Æ. Add a point T on the ray so that. ML. (Lesson 1.3) 20. H(º1, 3) 21. H(3, º1) 22. H(º5, 2) M(1, 7) M(8, 2) M(º4, 6) L(3, 3) L(3, 5) L(º6, 2)
|
|
|
- Avice Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 tra ractice escribe a pattern in the seuence of numbers. redict the net number. (Lesson.).,, 4, 2,,... 2., 2, 4, 7,,....,, 2,, , 2, 2,, 2, 2, 9, 2, 2,.... 2, 4, 72, 0,.... 2, º,, º4, omplete the conjecture based on the pattern ou observe in the specific cases. (Lesson.) onjecture: n negative number cubed is?. º = º º7 = º4 º = º27 º9 = º729 º = º º = º. how that n n + > (n + ) n for the values n =, 4, and. hen show that the values n = and n = 2 are countereamples to the conjecture that n n + > (n + ) n. (Lesson.) ketch the points, lines, segments, planes, and ras. (Lesson.2) 9. raw four collinear points,,, and. 0. raw two opposite ras Æ and Æ.. raw a plane that contains two intersecting lines.. raw three points,, and that are coplanar, but are not collinear.. raw two points, and. hen sketch Æ. dd a point on the ra so that is between and. Æ In the diagram of the collinear points, = 24, is the midpoint of, =, and =. ind each length. (Lesson.) Use the istance ormula to decide whether Æ Æ L. (Lesson.) 20. (º, ) 2. (, º) 22. (º, 2) (, 7) (, 2) (º4, ) L(, ) L(, ) L(º, 2) ame the verte and sides of the angle, then write two names for the angle. (Lesson.4) tra ractice 0
2 Use the ngle ddition ostulate to find the measure of the unknown angle. (Lesson.4) 2. m =? 27. m =? 2. m =? 0 L tate whether the angle appears to be acute, right, obtuse, or straight. hen estimate its measure. (Lesson.4) ind the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment with the given endpoints. (Lesson.) 2. (º4, 2). (º,.) 4. (º, 4) Q(, º4) Q(7, º.) Q(º, º) XY Æ is the angle bisector of UX. ind m UXY. (Lesson.).. 7. U Y (4r ) X Y (r 7) 4 X U (z 9) X (7z ) Y U ind the measure of each angle. (Lesson.). wo vertical angles are complementar. ind the measure of each angle. 9. he measure of one angle of a linear pair is times the measure of the other angle. ind the measures of the two angles. 40. he supplement of an angle is 0. ind the complement of the angle. ind the perimeter (or circumference) and area of the figure. (Where necessar, use π.4.) (Lesson.7) tudent esources
3 2 ewrite the conditional statement in if-then form. (Lesson 2.). It must be true if ou read it in a newspaper. 2. n apple a da keeps the doctor awa.. he suare of an odd number is odd. Write the inverse, converse, and contrapositive of the conditional statement. (Lesson 2.) 4. If =, then 2 = 44.. If ou are indoors, then ou are not caught in a rainstorm.. If four points are collinear, then the are coplanar. 7. If two angles are vertical angles, then the are congruent. Write the converse of the true statement. ecide whether the converse is true or false. If false, provide a countereample. (Lesson 2.). If two angles form a linear pair, then the are supplementar. 9. If 2 º = 7, then =. ewrite the biconditional statement as a conditional statement and its converse. (Lesson 2.2) 0. wo segments have the same length if and onl if the are congruent.. wo angles are right angles if and onl if the are supplementar.. = 0 if and onl if 2 = 00. etermine whether the statement can be combined with its converse to form a true biconditional statement. (Lesson 2.2). If is a right angle, then fi. 4. If and 2 are adjacent, supplementar angles, then and 2 form a linear pair.. If two angles are vertical angles, then the are congruent. Using p,, r, and s below, write the smbolic statement in words. (Lesson 2.) p:we go shopping. :We need a shopping list. r : We stop at the bank. s: We see our friends.. p 7. ~r ~s. r s 9. p 20. ~p ~s 2. p r iven that the statement is of the form p, write p and. hen write the inverse and the contrapositive of p both smbolicall and in words. (Lesson 2.) 22. If it is hot, a will go to the beach. 2. If the hocke team wins the game tonight, the will pla in the championship. 24. If ohn misses the bus, then he will be late for school. tra ractice 0
4 Use the propert to complete the statement. (Lesson 2.4) 2. efleive propert of eualit: =?. 2. mmetric propert of eualit: If =, then?. 27. ransitive propert of eualit: If = and =, then?. 2. ivision propert of eualit: If 2 =, then 2 = z?. 29. ubtraction propert of eualit: If =, then º 4 =?. op and complete the proof using the diagram and the given information. (Lesson 2.) 0. IV Æ Æ, is the midpoint of Æ and Æ Æ Æ OV tatements easons. is the midpoint of Æ and Æ. 2. =. = 4.?. =.? Æ Æ 7..? 2.?.? 4. iven.?. ransitive propert of eualit 7. efinition of congruent segments In ercises 2, use the diagram to complete the statement. (Lesson 2.). 2 and? are vertical angles. 2. QW is supplementar to?.. In the diagram, suppose that and 4 are complementar and that 4 and are complementar. rove that. (Lesson 2.) olve for each variable. (Lesson 2.) V U W (z ) ( 4) (4z ) (0 ) (9b ) (c ) (c 9) (7b 20) (r 44) (s ) (s 9) (r ) 7. Write a two-column proof. (Lesson 2.) IV and 4 are complementar, is a right angle. OV 2 and are complementar tudent esources
5 hink of each segment in the diagram as part of a line. ill in the blank with parallel, skew, or perpendicular. (Lesson.). and are?. 2. and are?.. and are?. hink of each segment in the diagram as part of a line. here ma be more than one right answer. (Lesson.). 4. ame a line parallel to.. ame a line perpendicular to.. ame a line skew to 7. ame a plane parallel to. omplete the statement with corresponding, alternate interior, alternate eterior, or consecutive interior. (Lesson.). and 7 are? angles and are? angles and 2 are? angles.. 4 and are? angles.. and are? angles.. ill in the blanks to complete the proof. (Lesson.2) Æ Æ IV fi, Æ bisects OV m = 4 tatements Æ Æ. fi 2.?. m = Æ bisects. m = m. m + m = m +? = 90. 2(m ) = m = 4 easons.? 2. efinition of perpendicular lines.? 4.?.?.? 7. ubstitution propert of eualit.? 9.? tra ractice 07
6 ind the values of and. plain our reasoning. (Lesson.) Which lines, if an, are parallel? plain. (Lesson.4) plain how ou would show that a b. tate an theorems or postulates that ou would use. (Lesson.) ind the slopes of,, and.which lines are parallel, if an? (Lesson.) 2. (, 7), (, ) 27. (º4, ), (, ) 2. (º, 2), (º, ) (4, ), (9, ) (º2, º), (4, º) (7, º), (7, 7) (2, ), (º, º) (º0, ), (4, º) (4, º), (4, º) Write an euation of the line that passes through point and is parallel to the line with the given euation. (Lesson.) 29. (º4, º), = º 7 0. (2, º), = º + 4. (º9, ), = º 2 ecide whether lines p and p 2 are perpendicular. (Lesson.7) 2. line p : º7 + =. line p : + = 4. line p : º 2 = line p 2 : º9 º 2 = line p 2 : º 2 = 9 line p 2 : º º 2 = Line j is perpendicular to the line with the given euation and line j passes through. Write an euation of line j. (Lesson.7). = º2 +, (4, º). 2 + = 20, (4, 0) 7. = +, (º2, º7) 2 0 tudent esources
7 4 In ercises 4, the variable epressions represent the angle measures of a triangle. ind the measure of each angle. hen classif the triangle b its angles. (Lesson 4.). m = 2. m = 0. m = 4. m = (2) m = m = m Q = (2 + 0) m = (2 º 4) m = m L = m = ( + 0) m U = (2 º 2). he measure of an eterior angle of a right triangle is. ind the measures of the interior angles of the triangle. (Lesson 4.) Identif an figures that can be proved congruent. or those that can be proved congruent, write a congruence statement. (Lesson 4.2) Use the triangles in ercise above. Identif all pairs of congruent corresponding angles and corresponding sides. (Lesson 4.2) Use the given information to find the value of. (Lesson 4.2) 0. Q,.,., 47 V ( 2). none; corresponding sides are congruent, but no information is given about the corresponding angles. 2 L ( ) ecide whether enough information is given to prove that the triangles are congruent. If there is enough information, state the congruence postulate ou would use. (Lesson 4.). XVY, ZVW 4., Q. X V Z Y W. Use the diagram in ercise. rove that XYW ZWY. Is it possible to prove that the triangles are congruent? If so, state the congruence postulate or theorem ou would use. (Lesson 4.4) tra ractice 09
8 Write a two-column proof or a paragraph proof. (Lesson 4.4) 20. IV Æ Æ, Æ Æ bisects OV tate which postulate or theorem ou can use to prove that the triangles are congruent. hen eplain how proving that the triangles are congruent proves the given statement. (Lesson 4.) Æ Æ 2. OV 22. OV 2. OV Q Use the diagram and the information given below. (Lesson 4.) IV 24. OV 2. OV Æ Æ 2. OV Æ Æ ind the values of and. (Lesson 4.) lace the figure in a coordinate plane. Label the vertices and give the coordinates of each verte. (Lesson 4.7) 0. 4 unit b unit rectangle with one verte at (º, 2). suare with side length and one verte at (, º4) In the diagram, is a right triangle. Its base is 0 units and its height is 0 units. (Lesson 4.7) 2. ive the coordinates of points and.. ind the length of the hpotenuse of. lace the figure in a coordinate plane and find the given information. (Lesson 4.7) (0, 20) 4. rectangle with length units and width units; find the length of a diagonal of the rectangle.. n isosceles right triangle with legs of 7 units; find the length of the hpotenuse. 0 tudent esources
9 Use the diagram shown. (Lesson.). In the diagram, Æ fi Æ Æ Æ and. ind. 2. In the diagram, Æ fi Æ Æ Æ and. ind.. In the diagram, Æ is the perpendicular bisector of Æ. ecause = =, what can ou conclude about the point? 20 Use the diagram shown. (Lesson.) 4. In the diagram, m = m = 0, m = m = 90, and =. ind.. In the diagram, Æ bisects, m = m = 90 and = = 0. What can ou conclude about point? In each case, find the indicated measure. (Lesson.2). he perpendicular bisectors of 7. he perpendicular bisectors of meet at point. ind. meet at point. ind. 0. he angle bisectors of 9. he angle bisectors of meet at point Q. ind W. meet at point. ind. 24 W 2 7 X Y 0 2 Use the figure below and the given information. (Lesson.) is the centroid of, = 4, X = 24, and Z =.. Æ. 0. ind the length of Y. ind the length of X Æ. Y Z. ind the length of Æ. X raw and label a large triangle of the given tpe and construct altitudes. Verif heorem. b showing that the lines containing the altitudes are concurrent and label the orthocenter. (Lesson.). an isosceles 4. an euilateral. a right isosceles tra ractice
10 Use, where X, Y, and Z are midpoints of the sides. (Lesson.4) Æ.?. Æ 7. XY?.. If =, then YZ =?. 9. If = 0, then XY =?. 20. If XZ =, then =?. Z X 2. If YZ = 4 º and = +, then YZ =?. Y 22. If Z = 4 º and XY = 2 +, then =?. ame the shortest and longest sides of the triangle. (Lesson.) ame the smallest and largest angles of the triangle. (Lesson.) 2. L omplete with >, <, or =. (Lesson.) 29.? 0. Q? U. m? m U 2.?. m? m 2 4. m? m L ?. XY? WV 7. m? m 2 L U U W 0 9 X V 9 0 Y Z tudent esources
11 ecide whether the figure is a polgon. If it is, use the number of sides to tell what kind of polgon the shape is. hen state whether the polgon is conve or concave. (Lesson.) Use the information in the diagram to solve for. (Lesson.) ( ) 0 ( ) 70 (4 0) (7 ) (7 ) ( 2) () 02 Use the diagram of parallelogram VWXY at the right. omplete each statement, and give a reason for our answer. (Lesson.2) 0. VW Æ?. VWX? V W. Æ XW?. V Æ? 4. XYW? Æ. WX?. VYX is supplementar to? and?. 7. oint is the midpoint of? and?. Y X re ou given enough information to determine whether the uadrilateral is a parallelogram? plain. (Lesson.) rove that the points represent the vertices of a parallelogram. (Lesson.) 2. (2, 4), (4, º), (9, º), (7, ) 22. (º7, º), (º, º2), (º4, º9), (º0, º) 2. (º, ), (, 4), (2, º), U(º9, º4) 24. (º7, º), (, 0), (, 4), Q(º, º9) tra ractice
12 List each uadrilateral for which the statement is true. (Lesson.4) 2. djacent angles are supplementar. 2. djacent angles are congruent. 27. djacent sides are perpendicular. 2. iagonals are congruent. 29. djacent sides are congruent. 0. Opposite sides are parallel. It is given that Q is a parallelogram. raph Q. ecide whether it is a rectangle, a rhombus, a suare, or none of the above. ustif our answer using theorems about uadrilaterals. (Lesson.4). (, 7), Q(º2, ), (, º), (4, ) 2. (º, ), Q(4, ), (7, 7), (º, ). (º2, 7), Q(4, 7), (4, ), (º2, ) 4. (º7, º2), Q(º2, º2), (º2, º7), (º7, º7) ind the missing angle measures. (Lesson.) U ind the value of. (Lesson.) What are the lengths of the sides of the kite? (Lesson.) What kind of uadrilateral could be? is not drawn to scale. (Lesson.) ind the area of the polgon. (Lesson.7) tudent esources
13 7 Use the graph of the transformation below. (Lesson 7.). ame the image of Q. 2. ame and describe the transformation.. ame two sides with the same length. 4. ame two angles with the same measure. Z 4 Y. ame the coordinates of the preimage of point Y. X. how two corresponding sides have the same length, using the istance ormula. œ ame and describe the transformation. hen name the coordinates of the vertices of the image. (Lesson 7.) 7.. L œ Use the diagrams to complete the statement. (Lesson 7.) ? 0.?.? Use the diagram at the right to name the image of after the reflection. If the reflection does not appear in the diagram, write not shown. (Lesson 7.2). eflection in the -ais. eflection in the -ais 4. eflection in the line =. eflection in the -ais, followed b a reflection in the -ais ind the coordinates of the reflection without using a coordinate plane. hen check our answer b plotting the image and preimage on a coordinate plane. (Lesson 7.2). (, 2) reflected in the -ais 7. (º2, 4) reflected in the -ais. (, º) reflected in the -ais 9. Q(, ) reflected in the -ais tra ractice
14 ind point on the -ais so + is a minimum. (Lesson 7.2) 20. (, 2), (, ) 2. (, 7), (, 7) 22. (º2, 7), (º9, ) ame the coordinates of the vertices of the image after a clockwise rotation of the given number of degrees about the origin. (Lesson 7.) O O 4 O In the diagram, a b, is reflected in line a and is reflected in line b. (Lesson 7.4) a b 2. translation of maps onto which triangle?? 27. Which lines are perpendicular to fl. 2. ame two segments parallel to fl op figure V and draw its image after the translation. hen describe the translation using a vector in component form. (Lesson 7.4) 29. (, ) ( º, + ) 0. (, ) ( +, º 4). (, ) ( º 7, + 7) 2. (, ) ( + 2, º ) ketch the image of (º, º2) after the described glide reflection. (Lesson 7.). ranslation: (, ) ( +, + ) 4. ranslation: (, ) ( + 4, º ) eflection: in the -ais eflection: in = º4 ketch the image of after a composition using the given transformations in the order the appear. (Lesson 7.). (, ), (º2, ), (º, º4). (2, ), (0,º), (º, º4) ranslation: (, ) ( º 7, ) ranslation: (, ) ( +, ) eflection: in the -ais eflection: in the -ais escribe each frieze pattern according to the following seven categories:,,, V,, V, and V. (Lesson 7.) 7.. V tudent esources
15 ewrite the fraction so that the numerator and denominator have the same units. hen simplif. (Lesson.) m. 2. f 2 0 cm 4 t d. 2 in. ft 4. 0 km 9 00 m Use ratios to solve the following problems. (Lesson.). he measures of the angles in a uadrilateral are in the etended ratio of :4::. ind the measures of the angles.. he perimeter of isosceles triangle is cm. he etended ratio of :: is ::. ind the lengths of the three sides. olve the proportion. (Lesson.) a 7. = 2. º = º 2 c = b º = 2 2. = f º. = g + d + º 9 9 g º 4 omplete the sentence. (Lesson.2). If = 0, then =? 0 0?. 4. If 9 4 =, then =? 4?.. If 9 = 2, then 4 =??.. If z z + =, then =??. ind the geometric mean of the two numbers. (Lesson.2) 7. 4 and 9. and and and 2. 2 and and 0,000 Use the diagram and the given information to find the unknown length. (Lesson.2) 2. IV =, find. 24. IV Q =, find In the diagram, Q ~ VWX. (Lesson.) 2. ind the scale factor of Q to VWX. 2. ind the scale factor of VWX to Q. 27. ind the values of u,, and z. 2. ind the perimeter of each polgon. 9 u X z V W tra ractice 7
16 etermine whether the triangles can be proved similar. If the are similar, write a similarit statement. If the are not similar, eplain wh. (Lesson.4) U V 0 ind coordinates for point Z so that OWX ~ OYZ. (Lesson.4) 2. O(0, 0), W(4, 0), X(0, ), Y(, 0). O(0, 0), W(2, 0), X(0, ), Y(, 0) 4. O(0, 0), W(º4, 0), X(0, 2), Y(º, 0). O(0, 0), W(º, 0), X(0, º4), Y(º, 0) re the triangles similar? If so, state the similarit and the postulate or theorem that justifies our answer. (Lesson.) etermine whether the triangles are similar. If the are, write a similarit statement and solve for the variable. (Lesson.) etermine whether the given information implies that Q Æ Æ. plain. (Lesson.) U 2 20 V ind the value of the variable. (Lesson.) Use the origin as the center of the dilation and the given scale factor to find the coordinates of the vertices of the image of the polgon. (Lesson.7) 4. (º2, ), (º, ), (, ), (2, º4), k = (2, 0), (, ), (4, ), (, ), k = 4. (, º), (, º), (, 9), (º, 9), k = 49. (4, º4), (, 4), (2, ), (º, º4), k = 4 tudent esources
17 9 Write similarit statements for the three similar triangles in the diagram. hen complete the proportion. (Lesson 9.). =? 2.? =. =? L ind the value of the variable. (Lesson 9.) U V ind the unknown side length. implif answers that are radicals. ell whether the side lengths form a thagorean triple. (Lesson 9.2) V U he variables r and s represent the lengths of the legs of a right triangle, and t represents the length of the hpotenuse. he values of r, s, and t form a thagorean riple. ind the unknown value. (Lesson 9.2) 0. r = 7, t = 2. r =, s =. s = 2, t =. r = 49, s = 4. s = 9, t = 202. r = 2, t = ind the area of the figure. ound decimal answers to the nearest tenth. (Lesson 9.2). cm 7.. cm cm cm cm 9 cm 9 cm L 4 cm ell whether the triangle is a right triangle. (Lesson 9.) 9. U X Z 2 Y tra ractice 9
18 ecide whether the numbers can represent the side lengths of a triangle. If the can, classif the triangle as right, acute, or obtuse. (Lesson 9.) 22. 7,, 9 2.,, 9 24.,, 2. 7, 9, 2. 00, 00, ,, 20 ind the value of each variable. Write answers in simplest radical form. (Lesson 9.4) ind the sine, the cosine, and the tangent of the acute angles of the triangle. press each value as a decimal rounded to four places. (Lesson 9.). 2. U 4 V. Y W X 29 Z ind the value of each variable. ound decimals to the nearest tenth. (Lesson 9.) 4... u v 42 w z 7 olve the right triangle. ound decimals to the nearest tenth. (Lesson 9.) raw vector Q Æ in a coordinate plane. Write the component form of the vector and find its magnitude. ound our answer to the nearest tenth. (Lesson 9.7) 40. (2, ), Q(, 7) 4. (º, º), Q(, ) 42. (º4, ), Q(2, º) Let a =,, b = º7, 2, c =, º, and d = 2, 9. ind the given sum. (Lesson 9.7) 4. a + b 44. a + c 4. c + d 4. b + c 20 tudent esources
19 0 atch the notation with the term that best describes it. (Lesson 0.) Æ.. ecant 2.. hord.. adius Æ 4.. iameter.. oint of tangenc.. ommon eternal tangent 7.. ommon internal tangent. Æ. enter ell whether the common tangent(s) are internal or eternal. (Lesson 0.) Use the diagram at the right. (Lesson 0.). What are the center and radius of?. What are the center and radius of? 4. escribe the intersection of the two circles.. escribe all the common tangents of the two circles. Æ Æ and are diameters. op the diagram. ind the indicated measure. (Lesson 0.2). m 7. m. m 9. m 20. m Q 2. m Q 22. m 2. m ind the value of each variable. (Lesson 0.) tra ractice 2
20 ind the value of. (Lesson 0.4) ind the value of. (Lesson 0.) ive the center and radius of the circle. (Lesson 0.) 9. ( º ) 2 + ( + ) 2 = ( + ) = ( +.) 2 + ( º 4.9) 2 = ( º ) 2 + ( + 7) 2 = Write the standard euation of the circle with the given center and radius. (Lesson 0.) 4. center (, ), radius 44. center ( 2, 7), radius 0 Use the given information to write the standard euation of the circle. (Lesson 0.) 4. he center is (2, 2); a point on the circle is (2, 0). 4. he center is (0, ); a point on the circle is (º, ). Use the graph at the right to write euation(s) for the locus of points in the coordinate plane that satisf the given condition. (Lesson 0.7) 47. euidistant from and 4. units from units from 0. units from 22 tudent esources
21 ind the sum of the measures of the interior angles of the conve polgon. (Lesson.). -gon 2. 4-gon. 0-gon gon ind the value of. (Lesson.) You are given the number of sides of a regular polgon. ind the measure of each eterior angle. (Lesson.) You are given the measure of each eterior angle of a regular n-gon. ind the value of n. (Lesson.) ind the measure of a central angle of a regular polgon with the given number of sides. (Lesson.2). 0 sides 7. sides. 2 sides sides ind the perimeter and area of the regular polgon. (Lesson.2) In ercises 2 2, the polgons are similar. ind the ratio (red to blue) of their perimeters and of their areas. (Lesson.) he ratio of the perimeters of two similar heagons is :. he area of the larger heagon is 20 suare inches. What is the area of the smaller heagon? (Lesson.) tra ractice 2
22 ind the indicated measure. (Lesson.4) 0. ircumference. adius r r in. r 7 ft ind the indicated measure. (Lesson.4) 2. Length of. ircumference 4. adius V U. Length of. ircumference 7. adius ind the area of the shaded region. (Lesson.) ind the probabilit that a point, selected randonl on Æ,is on the given segment. (Lesson.) Æ Æ Æ 4. ind the probabilit that a randoml chosen point in the figure lies in the shaded region. (Lesson.) Æ tudent esources
23 ell whether the solid is a polhedron. If it is, decide whether it is regular and/or conve. plain. (Lesson.). 2.. ount the number of faces, vertices, and edges of the polhedron. Verif our results using uler s heorem. (Lesson.) 4... escribe the cross section. (Lesson.) 7.. ind the surface area of the right prism. (Lesson.2) cm. 4 cm in. cm cm 0 cm in. 2 in. ind the surface area of the right clinder. ound the result to two decimal places. (Lesson.2). in.. cm 4. in. cm ind the surface area of the solid. he pramids are regular and the cone is right. (Lesson.). in.. rea 9. cm 2 7. cm in. cm in. cm cm tra ractice 2
24 about 9. cm ind the volume of the solid. (Lesson.4). ight rectangular prism 9. ight clinder 20. Obliue suare prism 90 in. about ft 0 cm ft in. ft 20 cm 0 in. in. cm 2. Obliue clinder 22. wo holes are drilled 2. suare hole is cut about in. through a cube. from a clinder. about ft 7 in. in. 2 cm cm ft 4 ft ft cm cm ind the volume of the pramid or cone. (Lesson.) cm cm in. cm cm 9 in. 40 cm 70.4 cm 2 in in. mm 7 in. ft ft 7. mm about. in. about.7 mm about 7.27 ft ind the surface area and the volume of the sphere. ound our result to two decimal places. (Lesson.) m cm in cm 2 ; 244. cm 2.72 m 2 ; m in. 2 ; 24, in. he solid is similar to a larger solid with the given scale factor. ind the surface area and volume V of the larger solid. (Lesson.7). cale factor 2: 4. cale factor :. cale factor :7 = 9 m 2 V = 4 m = 04π ft 2 V = 44π ft = 00π cm 2 V = 2 π cm 2 m 2 ; 2 m about 2.9π ft 2 ; about.7π ft ; 9π cm 2 ; 47} }π cm 2 tudent esources
Reteaching Inequalities in Two Triangles
 Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
b) A ray starts at one point on a line and goes on forever. c) The intersection of 2 planes is one line d) Any four points are collinear.
 Name: Review for inal 2016 Period: eometry 22 Note to student: This packet should be used as practice for the eometry 22 final exam. This should not be the only tool that you use to prepare yourself for
Name: Review for inal 2016 Period: eometry 22 Note to student: This packet should be used as practice for the eometry 22 final exam. This should not be the only tool that you use to prepare yourself for
Name Honors Geometry Final Exam Review. 1. The following figure is a parallelogram. Find the values of x and y.
 2013-2014 Name Honors Geometr Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Questions 1. The following figure is a parallelogram. Find the values of and. (+)⁰ 130⁰ (-)⁰ 85⁰ 2. Find the value of in the figure below. D is
2013-2014 Name Honors Geometr Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Questions 1. The following figure is a parallelogram. Find the values of and. (+)⁰ 130⁰ (-)⁰ 85⁰ 2. Find the value of in the figure below. D is
Lincoln Public Schools GEOMETRY REVIEW - Semester One CALCULATOR Revised 12/2007
 Lincoln Public chools GOMY VIW - emester One LULO evised /007. escribe the lines in the sketch.. coplanar and intersecting. coplanar and nonintersecting. noncoplanar and intersecting. noncoplanar and nonintersecting.
Lincoln Public chools GOMY VIW - emester One LULO evised /007. escribe the lines in the sketch.. coplanar and intersecting. coplanar and nonintersecting. noncoplanar and intersecting. noncoplanar and nonintersecting.
algebraic representation algorithm alternate interior angles altitude analytical geometry x x x analytical proof x x angle
 Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
BMGM-2 BMGM-3 BMGM-1 BMGM-7 BMGM-6 BMGM-5 BMGM-8 BMGM-9 BMGM-10 BMGM-11 DXGM-7 DXGM-23 BMGM-12 BMGM-13 BMGM-14 BMGM-15 BMGM-16 DXGM-9
 Objective Code Advance BMGM-2 BMGM-3 BMGM-1 BMGM-7 BMGM-6 BMGM-5 BMGM-8 BMGM-9 BMGM-10 BMGM-11 DXGM-7 DXGM-8 BMGM-12 BMGM-13 BMGM-14 BMGM-15 BMGM-16 DXGM-9 DXGM-10 DXGM-11 DXGM-15 DXGM-17 DXGM-16 DXGM-18
Objective Code Advance BMGM-2 BMGM-3 BMGM-1 BMGM-7 BMGM-6 BMGM-5 BMGM-8 BMGM-9 BMGM-10 BMGM-11 DXGM-7 DXGM-8 BMGM-12 BMGM-13 BMGM-14 BMGM-15 BMGM-16 DXGM-9 DXGM-10 DXGM-11 DXGM-15 DXGM-17 DXGM-16 DXGM-18
Reteaching Nets. Name Date Class
 Name ate lass eteaching Nets INV 5 You have worked with two and three-dimensional figures before. Now ou ll work with nets, which are - representations of 3- figures. Making a 3- Figure from a Net A net
Name ate lass eteaching Nets INV 5 You have worked with two and three-dimensional figures before. Now ou ll work with nets, which are - representations of 3- figures. Making a 3- Figure from a Net A net
GEOMETRY. Background Knowledge/Prior Skills. Knows ab = a b. b =
 GEOMETRY Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
GEOMETRY Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
Chapter 1-3 Parallel Lines, Vocab, and Linear Equations Review
 Geometry H Final Exam Review Chapter 1-3 Parallel Lines, Vocab, and Linear Equations Review 1. Use the figure at the right to answer the following questions. a. How many planes are there in the figure?
Geometry H Final Exam Review Chapter 1-3 Parallel Lines, Vocab, and Linear Equations Review 1. Use the figure at the right to answer the following questions. a. How many planes are there in the figure?
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Course: Geometry Level: Regular Date: 11/2016. Unit 1: Foundations for Geometry 13 Days 7 Days. Unit 2: Geometric Reasoning 15 Days 8 Days
 Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Geometry Curriculum Map
 Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
NOTES: Tangents to Circles
 Unit# ssign # TS: Tangents to ircles GL Identify segments and lines related to circles and use properties of a tangent to a circle VULRY circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant
Unit# ssign # TS: Tangents to ircles GL Identify segments and lines related to circles and use properties of a tangent to a circle VULRY circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Final Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of.
 Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of. 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 a. = 7 c. = 7 b. = 9 d. = 8 2. Find the best
Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of. 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 a. = 7 c. = 7 b. = 9 d. = 8 2. Find the best
Geometry. (F) analyze mathematical relationships to connect and communicate mathematical ideas; and
 (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life,
(1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life,
Name Honors Geometry Final Exam Review
 2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
ALLEGHANY COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
Form A. Choose the correct answer to each question and mark it on the Google form. You may use a calculator. You may write on this test.
 Form hoose the correct answer to each question and mark it on the Google form. You may use a calculator. You may write on this test. 1. Select the geometric figure that possesses all of the following characteristics:
Form hoose the correct answer to each question and mark it on the Google form. You may use a calculator. You may write on this test. 1. Select the geometric figure that possesses all of the following characteristics:
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes
 1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Aldine ISD Benchmark Targets /Geometry SUMMER 2004
 ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
DO NOT LOSE THIS REVIEW! You will not be given another copy.
 Geometry Fall Semester Review 2011 Name: O NOT LOS THIS RVIW! You will not be given another copy. The answers will be posted on your teacher s website and on the classroom walls. lso, review the vocabulary
Geometry Fall Semester Review 2011 Name: O NOT LOS THIS RVIW! You will not be given another copy. The answers will be posted on your teacher s website and on the classroom walls. lso, review the vocabulary
To identify congruence transformations To prove triangle congruence using isometries
 9-5 -0-1 ongruence ransformations ontent tandards G..7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G..6, G..8 bjective o identif congruence
9-5 -0-1 ongruence ransformations ontent tandards G..7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G..6, G..8 bjective o identif congruence
4. Describe the correlation shown by the scatter plot. 8. Find the distance between the lines with the equations and.
 Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
To identify congruence transformations To prove triangle congruence using isometries
 9-5 ongruence ransformations ommon ore tate tandards G-.B.7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G-.B.6, G-.B.8 M 1, M 3, M bjective
9-5 ongruence ransformations ommon ore tate tandards G-.B.7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G-.B.6, G-.B.8 M 1, M 3, M bjective
High School Geometry
 High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
CST Geometry Practice Problems
 ST Geometry Practice Problems. Which of the following best describes deductive reasoning? using logic to draw conclusions based on accepted statements accepting the meaning of a term without definition
ST Geometry Practice Problems. Which of the following best describes deductive reasoning? using logic to draw conclusions based on accepted statements accepting the meaning of a term without definition
Summer Dear Geometry Students and Parents:
 Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
Unit Overview. Learning Targets. Guiding Questions
 Content Area: Geometry Unit Title: Preparing for Geometry Target Course/Grade Level Geometry Duration 10 days Unit Overview Description : In this unit, students will review a number of topics and skills
Content Area: Geometry Unit Title: Preparing for Geometry Target Course/Grade Level Geometry Duration 10 days Unit Overview Description : In this unit, students will review a number of topics and skills
Reteaching Exploring Angles of Polygons
 Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
Geometry CP Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
104, 107, 108, 109, 114, 119, , 129, 139, 141, , , , , 180, , , 128 Ch Ch1-36
 111.41. Geometry, Adopted 2012 (One Credit). (c) Knowledge and skills. Student Text Practice Book Teacher Resource: Activities and Projects (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical
111.41. Geometry, Adopted 2012 (One Credit). (c) Knowledge and skills. Student Text Practice Book Teacher Resource: Activities and Projects (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Name Class Date. This shows that A corresponds to Q. Therefore, A Q. This shows that BC corresponds to RS. Therefore, BC RS.
 Name lass ate eteaching ongruent igures iven, find corresponding parts using the names. rder matters. or example, or example, his shows that corresponds to. herefore,. his shows that corresponds to. herefore,.
Name lass ate eteaching ongruent igures iven, find corresponding parts using the names. rder matters. or example, or example, his shows that corresponds to. herefore,. his shows that corresponds to. herefore,.
Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments
 Chapter/ Lesson 1/1 Indiana Standard(s) Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments What is inductive
Chapter/ Lesson 1/1 Indiana Standard(s) Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments What is inductive
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
Int. Geometry Unit 7 Test Review 1
 Int. Geometry Unit 7 est eview uestions -0: omplete each statement with sometimes, always, or never.. he diagonals of a trapezoid are congruent.. rhombus is equiangular.. rectangle is a square.. he opposite
Int. Geometry Unit 7 est eview uestions -0: omplete each statement with sometimes, always, or never.. he diagonals of a trapezoid are congruent.. rhombus is equiangular.. rectangle is a square.. he opposite
Geometry Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of 4 Congruence
 Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
2 nd Semester Final Exam Review
 2 nd Semester Final xam Review I. Vocabulary hapter 7 cross products proportion scale factor dilation ratio similar extremes scale similar polygons indirect measurements scale drawing similarity ratio
2 nd Semester Final xam Review I. Vocabulary hapter 7 cross products proportion scale factor dilation ratio similar extremes scale similar polygons indirect measurements scale drawing similarity ratio
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
Texas High School Geometry
 Texas High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Texas High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
correlated to the Michigan High School Content Expectations Geometry
 correlated to the Michigan High School Content Expectations Geometry McDougal Littell Integrated Mathematics 2 2005 correlated to the Michigan High School Content Expectations Geometry STANDARD L1: REASONING
correlated to the Michigan High School Content Expectations Geometry McDougal Littell Integrated Mathematics 2 2005 correlated to the Michigan High School Content Expectations Geometry STANDARD L1: REASONING
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview
 South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview In South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry, students build on the conceptual knowledge and skills they mastered in previous
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry Overview In South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Geometry, students build on the conceptual knowledge and skills they mastered in previous
7 or 1.17 as your ratio of the lengths when
 .5. What id You Learn? ore Vocabular directed line segment, p. 50 ore oncepts Section.5 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Side-ngle-Side (SS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Section. riangle Proportionalit
.5. What id You Learn? ore Vocabular directed line segment, p. 50 ore oncepts Section.5 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Side-ngle-Side (SS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Section. riangle Proportionalit
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses. Geometry. Course Outline
 The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
Objectives To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms To use relationships among diagonals of parallelograms
 6-2 roperties of arallelograms ontent tandards.o.11 rove theorems about parallelogram. s include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each
6-2 roperties of arallelograms ontent tandards.o.11 rove theorems about parallelogram. s include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Geometry. Instructional Activities:
 GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
Geometry Mathematics. Grade(s) 10th - 12th, Duration 1 Year, 1 Credit Required Course
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) Geometric Structure Measurement Similarity Course Overview GENERAL DESCRIPTION: In this course the student will become
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) Geometric Structure Measurement Similarity Course Overview GENERAL DESCRIPTION: In this course the student will become
Objectives To use the AA Postulate and the SAS and SSS Theorems To use similarity to find indirect measurements
 7-3 roving riangles imilar ontent tandards G..5 Use... similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. G.G.5 rove the slope criteria for parallel and
7-3 roving riangles imilar ontent tandards G..5 Use... similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. G.G.5 rove the slope criteria for parallel and
Special Segments in a Circle
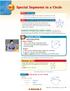 pecial egments in a ircle Find measures of segments that intersect in the interior of a circle. Find measures of segments that intersect in the eterior of a circle. are lengths of intersecting chords related?
pecial egments in a ircle Find measures of segments that intersect in the interior of a circle. Find measures of segments that intersect in the eterior of a circle. are lengths of intersecting chords related?
To draw and identify rotation images of figures
 9-3 -11 otations ontent Standards G..4 evelop definitions of rotations... in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. lso G.., G..6 bjective o draw and identify
9-3 -11 otations ontent Standards G..4 evelop definitions of rotations... in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. lso G.., G..6 bjective o draw and identify
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
Geometry Advanced (Master) Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology. A: The Tools of Geometry
 St. Michael Albertville High School Teacher: Nick Steve Geometry Advanced (Master) September 2015 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: What are the properties of the basic
St. Michael Albertville High School Teacher: Nick Steve Geometry Advanced (Master) September 2015 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: What are the properties of the basic
SOL Chapter Due Date
 Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
Geometry Mathematics. Grade(s) 9th - 12th, Duration 1 Year, 1 Credit Required Course
 Course Description will provide a careful development of both inductive and deductive reasoning. While emphasizing the formal geometric topics of points, lines, planes, congruency, similarity, and characteristics
Course Description will provide a careful development of both inductive and deductive reasoning. While emphasizing the formal geometric topics of points, lines, planes, congruency, similarity, and characteristics
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Use throughout the course: for example, Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Proving Lines Parallel. Polygons and Parallelograms Parallelograms
 Geometry Correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills TEKS Units Lessons G.1 Mathematical Process Standards The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
Geometry Correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills TEKS Units Lessons G.1 Mathematical Process Standards The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
Course Name - Strategic Math - Geometry Qtr./Mon. Content HSCE Essential Skills Assessment Vocabulary
 Sem. 1 Sept. Points & Lines G1.1.6 Recognize Euclidean geometry as an axiom system. Know the key axioms and understand the meaning of and distinguish between undefined terms, axioms, definitions, and theorems.
Sem. 1 Sept. Points & Lines G1.1.6 Recognize Euclidean geometry as an axiom system. Know the key axioms and understand the meaning of and distinguish between undefined terms, axioms, definitions, and theorems.
CORRELATION TO GEORGIA QUALITY CORE CURRICULUM FOR GEOMETRY (GRADES 9-12)
 CORRELATION TO GEORGIA (GRADES 9-12) SUBJECT AREA: Mathematics COURSE: 27. 06300 TEXTBOOK TITLE: PUBLISHER: Geometry: Tools for a Changing World 2001 Prentice Hall 1 Solves problems and practical applications
CORRELATION TO GEORGIA (GRADES 9-12) SUBJECT AREA: Mathematics COURSE: 27. 06300 TEXTBOOK TITLE: PUBLISHER: Geometry: Tools for a Changing World 2001 Prentice Hall 1 Solves problems and practical applications
Geometry Curriculum Guide Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA
 Geometry Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Geometry Prerequisite: Successful completion Algebra I This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra I. The course content
Geometry Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Geometry Prerequisite: Successful completion Algebra I This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra I. The course content
FLORIDA GEOMETRY EOC TOOLKIT
 FLORIDA GEOMETRY EOC TOOLKIT CORRELATION Correlated to the Geometry End-of-Course Benchmarks For more information, go to etacuisenaire.com\florida 78228IS ISBN 978-0-7406-9565-0 MA.912.D.6.2 Find the converse,
FLORIDA GEOMETRY EOC TOOLKIT CORRELATION Correlated to the Geometry End-of-Course Benchmarks For more information, go to etacuisenaire.com\florida 78228IS ISBN 978-0-7406-9565-0 MA.912.D.6.2 Find the converse,
Amarillo ISD Math Curriculum
 Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide
 Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Foundations Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Study Guide and Intervention
 IO 1-1 tudy Guide and Intervention oints, Lines, and lanes ame oints, Lines, and lanes In geometry, a point is a location, a line contains points, and a plane is a flat surface that contains points and
IO 1-1 tudy Guide and Intervention oints, Lines, and lanes ame oints, Lines, and lanes In geometry, a point is a location, a line contains points, and a plane is a flat surface that contains points and
Reteaching Golden Ratio
 Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Pacing Guide. Geometry. Quarter 1
 1 Start-Up/ Review ***************** ***** Note: Reteaching from Ready to Go On Quizzes indicate time built in for Intervention lessons/ student mastery of previously taught material. Wk 2 1.1: Understanding
1 Start-Up/ Review ***************** ***** Note: Reteaching from Ready to Go On Quizzes indicate time built in for Intervention lessons/ student mastery of previously taught material. Wk 2 1.1: Understanding
Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Program of Studies TJ Math 1
 Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Geometry Curriculum Guide Lunenburg County Public Schools June 2014
 Marking Period: 1 Days: 4 Reporting Category/Strand: Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations SOL G.1 The student will construct and judge the validity of a logical argument consisting of a set of premises
Marking Period: 1 Days: 4 Reporting Category/Strand: Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations SOL G.1 The student will construct and judge the validity of a logical argument consisting of a set of premises
Geometry Honors Curriculum Guide Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA
 Geometry Honors Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Geometry Honors Prerequisite: Successful Completion of Algebra I Honors K This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
Geometry Honors Dunmore School District Dunmore, PA Geometry Honors Prerequisite: Successful Completion of Algebra I Honors K This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
2 nd Semester Geometry Review Packet. In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE.
 In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE. Determine whether the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement and the postulate or theorem that
In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE. Determine whether the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement and the postulate or theorem that
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems
 Geometry efinitions, Postulates, and Theorems hapter : Similarity Section.1: Ratios, Proportions, and the Geometric ean Standards: Prepare for 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the
Geometry efinitions, Postulates, and Theorems hapter : Similarity Section.1: Ratios, Proportions, and the Geometric ean Standards: Prepare for 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the
Geometry Year-Long. September 2014
 St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Nick Steve Geometry Year-Long September 2014 NOTE: The topics covered in Geometry and in Advanced Geometry are basically the same. However, the Advanced Geometry
St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Nick Steve Geometry Year-Long September 2014 NOTE: The topics covered in Geometry and in Advanced Geometry are basically the same. However, the Advanced Geometry
Geometry Unit 3 Practice
 Lesson 17-1 1. Find the image of each point after the transformation (x, y) 2 x y 3, 3. 2 a. (6, 6) b. (12, 20) Geometry Unit 3 ractice 3. Triangle X(1, 6), Y(, 22), Z(2, 21) is mapped onto XʹYʹZʹ by a
Lesson 17-1 1. Find the image of each point after the transformation (x, y) 2 x y 3, 3. 2 a. (6, 6) b. (12, 20) Geometry Unit 3 ractice 3. Triangle X(1, 6), Y(, 22), Z(2, 21) is mapped onto XʹYʹZʹ by a
Geometry. Pacing Guide. Kate Collins Middle School
 Geometry Pacing Guide Kate Collins Middle School 2016-2017 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles 8/24 9/4 Geometry Pacing Chart 2016 2017 First Nine Weeks 1.1 Points, Lines, and Planes 1.2 Linear Measure and
Geometry Pacing Guide Kate Collins Middle School 2016-2017 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles 8/24 9/4 Geometry Pacing Chart 2016 2017 First Nine Weeks 1.1 Points, Lines, and Planes 1.2 Linear Measure and
1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line.
 1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line. 2) Find the next 3 terms in the sequence and describe the pattern in words. 1, 5, 9, 13,,, 3) Find the next 3 terms
1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line. 2) Find the next 3 terms in the sequence and describe the pattern in words. 1, 5, 9, 13,,, 3) Find the next 3 terms
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide
 Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
FONTANA UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 Standards and Objectives Pacing Map
 Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 1 August 9-13 2 August 16-20 *1.0 Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning.
Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 1 August 9-13 2 August 16-20 *1.0 Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning.
Geometry Honors Semester 1
 Geometry Honors Semester 1 Final Exam Review 2017-2018 Name: ate: Period: Formulas: efinitions: 1. Slope - 1. omplementary 2. Midpoint - 2. Supplementary 3. isect 3. istance - 4. Vertical ngles 4. Pythagorean
Geometry Honors Semester 1 Final Exam Review 2017-2018 Name: ate: Period: Formulas: efinitions: 1. Slope - 1. omplementary 2. Midpoint - 2. Supplementary 3. isect 3. istance - 4. Vertical ngles 4. Pythagorean
1. What is the sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle? Write the proof (Hint: it involves creating a parallel line.)
 riangle asics irst: Some basics you should already know. eometry 4.0 1. What is the sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle? Write the proof (Hint: it involves creating a parallel line.) 2. In
riangle asics irst: Some basics you should already know. eometry 4.0 1. What is the sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle? Write the proof (Hint: it involves creating a parallel line.) 2. In
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM
 M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
Ganado Unified School District Geometry
 Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
Lesson 13.1 The Premises of Geometry
 Lesson 13.1 he remises of Geometry Name eriod ate 1. rovide the missing property of equality or arithmetic as a reason for each step to solve the equation. olve for x: 5(x 4) 15 2x 17 olution: 5(x 4) 15
Lesson 13.1 he remises of Geometry Name eriod ate 1. rovide the missing property of equality or arithmetic as a reason for each step to solve the equation. olve for x: 5(x 4) 15 2x 17 olution: 5(x 4) 15
Angles of Polygons Concept Summary
 Vocabulary and oncept heck diagonal (p. 404) isosceles trapezoid (p. 439) kite (p. 438) median (p. 440) parallelogram (p. 411) rectangle (p. 424) rhombus (p. 431) square (p. 432) trapezoid (p. 439) complete
Vocabulary and oncept heck diagonal (p. 404) isosceles trapezoid (p. 439) kite (p. 438) median (p. 440) parallelogram (p. 411) rectangle (p. 424) rhombus (p. 431) square (p. 432) trapezoid (p. 439) complete
Department: Course: Chapter 1
 Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
