Introduction to Computer Science Exercises for Unit 4A: Classes and Objects 1. This compiles and runs. What is displayed?
|
|
|
- Tracy Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Computer Science Exercises for Unit 4A: Classes and Objects 1. This compiles and runs. What is 2. This compiles and runs. What percent of the time will s be true? What percent of the time will t be true? System.out.println( 3 < 5 ); System.out.println( 66 / 10!= 61 / 10 ); boolean p = false; boolean q = true; System.out.println( p && q ); System.out.println( p q ); System.out.println( p!= q ); boolean r = true; System.out.println( r && p && q ); System.out.println( r p q ); boolean s = Math.random() < 0.5; boolean t = Math.random() < 5; 3. If the user enters 17, what will be Scanner s = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print( "Enter a positive integer " ); int x = s.nextint(); boolean e = x % 2 == 0; System.out.println( e ); 4. If H is printed, what is the value of x? boolean x; // x is assigned a value 5. What are the possible values of num? 6. If num is 1, what is printed? 7. What has to happen for count to be 8. Could the code print just this? If the program prints the following numbers, what is the last number to be printed? if ( x ) System.out.println( "H" ); else System.out.println( "K" ); int num = (int)( 2*Math.random() ) + 1; boolean boo = num >= 2; if ( boo ) System.out.println( "A" ); else System.out.println( "B" ); int count = 0; boolean game_over = false; while( game_over == false ){ int num = (int)( 6*Math.random() ); count++; System.out.print( num + " " ); if ( num == 4 ) game_over = true; System.out.println( count ); 1
2 10. What is 11. What is 12. What is 13. What is public class PointEx{ Point pt1 = new Point( 5, 8 ); Point pt2 = new Point( -4, 1 ); double yak = pt2.gety(); System.out.println( yak ); double xray = pt1.getx(); System.out.println( xray ); public class GoodPoint{ Point p = new Point( ); Point pp = new Point( 3, 4 ); double d = p.distance( 12, 5 ); System.out.println( d ); d = p.distance( pp ); System.out.println( d ); public class PointyHat{ Point a = new Point( 5, 7 ); Point b = new Point( 3, 4 ); b.translate( 2, 6 ); a.move( 14, 1 ); double n1 = b.gety(); double n2 = a.getx(); System.out.println( n1 + ", " + n2 ); boolean boo = a.equals( b ); System.out.println( boo ); public class PointyStick{ Point g = new Point( -2, 7 ); Point h = new Point( 9, 7 ); Point k = new Point( 8, 8 ); double dist = h.distance( g ); System.out.println( dist ); dist = h.distance( k ); System.out.println( dist ); 2
3 14. What is Code inside the main method Point p1 = new Point( -2, -5 ); Point p2 = new Point( 6, 0 ); Point p3 = new Point( 7, 12 ); double num = p2.getx(); num = p3.gety(); num = p1.getx(); 15. What is Code inside the main method Point here = new Point(); Point there = new Point( 4, 3 ); double num = here.distance( there ); num = there.distance( here ); there.translate( 0, -2 ); here.move( 5, 7 ); num = here.distance( there ); num = here.distance( 5, 7 ); 16. Why does the second line NOT compile? Point pt = new Point( 3, 10 ); pt.translate( 4 ); 17. Why does the second line NOT compile? Point spot = new Point( -3, 0 ); int w = spot.getx(); 18. Why does the second line NOT compile? Point x = new Point(); double num = x.move( 4, 8 ); 19. Create a Point object that has these coordinates -2, 5. Then call the translate method and move the Point 3 units to the right (but not up or down). Then call the getx method and display the returned value. 20. Create a Point object at the origin (in the simplest manner possible). The find and display the distance from that Point to ( 39, 73). 3
4 21. What coordinates does the user have to enter to get You win! to be printed? 22. If the user enters 3 for the x coordinate and 4 for the y coordinate, what will be printed at the end? 23. If the user enters 2 for the x coordinate and 1 for the y coordinate, what will be printed at the end? import java.util.scanner; Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print( "Enter an x coordinate " ); int xx = scan.nextint(); System.out.print( "Enter a y coordinate " ); int yy = scan.nextint(); Point p1 = new Point( xx, yy ); Point p2 = new Point(); if ( p1.equals( p2 ) ) System.out.println( "You win!" ); p2.move( 2, 1 ); double d = p1.distance( p2 ); d = d*d; System.out.println( d ); Note. The actual numbers being printed by differ from your answers by or so. 24. What is different import java.util.scanner; about how the numbers are entered? 25. What are possible coordinates of the p2? Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print( "Enter x and y coordinates " ); int x = scan.nextint(); int y = scan.nextint(); Point p1 = new Point( x, y ); 26. What has to happen for the user to win? 27. What is the minimum number of tries? What is the maximum if the person guesses whatever they want? int other_x = (int)(2*math.random()); int other_y = (int)(2*math.random()); Point p2 = new Point( other_x, other_y ); int count = 1; while ( p1.equals( p2 ) == false ){ System.out.println( "Wrong." ); System.out.print( "Enter x and y again " ); x = scan.nextint(); y = scan.nextint(); p1.move( x, y ); count++; System.out.println( "You win!" ); System.out.println( "It took " + count + " tries" ); 4
5 28. What is 29. What is 30. What is import java.awt.rectangle; Rectangle rachel = new Rectangle( 3, 4 ); double num = rachel.gety(); num = rachel.getwidth(); boolean a = rachel.contains( 2, 2 ); System.out.println( a ); a = rachel.contains( 5, 1 ); System.out.println( a ); rachel.setbounds( 6, -3, 2, 11 ); System.out.println( rachel.gety() ); import java.awt.rectangle; Rectangle rock = new Rectangle( 1, 2, 3, 4 ); double num = rock.getx(); num = rock.getheight(); rock.translate( 4, -1 ); num = rock.getx(); num = rock.getheight(); import java.awt.rectangle; Rectangle r = new Rectangle( 5, 5 ); r.setbounds( -1, 4, 2, 3 ); double num = r.gety(); num = r.getwidth(); r.translate( 3, 0 ); num = r.getwidth() * r.getheight(); num = r.getx(); 5
6 31. What is Code inside the main method Rectangle rudolph = new Rectangle( 4, 1, 4, 4 ); Rectangle becky = new Rectangle( 3, 2, 4, 4 ); boolean b = becky.equals( rudolph ); System.out.println( b ); becky.translate( 1, -1 ); b = becky.equals( rudolph ); System.out.println( b ); rudolph.setbounds( -1, 0, 6, 3 ); double x = becky.getx(); System.out.println( x ); x = rudolph.getx(); System.out.println( x ); 32. Why does the second line NOT compile? Rectangle re = new Rectangle( 6, 8 ); int w = re.getwidth(); 33. Why does the second line NOT compile? Rectangle ar = new Rectangle( 1,1,1,1 ); double k = ar.setbounds( 2,2,2,2 ); 34. Why does the second line NOT compile? Rectangle e = new Rectangle( 6, 3 ); double y = e.gety( 3 ); 35. Create a Rectangle object. Its left corner is at 7, 2. Its width is 5 and its height is 9. Call the contains method and display OK if the rectangle contains the point at (x1, y1) 36. Create a Rectangle with a width of 4 and a height of 8. Its corner should be at the origin. Call the translate method and shift the rectangle by h in the x direction and v in the y direction. 37. Create two Rectangle objects (you pick the locations and sizes). Then call the intersects method and display OK if they intersect. int x1 = (int)(10*math.random()); int y1 = (int)(10*math.random()); int h = (int)(10*math.random()); int v = (int)(10*math.random()); 6
7 38. To the right is the Cat class. In the space below, create a Cat object and feed it 2 ounces of food. Then find out its age and display it. 39. To the right is the Dog class. In the space below, create a 45 pound Dog. Then let it eat for 5 minutes. If it is a good dog, print YES. 40. To the right is the Snake class. In the space below, create a 20 inch Snake. If it is deadly, print RUN. If it is not deadly, print OK. Call the crawl method and have it crawl for 30 minutes. Display how far it travelled. Cat class Constructor Cat() Methods return type, name, parameters int age() returns age void feed( int n ) n = ounces of food Dog class Constructor Dog( double w ) w = weight in lbs Methods return type, name, parameters void eat( int m ) m = minutes boolean good() returns true if good Snake class Constructor Snake( int n ) n = length in inches Methods return type, name, parameters boolean deadly() returns true if poisonous double crawl(int m) m = minutes returns distance traveled in inches 7
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises Note: Curly brackets { are optional if there is only one statement associated with the if (or ) statement. 1. If the user enters 82, what is 2. If the
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises Note: Curly brackets { are optional if there is only one statement associated with the if (or ) statement. 1. If the user enters 82, what is 2. If the
Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key
 CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
Introduction to Java Programs for Packet #4: Classes and Objects
 Introduction to Java Programs for Packet #4: Classes and Objects Note. All of these programs involve writing and using more than one class file. 1. Copy the Box class and compile it. But you won t be able
Introduction to Java Programs for Packet #4: Classes and Objects Note. All of these programs involve writing and using more than one class file. 1. Copy the Box class and compile it. But you won t be able
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 4B. Programs: Classes and Objects
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 4B. Programs: Classes and Objects This section must be updated to work with repl.it 1. Copy the Box class and compile it. But you won t be able to run it because it
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 4B. Programs: Classes and Objects This section must be updated to work with repl.it 1. Copy the Box class and compile it. But you won t be able to run it because it
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Assignment 2.4: Loops
 Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE SCHOOL OF COMPUTING TERM TEST #1 Semester 1 AY2006/2007 CS1101X/Y/Z PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY 16 September 2006 Time Allowed: 60 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS 1. This question paper
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE SCHOOL OF COMPUTING TERM TEST #1 Semester 1 AY2006/2007 CS1101X/Y/Z PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY 16 September 2006 Time Allowed: 60 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS 1. This question paper
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 3. Programs
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 3. Programs This section must be updated to work with repl.it Programs 1 to 4 require you to use the mod, %, operator. 1. Let the user enter an integer. Your program
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 3. Programs This section must be updated to work with repl.it Programs 1 to 4 require you to use the mod, %, operator. 1. Let the user enter an integer. Your program
BLOCK STRUCTURE. class block main method block do-while statement block if statement block. if statement block. Block Structure Page 1
 BLOCK STRUCTURE A block is a bundle of statements in a computer program that can include declarations and executable statements. A programming language is block structured if it (1) allows blocks to be
BLOCK STRUCTURE A block is a bundle of statements in a computer program that can include declarations and executable statements. A programming language is block structured if it (1) allows blocks to be
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
Problem Grade Total
 CS 101, Prof. Loftin: Final Exam, May 11, 2009 Name: All your work should be done on the pages provided. Scratch paper is available, but you should present everything which is to be graded on the pages
CS 101, Prof. Loftin: Final Exam, May 11, 2009 Name: All your work should be done on the pages provided. Scratch paper is available, but you should present everything which is to be graded on the pages
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Exercises
 Unit 4: Classes and Objects Exercises AP CS A 1. What is boolean a = 5 < 7; System.out.println( a ); 2. What does this display? boolean b = false; for ( int n = 1; n < 4; n++ ){ b =!b; System.out.print(
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Exercises AP CS A 1. What is boolean a = 5 < 7; System.out.println( a ); 2. What does this display? boolean b = false; for ( int n = 1; n < 4; n++ ){ b =!b; System.out.print(
AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises
 AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises 1. What is displayed? int [] a = new int[ 3 ]; System.out.println(a.length ); 2. What is displayed? int [] sting = { 34, 23, 67, 89, 12 ; System.out.println( sting[ 1 ] );
AP CS Unit 7: Arrays Exercises 1. What is displayed? int [] a = new int[ 3 ]; System.out.println(a.length ); 2. What is displayed? int [] sting = { 34, 23, 67, 89, 12 ; System.out.println( sting[ 1 ] );
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Selection Statements and operators
 Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSE115 Introduction to Computer Science I Coding Exercise #1 Retrospective Fall 2017
 In this exercise you were given four methods to define, focusing on transforming values passed in to the methods through parameters to produce return values. There were two versions of this exercise though
In this exercise you were given four methods to define, focusing on transforming values passed in to the methods through parameters to produce return values. There were two versions of this exercise though
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes
 Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes AP CS A Another Data Type. So far, we have used two types of primitive variables: ints and doubles. Another data type is the boolean data type. Variables of type boolean
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes AP CS A Another Data Type. So far, we have used two types of primitive variables: ints and doubles. Another data type is the boolean data type. Variables of type boolean
Algorithms and Conditionals
 Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
COMP 202. Programming With Iterations. CONTENT: The WHILE, DO and FOR Statements. COMP Loops 1
 COMP 202 Programming With Iterations CONTENT: The WHILE, DO and FOR Statements COMP 202 - Loops 1 Repetition Statements Repetition statements or iteration allow us to execute a statement multiple times
COMP 202 Programming With Iterations CONTENT: The WHILE, DO and FOR Statements COMP 202 - Loops 1 Repetition Statements Repetition statements or iteration allow us to execute a statement multiple times
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
Selection Statements and operators
 Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CS 101 Fall 2005 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
Selection and Repetition Revisited
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Advanced Java Concept Unit 1. Mostly Review
 Advanced Java Concept Unit 1. Mostly Review Program 1. Create a class that has only a main method. In the main method create an ArrayList of Integers (remember the import statement). Add 10 random integers
Advanced Java Concept Unit 1. Mostly Review Program 1. Create a class that has only a main method. In the main method create an ArrayList of Integers (remember the import statement). Add 10 random integers
CS141 Programming Assignment #8
 CS141 Programming Assignment #8 Due Sunday, April 14th. 1- Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2
CS141 Programming Assignment #8 Due Sunday, April 14th. 1- Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 24, Name: KEY 1
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Introduction to Arrays
 Introduction to Arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
Introduction to Arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
Java Coding 3. Over & over again!
 Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution
 4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CSC 1051 Villanova University. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Course website:
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
CS141 Programming Assignment #6
 CS141 Programming Assignment #6 Due Sunday, Nov 18th. 1) Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2 1
CS141 Programming Assignment #6 Due Sunday, Nov 18th. 1) Write a class with methods to do the following output: a) 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1 b) 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 * 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 * * * 3 2 1
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
Exam 1 - (20 points)
 Exam 1 - (20 points) Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Fill the correct bubble on your scantron sheet. Each correct answer is worth 1 point (unless otherwise stated).
Exam 1 - (20 points) Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Fill the correct bubble on your scantron sheet. Each correct answer is worth 1 point (unless otherwise stated).
Chap. 3. Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L,
 Chap. 3 Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L, 3.1 3.6 1 From last time: Account Declaring an Account object: Account acct1 = new Account
Chap. 3 Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L, 3.1 3.6 1 From last time: Account Declaring an Account object: Account acct1 = new Account
AYBUKE BUYUKCAYLI KORAY OZUYAR MUSTAFA SOYLU. Week 21/02/ /02/2007 Lecture Notes: ASCII
 AYBUKE BUYUKCAYLI KORAY OZUYAR MUSTAFA SOYLU Week 21/02/2007-23/02/2007 Lecture Notes: ASCII 7 bits = 128 characters 8 bits = 256characters Unicode = 16 bits Char Boolean boolean frag; flag = true; flag
AYBUKE BUYUKCAYLI KORAY OZUYAR MUSTAFA SOYLU Week 21/02/2007-23/02/2007 Lecture Notes: ASCII 7 bits = 128 characters 8 bits = 256characters Unicode = 16 bits Char Boolean boolean frag; flag = true; flag
Exam 2. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
Java I/O and Control Structures
 Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
CSE 8A Lecture 12. Reading for next class: : Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey!
 CSE 8A Lecture 12 Reading for next class: 8.1-8.3: Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey! A vote for CSE 8A Yen Chuan (Allen) Liu and Pin (Arthur) Chu 1) Solo: (30 sec)
CSE 8A Lecture 12 Reading for next class: 8.1-8.3: Sounds! Today s topics: Logical Operators:! && Start PSA 6: Chromakey! A vote for CSE 8A Yen Chuan (Allen) Liu and Pin (Arthur) Chu 1) Solo: (30 sec)
Selection and Repetition
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
RANDOM NUMBER GAME PROJECT
 Random Number Game RANDOM NUMBER GAME - Now it is time to put all your new knowledge to the test. You are going to build a random number game. - The game needs to generate a random number between 1 and
Random Number Game RANDOM NUMBER GAME - Now it is time to put all your new knowledge to the test. You are going to build a random number game. - The game needs to generate a random number between 1 and
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING INPUT AND OUTPUT Input devices Keyboard Mouse Hard drive Network Digital camera Microphone Output devices.
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING INPUT AND OUTPUT Input devices Keyboard Mouse Hard drive Network Digital camera Microphone Output devices.
Chapter 4 Loops. int x = 0; while ( x <= 3 ) { x++; } System.out.println( x );
 Chapter 4 Loops Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 4.1 4.7, 4.9 4.10 104 117, 122 128 2 9, 11 13,15 16,18 19,21 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,18,20,24,26,28,30,38 Loops Loops are used to make a program
Chapter 4 Loops Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 4.1 4.7, 4.9 4.10 104 117, 122 128 2 9, 11 13,15 16,18 19,21 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,18,20,24,26,28,30,38 Loops Loops are used to make a program
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Selection and Repetition Revisited
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
1. What does the following code fragment write to the monitor?
 1. What does the following code fragment write to the monitor? int sum = 14; if ( sum < 20 ) System.out.print("Under "); else System.out.print("Over "); System.out.println("the limit."); a. Under b. Over
1. What does the following code fragment write to the monitor? int sum = 14; if ( sum < 20 ) System.out.print("Under "); else System.out.print("Over "); System.out.println("the limit."); a. Under b. Over
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Final Exam Computer Programming 230 Dr. St. John Lehman College City University of New York Thursday, 17 December 2009
 Final Exam Computer Programming 230 Dr. St. John Lehman College City University of New York Thursday, 17 December 2009 NAME (Printed) NAME (Signed) E-mail Exam Rules Show all your work. Your grade will
Final Exam Computer Programming 230 Dr. St. John Lehman College City University of New York Thursday, 17 December 2009 NAME (Printed) NAME (Signed) E-mail Exam Rules Show all your work. Your grade will
Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects
 Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
Tutorial 12. Exercise 1: Exercise 2: CSC111 Computer Programming I
 College of Computer and Information Sciences CSC111 Computer Programming I Exercise 1: Tutorial 12 Arrays: A. Write a method add that receives an array of integers arr, the number of the elements in the
College of Computer and Information Sciences CSC111 Computer Programming I Exercise 1: Tutorial 12 Arrays: A. Write a method add that receives an array of integers arr, the number of the elements in the
Chapter 6. Repetition Statements. Animated Version The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 6 Repetition Statements Animated Version required for reproduction or display. Chapter 6-1 Objectives After you have read and studied this chapter, you should be able to Implement repetition control
Chapter 6 Repetition Statements Animated Version required for reproduction or display. Chapter 6-1 Objectives After you have read and studied this chapter, you should be able to Implement repetition control
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
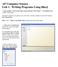 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
2.2 - Making Decisions
 2.2 - Making Decisions So far we have only made programs that execute the statements in order, starting with the statements at the top of the screen and moving down. However, you can write programs that
2.2 - Making Decisions So far we have only made programs that execute the statements in order, starting with the statements at the top of the screen and moving down. However, you can write programs that
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CSCI 1226 A Test #1. Wednesday, 10 October, 2018 Name: Student #: General Instructions Read and follow all directions carefully.
 General Instructions Read and follow all directions carefully. CSCI 1226 A Test #1 Wednesday, 10 October, 2018 Name: Student #: When writing programs or program segments, use the conventions used in the
General Instructions Read and follow all directions carefully. CSCI 1226 A Test #1 Wednesday, 10 October, 2018 Name: Student #: When writing programs or program segments, use the conventions used in the
private static final char[] Alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".tochararray();
![private static final char[] Alphabet = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz.tochararray(); private static final char[] Alphabet = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz.tochararray();](/thumbs/93/111251250.jpg) //Shelley Latreille Hang Man Game /* This program plays the game Hang Man with the user. Hang Man is a game that requires the user to guess the letters of a word before running out of incorrect guesses.
//Shelley Latreille Hang Man Game /* This program plays the game Hang Man with the user. Hang Man is a game that requires the user to guess the letters of a word before running out of incorrect guesses.
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2
 CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: public static int arraymystery(int[] array) { int x = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { if (array[i] > array[i
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: public static int arraymystery(int[] array) { int x = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { if (array[i] > array[i
Lecture 9. Assignment. Logical Operations. Logical Operations - Motivation 2/8/18
 Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
WES-CS GROUP MEETING #9
 WES-CS GROUP MEETING #9 Exercise 1: Practice Multiple-Choice Questions 1. What is output when the following code executes? String S1 = new String("hello"); String S2 = S1 +! ; S1 = S1 + S1; System.out.println(S1);
WES-CS GROUP MEETING #9 Exercise 1: Practice Multiple-Choice Questions 1. What is output when the following code executes? String S1 = new String("hello"); String S2 = S1 +! ; S1 = S1 + S1; System.out.println(S1);
AP CS Unit 8: Inheritance Exercises
 AP CS Unit 8: Inheritance Exercises public class Animal{ System.out.print("A"); public void m2(){ System.out.print("B"); public class Dog extends Animal{ System.out.print("C"); public void m3(){ System.out.print("D");
AP CS Unit 8: Inheritance Exercises public class Animal{ System.out.print("A"); public void m2(){ System.out.print("B"); public class Dog extends Animal{ System.out.print("C"); public void m3(){ System.out.print("D");
Tutorial # 4. Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise
 Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life
 Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
Arrays OBJECTIVES. In this chapter you will learn:
 7 Arrays Now go, write it before them in a table, and note it in a book. Isaiah 30:8 To go beyond is as wrong as to fall short. Confucius Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then
7 Arrays Now go, write it before them in a table, and note it in a book. Isaiah 30:8 To go beyond is as wrong as to fall short. Confucius Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then
Java Bootcamp - Villanova University. CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Arrays CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying Java Software Solutions
Arrays CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying Java Software Solutions
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/f13/ Some slides in
Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/f13/ Some slides in
Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Performing Actions and Using Object Methods Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Duration: 00:01:14 Hi Folks. This is the CS 170, Java Programming
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Performing Actions and Using Object Methods Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Duration: 00:01:14 Hi Folks. This is the CS 170, Java Programming
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: if Single-Selection Statement CSC 209 JAVA I. week 3- Control Statements: Part I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 3- Control Statements: Part I Objectives: To use the if and if...else selection statements to choose among alternative actions. To use the
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 3- Control Statements: Part I Objectives: To use the if and if...else selection statements to choose among alternative actions. To use the
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 7, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 7, 2013 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 7, 2013 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
Bjarne Stroustrup. creator of C++
 We Continue GEEN163 I have always wished for my computer to be as easy to use as my telephone; my wish has come true because I can no longer figure out how to use my telephone. Bjarne Stroustrup creator
We Continue GEEN163 I have always wished for my computer to be as easy to use as my telephone; my wish has come true because I can no longer figure out how to use my telephone. Bjarne Stroustrup creator
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 2, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2015 Name: Question Value 1 10 Score 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 2, 2015 Name: Question Value 1 10 Score 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays
 AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays Arrays. An array is an object that consists of an of similar items. An array has a single name and the items in an array are referred to in terms of their
AP Computer Science A Unit 7. Notes on Arrays Arrays. An array is an object that consists of an of similar items. An array has a single name and the items in an array are referred to in terms of their
AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises
 AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises A common standard is 24-bit color where 8 bits are used to represent the amount of red light, 8 bits for green light, and 8 bits for blue light. It is the combination
AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises A common standard is 24-bit color where 8 bits are used to represent the amount of red light, 8 bits for green light, and 8 bits for blue light. It is the combination
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case. Instructions:
 Name: New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case Instructions: KEEP TEST BOOKLET CLOSED UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO BEGIN. This exam is double sided (front
Name: New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case Instructions: KEEP TEST BOOKLET CLOSED UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO BEGIN. This exam is double sided (front
Data Structure and Programming Languages
 204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 9, Name: KEY
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 9, 2014 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 9, 2014 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Simple Java Programming Constructs 4
 Simple Java Programming Constructs 4 Course Map In this module you will learn the basic Java programming constructs, the if and while statements. Introduction Computer Principles and Components Software
Simple Java Programming Constructs 4 Course Map In this module you will learn the basic Java programming constructs, the if and while statements. Introduction Computer Principles and Components Software
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Conditional Programming
 COMP-202 Conditional Programming Chapter Outline Control Flow of a Program The if statement The if - else statement Logical Operators The switch statement The conditional operator 2 Introduction So far,
COMP-202 Conditional Programming Chapter Outline Control Flow of a Program The if statement The if - else statement Logical Operators The switch statement The conditional operator 2 Introduction So far,
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Model Solutions. COMP 102: Test 1. 6 April, 2016
 Family Name:.............................. Other Names:............................. ID Number:............................... Signature.................................. Model Solutions COMP 102: Test
Family Name:.............................. Other Names:............................. ID Number:............................... Signature.................................. Model Solutions COMP 102: Test
AP CS Unit 4: Classes and Objects Programs
 AP CS Unit 4: Classes and Objects Programs 1. Copy the Bucket class. Make sure it compiles (but you won t be able to run it because it does not have a main method). public class Bucket { private double
AP CS Unit 4: Classes and Objects Programs 1. Copy the Bucket class. Make sure it compiles (but you won t be able to run it because it does not have a main method). public class Bucket { private double
H212 Introduction to Software Systems Honors
 Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the Class The Scanner
 ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the run, depending on the data that is entered. The Scanner Class The Scanner class, which is part of the standard Java class provides convenient
ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the run, depending on the data that is entered. The Scanner Class The Scanner class, which is part of the standard Java class provides convenient
