MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following: a) draw a possibility tree for the outcomes. b) in how many ways can the event "rain on exactly one day" happen? c) what is the probability that it rains on exactly one of the three days? 2. Baskin-Robbins made itself famous for selling 31 flavors of ice cream. Suppose a Baskin - Robbins ice cream shop is selling those 31 flavors and you have a choice of regular cone, waffle cone or sugar cone in sizes kiddie, small, medium and large. How many different ways can you order ice cream that is in a cone at that shop? 3. In a certain state, license plates consist of two capital letters followed by either 3 or 4 digits. How many different license plates are there that have no repeated letters or digits? 4. In how many ways can a photographer at a wedding arrange six people in a row, including the bride and groom if: a) there is no restriction on where the people are to be placed? b) the bride must be next to the groom? c) the bride is not next to the groom? d) the bride is positioned somewhere to the left of the groom? 5. How many positive integers not exceeding 100 are divisible by 4 or by 6? What is the probability of randomly selecting a number that is divisible by 4 or by 6 when selecting from positive integers not exceeding 100? 6. When surveying 100 students it is found that : 33 are taking math 57 are taking biology 57 are taking chemistry 25 are taking math & biology 15 are taking math & chemistry 22 are taking biology & chemistry 10 are taking all three Construct and label a Venn diagram where the appropriate number is indicated in the regions using A=Math, B=Biology, C=Chemistry. And answer the following questions: a) How many students were taking biology but not chemistry? b) How many students were taking only one of the three classes? c) How many students are taking math and biology but not chemistry? d) How many students are not taking math, biology or chemistry?
2 7. A club has seven members. Three are to be chosen to travel as a group to a national meeting. a) How many distinct groups of three can be chosen? b) If the club contains four men and three women, how many distinct groups of three contain two men and one woman? c) If the club contains four men and three women, how many distinct groups of three contain at most two men? d) If the club contains four men and three women, how many distinct groups of three contain at least one woman? e) If the club contains four men and three women, what is the probability that a distinct group of three will contain at least one woman? f) If two members of the club refuse to travel together as part of the group (but each is willing to go if the other does not), how many distinct groups of three can be chosen? g) If two members of the club insist on either traveling together or not going at all how many distinct groups of three can be chosen? 8. Prove algebraically that for all integers 3 n P n 1,3 P n,3 3 P n,2. n k n n r 9. Prove algebraically for all integers n, k, and r with n k r that k r r k r. 10. Use the Binomial Theorem (you must set it up using the theorem and then simplify each 2 term) to expand: 5 x 2y. 11. What is the coefficient of x y in the expansion of 400 2x y? Questions refer to the graph with vertices A, B, C, D, E and edges AD, AC, BD, CC, CE, CD, DE, and DE. 12. Draw the graph. 13. Vertex A is adjacent to which vertices? 14. Find the degree of each vertex. 15. Does the graph have an Euler circuit? 16. Does the graph have an Euler Path? 17. Which edge is a bridge of the graph? (If none, answer "none.")
3 Questions refer to the following five graphs. Graph Which graph(s) has (have) an Euler circuit? 19. Which graph(s) has (have) a Hamilton circuit? 20. Which graphs are disconnected? 21. Which graph has no circuits? 22. In which graph is it true that every edge is bridge? 23. Are any of the graphs complete? If so which one(s)? Questions refer to the following situation: In a certain city there is a river running through the middle of the city. There are three islands and nine bridges as shown in the figure. North Bank A B C River South Bank 24. Draw the graph that represents this situation. 25. Does this graph have an Euler circuit? If so, state the circuit. 26. Does this graph have an Euler Path? Is so, state the path.
4 27. Draw a graph that represents the floor plan, then determine if it is possible to start outside and walk through each doorway exactly once. If so draw the route you would take, if not explain why not. 28. What is required of a graph that has an Euler circuit? 29. What is required of a graph that has an Euler path? 30. Find an Euler circuit starting at A. Number the edges in the order in which you use them. 31. Draw a Graph with 5 vertices that has an Euler Path. 32. Draw a graph with 5 vertices that does not have an Euler circuit or an Euler path. Questions refer to the following situation: A delivery truck must deliver packages to 5 different store locations (A, B, C, D, and E) The trip must start and end at A. The distances between the locations are as follows: A B C D E A B C D E Draw a graph to represent this situation. 34. How many distinct Hamilton circuits would have to be checked if the Brute Force algorithm was used to find the optimal solution?
5 35. Use the nearest neighbor algorithm starting at A to find the best route for the delivery truck. What is the total mileage for the route? 36. Use the repetitive nearest neighbor to find the best route for the delivery truck. Write the route starting from A once you have found it and give the total mileage. 37. Use the cheapest link algorithm to find a route starting from A, what is the total mileage? 38. Suppose you must visit several family members. You live in city A and you must visit cities B, C, and D before you return home. Find the optimal solution. (The route with the lowest total mileage.) What is the total mileage?
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4
 MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
Discrete Structures. Fall Homework3
 Discrete Structures Fall 2015 Homework3 Chapter 5 1. Section 5.1 page 329 Problems: 3,5,7,9,11,15 3. Let P(n) be the statement that 1 2 + 2 2 + +n 2 = n(n + 1)(2n + 1)/6 for the positive integer n. a)
Discrete Structures Fall 2015 Homework3 Chapter 5 1. Section 5.1 page 329 Problems: 3,5,7,9,11,15 3. Let P(n) be the statement that 1 2 + 2 2 + +n 2 = n(n + 1)(2n + 1)/6 for the positive integer n. a)
a) Graph 2 and Graph 3 b) Graph 2 and Graph 4 c) Graph 1 and Graph 4 d) Graph 1 and Graph 3 e) Graph 3 and Graph 4 f) None of the above
 Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
The Traveling Salesman Problem
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
6.2 Initial Problem. Section 6.2 Network Problems. 6.2 Initial Problem, cont d. Weighted Graphs. Weighted Graphs, cont d. Weighted Graphs, cont d
 Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
Finite Math A Chapter 6 Notes Hamilton Circuits
 Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
MA 111 Review for Exam 3
 MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
Note that there are questions printed on both sides of each page!
 Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
Math 574 Review Exam #1
 Math 574 Review Exam 1 1. How many 8-card hands, dealt from a standard deck of 5, consist of: (a). 5 of one suit and 3 of another suit? (b). 4 each of two suits. (c). 3 of one suit, 3 of a second suit,
Math 574 Review Exam 1 1. How many 8-card hands, dealt from a standard deck of 5, consist of: (a). 5 of one suit and 3 of another suit? (b). 4 each of two suits. (c). 3 of one suit, 3 of a second suit,
14 Graph Theory. Exercise Set 14-1
 14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics
 MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
CSE 21 Mathematics for
 CSE 21 Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Summer, 2005 Day 2 Basic Enumeration and Counting Arrangements How many arrangements of the letters l, a, j, o, l, l, a? We have 3 l s to place Choose
CSE 21 Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Summer, 2005 Day 2 Basic Enumeration and Counting Arrangements How many arrangements of the letters l, a, j, o, l, l, a? We have 3 l s to place Choose
6.2. Paths and Cycles
 6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall Exam #1
 Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall 2015 Exam #1 1.) Which of the following quantified predicate statements are true? Justify your answers. a.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 b.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 2.) Prove that
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall 2015 Exam #1 1.) Which of the following quantified predicate statements are true? Justify your answers. a.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 b.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 2.) Prove that
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Vertex-Edge Graphs. Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards. Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University
 Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
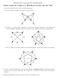 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
Euler and Hamilton circuits. Euler paths and circuits
 1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory. Applied Discrete Mathematics
 Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
UNC Charlotte Super Competition - Comprehensive Test with Solutions March 7, 2016
 March 7, 2016 1. The little tycoon Johnny says to his fellow capitalist Annie, If I add 7 dollars to 3/5 of my funds, I ll have as much capital as you have. To which Annie replies, So you have only 3 dollars
March 7, 2016 1. The little tycoon Johnny says to his fellow capitalist Annie, If I add 7 dollars to 3/5 of my funds, I ll have as much capital as you have. To which Annie replies, So you have only 3 dollars
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology
 MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Winter Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction to Topology 2 Topology and Childrens Drawings 3 Networks 4 Conclusion Geometric Topology
MATH 113 Section 9.2: Topology Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Winter Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction to Topology 2 Topology and Childrens Drawings 3 Networks 4 Conclusion Geometric Topology
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
1. A busy airport has 1500 takeo s perday. Provetherearetwoplanesthatmusttake o within one minute of each other. This is from Bona Chapter 1 (1).
 Math/CS 415 Combinatorics and Graph Theory Fall 2017 Prof. Readdy Homework Chapter 1 1. A busy airport has 1500 takeo s perday. Provetherearetwoplanesthatmusttake o within one minute of each other. This
Math/CS 415 Combinatorics and Graph Theory Fall 2017 Prof. Readdy Homework Chapter 1 1. A busy airport has 1500 takeo s perday. Provetherearetwoplanesthatmusttake o within one minute of each other. This
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees. March 23, 2008
 Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
Graph Theory CS/Math231 Discrete Mathematics Spring2015
 1 Graphs Definition 1 A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set and E is a binary relation on V. The set V is called the vertex set of G, and its elements are called vertices
1 Graphs Definition 1 A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set and E is a binary relation on V. The set V is called the vertex set of G, and its elements are called vertices
Brief History. Graph Theory. What is a graph? Types of graphs Directed graph: a graph that has edges with specific directions
 Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 192 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 192 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
08. First and second degree equations
 08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Pre-Calculus. Slide 1 / 192. Slide 2 / 192. Slide 3 / 192. Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Pre-Calculus Slide 2 / 192 Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Slide 1 / 192 Pre-Calculus Slide 2 / 192 Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Pre-Calculus Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Table of Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Discrete Structures Lecture The Basics of Counting
 Introduction Good morning. Combinatorics is the study of arrangements of objects. Perhaps, the first application of the study of combinatorics was in the study of gambling games. Understanding combinatorics
Introduction Good morning. Combinatorics is the study of arrangements of objects. Perhaps, the first application of the study of combinatorics was in the study of gambling games. Understanding combinatorics
1. trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) How many different spanning. trees does the network shown in figure (b) have?
 2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Pre-Calculus. Introduction to Matrices. Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192. Slide 3 / 192. Slide 4 / 192. Slide 6 / 192. Slide 5 / 192. Matrices
 Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Slide 1 / 192 Slide 2 / 192 Pre-Calculus Matrices 2015-03-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 192 Content Introduction to Matrices Matrix Arithmetic Scalar Multiplication Addition Subtraction Multiplication Solving
Graph Theory
 Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Graph Theory. 26 March Graph Theory 26 March /29
 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1
 Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Math 100 Homework 4 B A C E
 Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
IE 102 Spring Routing Through Networks - 1
 IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting
 Week Three Solutions Note: in these notes multiplication is assumed to take precedence over division, so 4!/2!2! = 4!/(2!*2!), and binomial coefficients are written horizontally: (4 2) denotes 4 choose
Week Three Solutions Note: in these notes multiplication is assumed to take precedence over division, so 4!/2!2! = 4!/(2!*2!), and binomial coefficients are written horizontally: (4 2) denotes 4 choose
Multi-edges, loops, and two or more pieces are all allowed. Example 4 (Not Graphs). None of the following are graphs.
 MA 111, Topic 4: Graph Theory Our last topic in this course is called Graph Theory. This is the mathematics of connections, associations, and relationships. Definition 1. A Graph is a set of points called
MA 111, Topic 4: Graph Theory Our last topic in this course is called Graph Theory. This is the mathematics of connections, associations, and relationships. Definition 1. A Graph is a set of points called
Basic Combinatorics. Math 40210, Section 01 Fall Homework 4 Solutions
 Basic Combinatorics Math 40210, Section 01 Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1.4.2 2: One possible implementation: Start with abcgfjiea From edge cd build, using previously unmarked edges: cdhlponminjkghc
Basic Combinatorics Math 40210, Section 01 Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1.4.2 2: One possible implementation: Start with abcgfjiea From edge cd build, using previously unmarked edges: cdhlponminjkghc
13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. 14. (a) E,E. (c) A,B,C,A. 16. (a) BF, FG
 13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. There are none. Such a circuit would consist of two vertices and two (different) edges connecting the vertices. 10. (a) 11. (a) C, B, A, H, F Other answers
13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. There are none. Such a circuit would consist of two vertices and two (different) edges connecting the vertices. 10. (a) 11. (a) C, B, A, H, F Other answers
Math 3336 Section 6.1 The Basics of Counting The Product Rule The Sum Rule The Subtraction Rule The Division Rule
 Math 3336 Section 6.1 The Basics of Counting The Product Rule The Sum Rule The Subtraction Rule The Division Rule Examples, Examples, and Examples Tree Diagrams Basic Counting Principles: The Product Rule
Math 3336 Section 6.1 The Basics of Counting The Product Rule The Sum Rule The Subtraction Rule The Division Rule Examples, Examples, and Examples Tree Diagrams Basic Counting Principles: The Product Rule
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, Graph Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Unit 7 Day 2 Section Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths
 Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
An Introduction to Graph Theory
 An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1
 Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00. Networks. Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow
 Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around
 Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARAMPALLI Department of Science and Humanities CS6702-GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATION
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARAMPALLI 635 854 Department of Science and Humanities DEGREE/BRANCH : B.E. CSE YEAR/ SEMESTER : IV/VII. CS6702-GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATION 1. Define graph. UNIT-I
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARAMPALLI 635 854 Department of Science and Humanities DEGREE/BRANCH : B.E. CSE YEAR/ SEMESTER : IV/VII. CS6702-GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATION 1. Define graph. UNIT-I
Simple Graph. General Graph
 Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
21-110: Problem Solving in Recreational Mathematics
 21-110: Problem Solving in Recreational Mathematics Homework assignment 8 solutions Problem 1. A loop is an edge that joins a vertex to itself. Multiple edges are two or more edges between the same pair
21-110: Problem Solving in Recreational Mathematics Homework assignment 8 solutions Problem 1. A loop is an edge that joins a vertex to itself. Multiple edges are two or more edges between the same pair
Formatting for TLM - Part I
 TLM Module A01 Formatting for TLM - Part I Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology 2002. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 2008 Formatting for TLM - Part I Statement
TLM Module A01 Formatting for TLM - Part I Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology 2002. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 2008 Formatting for TLM - Part I Statement
11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs
 11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs Introduction Definition A graph G is bipartite if we can partition the vertices into two disjoint subsets U and V such that every edge of G has one incident vertex in U and the
11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs Introduction Definition A graph G is bipartite if we can partition the vertices into two disjoint subsets U and V such that every edge of G has one incident vertex in U and the
Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006
 Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006 THE KIT: This kit contains materials for two Instant Insanity games, a student activity sheet with answer key and this instructor
Instant Insanity Instructor s Guide Make-it and Take-it Kit for AMTNYS 2006 THE KIT: This kit contains materials for two Instant Insanity games, a student activity sheet with answer key and this instructor
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles
 14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
Midterm 1 : Correction. Friday, Feb. 23.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Spring 00 Math Group F Midterm : Correction. Friday, Feb... (a) Draw a graph with vertices A, B, C and D in which the valence of vertices A and D is and the valence
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Spring 00 Math Group F Midterm : Correction. Friday, Feb... (a) Draw a graph with vertices A, B, C and D in which the valence of vertices A and D is and the valence
Week 12: Trees; Review. 22 and 24 November, 2017
 (1/24) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 12: Trees; Review http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 22 and 24 November, 2017 C C C C 1 Trees Recall... Applications: Chemistry Applications: Decision
(1/24) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 12: Trees; Review http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 22 and 24 November, 2017 C C C C 1 Trees Recall... Applications: Chemistry Applications: Decision
GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) UNIT 1
 GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) Sub code : 06CS42 UNIT 1 Introduction to Graph Theory : Definition and Examples Subgraphs Complements, and Graph Isomorphism Vertex Degree, Euler
GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) Sub code : 06CS42 UNIT 1 Introduction to Graph Theory : Definition and Examples Subgraphs Complements, and Graph Isomorphism Vertex Degree, Euler
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
Trees and Intro to Counting
 Trees and Intro to Counting CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 15 (B00), Day 10/11 (A00) February 15, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Another Special Type of Graph: Trees (Rooted) Trees: definitions
Trees and Intro to Counting CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 15 (B00), Day 10/11 (A00) February 15, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Another Special Type of Graph: Trees (Rooted) Trees: definitions
STUDENT NUMBER: MATH Final Exam. Lakehead University. April 13, Dr. Adam Van Tuyl
 Page 1 of 13 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MATH 1281 - Final Exam Lakehead University April 13, 2011 Dr. Adam Van Tuyl Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. If you need more room, answer on
Page 1 of 13 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MATH 1281 - Final Exam Lakehead University April 13, 2011 Dr. Adam Van Tuyl Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. If you need more room, answer on
Graph Theory. 1 Introduction to Graphs. Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC January 26, 2011
 Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
STRUCTURES AND STRATEGIES FOR STATE SPACE SEARCH
 Slide 3.1 3 STRUCTURES AND STRATEGIES FOR STATE SPACE SEARCH 3.0 Introduction 3.1 Graph Theory 3.2 Strategies for State Space Search 3.3 Using the State Space to Represent Reasoning with the Predicate
Slide 3.1 3 STRUCTURES AND STRATEGIES FOR STATE SPACE SEARCH 3.0 Introduction 3.1 Graph Theory 3.2 Strategies for State Space Search 3.3 Using the State Space to Represent Reasoning with the Predicate
Using Euler s Theorem
 Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
396 6 / Counting 6.1. Exercises
 396 6 / Counting 6.1 Exercises 1. There are 18 mathematics majors and 325 computer science majors at a college. a) In how many ways can two representatives be picked so that one is a mathematics major
396 6 / Counting 6.1 Exercises 1. There are 18 mathematics majors and 325 computer science majors at a college. a) In how many ways can two representatives be picked so that one is a mathematics major
Practice Final Exam Solutions
 1 (1 points) For the following problem, the alphabet used is the standard -letter English alphabet, and vowels refers only to the letters A, E, I, O, and U (a) ( points) How many strings of five letters
1 (1 points) For the following problem, the alphabet used is the standard -letter English alphabet, and vowels refers only to the letters A, E, I, O, and U (a) ( points) How many strings of five letters
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths. April 18, 2010
 Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Math 15 - Spring Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so:
 Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
γ(ɛ) (a, b) (a, d) (d, a) (a, b) (c, d) (d, d) (e, e) (e, a) (e, e) (a) Draw a picture of G.
 MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
Varying Applications (examples)
 Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS
 NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2015-2016 MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS May 2016 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains FIVE (5) questions
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2015-2016 MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS May 2016 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains FIVE (5) questions
The vertex set is a finite nonempty set. The edge set may be empty, but otherwise its elements are two-element subsets of the vertex set.
 Math 3336 Section 10.2 Graph terminology and Special Types of Graphs Definition: A graph is an object consisting of two sets called its vertex set and its edge set. The vertex set is a finite nonempty
Math 3336 Section 10.2 Graph terminology and Special Types of Graphs Definition: A graph is an object consisting of two sets called its vertex set and its edge set. The vertex set is a finite nonempty
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko. Graphs
 CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Graphs, Networks and Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is available online via SpringerLink.
 Lecture 1 First Steps in Graph Theory This lecture introduces Graph Theory, the main subject of the course, and includes some basic definitions as well as a number of standard examples. Reading: Some of
Lecture 1 First Steps in Graph Theory This lecture introduces Graph Theory, the main subject of the course, and includes some basic definitions as well as a number of standard examples. Reading: Some of
Math Exam 2 Solutions. Problem 1 (8 points) Problem 2 (8 points) Problem 3 (12 points) Problem 4 (26 points) Problem 5 (14 points)
 Math 400 - Exam 2 Solutions Name: ID: Problem 1 (8 points) Problem 2 (8 points) Problem 3 (12 points) Problem 4 (26 points) Problem 5 (14 points) Problem 6 (6 points) Problem 7 (12 points) Problem 8 (14
Math 400 - Exam 2 Solutions Name: ID: Problem 1 (8 points) Problem 2 (8 points) Problem 3 (12 points) Problem 4 (26 points) Problem 5 (14 points) Problem 6 (6 points) Problem 7 (12 points) Problem 8 (14
Study Guide Mods: Date:
 Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Binomial Coefficients
 Binomial Coefficients Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ May 6, 2016 Fixed-density Binary Strings How many length n binary strings
Binomial Coefficients Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ May 6, 2016 Fixed-density Binary Strings How many length n binary strings
Travel Every Edge 3. Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges?
 Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
