Design Optimization of Robotic Arms
|
|
|
- Aleesha Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design Optimization of Robotic Arms 1. Prof. L. S Utpat Professor, Mechanical Engineering Dept., MMCOE, Pune -52 Pune University, Maharashtra, India 2. Prof. Chavan Dattatraya K Professor, Mechanical Engineering Dept., MMCOE, Pune-52 Pune University, Maharashtra, India PhD scholar, JJT University, Rajasthan 3. Yeolekar N., Sahasrabudhe A, Mandke S. Graduate Students MMCOE, Pune I) Abstract: A robot can be defined as a programmable, self-controlled device consisting of electronic, electrical, and mechanical unit. The elements which are common to all robots can be considered as the basic elements and are as follows:- Manipulator:- Controller: - End Effecter: - Sensors: - Energy Source: - The robot manipulator can be divided into two sections, each with a different function: Arm and Body and the Wrist - The current design of the robotic arm consists of manipulators that have been over designed to meet reliability requirements. Hence these manipulators have been designed in a way that they do not make best use of material. They have a low payload to weight ratio. This limits the payload capacity and increases the power requirement for movement of the arms. Attempt has been made to optimize the design of the arms using FEA as a tool. Strength and stiffness have been kept as design criteria while optimizing the weight of the moving arms. The results have shown corresponding reduction in power requirement for arms movement.. \Keywords: Robot, manipulator, topology, optimization,arm,etc II) PROBLEM DEFINITION: The most important characteristic of an industrial robot is the weight to maximum payload ratio. The minimization of said ratio can only be achieved by reducing the weight of the robot manipulator. This will also result in increased payload capacity. However this will have to be achieved without severely compromising the static stiffness or the maximum allowable deflection of the individual linkages. Initially the components were over-designed to meet the reliability requirements. But in today s economy, the weight of industrial robots and its impact on initial and operating cost are of significant concern for both manufacturers and end users. Hence the components of the robot assembly to be taken into consideration for optimization include 1. The Primary Arm 2. The Secondary Arm CURRENT SPECIFICATIONS OF ROBOT: Manipulator Weights 1. Primary Arm kg 2. Secondary Arm 4.11 kg Combined Manipulator weight 7.27 kg Rated Payload - 2 kg 1 1
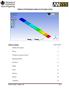
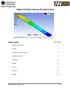
2 III) OPTIMIZATION: This analysis shall be based on the finite element method (FEM) and consists of completion of the design model using the dimensional data as design variables. Optimized structural design for the structures of the industrial robots have to meet certain criteria regarding dimensional design and shape, material consumption and adapt this to the functional requirements. To improve the static and dynamic behaviour of the industrial robot structure, the following requirements must be accomplished: Minimum weight structure; Maximum static stiffness of structural elements; Minimum deformation Max. precision at the end-effecter. TOPOLOGICAL OR LANDSCAPE OPTIMIZATION: The Primary arm was initially designed using empirical approach. The wall thicknesses were decided based on minimum permissible values for casting process. The box structure was stiffened with the help of a simple cross rib arrangement. INITIAL STUDIES For the calculation of initial stresses and deformation in the primary arm the forces acting were calculated. The forces for analysis are 1) Combined load of the Secondary arm, Secondary arm balancer and secondary arm motor of 98.1 N along the negative Z-axis applied at the face of the upper flange 2) The gravitational force acting globally in the negative Z- axis. Topology optimization is a mathematical approach that optimizes material layout within a given design space, for a given set of loads and boundary conditions such that the resulting layout meets a prescribed set of performance targets. Using topology optimization, engineers can find the best concept design that meets the design requirements. Topology optimization has been implemented through the use of finite element methods for the analysis, and optimization techniques based on the method of genetic algorithms, optimality criteria method, and level sets. The topological Optimization using FEM methods for Robotics was employed with shape optimization techniques Fig III.2 Results for Initial Design of Primary Arm Maximum Deformation: 6.296e-005m = microns Maximum Equivalent Stress = N/mm 2 Fig III.1 Visualization of existing robot INITIAL DESIGN OF PRIMARY ARM: INITIAL STATUS: 2 INITIAL DESIGN OF SECONDARY ARM: INITIAL STATUS: The Secondary arm was initially designed using empirical approach. The cross-section of the arm is circular to account for 2
3 maximum stiffness. The structure is symmetrical across the XY plane. INITIAL STUDIES For the calculation of initial stresses and deformation in the primary arm, the forces acting were calculated. The forces for analysis are The load of the gripper mechanism and the maximum payload of 29.43N along the negative Y-axis applied at the face of the front flange. The gravitational force acting globally in the negative Y- axis. optimization of the primary and secondary arms. The material values for the optimization was set for Aluminum alloy Al Si 12. Young s Modulus E = X 106 N/mm 2 Poisson s Ratio = 0.34 Density = 2710 kg/m 2 PRIMARY ARM OPTIMIZATION: The basic steps for optimization in Ansys are Define the structural problem: The optimization model of the primary arm consists of a completely solid structure. Select the element types: Element type selected is SOLID 95. Specify optimized and non-optimized regions: The top and bottom flanges are selected as the non-optimized regions while the rest of the structure is selected as the optimized region. Both these regions are given the element type of SOLID 95. Define and control the load cases or frequency extraction:. For the primary arm the completely extended position was considered. Forces acting are discussed in initial studies. The fixed support was given on the face of the bottom flange. Define and control the optimization process: The mesh size for this given problem is given as 5. This will create elements of equal size so as to facilitate measurement of the optimized shape. Figure shows the mesh of the structure. The required volume reduction is specified as 50% and the number of iterations given are 50. Fig III.3 Results for Initial Design of Secondary Arm Maximum Deformation: = microns Maximum Equivalent Stress = N/mm 2 TOPOLOGICAL OPIMIZATION The actual optimization of the primary and secondary arms was done using the Ansys topological optimization routine. The material used for the initial primary and secondary arms is Al Si 12.The same material is considered for the topological Fig III.4 Mesh of Structural Problem for Primary Arm REVIEW THE RESULTS: 3 3
4 The results obtained by the optimization routine are as seen the following figure. The blue colour represents material to be removed while the red represents material to be kept. Fig III.5 Optimization for Primary Arm The result is then refined as to show only the elements that are meant to be kept. Fig III.7 Structural Problem Definition for Secondary Arm The element type selected is SOLID 95. The top and bottom flanges are selected as the non-optimized regions while the rest of the structure is selected as the optimized region. Both these regions are given the element type of SOLID 95. For the primary arm the completely extended position was considered. Forces acting are discussed in initial studies. Fig III.6 Result of Optimization for Primary Arm(refined) CONCLUSIONS DRAWN: The material at the back of the arm can be removed. The material required to be kept increases gradually as we move from the upper flange to the lower flange. The material at the center of the arm can be removed keeping the side walls intact. Fig III.8 Mesh Secondary Arm REVIEW THE RESULTS: The results obtained by the optimization routine are as seen the following figure. The blue colour represents material to be removed while the red represents material to be kept. SECONDARY ARM OPTIMIZATION Similar steps as used for primary arm optimization were used. The optimization model of the primary arm consists of a completely solid structure as shown in the figure. Fig III.9 Optimization for Secondary Arm 4 4
5 The result is then refined as to show only the elements that are meant to be kept. Fig III.10 Result of Optimization for Secondary Arm(refined) The element type selected is PLANE 82. Specify optimized and non-optimized regions: The top and bottom flanges are selected as the non-optimized regions while the rest of the structure is selected as the optimized region. Both these regions are given the element type of PLANE 82. Define and control the optimization process: The mesh size for this given problem is smart size super fine mesh. This will create very small elements which will generate an optimized rib structure for a given problem. Figure shows the mesh of the structure. The required volume reduction is specified as 70% and the number of iterations give are 50. CONCLUSIONS DRAWN: The proposed section of the secondary arm should be an I section. The arm should taper towards the front while remaining thicker towards the boss side of the arm. IV) PRIMARY ARM RIBS OPTIMIZATION: It is has been seen that the thickness of some sections of the primary arm are too large to be manufactured by standard casting process. Hence it has been decided that a front face of the primary arm shall be ribbed for generating a better design. For generating the ribs of the primary arm a 2-D section of the arm shall be considered and same forces shall be applied to it. An assumption is made that the load is a direct load and not an eccentric load for this optimization process. The basic steps for optimization used were: Define the structural problem: The optimization model of the primary arm consists of a 2-D structure as shown in the figure. Fig IV.2 Mesh of Structural Problem for Primary Arm Ribs REVIEW THE RESULTS: The results obtained by the optimization routine are as seen in the following figure. The blue colour represents material to be removed while the red represents material to be kept. Fig IV.1 Structural Problem Definition for Primary Arm Ribs 5 Fig IV.3 Result of Optimization for Primary Arm Ribs 5
6 CONCLUSIONS DRAWN: This is the approximate shape of the best rib structure for the give element for the given load condition. The best rib pattern is a cross rib pattern. The approximate centre of the rib structure should have greater material as compared to the rest of the rib structure. PART NAME: Secondary Arm SIZE: 350 X 100 X 80 1 No V) FINAL SHAPES BASED ON OPTIMIZATION RESULTS: Based on the optimization results the following dimensions for both the primary and secondary arm were finalized. The final shapes were based on the conclusions of the Topological Optimization. Basic Design considerations like minimum cross-section as well as space for various mountings and electronic components are taken into consideration. Manufacturing constraints such as limitations in the pattern making process, casting process etc, were also taken into consideration. Based on these constraints we managed to reach a optimized shape of the two arms. These shapes were then compared with initial shapes and difference in weight was calculated. There was no real change in the manufacturing process of the initial and final shapes of the primary and secondary arms. However a completely new pattern was required for the casting of the final shapes. PART NAME: Primary Arm SIZE: 400 X 120 X No. Fig V.2 Final Shape of Secondary Arm ANALYSIS OF FINAL SHAPES: The final shapes are analysed so as to ensure that the values of stress and maximum have not increased beyond the previous values. The analysis of the final shapes shall be done considering the same forces that have been applied for the analysis of the initial shapes. Based on the 3D model, the volume and hence the weight is calculated. Density of Aluminium Alloy Al Si 12 = 2710 kg/m 2 Arm 2 Initial Volume= mm 3 Arm 2 Initial Weight = X 2.71 X 10-6 kg = 3.16 kg Arm 2 Final Volume = mm 3 Arm 2 Final Weight = X 2.71 X 10-6 kg = 2.61 kg Reduction in Weight = 0.55 kg % Reduction in Weight = % Fig V.1 Final Shape of Primary Arm Arm 1 Initial Volume = mm 3 Arm 1 Initial Weight = X 2.71 X 10-6 kg = 4.11 kg Arm 1 Final Volume = mm 3 Arm 1 Final Weight = X 2.71 X 10-6 kg = 3.15 kg Reduction in Weight = 0.95 kg % Reduction in Weight = % 6 6
7 Fig V.4 Analysis of Secondary Arm RESULTS: Maximum Deformation: 2.427e-006m = microns. Max. Equivalent Stress = 1.590e+005 N/m 2 =0.159 N/mm 2 Fig V.3 Analysis of Primary Arm RESULTS: Maximum Deformation: 2.390e-005m = 23.9 microns Maximum Equivalent Stress = 1.876e+006 N/m 2 =1.876 N/mm 2 ANALYTICAL CALCULATIONS: In order to guarantee that the optimized design has greater stiffness as compared to initial design the deflection analysis of the initial and optimized shapes is done analytically. The following assumptions are made in order to simplify the calculations. The Load acting on both the arms is static load. The load acting on the arm is acting along the centre of gravity of the arm. The cross-section of the arm is uniform throughout the length. The arm is completely fixed at the support end. CALCULATIONS: Bending stress and deflection for un-optimized arm I M.I. = mm 4 Bending moment of load acting at free end of cantilever beam 7 M = W L = = N.mm Bending stress using flexural formula for pure bending M/I = σ/y = E/R Where, M = Bending Moment I = Moment of Inertia σ = Bending stress 7
8 Current(Amperes) Y = Distance between extreme fibre to neutral axis E = Young Modulus R = Radius of curvature σ = 0.44 N/mm 2 Deflection for cantilever beam y = Wl 3 / 3E I = mm. Bending stress and deflection for optimized arm I Moment of inertia = Ixx = mm 4 Bending moment acting at the free end of the cantilever beam M= WL = = N.mm The bending stress using flexural formula for pure bending σ = MY/I = N/mm 2 Calculation for the deflection of cantilever beam y = Wl 3 /3E I = mm Bending stress and deflection for Un-optimized arm II Moment of inertia, I = mm 4 Bending moment acting at the free end of the cantilever beam M= WL = = 8829 N.mm Bending stress using flexural formula for pure bending σ = MY/I = N/mm 2 Deflection of cantilever beam y = mm Bending stress and deflection for optimized arm II Moment of Inertia by using parallel axis theorem M.I. = mm 4 Bending moment of load acting at free end of cantilever beam Unoptimized Arm 2 = mm Optimized Arm 2 = mm VALIDATION OF RESULTS: The effects of optimization have to be checked by implementation of the optimized shapes on the system. The values of current drawn by the motors for raising the payload are observed. The graphs of the current drawn by initial design and the current drawn by optimized design are plotted against the payload lifted for both the primary and secondary arm. For observations on the primary arm the secondary arm is kept in home position and only the primary arm is operated. It is to be noted that the current drawn by motors for lowering the load did not vary for initial or optimized design. Graph for Current Drawn by Primary Arm kg 0.5 kg 1 kg 1.5 kg 2 kg Payload(Kg) Optimized Shape Fig V.5 Graph of Current Drawn by Primary Arm Motor M = W L = = 8829 N.mm Bending stress using flexural formula for pure bending σ = MY/I = N/mm 2 Deflection for cantilever beam y = Wl3/ 3E I = mm Comparison between Initial and optimized shape deflections Unoptimized Arm 1 = mm Optimized Arm 1 = = mm 8 8
9 Current(Amperes) Graph for Current Drawn by Secondary Arm kg 0.5 kg 1 kg 1.5 kg 2 kg Payload(Kg) Initial Shape Fig V.6 Graph of Current Drawn by Secondary Arm Motor CONCLUSION ON OPTIMIZATION: Hence we can conclude that the final shapes of the primary and secondary arms are lighter in weight than the initial design. The reduction in weight for Primary arm = 23.11% The reduction in weight for Secondary arm = 15.23% The final shapes also have greater stiffness than the initial shapes at the same given loading conditions. For Primary Arm Initial design deflection = microns Optimized design deflection = 23.9 microns For secondary Arm Initial design deflection = microns. Optimized design deflection = microns. The power required by the motors of the primary and secondary arms is reduced using the optimized design. Bibliography. 1. Weight-optimized Design of a Commercial Truck Front Suspension Component - Dana Corporation Testimonial, 2. Topology Optimization in ANSYS - Brian King, IMPACT Engineering Solutions, 3. Optimization design for the structure of an RRR type industrial robot - Adrian Ghiorghe, U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 72, Iss. 4, Topology Optimization and Casting - Thorsten Schmidt, Technical Director, Heidenreich & Harbeck AG, Moelln, Germany, 5. Application of Topology Optimization and Manufacturing Simulations - Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2008 Vol II, IMECS 2008, March, 2008, Hong KongTruck. 6. DVP PLC Application Manual. 7. Ansys 11 Help. 8. Mechatronics An Introduction Robert H Bishop. 9. Machine Design B. B Bhandari. 10. ASM Metals HandBook Volume 02 - Properties and Selection Nonferrous Alloys and Special Purpose Materials. CONCLUSIONS: We succeeded in improving the design of the manipulators and hence reduced their weight. This also in turn improved the performance characteristics of the robot since less power was required by the motors for the same given payload. 9 9
Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post
 Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Optimization of Tapered Cantilever Beam Using Genetic Algorithm: Interfacing MATLAB and ANSYS
 Optimization of Tapered Cantilever Beam Using Genetic Algorithm: Interfacing MATLAB and ANSYS K R Indu 1, Airin M G 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, SCMS School of, Kerala, India 1 Assistant
Optimization of Tapered Cantilever Beam Using Genetic Algorithm: Interfacing MATLAB and ANSYS K R Indu 1, Airin M G 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, SCMS School of, Kerala, India 1 Assistant
Topology Optimization and Analysis of Crane Hook Model
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Topology Optimization and Analysis of Crane Hook Model Thejomurthy M.C 1, D.S Ramakrishn 2 1 Dept. of Mechanical engineering, CIT, Gubbi, 572216, India 2 Dept. of Mechanical engineering,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Topology Optimization and Analysis of Crane Hook Model Thejomurthy M.C 1, D.S Ramakrishn 2 1 Dept. of Mechanical engineering, CIT, Gubbi, 572216, India 2 Dept. of Mechanical engineering,
FEA and Topology Optimization of an Engine Mounting Bracket
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sanket
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sanket
TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF WING RIBS IN CESSNA CITATION
 TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF WING RIBS IN CESSNA CITATION [1],Sathiyavani S [2], Arun K K [3] 1,2 student, 3 Assistant professor Kumaraguru College of technology, Coimbatore Abstract Structural design optimization
TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF WING RIBS IN CESSNA CITATION [1],Sathiyavani S [2], Arun K K [3] 1,2 student, 3 Assistant professor Kumaraguru College of technology, Coimbatore Abstract Structural design optimization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY (IJDMT)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY (IJDMT) International Journal of Design and Manufacturing Technology (IJDMT), ISSN 0976 6995(Print), ISSN 0976 6995 (Print) ISSN 0976 7002 (Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY (IJDMT) International Journal of Design and Manufacturing Technology (IJDMT), ISSN 0976 6995(Print), ISSN 0976 6995 (Print) ISSN 0976 7002 (Online)
Design and Validation of XY Flexure Mechanism
 Design and Validation of XY Flexure Mechanism 1 Pratik M. Waghmare, 2 Shrishail B. Sollapur 1 Research Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1.2 Sinhgad Academy of Engineering,
Design and Validation of XY Flexure Mechanism 1 Pratik M. Waghmare, 2 Shrishail B. Sollapur 1 Research Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1.2 Sinhgad Academy of Engineering,
TOPOLOGICAL OPTIMIZATION OF STEERING KNUCKLE BY USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS
 TOPOLOGICAL OPTIMIZATION OF STEERING KNUCKLE BY USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS Prof.P.S.Gorane 1,Mr. Piyush Jain 2 Mechanical engineering, G. S.Mozecollege of engineering, Savitri Bai Phule Pune
TOPOLOGICAL OPTIMIZATION OF STEERING KNUCKLE BY USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING PROCESS Prof.P.S.Gorane 1,Mr. Piyush Jain 2 Mechanical engineering, G. S.Mozecollege of engineering, Savitri Bai Phule Pune
Settlement of a circular silo foundation
 Engineering manual No. 22 Updated: 02/2018 Settlement of a circular silo foundation Program: FEM File: Demo_manual_22.gmk The objective of this manual is to describe the solution to a circular silo foundation
Engineering manual No. 22 Updated: 02/2018 Settlement of a circular silo foundation Program: FEM File: Demo_manual_22.gmk The objective of this manual is to describe the solution to a circular silo foundation
Design and Analysis of a Single Notch Parallelogram Flexure Mechanism Based X-Y Nanopositioning Stage
 Design and Analysis of a Single Notch Parallelogram Flexure Mechanism Based X-Y Nanopositioning Stage Vithun S N *, Narendra Reddy T 1, Prakash Vinod 2, P V Shashikumar 3 Central Manufacturing Technology
Design and Analysis of a Single Notch Parallelogram Flexure Mechanism Based X-Y Nanopositioning Stage Vithun S N *, Narendra Reddy T 1, Prakash Vinod 2, P V Shashikumar 3 Central Manufacturing Technology
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF ROTARY TURRET PLATE OF POUCHER MACHINE
 DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF ROTARY TURRET PLATE OF POUCHER MACHINE Jigar G. Patel Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad 382481, India Email:14mmcc17@nirmuni.ac.in Mitesh B. Panchal Mechanical
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF ROTARY TURRET PLATE OF POUCHER MACHINE Jigar G. Patel Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad 382481, India Email:14mmcc17@nirmuni.ac.in Mitesh B. Panchal Mechanical
Design optimization of C Frame of Hydraulic Press Machine
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 79-89 www.iosrjournals.org Design optimization of C Frame of Hydraulic Press Machine Ameet B. Hatapakki 1, U D. Gulhane
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 79-89 www.iosrjournals.org Design optimization of C Frame of Hydraulic Press Machine Ameet B. Hatapakki 1, U D. Gulhane
Stress Analysis of thick wall bellows using Finite Element Method
 Stress Analysis of thick wall bellows using Finite Element Method Digambar J. Pachpande Post Graduate Student Department of Mechanical Engineering V.J.T.I. Mumbai, India Prof. G. U. Tembhare Assistant
Stress Analysis of thick wall bellows using Finite Element Method Digambar J. Pachpande Post Graduate Student Department of Mechanical Engineering V.J.T.I. Mumbai, India Prof. G. U. Tembhare Assistant
Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Validation of Lower Control Arm
 Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Validation of Lower Control Arm 1 Miss. P. B. Patil, 2 Prof. M. V. Kharade 1 Assistant Professor at Vishweshwaraya Technical Campus Degree wing, Patgaon, Miraj
Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Validation of Lower Control Arm 1 Miss. P. B. Patil, 2 Prof. M. V. Kharade 1 Assistant Professor at Vishweshwaraya Technical Campus Degree wing, Patgaon, Miraj
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses
 Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Design of Arm & L-bracket and It s Optimization By Using Taguchi Method
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 28-38 www.iosrjournals.org Design of Arm & L-bracket and It s Optimization By Using Taguchi Method S.
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X PP. 28-38 www.iosrjournals.org Design of Arm & L-bracket and It s Optimization By Using Taguchi Method S.
DESIGN & ANALYSIS OF CONNECTING ROD OF FORMING AND CUTTING DIE PILLAR STATION OF VACUUM FORMING MACHINE
 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 3, No. 3, July, 2014 2014 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved DESIGN & ANALYSIS OF CONNECTING ROD OF FORMING AND CUTTING DIE PILLAR STATION OF VACUUM FORMING MACHINE
Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 3, No. 3, July, 2014 2014 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved DESIGN & ANALYSIS OF CONNECTING ROD OF FORMING AND CUTTING DIE PILLAR STATION OF VACUUM FORMING MACHINE
ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLYWHEEL
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Sushama G Bawane et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 2, July 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLYWHEEL
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Sushama G Bawane et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 2, July 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLYWHEEL
EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY
 EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY J. Sauvé 1*, M. Dubé 1, F. Dervault 2, G. Corriveau 2 1 Ecole de technologie superieure, Montreal, Canada 2 Airframe stress, Advanced Structures,
EXACT BUCKLING SOLUTION OF COMPOSITE WEB/FLANGE ASSEMBLY J. Sauvé 1*, M. Dubé 1, F. Dervault 2, G. Corriveau 2 1 Ecole de technologie superieure, Montreal, Canada 2 Airframe stress, Advanced Structures,
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM
 Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
Effectiveness of Element Free Galerkin Method over FEM Remya C R 1, Suji P 2 1 M Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sri Vellappaly Natesan College of Engineering, Pallickal P O, Mavelikara, Kerala,
Analytical, Experimental Determination of Deflection of Curved Beams and its Validation
 Analytical, Experimental Determination of Deflection of Curved Beams and its Validation Yogesh Gangamwar 1, Sumit Chate 2, Makarand Bhandare 3, Vinit Deo 4, H.N.Deshpande 5 UG Student, Dept. of Mechanical
Analytical, Experimental Determination of Deflection of Curved Beams and its Validation Yogesh Gangamwar 1, Sumit Chate 2, Makarand Bhandare 3, Vinit Deo 4, H.N.Deshpande 5 UG Student, Dept. of Mechanical
Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla
 Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia redzuan@utm.my Keywords:
Non-Linear Analysis of Bolted Flush End-Plate Steel Beam-to-Column Connection Nur Ashikin Latip, Redzuan Abdulla 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia redzuan@utm.my Keywords:
Comparative Study of Topological Optimization of Beam and Ring Type Structures under static Loading Condition
 Comparative Study of Topological Optimization of Beam and Ring Type Structures under static Loading Condition Vani Taklikar 1, Anadi Misra 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, G.B.P.U.A.T,
Comparative Study of Topological Optimization of Beam and Ring Type Structures under static Loading Condition Vani Taklikar 1, Anadi Misra 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, G.B.P.U.A.T,
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR
 Phone: 01922 453038 www.hyperon-simulation-and-cad-services.co.uk Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR Date: 06 May 2017 Designer: Study name: AJWSP10033_FOLDED_STATIC Analysis type: Static Description
Phone: 01922 453038 www.hyperon-simulation-and-cad-services.co.uk Simulation of AJWSP10033_FOLDED _ST_FR Date: 06 May 2017 Designer: Study name: AJWSP10033_FOLDED_STATIC Analysis type: Static Description
Design Verification Procedure (DVP) Load Case Analysis of Car Bonnet
 Design Verification Procedure (DVP) Load Case Analysis of Car Bonnet Mahesha J 1, Prashanth A S 2 M.Tech Student, Machine Design, Dr. A.I.T, Bangalore, India 1 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical
Design Verification Procedure (DVP) Load Case Analysis of Car Bonnet Mahesha J 1, Prashanth A S 2 M.Tech Student, Machine Design, Dr. A.I.T, Bangalore, India 1 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical
Study of Design and Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket
 Study of Design and Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket Vyankatesh D. Pawade 1, Pushkaraj D. Sonawane 2 1 Student ME Mechanical Design Engineering, Maharashtra Institute of Technology,
Study of Design and Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket Vyankatesh D. Pawade 1, Pushkaraj D. Sonawane 2 1 Student ME Mechanical Design Engineering, Maharashtra Institute of Technology,
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE
 STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE 1 CHINMAY POTDAR, 2 AMEY PISE, 3 AISHWARYA DUBEY, 4 SUSHRUT JADHAV 1, 3 TATA Technologies Limited,
STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE 1 CHINMAY POTDAR, 2 AMEY PISE, 3 AISHWARYA DUBEY, 4 SUSHRUT JADHAV 1, 3 TATA Technologies Limited,
Analysis of Transverse Link under Static and Dynamic Loading Conditions
 Analysis of Transverse Link under Static and Dynamic Loading Conditions Rahul D. Sherke *1, A.P Tadamalle *2 * PG Scholar, ME Automotive Engineering, Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon (BK), Pune,
Analysis of Transverse Link under Static and Dynamic Loading Conditions Rahul D. Sherke *1, A.P Tadamalle *2 * PG Scholar, ME Automotive Engineering, Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon (BK), Pune,
Static Analysis of Five Degrees of Freedom Articulated Robot Arm Renish P. Vadhadiya 1 Prof. B.K. Patel 2 Chiragsinh Zala 3 Chintan C.
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 03, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Static Analysis of Five Degrees of Freedom Articulated Robot Arm Renish P. Vadhadiya
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 03, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Static Analysis of Five Degrees of Freedom Articulated Robot Arm Renish P. Vadhadiya
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism
 Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
Comparative Analysis of Marine Structural End Connections
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 12-20-2009 Comparative Analysis of Marine Structural End Connections Bret Silewicz
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 12-20-2009 Comparative Analysis of Marine Structural End Connections Bret Silewicz
Relief holes for the mitigation of stress concentration factor of a thin rectangular plate under in-plane loading
 Relief holes for the mitigation of stress concentration factor of a thin rectangular plate under in-plane loading S.R.Kambale 1, U.D.Gulhane 2 1 PG Student, Department of mechanical engineering, Finolex
Relief holes for the mitigation of stress concentration factor of a thin rectangular plate under in-plane loading S.R.Kambale 1, U.D.Gulhane 2 1 PG Student, Department of mechanical engineering, Finolex
NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN
 Vol 4 No 3 NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN Ass Lecturer Mahmoud A Hassan Al-Qadisiyah University College of Engineering hasaaneng@yahoocom ABSTRACT This paper provides some lighting
Vol 4 No 3 NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN Ass Lecturer Mahmoud A Hassan Al-Qadisiyah University College of Engineering hasaaneng@yahoocom ABSTRACT This paper provides some lighting
(Based on a paper presented at the 8th International Modal Analysis Conference, Kissimmee, EL 1990.)
 Design Optimization of a Vibration Exciter Head Expander Robert S. Ballinger, Anatrol Corporation, Cincinnati, Ohio Edward L. Peterson, MB Dynamics, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio David L Brown, University of Cincinnati,
Design Optimization of a Vibration Exciter Head Expander Robert S. Ballinger, Anatrol Corporation, Cincinnati, Ohio Edward L. Peterson, MB Dynamics, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio David L Brown, University of Cincinnati,
Design of a Flexural Joint using Finite Element Method
 Design of a Flexural Joint using Finite Element Method Abdullah Aamir Hayat, Adnan Akhlaq, M. Naushad Alam Abstract This paper presents the design and analysis of a compliant mechanism using hyperbolic
Design of a Flexural Joint using Finite Element Method Abdullah Aamir Hayat, Adnan Akhlaq, M. Naushad Alam Abstract This paper presents the design and analysis of a compliant mechanism using hyperbolic
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
Top Layer Subframe and Node Analysis
 Top Layer Subframe and Node Analysis By Paul Rasmussen 2 August, 2012 Introduction The top layer of the CCAT backing structure forms a critical interface between the truss and the primary subframes. Ideally
Top Layer Subframe and Node Analysis By Paul Rasmussen 2 August, 2012 Introduction The top layer of the CCAT backing structure forms a critical interface between the truss and the primary subframes. Ideally
THREE DIMENSIONAL ACES MODELS FOR BRIDGES
 THREE DIMENSIONAL ACES MODELS FOR BRIDGES Noel Wenham, Design Engineer, Wyche Consulting Joe Wyche, Director, Wyche Consulting SYNOPSIS Plane grillage models are widely used for the design of bridges,
THREE DIMENSIONAL ACES MODELS FOR BRIDGES Noel Wenham, Design Engineer, Wyche Consulting Joe Wyche, Director, Wyche Consulting SYNOPSIS Plane grillage models are widely used for the design of bridges,
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
Analysis and Design of Cantilever Springs
 Analysis and Design of Cantilever Springs Hemendra Singh Shekhawat, Hong Zhou Department of Mechanical Engineering Texas A&M University-Kingsville Kingsville, Texas, USA Abstract Cantilever springs are
Analysis and Design of Cantilever Springs Hemendra Singh Shekhawat, Hong Zhou Department of Mechanical Engineering Texas A&M University-Kingsville Kingsville, Texas, USA Abstract Cantilever springs are
DEVELOPMENT OF LEG WHEEL HYBRID HEXAPOD BOT
 DEVELOPMENT OF LEG WHEEL HYBRID HEXAPOD BOT Sai Srinivas Nallamothu, Sai Preetham Sata, P. Sateesh Kumar Reddy, B. Jaswanth Babu ABSTRACT The conventional mobile robotic platforms which either uses wheels
DEVELOPMENT OF LEG WHEEL HYBRID HEXAPOD BOT Sai Srinivas Nallamothu, Sai Preetham Sata, P. Sateesh Kumar Reddy, B. Jaswanth Babu ABSTRACT The conventional mobile robotic platforms which either uses wheels
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 2, Issue 3, September 2012
 Mitigation Curves for Determination of Relief Holes to Mitigate Concentration Factor in Thin Plates Loaded Axially for Different Discontinuities Shubhrata Nagpal, S.Sanyal, Nitin Jain Abstract In many
Mitigation Curves for Determination of Relief Holes to Mitigate Concentration Factor in Thin Plates Loaded Axially for Different Discontinuities Shubhrata Nagpal, S.Sanyal, Nitin Jain Abstract In many
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
Design and Analysis of Multifunctional Robot by using CATIA/PATRAN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design and Analysis of Multifunctional Robot by using CATIA/PATRAN Sruthi K V 1 Ramesh
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design and Analysis of Multifunctional Robot by using CATIA/PATRAN Sruthi K V 1 Ramesh
MEAM 550 Modeling and Design of MEMS Spring Solution to homework #3. In our notation and values, k = = =
 MEAM 550 Modeling and Design of MEMS Spring 004 Solution to homework # Problem 1 A fixed-guided beam (length = l, width = b, depth = h ) with a transverse tip load of F has the following formulas for maximum
MEAM 550 Modeling and Design of MEMS Spring 004 Solution to homework # Problem 1 A fixed-guided beam (length = l, width = b, depth = h ) with a transverse tip load of F has the following formulas for maximum
Analysis of Crank End of Connecting Rod using Finite Element Method
 Analysis of Crank End of Connecting Rod using Finite Element Method Mohammad Umair Zaki Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Noida International University Greater Noida, India e-mail-umairzaki@yahoo.com
Analysis of Crank End of Connecting Rod using Finite Element Method Mohammad Umair Zaki Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Noida International University Greater Noida, India e-mail-umairzaki@yahoo.com
GENERALIZED MODELLING OF THE STABILIZER LINK AND STATIC SIMULATION USING FEM
 ACTA UIVERSITATIS CIBINIENSIS TECHNICAL SERIES Vol. LXVIII 2016 DOI: 10.1515/aucts-2016-0004 GENERALIZED MODELLING OF THE STABILIZER LINK AND STATIC SIMULATION USING FEM COFARU Nicolae Florin professor
ACTA UIVERSITATIS CIBINIENSIS TECHNICAL SERIES Vol. LXVIII 2016 DOI: 10.1515/aucts-2016-0004 GENERALIZED MODELLING OF THE STABILIZER LINK AND STATIC SIMULATION USING FEM COFARU Nicolae Florin professor
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Smart actuator effectiveness improvement through modal analysis
 Smart actuator effectiveness improvement through modal analysis A. Joshi a and S. M. Khot b a Professor, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. b Research Scholar,
Smart actuator effectiveness improvement through modal analysis A. Joshi a and S. M. Khot b a Professor, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. b Research Scholar,
Simulation of a Steel Wire Straightening Taking into Account Nonlinear Hardening of Material
 ETASR - Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 2, No. 6, 2012, 320-324 320 Simulation of a Steel Wire Straightening Taking into Account Nonlinear Hardening of Material Ilya Khromov Dept.
ETASR - Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 2, No. 6, 2012, 320-324 320 Simulation of a Steel Wire Straightening Taking into Account Nonlinear Hardening of Material Ilya Khromov Dept.
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS PROGRAM OF FRAMES
 FINITE EEMENT ANAYSIS PROGRAM OF FRAMES Monica V. Pathak 1, Asst. Prof. G. B. Bhaskar 2 1 Student, M.Tech, 2 Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering, G. H. Raisoni Academy of Engineering &
FINITE EEMENT ANAYSIS PROGRAM OF FRAMES Monica V. Pathak 1, Asst. Prof. G. B. Bhaskar 2 1 Student, M.Tech, 2 Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering, G. H. Raisoni Academy of Engineering &
Using three-dimensional CURVIC contact models to predict stress concentration effects in an axisymmetric model
 Boundary Elements XXVII 245 Using three-dimensional CURVIC contact models to predict stress concentration effects in an axisymmetric model J. J. Rencis & S. R. Pisani Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Boundary Elements XXVII 245 Using three-dimensional CURVIC contact models to predict stress concentration effects in an axisymmetric model J. J. Rencis & S. R. Pisani Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA
 Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA Blessing O Fatola, Patrick Keogh and Ben Hicks Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Corresponding author bf223@bath.ac.uk Abstract. This paper
Modelling Flat Spring Performance Using FEA Blessing O Fatola, Patrick Keogh and Ben Hicks Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Corresponding author bf223@bath.ac.uk Abstract. This paper
Design and Analysis of Control Bay Used in Guided Missile
 Design and Analysis of Control Bay Used in Guided Missile Ragam Prashanth 1, D.Muppala 2, Nirmith Mishra 3 1PG Student, Department of Aerospace, MLR Inst of Tech and Management, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Design and Analysis of Control Bay Used in Guided Missile Ragam Prashanth 1, D.Muppala 2, Nirmith Mishra 3 1PG Student, Department of Aerospace, MLR Inst of Tech and Management, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
IJMH - International Journal of Management and Humanities ISSN:
 EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
In-plane principal stress output in DIANA
 analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections
 A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections Dawit Hailu +, Adil Zekaria ++, Samuel Kinde +++ ABSTRACT After the 1994 Northridge earthquake
A Multiple Constraint Approach for Finite Element Analysis of Moment Frames with Radius-cut RBS Connections Dawit Hailu +, Adil Zekaria ++, Samuel Kinde +++ ABSTRACT After the 1994 Northridge earthquake
Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using Ansys
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 9 ǁ September 2014 ǁ PP.18-23 Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 9 ǁ September 2014 ǁ PP.18-23 Static And Modal Analysis Of Rotating Wheel Rim Using
Topology Optimization of an Engine Bracket Under Harmonic Loads
 Topology Optimization of an Engine Bracket Under Harmonic Loads R. Helfrich 1, A. Schünemann 1 1: INTES GmbH, Schulze-Delitzsch-Str. 16, 70565 Stuttgart, Germany, www.intes.de, info@intes.de Abstract:
Topology Optimization of an Engine Bracket Under Harmonic Loads R. Helfrich 1, A. Schünemann 1 1: INTES GmbH, Schulze-Delitzsch-Str. 16, 70565 Stuttgart, Germany, www.intes.de, info@intes.de Abstract:
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
Design and development of optimized sprocket for Track hoe
 Design and development of optimized sprocket for Track hoe Mr. Laxmikant P.Sutar 1, Prof. Prashant.G. Karajagi 2, Prof. Rahul Kulkarni 3 1 PG Student, Siddhant College of Engineering, Pune, India 2 Assistant
Design and development of optimized sprocket for Track hoe Mr. Laxmikant P.Sutar 1, Prof. Prashant.G. Karajagi 2, Prof. Rahul Kulkarni 3 1 PG Student, Siddhant College of Engineering, Pune, India 2 Assistant
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF ROLLER BEARING
 Applied Computer Science, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 5 16 Submitted: 2016-02-09 Revised: 2016-03-03 Accepted: 2016-03-11 tapered roller bearing, dynamic simulation, axial load force Róbert KOHÁR *, Frantisek
Applied Computer Science, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 5 16 Submitted: 2016-02-09 Revised: 2016-03-03 Accepted: 2016-03-11 tapered roller bearing, dynamic simulation, axial load force Róbert KOHÁR *, Frantisek
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance
 Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Modeling, Simulation and Optimization Analysis on Steering Knuckle Component For Purpose of Weight Reduction
 Modeling, Simulation and Optimization Analysis on Steering Knuckle Component For Purpose of Weight Reduction W. M. Wan Muhamad 1, E. Sujatmika 1, Hisham Hamid 1 and Faris Tarlochan 2 1 UniKL Malaysia France
Modeling, Simulation and Optimization Analysis on Steering Knuckle Component For Purpose of Weight Reduction W. M. Wan Muhamad 1, E. Sujatmika 1, Hisham Hamid 1 and Faris Tarlochan 2 1 UniKL Malaysia France
Update On The Flexure Design
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY -LIGO- CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Technical Note LIGO-T007-00- D 00 Update On The Flexure Design Giles
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY -LIGO- CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Technical Note LIGO-T007-00- D 00 Update On The Flexure Design Giles
Dynamic Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket
 ISSN 2395-1621 Dynamic Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket #1 Vyankatesh D. Pawade, #2 Pushkaraj D. Sonawane 1 vdpawade@gmail.com 2 pushkaraj.sonawane@mitpune.edu.in 1 Student ME Design,
ISSN 2395-1621 Dynamic Analysis of Air Conditioner Compressor Mounting Bracket #1 Vyankatesh D. Pawade, #2 Pushkaraj D. Sonawane 1 vdpawade@gmail.com 2 pushkaraj.sonawane@mitpune.edu.in 1 Student ME Design,
Static Structural Analysis and Optimization of Engine Mounting Bracket
 ISSN 2395-1621 Static Structural Analysis and Optimization of Engine Mounting Bracket #1 Chandrashekhar B Tayde, #2 Prof. D. H. Burande 1 chandrashekhar.tayde@gmail.com 2 dhburande.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12
ISSN 2395-1621 Static Structural Analysis and Optimization of Engine Mounting Bracket #1 Chandrashekhar B Tayde, #2 Prof. D. H. Burande 1 chandrashekhar.tayde@gmail.com 2 dhburande.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
Topology Optimization Design of Automotive Engine Bracket
 Energy and Power Engineering, 2016, 8, 230-235 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/epe.2016.84021 Topology Optimization Design of Automotive
Energy and Power Engineering, 2016, 8, 230-235 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/epe.2016.84021 Topology Optimization Design of Automotive
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Stress analysis of toroidal shell
 Stress analysis of toroidal shell Cristian PURDEL*, Marcel STERE** *Corresponding author Department of Aerospace Structures INCAS - National Institute for Aerospace Research Elie Carafoli Bdul Iuliu Maniu
Stress analysis of toroidal shell Cristian PURDEL*, Marcel STERE** *Corresponding author Department of Aerospace Structures INCAS - National Institute for Aerospace Research Elie Carafoli Bdul Iuliu Maniu
Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Application of a FEA Model for Conformability Calculation of Tip Seal in Compressor
Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress
 Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress Nikhil B. Abattini 1, M. M. Mirza 2, P. V. Pawar 3 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, Islampur,
Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress Nikhil B. Abattini 1, M. M. Mirza 2, P. V. Pawar 3 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, Islampur,
An introduction to understanding the deflection of beams using the Push Me Pull Me models on Expedition Workshed
 Worksheet 2 Deflections of Beams An introduction to understanding the deflection of beams using the Push Me Pull Me models on Expedition Workshed introduction Understanding how structures deform and deflect
Worksheet 2 Deflections of Beams An introduction to understanding the deflection of beams using the Push Me Pull Me models on Expedition Workshed introduction Understanding how structures deform and deflect
Topology Optimization of Engine Structure of a Scooter Engine using OptiStruct
 Topology Optimization of Engine Structure of a Scooter Engine using OptiStruct Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Gyanendra Roy Senior Manager
Topology Optimization of Engine Structure of a Scooter Engine using OptiStruct Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Gyanendra Roy Senior Manager
studying of the prying action effect in steel connection
 studying of the prying action effect in steel connection Saeed Faraji Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Ahar Branch S-faraji@iau-ahar.ac.ir Paper Reference Number:
studying of the prying action effect in steel connection Saeed Faraji Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Ahar Branch S-faraji@iau-ahar.ac.ir Paper Reference Number:
Numerical Behavior Reproduction of a Truss Structure and Beam, Subjected to Concentrated Load
 ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVII, NR. 2, 2010, ISSN 1453-7397 Nedelcu Dorian, Ianici Draghita, Nedeloni Marian, Daia Daniel Numerical Behavior Reproduction of a Truss Structure and
ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVII, NR. 2, 2010, ISSN 1453-7397 Nedelcu Dorian, Ianici Draghita, Nedeloni Marian, Daia Daniel Numerical Behavior Reproduction of a Truss Structure and
IJREAS VOLUME 6, ISSUE 4 (April, 2016) (ISSN ) International Journal of Research in Engineering and Applied Sciences (IMPACT FACTOR 6.
 THICKNESS OPTIMIZATION OF CAR FRAME FOR STRENGTH Manoj Kumar Singh 1 R.Hussain Vali 2 P.Yagnasri 3 Associate Professor Assistant Professor Assistant Professor ABSTRACT Department of mechanical engineering,,
THICKNESS OPTIMIZATION OF CAR FRAME FOR STRENGTH Manoj Kumar Singh 1 R.Hussain Vali 2 P.Yagnasri 3 Associate Professor Assistant Professor Assistant Professor ABSTRACT Department of mechanical engineering,,
Mechanical simulation design of the shaft type hybrid mechanical arm based on Solidworks
 International Forum on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (IFEESD 2016) Mechanical simulation design of the shaft type hybrid mechanical arm based on Solidworks Liu Yande1, a Hu Jun2,b Ouyang
International Forum on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (IFEESD 2016) Mechanical simulation design of the shaft type hybrid mechanical arm based on Solidworks Liu Yande1, a Hu Jun2,b Ouyang
Introduction of Optimization Tools in BIW Design
 Introduction of Optimization Tools in BIW Design Himanshu Shekhar Deputy Manager, Maruti Suzuki India Ltd, Palam Gurgaon Road, Gurgaon. Vimal Kumar Deputy Manager, Maruti Suzuki India Ltd, Palam Gurgaon
Introduction of Optimization Tools in BIW Design Himanshu Shekhar Deputy Manager, Maruti Suzuki India Ltd, Palam Gurgaon Road, Gurgaon. Vimal Kumar Deputy Manager, Maruti Suzuki India Ltd, Palam Gurgaon
International Journal of Science Engineering and Advance Technology, IJSEAT, Vol 2, Issue 12
 Contact Stress Analysis of Helical Gear by Using AGMA and ANSYS S.Sai Anusha 1 P.Satish Reddy 2 P.Bhaskar 3 M Manoj 4 PG Scholar, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor, Asst Professor Dept of Mechanical Engineering,
Contact Stress Analysis of Helical Gear by Using AGMA and ANSYS S.Sai Anusha 1 P.Satish Reddy 2 P.Bhaskar 3 M Manoj 4 PG Scholar, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor, Asst Professor Dept of Mechanical Engineering,
Computations of stresses with volume-elements in rectangular and HE sections
 CT3000: Bachelor Thesis Report, Izik Shalom (4048180) Computations of stresses with volume-elements in rectangular and HE sections Supervisors: dr. ir. P.C.J. Hoogenboom en Ir. R. Abspoel June 2013 Preface
CT3000: Bachelor Thesis Report, Izik Shalom (4048180) Computations of stresses with volume-elements in rectangular and HE sections Supervisors: dr. ir. P.C.J. Hoogenboom en Ir. R. Abspoel June 2013 Preface
ME Optimization of a Frame
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
Comparison of Flexural Joints Used in Precision Scanning Mechanism Using FEA Tool
 ISSN 2395-1621 Comparison of Flexural Joints Used in Precision Scanning Mechanism Using FEA Tool #1 D M Bhoge, #2 S P Deshmukh 1 dhananjay.bhoge@rediffmail.com 2 suhas.deshmukh@gmail.com 1,2 Mechanical
ISSN 2395-1621 Comparison of Flexural Joints Used in Precision Scanning Mechanism Using FEA Tool #1 D M Bhoge, #2 S P Deshmukh 1 dhananjay.bhoge@rediffmail.com 2 suhas.deshmukh@gmail.com 1,2 Mechanical
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 ISSN (ONLINE): 2321-3051 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Abstract STATIC ANALYSIS OF EIGHT DEGREES OF FREEDOM ARTICULATED ROBOT ARM UNDER VARYING LOAD CONDITIONS
ISSN (ONLINE): 2321-3051 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Abstract STATIC ANALYSIS OF EIGHT DEGREES OF FREEDOM ARTICULATED ROBOT ARM UNDER VARYING LOAD CONDITIONS
Finite Element Analysis of Structure of a Leather Cutting Machine
 e-issn 2455 1392 Volume 2 Issue 8, August 2016 pp. 199 206 Scientific Journal Impact Factor : 3.468 http://www.ijcter.com Finite Element Analysis of Structure of a Leather Cutting Machine Asif S. Pathan
e-issn 2455 1392 Volume 2 Issue 8, August 2016 pp. 199 206 Scientific Journal Impact Factor : 3.468 http://www.ijcter.com Finite Element Analysis of Structure of a Leather Cutting Machine Asif S. Pathan
FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS USING MODAL PARAMETERS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 12 (2016) 1758-1770 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 12 (2016) 1758-1770 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS
LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results
 LIGO-T980125-00-D HYTEC-TN-LIGO-31 LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results Eric Swensen and Franz Biehl August 30, 1998 Abstract Static structural tests were conducted on the LIGO scissors
LIGO-T980125-00-D HYTEC-TN-LIGO-31 LIGO Scissors Table Static Test and Analysis Results Eric Swensen and Franz Biehl August 30, 1998 Abstract Static structural tests were conducted on the LIGO scissors
