Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
|
|
|
- Paulina Perry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend a Telnet session. Engage in multiple Telnet sessions. Return to the suspended session. Disconnect from the Telnet session. Background/Preparation It is often desirable to have Telnet sessions to multiple routers simultaneously in order to check and compare configuration information. This lab focuses on the ability to Telnet to multiple routers, suspend those sessions, and switch between the active sessions. A list of active connections can also be displayed in the process. Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements may be used. Possible routers include 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, 2600 routers, or a combination. Refer CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. The following steps are intended to be executed on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session as performed in the Establishing a HyperTerminal session lab. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing. Step 1 Configure the GAD, BHM and PHX routers using the tables a. Configure the three routers as indicated in the Copying, Editing, and Pasting Configurations lab. b. If there are any difficulties configuring hostname or passwords, refer to the Configuring Router Passwords lab. If there are any difficulties configuring interfaces or the routing protocol, refer to the Configuring Host Tables lab. c. Verify the routers configurations by performing a show running-config on each router. If not correct, fix any configuration errors and verify. Step 2 Login to Router 1 and verify the connection to Routers 2 and 3 a. Login to the GAD router. b. Verify the connection between the two routers. Ping the serial 0 interface of the BHM router. If the ping is not successful, return to Step 1 and troubleshoot the configuration. Step 3 Telnet to a remote router a. Enter telnet BHM if IP host tables were configured. Otherwise, enter ip address at the router prompt to connect to the BHM router. Enter the password cisco to enter the router. b. What prompt did the router display? BHM> Step 4 Look at the interfaces on the remote router a. Enter show interface at the router prompt. b. Are both the serial 0 and the FastEthernet 0 interfaces up? Yes Step 5 Suspend the current Telnet session a. Enter Ctrl-Shift-6 followed by the x key. This only suspends the session and returns to the previous router. It does not disconnect from this router. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Step 6 Establish another Telnet session a. Enter telnet router-name if IP host tables were configured. Otherwise, enter telnet ip address at the router prompt to connect to the PHX router. Enter the password cisco to enter the router. b. What prompt did the router display? PHX> CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 Step 7 Suspend the current Telnet session a. Enter Ctrl-Shift-6 followed by the x key. This only suspends the session and returns to the previous router. It does not disconnect from this router. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Step 8 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. This will reveal that 2 sessions are in use. Step 9 Resume the previously suspended Telnet session a. Type resume 1 and the number of the session that is to be resumed followed by the Enter key at the router prompt. The router will respond with: [Resuming connection 1 to X.X... ] b. Press the Enter key. This will resume a Telnet session that was previously suspended. c. What prompt did the router display? BHM> Step 10 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. b. How many sessions are shown? % No connections open c. There were two the last time. What is the difference? The last time the command was issued on the GAD router, this time it is issued from the BHM router. Step 11 Close a Telnet session a. Enter the command exit while in a Telnet session. This will terminate the Telnet session. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Note: Do not do this now. To disconnect from a suspended Telnet session, type disconnect and press Enter. Step 12 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. b. How many sessions are shown? One session is shown connected to PHX. c. There were two on this router the last time. What is the difference? The telnet session to BHM was closed in Step 11 so there is only 1 session left. Step 13 Resume the previously suspended Telnet session a. Press the Enter key. The router will respond with: [Resuming connection 2 to X.X... ] Press the Enter key. This will resume a Telnet session that was previously suspended CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 b. What prompt did the router display? PHX> Step 14 Close a Telnet session Enter the command exit while in a Telnet session. This will terminate the Telnet session. Step 15 Problems with linked Telnet sessions on multiple routers a. When working with Telnet, one of the most common problems is remembering the focus of the session. Focus means the device that is the focus of the commands that are being issued. Many times people Telnet to a router and then Telnet from that router to another and so on. Without host names, or if the routers have similar hostnames, confusion can happen. For example: b. Telnet to the PHX router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 16 Telnet to the BHM router a. Telnet to the BHM router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 17 Telnet back to the PHX router a. Telnet back to the PHX router. b. By looking at the prompt, it is not evident whether the Telnet worked or not. Step 18 Telnet to the GAD router a. Telnet to the GAD router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 19 Telnet to the BHM router a. Telnet to the BHM router. b. Type show sessions. c. How many sessions are there running? Two d. Why are there that many? There are two telnet sessions into the BHM router. e. Now type exit three times. f. What router are you on? BHM> g. How many Telnet sessions are still open? One Step 20 Exiting from all sessions a. Keep typing exit until the following prompt appears: Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. b. Scroll back up the HyperTerminal listing. c. How many session closed messages were displayed? Five d. Is that the number listed in the how many Telnet sessions are still open question? No Upon completion of the previous steps, logoff by typing exit. Turn the router off CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If class does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router(config)#reloadRouter#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started Press Enter. The router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) Interface # FastEthernet 0/0 FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (FA0/0) (S0/1) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify the type of router as well as how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 GAD#telnet phx Trying PHX ( )... Open User Access Verification PHX> GAD#show user Conn Host Address Byte Idle Conn Name 1 bhm bhm * 2 phx phx GAD# [Resuming connection 2 to phx... ] GAD# [Resuming connection 1 to bhm... ] BHM>exit [Connection to bhm closed by foreign host] GAD#phx Trying PHX ( )... Open User Access Verification PHX>bhm Trying BHM ( )... Open User Access Verification BHM>phx Trying PHX ( )... Open User Access Verification PHX>gad Trying GAD ( )... Open User Access Verification GAD>bhm Trying BHM ( )... Open User Access Verification CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 BHM>show sessions % No connections open BHM>exit [Connection to bhm closed by foreign host] GAD>exit [Connection to gad closed by foreign host] PHX>exit [Connection to phx closed by foreign host] BHM>exit [Connection to bhm closed by foreign host] PHX>exit [Connection to phx closed by foreign host] GAD#exit GAD#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 709 bytes version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname GAD enable secret 5 $1$1jLu$0Kyymtnex1jGnNLXeBbyl0 enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host BHM interface Ethernet0 ip address interface Serial0 no ip address interface Serial1 ip address interface BRI0 no ip address CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
9 shutdown router rip network network ip classless ip http server line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end BHM#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 730 bytes version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname BHM enable secret 5 $1$3paR$r57FdEaxs5i8TmC6/p7Gu1 enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host GAD interface Ethernet0 ip address interface Serial0 ip address clockrate interface Serial1 ip address CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
10 router rip network network network ip classless ip http server line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end PHX#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 751 bytes version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname PHX enable secret 5 $1$IDPr$uvmFGelwjStThFQkzUlnK/ enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host BHM ip host GAD interface Ethernet0 ip address interface Serial0 ip address no fair-queue clockrate interface Serial1 no ip address shutdown CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
11 interface BRI0 no ip address shutdown router rip network network ip classless ip http server line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
12 Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2600 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend a Telnet session. Engage in multiple Telnet sessions. Return to the suspended session. Disconnect from the Telnet session. Background/Preparation It is often desirable to have Telnet sessions to multiple routers simultaneously in order to check and compare configuration information. This lab focuses on the ability to Telnet to multiple routers, suspend those sessions, and switch between the active sessions. A list of active connections can also be displayed in the process. Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements may be used. Possible routers include 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, 2600 routers, or a combination. Refer CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
13 to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. The following steps are intended to be executed on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session as performed in the Establishing a HyperTerminal session lab. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing. Step 1 Configure the GAD, BHM and PHX routers using the tables a. Configure the three routers as indicated in the Copying, Editing, and Pasting Configurations lab. b. If there are any difficulties configuring hostname or passwords, refer to the Configuring Router Passwords lab. If there are any difficulties configuring interfaces or the routing protocol, refer to the Configuring Host Tables lab. c. Verify the routers configurations by performing a show running-config on each router. If not correct, fix any configuration errors and verify. Step 2 Login to Router 1 and verify the connection to Routers 2 and 3 a. Login to the GAD router. b. Verify the connection between the two routers. Ping the serial 0 interface of the BHM router. If the ping is not successful, return to Step 1 and troubleshoot the configuration. Step 3 Telnet to a remote router a. Enter telnet BHM if IP host tables were configured. Otherwise, enter ip address at the router prompt to connect to the BHM router. Enter the password cisco to enter the router. b. What prompt did the router display? BHM> Step 4 Look at the interfaces on the remote router a. Enter show interface at the router prompt. b. Are both the serial 0 and the FastEthernet 0 interfaces up? Yes Step 5 Suspend the current Telnet session a. Enter Ctrl-Shift-6 followed by the x key. This only suspends the session and returns to the previous router. It does not disconnect from this router. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Step 6 Establish another Telnet session a. Enter telnet router-name if IP host tables were configured. Otherwise, enter telnet ip address at the router prompt to connect to the PHX router. Enter the password cisco to enter the router. b. What prompt did the router display? PHX> CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
14 Step 7 Suspend the current Telnet session a. Enter Ctrl-Shift-6 followed by the x key. This only suspends the session and returns to the previous router. It does not disconnect from this router. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Step 8 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. This will reveal that 2 sessions are in use. Step 9 Resume the previously suspended Telnet session a. Type resume 1 and the number of the session that is to be resumed followed by the Enter key at the router prompt. The router will respond with: [Resuming connection 1 to X.X... ] b. Press the Enter key. This will resume a Telnet session that was previously suspended. c. What prompt did the router display? BHM> Step 10 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. b. How many sessions are shown? % No connections open. c. There were two the last time. What is the difference? The last time the command was issued on the GAD router, this time it is issued from the BHM router. Step 11 Close a Telnet session a. Enter the command exit while in a Telnet session. This will terminate the Telnet session. b. What prompt did the router display? GAD# Note: Do not do this now. To disconnect from a suspended Telnet session, type disconnect and press Enter. Step 12 Use the show session command to see the connections a. Enter show sessions at the command prompt. b. How many sessions are shown? One session is shown connected to PHX. c. There were two on this router the last time. What is the difference? The Telnet session to BHM was closed in Step 11 so there is only one session left. Step 13 Resume the previously suspended Telnet session a. Press the Enter key. The router will respond with: [Resuming connection 2 to X.X... ] Press the Enter key. This will resume a Telnet session that was previously suspended. b. What prompt did the router display? PHX> CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
15 Step 14 Close a Telnet session Enter the command exit while in a Telnet session. This will terminate the Telnet session. Step 15 Problems with linked Telnet sessions on multiple routers a. When working with Telnet, one of the most common problems is remembering the focus of the session. Focus means the device that is the focus of the commands that are being issued. Many times people Telnet to a router and then Telnet from that router to another and so on. Without host names, or if the routers have similar hostnames, confusion can happen. For example: b. Telnet to the PHX router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 16 Telnet to the BHM router a. Telnet to the BHM router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 17 Telnet back to the PHX router a. Telnet back to the PHX router. b. By looking at the prompt, it is not evident whether the Telnet worked or not. Step 18 Telnet to the GAD router a. Telnet to the GAD router. From the configuration prompt type no hostname. Step 19 Telnet to the BHM router a. Telnet to the BHM router. b. Type show sessions. c. How many sessions are there running? Two d. Why are there that many? There are two Telent sessions into the BHM router. e. Now type exit three times. f. What router are you on? BHM> g. How many Telnet sessions are still open? One Step 20 Exiting from all sessions a. Keep typing exit until the following prompt appears: Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. b. Scroll back up the HyperTerminal listing. c. How many session closed messages were displayed? Five d. Is that the number listed in the how many Telnet sessions are still open question? No Upon completion of the previous steps, logoff by typing exit. Turn the router off CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
16 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If class does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router(config)#reloadRouter#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started Press Enter. The router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
17 Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) Interface # FastEthernet 0/0 FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (FA0/0) (S0/1) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify the type of router as well as how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
18 GAD#telnet BHM Trying BHM ( )... Open User Access Verification BHM>show interface Serial 0/0 Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is PowerQUICC Serial Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Last input 00:00:08, output 00:00:03, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:15:01 Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 91 packets input, 6184 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 91 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 89 packets output, 6056 bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 10 interface resets 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out 1 carrier transitions DCD=up DSR=up DTR=up RTS=up CTS=up BHM>show interface fa0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is c0 (bia c0) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, 100BaseTX/FX ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:37, output 00:00:02, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 16 packets input, 6032 bytes Received 16 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog 0 input packets with dribble condition detected 154 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
19 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out GAD#telnet PHX Trying PHX ( )... Open User Access Verification PHX> GAD#sho user Conn Host Address Byte Idle Conn Name 1 BHM BHM * 2 PHX PHX GAD#1 [Resuming connection 1 to BHM... ] BHM>show user % No connections open BHM>exi [Connection to BHM closed by foreign host] GAD#show user Conn Host Address Byte Idle Conn Name * 2 PHX PHX GAD#1 % 1 is not an open connection GAD# GAD#2 [Resuming connection 2 to PHX... ] PHX>exit [Connection to PHX closed by foreign host] GAD#telnet PHX Trying PHX ( )... Open User Access Verification PHX>en PHX#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. PHX(config)#no hostname Router(config)#exit Router#telnet BHM Trying BHM ( )... Open CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
20 User Access Verification BHM>en BHM#config terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. BHM(config)#no hostname Router(config)#exit Router#telnet GAD Trying GAD ( )... Open User Access Verification GAD>en GAD#config terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. GAD(config)#no hostname Router(config)#exit Router#t 00:21:09: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 ( elnet BHM ^ % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. Router#telnet BHM Trying BHM ( )... Open User Access Verification Router>enable Router#show user % No connections open Router#show users Line User Host(s) Idle Location 0 con 0 idle 00:06:31 66 vty 0 GAD 00:00:00 PHX * 67 vty 1 idle 00:00:00 GAD Interface User Mode Idle Peer Address Router#exit [Connection to BHM closed by foreign host] Router#write terminal Building configuration... Current configuration : 884 bytes version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
21 no service password-encryption hostname Router enable secret 5 $1$YWQ3$9yxnEcyZyFuFQThPcqjdl/ enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host BHM ip host GAD call rsvp-sync interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto Router#exit [Connection to GAD closed by foreign host] Router#exit [Connection to BHM closed by foreign host] Router#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 877 bytes version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Router enable secret 5 $1$LpHj$7pWn7fjWUwPoWzRNzBbMx/ enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host BHM ip host GAD call rsvp-sync interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address Router#show sessions % No connections open CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
22 Router#show users Line User Host(s) Idle Location 0 con 0 idle 00:07:39 * 66 vty 0 idle 00:00:00 GAD Interface User Mode Idle Peer Address Router#show user % No connections open Router#exit [Connection to PHX closed by foreign host] Router#exit Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started. User Access Verification Router>en Router# Router#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 884 bytes version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Router enable secret 5 $1$YWQ3$9yxnEcyZyFuFQThPcqjdl/ enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host BHM ip host GAD call rsvp-sync interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0 ip address no fair-queue CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
23 clockrate interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/1 no ip address router rip network network ip classless ip http server dial-peer cor custom line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end Router# Router#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 930 bytes version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Router enable secret 5 $1$R4a2$fw5JOv1b753yRuXQo/JlJ1 enable password cisco ip subnet-zero ip host PHX ip host BHM ip host GAD call rsvp-sync interface FastEthernet0/ CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
24 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0 ip address no fair-queue clockrate interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/1 ip address router rip network network network ip classless ip http server dial-peer cor custom line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end Router# Router#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 877 bytes version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Router enable secret 5 $1$LpHj$7pWn7fjWUwPoWzRNzBbMx/ enable password cisco ip subnet-zero CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
25 ip host PHX ip host BHM ip host GAD call rsvp-sync nterface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0 no ip address shutdown no fair-queue interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/1 ip address router rip network network ip classless ip http server dial-peer cor custom line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login end Router# CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab Troubleshooting RIP
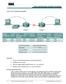 Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab Configuring a Serial Interface
 Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab Configuring Router Passwords. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions
 Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
 Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab Command Modes and Router Identification. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Backing up Configuration Files
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab Using the Boot System Command. Objective. Background/Preparation
 Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Management IP Interface
 The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The configuration of the router at the initial stage was fairly simple (quoting only significant commands, not the entire config):
 Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Lab Verifying PPP Configuration
 Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Lab Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Configuring Interfaces on the ML-Series Card
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
Cisco Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam. Practice Test. Version 2.2. https://certkill.com
 Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Lab Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface)
 Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router.
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab - Exploring Router Physical Characteristics
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Lab Configuring DHCP
 Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Configuring IRB. Integrated Routing and Bridging CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH
 BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
Lab Exploring Cisco IOS and Configuring Basic Switch Settings
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Lab Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
Lab Modifying OSPF Cost Metric
 Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE
 Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces
 Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers
 Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Lab Configuring Dialer Profiles
 Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Lab b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Configuring Serial Interfaces
 This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async/Sync R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network and raw socket. It includes the following sections:
This chapter configures the serial interface module (PN: A900-IMASER14A/S) Async/Sync R232 serial data using Transparent Pseudowire (PW) over MPLS network and raw socket. It includes the following sections:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Configuring the SM-1-STM1
 4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
Lab Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to use
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to use
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Lab 15d. PPPoE Troubleshooting
 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Peter, Please approve us apply a new ISP connection to separate with CCA for ccahalmar. The bandwidth is 100M.
 All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter This chapter contains the following sections: Using the EXEC Command Interpreter, page 4-1 Configuring the Interfaces, page 4-2 Checking the
CHAPTER 4 Configuring the SS7 Q.703 High Speed Port Adapter This chapter contains the following sections: Using the EXEC Command Interpreter, page 4-1 Configuring the Interfaces, page 4-2 Checking the
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable
 Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
