Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP
|
|
|
- Buck Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP Document ID: ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used Related Products onventions onfigure Network Diagram onfigurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting ommands Related Information Introduction In some environments, it may be necessary to bundle multiple serial links to act as single link with aggregated bandwidth. This document describes how to configure isco 4500 routers to bundle four serial interfaces using a virtual template interface. This configuration can be used for routers connected over leased lines or routers that have the hannel Service Unit/Data Service Unit (SU/DSU). You can add additional features to this configuration depending on your needs. Prerequisites Requirements There are no specific requirements for this document. omponents Used The information in this document is based on the software and hardware versions below. isco 4500 routers in a lab environment with cleared configurations. isco IOS version 12.2(10b) was running on both routers. The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before using it. Related Products This configuration can also be used with the following hardware and software versions.
2 Any two routers with four serial interfaces each. WI 1T and WI 2T serial interfaces can be used. onventions For more information on document conventions, see the isco Technical Tips onventions. onfigure In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document. Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the ommand Lookup Tool (registered customers only). Network Diagram This document uses the network setup shown in the diagram below. onfigurations This configuration was tested using isco IOS Software Release 12.2(10b) on 4500 series routers. The same configuration concepts apply to a similar router topology or other isco IOS releases. This document uses the configurations shown below. RouterA version 12.2 hostname RouterA username RouterB password xxx ip subnet zero multilink virtual template 1 interface loopback 0 ip address interface Virtual Template1 ip unnumbered loopback0 ppp authentication chap
3 interface Serial0 interface Serial1 interface Serial2 interface Serial3 interface FastEthernet0 ip address router rip network network end RouterB version 12.2 hostname RouterB username RouterA password xxx ip subnet zero multilink virtual template 1 interface loopback 0 ip address interface Virtual Template1 ip unnumbered loopback0 ppp authentication chap interface Serial0
4 interface Serial1 interface Serial2 interface Serial3 interface Ethernet0 ip address router rip network network end onfigure the following to implement the above configuration: multilink virtual template interface virtual template PPP multilink in each of the serial interfaces in which bundling has to be done. An RIP as the IP routing protocol Interface loopback 0 is configured so that it never fails, and ip unnumbered loopback 0 enhances the bundling of more than five serial interfaces with the same IP address. When all the serial interfaces are up, and user traffic is to be sent, multilink PPP creates a virtual access interface and the PPP negotiation takes place. The configuration for this virtual access interface is cloned from the virtual template. The number of serial interfaces that are up are bundled in this virtual access interface and an aggregate bandwidth is created. Verify This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly. ertain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only), which allows you to view an analysis of show command output. show ip route show ip rip database show show interface virtual access 1 RouterA#show ip route
5 odes: connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set R /16 [120/1] via , 00:00:19, Virtual Access /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, FastEthernet /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /24 is directly connected, Loopback /32 is directly connected, Virtual Access1 RouterA#show ip route connected /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, FastEthernet /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /24 is directly connected, Loopback /32 is directly connected, Virtual Access1 RouterB#show ip route odes: connected, S static, I IGRP, R RIP, M mobile, B BGP D EIGRP, EX EIGRP external, O OSPF, IA OSPF inter area N1 OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 OSPF external type 1, E2 OSPF external type 2, E EGP i IS IS, L1 IS IS level 1, L2 IS IS level 2, ia IS IS inter area * candidate default, U per user static route, o ODR P periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set R /16 is directly connected, Ethernet /8 [120/1] via , 00:00:18, Virtual Access /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /32 is directly connected, Virtual Access /24 is directly connected, Loopback0 RouterB#show ip route connected /16 is directly connected, Ethernet /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /32 is directly connected, Virtual Access /24 is directly connected, Loopback0 RouterA#show ip rip database /8 auto summary /24 directly connected, FastEthernet /16 auto summary /16 [1] via , 00:00:34, Virtual Access /24 auto summary /24 directly connected, Loopback /32 directly connected, Virtual Access1 RouterB#show ip rip database /8 auto summary /8 [1] via , 00:00:13, Virtual Access /16 auto summary /16 directly connected, Ethernet /24 auto summary /24 directly connected, Loopback /32 directly connected, Virtual Access1
6 RouterA#show Virtual Access1, bundle name is RouterB Bundle up for 17:01:59 0 lost fragments, 0 reordered, 0 unassigned 0 discarded, 0 lost received, 1/255 load 0xD3 received sequence, 0x1180 sent sequence Member links: 4 (max not set, min not set) Serial0, since 17:01:59, last rcvd seq 000D38 Serial1, since 17:01:50, last rcvd seq 000D39 Serial2, since 17:01:46, last rcvd seq 000D3A Serial3, since 17:01:41, last rcvd seq 000D3B RouterB#show Virtual Access1, bundle name is RouterA Bundle up for 12:47:33 0 lost fragments, 0 reordered, 0 unassigned 0 discarded, 0 lost received, 1/255 load 0x1186 received sequence, 0xD40 sent sequence Member links: 4 (max not set, min not set) Serial0, since 12:47:33, last rcvd seq Serial1, since 12:47:27, last rcvd seq Serial2, since 12:47:23, last rcvd seq Serial3, since 12:47:20, last rcvd seq RouterA#show interface virtual access 1 Virtual Access1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Virtual Access interface Interface is unnumbered. Using address of Loopback0 ( ) MTU 1500 bytes, BW 6176 Kbit, DLY usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) DTR is pulsed for 5 seconds on reset LP Open, multilink Open Open: IPP Last input 00:00:00, output never, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters 17:05:41 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 1711 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 R, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 2256 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out 0 carrier transitions RouterB#show interface virtual access 1 Virtual Access1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Virtual Access interface Interface is unnumbered. Using address of Loopback0 ( ) MTU 1500 bytes, BW 6176 Kbit, DLY usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) DTR is pulsed for 5 seconds on reset LP Open, multilink Open Open: IPP Last input 00:00:20, output never, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters 12:54:17 Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
7 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 2256 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 R, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 1714 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out 0 carrier transitions Troubleshoot This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration. Troubleshooting ommands ertain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only), which allows you to view an analysis of show command output. Note: Before issuing debug commands, please see Important Information on Debug ommands. debug ppp negotiation To see if a client is passing PPP negotiation; this command is used to check for address negotiation. debug ppp authentication To see if a client is passing authentication. If you are using a isco IOS Software Release prior to 11.2, use the debug ppp chap command instead. debug ppp error To display protocol errors and error statistics associated with PPP connection negotiation and operation. debug vtemplate To display the Virtual Template cloning to form a Virtual Access interface. debug events To see PPP multilink events debugging. Displays information about events affecting multilink groups. show To see the members of the multilink bundle. The following outputs were obtained from the isco 4500 routers. They show the routers establishing a multilink PPP connection. RouterA#debug vtemplate Virtual Template debugging is on *Dec 1 17:24:16.519: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: Reuse Vi1, recycle queue size 0 *Dec 1 17:24:16.519: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: Set default settings with ip unnumbered *Dec 1 17:24:16.539: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: Hardware address 00d0.bbfa.f579 *Dec 1 17:24:16.543: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: Has a new cloneblk vtemplate, now it has vtemplate *Dec 1 17:24:16.543: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: ********** LONE VAESS1 *********** *Dec 1 17:24:16.543: Vi1 VTEMPLATE: lone from Virtual Template1 interface Virtual Access1 default ip address encap ppp ip unnumbered loopback0 end *Dec 1 17:24:16.595: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up *Dec 1 17:24:17.515: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0, changed state to up *Dec 1 17:24:17.595: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up
8 RouterA#debug ppp negotiation PPP protocol negotiation debugging is on Dec 11 19:39:14.523: %LINK 5 HANGED: Interface Serial0, changed state to reset Dec 11 19:39:14.523: Se0 LP: State is losed Dec 11 19:39:14.627: %SYS 5 ONFIG_I: onfigured from console by console Dec 11 19:39:16.523: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 PPP: Treating connection as a dedicated line Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 LP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 25 len 24 Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0xD4BA693 (0x0506D4BA693) Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:39:16.523: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterA (0x130A01506F6D65726F6) Dec 11 19:39:16.535: Se0 LP: I ONFREQ [REQsent] id 33 len 25 Dec 11 19:39:16.535: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0x03200E36 (0x E36) Dec 11 19:39:16.535: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterB (0x130B E79) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: O ONFAK [REQsent] id 33 len 25 Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0x03200E36 (0x E36) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterB (0x130B E79) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: I ONFAK [AKsent] id 25 len 24 Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0xD4BA693 (0x0506D4BA693) Dec 11 19:39:16.539: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:39:16.543: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterA (0x130A01506F6D65726F6) Dec 11 19:39:16.543: Se0 LP: State is Open Dec 11 19:39:16.543: Se0 PPP: Phase is VIRTUALIZED [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:39:16.555: Vi1 PPP: Phase is DOWN, Setup [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:39:16.587: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 PPP: Treating connection as a dedicated line Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 LP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 1 len 29 Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 LP: AuthProto HAP (0x ) Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 LP: MagicNumber 0xD4BA6D4 (0x0506D4BA6D4) Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterA (0x130A01506F6D65726F6) Dec 11 19:39:16.587: Vi1 PPP: Phase is UP [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:39:16.591: Vi1 IPP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:39:16.591: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80101) Dec 11 19:39:16.591: Vi1 MLP: Added first link Se0 to bundle RouterB Dec 11 19:39:16.623: Vi1 IPP: I ONFREQ [REQsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:39:16.623: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80102) Dec 11 19:39:16.623: Vi1 IPP: O ONFAK [REQsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:39:16.623: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80102) Dec 11 19:39:16.623: Vi1 IPP: I ONFAK [AKsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:39:16.627: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80101) Dec 11 19:39:16.627: Vi1 IPP: State is Open Dec 11 19:39:16.627: Vi1 IPP: Install route to Dec 11 19:39:17.543: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:39:17.587: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up RouterB#debug ppp negotiation PPP protocol negotiation debugging is on Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 LP: I ONFREQ [losed] id 25 len 24 Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0xD4BA693 (0x0506D4BA693) Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterA (0x130A01506F6D65726F6) Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 LP: Lower layer not up, Fast Starting Dec 11 19:38:08.975: Se0 PPP: Treating connection as a dedicated line Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 33 len 25 Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0x03200E36 (0x E36)
9 Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterB (0x130B E79) Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: O ONFAK [REQsent] id 25 len 24 Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0xD4BA693 (0x0506D4BA693) Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:38:08.979: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterA (0x130A01506F6D65726F6) Dec 11 19:38:08.979: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 LP: I ONFAK [AKsent] id 33 len 25 Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 LP: MagicNumber 0x03200E36 (0x E36) Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterB (0x130B E79) Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 LP: State is Open Dec 11 19:38:08.987: Se0 PPP: Phase is VIRTUALIZED [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:38:08.999: Vi1 PPP: Phase is DOWN, Setup [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:38:09.039: Se0 IPP: Packet buffered while building MLP bundle interface Dec 11 19:38:09.043: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 PPP: Treating connection as a dedicated line Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 PPP: Phase is ESTABLISHING, Active Open [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 LP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 1 len 30 Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 LP: AuthProto HAP (0x ) Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 LP: MagicNumber 0x03200E78 (0x E78) Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 LP: MRRU 1524 (0x110405F4) Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 LP: EndpointDisc 1 RouterB (0x130B E79) Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 PPP: Phase is UP [0 sess, 1 load] Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 IPP: O ONFREQ [losed] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:38:09.043: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80102) Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 MLP: Added first link Se0 to bundle RouterA Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 PPP: Pending ncpq size is 1 Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Se0 IPP: Redirect packet to Vi1 Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 IPP: I ONFREQ [REQsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80101) Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 IPP: O ONFAK [REQsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:38:09.047: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80101) Dec 11 19:38:09.051: Vi1 IPP: I ONFAK [AKsent] id 1 len 10 Dec 11 19:38:09.051: Vi1 IPP: Address (0x03060A80102) Dec 11 19:38:09.051: Vi1 IPP: State is Open Dec 11 19:38:09.051: Vi1 IPP: Install route to Dec 11 19:38:09.987: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:38:10.043: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up RouterB#debug events Multilink events debugging is on Dec 11 19:41:30.239: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:41:30.243: Se0 MLP: Request add link to bundle Dec 11 19:41:30.243: Se0 MLP: Adding link to bundle Dec 11 19:41:30.255: Vi1 MLP: VP: lone from Vtemplate 1 block=1 Dec 11 19:41:30.299: %LINK 3 UPDOWN: Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up Dec 11 19:41:30.299: Vi1 MLP: Added first link Se0 to bundle RouterA Dec 11 19:41:31.243: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0, changed state to up Dec 11 19:41:31.243: Se0 MLP: cdp packet forwarded to wrong interface Dec 11 19:41:31.299: %LINEPROTO 5 UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual Access1, changed state to up Related Information Virtual Profiles Virtual Interface Template Service onfiguring PPP and Authentication Displaying aller Statistics Multilink PPP RF 1717 onfiguring Peer to Peer DDR with Dialer Profiles
10 WAN Technology Support Pages Technical Support isco Systems ontacts & Feedback Help Site Map isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & onditions Privacy Statement ookie Policy Trademarks of isco Systems, Inc. Updated: Sep 15, 2005 Document ID: 10235
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE
 Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPP Dialin with External Modems
 Configuring PPP Dialin with External Modems Document ID: 9581 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Configuring PPP Dialin with External Modems Document ID: 9581 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
Async Multilink PPP Troubleshooting Diagnostic Output
 CHAPTER 3 Async Multilink PPP Troubleshooting Diagnostic Output The diagnostic output provided in this chapter present examples illustrating the process of diagnosing problems addressed in Async MPPP Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 3 Async Multilink PPP Troubleshooting Diagnostic Output The diagnostic output provided in this chapter present examples illustrating the process of diagnosing problems addressed in Async MPPP Troubleshooting
Configuring IRB. Integrated Routing and Bridging CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control Using PBR. Topology. Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Management IP Interface
 The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
15d. PPPoE Troubleshooting
 Rev. 0800.0900 d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com PPPoE troubleshooting has been a part of the CCNA longer than certification guide authors have made any serious attempt to cover the topic.
Rev. 0800.0900 d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com PPPoE troubleshooting has been a part of the CCNA longer than certification guide authors have made any serious attempt to cover the topic.
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP
 Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Lab 15d. PPPoE Troubleshooting
 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
Failover with EIGRP Using VRF Configuration Example
 Failover with EIGRP Using VRF onfiguration Example ocument I: 113446 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Hardware and Software Versions onventions onfigure Network iagram onfigurations Verify Show ommands
Failover with EIGRP Using VRF onfiguration Example ocument I: 113446 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Hardware and Software Versions onventions onfigure Network iagram onfigurations Verify Show ommands
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
MPLS Troubleshooting. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
 MPLS Troubleshooting Document ID: 12492 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions Troubleshoot Procedures Verify That Routing Protocol Runs Verify EF Switching Verify MPLS
MPLS Troubleshooting Document ID: 12492 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions Troubleshoot Procedures Verify That Routing Protocol Runs Verify EF Switching Verify MPLS
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms
 1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers
 Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles
 Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
Lab Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Configuring Interfaces on the ML-Series Card
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
Configuring the Cisco 827 Router as a PPPoE Client With NAT
 Configuring the Cisco 827 Router as a PPPoE Client With NAT Document ID: 8514 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Configuring the Cisco 827 Router as a PPPoE Client With NAT Document ID: 8514 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Configuring Virtual Interfaces
 Configuring Virtual Interfaces Virtual interfaces are software-based interfaces that you create in the memory of the networking device using Cisco IOS commands. Virtual interfaces do not have a hardware
Configuring Virtual Interfaces Virtual interfaces are software-based interfaces that you create in the memory of the networking device using Cisco IOS commands. Virtual interfaces do not have a hardware
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
The configuration of the router at the initial stage was fairly simple (quoting only significant commands, not the entire config):
 Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Distance vector Routing protocols. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1
 Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
Understanding and Configuring the ip unnumbered Command
 Understanding and onfiguring the ip unnumbered ommand Document D: 13786 ontents ntroduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions What is an Unnumbered nterface? P and P Unnumbered onfiguration
Understanding and onfiguring the ip unnumbered ommand Document D: 13786 ontents ntroduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions What is an Unnumbered nterface? P and P Unnumbered onfiguration
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable
 Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring the 4-Port Serial Interface SPA
 This chapter provides information about configuring the 4-Port Serial Interface SPA on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. Configuration Tasks, page 1 Verifying the Interface Configuration, page 11 Configuration
This chapter provides information about configuring the 4-Port Serial Interface SPA on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. Configuration Tasks, page 1 Verifying the Interface Configuration, page 11 Configuration
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay
 Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Ethernet over GRE Tunnels
 The feature allows customers to leverage existing low end residential gateways to provide mobility services to mobile nodes using Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunneling
The feature allows customers to leverage existing low end residential gateways to provide mobility services to mobile nodes using Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunneling
Configuring the Cisco Router and VPN Clients Using PPTP and MPPE
 Configuring the Cisco Router and VPN Clients Using PPTP and MPPE Document ID: 29781 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Conventions PPTP Router Configuration
Configuring the Cisco Router and VPN Clients Using PPTP and MPPE Document ID: 29781 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram Conventions PPTP Router Configuration
Lab - Exploring Router Physical Characteristics
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
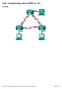 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Using Serial Ports to Connect to ATM with DXI Encapsulation
 Using Serial Ports to Connect to ATM with DXI Encapsulation Document ID: 10418 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Physical Setup ATM DXI Modes ATM DXI Headers
Using Serial Ports to Connect to ATM with DXI Encapsulation Document ID: 10418 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Physical Setup ATM DXI Modes ATM DXI Headers
Application Notes for ADTRAN NetVanta 3205 Access Router and IP Office Using Frame Relay over T1 - Issue 1.0
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for ADTRAN NetVanta 3205 Access Router and IP Office Using Frame Relay over T1 - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application Notes describe a sample
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for ADTRAN NetVanta 3205 Access Router and IP Office Using Frame Relay over T1 - Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application Notes describe a sample
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Configuring Serial Interfaces
 This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network on the Cisco ASR 900 Series Router. It includes the
This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network on the Cisco ASR 900 Series Router. It includes the
Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers
 Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers Document ID: 28080 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dialing Method V.25 or V.25bis Dialing DTR Dialing Keypad
Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers Document ID: 28080 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dialing Method V.25 or V.25bis Dialing DTR Dialing Keypad
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Cisco Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam. Practice Test. Version 2.2. https://certkill.com
 Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interfaces
 IPsec virtual tunnel interfaces (VTIs) provide a routable interface type for terminating IPsec tunnels and an easy way to define protection between sites to form an overlay network IPsec VTIs simplify
IPsec virtual tunnel interfaces (VTIs) provide a routable interface type for terminating IPsec tunnels and an easy way to define protection between sites to form an overlay network IPsec VTIs simplify
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
Frame Relay for R&S CCIE Candidates
 Frame Relay for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
Frame Relay for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router
 Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Problem Solution Scenario 1. High Bandwidth Ingress Interface(s) and Low Bandwidth
Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Problem Solution Scenario 1. High Bandwidth Ingress Interface(s) and Low Bandwidth
Peter, Please approve us apply a new ISP connection to separate with CCA for ccahalmar. The bandwidth is 100M.
 All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
Chapter 1 Frame Relay Configuration and Management
 Chapter 1 Frame Relay Configuration and Management 1 This chapter describes the configuration tasks for the Cisco frame relay packet-switched software. You will find the following information in this chapter:
Chapter 1 Frame Relay Configuration and Management 1 This chapter describes the configuration tasks for the Cisco frame relay packet-switched software. You will find the following information in this chapter:
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
15c. PPPoE. Encapsulation and Tunneling. The Dialer Interface. Client Dialer Interface
 Rev. 0. c. PPPoE c cnac o okbook.com PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) Encapsulates PPP frames within Ethernet frames, allowing PPP to be used with technologies like DSL and cable where ISP-supplied modems have
Rev. 0. c. PPPoE c cnac o okbook.com PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) Encapsulates PPP frames within Ethernet frames, allowing PPP to be used with technologies like DSL and cable where ISP-supplied modems have
Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter This chapter contains the following sections: Using the EXEC Command Interpreter, page 4-1 Configuring the Interfaces, page 4-2 Checking the
CHAPTER 4 Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter This chapter contains the following sections: Using the EXEC Command Interpreter, page 4-1 Configuring the Interfaces, page 4-2 Checking the
Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay
 Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay Document ID: 16563 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device. Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay Document ID: 16563 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device. Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA
 CHAPTER 12 Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA This chapter provides information about configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA on Cisco 12000 Series Routers. It includes the following
CHAPTER 12 Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA This chapter provides information about configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA on Cisco 12000 Series Routers. It includes the following
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection Last Updated: December 8, 2011 This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) on a router. Finding Feature Information,
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection Last Updated: December 8, 2011 This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) on a router. Finding Feature Information,
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
Understanding Buffer Misses and Failures
 Understanding Buffer Misses and Failures Document ID: 14620 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Buffer Misses and Failures Buffer Pools buffers Configuration Command
Understanding Buffer Misses and Failures Document ID: 14620 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Buffer Misses and Failures Buffer Pools buffers Configuration Command
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
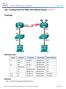 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Double Authentication Design and Implementation Guide
 Double Authentication Design and Implementation Guide Document ID: 10221 A Case Study Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Why Double Authentication?
Double Authentication Design and Implementation Guide Document ID: 10221 A Case Study Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Why Double Authentication?
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Troubleshooting Ethernet Collisions
 Troubleshooting Ethernet Collisions Document ID: 12768 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Are Collisions? The Deferred Counter The Collisions Counter Late
Troubleshooting Ethernet Collisions Document ID: 12768 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Are Collisions? The Deferred Counter The Collisions Counter Late
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID
 ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID Document ID: 15925 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID Document ID: 15925 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces
 Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces Document ID: 8625 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Traditional Reasons for Input Drops Understanding Throttles
Troubleshooting Input Drops on ATM Router Interfaces Document ID: 8625 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Traditional Reasons for Input Drops Understanding Throttles
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC
 Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC Document ID: 12889 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC Document ID: 12889 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
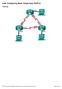 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
Configuring Serial Interfaces
 This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async/Sync R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network and raw socket. It includes the following sections:
This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async/Sync R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network and raw socket. It includes the following sections:
