CIAO Exercises. Table of Contents. Introduction. Getting to know Chandra data Download dataset. Exercise 10. Review V&V report.
|
|
|
- Marshall Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIAO Exercises Table of Contents Introduction Getting to know Chandra data Download dataset Exercise 1 Review V&V report Exercise 2 Display data in ds9 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Exercise 5 Exercise 6 Inspect headers Exerise 7 Exercise 8 Reprocess dataset Exercise 9 Imaging Basics (Spatial analysis) Detect Sources Exercise 10 Create regions in ds9 Exercise 11 Exercise 12 Aperture Photometry Exercise 13 Exercise 14
2 Simulate PSF Exercise 15 Create 3-color image Exercise 16 Extra credit Timing Analysis Extract lightcurve Exercise 17 Exercise 18 Extra credit Check for background flares Exercise 19 Spectral Analysis Extract spectra Exercise 20 Sherpa: Modeling and Fitting Exercise 21
3 Introduction These exercises are designed to familiarize students with Chandra data and some of the basics of X-ray data analysis using CIAO with Chandra data. Students will use a variety of tools and scripts to perform typical Chandra data analysis tasks. These exercises are not intended to be a Cookbook for all Chandra data analysis, but rather are meant to expose students to basic X-ray analysis techniques. Students should already have CIAO installed on their systems. The exercises here have been developed with CIAO 4.9, using the CIAO contributed scripts package, with Chandra CALDB These exercises can be performed with either the Python 2 or the Python 3 editions of CIAO. Students should also have MARX installed. These exercises have been developed using MARX The install_marx script in CIAO can be used to automate the installation process. Getting to know Chandra data In this section students will obtain Chandra data and learn some techniques to inspect the quality of the data and how to reprocess their dataset. Download dataset Exercise 1 Obtain the standard data distribution for Chandra OBS_ID Q: How did you obtain the data (Chaser, download_chandra_obsid, FTP)? Students may want to uncompress, gunzip, all of the files in the top-level directory, along with the primary and secondary directories at this point.
4 Review V&V report Exercise 2 Read the Chandra Verification and Validation report in the top level directory of the data distribution: axaff13858n001_vv001_vv2.pdf Q: Summarize the V&V comments: Q: What is the target of this observation? Q: What is the sequence number SEQ_NUM of this observation? Display data in ds9 Locate the event files. There are two event files included in the standard data distribution. The Level 1 event file, evt1, is in the secondary/ directory, the Level 2 event file, evt2, is in the primary/ directory. Exercise 3 Display the Level 2 event file using ds9. Make sure to use Log scale. Q: Using the cursor, record the coordinate of the bright source in the center of the image: Exercise 4 By default, ds9 only shows part of the Chandra dataset. Use the Bin menu to bin the data by a factor of 4 and then by a factor of 8. Binning is different than Zooming. Zooming is done to the image (so after the event file has been binned). Set bin=1, and then zoom to ⅛.
5 Q: Describe why the Bin 8 image is different than the image Zoom'ed by ⅛: Exercise 5 ds9 bins all the events in the event file into an image. That includes all events for all time and with all energies. Use the Bin Binning Parameters menu to add an energy=500:7000 as a Bin Filter. Q: Describe the difference in the images compared to the unfiltered image: Q: What unit is energy in? Try different energy ranges. Try different time ranges. Exercise 6 1. With the Level 2 event file still loaded, create a new frame. 2. Open the Level 1 event in the new frame. 3. Use Frame Tile Frames to display the two datasets side-by-side. 4. Bin both frames by 4. Both using Log scaling. Q: Describe the difference between the Level 1 and Level 2 event files: Students can now exit from ds9 or put ds9 into the background. Inspect headers
6 Most Chandra data products are FITS files, specifically FITS binary tables, with extensive headers that fully describe the dataset. Students should become familiar with some of the basic keywords and tool used to examine those keywords Exerise 7 Open the Level 2 event file in prism The EVENTS extension is automatically selected. The Header Keywords are shown in the top, right pane. Q: Record the value for the following keywords: MISSION TELESCOP INSTRUME DETNAM GRATING DATAMODE READMODE DATE-OBS OBSERVER ONTIME Q: What units are the ACIS focal plane temperature, FP_TEMP, recorded in? Students can exit prism now. Exercise 8 Use dmlist with the header option to display the header. Q: Record the value for the following header keywords: RA_TARG DEC_TARG RA_NOM DEC_NOM RA_PNT DEC_PNT ROLL_PNT
7 SIM_X SIM_Y SIM_Z DTCOR ASCDSVER CALDBVER Q: This is an "ACIS-S" observation. How can you tell this from the event file header information? Use dmkeypar with echo=yes to get the value for the TIMEDEL keyword in the Level 2 event file. Use dmmakepar to get a copy of the EVENTS extension in the Level 2 event file. Use plist, pdump, and pget to get the same header keyword values. Use dmhistory to extract the acis_process_events history records. Reprocess dataset The Chandra calibration database (CALDB) is continually updated. The then most recent CALDB is used for observations as they are taken. Some calibrations, such as the time dependent gain calibrations, can only be definitively computed based on historical observations; thus the file in the current CALDB is always predicted. These calibrations are later updated to be definitive post facto. The CIAO team strongly advises users to always reprocess data obtained from the archive. Exercise 9
8 Use chandra_repro to reprocess the dataset. Q: Compare the header keyword values in the _repro_evt2.fits file with the evt2 file obtained from the archive. Discuss the differences: Q: What version of the CALDB is installed? What is the value of the CALDBVER keyword? Q: Compare the number of events in the reprocessed Level 2 event file with the number of events in the archived Level 2 event file. Why are they same (or not the same)? Imaging Basics (Spatial analysis) In this section students will exercise some of the basic CIAO tools and scripts needed to perform basic imaging tasks. Detect Sources One of the most common analysis tasks is to detect sources. Please keep in mind: CIAO detect tools only detect candidate sources and they are not photometric tools. The output from the detect tools should be used to guide further analysis. See also: Wavdetect thread: Using detect output: Exercise 10 In this exercise students should complete the following steps
9 1. Create image and exposure map. Run the fluximage script on the dataset. Students should be sure to set the binsize=1 and set bands=default or bands=broad. 2. Create the psfmap. Run mkpsfmap using the fluximage output image as input. Students should use energy= ecf= Detect Sources. Run wavdetect on the fluximage output counts image, using the exposure map and psfmap. Students should select a set of wavelet scales to use that is appropriate for the dataset being analyzed. Q: Display the PSF map in ds9. Why does it look the way it does? Q: Record choice of wavelet scales and why that set was selected: Q: Open the broad-band image in ds9 and load the source list as a region file. Comment on the detected sources and any missed detections: Q: Are the ellipses the position error or the apparent size of the source? Try different wavelet scales. Try different significance thresholds, sigthresh. Try different ecf values when making the PSF map. Try different energy bands. Try using the celldetect tool.
10 Try using the vtpdetect tool. Create regions in ds9 The detect tools are one way to create regions automatically. However, often users analyzing a single source in an observation will simply create their own region in ds9 and then use those regions with the CIAO tools. Exercise Open the broad-band counts image in ds9. 2. Create a source region. Draw a circular source region around the bright source in the center of the image. 3. Save the region, ds9_src.reg. Use ds9 format and celestial (world) coordinates. 4. Delete the source region. 5. Create a background region. Draw an annulus around the same source. The inner annulus region should be larger than the source region. The outer region should be large enough to get a large number of counts, but should be small enough to avoid any nearby source or any instrumental features (like the gaps between chips). 6. Save the region, ds9_bkg.reg. Use CIAO format and physical coordinates. Q: Record the source location used: Q: Describe the differences between the CIAO format and the ds9 format regions: Exercise 12 Compute source centroid. In this exercise students will use the dmstat tool to compute the source centroid in their region. 1. Use dmcopy to filter the flux image thresh.img using the source region file.
11 2. Use dmlist with the blocks option to display info about the filtered output image. 3. Use dmstat with the centroid=yes option to compute the centroid of the counts in the filtered image. 4. Use dmcopy to filter the Level 2 event file using the source region file and to bin it into an image with binsize=1. 5. Use dmlist with the blocks option to display info about the filtered and binned image. 6. Use dmstat with centroid=yes option to compute the centroid of the counts in the filtered and binned image. Q: Is the filtered image the same size as the fluximage output image size? Why? Q: Record the centroid of fluximage output filtered image: Q: What are the good and null values that dmstat reports? Q: Is the image created by filtering and binning the event file the same size as the other images? Why? Q: Record the centroid of the event file filter and binned image: Q: Is the centroid the same for the two images? Why? [Hint: what energies are being used?] Aperture Photometry Obtaining the counts (or count rate) is the first step in computing the source flux. Exercise 13 In this exercise students will use the CIAO analysis menu, aka dax, to get the net counts in their regions (from Exercise 11 ).
12 1. Open the fluximage thresh.img in ds9. 2. Load the source region file created in Exercise 11 step Load the background region file created in Exercise 11 step Double click on the background annulus to display the region properties. 5. Under the Property menu, select Background. The region will now be drawn with a dashed line. Close the properties window. 6. In the main ds9 window, goto Analysis CIAO Statistics Net Counts. 7. A text window will be display containing the information about the current regions. 8. Try adjusting the source and background radii and repeating the analysis. Q: From step 7, record the following information from the Net Counts task: Net counts with error: Source counts: Background counts: Q: From step 8, describe how the net counts and net rates vary with changes to the source and background regions: Exercise 14 In this exercise students will use the srcflux script to get various estimates of the flux of the source. 1. Obtain the source location in celestial coordinates from the source region file created in Exercise 11 step Run the srcflux script on the reprocessed level 2 event file, using the position, pos, from step 1. All other parameters should remain at their defaults. 3. Repeat step 2, using a different outroot and psfmethod=arfcorr 4. Repeat step 3, using a different outroot, model="xsbbody.black_body" and paramvals="black_body.kt=1". 5. Repeat step 4, using bands="hard". Q: Record the net count rate, model independent flux, model flux from steps 2 through 5
13 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Count Rate Flux Model Flux Q: Discuss the differences in the estimated fluxes obtained in steps 2 through 5. Try using psfmethod=quick, psfmethod=arfcorr, and psfmethod=marx. Try other spectral model and other model parameters. Try other energy bands (2-10 kev is a common band in the literature). Simulate PSF The Chandra Point Spread Function (PSF) varies spatially across the field of view as well with energy. There is no analytic model of the PSF. The only way to obtain an estimate of the Chandra PSF for detailed spatial analysis is by simulation. The psfmethod used by srcflux are only appropriate when integrating over a region. The pixel-to-pixel variations used in those methods is insufficient for any type of analysis that requires detailed spatial information. There are two different simulators users can use.
14 1. SAOTrace is the definitive mirror model and is made available to users via the ChaRT web interface. 2. MARX is the end-to-end Chandra simulator used to calibrate the HETG gratings and includes a fairly accurate mirror model and detector models. Exercise 15 In this exercise Students will simulate the PSF using ChaRT and with MARX. The simulate_psf script is used to create PSF images that are appropriate for further data analysis. 1. Ensure that MARX is installed and that MARX_ROOT is set. 2. Run ChaRT. To run ChaRT users need to know the source location (celestial coordinates), an estimate of the photon flux (from the srcflux.flux output files), and an estimate of the energy. Students may be provided with a set of ChaRT output ray files. 3. Run the simulate_psf script. Use the reprocessed level 2 event file as the infile and the coordinates of the source, in decimal degrees, for the ra and dec parameters. Use simulator=file and provide the stack of ray files obtained from ChaRT for the rayfile parameter. Set minsize=128 to obtain a reasonable size output image. 4. Display the reprocessed level 2 event file in one ds9 frame and the simulate_psf output PSF in a 2nd frame. Tile the frames horizontally and save the image as a PNG file. 5. Run simulate_psf with a different outroot, this time using simulator=marx and set the numiter parameter to the same number of iterations as were used with ChaRT. monoenergy=1.0 and flux=1e-4 can be used for the spectral model. 6. Repeat step 4 using the MARX generated PSF. Q: Comment on a visual comparison of the ChaRT/SAOTrace PSF to the observation: Q: Comment on a visual comparison of the MARX PSF to the observation: Q: Describe any differences between the MARX and ChaRT PSFs:
15 Q: Is this a point source? Try setting simulate_psf readout_streak=yes. Try pileup=yes. Try blur=0.20 Run the Lucy-Richardson deconvolution tool arestore using the broad band flux image and the PSFs simulated here. Try with different numbers of iterations. Create a 3-color image Three color (aka "true color" or "tri-color") images can be useful to help guide analysis by providing visual clues about changes in spectra. Exercise Obtain the data for OBS_ID These data will only be used for this exercise. 2. Reprocess the data using chandra_repro 3. Run fluximage on the reprocessed level 2 event file. Use binsize=8 and bands=csc. 4. Load the soft, medium, and hard band flux.img images into ds9. This can be done in the GUI by creating a new RGB frame and then loading the files individually or on the command line $ ds9 -rgb -red root_soft_flux.img \ -green root_medium_flux.img \ -blue root_hard_flux.img 5. Log scale each of the images. 6. Use the Analysis Smooth on each of the images. 7. Save the image in PNG format. 8. Exit ds9 9. Use dmimg2jpg to create a similar 3-color image.
16 Q: Discuss the differences in the output from ds9 and dmimg2jpg. Extra credit Smooth the images with aconvolve before displaying Smooth the images with csmooth before displaying Smooth the images with dmimgadapt before displaying Obtain overlapping multi-spectral images of this region from other archives. Use reproject_image to project the other datasets to the same tangent plane as the Chandra dataset. Create tri-color image using red for the lowest energy, and blue for the highest energy datasets. Obtain the data for OBS_ID 635 and reprocess it with chandra_repro. Split the event file into 3 equal time intervals by filtering on the TIME column. Run fluximage on each time interval using the broad energy band. Use the 3 time-slices to create a 3 color image. Timing Analysis References CIAO provides several tools to perform basic timing analysis. Extract lightcurve References:
17 In X-ray astronomy the term "light curve" is used to describe the flux of a source vs time. Exercise Create a light curve using the dmextract tool with the reprocessed level 2 event file filtered with the source and background regions created in Exercise 11 steps 3 and 6. Use a 100 second bin width: [bin time=::100]. 2. Repeat 1, using the following bin widths: 200, 500, 1000, Plot each of the light curves using chips. chips> make_figure("out_bin100.lc[cols dt,count_rate]") chips> print_window("out_bin100.png") Q: Why is there a gap at the beginning and at the end of the light curves with count_rate=0? Q: Is the delta-time, dt, column actually a column in the dmextract output file? Q: What can be learned from the light curve with 1 second time resolution? Q: What energy events were used to make these light curves? Does using an energy filter change things and if so how? Q: ACIS event files contain multiple good time intervals (one for each chip). Which GTI was use?
18 Exercise Create a light curve using the glvary tool using the reprocessed level 2 event file with the source region. 2. Repeat 1 using the background region. 3. Plot the glvary source and background lightcurves using chips Q: Describe how the glvary lightcurves differ from the dmextract light curves. Q: Could any variability in the source region be due to variability in the background? Extra credit Use the dither_region tool to compute the time resolved area fraction of the source and separately the background regions. Try using those as input to dmextract and glvary as exposure corrections. Compare to the results without those corrections. Check for background flares Reference: Background flares may influence results especially when working with large source regions such as supernovae remnants or clusters. For an on-axis point source, users should carefully consider whether excluding time due to a background flare would be better than accepting the time in order to obtain higher signal to noise.
19 Exercise 19 In this exercise, students will extract a light curve for a background, source-free region and use it to search for any evidence of a background flare. 1. Using dmcoords, dmstat, dmlist, or ds9+dax, determine the CCD_ID where the bright source in the center of the field is located. 2. Use dmcopy to exclude the wavdetect sources detected in Exercise 10 step 3 from the reprocessed Level 2 event file. dmcopy "evt2.fits[exclude sky=region(wavdetect.src)]"\ source_free_evts.fits 3. Use dmextract to create a light curve using the source free event file, use a CCD_ID filter to select events from chip you found in step 1. Use a bin-width of seconds. 4. Use the deflare tool to search for background flares on the source chip using method=clean. 5. Use dmcopy to apply the deflare output good-time interval, GTI, file to the reprocessed level 2 event file. Q: What CCD_ID was found in step 1? Which tool(s) were used? Q: Was there any evidence of a background flare in this observation, on this chip? If so, describe the flare (when did it occur within the observation, duration, etc.): Try different bin-widths when creating the light curve. Does it affect the results? Try different deflare method options. Try looking for flares on the other CCD's used in this observation.
20 Spectral Analysis The energy resolution and sensitivity of the ACIS detector allows for spectral analysis roughly in the 0.3 to 7.0 kev range. Extract spectra Reference Exercise 20 In this exercise Students will use the specextract tool to extract the spectrum, ARF, and RMF files for the source and background regions. 1. Run the specextract script using the reprocessed level 2 event file with the source region from Exercise 11 step 3 and the background region from step 6 with the default parameter settings. 2. Run specextract as in step 1 with a different outroot and setting weight=no 3. Run specextract as in step 2 with a different outroot and setting correctpsf=yes 4. Use dmdiff to compare the spectra (.pha ) from steps 2 and 3 to the spectrum in step Use dmdiff to compare the auxiliary response file (.arf ) from steps 2 and 3 to the ARF in step Use dmlist to get the BACKSCAL and EXPOSURE keywords from the source and background spectra. Q: Record the BACKSCAL and EXPOSURE keywords. Why are these keywords important? Q: Describe and discuss the differences, if any, from step 4.
21 Q: Describe and discuss the differences, if any, from step 5: Use the rmfimg tool to convert the RMF into an image and display in ds9. Sherpa: Modeling and Fitting References sherpa is the fitting and modeling package developed for CIAO. It allows users to obtain best fit model parameters based on a number of models, fitting methods, and statistics used for uncertainty. The exercise shown here is an extremely simple sherpa use case. More advanced usage includes user supplied models, linked model parameters, simultaneously fitting multiple datasets, fitting images, etc. Exercise 21 In this exercise Students will begin to use sherpa to model and fit the spectrum of the source. 1. Load the ungrouped source spectrum obtained from Exercise 20 step 1 into sherpa sherpa> load_data("source.pha") 2. Plot the spectrum using the plot_data command 3. Group the data using group_counts(). Select a reasonable number of counts for the dataset. Replot the data.
22 4. Restrict the energy range to a reasonable energy range using the notice() command. Replot the data. 5. Set the source model to be an absorbed powerlaw using the set_source() command. sherpa> set_source(xswabs.abs1*xspowerlaw.p1) 6. Set the absorption nh to the value listed in the header of the spectrum file. 7. Use plot_model() to see the model folded through the instrument responses (ARF and RMF). 8. Use show_all() to see all the data and model details. 9. subtract() the background. Replot the data. 10.fit() the data. 11.Use plot_fit() to see the data with the model overplotted. 12.Use plot_fit_delchi() to see the data with the error weighted residuals. 13.Use conf() to obtain uncertainties on the fitted parameters. 14.Use set_method() to try different minimization techniques and repeat the fit(). 15.Use set_stat() to try different fit statistics and repeat the fit(). 16.Try different grouping schemes. 17.Try different spectral models in the set_source() command. 18.Repeat this exercise using the spectrum, ARF and RMF obtain in Exercise 20 steps 2 and 3. Q: Which fit method works best? Q: Which spectrum fits best? Q: Which model/param is best? Q: How does grouping affect the results? Q: What are the advantages/disadvantages of one method over another?
23
CIAO Quick Start. Abbreviated CIAO threads to get started with the most common Chandra data reduction tasks.
 CIAO Quick Start Abbreviated CIAO threads to get started with the most common Chandra data reduction tasks. I want to... install CIAO Goto http://cxc.cfa.harvard.edu/ciao/download Select Standard Install
CIAO Quick Start Abbreviated CIAO threads to get started with the most common Chandra data reduction tasks. I want to... install CIAO Goto http://cxc.cfa.harvard.edu/ciao/download Select Standard Install
Using the ACIS "Blank Sky" Background Files
 Using the ACIS "Blank Sky" Background Files CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Using the ACIS "Blank Sky" Background Files 1 Table of Contents Get Started Download the background files Download the scripts Finding
Using the ACIS "Blank Sky" Background Files CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Using the ACIS "Blank Sky" Background Files 1 Table of Contents Get Started Download the background files Download the scripts Finding
Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources
 Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources 1 Table of Contents Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources CIAO 3.4 Get Started CALDB 3.3.0.1
Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources 1 Table of Contents Weighting ARFs and RMFs: multiple sources CIAO 3.4 Get Started CALDB 3.3.0.1
Analysis of Extended Sources
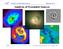 Analysis of Extended Sources Michael Wise 1 Analysis of Extended Sources 5th Chandra/CIAO Workshop, 29-31 October 2003 2 Online documentation http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao/guides/esa.html Background subtraction
Analysis of Extended Sources Michael Wise 1 Analysis of Extended Sources 5th Chandra/CIAO Workshop, 29-31 October 2003 2 Online documentation http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao/guides/esa.html Background subtraction
Introduction to the Data Model
 DM Intro CIAO 34 Introduction to the Data Model CIAO 34 Science Threads Introduction to the Data Model 1 Table of Contents DM Intro CIAO 34 Get Started Data Model Tools Running Data Model Tools Virtual
DM Intro CIAO 34 Introduction to the Data Model CIAO 34 Science Threads Introduction to the Data Model 1 Table of Contents DM Intro CIAO 34 Get Started Data Model Tools Running Data Model Tools Virtual
Introduction to CIAO
 1 Introduction to CIAO (Chandra Interactive Analysis of Observations) CIAO: Chandra's data analysis system Fruscione et al. 2006, SPIE Proc. 6270, 62701V, D.R. Silvia & R.E. Doxsey, eds. THE PEOPLE WHO
1 Introduction to CIAO (Chandra Interactive Analysis of Observations) CIAO: Chandra's data analysis system Fruscione et al. 2006, SPIE Proc. 6270, 62701V, D.R. Silvia & R.E. Doxsey, eds. THE PEOPLE WHO
The CIAO Contributed Scripts (and a brief introduction to CIAO)
 The CIAO Contributed Scripts (and a brief introduction to CIAO) Jonathan McDowell & The CIAO Scripts Team Part 1: a brief introduction to CIAO What is CIAO? CIAO is a free, open-source software package
The CIAO Contributed Scripts (and a brief introduction to CIAO) Jonathan McDowell & The CIAO Scripts Team Part 1: a brief introduction to CIAO What is CIAO? CIAO is a free, open-source software package
Introduction and Scripts. Jonathan McDowell Chandra X-ray Center, SAO
 Introduction and Scripts Jonathan McDowell Chandra X-ray Center, SAO 2014 Nov CXC Scope Caveat: will cover ACIS imaging data only Basics the same for HRC and gratings, but with extra wrinkles Introduction
Introduction and Scripts Jonathan McDowell Chandra X-ray Center, SAO 2014 Nov CXC Scope Caveat: will cover ACIS imaging data only Basics the same for HRC and gratings, but with extra wrinkles Introduction
Using A Pileup Model
 Using A Pileup Model Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Using A Pileup Model 1 Table of Contents Background Information Remove the acis_detect_afterglow Correction Getting Started Reading in Data & Instrument Responses
Using A Pileup Model Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Using A Pileup Model 1 Table of Contents Background Information Remove the acis_detect_afterglow Correction Getting Started Reading in Data & Instrument Responses
Create a PSF CIAO 3.4 Science Threads
 Create a PSF CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Create a PSF 1 Table of Contents Create a PSF CIAO 3.4 The PSF Libraries Get Started Characterizing the Source What is the energy of the source? (dmextract) How far
Create a PSF CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Create a PSF 1 Table of Contents Create a PSF CIAO 3.4 The PSF Libraries Get Started Characterizing the Source What is the energy of the source? (dmextract) How far
Extracting Extended Source Spectra and Responses
 Extracting Extended Source Spectra and Responses CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Extracting Extended Source Spectra and Responses 1 Table of Contents Getting Started CALDB 3.3.0.1 patch Using Consistent Calibration:
Extracting Extended Source Spectra and Responses CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Extracting Extended Source Spectra and Responses 1 Table of Contents Getting Started CALDB 3.3.0.1 patch Using Consistent Calibration:
Chandra Source Catalog Quality Assurance Specifications
 I. General Chandra Source Catalog Quality Assurance Specifications August 17, 2007 Ian Evans (ievans@cfa.harvard.edu) 1. Quality Assurance Mechanisms Chandra Source Catalog quality assurance is achieved
I. General Chandra Source Catalog Quality Assurance Specifications August 17, 2007 Ian Evans (ievans@cfa.harvard.edu) 1. Quality Assurance Mechanisms Chandra Source Catalog quality assurance is achieved
1 acis make bkgd. MEMORANDUM May 11, Description. 1.2 Parameters
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM May 11, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn Allen (SDS) for the ACIS Background Working Group Subject: acis make bkgd Revision:
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM May 11, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn Allen (SDS) for the ACIS Background Working Group Subject: acis make bkgd Revision:
Introduction to CIAO (Chandra Interactive Analysis of Observations)
 Introduction to CIAO (Chandra Interactive Analysis of Observations) From "ahelp ciao"... A powerful data analysis system originally written for the needs of users of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Built
Introduction to CIAO (Chandra Interactive Analysis of Observations) From "ahelp ciao"... A powerful data analysis system originally written for the needs of users of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Built
Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations
 Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations 1 Table of Contents Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations CIAO 3.4 Getting
Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations 1 Table of Contents Merging Data from Multiple Imaging Observations CIAO 3.4 Getting
Introduction to Prism
 Introduction to Prism CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Introduction to Prism 1 Table of Contents Introduction to Prism CIAO 3.4 Getting Started Launching prism The Basic Display Column filtered Viewing Viewing
Introduction to Prism CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Introduction to Prism 1 Table of Contents Introduction to Prism CIAO 3.4 Getting Started Launching prism The Basic Display Column filtered Viewing Viewing
1 Overview. MEMORANDUM November 4, 2015
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 4, 2015 To: File From: David P. Huenemoerder, Glenn E. Allen Subject: Description of enhancements to HETG/ACIS CC-mode processing Revision:
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 4, 2015 To: File From: David P. Huenemoerder, Glenn E. Allen Subject: Description of enhancements to HETG/ACIS CC-mode processing Revision:
Progress Report. Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team. Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 22, 2013
 Progress Report Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 22, 2013 Current Catalog Release Summary Current catalog version: 1.1; Released: 2010
Progress Report Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 22, 2013 Current Catalog Release Summary Current catalog version: 1.1; Released: 2010
Detecting Sources in Chandra Data
 Detecting Sources in Chandra Data Goal Identify statistically significant brightness enhancements, over local background, deriving from both unresolved (point) and resolved (extended) x-ray sources. Emphasize
Detecting Sources in Chandra Data Goal Identify statistically significant brightness enhancements, over local background, deriving from both unresolved (point) and resolved (extended) x-ray sources. Emphasize
Chandra X-Ray Center. CIAO Workshop
 Chandra X-Ray Center 1 CIAO Workshop Introduction to X-Ray Data Analysis David Huenemoerder (MIT) Randall Smith (CfA) Abstract We describe in general terms how flux incident on an X-Ray telescope observatory
Chandra X-Ray Center 1 CIAO Workshop Introduction to X-Ray Data Analysis David Huenemoerder (MIT) Randall Smith (CfA) Abstract We describe in general terms how flux incident on an X-Ray telescope observatory
Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data
 Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data 1 Table of Contents Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data CIAO 3.4 Data Preparation
Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data 1 Table of Contents Obtain Grating Spectra from LETG/HRC I Data CIAO 3.4 Data Preparation
Ahelp: tg_create_mask CIAO 3.4. tg_create_mask infile outfile input_pos_tab grating_obs [opt_parameters]
![Ahelp: tg_create_mask CIAO 3.4. tg_create_mask infile outfile input_pos_tab grating_obs [opt_parameters] Ahelp: tg_create_mask CIAO 3.4. tg_create_mask infile outfile input_pos_tab grating_obs [opt_parameters]](/thumbs/74/71010728.jpg) Ahelp: tg_create_mask CIAO 3.4 URL: http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao3.4/tg_create_mask.html Last modified: December 2006 AHELP for CIAO 3.4 tg_create_mask Context: tools Jump to: Description Examples Parameters
Ahelp: tg_create_mask CIAO 3.4 URL: http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao3.4/tg_create_mask.html Last modified: December 2006 AHELP for CIAO 3.4 tg_create_mask Context: tools Jump to: Description Examples Parameters
Ahelp: tgdetect CIAO 3.4. Jump to: Description Examples Parameters CHANGES IN CIAO 3.3 Bugs See Also
 Ahelp: tgdetect CIAO 3.4 URL: http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao3.4/tgdetect.html Last modified: December 2006 AHELP for CIAO 3.4 tgdetect Context: tools Jump to: Description Examples Parameters CHANGES IN CIAO
Ahelp: tgdetect CIAO 3.4 URL: http://cxc.harvard.edu/ciao3.4/tgdetect.html Last modified: December 2006 AHELP for CIAO 3.4 tgdetect Context: tools Jump to: Description Examples Parameters CHANGES IN CIAO
Using FTOOLS and Fv for Data Analysis: Chandra
 Using FTOOLS and Fv for Data Analysis: Chandra This tutorial is designed to build upon your current knowledge of FTOOLS and to also provide an introduction to the imaging program Fv. It is strongly recommended
Using FTOOLS and Fv for Data Analysis: Chandra This tutorial is designed to build upon your current knowledge of FTOOLS and to also provide an introduction to the imaging program Fv. It is strongly recommended
Specifications: tgfindzo Algorithm and Interface
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center Specifications: tgfindzo Algorithm and Interface David Huenemoerder December 13, 2011 Revision History 1. 2011.12.13 version 1.0; corrections from JC; and more
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center Specifications: tgfindzo Algorithm and Interface David Huenemoerder December 13, 2011 Revision History 1. 2011.12.13 version 1.0; corrections from JC; and more
XRT Data Analysis I E. Troja (NASA/GSFC/ORAU)
 XRT Data Analysis I E. Troja (NASA/GSFC/ORAU) with thanks to Kim Page (U. Leicester) 1 Introduction to XRT Basic steps: Outline - XRT data processing (from Level 1 to Level 3) - create images, light curves
XRT Data Analysis I E. Troja (NASA/GSFC/ORAU) with thanks to Kim Page (U. Leicester) 1 Introduction to XRT Basic steps: Outline - XRT data processing (from Level 1 to Level 3) - create images, light curves
Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data
 Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data 1 Table of Contents Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data CIAO 3.4 Data Preparation
Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data 1 Table of Contents Obtain Grating Spectra from HETG/ACIS S Data CIAO 3.4 Data Preparation
CIAO. Jonathan McDowell. Science Data Systems
 CIAO Jonathan McDowell Science Data Systems CUC Oct 2011 Science Data Systems activities - update Data Systems activities SDS develops requirements and algorithms for the CXCDS (Data Systems) team, then
CIAO Jonathan McDowell Science Data Systems CUC Oct 2011 Science Data Systems activities - update Data Systems activities SDS develops requirements and algorithms for the CXCDS (Data Systems) team, then
ChaRT. Margarita Karovska. and the ChaRT Team CXC. 5 th Chandra/CIAO Workshop, October 2003
 1 ChaRT and the ChaRT Team I. ChaRT Overview 2 ChaRT (Chandra Ray Tracer) is a user friendly web interface that allows the user to simulate High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) Point Spread Functions
1 ChaRT and the ChaRT Team I. ChaRT Overview 2 ChaRT (Chandra Ray Tracer) is a user friendly web interface that allows the user to simulate High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) Point Spread Functions
Fitting Grating Data
 Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Fitting Grating Data 1 Table of Contents Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Getting Started Reading the Spectrum Files Building the Instrument
Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Fitting Grating Data 1 Table of Contents Fitting Grating Data Sherpa Getting Started Reading the Spectrum Files Building the Instrument
FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX
 FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX Date: 1 Oct 2018 Revision: - CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 INGREDIENTS... 1 3 INSPECTING THE CUBE... 3 4 COMPARING TO A REFERENCE IMAGE... 5 5 REFERENCE VELOCITY
FIFI-LS: Basic Cube Analysis using SOSPEX Date: 1 Oct 2018 Revision: - CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 INGREDIENTS... 1 3 INSPECTING THE CUBE... 3 4 COMPARING TO A REFERENCE IMAGE... 5 5 REFERENCE VELOCITY
dph/h3/cxc/icd/specs tgextract2-1.0/tgextract2.tex
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 16, 2015 To: From: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader; Kenny Glotfelty, DS Tools Lead David Huenemoerder, SDS Subject: tgextract2 Specifications
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 16, 2015 To: From: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader; Kenny Glotfelty, DS Tools Lead David Huenemoerder, SDS Subject: tgextract2 Specifications
Extract Coadded and Grouped Nth Order Source & Background Spectra and ARFs
 Extract Coadded and Grouped Nth Order Source & Background Spectra and ARFs CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Extract Coadded and Grouped Nth Order Source & Background Spectra and ARFs 1 Table of Contents Get Started
Extract Coadded and Grouped Nth Order Source & Background Spectra and ARFs CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Extract Coadded and Grouped Nth Order Source & Background Spectra and ARFs 1 Table of Contents Get Started
RGS data reduction and analysis of point-like sources
 14 th ESAC SAS Workshop 2 nd 6 th June 2014 RGS data reduction and analysis of point-like sources Rosario González-Riestra XMM-Newton SOC ESAC Processing RGS data (I) from... to... FRAME Time CCD, node,
14 th ESAC SAS Workshop 2 nd 6 th June 2014 RGS data reduction and analysis of point-like sources Rosario González-Riestra XMM-Newton SOC ESAC Processing RGS data (I) from... to... FRAME Time CCD, node,
1 acis build chip gti
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM June 22, 2014 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build chip gti Revision: 2.0 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#gti
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM June 22, 2014 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build chip gti Revision: 2.0 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#gti
Progress Report. Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team. Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 25, 2010
 Progress Report Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 25, 2010 Executive Summary Summary Catalog version 1.1 was released on 2010 Aug 10
Progress Report Ian Evans On behalf of the Chandra Source Catalog Project Team Chandra Users Committee Meeting October 25, 2010 Executive Summary Summary Catalog version 1.1 was released on 2010 Aug 10
1 acis build chip gti
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM July 15, 2014 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build chip gti Revision: 2.1 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#gti
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM July 15, 2014 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build chip gti Revision: 2.1 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#gti
OUTLINE. 6th CIAO Workshop, October, 2008
 1 OUTLINE Introduction Goals and Realities Chandra Challenges for Source Detection Intro to CIAO Detect Tools CELLDETECT VTPDETECT WAVDETECT Tool Comparison 2 Contributors Tom Calderwood Francesco Damiani
1 OUTLINE Introduction Goals and Realities Chandra Challenges for Source Detection Intro to CIAO Detect Tools CELLDETECT VTPDETECT WAVDETECT Tool Comparison 2 Contributors Tom Calderwood Francesco Damiani
Create a Color Spectrum
 Create a Color Spectrum CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Create a Color Spectrum 1 Table of Contents Create a Color Spectrum CIAO 3.4 Get Started Filter the Event File Create a Color Spectrum A. In Sky Coordinates
Create a Color Spectrum CIAO 3.4 Science Threads Create a Color Spectrum 1 Table of Contents Create a Color Spectrum CIAO 3.4 Get Started Filter the Event File Create a Color Spectrum A. In Sky Coordinates
Estimating Errors and Confidence Levels
 Estimating Errors and Confidence Levels Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Estimating Errors and Confidence Levels 1 Table of Contents Errors & Confidence Levels Sherpa Getting Started Downloading the data Downloading
Estimating Errors and Confidence Levels Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Estimating Errors and Confidence Levels 1 Table of Contents Errors & Confidence Levels Sherpa Getting Started Downloading the data Downloading
SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis
 SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis Eduard Kontar School of Physics and Astronomy University of Glasgow, UK CESRA Summer School, Glasgow, August 2015 SSW Pre-school installation guide for IDL, SSW and
SSW, Radio, X-ray, and data analysis Eduard Kontar School of Physics and Astronomy University of Glasgow, UK CESRA Summer School, Glasgow, August 2015 SSW Pre-school installation guide for IDL, SSW and
X-ray Spectra Part I: Loading, Visualizing, & Grouping Data
 X-ray Spectra Part I: Loading, Visualizing, & Grouping Data Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu May 12, 2016 Starting up ISIS This exercise presumes that you ve downloaded and installed the.isisrc files
X-ray Spectra Part I: Loading, Visualizing, & Grouping Data Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu May 12, 2016 Starting up ISIS This exercise presumes that you ve downloaded and installed the.isisrc files
Astrosat Project Soft X-Ray Telescope (SXT)
 Astrosat Project Soft X-Ray Telescope (SXT) Standard Operating Procedure AS1SXTLevel2-1.0 Software Prepared by TIFR SXT Team 4 December 2015 Department of Astrophysics & Astronomy Tata Institute of Fundamental
Astrosat Project Soft X-Ray Telescope (SXT) Standard Operating Procedure AS1SXTLevel2-1.0 Software Prepared by TIFR SXT Team 4 December 2015 Department of Astrophysics & Astronomy Tata Institute of Fundamental
ICD for REEF circular Encircled Energy calibration file. Parameter data cube HDU for PSF encircled energy. Version: 2008 Aug 25.
 ICD for REEF circular Encircled Energy calibration file Parameter data cube HDU for PSF encircled energy Contents Version: 2008 Aug 25 1 Introduction 2 2 PSF encircled energy file 2 2.1 IMAGE HDU header.........................
ICD for REEF circular Encircled Energy calibration file Parameter data cube HDU for PSF encircled energy Contents Version: 2008 Aug 25 1 Introduction 2 2 PSF encircled energy file 2 2.1 IMAGE HDU header.........................
X-ray Spectra Part II: Fitting Data and Determining Errors
 X-ray Spectra Part II: Fitting Data and Determining Errors Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu May 12, 2016 Setting Up the Data This exercise presumes that you ve downloaded and installed the.isisrc files
X-ray Spectra Part II: Fitting Data and Determining Errors Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu May 12, 2016 Setting Up the Data This exercise presumes that you ve downloaded and installed the.isisrc files
1 Description. MEMORANDUM February 19, 2013
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM February 19, 2013 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: DELTOCLK spec Revision: 3.2 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#deltoclk
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM February 19, 2013 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: DELTOCLK spec Revision: 3.2 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#deltoclk
1 Introduction. 2 Replacement. MEMORANDUM May 13, Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader Glenn E. Allen, SDS Bias repair
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM May 13, 2010 To: From: Subject: Revision: 5.4 URL: File: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader Glenn E. Allen, SDS Bias repair http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM May 13, 2010 To: From: Subject: Revision: 5.4 URL: File: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader Glenn E. Allen, SDS Bias repair http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
1 Bias-parity errors. MEMORANDUM August 18, Description. 1.2 Input
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM August 18, 2010 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias-parity error spec Revision: 0.2 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#berr
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM August 18, 2010 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias-parity error spec Revision: 0.2 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#berr
1 Introduction. 2 Replacement. MEMORANDUM April 7, 2010
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM April 7, 2010 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias repair Revision: 4.4 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM April 7, 2010 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias repair Revision: 4.4 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
Data products. Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda
 Data products Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda Pipeline (levels 1 à 2) The pipeline consists in a sequence of modules. For each module, files are created and read
Data products Dario Fadda (USRA) Pipeline team Bill Vacca Melanie Clarke Dario Fadda Pipeline (levels 1 à 2) The pipeline consists in a sequence of modules. For each module, files are created and read
DETECT Talk for CIAO workshop D. Harris
 DETECT Talk for CIAO workshop D. Harris 1.0 GENERAL - Philosophy...what it is, and what it isn t. 2.0 CELLDETECT 3.0 WAVDETECT 4.0 VTPDETECT 5.0 EVALUATION OF ALGORITHMS VIA DEEP FIELDS 6.0 SUMMARY 1.0
DETECT Talk for CIAO workshop D. Harris 1.0 GENERAL - Philosophy...what it is, and what it isn t. 2.0 CELLDETECT 3.0 WAVDETECT 4.0 VTPDETECT 5.0 EVALUATION OF ALGORITHMS VIA DEEP FIELDS 6.0 SUMMARY 1.0
1 Introduction. 2 Replacement. MEMORANDUM November 13, 2009
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 13, 2009 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias repair Revision: 4.1 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM November 13, 2009 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Bias repair Revision: 4.1 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#bias
Introduction to Fitting ASCII Data with Errors: Single Component Source Models
 Fitting ASCII Data Sherpa Introduction to Fitting ASCII Data with Errors: Single Component Source Models Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Introduction to Fitting ASCII Data with Errors: Single Component Source
Fitting ASCII Data Sherpa Introduction to Fitting ASCII Data with Errors: Single Component Source Models Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Introduction to Fitting ASCII Data with Errors: Single Component Source
VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook
 European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook VLT-SPE-ESO-19500-5652 Issue 1.0 10 July 2012 Prepared: Mark Westmoquette
European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere VERY LARGE TELESCOPE 3D Visualization Tool Cookbook VLT-SPE-ESO-19500-5652 Issue 1.0 10 July 2012 Prepared: Mark Westmoquette
New Results of Fully Bayesian
 of Fully Bayesian UCI February 7, 2012 of Fully Bayesian Calibration Samples Principle Component Analysis Model Building Three source parameter sampling schemes Simulation Quasar data sets New data sets
of Fully Bayesian UCI February 7, 2012 of Fully Bayesian Calibration Samples Principle Component Analysis Model Building Three source parameter sampling schemes Simulation Quasar data sets New data sets
MOS CCD NOISE. Andy Read. Tao Song, Steve Sembay, Tony Abbey
 MOS CCD NOISE Andy Read Tao Song, Steve Sembay, Tony Abbey Noise in MOS CCDs Low energy plateau (
MOS CCD NOISE Andy Read Tao Song, Steve Sembay, Tony Abbey Noise in MOS CCDs Low energy plateau (
Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013
 Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013 In this activity, we will use calibrated visibilities from the Submillimeter Array to create an image of a disk around a nearby young
Deconvolution and Imaging ASTR 240: In-class activity, April 1, 2013 In this activity, we will use calibrated visibilities from the Submillimeter Array to create an image of a disk around a nearby young
4Kx4K CCD Imager for the 3.6m DOT
 4Kx4K CCD Imager for the 3.6m DOT As an in-house developmental activity, the 4KX4K CCD Imager is designed and assembled as a first light instrument for the axial port of the 3.6m DOT using the f/9 beam
4Kx4K CCD Imager for the 3.6m DOT As an in-house developmental activity, the 4KX4K CCD Imager is designed and assembled as a first light instrument for the axial port of the 3.6m DOT using the f/9 beam
2. ctifile,s,h, CALDB,,, ACIS CTI ARD file (NONE none CALDB <filename>)
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM January 17, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Adjusting ACIS Event Data to Compensate for CTI Revision:
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM January 17, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Adjusting ACIS Event Data to Compensate for CTI Revision:
GIANO: The Graphical User Interface Manual
 1/22 GIANO: The Graphical User Interface Manual Document: TNG-GIANO-001 Issue: 1.0 Prepared by : Name: S. Scuderi Institute: INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Catania Date : Approved by : Name: L. Origlia
1/22 GIANO: The Graphical User Interface Manual Document: TNG-GIANO-001 Issue: 1.0 Prepared by : Name: S. Scuderi Institute: INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Catania Date : Approved by : Name: L. Origlia
Relevant Documents. MEMORANDUM February 24, 2015
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM February 24, 2015 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: David Huenemoerder, John Davis, SDS Subject: ACIS Dead Area Algorithm and File Specifications
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM February 24, 2015 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: David Huenemoerder, John Davis, SDS Subject: ACIS Dead Area Algorithm and File Specifications
1 Introduction. 2 destreak is Too Conservative. MEMORANDUM June 12, 2013
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM June 12, 2013 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: John C. Houck, SDS Subject: A better row-loss upper limit for destreak Revision: 1.1 URL:
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM June 12, 2013 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: John C. Houck, SDS Subject: A better row-loss upper limit for destreak Revision: 1.1 URL:
ESAS into SAS ESAC. XMM-Newton. Carlos GABRIEL & Aitor IBARRA. XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre ESAC / ESA SAS
 E into Carlos GABRIEL & Aitor IBARRA Science Operations Centre / ESA What is E? Extended Source Analysis Software (E): * package for the analysis of EPIC MOS and pn observations (by SS & KK), [suited especially
E into Carlos GABRIEL & Aitor IBARRA Science Operations Centre / ESA What is E? Extended Source Analysis Software (E): * package for the analysis of EPIC MOS and pn observations (by SS & KK), [suited especially
2. ctifile,s,h, CALDB,,, ACIS CTI ARD file (NONE none CALDB <filename>)
 MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM August 11, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Adjusting ACIS Event Data to Compensate for CTI Revision:
MIT Kavli Institute Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM August 11, 2006 To: Jonathan McDowell, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: Adjusting ACIS Event Data to Compensate for CTI Revision:
MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015
 MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015 Presenter Dave Jacobsen Senior Application Engineer at Lambda Research Corporation for
MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015 Presenter Dave Jacobsen Senior Application Engineer at Lambda Research Corporation for
3-D. Here red spheres show the location of gold nanoparticles inside/around a cell nucleus.
 3-D The CytoViva 3-D System allows the user can locate objects of interest in a 3-D space. It does this by acquiring multiple Z planes and performing our custom software routines to locate and observe
3-D The CytoViva 3-D System allows the user can locate objects of interest in a 3-D space. It does this by acquiring multiple Z planes and performing our custom software routines to locate and observe
Basic Use of SExtractor Catalogs With TweakReg - I
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2015-04 Basic Use of SExtractor Catalogs With TweakReg - I Ray A. Lucas and Bryan Hilbert May 27, 2015 ABSTRACT We describe using external SExtractor (v2.8.6) catalogs from
Instrument Science Report ACS 2015-04 Basic Use of SExtractor Catalogs With TweakReg - I Ray A. Lucas and Bryan Hilbert May 27, 2015 ABSTRACT We describe using external SExtractor (v2.8.6) catalogs from
Basic PyRAF. Version 2.0 July Space Telescope Science Institute 3700 San Martin Drive Baltimore, Maryland 21218
 Version 2.0 July 2014 Basic PyRAF Space Telescope Science Institute 3700 San Martin Drive Baltimore, Maryland 21218 Operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., for the
Version 2.0 July 2014 Basic PyRAF Space Telescope Science Institute 3700 San Martin Drive Baltimore, Maryland 21218 Operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., for the
simx: A General-Purpose X-ray Event Simulator Randall Smith
 simx: A General-Purpose X-ray Event Simulator Randall Smith Download simx from http://hea-www.harvard.edu/simx Install via: (requires c compiler) unix% tar -zxf simx-2.4.2.tar.gz unix% cd simx-2.4.2 unix%./configure
simx: A General-Purpose X-ray Event Simulator Randall Smith Download simx from http://hea-www.harvard.edu/simx Install via: (requires c compiler) unix% tar -zxf simx-2.4.2.tar.gz unix% cd simx-2.4.2 unix%./configure
Introduction to Raman spectroscopy measurement data processing using Igor Pro
 Introduction to Raman spectroscopy measurement data processing using Igor Pro This introduction is intended to minimally guide beginners to processing Raman spectroscopy measurement data, which includes
Introduction to Raman spectroscopy measurement data processing using Igor Pro This introduction is intended to minimally guide beginners to processing Raman spectroscopy measurement data, which includes
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
CanariCam: Polarimetry & Data Reduction
 Acknowledgements CanariCam: Polarimetry & Data Reduction Chris Packham, Charlie Telesco & The CanariCam Team University of Florida Text heavily drawn from Polpack Starlink manual by Berry & Gledhill Longevity
Acknowledgements CanariCam: Polarimetry & Data Reduction Chris Packham, Charlie Telesco & The CanariCam Team University of Florida Text heavily drawn from Polpack Starlink manual by Berry & Gledhill Longevity
Spectroscopy techniques II. Danny Steeghs
 Spectroscopy techniques II Danny Steeghs Conducting long-slit spectroscopy Science goals must come first, what are the resolution and S/N requirements? Is there a restriction on exposure time? Decide on
Spectroscopy techniques II Danny Steeghs Conducting long-slit spectroscopy Science goals must come first, what are the resolution and S/N requirements? Is there a restriction on exposure time? Decide on
This document is divided into the following sections.
 Chip Algorithm Setup S1 Purpose The purpose of this document is to assist trained 5DX programmers with setting up the Chip algorithms. In this document This document is divided into the following sections.
Chip Algorithm Setup S1 Purpose The purpose of this document is to assist trained 5DX programmers with setting up the Chip algorithms. In this document This document is divided into the following sections.
THE EPIC SIMULATOR AND PILE-UP MODELLING. Prashin Jethwa EPIC BOC /3/2012
 THE EPIC SIMULATOR AND PILE-UP MODELLING Prashin Jethwa EPIC BOC 2012 7/3/2012 OUTLINE Introduction to the EPIC simulator What is it? How does it work? Validation Pile-up modelling Flux losses Spectral
THE EPIC SIMULATOR AND PILE-UP MODELLING Prashin Jethwa EPIC BOC 2012 7/3/2012 OUTLINE Introduction to the EPIC simulator What is it? How does it work? Validation Pile-up modelling Flux losses Spectral
WSDC Subsystem Peer Review
 WSDC Subsystem Peer Review Multiband DETector () Ken Marsh (IPAC/Caltech) 1 Outline Relationship of to other WSDS pipeline modules Why multiband? Theoretical basis Procedure - Steps involved - Allowance
WSDC Subsystem Peer Review Multiband DETector () Ken Marsh (IPAC/Caltech) 1 Outline Relationship of to other WSDS pipeline modules Why multiband? Theoretical basis Procedure - Steps involved - Allowance
7.3 ACS/WFC: Optimizing the Image Alignment for Multiple Visits
 ACS/WFC: Optimizing the Image Alignment for Multiple Visits 186 7.3 ACS/WFC: Optimizing the Image Alignment for Multiple Visits Introduction Three ACS/WFC images of a crowded stellar field, obtained at
ACS/WFC: Optimizing the Image Alignment for Multiple Visits 186 7.3 ACS/WFC: Optimizing the Image Alignment for Multiple Visits Introduction Three ACS/WFC images of a crowded stellar field, obtained at
ENVI Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis
 ENVI Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...2 DEFINE ROIS...3 Load AVIRIS Data...3 Create and Restore ROIs...3 Extract Mean Spectra from ROIs...4 DISCRIMINATE
ENVI Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...2 DEFINE ROIS...3 Load AVIRIS Data...3 Create and Restore ROIs...3 Extract Mean Spectra from ROIs...4 DISCRIMINATE
From multiple images to catalogs
 Lecture 14 From multiple images to catalogs Image reconstruction Optimal co-addition Sampling-reconstruction-resampling Resolving faint galaxies Automated object detection Photometric catalogs Deep CCD
Lecture 14 From multiple images to catalogs Image reconstruction Optimal co-addition Sampling-reconstruction-resampling Resolving faint galaxies Automated object detection Photometric catalogs Deep CCD
Gamma spectroscopic measurements using the PID350 pixelated CdTe radiation detector
 Gamma spectroscopic measurements using the PID350 pixelated CdTe radiation detector K. Karafasoulis, K. Zachariadou, S. Seferlis, I. Papadakis, D. Loukas, C. Lambropoulos, C. Potiriadis Abstract Spectroscopic
Gamma spectroscopic measurements using the PID350 pixelated CdTe radiation detector K. Karafasoulis, K. Zachariadou, S. Seferlis, I. Papadakis, D. Loukas, C. Lambropoulos, C. Potiriadis Abstract Spectroscopic
Diffuse Source Absolute Sensitivity and Point Source Relative Sensitivity as a Function of Extraction Slit Height for STIS First-Order Modes
 Instrument Science Report STIS 98-01 Diffuse Source Absolute Sensitivity and Point Source Relative Sensitivity as a Function of Extraction Slit Height for STIS First-Order Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope
Instrument Science Report STIS 98-01 Diffuse Source Absolute Sensitivity and Point Source Relative Sensitivity as a Function of Extraction Slit Height for STIS First-Order Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope
444/544 Advanced Lab Manual Astronomy
 444/544 Advanced Lab Manual Astronomy INTRODUCTION The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with contemporary astronomical methods. Astronomers use CCD detectors to measure light variations
444/544 Advanced Lab Manual Astronomy INTRODUCTION The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with contemporary astronomical methods. Astronomers use CCD detectors to measure light variations
TracePro Stray Light Simulation
 TracePro Stray Light Simulation What Is Stray Light? A more descriptive term for stray light is unwanted light. In an optical imaging system, stray light is caused by light from a bright source shining
TracePro Stray Light Simulation What Is Stray Light? A more descriptive term for stray light is unwanted light. In an optical imaging system, stray light is caused by light from a bright source shining
Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26
 Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26 Section 1: First setup computer. (If this step is not correctly setup, nothing will work properly.) 1. Verify that lab computer is booted in windows
Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26 Section 1: First setup computer. (If this step is not correctly setup, nothing will work properly.) 1. Verify that lab computer is booted in windows
MIT Center for Space Research. Chandra X-Ray Center. 1 acis build mask. MEMORANDUM April 26, Description. 1.2 Input. 1.
 MIT Center for Space Research Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM April 26, 2004 To: Martin Elvis, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build mask Revision: 3.9 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#msk
MIT Center for Space Research Chandra X-Ray Center MEMORANDUM April 26, 2004 To: Martin Elvis, SDS Group Leader From: Glenn E. Allen, SDS Subject: acis build mask Revision: 3.9 URL: http://space.mit.edu/cxc/docs/docs.html#msk
ASKAP Pipeline processing and simulations. Dr Matthew Whiting ASKAP Computing, CSIRO May 5th, 2010
 ASKAP Pipeline processing and simulations Dr Matthew Whiting ASKAP Computing, CSIRO May 5th, 2010 ASKAP Computing Team Members Team members Marsfield: Tim Cornwell, Ben Humphreys, Juan Carlos Guzman, Malte
ASKAP Pipeline processing and simulations Dr Matthew Whiting ASKAP Computing, CSIRO May 5th, 2010 ASKAP Computing Team Members Team members Marsfield: Tim Cornwell, Ben Humphreys, Juan Carlos Guzman, Malte
Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26
 Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26 Section 1: First setup computer. (If this step is not correctly setup, nothing will work properly.) 1. Verify that lab computer is booted in windows
Astronomy 150 Asteroid Lab Due in Class: Monday, Oct. 26 Section 1: First setup computer. (If this step is not correctly setup, nothing will work properly.) 1. Verify that lab computer is booted in windows
Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial
 Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial The ENVI Crop Science platform contains remote sensing analytic tools for precision agriculture and agronomy. In this tutorial you will go through a typical workflow
Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial The ENVI Crop Science platform contains remote sensing analytic tools for precision agriculture and agronomy. In this tutorial you will go through a typical workflow
Software Survey Results
 Software Survey Results http://icxc.harvard.edu/sds/survey/results.html CXC Groups Last modified: 21 May 2003 Software Survey Results Presented here are the results from the CXC Software User Survey conducted
Software Survey Results http://icxc.harvard.edu/sds/survey/results.html CXC Groups Last modified: 21 May 2003 Software Survey Results Presented here are the results from the CXC Software User Survey conducted
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD (301) (301) fax
 Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Galaxie Report Editor
 Varian, Inc. 2700 Mitchell Drive Walnut Creek, CA 94598-1675/USA Galaxie Report Editor User s Guide Varian, Inc. 2008 Printed in U.S.A. 03-914949-00: Rev 6 Galaxie Report Editor i Table of Contents Introduction...
Varian, Inc. 2700 Mitchell Drive Walnut Creek, CA 94598-1675/USA Galaxie Report Editor User s Guide Varian, Inc. 2008 Printed in U.S.A. 03-914949-00: Rev 6 Galaxie Report Editor i Table of Contents Introduction...
ENVI Classic Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis
 ENVI Classic Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis Basic Hyperspectral Analysis 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 Define ROIs 3 Load AVIRIS Data 3 Create and Restore ROIs 3 Extract Mean Spectra from ROIs
ENVI Classic Tutorial: Basic Hyperspectral Analysis Basic Hyperspectral Analysis 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 Define ROIs 3 Load AVIRIS Data 3 Create and Restore ROIs 3 Extract Mean Spectra from ROIs
ALMA REMOTE MINING EXPERIMENT ARTEMIX. Yaye Awa Ba, Philippe. Salomé, Michel. Caillat (LERMA) with credits to : L. Loria, N.
 ALMA REMOTE MINING EXPERIMENT Yaye Awa Ba, Philippe. Salomé, Michel. Caillat (LERMA) with credits to : L. Loria, N. Kasradze Archive and Data Mining Goals (i) Search by products not by instrumental configuration
ALMA REMOTE MINING EXPERIMENT Yaye Awa Ba, Philippe. Salomé, Michel. Caillat (LERMA) with credits to : L. Loria, N. Kasradze Archive and Data Mining Goals (i) Search by products not by instrumental configuration
Chandra/ACIS Subpixel Event Repositioning. II. Further Refinements and Comparison between Backside and Front-side Illuminated X-ray CCDs
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Articles 2004 Chandra/ACIS Subpixel Event Repositioning. II. Further Refinements and Comparison between Backside and Front-side Illuminated X-ray CCDs
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Articles 2004 Chandra/ACIS Subpixel Event Repositioning. II. Further Refinements and Comparison between Backside and Front-side Illuminated X-ray CCDs
Tutorial 2: Analysis of DIA/SWATH data in Skyline
 Tutorial 2: Analysis of DIA/SWATH data in Skyline In this tutorial we will learn how to use Skyline to perform targeted post-acquisition analysis for peptide and inferred protein detection and quantification.
Tutorial 2: Analysis of DIA/SWATH data in Skyline In this tutorial we will learn how to use Skyline to perform targeted post-acquisition analysis for peptide and inferred protein detection and quantification.
Overview of Post-BCD Processing
 Overview of Post-BCD Processing Version 1.1 Release Date: January 7, 2004 Issued by the Spitzer Science Center California Institute of Technology Mail Code 314-6 1200 E. California Blvd Pasadena, California
Overview of Post-BCD Processing Version 1.1 Release Date: January 7, 2004 Issued by the Spitzer Science Center California Institute of Technology Mail Code 314-6 1200 E. California Blvd Pasadena, California
1. ABOUT INSTALLATION COMPATIBILITY SURESIM WORKFLOWS a. Workflow b. Workflow SURESIM TUTORIAL...
 SuReSim manual 1. ABOUT... 2 2. INSTALLATION... 2 3. COMPATIBILITY... 2 4. SURESIM WORKFLOWS... 2 a. Workflow 1... 3 b. Workflow 2... 4 5. SURESIM TUTORIAL... 5 a. Import Data... 5 b. Parameter Selection...
SuReSim manual 1. ABOUT... 2 2. INSTALLATION... 2 3. COMPATIBILITY... 2 4. SURESIM WORKFLOWS... 2 a. Workflow 1... 3 b. Workflow 2... 4 5. SURESIM TUTORIAL... 5 a. Import Data... 5 b. Parameter Selection...
CRISM (Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars) on MRO. Calibration Upgrade, version 2 to 3
 CRISM (Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars) on MRO Calibration Upgrade, version 2 to 3 Dave Humm Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD 20723 18 March 2012 1 Calibration Overview 2 Simplified
CRISM (Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars) on MRO Calibration Upgrade, version 2 to 3 Dave Humm Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD 20723 18 March 2012 1 Calibration Overview 2 Simplified
IVOA Spectral Energy Distribution (SED) Data Model
 International Virtual Observatory Alliance IVOA Spectral Energy Distribution (SED) Data Model Version 1.0 IVOA Working Draft, 2012 October 15 This version: WD-SEDDM-1.0-20121015 Previous version(s): http://www.ivoa.net/internal/ivoa/interopmay2011sed/seddm-20110515.pdf
International Virtual Observatory Alliance IVOA Spectral Energy Distribution (SED) Data Model Version 1.0 IVOA Working Draft, 2012 October 15 This version: WD-SEDDM-1.0-20121015 Previous version(s): http://www.ivoa.net/internal/ivoa/interopmay2011sed/seddm-20110515.pdf
SPICAM Archive Tutorial. Principal Investigator : J.L. Bertaux Archive Manager : A. Reberac
 SPICAM Archive Tutorial Principal Investigator : J.L. Bertaux Archive Manager : A. Reberac 1 SPICAM Archive Tutorial SPICAM Instrument SPICAM data levels/products SPICAM Archive volume set organization
SPICAM Archive Tutorial Principal Investigator : J.L. Bertaux Archive Manager : A. Reberac 1 SPICAM Archive Tutorial SPICAM Instrument SPICAM data levels/products SPICAM Archive volume set organization
