ICT 5305 Mobile Communications. Lecture - 8 April Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa
|
|
|
- Garry Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICT 5305 Mobile Communications Lecture - 8 April 2016 Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa
2 MAC management Synchronization try to find a LAN, try to stay within a LAN timer etc. Power management sleep-mode without missing a message periodic sleep, frame buffering, traffic measurements Association/Reassociation integration into a LAN roaming, i.e. change networks by changing access points scanning, i.e. active search for a network MIB - Management Information Base managing, read, write
3 Synchronization using a Beacon (infrastructure) beacon interval (20ms 1s) access point medium B B B B busy busy busy busy value of the timestamp B beacon frame t
4 Synchronization using a Beacon (ad-hoc) beacon interval station 1 B 1 B 1 station 2 medium B 2 B 2 busy busy busy busy t value of the timestamp B beacon frame random delay
5 Power management Idea: switch the transceiver off if not needed States of a station: sleep and awake Timing Synchronization Function (TSF) stations wake up at the same time Infrastructure Traffic Indication Map (TIM) list of unicast receivers transmitted by AP Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM) list of broadcast/multicast receivers transmitted by AP Ad-hoc Ad-hoc Traffic Indication Map (ATIM) announcement of receivers by stations buffering frames more complicated - no central AP collision of ATIMs possible (scalability?) APSD (Automatic Power Save Delivery) new method in e replacing above schemes
6 Power saving with wake-up patterns (infrastructure) TIM interval DTIM interval access point medium D B busy T T d D busy busy busy B station T TIM D DTIM p awake d t B broadcast/multicast p PS poll d data transmission to/from the station
7 Power saving with wake-up patterns (ad-hoc) ATIM window beacon interval station 1 B 1 A D B 1 station 2 B 2 B 2 a d t B beacon frame random delay A transmit ATIM D transmit data awake a acknowledge ATIM d acknowledge data
8 No or bad connection? Then perform: Scanning Roaming scan the environment, i.e., listen into the medium for beacon signals or send probes into the medium and wait for an answer Reassociation Request station sends a request to one or several AP(s) Reassociation Response success: AP has answered, station can now participate failure: continue scanning AP accepts Reassociation Request signal the new station to the distribution system the distribution system updates its data base (i.e., location information) typically, the distribution system now informs the old AP so it can release resources Fast roaming r e.g. for vehicle-to-roadside networks
9 IEEE ac The (current) high-speed standard for WLANs Single link throughput > 500Mbit/s, multi-station > 1 Gbit/s Bandwidth up to 160 MHz (80 MHz mandatory), up to 8x MIMO, up to 256 QAM, beamforming, SDMA via MIMO Example home configuration: 8-antenna access point, 160 MHz bandwidth, 6.77 Gbit/s 4-antenna digital TV, 3.39 Gbit/s 2-antenna tablet, 1.69 Gbit/s Two 1-antenna smartphones, 867 Mbit/s each Redefinition of many protocol fields and procedures!
10 Basic idea Bluetooth Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, PDAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices, goal: 5 /device (already < 1 ) Short range (10 m), low power consumption, license-free 2.45 GHz ISM Voice and data transmission, approx. 1 Mbit/s gross data rate One of the first modules (Ericsson).
11 History Bluetooth 1994: Ericsson (Mattison/Haartsen), MC-link project Renaming of the project: Bluetooth according to Harald Blåtand Gormsen [son of Gorm], King of Denmark in the 10th century 1998: foundation of Bluetooth SIG, : erection of a rune stone at Ercisson/Lund ;-) 2001: first consumer products for mass market, spec. version 1.1 released 2005: 5 million chips/week (was: ) Special Interest Group Original founding members: Ericsson, Intel, IBM, Nokia, Toshiba Added promoters: 3Com, Agere (was: Lucent), Microsoft, Motorola > members Common specification and certification of products
12 History and hi-tech
13 and the real rune stone Located in Jelling, Denmark, erected by King Harald Blåtand in memory of his parents. The stone has three sides one side showing a picture of Christ. Inscription: "Harald king executes these sepulchral monuments after Gorm, his father and Thyra, his mother. The Harald who won the whole of Denmark and Norway and turned the Danes to Christianity." Btw: Blåtand has nothing to do with a blue tooth This could be the original colors of the stone. Inscription: auk tani karthi kristna (and made the Danes Christians)
14 Characteristics of the classical system 2.4 GHz ISM band, 79 (23) RF channels, 1 MHz carrier spacing Channel 0: 2402 MHz channel 78: 2480 MHz G-FSK modulation, mw transmit power FHSS and TDD Frequency hopping with 1600 hops/s Hopping sequence in a pseudo random fashion, determined by a master Time division duplex for send/receive separation Voice link SCO (Synchronous Connection Oriented) FEC (forward error correction), no retransmission, 64 kbit/s duplex, point-to-point, circuit switched Data link ACL (Asynchronous ConnectionLess) Asynchronous, fast acknowledge, point-to-multipoint, up to kbit/s symmetric or 723.2/57.6 kbit/s asymmetric, packet switched Topology Overlapping piconets (stars) forming a scatternet
15 Piconet Collection of devices connected in an ad hoc fashion S P M S P One unit acts as master and the others as slaves for the lifetime of the piconet SB P SB S Master determines hopping pattern, slaves have to synchronize M=Master S=Slave P=Parked SB=Standby
16 All devices in a piconet hop together Master gives slaves its clock and device ID Addressing Forming a piconet Hopping pattern: determined by device ID (48 bit, unique worldwide) Phase in hopping pattern determined by clock Active Member Address (AMA, 3 bit) Parked Member Address (PMA, 8 bit) SB SB SB SB SB SB SB SB SB S SB P P M SB S S P
17 Scatternet Linking of multiple co-located piconets through the sharing of common master or slave devices Devices can be slave in one piconet and master of another Communication between piconets Devices jumping back and forth between the piconets S SB P M S S P S M P Piconets (each with a capacity of 720 kbit/s) M=Master S=Slave P=Parked SB=Standby P SB S SB
18 Bluetooth protocol stack audio apps. NW apps. vcal/vcard telephony apps. mgmnt. apps. TCP/UDP OBEX IP BNEP PPP AT modem commands TCS BIN SDP Control Audio Baseband Radio RFCOMM (serial line interface) Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) Link Manager Host Controller Interface AT: attention sequence OBEX: object exchange TCS BIN: telephony control protocol specification binary BNEP: Bluetooth network encapsulation protocol SDP: service discovery protocol RFCOMM: radio frequency comm.
19 Frequency selection during data transmission 625 µs f k f k+1 f k+2 f k+3 f k+4 f k+5 f k+6 M S M S M S M t f k f k+3 f k+4 f k+5 f k+6 M S M S M t f k f k+1 f k+6 M S M t
20 Piconet/channel definition Low-level packet definition Access code Baseband Channel, device access, e.g., derived from master Packet header 1/3-FEC, active member address (broadcast + 7 slaves), link type, alternating bit ARQ/SEQ, checksum 68(72) bits access code packet header payload 4 64 (4) bits preamble sync. (trailer) AM address type flow ARQN SEQN HEC
21 SCO payload types payload (30) HV1 audio (10) FEC (20) HV2 audio (20) FEC (10) HV3 audio (30) DV audio (10) header (1) payload (0-9) 2/3 FEC CRC (2) (bytes)
22 ACL Payload types payload (0-343) header (1/2) payload (0-339) CRC (2) DM1 header (1) payload (0-17) 2/3 FEC CRC (2) DH1 header (1) payload (0-27) CRC (2) (bytes) DM3 DH3 header (2) payload (0-121) 2/3 FEC header (2) payload (0-183) CRC (2) CRC (2) DM5 DH5 header (2) payload (0-224) 2/3 FEC header (2) payload (0-339) CRC (2) CRC (2) AUX1 header (1) payload (0-29)
23 Baseband data rates ACL 1 slot 3 slot 5 slot SCO Payload User Symmetric Asymmetric Header Payload max. Rate max. Rate [kbit/s] Type [byte] [byte] FEC CRC [kbit/s] Forward Reverse DM /3 yes DH no yes DM /3 yes DH no yes DM /3 yes DH no yes AUX no no HV1 na 10 1/3 no 64.0 HV2 na 20 2/3 no 64.0 HV3 na 30 no no 64.0 DV 1 D 10+(0-9) D 2/3 D yes D D Data Medium/High rate, High-quality Voice, Data and Voice
24 Baseband link types Polling-based TDD packet transmission 625µs slots, master polls slaves SCO (Synchronous Connection Oriented) Voice Periodic single slot packet assignment, 64 kbit/s full-duplex, point-to-point ACL (Asynchronous ConnectionLess) Data Variable packet size (1, 3, 5 slots), asymmetric bandwidth, point-to-multipoint MASTER SCO ACL SCO ACL SCO ACL SCO ACL f 0 f 6 f 8 f 12 f 4 f 20 f 14 f 18 SLAVE 1 f 1 f 7 f 9 f 13 f 19 SLAVE 2 f 5 f 21 f 17
25 Robustness Slow frequency hopping with hopping patterns determined by a master Protection from interference on certain frequencies Separation from other piconets (FH-CDMA) Retransmission ACL only, very fast Forward Error Correction SCO and ACL Error in payload (not header!) NAK ACK MASTER A C C F H SLAVE 1 B D E SLAVE 2 G G
26 Baseband states of a Bluetooth device standby unconnected detach inquiry page connecting transmit AMA connected AMA active park PMA hold AMA sniff AMA low power Standby: do nothing Inquire: search for other devices Page: connect to a specific device Connected: participate in a piconet Park: release AMA, get PMA Sniff: listen periodically, not each slot Hold: stop ACL, SCO still possible, possibly participate in another piconet
27 Example: Power consumption/csr BlueCore2 Typical Average Current Consumption1 VDD=1.8V Temperature = 20 C Mode SCO connection HV3 (1s interval Sniff Mode) (Slave) SCO connection HV3 (1s interval Sniff Mode) (Master) SCO connection HV1 (Slave) SCO connection HV1 (Master) ACL data transfer 115.2kbps UART (Master) ACL data transfer 720kbps USB (Slave) ACL data transfer 720kbps USB (Master) ACL connection, Sniff Mode 40ms interval, 38.4kbps UART ACL connection, Sniff Mode 1.28s interval, 38.4kbps UART Parked Slave, 1.28s beacon interval, 38.4kbps UART 26.0 ma 26.0 ma 53.0 ma 53.0 ma 15.5 ma 53.0 ma 53.0 ma 4.0 ma 0.5 ma 0.6 ma Standby Mode (Connected to host, no RF activity) 47.0 µa Deep Sleep Mode µa Notes: 1 Current consumption is the sum of both BC212015A and the flash. 2 Current consumption is for the BC212015A device only.
28 Example: Bluetooth/USB adapter (2002: 50, today: some cents if integrated)
29 L2CAP - Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Simple data link protocol on top of baseband Connection oriented, connectionless, and signaling channels Protocol multiplexing RFCOMM, SDP, telephony control Segmentation & reassembly Up to 64kbyte user data, 16 bit CRC used from baseband QoS flow specification per channel Follows RFC 1363, specifies delay, jitter, bursts, bandwidth Group abstraction Create/close group, add/remove member
30 L2CAP logical channels Slave Master Slave L2CAP baseband L2CAP L2CAP 2 d 1 1 d d d d 1 1 d d 2 baseband baseband signalling ACL connectionless connection-oriented
31 L2CAP packet formats Connectionless PDU bytes length CID=2 PSM payload Connection-oriented PDU bytes length CID payload Signalling command PDU 2 2 bytes length CID=1 One or more commands code ID length data
32 Security PIN (1-16 byte) User input (initialization) Pairing PIN (1-16 byte) E 2 Authentication key generation (possibly permanent storage) E 2 link key (128 bit) Authentication link key (128 bit) E 3 Encryption key generation (temporary storage) E 3 encryption key (128 bit) Encryption encryption key (128 bit) Keystream generator Keystream generator Data payload key Ciphering Cipher data payload key Data
33 SDP Service Discovery Protocol Inquiry/response protocol for discovering services Searching for and browsing services in radio proximity Adapted to the highly dynamic environment Can be complemented by others like SLP, Jini, Salutation, Defines discovery only, not the usage of services Caching of discovered services Gradual discovery Service record format Information about services provided by attributes Attributes are composed of an 16 bit ID (name) and a value values may be derived from 128 bit Universally Unique Identifiers (UUID)
34 RFCOMM Additional protocols to support legacy protocols/apps. Emulation of a serial port (supports a large base of legacy applications) Allows multiple ports over a single physical channel Telephony Control Protocol Specification (TCS) Call control (setup, release) Group management OBEX Exchange of objects, IrDA replacement WAP Interacting with applications on cellular phones
35 Protocols Profiles Represent default solutions for a certain usage model Vertical slice through the protocol stack Basis for interoperability Generic Access Profile Service Discovery Application Profile Cordless Telephony Profile Intercom Profile Serial Port Profile Headset Profile Dial-up Networking Profile Fax Profile LAN Access Profile Generic Object Exchange Profile Object Push Profile File Transfer Profile Synchronization Profile Applications Profiles Additional Profiles Advanced Audio Distribution PAN Audio Video Remote Control Basic Printing Basic Imaging Extended Service Discovery Generic Audio Video Distribution Hands Free Hardcopy Cable Replacement
36 Bluetooth versions Bluetooth 1.1 also IEEE Standard initial stable commercial standard Bluetooth 1.2 also IEEE Standard esco (extended SCO): higher, variable bitrates, retransmission for SCO AFH (adaptive frequency hopping) to avoid interference Bluetooth EDR (2004, no more IEEE) EDR (enhanced date rate) of 3.0 Mbit/s for ACL and esco lower power consumption due to shorter duty cycle Bluetooth EDR (2007) better pairing support, e.g. using NFC improved security Bluetooth HS (2009) Bluetooth EDR + IEEE a/g = 54 Mbit/s Bluetooth 4.0 (2010) Low Energy, much faster connection setup
37 WPAN: IEEE Bluetooth Data rate Synchronous, connection-oriented: 64 kbit/s Asynchronous, connectionless kbit/s symmetric / 57.6 kbit/s asymmetric Transmission range POS (Personal Operating Space) up to 10 m with special transceivers up to 100 m Frequency Free 2.4 GHz ISM-band Security Challenge/response (SAFER+), hopping sequence Availability Integrated into many products, several vendors Connection set-up time Depends on power-mode Max. 2.56s, avg. 0.64s Quality of Service Guarantees, ARQ/FEC Manageability Public/private keys needed, key management not specified, simple system integration Special Advantages/Disadvantages Advantage: already integrated into several products, available worldwide, free ISM-band, several vendors, simple system, simple ad-hoc networking, peer to peer, scatternets Disadvantage: interference on ISM-band, limited range, max. 8 active devices/network, high set-up latency
38 WPAN: IEEE additional developments : Co-existance Coexistence of Wireless Personal Area Networks (802.15) and Wireless Local Area Networks (802.11), quantify the mutual interference : High-Rate Standard for high-rate (20Mbit/s or greater) WPANs, while still low-power/low-cost Data Rates: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55 Mbit/s Quality of Service isochronous protocol Ad hoc peer-to-peer networking Security Low power consumption Low cost Designed to meet the demanding requirements of portable consumer imaging and multimedia applications
39 WPAN: IEEE additional developments Several working groups extend the standard a: - withdrawn - Alternative PHY with higher data rate as extension to Applications: multimedia, picture transmission b: Enhanced interoperability of MAC Correction of errors and ambiguities in the standard c: Alternative PHY at GHz Goal: data rates above 2 Gbit/s Not all these working groups really create a standard, not all standards will be found in products later
40 WPAN: IEEE additional developments : Low-Rate, Very Low-Power Low data rate solution with multi-month to multi-year battery life and very low complexity Potential applications are sensors, interactive toys, smart badges, remote controls, and home automation Data rates of kbit/s, latency down to 15 ms Master-Slave or Peer-to-Peer operation Up to 254 devices or simpler nodes Support for critical latency devices, such as joysticks CSMA/CA channel access (data centric), slotted (beacon) or unslotted Automatic network establishment by the PAN coordinator Dynamic device addressing, flexible addressing format Fully handshaked protocol for transfer reliability Power management to ensure low power consumption 16 channels in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, 10 channels in the 915 MHz US ISM band and one channel in the European 868 MHz band Base of the ZigBee technology
41 ZigBee Relation to similar to Bluetooth / Pushed by Chipcon (now TI), ember, freescale (Motorola), Honeywell, Mitsubishi, Motorola, Philips, Samsung More than 260 members see about 11 promoters, 160 participants, 240 adopters must be member to commercially use ZigBee spec ZigBee platforms comprise IEEE for layers 1 and 2 ZigBee protocol stack up to the applications
42 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (1) Data rate Transmission of ID only (e.g., 48 bit, 64kbit, 1 Mbit) kbit/s Transmission range Passive: up to 3 m Active: up to m Simultaneous detection of up to, e.g., 256 tags, scanning of, e.g., 40 tags/s Frequency 125 khz, MHz, 433 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz and many others Security Application dependent, typ. no crypt. on RFID device Cost Very cheap tags, down to 1 (passive) Availability Many products, many vendors Connection set-up time Depends on product/medium access scheme (typ. 2 ms per device) Quality of Service none Manageability Very simple, same as serial interface Special Advantages/Disadvantages Advantage: extremely low cost, large experience, high volume available, no power for passive RFIDs needed, large variety of products, relative speeds up to 300 km/h, broad temp. range Disadvantage: no QoS, simple denial of service, crowded ISM bands, typ. one-way (activation/ transmission of ID)
43 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (2) Function Standard: In response to a radio interrogation signal from a reader (base station) the RFID tags transmit their ID Enhanced: additionally data can be sent to the tags, different media access schemes (collision avoidance) Features No line-of sight required (compared to, e.g., laser scanners) RFID tags withstand difficult environmental conditions (sunlight, cold, frost, dirt etc.) Products available with read/write memory, smart-card capabilities Categories Passive RFID: operating power comes from the reader over the air which is feasible up to distances of 3 m, low price (1 ) Active RFID: battery powered, distances up to 100 m
44 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (3) Applications Total asset visibility: tracking of goods during manufacturing, localization of pallets, goods etc. Loyalty cards: customers use RFID tags for payment at, e.g., gas stations, collection of buying patterns Automated toll collection: RFIDs mounted in windshields allow commuters to drive through toll plazas without stopping Others: access control, animal identification, tracking of hazardous material, inventory control, warehouse management,... Local Positioning Systems GPS useless indoors or underground, problematic in cities with high buildings RFID tags transmit signals, receivers estimate the tag location by measuring the signal s time of flight
45 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (4) Security Denial-of-Service attacks are always possible Interference of the wireless transmission, shielding of transceivers IDs via manufacturing or one time programming Key exchange via, e.g., RSA possible, encryption via, e.g., AES Future Trends RTLS: Real-Time Locating System big efforts to make total asset visibility come true Integration of RFID technology into the manufacturing, distribution and logistics chain Creation of electronic manifests at item or package level (embedded inexpensive passive RFID tags) 3D tracking of children, patients
46 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (5) Relevant Standards American National Standards Institute ANSI, Automatic Identification and Data Capture Techniques JTC 1/SC 31, European Radiocommunications Office ERO, European Telecommunications Standards Institute ETSI, Identification Cards and related devices JTC 1/SC 17, Identification and communication ISO TC 104 / SC 4, Road Transport and Traffic Telematics CEN TC 278, Transport Information and Control Systems ISO/TC204,
47 RFID Radio Frequency Identification (6) ISO Standards ISO MH Data Identifiers EAN.UCC Application Identifiers ISO Syntax for High Capacity ADC Media ISO Transfer Syntax ISO Part 2, khz Part 3, MHz Part 4, 2.45 GHz Part 5, 5.8 GHz Part 6, UHF ( MHz, 433 MHz) ISO RFID Device Conformance Test Methods ISO RF Tag and Interrogator Performance Test Methods
Networked Embedded Systems: Bluetooth
 Networked Embedded Systems: Bluetooth Prof. António Grilo Instituto Superior Técnico (IST), Lisboa, Portugal Prof. Dr. António Grilo 7.1 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless
Networked Embedded Systems: Bluetooth Prof. António Grilo Instituto Superior Técnico (IST), Lisboa, Portugal Prof. Dr. António Grilo 7.1 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth. Acknowledgements. Based on Jochen Schiller slides. Supporting text
 BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
5.7 WRAN: IEEE (1)
 5.7 WRAN: IEEE 802.22 (1) Wireless Regional Area Network long range up to 100 km Standard published in 2011 Enabling Rural Broadband Wireless Access Using Cognitive Radio Technology in TV Whitespaces Use
5.7 WRAN: IEEE 802.22 (1) Wireless Regional Area Network long range up to 100 km Standard published in 2011 Enabling Rural Broadband Wireless Access Using Cognitive Radio Technology in TV Whitespaces Use
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Wireless LANs. Characteristics Bluetooth. PHY MAC Roaming Standards
 Wireless LANs Characteristics 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming Standards Bluetooth 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, FU-Berlin www.jochenschiller.de
Wireless LANs Characteristics 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming Standards Bluetooth 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, FU-Berlin www.jochenschiller.de
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison 7.1 Mobile Communication
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison 7.1 Mobile Communication
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Prof. Dr.-Ing Jochen H. Schiller Inst. of Computer Science Freie Universität Berlin Germany Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h,
Prof. Dr.-Ing Jochen H. Schiller Inst. of Computer Science Freie Universität Berlin Germany Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h,
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
MOBILE COMPUTING 4/3/18. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. CSE 40814/60814 Spring 2018
 MOBILE COMPUTING CE 40814/60814 pring 2018 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, PDAs, cell phones
MOBILE COMPUTING CE 40814/60814 pring 2018 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, PDAs, cell phones
Bluetooth. Bluetooth: History. What is a PAN? EEC173B/ECS152C, Spring Wireless Personal Area Networks (PAN)
 EEC173B/EC152C, pring 2009 What is a AN? Wireless ersonal Area Networks (AN) Bluetooth and Wireless AN (802.15) IEEE 802.15.4 and Zigbee RFIDs WAN LAN MAN AN Acknowledgment: elected slides from rof. chiller
EEC173B/EC152C, pring 2009 What is a AN? Wireless ersonal Area Networks (AN) Bluetooth and Wireless AN (802.15) IEEE 802.15.4 and Zigbee RFIDs WAN LAN MAN AN Acknowledgment: elected slides from rof. chiller
10/6/08. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Chapter 5 (Part 3) LINK LAYER
 Chapter 5 (Part 3) LINK LAYER Distributed Computing Group Computer Networks Summer 2007 Overview More Wireless Basics IEEE 802.11 Architecture, Protocol PHY, MAC Cyclic Redundancy codes Roaming, Security
Chapter 5 (Part 3) LINK LAYER Distributed Computing Group Computer Networks Summer 2007 Overview More Wireless Basics IEEE 802.11 Architecture, Protocol PHY, MAC Cyclic Redundancy codes Roaming, Security
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Mobile Communications Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming.11a, b, g, h, I, n z Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Mobile Communications Wireless LANs 1 Mobile
Mobile Communications Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming.11a, b, g, h, I, n z Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Mobile Communications Wireless LANs 1 Mobile
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
MAC in /20/06
 MAC in 802.11 2/20/06 MAC Multiple users share common medium. Important issues: Collision detection Delay Fairness Hidden terminals Synchronization Power management Roaming Use 802.11 as an example to
MAC in 802.11 2/20/06 MAC Multiple users share common medium. Important issues: Collision detection Delay Fairness Hidden terminals Synchronization Power management Roaming Use 802.11 as an example to
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
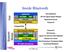 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Mobile Communication Technology. WiMAX. according to IEEE. ZigBee. Bluetooth m LAN. WiFi x <10m PAN. IEEE 802.
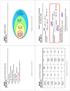 Range of Wireless Data choices Wide Area Networks 2G and 3G cellular data systems etropolitan Area Networks 802.16, Wiax - wireless broadband Local Area Networks 802.11/a/b/g/, wireless LAN ersonal Area
Range of Wireless Data choices Wide Area Networks 2G and 3G cellular data systems etropolitan Area Networks 802.16, Wiax - wireless broadband Local Area Networks 802.11/a/b/g/, wireless LAN ersonal Area
Chapter 4 WIRELESS LAN
 Chapter 4 WIRELESS LAN Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Winter 2005 / 2006 Overview Design goals Characteristics IEEE 802.11 Architecture, Protocol PHY, MAC Cyclic Redundancy codes Roaming,
Chapter 4 WIRELESS LAN Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Winter 2005 / 2006 Overview Design goals Characteristics IEEE 802.11 Architecture, Protocol PHY, MAC Cyclic Redundancy codes Roaming,
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 7: Wireless LAN
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks
 Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goals of this chapter Look at two most prominent examples of local, non-cellular
Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goals of this chapter Look at two most prominent examples of local, non-cellular
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
CCM 4300 Lecture 16. 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications. Dr S Rahman. Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems
 CCM 4300 Lecture 16 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications Dr S Rahman 1 Session Content Recap of last session Lesson Objectives Roadmap
CCM 4300 Lecture 16 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications Dr S Rahman 1 Session Content Recap of last session Lesson Objectives Roadmap
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Introduction to IEEE
 Introduction to IEEE 802.11 Characteristics of wireless LANs Advantages very flexible within the reception area Ad hoc networks without previous planning possible (almost) no wiring difficulties more robust
Introduction to IEEE 802.11 Characteristics of wireless LANs Advantages very flexible within the reception area Ad hoc networks without previous planning possible (almost) no wiring difficulties more robust
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks
 Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goals of this chapter Look at two most prominent examples of local, non-cellular
Mobile Communications Chapter 5: Wireless local area networks Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goals of this chapter Look at two most prominent examples of local, non-cellular
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
Advanced Computer Networks. Medium Access, WLAN & Bluetooth
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 Medium Access, WLAN & Bluetooth Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Last Week Signal Propagation Path loss model Log normal shadowing model
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 Medium Access, WLAN & Bluetooth Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Last Week Signal Propagation Path loss model Log normal shadowing model
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
Computer Communication III
 Computer Communication III Wireless Media Access IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Advantages of Wireless LANs Using the license free ISM band at 2.4 GHz no complicated or expensive licenses necessary very cost
Computer Communication III Wireless Media Access IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Advantages of Wireless LANs Using the license free ISM band at 2.4 GHz no complicated or expensive licenses necessary very cost
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Wireless Communication Session 4 Wi-Fi IEEE standard
 Wireless Communication Session 4 Wi-Fi IEEE802.11 standard M. Daneshvar Farzanegan Soourosh.blogfa.com smdanesh@yahoo.com 1 Reminder on frequencies and wavelenghts twisted pair coax cable optical transmission
Wireless Communication Session 4 Wi-Fi IEEE802.11 standard M. Daneshvar Farzanegan Soourosh.blogfa.com smdanesh@yahoo.com 1 Reminder on frequencies and wavelenghts twisted pair coax cable optical transmission
7. Wireless Local Area Networks. Characteristics of Wireless LANs
 7. Wireless Local Area Networks Characteristics IEEE 802.11 HIPERLAN, WATM, BRAN, HIPERLAN2 Bluetooth RF Comparison 2005 Burkhard Stiller and Jochen Schiller FU Berlin M7 1 Characteristics of Wireless
7. Wireless Local Area Networks Characteristics IEEE 802.11 HIPERLAN, WATM, BRAN, HIPERLAN2 Bluetooth RF Comparison 2005 Burkhard Stiller and Jochen Schiller FU Berlin M7 1 Characteristics of Wireless
Electromagnetic Spectrum (3kHz 300GHz)
 Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon. Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
 ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
CS601 Wireless Communication and Networks. Wireless LAN Technology-IEEE Standards-HIPER LAN and Bluetooth-Role of Wireless local loops.
 UNIT III WIRELESS LANS Wireless LAN Technology-IEEE 802.11 Standards-HIPER LAN and Bluetooth-Role of Wireless local loops. WIRELESS LAN TECHNOLOGY Advantages of WLAN Flexibility Planning o Ad-hoc networks
UNIT III WIRELESS LANS Wireless LAN Technology-IEEE 802.11 Standards-HIPER LAN and Bluetooth-Role of Wireless local loops. WIRELESS LAN TECHNOLOGY Advantages of WLAN Flexibility Planning o Ad-hoc networks
BT-22 Product Specification
 BT-22 Product Specification Features Amp ed RF, Inc. Description 10.4 mm x 13.5 mm Our micro-sized Bluetooth module is the smallest form factor available providing a complete RF platform. The BT-22 is
BT-22 Product Specification Features Amp ed RF, Inc. Description 10.4 mm x 13.5 mm Our micro-sized Bluetooth module is the smallest form factor available providing a complete RF platform. The BT-22 is
Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE)
 Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE) Lab 11 Lunch April 23rd, 2014 Noah Klugman Josh Adkins 1 Outline History of Bluetooth Introduction to BLE Architecture Controller Host Applications Power Topology Example:
Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE) Lab 11 Lunch April 23rd, 2014 Noah Klugman Josh Adkins 1 Outline History of Bluetooth Introduction to BLE Architecture Controller Host Applications Power Topology Example:
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Characteristics of Wireless LANs
Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Characteristics of Wireless LANs
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
Image acquisition and Communication
 Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
