Introduction to Fireworks CS3
|
|
|
- Lawrence Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Fireworks CS3 Carol Green The files used in activities and exercises within this book are not available for preview.
2 Introduction to Fireworks CS3 Carol Green FWCS ISBN: Natcoll Publishing PO Box Christchurch 8013, New Zealand +64 (0) (0) fax Find us on the World Wide Web at: Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Notice of rights All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. For information on obtaining permission for reprints and excerpts, contact Natcoll Publishing. Notice of liability The information in this book is distributed on an as is basis, without warranty. While every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this book, Natcoll Publishing shall not have any liability to be caused directly or indirectly by the instructions contained in this book or by the computer software or hardware products described herein. Trademarks Natcoll and the Natcoll Design Technology logo are registered trademarks of Natcoll Design Technology in New Zealand and/or other countries. All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners. Rather than place a trademark symbol in every occurrence of a trademarked name, we state we are using the names only in an editorial fashion and to the benefit of the trademark owner with no intention of infringement of the trademark.
3 Contents What is Fireworks CS3?... 1 What this guide covers... 1 How to use this guide... 1 Acknowledgements... 1 The workspace... 2 The Tools panel... 3 The Properties panel... 4 The panels... 4 The document window... 4 Selection techniques... 5 Making a marquee selection...5 Selecting a paint colour...5 Painting inside selections...6 Erasing selections...6 Cancelling selections...6 Making a Lasso selection...7 Making a Polygon Lasso selection...7 Adding to selections...7 Subtracting from selections...7 Inverting a selection...8 Filling a selection...8 Setting opacity for a stroke or fill...8 Making a Magic Wand selection...9 Undo and Undo History... 9 Saving...10 PNG format...10 Save As...10 The Crop tool...10 Using Layers...11 Making a new Layer set...11 Making a new Bitmap image layer...11 Duplicating a layer...11 Renaming a layer...11 Hiding and showing layers...11 Changing the stacking order of layers...11 Transforming objects...12 Resizing an object...12 Rotating an object...12 Skewing an object...12 Distorting an object...12 Making new documents...15 What is resolution?...15 The Gradient tool...16 Making a preset gradient...16 Making a custom gradient...17 The Rubber Stamp tool...18 Cloning an image...18 Adjusting image size...19 Adjusting canvas size...20 Exporting web graphics...21 Image types...21 The GIF format...21 The JPEG format...21 Exporting a web image...22 Filters...24 Adjusting colour...24 Blurring images...25 Fireworks bitmap and vector modes...29 Bitmap vs vector graphics...29 Working in vector mode...30 Drawing vector shapes...30 Using Auto Shapes...30 Changing a vector path...30 Drawing with the Pen tool...31 Combining shapes...32 Transparent GIFs...33 Working with text...33 Graphic vs regular text...33 Making a text heading...34 Adding filter effects...34 Designing a website in Fireworks...37 Slicing...37 Slicing an image...38 Saving palettes...38 Composing multiple page web sites...40 Adding new pages...40 Duplicating pages...40 Using a master page...40 Sharing layers between pages...40 Interactive navigation buttons and rollovers...41 Creating buttons using slices...41 Creating buttons using symbols...42 Enabling 9-slice scaling...43 Remote rollovers...44 Image maps...44 Creating image maps...44 Modifying image maps...45 Creating rollovers with image maps...45 Animations...46 Making an animated GIF...46 The Tools panel...49 Select tools...49 Bitmap tools...49 Vector tools...50 Web tools...50 Color tools...50 View tools...50 The panels...51 Pages, Layers, Frames and History panel group...51 Assets panel group...51 Colors panel group...51 Optimize and Align panel group...52 Ungrouped panels...52 Shortcut keys...54 Mac OS shortcut keys...54 Windows shortcut keys...55 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Contents iii
4 iv INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
5 Introduction to Fireworks CS3 What is Fireworks CS3? Fireworks is an application that is used for creating web graphics of all types; static, animated, text, interactive. It uses both bitmap and vector formats to create images, and also has a large set of website generation tools. Fireworks also has very close integration with other applications, such as Dreamweaver. What this guide covers This guide will introduce Fireworks tools and image editing capabilities, as well as some simple web animation and slicing techniques. It has a web focus but will not cover all of the advanced web tools in detail. How to use this guide This guide has been designed to progressively build up skills in the following order: Getting started and finding your way around the Fireworks interface. Saving files, making selections and creating images with the paint tools. Controlling images using layers and adjusting images using transform tools. Making new documents and adjusting the size of existing documents. Creating gradients and cloning pixels. Exporting web graphics with appropriate compression. Adjusting images using filters. Creating images using vector tools. Using text and adding effects to objects. Composing, slicing and exporting web pages complete with rollover navigation bars. Making animated GIFs. Each section is set out in the following way: A new tool or concept is introduced, and an explanation is given about when and why you might use it. Instructions are given for how to use it, and after one or more set of instructions there is an exercise to try out these new tools or concepts. At the end of most chapters there will be a set of projects for you to complete, which will put into practice the things that you have learned so far; the projects generally increase in their complexity. Acknowledgements Originally written and illustrated by Carol Green. Revised and extended for version Fireworks CS3 by Jamie Campbell. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Introduction 1
6 Getting started Introducing the Fireworks CS3 interface In this section In this section, you will be introduced to: The Fireworks workspace. The Tools panel. The Properties panel. The workspace The panels. The document window. The Fireworks workspace may be familiar to you if you have used a graphics program such as Adobe Photoshop or Macromedia FreeHand. The workspace consists of the document window, surrounded by the Tools panel, the Properties panel, various other panels (usually on the right-hand side), as well as the menus at the top of the screen (see below). Menus Tools panel Document window Properties panel Menus Tools panel Panels Example of the workspace Mac OSX Panels Document window Properties panel Example of the workspace Windows XP 2 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
7 The Tools panel You will use many of the tools in this panel regularly to create and modify images. Click on a tool in the Tools panel to select it and use it in the current document. Some tools have a number of options. If you see a small black triangle underneath the tool s icon, click and hold your mouse in the same place to see the other tools which are stored there. The names of the tools are displayed when you hover over the tool, or when you click and hold on a tool which has options. See the appendix for an explanation of what each tool does. Pointer (V, 0) Scale (Q) Marquee (M) Magic Wand (W) Pencil (B) Blur (R) Line (N) Rectangle (U) Freeform (O) Rectangle Hotspot (J) Hide Hotspots and Slices (2) Eyedropper (I) Default Colors (D) No Stroke or Fill Standard (F) Hand (H) Subselection (A, 1) Crop (C) Lasso (L) Brush (B) Eraser (E) Rubber Stamp (S) Pen (P) Text (T) Knife (Y) Slice (K) Show Hotspots and Slices (2) Paint Bucket (G) Stroke Color Fill Color Switch Fill and Stroke (X) Full Screen (F) Full Screen with menus (F) Magnify (Z) Select Behind (V, 0) Skew (Q) Distort (Q) Export Area (C) Oval Marquee (M) Polygon Lasso (L) Sharpen (R) Dodge (R) Burn (R) Smudge (R) Replace Color Red Eye Removal Vector Path (P) Redraw Path (P) tip Ellipse (U) Polygon (U) Auto shapes Reshape (O) Path Scrubber + Path Scrubber Ellipse Hotspot (J) Polygon Hotspot (J) Tool shortcut keys The letter in brackets shown beside the name of a tool is the shortcut key. Press the shortcut key (without /Ctrl) to quickly select the tool. Toggle between tools with the same shortcut key. tip Showing and hiding the Tools panel If the Tools panel is not visible, choose Window > Tools. Pressing Tab will hide and reveal the Tools panel and other palettes. Polygon Slice (K) Gradient (G) Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 1: Getting started 3
8 The Properties panel The Properties panel is context sensitive, meaning that it changes depending on what is selected in the document window. It can display current selection properties, current tool options, or document properties. You can expand the Properties panel to show more options for a selected item by clicking the small expand triangle at the bottom right of the panel (see below). The Properties panel with a filled path selected The Properties panel with a slice selected The panels The panels let you apply different settings to the objects in your document, with some of the panels arranged in sets. Panels and panel sets can be closed and reopened as you wish. To see a panel that isn t visible, choose its name from the Window menu. To restore the layout of the panel sets, choose Window > Workspace Layouts from the menu, then the resolution of your screen. You can even save your own layout. Panels are often nested together into groups; you can select another panel in a group by clicking on its tabs. To move a panel from one group to another, drag the panel s tab into another group. When a black outline appears around the group, you know that it is ready to accept the new panel. See the appendix for an explanation of what each panel does. The document window The document window has some useful buttons in it which will make your job easier when creating or modifying documents. The Original button shows the original, editable version of the document. The Preview button allows you to see how your document will look when the Optimize panel settings have been applied. The 2-Up and 4-Up buttons allow you to compare the original document with 1 or 3 other settings. Click this triangle to expand the Properties panel This menu contains shortcuts to preview in browser software or to export and edit in other software applications like Dreamweaver. This button allows you to upload your image to a website, if the image file is part of a Dreamweaver site. This shows the optimisation settings for selected slices or the document. The playhead buttons allow you to control animations. This button exits bitmap mode. The Zoom pop-up lets you quickly change the magnification of the document. 4 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
9 Modifying images Using selection, paint and transformation tools In this section In this section, you will learn how to: Make a Marquee selection. Select a colour and paint with the Brush tool. Erase and cancel selections. Make Lasso and Polygon Lasso selections. Add to, or subtract from selections using Shift and Option/Alt. Invert and fill selections. Set opacity for a Stroke or Fill. Selection techniques There are several types of selection tools in Fireworks which can be used to select pixels and areas of a document. Selections can then be used together with other functions (move, erase, paint, etc) to alter images. Only the pixels inside the selection will be altered. Making a marquee selection Make Magic Wand selections. Undo mistakes. Save files in the PNG format. Crop images. Make new Layer sets and Bitmap image layers. Reorder and duplicate layers. Scale, Rotate, Skew and Distort objects. Choose the Marquee selection tool ( ), then drag to draw a selection (see right). Drag To make a precise selection, it helps to zoom into the document, either using the Set Magnification pop-up at the bottom of the document window (see far right), or by drawing a rectangle around the area with the Zoom tool ( ) (see right). Choose the Oval Marquee tool ( ) to draw an elliptical or circular selection. Selecting a paint colour Choose a paint brush colour by clicking once on the Stroke Color box, then choosing a colour from the pop-up palette (see far right). If the colour that you want is not shown in the palette, click the colour wheel icon at the top of the palette to show the OS colour pickers. To choose an existing colour from your document. Click the Stroke Color box to display the Colors palette, then move your mouse over the document. You will see the Eyedropper cursor appear and you can click once again to pick up this colour. If you know the RGB, CMYK or HSL values for the colour that you want to use, choose Window > Others > Color Palette. Under the Selector tab you can choose the colour system, then enter colour values in the boxes. Under the Mixers tab of the Color Palette you can experiment with colour combinations by choosing up to four different colours and then dragging the colour indicated in the mini colour wheel in the bottom right of the palette. Under the Blender tab you can create a blend between two colours. Drawing square and circle marquees Shift-dragging the Marquee or Oval Marquee tool will draw a perfect square or a circle instead of a rectangle or an oval. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 2: Modifying images 5 tip Click Stroke Color tip Drawing marquees from the centre out Option/Alt-dragging a rectangle or oval selection will draw the selection from the centre rather than the top left-hand corner. Drag to zoom in. Set Magnification. Click here to show the OS color picker. To choose an existing colour, move the mouse over the image and click. The Colour Palette provides more powerful mixing options.
10 exercise 2.1 Painting inside selections Once you have made your selection and you can see the marquee line animating (sometimes called marching ants ) you can paint across the selection without fear of painting over other parts of the image. 1 Select the Brush tool ( ). 2 Using the Properties panel, choose the size and shape of the brush that you want to use (see below). When you move your mouse over the image, you should see the size of the brush (see right). 3 Drag over the selection. You will see that you can only paint inside the selection, leaving the rest of the image unaffected. Brush size Brush shape Properties panel with the Brush tool selected Erasing selections Erasing using a selection allows you to be precise about what will and won t be erased. 1 Select the Eraser tool ( ). 2 Using the Properties panel, choose an eraser Size and Shape (see below). Properties panel with the Eraser tool selected 3 Do one of the following: Erase over the selection. Press Delete to erase the entire contents of the selection. You will see that you can only erase inside the selection, leaving the rest of the image unaffected. The eraser will show whatever is in the layer directly underneath the erased section. If there are no layers underneath, the eraser will show a grey and white checked pattern which represents transparency (see right). Cancelling selections Choose Select > Deselect, or with the Marquee tool ( Tidying up a scan Brush colour (matches Stroke Color chip) ) click elsewhere on the image. For this exercise, use the file house.png from the exercise_resources folder. This file is a scan of a line drawing. It has some spots and marks which need tidying up. 1 Use the Rectangle and Oval Marquee tools to make a selection around one spot at a time. Zoom in to the spots if you need to. 2 Use the Brush tool to paint out some of these spots remember to use the Stroke Color box to pick exactly the same colour to paint with. 3 Once you have removed all of the spots and marks, try selecting the doors and windows in the image and painting them with colour. 4 You should end up with an image something like the one on the right. Selection Indication of brush size Transparency 6 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
11 Making a Lasso selection The Lasso tool allows you to make a freeform selection, which can be easily added to and subtracted from. 1 Select the Lasso tool ( ) and in the Properties panel, choose an Edge setting and a Feather setting if you need one (see below). Edge setting Feather setting Properties panel with Lasso tool selected 2 Drag across your document to draw a selection. 3 When the cursor gets back to where you started it will show a small black square (see right) this means that if you release the mouse button it will close the selection. Making a Polygon Lasso selection The Polygon Lasso tool works by clicking around the edge of a shape, like a join-the-dots picture. Use the Polygon Lasso tool when the edges of the selection that you want to make are mostly straight. 1 Select the Polygon Lasso tool ( ) and in the Properties panel, choose an Edge setting and a Feather setting if you need one, the same way as with the Lasso tool (see top). 2 Make a series of clicks, marking out the selection. 3 When the cursor gets back to where you started it will show a small black square to indicate that it will close the selection. Edge and feather settings All selections (and some other tools, like text for example) have antialiasing capabilities. This helps shapes to look smoother. Bitmap images are made up of square pixels and, because of this, curved selections are actually a series of steps making it impossible to get a true curve. You can see this by zooming in very close to a curve. To smooth out the edges of selections, you can use a technique called antialiasing. This works by partially selecting the edge pixels, giving them a slightly fuzzy appearance which tricks the eye into thinking that the curve is much smoother than it really is. You can further fuzz edges of the selection by using a Feather setting. Choose Edge and Feather settings in the Properties panel. Note: If the Live marquee option is ticked, you can modify these settings after you have made the selection. Adding to selections All selections can be easily added to using one of the selection tools and holding Shift. 1 Select the tool that you want to use. 2 Shift -drag to draw a new part of the selection a small plus (+) symbol will appear next to the tool s cursor. You don t have to get every bit first time, just finishing selecting one small bit and then repeat for other areas. Subtracting from selections Selections can also be subtracted from using one of the selection tools and holding down Option/Alt. 1 Select the tool that you want to use. A selection filled with colour with Edge set to Hard. A selection filled with colour with Edge set to Antialias. Notice the fuzzy edge. A selection filled with colour with Edge set to Antialias, and Feather set to 5 pixels. 2 Option/Alt-drag to draw a new piece that you want to take away a small minus ( ) symbol will appear next to the tool s cursor. Add to a selection by holding down Shift. Subtract from a selection by holding down Option/Alt. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 2: Modifying images 7
12 exercise 2.2 Inverting a selection Sometimes it is simpler to select part of an image that you don t want to use. You can then inverse the selection, making everything else active. Choose Select > Select Inverse. Filling a selection It s easy to fill large selections quickly using the Paint Bucket tool. 1 Select the Paint Bucket tool ( ). 2 In the Properties panel, choose a colour from the pop-up menu (see below). 3 Tick the Fill Selection box (see below), which will make sure that the paint fills the entire selection if you do not, only areas of similar colour will be filled. 4 Click once in the selected area to fill with your choice of colour. Setting opacity for a stroke or fill To make strokes (using the Brush tool, for example) or fills (using the Paint Bucket tool, for example) appear softer or transparent, adjust the Opacity setting in the Properties panel (see above). Neat effects can be achieved by layering semi-transparent objects. Clear-cutting an image For this exercise, use the file shampoo.png from the exercise_resources folder. This file is a photograph of some shampoo bottles, on a distracting background. You will cut-out the bottles and fill the background with a plain colour. 1 Use the Lasso and Polygon Lasso tools to make a selection around the edges of the bottles. You will need to use Shift and Option/Alt to add and subtract from selections. Be careful not to deselect by accident! 2 Once the bottles are selected, inverse the selection so that the area outside of the bottles is selected, not the bottles. 3 Use the Paint Bucket tool to fill the space around the bottles with a colour of your choice. A light colour will work better than a dark colour. 4 Before you deselect, paint a shadow underneath the bottles. Start with a large paintbrush, with the Opacity setting on the Properties panel set to about 20%. Use broad, sweeping strokes, then choose a smaller brush with a higher Opacity setting to paint again. The shadow should appear darker the closer it gets to the bottles. 5 Deselect the selection and save the image. Paint Bucket colour (matches Fill Color chip) Properties panel with the Paint Bucket tool selected tip Careful clicking! When you are in the process of adding to, or subtracting from a selection, make sure that you don t click anywhere else on the image by mistake you could end up losing the selection you have just spent hours sweating over! The same goes for making a selection and then choosing a painting or erasing tool. Tick this box to fill the entire selection. Opacity setting (percentage) 8 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
13 exercise 2.3 Making a Magic Wand selection Use the Magic Wand tool when you want to select areas of a similar colour. It works well when selections would be very difficult to make using the Lasso tool. 1 Select the Magic Wand tool ( ). 2 In the Properties panel, choose a Tolerance setting (see below). The default value is 32. Increase this value if not enough shades of the colour are selected. Decrease it if unwanted colours or shades are selected. Properties panel with the Magic Wand tool selected 3 Shift or Option/Alt-click to add or subtract parts from the selection (see right). 4 Select all the areas of the same colour easily by choosing Select > Select Similar. Selecting by colour For this exercise, use the file hibiscus.png from the exercise_resources folder. This file is a drawing of some flowers. You will alter the colour of some of the flowers and the stamens, to make it a more interesting image. 1 Use the Magic Wand tool to select a certain colour in the image. Experiment with the Tolerance setting to try to get a broad range of colour without selecting other colours. 2 Use Shift and Option/Alt to add and subtract to and from an existing selection. 3 Once you have made a selection, try choosing Select > Select Similar to select all the pixels of a similar colour. 4 Use the Paint Bucket tool to fill areas with solid colour. Don t forget to tick the Fill Selection box on the Property Inspector! 5 Save the image. Undo and Undo History If you make a mistake, Fireworks has the ability to undo a number of steps, like most software packages. To undo a mistake, choose Edit > Undo. It will be specific about what you want to undo, for example, Undo Brush tool. tip How does the Magic Wand work? The Magic Wand tool makes selections based on colour. Tell the Magic Wand how similar colours have to be to be selected, using the Tolerance setting in the Properties panel. The higher the Tolerance number, the wider the range of colour variations selected. Alter the appearance of the selection edge by choosing Anti-alias or Feather Edge setting. To redo the last thing that you undid, choose Edit > Redo. It will be specific about what you want to redo, for example, Redo Eraser tool. Fireworks also has a History panel, which shows a list of all these undos, up to 20 stages (the default amount). To return to a history state using the History panel, move the history slider up to a previous step (see right). After you have adjusted the history slider, further changes you make to the document will over write the remaining stages. Add to a selection by Shift-clicking. The History panel allows you to step back to one or more previous steps of your document. History slider Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 2: Modifying images 9
14 exercise 2.4 Saving It is vital to save your files as you go you probably know this already from other software applications. So far during this book you have been saving over the top of the existing file, using the File > Save command. All of the files you have been dealing with have been PNG files. PNG format The PNG format (often pronounced ping ) is the Fireworks native format, and preserves all of the information that Fireworks uses, such as layers, editable text, masks and editable vector shapes, which are all covered later in this guide. Save As Often it is important to save your file with a different filename, so that you can keep the original. The File > Save As command allows you to save your file with a different name, or in a different directory. 1 Choose File > Save As to save your file with a different name or in a different location. 2 The Save As dialog box will appear and you should use the normal method of saving files for your computer system. 3 Choose Fireworks PNG (*.png) as the file type. Remember that your Fireworks files should have.png file extensions so that they can easily be transferred between computers. The Crop tool The Crop tool lets you select a square or rectangular portion of an image and discard the rest. You might use it when you have started working on a document size that is too large for the image, or, in conjunction with the Save As command, you can use it to save different areas of the same image as different files. 1 Select the Crop tool ( ). 2 Drag a cropping selection around the part of the image that you want to keep (see right). Shift-drag to make a square selection. 3 If the cropping selection isn t right first time around, click on the selection handles and drag them into the right position (see right). 4 Double-click in the middle of the cropping selection or press Return/Enter to discard the rest of the document. Cropping an image For this exercise, use the file sky.png from the exercise_resources folder. This file is a photograph of a beach landscape. You will crop the sky to use as a separate image. 1 Use the Crop tool to crop the top and bottom from the image, leaving only the sky. 2 Adjust the cropping selection handles as necessary. 3 Once you have cropped the image to suit, save it as a different file. Don t forget the.png file extension! Save As dialog box using Mac OSX Save As dialog box using Windows XP Cropping selection Move selection handles to reshape a cropping selection. 10 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
15 exercise 2.5 Using Layers A layer is like a transparent sheet that contains objects in your document. You can stack several layers on top of each other, change their order in the stack and make them visible or invisible. Layers allow you to move elements in an image independently of each other. Making a new Layer set Making a new Layer will create what can also be referred to as a Layer set, which can contain individual objects such as bitmap images, vector shapes and text. To make a new Layer set, click the New/Duplicate layer button. Using the New sub layer button, additional sub-layer sets can be created within existing layer sets to help organise complex documents. Making a new Bitmap image layer Bitmap image layers (inside Layer sets) contain bitmap objects. To make a new Bitmap image layer, click the New bitmap image layer button in the Layers panel (see top). Duplicating a layer Drag the Layer or Bitmap image layer which you want to duplicate to the Add/Duplicate layer button (see top). Renaming a layer Get into the habit of renaming layers so that they are easier to recognise later on. Double-click the name of the layer and enter a new name in the box (see right). Hiding and showing layers Use the Hide/Show layer button (see top) to hide or show individual Bitmap image layers and Layer sets. This can be useful when trying to remember what is on a single layer. Changing the stacking order of layers Expand layer Hide/Show layer Layer Bitmap image layer To change the order in which layers appear, grab a layer in the Layers panel, and drag-anddrop it above or below another layer, according to where it should appear. Layering a document For this exercise, use the file dress_up.png from the exercise_resources folder. This file is a drawing of a girl. You will see that the girl and the pants objects are on two layers inside the Layer set, and the background colour and shadow is in another Layer set. You will create some more clothes and change their layer order. 1 Use selection and paint tools to create two new items of clothing (suggestion; a T-shirt and a skirt), each on separate layers. Select shapes using the Polygon Lasso tool and fill the selections using the Paint Bucket tool. It is up to you to create the clothes however you like. 2 Make a new Layer set and rename it as clothes. Drag the existing pants Bitmap image layer into this new Layer set. Create all of the new clothes inside this set. 3 Change the stacking order and visibility of the layers for different effects. 4 Save several versions of the file, with different combinations of clothes. New/Duplicate layer New bitmap image layer New sub Delete layer selection tip Where s my new Bitmap image layer gone? If you make a new Bitmap image layer, but don t draw anything in it and then click on, or work another layer, Fireworks will delete it. This is so that you don t get left with a lot of empty layers. When you make a Bitmap image layer, make sure you use it! Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 2: Modifying images 11
16 exercise 2.6 Transforming objects The transform (Scale, Skew, Distort) tools can be used to quickly change an object. Resizing an object 1 Select part of your image, or an object in your image, then select the Scale tool ( ). A box with resize handles will appear around the selected item. 2 Position your mouse over one of the handles. You will see the cursor change. If you move your mouse over one of the corner handles, you will see the cursor change into a two-headed arrow ( ) which will allow you to scale both the horizontal and vertical sides at once. 3 Drag the handles to resize the object. Shift-drag if you want to keep the object s proportions the same as you resize. Rotating an object 1 Select part of, or an object in your image then select any of the transform tools. A box with resize handles will appear around the selected item. 2 Position your mouse outside one of the corners of the box, and you will see that the cursor turns into a circular arrow ( ) which shows that you can rotate the object. 3 Drag to rotate the object. The object will rotate around its centre point. To alter this rotation point, drag-and-drop the dot in the middle of the selected item to a new position (see right). Shift-dragging will rotate the object in 15 degree increments. Skewing an object 1 Select part of your image, or an object in your image then select the Skew tool ( ). A box with resize handles will appear around the selected item. 2 If you drag one of the centre handles, the item will lean to one side (see right). If you drag one of the corner handles, two corners of the item will move in or out (see centre right). Distorting an object 1 Select part of your image, or an object in your image then select the Distort tool ( ). A box with resize handles will appear around the selected item. 2 Drag any of the handles of the box. You can move each one independently (see right). Transforming objects For this exercise, use the file flags.png from the exercise_ resources folder. This file is a collection of world flags, each on a separate layer, and each with a drop shadow (which you will learn to apply later in this guide). Use the transform tools to create a montage of these flags. 1 Use all of the transform tools Scale, Rotate, Skew and Distort. 2 Change the stacking order of the layers to alter which flags are at the front. 3 You don t have to use all of the flags delete some layers or turn off their visibility. 4 Save several different versions of the file and compare the results. Resize handles Move this dot to change the centre of rotation. 12 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
17 project project 1 2 Bridge silhouette For this project, use the file bridge.png from the exercise_resources folder, which is a photograph of a bridge. Use the tools that you have used in previous exercises to create a stylised silhouette image like the one you see below right. Try some of the following techniques: Use the Polygon Lasso tool, the Lasso tool and the Paint Bucket tool to recreate the silhouette of the bridge and fill it with black. Select one of the colours from the water with the Eyedropper tool, then fill a Rectangle Marquee selection approximately the same shape as the water with that colour. Repeat the same process to make the sky. Change the order of the layers so that the bridge silhouette sits on top. Tracing faces For this project, use the file trace.png from the exercise_resources folder, or your own photographic image of a person s face. Use the tools that you have used in previous exercises, and the techniques you used in the previous project to trace over the image with selection tools and fill the selections with block colours. Try some of the following techniques: Use layers to separate the areas of colour. That way you can have overlapping edges. By reordering layers you should be able to get the effect you want. Alter the colours so that you get a different effect you could try black and white, pastel, psychedelic, etc. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 2: Modifying images 13
18 project 3 Montage For this project, use the file montage.png (which is a blank file) as a starting document, and the images from the montage_ resources folder inside the exercise_resources folder, or use your own images. Use the tools and techniques that you have used in previous exercises and projects, to create a montage of photos, similar to (but not the same as) the one on the right. Try some of the following techniques: Open each image separately and make some modifications to them, one-by-one. Make selections and paint out or delete sections. Edit > Cut or Copy and Edit > Paste the selections from the individual files into the main montage document. Once all the parts of images are in the main document, you can fine-tune the Scale and Rotation etc. of each part. Put each element of the image on a separate layer so that you can move things around and change things easily. 14 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
19 Creating pixels Using gradients, cloning images, applying filters and saving files In this section In this section, you will learn how to: Make new documents. Choose gradient settings and draw gradients. Make custom gradients. Clone pixels using the Rubber Stamp tool. Choose source pixels for the Rubber Stamp tool. Adjust Image Size and Canvas Size. Preview export optimisation settings. Making new documents All the documents that you have made so far have been based on modifying existing documents. Often you will need to create new, blank documents. To make a new document: 1 Choose File > New. The New Document dialog box appears. 2 Choose a Width and Height for your document. As web images are viewed on a monitor, and monitor resolution is measured in pixels, it s important to get into the habit of using pixels as the unit of measurement. 3 Set the document Resolution to 72 pixels per inch. This matches the resolution of a computer monitor. 4 Choose a Canvas Color; White, Transparent or Custom (choosing the colour from the colour chip). 5 Click OK. An empty document will appear, ready for editing. What is resolution? Bitmap (raster) images are made up of pixels, small blocks of colour. Export web graphics with appropriate compression settings. Make interlaced GIFs and progressive JPEGs. Adjust the colour balance of an image. Colorize an image. Adjust canvas colour. Add Gaussian blur to images. The resolution of an image is the number of pixels that the image contains, and is usually measured in pixels per inch. The resolution of web images should always be 72 ppi because this is the resolution of computer monitors. If you print a 72 ppi image onto paper, you will be able to see the pixels, which is why the quality of printed web images is poor. Printed images often contain 300 pixels per inch (which can also be referred to as dots per inch (dpi) and sometimes contain many more than that. 1 inch 1 inch 10 pixels per inch 1 inch 20 pixels per inch 1 inch 40 pixels per inch 80 pixels per inch Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 15
20 exercise 3.1 The Gradient tool The Gradient tool can be used to make smooth transitions between two or more colours in a number of different directions. Gradients can be used to fill shapes, to make backgrounds and to add dimension to shapes. Making a preset gradient 1 Select the Gradient tool ( ). 2 From the Properties panel, choose a Gradient type (see right). All of the gradient types appear in the pop-up menu so that you can see what they look like. 3 Choose a Preset colour from the Gradient colour pop-up menu (see right). 4 Drag the Gradient tool across the document. You ll see a circle where the gradient starts and a square where it ends (see right). Repeat this process until you get an effect you like (the gradient will be redrawn each time). Drag to draw gradient Creating a 3D gradient Choose a gradient Colour. Properties panel with the Gradient tool selected. tip Beware gradient-sickness! Be careful when you use gradients! Over-use of gradients can destroy the design of your image or web-page. Gradients can also be hard to print and hard to display smoothly on the web. Be subtle! Choose a gradient Preset For this exercise, you will make a new document and in it, create a circle with a gradient, to make it look three dimensional. 1 Create a new document (suggested size 300 x 250 pixels). Choose any colour background (not black or white). 2 Make a circular selection. Remember to Shift-drag to draw a perfect circle, and that Option/Alt-dragging will draw the circle from the centre. 3 Choose a Radial gradient, with White, Black as the colour Preset. 4 Drag to draw the gradient, the centre point (the white part) of which should be in the top right of the circle. This will make it appear as if the ball is shiny and has light reflecting off it (see right). 5 Save the image. Choose a gradient Type from the pop-up menu. 16 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
21 exercise 3.2 Making a custom gradient 1 In the Properties panel, click on the Gradient Colour pop-up. 2 Change the Colour Markers (below the Gradient Colours box) and the Opacity Markers (above the Gradient Colours box). The following should help; Click on a Colour Marker to choose a new colour. Click on an Opacity Marker and use the Opacity slider to adjust the opacity. Click just below the Gradient Colours box to add a Colour Marker. Click just above the Gradient Colours box to add an Opacity Marker. To adjust how the gradient or opacity changes, drag the Markers left or right. To delete a Marker, drag it away from the Gradient Colours box. Creating a sunset scene Gradient colours box Click on an Opacity marker and the Opacity slider will pop up. Click on a Colour marker and the Color palette will pop up. For this exercise, you will make a new document and in it, create a scene showing sky, sea, an island (or mountain) and a sun. 1 Create a new document (suggested size 400 x 300 pixels). Choose any colour background. 2 Create a new custom Linear gradient which will represent the sky at sunset (suggested colours; red, orange, pink, yellow). All of the colours should have 100% Opacity. Draw the gradient from the top to the bottom of the document. You will need to make a new Bitmap Image layer first. 3 Create another new custom Linear gradient which will represent the sea (suggested colours; blue, purple, pink). On a new Bitmap image layer, make a rectangle selection in the bottom half of the document and fill it with the gradient (drawing from top to bottom of the selection). 4 Create a new custom Radial Gradient which will represent the sun. Place two Colour markers at either end in yellow, and two Opacity markers at either end, the left of which is 100% opaque, and the right of which is 100% transparent. 5 Select the Oval Marquee tool and make sure that the edge has a Feather of at least 10 pixels. Draw a circular selection on a new Bitmap image layer and fill it with this latest custom gradient. 6 Lastly, draw some black mountains on a new Bitmap image layer. 7 Save the image. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 17
22 exercise 3.3 The Rubber Stamp tool The Rubber Stamp tool can be used to clone (copy) one part of an image and paint it onto another part of an image. It is useful for re-creating repeating patterns (like bricks in a wall, for example), textures or photographic elements (adding another cloud to a sky, for example); images which would be very hard to convincingly re-create any other way. Cloning an image The first stage of using the Rubber Stamp tool is to choose the area which will be cloned. 1 Select the Rubber Stamp tool ( ). When you move the mouse over the image, you ll see the cursor change into a target ( ). Click on part of the image to pick up that area for painting (see below). The next stage is to paint with the image that you have just picked up. 2 Choose brush settings in the Properties panel (see below). Choosing a large brush at first will make it easier for you to understand what is happening. Properties panel with the Rubber Stamp tool selected 3 If Source Aligned is ticked, it means that the source will always be chosen from an area relative to the position of the brush. If it is switched off, the source will remain in the same place (see below). Original image pick up area paint area Source Aligned turned on: pick up area moves relative to paint area. 4 When you paint on the image, you ll see a small cross in the pick up area, and a circle representing the size of the brush in the paint area. 5 To choose a new pick up area, Option/Alt-click on the new area. You will see the target again. Spraying graffiti pick up area For this exercise, use the file graffiti.png from the exercise_resources folder. You will see an image of some spraycan art on a wall. You will use the Rubber Stamp tool to fill the gaps, covering up the walls. 1 Use the Rubber Stamp tool to pick up areas to be cloned and paint with them on different parts of the wall. 2 Try with the Source Aligned setting both on and off and see if you can spot the difference. 3 Repeat the cloning process until you can no longer see the walls and you are left with an entire canvas of spraycan art. (Remember: use Option/Alt-click to set a new pick up area.) 4 Save the image. paint areas Source Aligned turned off: pick up area is fixed. 18 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
23 Adjusting image size Often you will need to adjust the size of your image to fit a specific space in a document or web page. For example, images taken on digital cameras are usually much bigger than necessary for screen-based projects. Resizing your images first will also mean that your computer has less work to do when editing them. Web graphics should be sized in Fireworks and never by scaling with HTML code. A 120k image which is 400 x 300 pixels will still be 120k if it is resized to 40 x 30 pixels on the web page, meaning that viewers will have to wait ten times as long as is necessary for the image to download. The resolution of web graphics should always be 72 ppi. Why? Because this is the number of pixels that your monitor displays. 1 To adjust image size, do one of the following: Choose Modify > Canvas > Image Size Without anything selected, click Image Size on the Properties panel (see below). Properties panel with nothing selected 2 In the Image Size dialog box, choose a new size for the image, using the Pixel Dimensions area at the top of the window, rather than the Print Size area at the bottom of the window (see right). Get used to thinking about measuring your document in pixels! 3 Make sure that you have the Constrain Proportions box ticked to stop your image from distorting. 4 The Resample Image box should normally be ticked, unless your image has a resolution higher than 72 ppi and a small print size. In this case, uncheck Resample Image and you will see that the Pixel Dimensions cannot be resized. Then it is safe to change the Resolution to 72 ppi (see below). tip Avoid scaling up Avoid making Image Size bigger (including resolution)! You cannot use pixels which aren t there, so a scaled up image will always reduce quality. Change image dimensions here High resolution Small Print Size Pixel Dimensions cannot be changed For an image with a high resolution and a small Print Size, uncheck Resample Image and you will see that the pixel dimensions will remain constant. Then you can change the Resolution without fear of getting rid of too many pixels. 5 When you click OK, the image may look like it has shrunk on your screen, but is probably just displaying much smaller than it actually is. To see an accurate picture on the screen, display the image at 100%, either by double-clicking the Zoom tool or using the Zoom pop-up menu at the bottom of the document window. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 19
24 exercise exercise Adjusting image size For this exercise, use the file flax.png from the exercise_resources folder, or use an image of your own. It is an image taken from a digital camera, and is 800 x 600 pixels. 1 Resize the image to 250 x 188 pixels, making sure that the resolution is also 72 ppi. 2 Save the image. Adjusting canvas size Often you will need to adjust the size of your canvas, either to put more space around the image, or to make the image a specific size. Cropping is one way of making an image smaller changing the Canvas Size is a more precise way to get exact pixel values. 1 To adjust canvas size, do one of the following: Choose Modify > Canvas > Canvas Size Without anything selected, click Canvas Size on the Properties panel. 2 In the Canvas Size dialog box (see right), choose a new size for the image. A larger size will add extra space around the image, a smaller size will crop the image. (Bear in mind if you make it smaller that you may lose some of your hard work!) The current size of the image is displayed at the bottom of the box. 3 Choose an Anchor for your image. If the Anchor is in the centre, space will be added (or taken away) equally all around the image. If it is in the top left-hand corner, space will be added (or taken away) on the right and at the bottom (see right). 4 If you need to, match the canvas colour to the background of your image by clicking on the Canvas colour chip on the Properties panel (see below). The Properties panel with nothing selected Adjusting canvas size Canvas colour chip For this exercise, use the file timetrac.png from the exercise_resources folder. It is a corporate logo, and has an uneven amount of space around it. 1 Change the Canvas Size of the image to 287 x 134 pixels, making sure that the extra space is added at the top and on the left. The image should now sit evenly on the canvas. 2 Change the colour of the canvas to one that you like. 3 Save the image. tip Image size Web image size is always relative to monitor and browser window size. A common monitor resolution is 800 x 600 pixels. A maximised browser window on an 800 x 600 pixel monitor shows up to 760 x 420 pixels. People with larger monitor sizes don t always have their browser windows maximised! 20 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
25 Exporting web graphics So far you have been saving images in PNG format, the Fireworks native format. In order to save images to display on the web, or to send via , you must save them in a slightly different way, and usually in a different file format. tip PNG compression Since web and images get transmitted across the internet to other people s computers, you should keep in mind that the smaller the image, the faster the download time. Of course, it s also important that your image looks good, so the trick is maintaining the quality of the image while keeping the file size at a minimum. You can do this by recognising what type of image you have and deciding what sort of compression to use. Image types You can normally classify web images into one of the following three categories: Flat-colour images have areas of solid colour which usually contain a limited number of colours (less than 256). Line art, logos and illustrations are all examples of flat-colour. These types of images should be exported with GIF compression. Full-colour images contain a broad colour range and continuous tones which can contain a large number (up to 16+ million) of colours. Photographs, paintings and images with gradients are all full-colour, because you can t tell where one colour ends and another begins. These types of images should be exported with JPEG compression. Greyscale images contain shades of grey anywhere between and including black and white. Black and white photographs and pencil or charcoal illustrations are all examples of greyscale. Depending on what s in the image, greyscale images can be exported with either GIF or JPEG compression. The GIF format GIF compression reduces the number of colours in an image to 256 colours or less. Fewer colours = smaller file size = faster download time. The idea is to get as few colours as possible in the image without affecting the quality of the image too much. Remember that GIF compression is best applied to flat-colour images. GIF compression produces some obvious issues when applied to photographic images (see right). The JPEG format JPEG compression discards data that is not likely to be important. Less data = smaller file size = faster download time. Image type The idea is to lower the quality of the image as far as possible without affecting the look of the image too much. Remember that JPEG compression is best applied to full-colour images. JPEG compression produces some obvious issues when applied to flat-colour images (see right). As well as being the Fireworks native format, the PNG format can be used to compress both types of images (PNG-8 for flat-colour images, and PNG-24 for full-colour images) and has excellent support for transparency, but a larger file size. Although supported, PNG files are not widely used by the web design industry. Flat-colour Full-colour Gradient Greyscale Black and white Photographic Contains transparency Animation File format GIF/PNG-8 JPEG JPEG GIF or JPEG GIF/PNG-8 JPEG GIF/PNG-8 GIF Saving photographic images with GIF compression results in noticeable banding. Saving flat-colour images with JPEG compression often results in noticeable artefacts. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 21
26 Exporting a web image 1 At the top of the document window you should see a series of buttons: Original, Preview, 2-Up and 4-Up. 2-Up and 4-Up allow you to compare the original image with a preview of the compressed version or versions (see below). Compression type Size of compressed file Download time Click here to see (and edit) the original image. Click here to see original image plus 3 other export previews. 2 Using the 2-Up or 4-Up view, select one of the preview images. Compression settings 3 In the Optimise panel, choose settings to apply to your image. You will see the compression information change, and you will also see how large the resulting exported file would be, and how long it would take to download (see above right). 4 Choose File > Export. The Export dialog box opens, (see below) and from there you can choose a file name for your image (remember that it must have a threeletter file extension!) and save it into an appropriate place on your computer. The Save As option in the lower half of the window should be set to Images Only (otherwise you will export all sorts of other files that you may not need). tip Image size Exporting If, when you choose File > Export, Export is greyed out, click back on the image with the Pointer tool. Export dialog box Windows XP Export dialog box Mac OSX 22 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
27 exercise 3.6 GIF settings The Optimize panel shows a number of options when you export a GIF file. From the Maximum number of colours pop-up menu, choose a preset number of colours, or type in your own number. You will see the preview changing to reflect this. Remember, the less colours used, the smaller the file. From the Indexed palette pop-up menu, choose a palette to map your image to. This refers to the palette of colours that Fireworks will choose from (see table on right). There are a number of predefined palettes in Fireworks and the best way to understand what they do is to play around a bit and see the effect that you get. Export file format pop-up menu Indexed palette pop-up menu Dither amount Change the dither amount from the Dither pop-up menu. Dithering is a way to simulate colours that are not available in the chosen colour palette by alternating two pixels of colours that are (see right). When the Dither option is set to 0%, all colours in the image shift to the nearest colour in the palette. Dithering an image can increase its quality, particularly if the original has lots of colours. You can turn Interlacing on in the Options pop-up menu on the Optimize panel. An interlaced image loads blurry then gradually increases in detail. Colour palettes Adaptive Web Adaptive Web 216 Exact Grayscale JPEG settings The Optimize panel shows a number of options when you want to export a JPEG. From the Quality slider pop-up, choose a quality for your image. You can also type the number into this box. The lower the quality, the smaller the file size. Turn on Progressive JPEG in the Options pop-up menu on the Optimize panel. A progressive image loads blurry then gradually increases in detail, similar to an interlaced GIF file. Exporting images Options (to set Interlacing) Maximum number of colours For this exercise, use the files mountain.png, aksamba.png and kete.png from the exercise_resources folder, or use your own images one photographic image, one flat-colour image and one mixed image. Open each image in turn and, after choosing Optimize settings for it, Export it, remembering to give it the appropriate file extension. The kete image, with mixed graphic types, will require experimentation with Optimize settings. Compare the quality and file size and choose the one which you think suits the image best. The most common colours from your image. Colours close to web safe colours shift to nearest web safe colour 216 colours that always display consistently crossplatform (Mac-PC). Exactly colour matches. Only available if 256 or fewer colours used. 256 or less shades of grey. This is the same (zoomed in) image of two shades of pink; the first one uses a number of colours to make the exact colours; the second one uses red and white and dithering to make it seem as if there is pink. Options JPEG quality Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 23
28 Filters Fireworks has a limited number of Filters which can be applied to change an image. Use the Filters menu when you want to blur or sharpen part of an image, or alter the colour or brightness of an image, amongst other things. First, select the image, either by clicking on the image with the Pointer tool, or by selecting the Bitmap Image layer in the Layers panel. If the image is not selected, the Filters menu will not be active. All of the filters can also be applied to part of an image only. Use selection tools to isolate part of an image to change. Adjusting colour Auto Levels Choose Filters > Adjust Color > Auto Levels. This will adjust the brightness and contrast of the whole image so that black is really black and white is really white. Most of the time the Auto Levels command will do a good job (see right). However, if you have an unusual image, or if you want an unusual effect, you may have to try adjusting the levels manually (Filters > Adjust Color > Levels). Brightness/Contrast Choose Filters > Adjust Color > Brightness/Contrast and the Brightness/Contrast dialog box will open (see below). Adjust the controls to change the image (see right). If you have the Preview option ticked, you will be able to see the adjustment before you click OK. Hue/Saturation Choose Filters > Adjust Color > Hue/Saturation and the Hue/Saturation dialog box will open (see below right). Adjusting the Hue slider will control the colour of the image. Adjusting the Saturation slider will control the amount of colour in the image, and adjusting the Brightness slider will lighten the entire image. If you tick the Colorize box, all of the colours in the image will be converted to different shades of the same colour. Using the Colorize box and a yellowish hue will create a sepia tone, like an old photograph. Bringing the Saturation down as far as it will go will result in a greyscale image. tip Double-compression Because the JPEG format discards data, it is important to export JPEG files only once never reopen an exported JPEG file and export it again. Edit and save your image in a format that does not discard data (such as the Fireworks PNG format), and export in JPEG format only as a final step. Original image Original image Original image After Auto Levels applied. After Brightness/Contrast adjusted. After Hue/Saturation adjusted. 24 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
29 exercise exercise Adjusting colour For this exercise, use the file alicia.png from the exercise_resources folder. It is a fairly dark image, without much contrast, and has a distinctly blue tint. 1 Apply the Auto Levels filter to give the image more contrast. 2 Use the Hue/Saturation filter to Colorize the image and give it a sepia tint. 3 Save the image and export it as a JPEG file, using the Optimize panel to achieve a high quality, small sized file. Blurring images Gaussian blur Original image After Auto Levels applied. After sepia tint applied. There are a few blur filters to choose from in Fireworks. Gaussian Blur will give you much more control than just a standard Blur filter. To apply a Gaussian Blur, select the image, or part of the image that you want to adjust, and choose Filters > Blur > Gaussian Blur. The Gaussian Blur dialog box will appear and you can adjust the amount of blur and preview the results. Applying Gaussian Blur For this exercise, use the file pohutakawa.png from the exercise_resources folder. You will blur part of this image. 1 Draw a selection around the pohutakawa flowers on the right-hand side of the image, using the Lasso tool with a 20 pixel Edge Feather. The selection doesn t have to be very accurate since the feather will smooth out inconsistencies. 2 When the selection joins up, the dotted selection line will look very rounded with little detail. Don t worry! This is because of the feather (see below). 3 Choose Select > Select Inverse to select everything except the flowers. 4 Apply a Gaussian Blur with a setting that you like. 5 Save the image and also export it as a JPEG. Original image After Gaussian Blur applied to part of the image. The Lasso selection as it is being drawn. The Lasso selection showing smoothing of Feather setting. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 25
30 project project 4 5 Repeating background gradient You may have seen some websites, like the ones pictured right, which have a gradient running down the left hand side or running across the top. These are simply long skinny images which are repeated down (or across) the page. In this project you will make an image which is suitable for this purpose. 1 Make a new document of approximately 150 x 150 pixels. This is a different size and shape from the final file, but it will be much easier to fill this shape with a gradient. 2 Make a custom gradient and draw it horizontally across the document (see right and below right). 3 Crop the document so that it is only about 10 pixels high. 4 Change the Canvas Size of the document so that it is 1500 pixels wide (wide enough so that people with large monitors don t see it repeat horizontally). Make sure the gradient is anchored on the left side of the document. 5 You should now be left with an image like the one below. Save and export the file with an appropriate file format. Photo retouch The Rubber Stamp tool can be used to get rid of marks or scratches from old or damaged photographs, or to get rid of someone s spots or wrinkles. This kind of technique is often called photo retouching. Use your own scan of an old photograph, or use the file retouch.png from the exercise_ resources folder. 1 Use the Rubber Stamp tool to get rid of the scratches, blotches and marks from the photo. Use a small brush size and zoom in for more accurate work. 2 Think about making a new layer for the cloned areas that way mistakes can be easily erased. You must tick the Use all Layers option in the Properties panel to use this technique. 3 Save the file, then export it using an appropriate format. Original image Retouched image 26 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
31 project project 6 7 Colour details Changing the Hue and Saturation of just part of an image can be used to good effect if you want part of a black and white image to be coloured. Use the file nzflag.png from the exercise_resources folder, or use your own image. 1 Resize the image so that it is 400 pixels wide. 2 Using the Lasso tool or another selection technique, select the flag from the middle of the photograph. Consider using a small Edge Feather setting. 3 Inverse the selection to select everything except the flag. 4 Using the Hue/Saturation filter, reduce the colour saturation of the selected area so that it appears to be greyscale. 5 Save the file, then export it with an appropriate format. Blur gradient By combining some of the techniques that you have used in the previous section, you can obtain some quite sophisticated effects. Use the file harakeke.png from the exercise_resources folder, or use your own image to recreate the effect that you see below right, which might be suitable for a web page heading image. 1 Use a feathered selection and a Gaussian Blur to blur the bottom edge of the photograph. 2 Use a custom gradient on a layer above the photograph, with one end of the gradient being a colour with 0% Opacity. 3 Save the file, then export it using an appropriate format. Final image Opaque to transparent gradient Feathered selection Final image Cropped image with feathered selection, Gaussian blur Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 3: Creating pixels 27
32 project 8 Mix and match The Rubber Stamp tool can also be used to have fun with details. Use a photograph of yourself and a friend, or scan some images of well-known people and use the Rubber Stamp tool to clone part of one person onto another. Consider the following things while you make your image(s): When you are taking or scanning your photograph, try to get both people face on, at the same distance from the camera. That way the faces and features will be more equal in size. Use small brush sizes for fine details. Make lots of variations of the image get really weird if you have time! Try applying Auto Levels to the images to help balance the colours before you start. Save and export a number of versions of the image. 28 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
33 Creating vectors Using vector tools, adding text and applying filters In this section In this section, you will learn how to: Create simple vector shapes and Auto Shapes. Reshape vector paths using the Reshape Area and Freeform tools. Draw curved, tangent and corner points using the Pen tool. Combine shapes using the Combine Shapes commands. Fireworks bitmap and vector modes Fireworks has two different modes to work in, bitmap mode and vector mode. Bitmap mode allows you to edit bitmap images by painting pixels onto them, adjusting their colours and applying filters. Editing done in bitmap mode is hard to adjust afterwards. You have to either go over what you have done, or undo the editing and try again another way. Vector mode allows for more versatile editing because vector shapes can be manipulated easily by moving the adjustment handles on the vector paths. When the image is exported as a web-ready file, the vector image is converted into a bitmap image (rasterised). Fireworks will automatically switch between the two modes, depending on what tool you are using. Bitmap vs vector graphics Many graphics applications use the terms bitmap (or raster) and vector graphics. It is important that you understand the difference between these two formats. Bitmap graphics are made up of pixels. This means that an image is made up of a grid of colours (the pixels). Each pixel is assigned a specific location and colour value. With bitmaps the bigger the image size, the larger the size of the file. Resizing a bitmap can affect the quality of the image. Vector graphics are up made of lines and curves defined by mathematical objects called vectors. Vector shapes contain points, which join paths, and can have fills. Vector graphics can be reshaped very easily, and you can change their size without affecting their quality. A vector graphic is scalable; it doesn t matter how big you make it, the file size and quality will stay the same. Make a transparent GIF. Specify a Matte colour for transparency. Make and format text for text headings. Add live filters to objects. Adjust filters. This vector circle is made up of four points joined by a mathematical equation. This bitmap circle is made up of squares or pixels of colour. This is a bitmap and a vector object at 100%. They are both of equal quality. This is the same image scaled to 400%. Notice how the oval that was on the left (the bitmap) has become very pixelated around the edges and decreased in quality. The vector oval on the right has been scaled without any loss of quality. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 4: Creating vectors 29
34 Working in vector mode Fireworks has a range of tools for drawing, from basic shape tools to freeform tools for drawing more complex shapes. All vector shapes are editable after they have been drawn. You can change their size, shape and the number of points they have. The advantage of working with vector shapes and paths is that you can easily scale objects up and down without losing quality. On export, Fireworks converts these vector-based objects into bitmaps, so that they will display on a web page. Drawing vector shapes There are a number of pre-defined vector shapes that you can use. 1 Select one of the vector shape tools (see right). In the Properties panel, choose a fill colour, a stroke colour and a stroke width for the shape (see below). 2 Drag across the document to draw a shape. Shift-drag to constrain the proportions of the shape that you are drawing. Option/Alt-drag to draw from the middle of a Rectangle or Ellipse. Properties panel with the Ellipse tool selected Using Auto Shapes There is a series of Auto Shapes grouped with the simple vector shape tools (see right). These all work in different ways, but all of them have yellow modification handles which allow certain editing of the shape. Hovering your mouse over one of the modification handles often brings up a tool tip showing what that handle does (see below for examples of Arrow, Pie and Star). Choose Stroke and Fill settings for these shapes the same way that you would for simple shapes, using the Properties panel. Roundness Vertical position Arrow size Arrow tip Horizontal position Thickness Changing a vector path Option/Alt-drag to segment. Click to reset. Point angles Number of points Inside angles Roundness Inside roundness Reshape Area tool The Reshape Area tool is a visual way of changing vector path outlines quickly and easily. 1 Select the Reshape Area tool ( ), and in the Properties panel, choose a Size and a Strength for the tool (see below). The pointer s inner circle is the boundary of the tool at full strength. The area between the inner and outer circle reshapes paths at less than full strength. 2 Drag the tool across the path. You will see the inner and outer circles, representing the gravitational pull of the tool (see right). Rectangle tool Ellipse tool Polygon tool Arrow Beveled Rectangle Chamfer Rectangle Connector Line Doughnut L-Shape Pie Rounded Rectangle Smart Polygon Spiral Star Properties panel with the Reshape Area tool selected. 30 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
35 Freeform tool The Freeform tool works in a similar way to the Reshape Area tool, but allows you to pull, as well as push the line. 1 Select the Freeform tool ( ), and in the Properties panel, choose a Size for the tool. Properties panel with the Freeform tool selected. 2 Move the mouse near to the outside of the shape, and you will see the cursor change into a pull cursor ( ). Drag to pull the vector path into shape. 3 Drag inside the path to push the vector path into shape. The cursor will turn into a circle (see right). tip Ungrouping shapes If you want to use the Freeform or Reshape Area tools on a rectangle, you may have to ungroup the shape to turn it into an editable path. Choose Modify > Ungroup. Drawing with the Pen tool The Pen tool lets you create complex paths. The best way to understand how the Pen tool works is to practise using it. 1 Select the Pen tool ( ), and choose Fill and Stroke settings in the Properties panel. Properties panel with Pen tool selected. tip 2 Use a combination of clicks and drags to create a path. Once the mouse gets back to the starting point, the shape will close and fill with the appropriate setting. See below for an explanation of how combinations of clicks and drags create paths. The anatomy of a point Points on a path are either corner points, tangent points or curve points. Change what type of point exists by clicking on it with the Pen tool: Curve point + click = corner point. Corner point + drag = curve point. Editing Auto Shapes It is possible to edit an Auto Shape, but the auto elements may not work predictably afterwards. A warning may pop up and tell you this. Create a tangent point by Option/Alt-dragging on a corner point, using the Subselection tool ( ). Click and drag to make a curve point. Tangent point (one or two control handles). Connects straight or curved paths with curved paths. Curve point (two control handles). Connects two curved paths. Moving one control handle always moves the other in the opposite direction. Corner point (no control handles). A path between two corner points is always straight. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 4: Creating vectors 31
36 exercise 4.1 Combining shapes You can also create complex shapes by combining basic shapes, using the Modify > Combine Paths set of commands. Two shapes. Union removes overlap creating one big shape. Creating a vector face Punch knocks the top shape out of the bottom shape. For this exercise, you will make a drawing of a face, entirely using vector shapes and the Pen tool. Three shapes. Intersect makes a shape only where the three shapes overlap. 1 Create a new document (suggested size 300 x 300 pixels). Choose any colour background (not black). 2 Using the Ellipse tool, make a shape suitable for the face. Using the Freeform or Reshape Area tool, push out a chin and two ears. Use the Freeform or Reshape Area 3 Make another filled ellipse, this time for the hair. Switch the layers so that the hair is behind the face. tool to make a chin and ears. 4 Make a dip in the top of the face so that it looks as if the hair comes down over the face like a fringe. 5 Use the Pen tool to draw a mouth. 6 Use the Pen tool to draw a shirt, on a layer underneath the face. 7 Use an Auto Shape to draw two lenses for sunglasses. Join the lenses up with another shape, then join the two shapes using Modify > Combine Paths > Union. Use the Pen tool to draw a mouth. 8 Save the image and export it, using an appropriate compression type. Crop makes a shape only where the topmost shape overlaps those underneath. Join makes a compound path from all the paths. Split attempts to split apart a compound path. Use the Reshape Area tool to make a fringe. Tangent points Curve points Use this as guide to know where to place your points. Make sure the layers are in the right order. 32 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
37 Transparent GIFs The GIF format allows you to specify transparent areas in an image. This is particularly useful if you want an image to blend seamlessly onto the coloured or patterned background of a web page instead of looking like a box placed on the page. Any transparency in a Fireworks file (a transparent background, for example) can easily be specified as being transparent when the image is exported. 1 In the Optimize panel, choose GIF format (only GIF and PNG support transparency) and choose a number of colours for the image. Always compare how the image looks and how big the file size is. Also make sure that you have the Transparency setting set to Alpha Transparency (see right), which uses any transparency in the document. 2 By default, Fireworks assumes that the background of your web page will be white. If you leave the Matte colour as it is, on white, you will get a noticeable halo effect around your text when you put it into a coloured web page (see right). To match the colours perfectly, always write down the background colour of web pages that you make. 3 Set the Matte colour chip to match the colour of your web page. If you haven t yet made a web page, you will need to export your image again when you have, so that you can set exactly the right colour. In the Preview window (see right), the effect will be noticeable, but don t worry! On a web page of the same colour it will look perfect! Working with text You can make text in Fireworks and have quite a lot of control over its appearance. Text in Fireworks is live, meaning that it can be edited at any time even when it has effects applied to it, as long as you save your files using the PNG format. Text images made in Fireworks can be used as headings or titles for web pages, or as text on buttons which control interactivity on a website (see below). Graphic vs regular text Text made in Fireworks should only be used for headings and buttons on a web page, never for large blocks of text. Text blocks are best made as HTML text, in a text editor or software like Dreamweaver. This is because the file size of an image is much larger than a block of HTML text, meaning that it will take much longer to download. Matted onto white. See the halo? Graphic text Matte colour Transparency setting Matted onto purple. Perfect! Regular text Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 4: Creating vectors 33
38 Making a text heading When making a web page, you will often need to create text headings using image editing software like Fireworks. This allows you to use fancy fonts and to add effects like drop shadows. Select the Text tool ( ), and choose settings for it in the Properties panel (see below). Tool tips will appear when you hold your mouse over settings, explaining what each one does. Text will take on these settings. Properties panel with the Text tool selected. To change the settings of text after it has been typed, make sure that you select it first and then change the settings, just as you do with any software program. Adding filter effects Fireworks allows you to apply typical web effects, such as, bevels, drop shadows, glows and embossing. These effects can be applied to any vector or bitmap object, including text, using the Filters pop-up menu on the right-hand side of the Properties panel. Filters are live, meaning that when you edit an object, the filter is updated at the same time. The Filters menu also allows you to apply Filters as live filters. You can add lots of filters to the same object. 1 Select the object and click the Add filter button at the right-hand side of the Properties panel. The new items in the Filters menu are Bevel and Emboss and Shadow and Glow menus. All of the other items are also in the Filters menu. 2 Choose the filter that you want to apply. Adjustment panels for each filter will show, allowing you to choose particular settings for the filter (see below). Bevel edge shape Width Softness Angle Button Preset This is an Inner Bevel from the Bevel and Emboss menu, with the displayed settings applied. Note: If it is likely that the file will be edited later using Photoshop, choose effects from only the Photoshop Live Effects filter as these are fully compatible with Photoshop. To adjust a filter, double-click its name in the Filters box of the Properties panel. The filter adjustment panel will display again. To remove a filter, select it in the Filters box and click Remove Filter. To hide and show a filter, toggle it on and off by clicking Hide/Show Filter in the Filters box. Font Alignment Kerning (space between letters) Leading (space between lines) Anti-alias settings Contrast Distance Colour Opacity Softness Angle Show only shadow This is a Drop Shadow from the Shadow and Glow menu, with the displayed settings applied. Add filter Hide/Show filter Remove filter Many of the effects found in Photoshop Live Effects are similar to Fireworks filters, however they are editable in Photoshop if the document is saved as a Photoshop (.psd) file. 34 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
39 project exercise Creating a text heading For this exercise, you will make a text heading suitable for placing onto a web page. 1 Create a new document (suggested size 450 x 80 pixels) which has a Transparent background. This background is very important for later when you want to export some transparency with the image. 2 Type Welcome or something similar in any language, anywhere on the document. Format the text however you like, in whatever colour you like. Try changing at least the font, size, colour and kerning of your text. 3 Add a drop shadow to the text from the Add Filter pop-up list (Shadow and Glow > Drop Shadow). Adjust the shadow to suit (see right). 4 Experiment with the text settings and the filter settings until you get a look that you are happy with, and which doesn t make it difficult to read and understand the text. 5 Save and export your text heading as a GIF, with a transparent background. Although you don t have a web page to put this heading onto, Matte the image onto a coloured background in the Optimize panel, so that you can have a go at setting the Transparency settings. In this case it is vital that you save your file as a PNG, because you may want to come back later and choose a different matte colour. Button The shape tools, combined with the Text tool and Fireworks live filters can be used to good effect to make buttons for websites that is, images which appear to stand out from the page. In this project you will make a button using shapes, text and effects. 1 Make a new document which is fairly small (suggested size 100 x 50 pixels) with a Transparent background. 2 Make a Rounded Rectangle Auto Shape for the button itself and control its appearance, including how round the corners are, using the Adjustment handles surrounding the shape. The tool tips will tell you what each handle does. 3 Add a bevel effect to the button. Experiment with the different types of bevels in the Filters menu until you find one that you like. An Inner Bevel setting is shown on the right. 4 Make some text for the button, which will automatically appear on a new layer. Make sure the type is legible and fits in with the style and colour of the button. 5 Save and export the button with transparency and a colour matte. Transparent background Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 4: Creating vectors 35
40 project project Logo trace Vector mode is really useful for re-creating logos that way the logo can be resized and easily re-coloured to fit on any sort of web page. In this exercise you will trace a logo which has been supplied to you. The owner of this logo wants it to be bigger and to be on a dark red, rather than a blue background. The file they have given you is a bitmap image, so cannot be scaled up without losing quality, and to try to select the blue and change it would be extremely difficult. In this case, the easiest thing is to use the existing logo as a guide to trace over using the Pen and Text tools. Use the file logo.png from the exercise_resources folder. 1 This file is the correct size already, and has the existing logo locked into the background layer. You will work on layers above the background layer. 2 Trace the outline using the Pen tool, and a combination of corner and curve points, Shiftclicking to make exactly straight lines (see right to find out the best place to put the points). 3 Use a different colour to trace objects at first, so that you can see what you are doing better. Once you have finished you can change them to the correct colours. 4 Duplicate the layer with the outline, and give the bottom layer a bigger and lighter yellow stroke. This will give the illusion of a line with an outline. See right for an idea of the layers you might end up with. 5 Use individual text letters for the text at the bottom (suggested font; Arial Black). You will probably have to use the Scale tool to match the size of the letters more accurately. 6 You will have to make the middle letter yourself using the Pen tool to make two shapes (one for the letter and one for the hole in the middle) and using the Punch command to knock the hole out of the middle of the letter. 7 Don t forget the drop shadow on the text! 8 Make the background layer invisible to check and export your work. 9 Save and export the logo with a transparent background, matted onto a dark red colour (for example, #99FFFF). Create a logo Using vector shapes, text, effects and the Pen tool, design a logo for yourself. Put your ideas down on paper first you will find it much easier when you come to work on the computer. Don t go overboard with colour or special effects remember that the logo should convey something about you you don t want people associating you with chaos or bad taste! The existing logo 36 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
41 Composing web pages Building, slicing and exporting web site page layouts with buttons and rollovers In this section In this section, you will learn how to: Make and name slices. Optimise slices. Save a GIF palette. Load a saved palette. Export individual slices and multiple slices. Designing a website in Fireworks When designing a web page it is easier to design the whole layout as a single document rather than several individual files for images, buttons, rollovers, etc. However, you do not want the web page to load as one large image as this will create a large inefficient file. Slicing is a feature that allows you to divide a layout into multiple parts, eg individual navigation buttons, images, or other content areas. Each part can later be saved as an individual file with its own optimisation settings. The parts can then be reassembled on the web page so that they look like a single image again. Empty or text areas of the page can be replaced with more efficient (X)HTML code. Using the Pages panel you can create multiple pages for your website within the same Fireworks document. The Frames panel or symbol buttons allow for different rollover states to be specified. Create multiple paged documents. Create navigation buttons using slicing and button symbols. Create rollover images. Create hotspots for image maps. The Export feature can be used to generate (X)HTML to layout the slices. Links can be generated, however scripting for rollovers, image maps or other special features must added manually. Many web designers prefer the option to export only the slices so that they can manually assemble the entire page using hand coding or a web design application. Slicing The aim of slicing is to isolate areas of the page that require (or could benefit from) special treatment. Consider the following areas of a page to slice: Navigation buttons. Hotspots and rollover areas. Areas of plain colour that could be replaced with code. Flat areas suitable for GIF or PNG compression. Continuous tone areas suitable for JPEG compression. Areas of the layout that change across multiple pages in a site. Note: Avoid making too many little slices as this may have a negative efficiency as they require more code, more calls to the server and more work for the browser to do. This typical web page layout has been sliced so that the title and button graphics will be exported separately. The large area designated for text can be replaced with (X)HTML code. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 5: Composing web pages 37
42 Slicing an image It is important, before you start slicing images up in Fireworks, to plan on paper how you will make the slices. The aim is to make the least number of slices possible, to slice in sensible places, and to use optimisation wisely. 1 Using the Slice tool ( ), draw a box around the area that you want to be the first slice. You will see a green overlay on your image. If you don t, make sure that Show Hotspots and Slices is turned on ( ). In the Layers panel, you will also be able to see one green shape in the Web Layer set (see right). 2 You should get into the habit of naming all of your slices, so that when you are making complicated documents with lots of slices, you are quite clear about which slice is which. Fireworks will assign names to slices, but they are hard to make sense of. Select the slice with the Pointer tool, and in the Properties panel, give it a sensible name in the Slice Name box (see below). 3 Separate slices can be optimised individually. This means that part of your image can be exported as a JPEG, and another part as a GIF, if that is what suits your image. Check the Preview, 2-Up or 4-Up window to see how the compression looks. 4 To export the sliced document, choose File > Export. 5 From the Export options choose to export HTML and Images or Images Only if you want to assemble the slices manually by code or using a web page editor such as Dreamweaver. By default the HTML produced is Dreamweaver style XHTML using tables for assembling the slices. Click the Options button to modify the code output options. Note: If you want to have your slices assembled using CSS you can choose the CSS Layers option from the Export options, however, be aware that the HTML code produced is not XHTML, even if you have XHTML selected in the options! 6 Choose any other options. Put images in Subfolder is recommended if you are exporting HTML. The Selected Slices Only option is useful if you are just updating a portion of your page (selected beforehand). 7 Navigate to a suitable location and provide a file name. This name is used for any HTML files and as a basename for any unnamed slices. 8 Click Export. Properties panel with a slice selected Saving palettes Slice Name When you slice up a GIF-type image, you will end up with two or more images which you want to join up on a web page. In order to make the colours exactly the same, and so join seamlessly, the colour palette that you use should be exactly the same for both images. For empty or plain coloured slices you can change the Type to HTML to prevent unnecessary image files being exported. 1 Set optimisation for a slice in the image which contains the Add colour most colours. If you need to add a colour or colours to the palette manually, you can do that by clicking the Add colour button at the bottom of the Optimize panel (see right). 2 From the drop-down Options menu in the top right-hand corner of the Optimize panel (see right), choose Save Palette (see right). Save it somewhere sensible (probably the folder which you are working from) because you will need it later. tip Hiding slices After you ve edited slices, click in the Tools panel to hide the distracting green overlays. Options 38 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
43 exercise exercise Slicing an image For this exercise, you will slice up an image file, making two images to stick together later in an HTML editing program. Use the file ruapehu.png from the exercise_ resources folder. This file contains different types of images (photographic and graphic) and requires two different sorts of optimisation. mountain 1 Make slices to divide up the areas of the image as shown on the right. Name each slice. 2 Select each slice individually and choose optimisation settings that you think are suitable, checking the 2-Up or 4-Up window to compare with the original. 3 Save the PNG file and export both of the images (but no HTML code). Slicing a web page 3 Select each slice (or /Ctrl-select several slices at once) and from the Options menu in the Optimize panel, choose Load Palette Browse to the palette which you previously saved. This will ensure that all of the colours, particularly the ones which join up, are exactly the same. For this exercise, you will slice up a web page, making several images to stick together later in an HTML editing program. Use the file squidgee.png from the exercise_ resources folder. Some dummy text has been placed into the document to show where the regular text will go when the web heading page is constructed. 1 Make slices to divide up the areas of the image as shown on the right. legs 2 Name each slice. home 3 Select the topmost slice These centre sections can be and choose some GIF about exported once and optimisation settings that reused twice, as project you think are suitable, they are exactly the same. checking the 2-Up or 4-Up bottom window to compare with the original. 4 Save the palette so that you can make sure the colours are exactly the same. 5 Select each of the other slices and load the saved palette in the Optimize panel. 6 Save the PNG file and export all of the images and HTML code if you like. 7 Assemble/edit the page in a web page editor. Regular text not exported words tip Reusing slice images Check your document for slices that share the same content. In this exercise the slices between the navigation buttons are exactly the same. In a code editor you can change the image link code to use only one of the gap slice images and discard the rest. This will help reduce the page download time. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 5: Composing web pages 39
44 Composing multiple page web sites Most web sites will have more than one page, yet they typically maintain a consistent structure with only the content that changes. To help maintain consistency and save time, it makes sense to develop the different pages or sections of a web site in the same document. This can be done using the Pages panel. Choose Window > Pages (or click the Pages tab) to display the Pages panel. Adding new pages To create a new blank page: Click the Add/Duplicate Page button at the bottom of the Pages panel. Note: Each page has its own set of layers and you can modify the size of each page. To view a different page, simply click on it. Duplicating pages Often each web page will have the same general layout, while the content changes. To ensure consistency and save time you can duplicate a page and then modify only those layers that need changing. For example, after duplicating you can modify a title while retaining all formatting and styling. To duplicate a page: Drag the page (in the Pages panel) onto the Add/Duplicate page button. Using a master page When page is defined as a master page, its contents are copied to the bottom layer of all other pages in a document. The advantage of this method over duplicating pages is that common elements cannot be accidently changed, and if changes are required they only need to be made to the master page. A disadvantage is that items cannot be modified on individual pages, so make sure you don t include items that will change, eg titles. To define a master page Select a page and choose Set As Master Page from the Page panel s menu. Linking existing pages to the master page When a master page is defined any existing pages will take on only the master page s content and not its page properties (canvas size and colour). To match an existing page s properties with the master page, click the column to the left of the layer to link it. Removing master pages from a single page Select the page and then in the Layers panel, drag the Master Page Layer to the trash. Alternatively you can hide it by turning off the layer visibility. Resetting the master page From the Pages panel s menu choose Reset Master Page. Sharing layers between pages Yet another way to consistently apply a layer between a range of pages is by sharing. 1 Select the layer to share and choose Share Layer to Pages from the Layers panel menu. 2 Use the Add or Remove pages to specify which pages will include the shared layer, then click OK. Layers that are shared from another page are highlighted in yellow. If they are edited on one page, the changes are updated on all pages that share the layer. To remove a layer from pages, repeat steps 1 2 and use the Remove button to exclude the layer from those pages. 40 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Click here to hide master layer contents. Drag an existing page to duplicate it. Add/Duplicate Page tip Rename pages Double-click on a page s name to rename it with something more descriptive. Panel menu Click in this column to link an existing layer to a new master page. Panel menu Drag master page layer to trash to remove it from a single layer. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
45 exercise 5.3 Interactive navigation buttons and rollovers Buttons that provide visual feedback to users will enhance the experience a visitor has when navigating about your web page. For example, navigation buttons that glow a different colour when the mouse is over them will confirm that they are meant to be pressed. If the button then changes appearance again when clicked, this will reassure the visitor that the button has worked. Creating buttons using slices Creating buttons from slices is the traditional way of making navigation buttons sets and is ideal if you want to create a unified navigation bar design rather than several button components butted together. 1 Use drawing and text tools to create one or more buttons. These should be appear as they will in the up (normal) state. 2 Create slices for each individual button. The slice area should encompass the entire active zone for the button. 3 When a slice is selected you can enter a Link (URL) and Alt (alternative text). Note: You can skip this step if you will be exporting images only. 4 Display the Frames panel, either by clicking its tab or by choosing Window > Frames and then drag Frame 1 onto the Add/Duplicate Frame button at the bottom of the Frame panel. 5 Make changes to the visual appearance each button. This will be the over state. One easy way is to use filter effects to add glows, embosses, or colour changes. Subtle changes are often best. Note: Any visual changes to a button must be contained within the slice area. 6 (Optional) repeat steps 5 6 to add a down state in Frame 3 and a down while over state in Frame 4. 7 Shift-click to select each of the button slices. 8 Display the Behavior panel by choosing Window > Behavior, then do either of the following: If you only created an over for your buttons, click the + sign and choose Simple Rollover from the list. If you have created multiple buttons states click the + sign and choose Nav Bar Image from the list. In the dialog box that appears choose the Include Over While Down state option if you have created this extra state in frame 4. 9 You can test the button rollovers using the Preview mode and hiding the slices. Alternatively you can preview the effect in a web browser by choosing File > Preview in Browser > and then choosing a listed browser. Note: When you use the Nav Bar Image behaviour, a button will stay in its down state after being pressed until another button in the set is pressed (assuming that the linked page contains the same navigation buttons). Create a button using slices and styles Up state Over state the button colour has been altered. Down state filter settings have been modified to create an inset look. Text has been moved slightly to enhance the effect. You may find it useful to rename each frame. You can do this by double-clicking on each one. Click the Preview button at the top of the document to test button rollovers. 1 Use the drawing tools to draw a simple button shape, eg a rounded rectangle. 2 Click on one of the styles in the Styles panel and add some text. 3 Create a slice around the button. 4 Add frames for different button states you want to create. 5 Create style variations of the button for different states by editing the Filter settings that were applied by the style. Subtle changes are often best! 6 Apply a behavior and test the button. Up: Style applied to shape. Over: Hue/Saturation modified. Down: Inner Shadow added. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 5: Composing web pages 41
46 exercise 5.4 Exporting web site with multiple pages and rollovers 1 Open the file Parkour.png. 2 Make suitable slices to divide up the areas of the page and create buttons in the navigation bar. 3 Name each slice appropriately. The slice containing the site s introduction text should be set as a HTML slice type as this will be replaced using code. 4 Name the first page home. 5 Create new pages for the News, Lessons, Photos, Videos, Forum and Contact sections of the web site. For each page activate a different graphic from the Side images folder. Creating buttons using symbols An alternative method for creating buttons is to use symbols. This is a modular approach where you simply create one button and reuse it to make multiple buttons. This can be a tidier, more efficient method to use. Using button symbols from the Common Library Each section should have its own title displayed in the tab. Edit the Parkour Downunder text layer (in the Page content layer folder) to provide a suitable title for each section, eg Parkour News. You do not need to create new content for each page (unless you want to), as this will not be exported. 6 Create two new frames and modify the button styles to create an over and down state. Apply suitable behaviours and test them. 7 Save the PNG file then optimise and export the slices (and HTML if you like) for all pages in the document. 8 (Optional) Complete the web site using a web page editor such as Dreamweaver, or by hand coding. Remember to link each button to the appropriate page. Fireworks ships with many ready-to-use buttons that you should experiment with first to give you some ideas. 1 Choose Window > Common library and then click the triangle beside the buttons folder to expand its contents. 2 Click through the various buttons to see a preview of each one. Drag the one that you would like to use to the page. 3 Select the placed symbol and choose Edit > Clone, then Shift-drag to move the copy down or across, in-line with the first button. Repeat this to create as many buttons as you need. 4 Select each button in turn, and change the Text property in the Properties panel to re-label each button. Also specify a Link and Alt text while your at it. Stack buttons vertically or horizontally to form a nav bar. 5 Test the buttons using Preview mode or in a browser. You can modify a cloned button s Text, Link, Alt text and Filters in the Properties panel. 42 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
47 Creating your own button symbols 1 Do either of the following: Choose Edit > Insert > New Button to create a whole new button. Select an existing button that you ve drawn and choose Modify > Symbol > Convert to Symbol (F8), then enter a name for the symbol and choose the Button option. 2 The Button Editor will appear, it is like a separate little document where you can create or modify the different states for the button. Begin with creating the Up state if you haven t already. Note: Refer to the topic regarding 9-slice scaling ahead. 3 Click the Over tab at the top of the Button Editor and then create the Over state for the button. To save time and ensure consistency you can click the Copy Up Graphic button and then modify the button. 4 Repeat to process to create other states if desired. Under the Active Area tab you can modify the hit area for the button if the automatic setting is not suitable. Note: The active area will become the slice area for the button. Ensure that you allow extra space for any effects applied to other states, eg drop shadows or glows, otherwise they will be trimmed. 5 Click Done. The button will be listed in the Library panel (Window > Library), where it can be reused within the document. To make it available for use in other documents, select it in the Library panel, then choose Save to Common Library and provide a descriptive name. It will be placed in the Custom Symbols folder in the Common Library panel. Editing symbol buttons Double-click a placed symbol to open it in the Button Editor for editing. Caution: Any changes that you make to a symbol will be automatically made to every instance of that symbol in the document. This can be a good thing or a bad thing. If you wanted to modify just one of the buttons, eg end the late button with a curve rather than a straight edge, then you need to redefine that as a separate symbol first. Choose Modify > Symbol > Convert to Symbol (F8), then enter a different name for the symbol and choose the Button option again. Enabling 9-slice scaling Original button A useful feature of button symbols is that they can be easily reused in other documents. Traditionally if you wanted make a symbol larger or wider, the whole button would scale, causing text to stretch or the radius of subtle round edges to become enlarged, spoiling the aesthetics of the original design. 9-slice scaling can be used to specify areas of the symbol that should not be scaled with the rest of the symbol. You need to set up a symbol for 9-slice scaling first, to do this: 1 Double-click on a placed symbol to open the editor. 2 Select the Enable option. 3 Drag the guides to position them just within edges of a button so they clear any rounded corners. 4 Select the Lock option to protect the guide positions and then click Done. Now you can scale the button without distortion. When you create a new state click here to copy the previous. Create as many, or as few states as you want. The Active area must allow room for effects such as glows. Symbols scaled without 9-slice scaling become distorted. Symbols scaled with 9-slice enabled maintain proportions. Click enable and drag the guides so they are within any rounded corner, as shown. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 5: Composing web pages 43
48 exercise 5.5 Remote rollovers It is possible when rolling over one image or button to swap the graphic in another slice. For example, imagine that your website was selling a product with various colour options. A visitor could hover over a button labelled blue, and the image of the product will change to show the blue option without the visitor having to click it. 1 Create a slice around the image that will change and each button that will trigger the change. 2 Using the Frames panel, create a new frame for each different image that will be triggered and modify the content in each frame. 3 Click on the first trigger slice. You will notice a white target symbol in the middle. Drag this target onto the slice of the image that you want to change. 4 In the dialog box that appears, choose the frame number that contains the image for this trigger. 5 Repeat steps 3 4 for each other trigger slices. Create a navigation bar using button symbols 1 Design a button and convert it to a button symbol. 2 Create different button states using the Button Editor. 3 Using the button symbol, create a navigation bar containing several buttons. Image maps Image maps link areas of an image to a URL. An image map can have several hotspot areas, each with a different link. Image maps have advantages over using linked slices: Only one image file is created. A variety of different shapes can be used (rectangles, circles, polygons). Creating image maps 6 (Optional) You can trigger more than one slice, including the trigger slice itself. Simply drag the target onto other slices, or back onto the trigger slice itself. You ll also need to make visual changes in the applicable frames too. Use the Behaviors panel to manage multiple trigger. 1 Choose the Rectangle/Circle/Polygon Hotspot Tool from the Tools panel. 2 Drag to mark out rectangle or circle image map areas, or click to place corner points for a polygon area. 3 In the Properties panel enter a Name and Link and Alt text for the image map area. 4 Repeat steps 1 3 to create additional hotspots. 5 Export the competed image map using the HTML and Images option. This button set is saved as a single image but uses an image map to define the hotspot regions for each button. A circular image map area is used to define the middle button and rectangular image map areas are used to define the side buttons. Note: The information relating to the hotspots is only stored within the HTML code. If you are intending to build the page using your own code, you must still export an HTML file, then copy and paste the information for the image found between the <map> tags. You could also choose Copy to Clipboard for the HTML option and paste the code into your own code, then remove the extra page code. In this example, the product image is swapped with the correct colour option whenever the mouse is rolls over a colour option. Drag the target from the button, onto the image that you want to remotely rollover. Usually you needn t be too precise with the shape of hotspots. By default hotspots are indicated by cyan coloured overlays (though you can change the colour in the Properties panel). They will be invisible when displayed in a web browser. 44 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
49 exercise project Modifying image maps 1 Choose Show Slices and Hotspots from the Tools panel if necessary. 2 Click the hotspot that you want to modify. Note: You can also select image maps from the Web Layer folder in the Layers panel. 3 Do any of the following: Drag to reposition it. Drag the control handles to change its shape. Alter the Link or other options in the Properties panel. Press Delete/Backspace to discard it. Creating rollovers with image maps Creating an image map For this exercise, you will create an image map to make clickable regions on a map of Australia and New Zealand. 1 Open the file Map.png. 2 Use the Polygon Hotspot Tool to mark out the approximate area of each coloured region. 3 Name the hotspots with an appropriate name and add equivalent links (to.htm files) and Alt text. If you don t know the name of each region just use area1, area2, etc. 4 Save the document and then export it as an optimised GIF with transparency and HTML code. Create a sliced website A hotspot can be used to trigger a rollover, however, the rollover area must be contained within a slice. Create rollovers from a hotspot using the same technique as creating a hotspot from a slices. Note: If you use the Polygon Slice tool it will create a slice with a polygon hotspot inside. Using the techniques that you have learned in this chapter, create your own web site design that makes use of slices and rollover navigation buttons. The site can be related to a subject of your choice. 1 Design the website on paper first before developing it in Fireworks. Make sure that there are navigation buttons, and some space for regular text. 2 Slice up the page and name each slice. 3 Use the Pages panel to create multiple pages. 4 Create rollovers for the navigation buttons. 5 Optimise and save the slices. 6 (Optional) Complete the web site in an web page editor or by hand coding. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 5: Composing web pages 45
50 Animation Creating animations for web pages In this section In this section, you will learn how to: Make an animated GIF. Duplicate frames. Preview an animation. Animations One of the most basic forms of animation on the web is an animated GIF. Animated GIFs are a series of GIF images played one after the other, like a traditional flip-book, but using the computer. One advantage of GIF animation other other formats is that they work in virtually any browser without the viewer being required to install any special plug-ins. Animations are an easy way to add a bit of excitement to a website. Each frame (or page of the flip-book) is displayed in the Frames panel. Making an animated GIF 1 Plan out on paper what you want to animate. This will make the whole process a lot easier! 2 Create a document with a static image. This will be frame 1, the starting point of your animation. 3 An easy way to make sure that there is continuity between the frames is to duplicate Frame 1 as a basis for Frame 2. In the Frames panel, drag frame 1 downwards and drop it on top of the Add/Duplicate Frame button (see right). This will make an exact copy of Frame 1 and call it Frame 2. Adjust the contents of frame 2. This is the start of your animation! Flick between Frame 1 and 2 and you will see the objects moving. 4 Repeat the technique above of duplicating and adjusting frames, so that your animation runs as you designed it to. 5 At the bottom of the document window there are a number of animation controls (Play, Stop, Step forward, Step backwards etc.) which are useful for checking that the action is smooth (see right). Click the Play button to make sure that all your frames are in the correct order. If they aren t, reorder the frames in the Frames panel, just the same way that you would reorder layers in the Layers panel. Set an animation s frame delay. Set looping on an animation. Optimise and export an animation. tip Animation pitfalls There are a couple of things to remember if you are making your animations for a website: Animations can sometimes get very distracting and can very easily become incredibly annoying use them wisely. Animations contain multiple frames, each one of which is an image in itself, so file size can get very big very quickly. Be subtle and be cautious! Drag from here to here to duplicate a frame. Rewind Play/Stop Forward Frame number Step backwards Step Forwards 46 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
51 exercise Change the Frame Delay settings to slow down or speed up your animation. Each frame can have a different amount of delay. Select a frame, or Shift-select a number of frames, then double-click on the right-hand side of the panel, which shows the Frame Delay number. Change the Frame Delay amount in the popup window (see right). A smaller number means a faster animation. 7 At the bottom of the Frames panel you can set the looping options for the animation (see right). Web animations usually loop forever, but there might be an instance where you want the animation to loop a specific number of times, or not to loop at all. 8 Make sure that the Export file format in the Optimize panel is set to Animated GIF. This will ensure that an animated and not a static GIF is exported. You may find that the Preview window and the 2-Up and 4-Up windows take a little while to display a preview. This is because Fireworks is having to work harder to display a number of frames. tip Animating text 9 Reduce the number of colours to make a smaller file, just the same way that you would do with a normal GIF file. Pay particular attention to the file size indicator in the Preview window. Animated GIFs can get very big, very fast! The file will have a.gif extension, just like a static image. Creating an animated GIF If you are animating text, you must make sure that the text is on screen and static for long enough for the viewer to read and understand. Try to get someone who has never seen the text before to look at it, so that they can give you an objective view. It may seem quite slow to you, but to them it will probably be just right. For this exercise, you will animate existing objects in a file, to make a standard size web animation banner (468 x 60 pixels). Use the file space_race.png from the exercise_resources folder. 1 The animation will start with only the spaceship showing on the screen and the text will slide into view over time. Shift-drag each text object so that they sit outside the edges of the document (see right). They will disappear, but will still be selectable for the purposes of editing. Move the spaceship across to the left hand side of the document. 2 Duplicate frame 1 as a basis for frame 2 and adjust frame 2 so that the text starts to creep into the document. 3 Create frames 3 to 7, repeating the technique above of duplicating and adjusting frames. Match the pictures on the right, so that your animation runs from frame 1 to 7. 4 If the animation is running too fast (which it no doubt will be), change the Frame Delay of the first 6 frames so that there is time to register and read the text as it comes onto the screen (suggestion; 20/100 sec), and change the Frame Delay of the final frame so that it pauses on screen (suggestion; 200/100 sec). 5 Set looping to Forever so that the animation continues endlessly. 6 Save and export the file, making sure that you choose Animated GIF as the Export file format. Looping options Export file format Frame Delay Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4 Frame 5 Frame 6 Frame 7 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Chapter 6: Animation 47
52 project project project Animated button Create a subtle animated button for a website, one which could be placed on the first page of a website, saying enter site. 1 Use vector shapes and effects to create a button look. 2 Animate the colour and create movement to attract attention. Banner advert Using an existing advertising campaign that you have seen on a billboard, or in a magazine, create an animated web banner using vector and bitmap tools. 1 Put your ideas down on paper first you will find it much easier when you come to work on the computer. Use the concepts, ideas, imagery and slogans from the existing adverts. 2 Create a document which is 468 x 60 pixels, or 60 x 468 pixels. These are two standard sizes for banner adverts. 3 As your animation progresses, keep checking in the Preview window to see that the size isn t getting too big try to keep the file size down to under 60k. This might seem very small, but because this image is intended for web delivery, size must be kept to a minimum! 4 Make sure that any text you use is checked by someone else for timing. Cartoon Go wild with this one! Create an animation this time it won t be for the web, so won t have any size restrictions. However, the larger your animation, and the more that each frame contains, the slower it will run, as the computer tries to keep up. Animate whatever you like. You can use these as starting points: Make a cartoon depicting something you have done today. (Tip: The South Park jerky style of animation works well.) Animate the text of a poem and add some small drawings or designs. Animate a photograph of your face. Warning! This one, using photographic images could get very big very quickly, and you will have to settle for GIF compression on a photograph. Make an advert for your favourite object or favourite past time. 48 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
53 Appendix The Tools panel Select tools The Pointer tool selects and moves objects around the document. You can use it to resize simple objects in vector mode. The Select Behind tool selects the object behind the currently selected object. The Subselection tool allows you to select, edit and move vector paths. When you select a vector object with the Subselection tool, the points that make up the path become editable. You can also use the Subselection tool to select objects within a group. The Scale tool resizes and rotates objects. Likewise, the Distort tool distorts objects. The Skew tool allows you to shear, rotate or change the perspective of an object. The Crop tool lets you get rid of parts of your document that you no longer need. You may start working with a document that is larger than you need, and the Crop tool lets you make your document smaller. The Export Area tool allows you to select an area of your document which you can then export independently. Bitmap tools The Marquee and Oval Marquee tools allow you to select areas of a bitmap image so that you can edit them independently from the rest of the image. The Lasso tool allows you to select freeform areas of a bitmap image for editing. Likewise, the Polygon Lasso tool lets you select polygonal areas of a bitmap image. The Magic Wand tool lets you select areas of similar colour in a bitmap image. The Brush tool draws freehand lines in bitmap mode and freehand paths in vector mode. The Pencil tool draws freehand lines a pixel wide in bitmap mode, and freehand paths in vector mode. The Eraser tool erases pixels from a bitmap image. It is only available in bitmap mode. The Blur tool decreases the focus of selected areas in an image. Likewise, the Sharpen tool sharpens areas in an image. The Dodge tool lightens parts of an image, while the Burn tool darkens parts of an image. The Smudge tool picks up colour and pushes it in the direction that you drag in an image. The Rubber Stamp tool lets you duplicate an area of a bitmap image. The Replace Color tool paints over a specified color with another colour. The Red-eye Removal tool reduces the appearance of red eye in photographs. The Eyedropper tool picks up colour from anywhere in the document window and sets either the stroke or fill colour in the Tools panel depending on which one is active. The Paint Bucket tool fills areas with flat colour, while the Gradient tool lets you fill bitmap or vector objects with a combination of colours in adjustable patterns. Pointer tool Select Behind tool Subselection tool Scale tool Skew tool Distort tool Crop tool Export Area tool Marquee tool Oval marquee tool Lasso tool Polygon Lasso tool Magic Wand tool Brush tool Pencil tool Eraser tool Blur tool Sharpen tool Dodge tool Burn tool Smudge tool Rubber Stamp tool Replace Color tool Red Eye Removal tool Eyedropper tool Paint Bucket tool Gradient tool Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Appendix 49
54 Vector tools The Line tool lets you draw an editable path in a straight line. The Pen tool lets you draw editable shapes by placing points along the path as you draw it. Similarly the Vector Path tool lets you draw vector-based paths using a variety of brush strokes. The Redraw Path tool allows you to reform an existing path by clicking on a part of it and redrawing it. Depending on where you click, the path may be extended or existing parts may be deleted and a new path drawn. The Rectangle, Ellipse and Polygon and the other Auto Shapes tools let you draw editable paths of various shapes. The Text tool lets you add text blocks to your document. The Properties panel lets you choose fonts, type sizes and other typographic features. The Freeform tool allows you to reshape a path by pushing and pulling on a path. The Reshape Area tool lets you alter a path using a round shaped cursor to push the existing path into a different shape. The Path Scrubber tools work in conjunction with a pressure sensitive stylus and allow you alter a path s characteristics. The Knife tool cuts paths into segments. It is only available in vector mode. Web tools The Rectangle, Circle and Polygon Hotspot tools let you draw image map hotspots onto your document. The Slice and Polygon Slice tools let you divide your document up into the areas that will make up an HTML table when you export your document. Sliced areas are also needed to create rollovers and other effects. The Hide and Show Hotspots and Slices buttons show or hide hotspots and slices. Color tools The Stroke and Fill Colour buttons show the currently selected colours. Clicking on the colour chip on the buttons brings up the colour picker. The Default Colours button resets the Stroke Colour to black and the Fill Colour to white. The No Stroke or Fill button removes either the Stroke or Fill of an object depending on which part was clicked when selecting it. The Switch Fill and Stroke button switches the Fill and Stroke colours. View tools The View Mode buttons allow you to view your workspace in different ways. Standard Screen is the default document window view. Full Screen with Menus is a maximised document window with menus, toolbars, scroll bars and panels visible, while Full Screen is a maximised document window without any menus, etc. The Hand tool lets you drag to navigate your document while zoomed in. The Magnify tool lets you zoom in and out of your document. Line tool Pen tool Vector Path tool Redraw Path tool Rectangle tool Ellipse tool Polygon tool Auto Shapes tools Text tool Freeform tool Reshape Area tool Path Scrubber tool additive Path Scrubber tool subtractive Knife tool Rectangle Hotspot tool Circle Hotspot tool Polygon Hotspot tool Slice tool Polygon Slice tool Hide Hotspots and Slices Show Hotspots and Slices Stroke Colour Fill Colour Switch Fill and Stroke Default Colours No Stroke or Fill Standard mode Full Screen mode Full Screen with menus mode Hand Magnify 50 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
55 The panels Pages, Layers, Frames and History panel group The Pages panel lets you create multiple pages in the same document. Pages are useful for prototyping an entire site. The Layers panel lets you organise your document by grouping objects on independent layers. The Web Layer holds slice and hotspot information. The History panel records everything you do. You can use it to undo actions. The Frames panel holds the information used to create rollovers and animations. Assets panel group The Styles panel holds presets of colours, strokes, fills and effects that can be applied to objects. Any symbols used in a document are placed in the Library panel so that they can be reused easily. Editing a symbol in the Library affects every other instance of that symbol used in the document. The URL panel stores web addresses, saving you from having to retype them. The Shapes panel contains Auto Shapes that are not displayed in the Tools panel. They can be dragged and dropped from the Shapes panel to the document window. Colors panel group The Mixer panel lets you create and edit colours and tints using different colour models. The Swatches panel lets you pick colours for paths and objects. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Appendix 51
56 Optimize and Align panel group The Optimize panel lets you control the export settings of the document and also individual slices. The Align panel lets you align and distribute selected objects in your document. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Align. Ungrouped panels The Auto Shape Properties panel lets you modify the properties of a selected auto shape object. The Image Editing panel provides convenient access to a collection of frequently used image editing tools and menu commands. The Info panel lets you view the dimensions, position and colour value of objects. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Info. The Behaviors panel lets you add dynamic effects such as rollovers and pop-up menus. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Behaviors. The Find panel lets you search for and replace elements such as text, URLs, fonts and colours in a document or multiple documents. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Find. The Special Characters panel can be used to insert non-keyboard characters when using the Text tool. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Others> Special Characters. The Path panel provides shortcut buttons to apply many of the vector editing features found in the Modify menu or done using tools. Rest the mouse pointer over each button to display a label if you are not sure what a button does. It is not displayed in the default layout, you need to choose Window > Others > Path. 52 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS CS3 FWCS3 1.0 Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing
57 The Common Library panel (choose Window > Common Library) contains a range of user interface components and other useful items that can be dragged and dropped into your document. You can save a symbol of your own here by selecting it choosing Save to Common Library in the Library palette options. The Symbol Properties panel (choose Window > Symbol Properties) will display any editable properties that are available when certain (rich) symbols are placed from the Common Library. The Color Palette panel (choose Window > Others > Color Palette) provides more advanced colour mixing options than the standard pop-up colour palette. Copyright 2007 Natcoll Publishing Appendix 53
Education and Training CUFMEM14A. Exercise 2. Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics
 Education and Training CUFMEM14A Exercise 2 Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics Menu Exercise 2 Exercise 2a: Scarecrow Exercise - Painting and Drawing Tools... 3 Exercise 2b: Scarecrow Exercise
Education and Training CUFMEM14A Exercise 2 Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics Menu Exercise 2 Exercise 2a: Scarecrow Exercise - Painting and Drawing Tools... 3 Exercise 2b: Scarecrow Exercise
Adobe Photoshop CS2 Reference Guide For Windows
 This program is located: Adobe Photoshop CS2 Reference Guide For Windows Start > All Programs > Photo Editing and Scanning >Adobe Photoshop CS2 General Keyboarding Tips: TAB Show/Hide Toolbox and Palettes
This program is located: Adobe Photoshop CS2 Reference Guide For Windows Start > All Programs > Photo Editing and Scanning >Adobe Photoshop CS2 General Keyboarding Tips: TAB Show/Hide Toolbox and Palettes
Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand
 Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand Photoshop is the software for image processing. With this you can manipulate your pictures, either scanned or otherwise inserted to a great extant.
Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand Photoshop is the software for image processing. With this you can manipulate your pictures, either scanned or otherwise inserted to a great extant.
2. If a window pops up that asks if you want to customize your color settings, click No.
 Practice Activity: Adobe Photoshop 7.0 ATTENTION! Before doing this practice activity you must have all of the following materials saved to your USB: runningshoe.gif basketballshoe.gif soccershoe.gif baseballshoe.gif
Practice Activity: Adobe Photoshop 7.0 ATTENTION! Before doing this practice activity you must have all of the following materials saved to your USB: runningshoe.gif basketballshoe.gif soccershoe.gif baseballshoe.gif
USING THE PHOTOSHOP TOOLBOX
 IN THIS CHAPTER USING THE PHOTOSHOP TOOLBOX Using the Options Bar 44 Using the Selection Tools 45 Using the Crop and Slice Tools 46 Using the Retouching Tools 46 Using the Painting Tools 49 Using the Drawing
IN THIS CHAPTER USING THE PHOTOSHOP TOOLBOX Using the Options Bar 44 Using the Selection Tools 45 Using the Crop and Slice Tools 46 Using the Retouching Tools 46 Using the Painting Tools 49 Using the Drawing
Graphic Design & Digital Photography. Photoshop Basics: Working With Selection.
 1 Graphic Design & Digital Photography Photoshop Basics: Working With Selection. What You ll Learn: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools, reposition a selection marquee, move and
1 Graphic Design & Digital Photography Photoshop Basics: Working With Selection. What You ll Learn: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools, reposition a selection marquee, move and
Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding. Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a. Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting
 Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects
Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects
 9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
In this lesson, you ll learn how to:
 LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
Using Masks for Illustration Effects
 These instructions were written for Photoshop CS4 but things should work the same or similarly in most recent versions Photoshop. 1. To download the files you ll use in this exercise please visit: http:///goodies.html
These instructions were written for Photoshop CS4 but things should work the same or similarly in most recent versions Photoshop. 1. To download the files you ll use in this exercise please visit: http:///goodies.html
Adobe photoshop Using Masks for Illustration Effects
 Adobe photoshop Using Masks for Illustration Effects PS Preview Overview In this exercise you ll see a more illustrative use of Photoshop. You ll combine existing photos with digital art created from scratch
Adobe photoshop Using Masks for Illustration Effects PS Preview Overview In this exercise you ll see a more illustrative use of Photoshop. You ll combine existing photos with digital art created from scratch
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP Using Masks for Illustration Effects
 ADOBE PHOTOSHOP Using Masks for Illustration Effects PS PREVIEW OVERVIEW In this exercise, you ll see a more illustrative use of Photoshop. You ll combine existing photos with digital art created from
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP Using Masks for Illustration Effects PS PREVIEW OVERVIEW In this exercise, you ll see a more illustrative use of Photoshop. You ll combine existing photos with digital art created from
Introduction To Inkscape Creating Custom Graphics For Websites, Displays & Lessons
 Introduction To Inkscape Creating Custom Graphics For Websites, Displays & Lessons The Inkscape Program Inkscape is a free, but very powerful vector graphics program. Available for all computer formats
Introduction To Inkscape Creating Custom Graphics For Websites, Displays & Lessons The Inkscape Program Inkscape is a free, but very powerful vector graphics program. Available for all computer formats
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE)
 A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
Adobe Fireworks is an incredible application with specific solutions to
 Chapter 1: Introducing Fireworks CS4 In This Chapter Understanding when you should use Fireworks Discovering the workspace Finding out about the tools Looking into the views Using the basic selection tools
Chapter 1: Introducing Fireworks CS4 In This Chapter Understanding when you should use Fireworks Discovering the workspace Finding out about the tools Looking into the views Using the basic selection tools
How to draw and create shapes
 Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Introduction to Photoshop. Training Documentation
 Introduction to Photoshop Training Documentation 1 Introduction to Photoshop... 3 What is Photoshop?... 3 Tool Palate... 3 Gradient: Allows transition between two or more chosen colors... 4 Other Terms:...
Introduction to Photoshop Training Documentation 1 Introduction to Photoshop... 3 What is Photoshop?... 3 Tool Palate... 3 Gradient: Allows transition between two or more chosen colors... 4 Other Terms:...
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP BOOK SAHALSOFTWARE. Frist Editing. Contents
 ADOBE PHOTOSHOP BOOK SAHALSOFTWARE Frist Editing Contents Lesson 01: Introduction of Adobe Photoshop Lesson 02: How to Open Photoshop Lesson 03: Environment Lesson 04: Tools in Adobe Photoshop Lesson 05:
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP BOOK SAHALSOFTWARE Frist Editing Contents Lesson 01: Introduction of Adobe Photoshop Lesson 02: How to Open Photoshop Lesson 03: Environment Lesson 04: Tools in Adobe Photoshop Lesson 05:
INTRODUCTION and TOOLS TUTORIAL
 Adobe Photoshop cs2 INTRODUCTION and TOOLS TUTORIAL OBJECTIVE - This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of the frequently used tools and actions in Photoshop. All samples used will be found
Adobe Photoshop cs2 INTRODUCTION and TOOLS TUTORIAL OBJECTIVE - This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of the frequently used tools and actions in Photoshop. All samples used will be found
Chapter 1. Getting to Know Illustrator
 Chapter 1 Getting to Know Illustrator Exploring the Illustrator Workspace The arrangement of windows and panels that you see on your monitor is called the workspace. The Illustrator workspace features
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Illustrator Exploring the Illustrator Workspace The arrangement of windows and panels that you see on your monitor is called the workspace. The Illustrator workspace features
Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash Fall 2010, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Downloading the Data Files...3
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash Fall 2010, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Downloading the Data Files...3
Photoshop Basics A quick introduction to the basic tools in Photoshop
 Photoshop Basics A quick introduction to the basic tools in Photoshop Photoshop logo courtesy Adobe Systems Inc. By Dr. Anthony R. Curtis Mass Communication Department University of North Carolina at Pembroke
Photoshop Basics A quick introduction to the basic tools in Photoshop Photoshop logo courtesy Adobe Systems Inc. By Dr. Anthony R. Curtis Mass Communication Department University of North Carolina at Pembroke
November 19,
 http://www.eee.uci.edu/workshops/ Web Images: A Snapshot What kinds of images are GIF JPEG used on the web? What does the name stand for? Graphics Interchange Format Joint Photographic Experts Group Animations
http://www.eee.uci.edu/workshops/ Web Images: A Snapshot What kinds of images are GIF JPEG used on the web? What does the name stand for? Graphics Interchange Format Joint Photographic Experts Group Animations
Keyboard Shortcuts. Command Windows Macintosh
 S00ILCS5.qxp 3/19/2010 1:11 AM Page 477 Keyboard Shortcuts k Adobe Illustrator CS5 If a command on a menu includes a keyboard reference, known as a keyboard shortcut, to the right of the command name,
S00ILCS5.qxp 3/19/2010 1:11 AM Page 477 Keyboard Shortcuts k Adobe Illustrator CS5 If a command on a menu includes a keyboard reference, known as a keyboard shortcut, to the right of the command name,
2 Working with Selections
 2 Working with Selections Learning how to select areas of an image is of primary importance you must first select what you want to affect. Once you ve made a selection, only the area within the selection
2 Working with Selections Learning how to select areas of an image is of primary importance you must first select what you want to affect. Once you ve made a selection, only the area within the selection
4 Working with Selections
 4 Working with Selections Learning how to select areas of an image is of primary importance you must first select what you want to affect. Once you ve made a selection, only the area within the selection
4 Working with Selections Learning how to select areas of an image is of primary importance you must first select what you want to affect. Once you ve made a selection, only the area within the selection
3 WORKING WITH SELECTIONS
 3 WORKING WITH SELECTIONS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools. Reposition a selection marquee. Move and duplicate
3 WORKING WITH SELECTIONS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools. Reposition a selection marquee. Move and duplicate
2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING
 2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Differentiate between the various selection tools and employ different selection techniques. Recognize Smart
2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Differentiate between the various selection tools and employ different selection techniques. Recognize Smart
Drawing shapes and lines
 Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques
 Creating a superhero using the pen tool Topics covered: Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques Getting Started 1. Reset your work environment
Creating a superhero using the pen tool Topics covered: Pen Tool, Fill Layers, Color Range, Levels Adjustments, Magic Wand tool, and shadowing techniques Getting Started 1. Reset your work environment
ENGL 323: Writing for New Media Repurposing Content for the Web Part Two
 ENGL 323: Writing for New Media Repurposing Content for the Web Part Two Dr. Michael Little michaellittle@kings.edu Hafey-Marian 418 x5917 Using Color to Establish Visual Hierarchies Color is useful in
ENGL 323: Writing for New Media Repurposing Content for the Web Part Two Dr. Michael Little michaellittle@kings.edu Hafey-Marian 418 x5917 Using Color to Establish Visual Hierarchies Color is useful in
EDITING AND COMBINING SHAPES AND PATHS
 4 EDITING AND COMBINING SHAPES AND PATHS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Cut with the Scissors tool. Join paths. Work with the Knife tool. Outline strokes. Work with
4 EDITING AND COMBINING SHAPES AND PATHS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Cut with the Scissors tool. Join paths. Work with the Knife tool. Outline strokes. Work with
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial
 Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
HO-1: INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS
 HO-1: INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS The Fireworks Work Environment Adobe Fireworks CS4 is a hybrid vector and bitmap tool that provides an efficient design environment for rapidly prototyping websites and
HO-1: INTRODUCTION TO FIREWORKS The Fireworks Work Environment Adobe Fireworks CS4 is a hybrid vector and bitmap tool that provides an efficient design environment for rapidly prototyping websites and
INDESIGN AND PHOTOSHOP
 NEIL MALEK, ACI With just a few basic tools, anyone can professionally polish photos in Photoshop and arrange them into a layout in InDesign. The incredible power and diverse tools can be intimidating,
NEIL MALEK, ACI With just a few basic tools, anyone can professionally polish photos in Photoshop and arrange them into a layout in InDesign. The incredible power and diverse tools can be intimidating,
Shortcut Keys for Adobe Photoshop (Educational Support)
 Shortcut Keys for Adobe Photoshop (Educational Support) http:// SHORTCUT KEYS - I Adobe Photoshop Tools V Move M Marquee tools L Lasso tools W Quick Selection, Magic Wand C Crop and Slice Tools I Eyedropper,
Shortcut Keys for Adobe Photoshop (Educational Support) http:// SHORTCUT KEYS - I Adobe Photoshop Tools V Move M Marquee tools L Lasso tools W Quick Selection, Magic Wand C Crop and Slice Tools I Eyedropper,
The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop
 102640 ch15.1.qxp 3/10/07 11:23 AM Page 303 Making Selections The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop documents. A selection isolates an area of an image so that you can apply
102640 ch15.1.qxp 3/10/07 11:23 AM Page 303 Making Selections The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop documents. A selection isolates an area of an image so that you can apply
HYPERSTUDIO TOOLS. THE GRAPHIC TOOL Use this tool to select graphics to edit. SPRAY PAINT CAN Scatter lots of tiny dots with this tool.
 THE BROWSE TOOL Us it to go through the stack and click on buttons THE BUTTON TOOL Use this tool to select buttons to edit.. RECTANGLE TOOL This tool lets you capture a rectangular area to copy, cut, move,
THE BROWSE TOOL Us it to go through the stack and click on buttons THE BUTTON TOOL Use this tool to select buttons to edit.. RECTANGLE TOOL This tool lets you capture a rectangular area to copy, cut, move,
ILLUSTRATOR TUTORIAL-1 workshop handout
 Why is Illustrator a powerful tool? ILLUSTRATOR TUTORIAL-1 workshop handout Computer graphics fall into two main categories, bitmap graphics and vector graphics. Adobe Illustrator is a vector based software
Why is Illustrator a powerful tool? ILLUSTRATOR TUTORIAL-1 workshop handout Computer graphics fall into two main categories, bitmap graphics and vector graphics. Adobe Illustrator is a vector based software
Chapter 1 Introduction to Photoshop CS3 1. Exploring the New Interface Opening an Existing File... 24
 CONTENTS Chapter 1 Introduction to Photoshop CS3 1 Exploring the New Interface... 4 Title Bar...4 Menu Bar...5 Options Bar...5 Document Window...6 The Toolbox...7 All New Tabbed Palettes...18 Opening an
CONTENTS Chapter 1 Introduction to Photoshop CS3 1 Exploring the New Interface... 4 Title Bar...4 Menu Bar...5 Options Bar...5 Document Window...6 The Toolbox...7 All New Tabbed Palettes...18 Opening an
Adobe illustrator Introduction
 Adobe illustrator Introduction This document was prepared by Luke Easterbrook 2013 1 Summary This document is an introduction to using adobe illustrator for scientific illustration. The document is a filleable
Adobe illustrator Introduction This document was prepared by Luke Easterbrook 2013 1 Summary This document is an introduction to using adobe illustrator for scientific illustration. The document is a filleable
SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC
 Photo Effects: Snowflakes Photo Border (Photoshop CS6 / CC) SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun snowflakes photo border,
Photo Effects: Snowflakes Photo Border (Photoshop CS6 / CC) SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun snowflakes photo border,
Learning to use the drawing tools
 Create a blank slide This module was developed for Office 2000 and 2001, but although there are cosmetic changes in the appearance of some of the tools, the basic functionality is the same in Powerpoint
Create a blank slide This module was developed for Office 2000 and 2001, but although there are cosmetic changes in the appearance of some of the tools, the basic functionality is the same in Powerpoint
Photoshop Creative Cloud (CC)
 Photoshop Creative Cloud (CC) Photoshop is an image editing and design software. Photoshop can be used to add special effects to an image, correct color and image flaws, and even remove parts of an image
Photoshop Creative Cloud (CC) Photoshop is an image editing and design software. Photoshop can be used to add special effects to an image, correct color and image flaws, and even remove parts of an image
3 WOrkinG WiTH SElECTiOnS lesson overview
 3 Working with Selections Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools. Reposition a selection marquee. Move and duplicate
3 Working with Selections Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Make specific areas of an image active using selection tools. Reposition a selection marquee. Move and duplicate
Using Selection Tools and Layers
 Using Selection Tools and Layers A version of the melon head. Yours does not need to look just like this. Start by opening the Lesson 02 Start file provided. Select File>Save As and rename file adding
Using Selection Tools and Layers A version of the melon head. Yours does not need to look just like this. Start by opening the Lesson 02 Start file provided. Select File>Save As and rename file adding
The Photoshop Workspace
 Adobe Photoshop: Chapter 2: The Photoshop Workspace When you first open or start Photoshop the work area is made up of a set of default or standard Tools, Palettes and menus. Photoshop s Tools are contained
Adobe Photoshop: Chapter 2: The Photoshop Workspace When you first open or start Photoshop the work area is made up of a set of default or standard Tools, Palettes and menus. Photoshop s Tools are contained
ITP 101 Project 2 - Photoshop
 ITP 101 Project 2 - Photoshop Project Objectives Learn how to use an image editing application to create digital images. We will use Adobe Photoshop for this project. Project Details To continue the development
ITP 101 Project 2 - Photoshop Project Objectives Learn how to use an image editing application to create digital images. We will use Adobe Photoshop for this project. Project Details To continue the development
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS
 4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
Advanced Special Effects
 Adobe Illustrator Advanced Special Effects AI exercise preview exercise overview The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects
Adobe Illustrator Advanced Special Effects AI exercise preview exercise overview The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects
Step 1: Create A New Photoshop Document
 Snowflakes Photo Border In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple snowflakes photo border, which can be a fun finishing touch for photos of family and friends during the holidays,
Snowflakes Photo Border In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple snowflakes photo border, which can be a fun finishing touch for photos of family and friends during the holidays,
Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo
 Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo Final Figure Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is used primarily for the analysis of large molecules such as proteins
Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo Final Figure Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is used primarily for the analysis of large molecules such as proteins
Animated Gif - Illustrator /Text and Shapes
 - Illustrator /Text and Shapes Use Adobe Illustrator to create an animated gif. Use a variety of shapes, outlined type, or live traced objects as your subjects. Apply all the skills that we have developed
- Illustrator /Text and Shapes Use Adobe Illustrator to create an animated gif. Use a variety of shapes, outlined type, or live traced objects as your subjects. Apply all the skills that we have developed
14. Using Illustrator CC with Other Adobe Applications
 14. Using Illustrator CC with Other Adobe Applications Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Place linked and embedded graphics in an Illustrator file. Place multiple images
14. Using Illustrator CC with Other Adobe Applications Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Place linked and embedded graphics in an Illustrator file. Place multiple images
Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks
 Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks Items needed to complete the Navigation Bar: Unit 21 - House Style Unit 21 - Graphics Sketch Diagrams Document ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks Items needed to complete the Navigation Bar: Unit 21 - House Style Unit 21 - Graphics Sketch Diagrams Document ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EDITING SHAPES. Lesson overview
 3 CREATING AND EDITING SHAPES Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Create a document with multiple artboards. Use tools and commands to create basic shapes. Work with drawing
3 CREATING AND EDITING SHAPES Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Create a document with multiple artboards. Use tools and commands to create basic shapes. Work with drawing
SETTINGS AND WORKSPACE
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Adobe Illustrator is a program used to create vector illustrations / graphics (.ai/.eps/.svg). These graphics will then be used for logos, banners, infographics, flyers... in print and
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Adobe Illustrator is a program used to create vector illustrations / graphics (.ai/.eps/.svg). These graphics will then be used for logos, banners, infographics, flyers... in print and
Contents. Introducing Clicker Paint 5. Getting Started 7. Using The Tools 10. Using Sticky Points 15. Free resources at LearningGrids.
 ClickerPaintManualUS.indd 2-3 13/02/2007 13:20:28 Clicker Paint User Guide Contents Introducing Clicker Paint 5 Free resources at LearningGrids.com, 6 Installing Clicker Paint, 6 Getting Started 7 How
ClickerPaintManualUS.indd 2-3 13/02/2007 13:20:28 Clicker Paint User Guide Contents Introducing Clicker Paint 5 Free resources at LearningGrids.com, 6 Installing Clicker Paint, 6 Getting Started 7 How
Expression Design Lab Exercises
 Expression Design Lab Exercises Creating Images with Expression Design 2 Beaches Around the World (Part 1: Beaches Around the World Series) Information in this document, including URL and other Internet
Expression Design Lab Exercises Creating Images with Expression Design 2 Beaches Around the World (Part 1: Beaches Around the World Series) Information in this document, including URL and other Internet
Basic Tools. Chapter 1. Getting started
 Chapter 1 Basic Tools Getting started Jasc Paint Shop Pro is a powerful art package which you can use to paint, write text, retouch photos and make images ready for the web. After only a few lessons you
Chapter 1 Basic Tools Getting started Jasc Paint Shop Pro is a powerful art package which you can use to paint, write text, retouch photos and make images ready for the web. After only a few lessons you
Using Flash Animation Basics
 Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
On the Web sun.com/aboutsun/comm_invest STAROFFICE 8 DRAW
 STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
Paint/Draw Tools. Foreground color. Free-form select. Select. Eraser/Color Eraser. Fill Color. Color Picker. Magnify. Pencil. Brush.
 Paint/Draw Tools There are two types of draw programs. Bitmap (Paint) Uses pixels mapped to a grid More suitable for photo-realistic images Not easily scalable loses sharpness if resized File sizes are
Paint/Draw Tools There are two types of draw programs. Bitmap (Paint) Uses pixels mapped to a grid More suitable for photo-realistic images Not easily scalable loses sharpness if resized File sizes are
Overview of Adobe Fireworks
 Adobe Fireworks Overview of Adobe Fireworks In this guide, you ll learn how to do the following: Work with the Adobe Fireworks workspace: tools, Document windows, menus, and panels. Customize the workspace.
Adobe Fireworks Overview of Adobe Fireworks In this guide, you ll learn how to do the following: Work with the Adobe Fireworks workspace: tools, Document windows, menus, and panels. Customize the workspace.
Recitation 3 Further Work with Dreamweaver and Photoshop: Refining your Web Site
 Recitation 3 Further Work with Dreamweaver and Photoshop: Refining your Web Site More Photoshop skills Selecting areas of the image - using the selection tools In Recitation 2 we learned there are several
Recitation 3 Further Work with Dreamweaver and Photoshop: Refining your Web Site More Photoshop skills Selecting areas of the image - using the selection tools In Recitation 2 we learned there are several
The Macromedia Flash Workspace
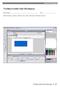 Activity 5.1 Worksheet The Macromedia Flash Workspace Student Name: Date: Identify the Stage, workspace, Timeline, layers, panels, Tools panel, and Property inspector. The Macromedia Flash Workspace 5-35
Activity 5.1 Worksheet The Macromedia Flash Workspace Student Name: Date: Identify the Stage, workspace, Timeline, layers, panels, Tools panel, and Property inspector. The Macromedia Flash Workspace 5-35
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
In this exercise you will be creating the graphics for the index page of a Website for children about reptiles.
 LESSON 2: CREATING AND MANIPULATING IMAGES OBJECTIVES By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: create and import graphics use the text tool attach text to a path create shapes create curved and
LESSON 2: CREATING AND MANIPULATING IMAGES OBJECTIVES By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: create and import graphics use the text tool attach text to a path create shapes create curved and
Creative Effects with Illustrator
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Creative Effects with Illustrator PREVIEW OVERVIEW The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects and photographs.
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Creative Effects with Illustrator PREVIEW OVERVIEW The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects and photographs.
This document should only be used with the Apple Macintosh version of Splosh.
 Splosh 1 Introduction Splosh is an easy to use art package that runs under both Microsoft Windows and the Macintosh Mac OS Classic or Mac OS X operating systems. It should however be noted that the Apple
Splosh 1 Introduction Splosh is an easy to use art package that runs under both Microsoft Windows and the Macintosh Mac OS Classic or Mac OS X operating systems. It should however be noted that the Apple
Adobe Illustrator CC 2018 Tutorial
 Adobe Illustrator CC 2018 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Illustrator CC is an illustration program that can be used for print, multimedia and online graphics. Whether you plan to design or illustrate multimedia
Adobe Illustrator CC 2018 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Illustrator CC is an illustration program that can be used for print, multimedia and online graphics. Whether you plan to design or illustrate multimedia
L E S S O N 2 Background
 Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
Interface. 2. Interface Photoshop CS/ImageReady CS for the Web H O T
 2. Interface Photoshop CS/ImageReady CS for the Web H O T 2. Interface The Welcome Screen Interface Overview Using the Toolbox Using Palettes Using the Options Bar Creating a Tool Preset Resetting Tools
2. Interface Photoshop CS/ImageReady CS for the Web H O T 2. Interface The Welcome Screen Interface Overview Using the Toolbox Using Palettes Using the Options Bar Creating a Tool Preset Resetting Tools
Adobe Graphic Master. BIGROCKDESIGNS computer training consultants. Course Outline LEVEL: Section 1 Illustrator CC (Day 1 & 2) DURATION:
 Adobe Graphic Master Course Outline This course has been created to provide the user with the skills required to incorporate all the packages of Adobe Creative Suite CC/CS6 so as to develop all print requirements
Adobe Graphic Master Course Outline This course has been created to provide the user with the skills required to incorporate all the packages of Adobe Creative Suite CC/CS6 so as to develop all print requirements
Adobe Flash CS3 Reference Flash CS3 Application Window
 Adobe Flash CS3 Reference Flash CS3 Application Window When you load up Flash CS3 and choose to create a new Flash document, the application window should look something like the screenshot below. Layers
Adobe Flash CS3 Reference Flash CS3 Application Window When you load up Flash CS3 and choose to create a new Flash document, the application window should look something like the screenshot below. Layers
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
Introduction to Flash CS3
 Introduction to Flash CS3 Danny Bishop, Carol Green & Nick Ford The files used in activities and exercises within this book are not available for evaluation. Introduction to Flash CS3 Danny Bishop, Carol
Introduction to Flash CS3 Danny Bishop, Carol Green & Nick Ford The files used in activities and exercises within this book are not available for evaluation. Introduction to Flash CS3 Danny Bishop, Carol
Fig. A. Fig. B. Fig. 1. Fig. 2. Fig. 3 Fig. 4
 Create A Spinning Logo Tutorial. Bob Taylor 2009 To do this you will need two programs from Xara: Xara Xtreme (or Xtreme Pro) and Xara 3D They are available from: http://www.xara.com. Xtreme is available
Create A Spinning Logo Tutorial. Bob Taylor 2009 To do this you will need two programs from Xara: Xara Xtreme (or Xtreme Pro) and Xara 3D They are available from: http://www.xara.com. Xtreme is available
Adobe Photoshop CS2/CS3: introduction
 Adobe Photoshop CS2/CS3: introduction Lessons Lesson 1: Overview of Adobe Photoshop CS2/CS3 After you learn about the Photoshop workspace, you'll learn to create a new image, select it, and make an example
Adobe Photoshop CS2/CS3: introduction Lessons Lesson 1: Overview of Adobe Photoshop CS2/CS3 After you learn about the Photoshop workspace, you'll learn to create a new image, select it, and make an example
Exploring the Flash MX 2004 Workspace
 1 Chapter Exploring the Flash MX 2004 Workspace COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL This first chapter is a warm-up to prepare you for your Flash MX 2004 adventure. It provides a quick introduction to Flash, and is a
1 Chapter Exploring the Flash MX 2004 Workspace COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL This first chapter is a warm-up to prepare you for your Flash MX 2004 adventure. It provides a quick introduction to Flash, and is a
Microsoft Word
 OBJECTS: Shapes (part 1) Shapes and the Drawing Tools Basic shapes can be used to graphically represent information or categories. The NOTE: Please read the Objects (add-on) document before continuing.
OBJECTS: Shapes (part 1) Shapes and the Drawing Tools Basic shapes can be used to graphically represent information or categories. The NOTE: Please read the Objects (add-on) document before continuing.
1. New document, set to 5in x 5in, no bleed. Color Mode should be default at CMYK. If it s not, changed that when the new document opens.
 art 2413 typography fall 17 software review This exercise will reacquaint students with Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign. These are the three main design programs used by the industry. There
art 2413 typography fall 17 software review This exercise will reacquaint students with Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign. These are the three main design programs used by the industry. There
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
Photoshop tutorial: Final Product in Photoshop:
 Disclaimer: There are many, many ways to approach web design. This tutorial is neither the most cutting-edge nor most efficient. Instead, this tutorial is set-up to show you as many functions in Photoshop
Disclaimer: There are many, many ways to approach web design. This tutorial is neither the most cutting-edge nor most efficient. Instead, this tutorial is set-up to show you as many functions in Photoshop
Sample Hands-On-Training Chapter Review Copy Only Contact Information Notice of Rights Notice of Liability Trademarks
 Sample Hands-On-Training Chapter Review Copy Only Copyright 2000-2003 by lynda.com, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and Distribution Strictly Prohibited. This electronically distributed Hands-On-Training
Sample Hands-On-Training Chapter Review Copy Only Copyright 2000-2003 by lynda.com, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and Distribution Strictly Prohibited. This electronically distributed Hands-On-Training
HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER
 HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun Happy Holidays winter photo border! Photoshop ships with some great snowflake shapes that we can use in
HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun Happy Holidays winter photo border! Photoshop ships with some great snowflake shapes that we can use in
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial
 Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
FACULTY AND STAFF COMPUTER FOOTHILL-DE ANZA. Office Graphics
 FACULTY AND STAFF COMPUTER TRAINING @ FOOTHILL-DE ANZA Office 2001 Graphics Microsoft Clip Art Introduction Office 2001 wants to be the application that does everything, including Windows! When it comes
FACULTY AND STAFF COMPUTER TRAINING @ FOOTHILL-DE ANZA Office 2001 Graphics Microsoft Clip Art Introduction Office 2001 wants to be the application that does everything, including Windows! When it comes
6 COLOR AND PAINTING. Lesson overview
 6 COLOR AND PAINTING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use color modes and color controls. Create, edit, and paint with colors using the Control panel and shortcuts.
6 COLOR AND PAINTING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use color modes and color controls. Create, edit, and paint with colors using the Control panel and shortcuts.
ILLUSTRATOR. Introduction to Adobe Illustrator. You will;
 ILLUSTRATOR You will; 1. Learn Basic Navigation. 2. Learn about Paths. 3. Learn about the Line Tools. 4. Learn about the Shape Tools. 5. Learn about Strokes and Fills. 6. Learn about Transformations. 7.
ILLUSTRATOR You will; 1. Learn Basic Navigation. 2. Learn about Paths. 3. Learn about the Line Tools. 4. Learn about the Shape Tools. 5. Learn about Strokes and Fills. 6. Learn about Transformations. 7.
Quick Guide for Photoshop CC Basics April 2016 Training:
 Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
Drawing tool gallery 2 06/06/07 09:21:26. Illustrator provides the following drawing tools: The Add Anchor Point tool (+) adds anchor points to paths.
 pport/adobe/adobehelpdata/cache/illustrator/12.0/en_us/htmłpage/ws714a382cdf7d304e7e07d0100196cbc5f-6266.html Drawing tool gallery Drawing tool gallery Illustrator provides the following drawing tools:
pport/adobe/adobehelpdata/cache/illustrator/12.0/en_us/htmłpage/ws714a382cdf7d304e7e07d0100196cbc5f-6266.html Drawing tool gallery Drawing tool gallery Illustrator provides the following drawing tools:
Working With Images: Intermediate Photoshop
 Working With Images: Intermediate Photoshop Viewing Information in the Layers Palette 1. Choose File > Open and open the Start.psd file in the Lesson01 folder located in the PS_Workshop folder on the desktop.
Working With Images: Intermediate Photoshop Viewing Information in the Layers Palette 1. Choose File > Open and open the Start.psd file in the Lesson01 folder located in the PS_Workshop folder on the desktop.
Adobe Fireworks CS Essential Techniques
 Adobe Fireworks CS4 HOW-TOs 100 Essential Techniques Jim Babbage 140 64 Creating Graphic Symbols Resizing Symbols When you resize any bitmap to a smaller size, pixel information is discarded. This is normally
Adobe Fireworks CS4 HOW-TOs 100 Essential Techniques Jim Babbage 140 64 Creating Graphic Symbols Resizing Symbols When you resize any bitmap to a smaller size, pixel information is discarded. This is normally
Creative Effects with Illustrator
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR PREVIEW Creative Effects with Illustrator AI OVERVIEW The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects and
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR PREVIEW Creative Effects with Illustrator AI OVERVIEW The object is to create a poster with a unified color scheme by compositing artwork drawn in Illustrator with various effects and
If you have been using CorelDRAW, you may have turned off this opening screen. If so, skip to step 5.
 Opening CorelDRAW If you have been using CorelDRAW, you may have turned off this opening screen. If so, skip to step 5. 1. When CorelDRAW is loaded, a new section is created on the Start Menu. To open
Opening CorelDRAW If you have been using CorelDRAW, you may have turned off this opening screen. If so, skip to step 5. 1. When CorelDRAW is loaded, a new section is created on the Start Menu. To open
Corel Draw 11. What is Vector Graphics?
 Corel Draw 11 Corel Draw is a vector based drawing that program that makes it easy to create professional artwork from logos to intricate technical illustrations. Corel Draw 11's enhanced text handling
Corel Draw 11 Corel Draw is a vector based drawing that program that makes it easy to create professional artwork from logos to intricate technical illustrations. Corel Draw 11's enhanced text handling
Paint Tutorial (Project #14a)
 Paint Tutorial (Project #14a) In order to learn all there is to know about this drawing program, go through the Microsoft Tutorial (below). (Do not save this to your folder.) Practice using the different
Paint Tutorial (Project #14a) In order to learn all there is to know about this drawing program, go through the Microsoft Tutorial (below). (Do not save this to your folder.) Practice using the different
Page Number Mouse Menu
 Adobe Photoshop CS5 Quick Reference Summary Adobe Photoshop CS5 Quick Reference Summary Number Mouse Adjustment Layer PS 187 Clip to Layer button on Adjustments Layer New Adjustment Layer Background Eraser
Adobe Photoshop CS5 Quick Reference Summary Adobe Photoshop CS5 Quick Reference Summary Number Mouse Adjustment Layer PS 187 Clip to Layer button on Adjustments Layer New Adjustment Layer Background Eraser
