.edu What is the problem? Not enough memory Have enough memory is not possible with current technology
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017
 CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017 Lecture 12: Paging Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient translations (TLBs)
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017 Lecture 12: Paging Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient translations (TLBs)
Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory Dr. George Michelogiannakis EECS, University of California at Berkeley CRD, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 - Virtual Memory Dr. George Michelogiannakis EECS, University of California at Berkeley CRD, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152
6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory
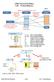 6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory Page Table (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page
6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory Page Table (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page
Module 9: Virtual Memory
 Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmentation Operating
Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmentation Operating
Virtual Memory: Concepts
 Virtual Memory: Concepts 5-23: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, March 2, 27 Instructors: Franz Franchetti & Seth Copen Goldstein Hmmm, How Does This Work?! Process Process 2 Process n Solution:
Virtual Memory: Concepts 5-23: Introduction to Computer Systems 7 th Lecture, March 2, 27 Instructors: Franz Franchetti & Seth Copen Goldstein Hmmm, How Does This Work?! Process Process 2 Process n Solution:
virtual memory Page 1 CSE 361S Disk Disk
 CSE 36S Motivations for Use DRAM a for the Address space of a process can exceed physical memory size Sum of address spaces of multiple processes can exceed physical memory Simplify Management 2 Multiple
CSE 36S Motivations for Use DRAM a for the Address space of a process can exceed physical memory size Sum of address spaces of multiple processes can exceed physical memory Simplify Management 2 Multiple
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Learning Outcomes. An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory.
 Virtual Memory 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory. 2 Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function
Virtual Memory 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory. 2 Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Virtual Memory
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory ECE468 vm.1 Review: The Principle of Locality Probability of reference 0 Address Space 2 The Principle of Locality: Program access a relatively
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory ECE468 vm.1 Review: The Principle of Locality Probability of reference 0 Address Space 2 The Principle of Locality: Program access a relatively
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 13 Virtual memory and memory management unit In the last class, we had discussed
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 13 Virtual memory and memory management unit In the last class, we had discussed
