STUDY OF ZMP MEASUREMENT FOR BIPEDROBOT USING FSR SENSOR
|
|
|
- Morgan Chastity Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDY OF ZMP MEASUREMENT FOR BIPEDROBOT USING FSR SENSOR Bong Gyou Shim, *Eung Hyuk Lee, **Hong Ki Min, Seung Hong Hong Department of Electronic Engineering, Inha University *Department of Electronic Engineering, Korea Polytechnic University **Department of Information & Telecom Engineering, University of Incheon bipedrobot@empal.com, *ehlee@kpu.ac.kr, **mkmin@incheon.ac.kr, shhong@inha.ac.kr Abstract: This paper discuss a method measuring ZMP for biped robot. We obtained feet-bottom pressure distribution using FSR sensors attaching feet-bottom. We calculate value of ZMP coordinates that is the center of gravity for biped robot using their pressure distribution. Value of Biped Robot ZMP coordinates always exists in feet-bottom. When walking limbs of biped robot are controlled, inverse kinematics use method supposed by author. We introduce it in this paper. Keywords: Biped Robot, FSR Sensor, ZMP, feet-bottom 1 INTRODUCTION To improve life quality, human request robot that can alternate one's work. This robot is calling humanoid. Robot Technology goal is humanoid. We may try humanoid robot being. Recently, study of humanoid robot is proceeding in many place. Generation of car model robot driven by wheels sooner or later replace with wakling robot generation. And, we might oppose that we may replace human effort as role of home robot as well as industry robot. Walking is a essential basal condition so that anthropomorphic robot adapts to human environment. In this study, author formerly makes a small-sized humanoid oneself. This humanoid names DORRAE. Humanoid DORRAE is korean that means pulley. Pulley symbolizes balance and control of force. From a robot kinematical point of view, DORRAE is robot which was made farther nearly human structure. Existing DORRAE gait formula is method realized via sequential pattern tracing using walking pattern reference. But, the center of gravity caused by robot weight, that is, Zero Moment Point(ZMP) must be measured and controlled in realtime operation so that robot can overcome to tumble due to unexpected noise. therefore, measuring ZMP is preceded. In this paper, when we control humanoid robot walking, the upper limbs is fixed and the nether limbs is controlled using inverse-kinematics method proposed by author. In this condition, for measuring and maintaining ZMP, we use to attach four FSR sensors a foot in exiting study but three FSR sensors a foot in this paper. This paper experiment shows measurement ability to attach three FSR sensors per foot. 2. ABOUT DORRAE ROBOT DORRAE appearance is showed by figure 1. Special feature of DORRAE is 1) autonomous locomotion 2) remote robot control(using Bluetooth) 3) realization of varying posture made by twenty joint. Figure 1. Biped robot made for experiment DORRAE has twenty degree of freedom(dof) which consist of each two unit that arm has four DOF and leg has six DOF. Height is 350mm and weight is 2.5kg. DORRAE joint organization is like figure 2.
2 Main processor of DORRAE is ATmega128 which is RISC 8bit prosessor AVR. Therefore, we can remote control using Bluetooth. If robot tumbled, Robot can pick oneself up as it trace sequential pattern reference. In the future, when robot is tumbled, it will add function picking oneself up via balance and gyro sensor. arm leg head Joint quantity pitch 0 yaw 0 roll 2 shoulder pitch 2 yaw 2 elbow pitch 2 wrist pitch 0 hand pitch 0 waist pitch 0 yaw 0 roll 2 hip pitch 2 yaw 2 knee pitch 2 ankle roll 2 pitch 2 figure 2. DORRAE joint formation In order to control robot, kinematics modeling must be preceded. Generally, biped robot is been modeling as kinematical analysis divisor like Denavit- Hartenberg notation(d-h notation) applying to manipulator(robot arm) which often use the progress of industrial work. But it is difficult to realize lowcost microprocessor because this exiting methods have long operation time. By the way, Walking human leg is working space and motion is more limitary than manipulator. Thus, modeling method which can reduce operation time was issued by author. [4] Simply to discuss this, Walking demanded motion of leg regard as three motion. The three motion is to regulate leg length using knee, to move foot to front or back and to move foot to left or right. Thus, we obtain angle of each joint through degree of the three motion. 3.1 Re-modeling about leg length Prismatic joint structure regard as knee joint of robot like figure 3, and then it analyzes. l2 l1 d2 d3 d1 x r z 3. JOINT CONTROL DORRAE is modeling like figure 2. Figure 3. Re-modeling to regulate leg length using knee 3.2 Re-modeling to move foot to front or back α4 α3 α2 z x α1 Figure 2. Biped robot(dorrae) model Figure 4. Re-modeling to move foot to front or back
3 Like as figure 4, four variables which is α1, α2, α3, α4 assign in two joint took part in motion to move foot to front or back. α2, α3 move to same angle and α1, α4 indicate direction angle of the upper and lower each joint. By α2(=α3), The value of x coordinates from center to foot is obtained. 3.3 Re-modeling to move foot to left or right Like as figure 5, four variables which is δ1, δ2, δ3, δ4 assign in two joint took part in motion to move foot to front or back. δ2, δ3 move to same angle and α1, α4 indicate direction angle of the upper and lower each joint. By δ2(=δ3), The value of y coordinates from center to foot is obtained. accelerometer in the center of all link gravity and then calculation ZMP using value measured these. But, this method is difficult to realize system. more simplicity and efficient method is to measure ZMP using FSR(Force Sensing Resistors). Method measuring ZMP using FSR seek the center of gravity. Using FSR, we easily trace movement of ZMP. Like as equation (1), we can obtain the coordinate values of ZMP. (1) When we calculate the coordinate values of ZMP, absolute magnitude of force measured via FSR isn't significant. It is because relative value is decided. Figure 5. Re-modeling to move foot to left or right 4. ZMP MEASUREMENT We obtained feet-bottom pressure distribution using FSR sensors attaching feet-bottom. We calculate value of ZMP(Zero Moment Point) coordinates that is the center of gravity for biped robot using their pressure distribution. Formerly ZMP Measurement is used to attach feetbottom to four FSR sensors like Figure 3. In this paper, it is used for ZMP Measurement to attach feetbottom to three FSR sensors like Figure 4. We made a experiment foot like Figure 9.(b) and equation to calculate pressure about each coordinates. We lay a counterweight in each coordinates and then measured all FSR value. We contrasted pressure value based on equation with measuring pressure value. Using experiment result we made equation to calculate ZMP coordinates value about each FSR sensor value. This experiment show that equation to calculate ZMP coordinates value proposed by author is adequate. 4.1 The existing method of ZMP measurement In order to obtain precise ZMP, we install Figure 6. Attached four FSR sensors a foot In figure 6, a, b, c, d are measured values via p1, p2, p3, p4. When na, nb, nc, nd ( n is optional integer), we anticipate to calculate same ZMP constantly. Hence this has two meaning. First, If force values measured via each FSR is very
4 small, ZMP seriously is changed by measured error. Second, with make foot-bottom precisely it must have structure that force distribution uniform. If it isn't so, measured ZMP values are imprecise. 4.2 The improved method of ZMP measurement When measured FSR values are f1 >fmin, f2 >fmin, f3 >fmin, f4 >fmin, value of optional one - for instance, f1 - can alternatives value used by equation (2). Thus, to use three FSR that isn't four FSR can reduce the number of FSR. It is proved by experiments executed in this paper. f1 = f2 f4 / f3 (2) Shown figure 8, force Sensing Resistors(FSR) are a polymer thick film (PTF) device which exhibits a decrease in resistance with an increase in the force applied to the active surface. Its force sensitivity is optimized for use in human touch control of electronic devices. FSRs are not a load cell or strain gauge, though they have similar properties. FSRs are not suitable for precision measurements. When we calculate the coordinate values of ZMP, absolute magnitude of force measured via FSR isn't significant. It is because relative value is decided. Like as figure 9.(a), length(axis of x) is 120mm, width(axis of y) is 80mm, and four corner which support upper body of foot-bottom are a regular square that length of a side is 25mm. Both surface attaching FSR select material to be able to press on it softly then to absorb shock. figure 9.(b) is the picture of feet-bottom made by author. Figure 7. Attached Three FSR sensors a foot 4.3 Design of biped robot foot-bottom for ZMP measuring (a) Standard of foot-bottom (b) Picture of foot-bottom Figure 8. FSR sensors attaching in biped robot footbottom Figure 9. Foot-bottom attached Four FSR Sensors
5 4.4 ZMP measuring experiment The value of coordinates for experiment is that axis of x is value from +40mm to -40mm maintaining 10mm gap and axis of y is value from +20mm to - 20mm maintaining 5mm gap. This is the appointed value of coordinates(o). When it is inflicted that weight of 3kg on surface that the appointed value of coordinates is the center of circle and a diameter is 10mm, pressure value of f1,f2,f3,f4 is measured. To assign f1,f2,f3,f4 to equation (1), the measured value of coordinates(+) can be obtained. To subtract the appointed value of coordinates(o) from the measured value of coordinates(+), an error be obtained. Figure 10 shows the appointed value of coordinates(o) and the measured value of coordinates(+). In this way, the measured value of coordinates(+) is obtained to replace one by one input value of FSR as equation (2). although we remove one among F1, F2, F3, F4, the result doesn't very differ from using four sensor and other three sensor. Figure 11 shows the appointed value of coordinates(o) and the measured value of coordinates(+) using three FSR that F1 be replaced by equation (2). 4.5 The result of experiment To subtract the appointed value of coordinates(o) from the measured value of coordinates(+) in section 4.4, an error be obtained. figure 12 shows average errors. average error(mm) used FSRs coordinates of x coordinates of y F1, F2, F3, F F2, F3, F F1, F3, F F1, F2, F F1, F2, F Figure 10. The measured value of coordinates(+) using four FSRs about he appointed value of coordinates(o) Figure 12. Average errors with used FSRs As a result of this experiment, when we measure the center of robot gravity, although we use optional three FSRs among four FSRs, these errors don't cause problem which make tumble robot. Thus, this experiment shows that to measure ZMP using this method isn't influence. Figure 11. The appointed value of coordinates(o) and the measured value of coordinates(+) using three FSRs that F1 be replaced by equation (2). 5. CONCLUSION Processors of DORRAE are ATmega128 which is RISC 8bit prosessor AVR. Prodessors are the number of two. one is main processor which control motion pattern. another is slave processor which control the 32 of RC-servo simultaneously. unsynchronous serial communication is used between main processor and slave processor. In the result, to attach three FSRs which is four FSRs in foot-bottom, we can measure ZMP. Thus, for the first time, humanoid can flexibly adjust against the ground condition and the force which is caused to outer disturbance. Hence, compensation algorithm in static and dynamic status should study.
6 REFERENCES [1] John J.Craig, "Introduction To Robotics", Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, [2] S.Hashimoto S Narita, T.Kobayashi, A. Takanishi, J. Yamaguchi, P. Dario and H. Takanobu :Development of a Biped Humanoid Robot "WABIAN", Video Proc. Of the 1998 ICRA, [3] S.Kajita and K.Tani, "Experimental Study of Biped Dynamic Walking", IEEE Control Systems Magazine, Vol. 16, No. 1, pp , [4] Bong Gyou Shim, Hyeon Min Shim, Se Kee Kil, Eung Hyuk Lee, Seung Hong Hong, "Static Gait Control of Anthropomorphic Biped Robot Based on Kinematical Re-modeling and ZMP Control", HCI Conference, Vol. 1, No. 2, pp , 2004 [5] M Hirose, "Development of Humanoid Robot ASIMO," Proc. Int. Confernce on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Workshop [6] H.Inoue et al., HRP: Humanoid Robotics Project of MITI, IEEE Humanoid 2000 [7] K. Hirai, "Current and Future Perspective of Honda Humanoid Robot", Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conference on Intelligent Robots and systems, PP , 1997.
Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots using Artificial Neural Networks
 Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots using Artificial Neural Networks Javier de Lope, Rafaela González-Careaga, Telmo Zarraonandia, and Darío Maravall Department of Artificial Intelligence Faculty of
Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots using Artificial Neural Networks Javier de Lope, Rafaela González-Careaga, Telmo Zarraonandia, and Darío Maravall Department of Artificial Intelligence Faculty of
Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots Using Artificial Neural Networks
 Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots Using Artificial Neural Networks Javier de Lope, Rafaela González-Careaga, Telmo Zarraonandia, and Darío Maravall Department of Artificial Intelligence Faculty of
Inverse Kinematics for Humanoid Robots Using Artificial Neural Networks Javier de Lope, Rafaela González-Careaga, Telmo Zarraonandia, and Darío Maravall Department of Artificial Intelligence Faculty of
A sliding walk method for humanoid robots using ZMP feedback control
 A sliding walk method for humanoid robots using MP feedback control Satoki Tsuichihara, Masanao Koeda, Seiji Sugiyama, and Tsuneo oshikawa Abstract In this paper, we propose two methods for a highly stable
A sliding walk method for humanoid robots using MP feedback control Satoki Tsuichihara, Masanao Koeda, Seiji Sugiyama, and Tsuneo oshikawa Abstract In this paper, we propose two methods for a highly stable
Serially-Linked Parallel Leg Design for Biped Robots
 December 13-15, 24 Palmerston North, New ealand Serially-Linked Parallel Leg Design for Biped Robots hung Kwon, Jung H. oon, Je S. eon, and Jong H. Park Dept. of Precision Mechanical Engineering, School
December 13-15, 24 Palmerston North, New ealand Serially-Linked Parallel Leg Design for Biped Robots hung Kwon, Jung H. oon, Je S. eon, and Jong H. Park Dept. of Precision Mechanical Engineering, School
Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot
 Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 321 334 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot Xiaohua Wu 1,3, Jian Yi 2 Abstract. Freestyle skiing robot
Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 321 334 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot Xiaohua Wu 1,3, Jian Yi 2 Abstract. Freestyle skiing robot
Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot
 Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot Jung-Yup Kim *, Christopher G. Atkeson *, Jessica K. Hodgins *, Darrin C. Bentivegna *,** and Sung Ju Cho * * Robotics
Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot Jung-Yup Kim *, Christopher G. Atkeson *, Jessica K. Hodgins *, Darrin C. Bentivegna *,** and Sung Ju Cho * * Robotics
Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk
 Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk Hafez Farazi #*1, Farzad Ahmadinejad *2, Farhad Maleki #3, M.E Shiri #4 # Mathematics and Computer Science Department, Amirkabir
Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk Hafez Farazi #*1, Farzad Ahmadinejad *2, Farhad Maleki #3, M.E Shiri #4 # Mathematics and Computer Science Department, Amirkabir
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Cerebellar Augmented Joint Control for a Humanoid Robot
 Cerebellar Augmented Joint Control for a Humanoid Robot Damien Kee and Gordon Wyeth School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering University of Queensland, Australia Abstract. The joints
Cerebellar Augmented Joint Control for a Humanoid Robot Damien Kee and Gordon Wyeth School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering University of Queensland, Australia Abstract. The joints
Online Generation of Humanoid Walking Motion based on a Fast. The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan,
 Online Generation of Humanoid Walking Motion based on a Fast Generation Method of Motion Pattern that Follows Desired ZMP Koichi Nishiwaki 1, Satoshi Kagami 2,Yasuo Kuniyoshi 1, Masayuki Inaba 1,Hirochika
Online Generation of Humanoid Walking Motion based on a Fast Generation Method of Motion Pattern that Follows Desired ZMP Koichi Nishiwaki 1, Satoshi Kagami 2,Yasuo Kuniyoshi 1, Masayuki Inaba 1,Hirochika
SYNTHESIS AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF MOTION FOR A FOUR-LEGGED MAMMAL-STRUCTURED ROBOT
 SYNTHESIS AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF MOTION FOR A FOUR-LEGGED MAMMAL-STRUCTURED ROBOT Macie Tronacki* Industrial Research Institute for Automation and Measurements, Warsaw, Poland Corresponding author (mtronacki@piap.pl)
SYNTHESIS AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF MOTION FOR A FOUR-LEGGED MAMMAL-STRUCTURED ROBOT Macie Tronacki* Industrial Research Institute for Automation and Measurements, Warsaw, Poland Corresponding author (mtronacki@piap.pl)
David Galdeano. LIRMM-UM2, Montpellier, France. Members of CST: Philippe Fraisse, Ahmed Chemori, Sébatien Krut and André Crosnier
 David Galdeano LIRMM-UM2, Montpellier, France Members of CST: Philippe Fraisse, Ahmed Chemori, Sébatien Krut and André Crosnier Montpellier, Thursday September 27, 2012 Outline of the presentation Context
David Galdeano LIRMM-UM2, Montpellier, France Members of CST: Philippe Fraisse, Ahmed Chemori, Sébatien Krut and André Crosnier Montpellier, Thursday September 27, 2012 Outline of the presentation Context
Generating Whole Body Motions for a Biped Humanoid Robot from Captured Human Dances
 Generating Whole Body Motions for a Biped Humanoid Robot from Captured Human Dances Shinichiro Nakaoka Atsushi Nakazawa Kazuhito Yokoi Hirohisa Hirukawa Katsushi Ikeuchi Institute of Industrial Science,
Generating Whole Body Motions for a Biped Humanoid Robot from Captured Human Dances Shinichiro Nakaoka Atsushi Nakazawa Kazuhito Yokoi Hirohisa Hirukawa Katsushi Ikeuchi Institute of Industrial Science,
Motion Control of Wearable Walking Support System with Accelerometer Considering Swing Phase Support
 Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, August 1-3, Motion Control of Wearable Walking Support
Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, August 1-3, Motion Control of Wearable Walking Support
Modelling and simulation of the humanoid robot HOAP-3 in the OpenHRP3 platform
 Modelling and simulation of the humanoid robot -3 in the 3 platform C.A. Monje, P. Pierro, T. Ramos, M. González-Fierro, C. Balaguer. Abstract The aim of this work is to model and simulate the humanoid
Modelling and simulation of the humanoid robot -3 in the 3 platform C.A. Monje, P. Pierro, T. Ramos, M. González-Fierro, C. Balaguer. Abstract The aim of this work is to model and simulate the humanoid
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics
 Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Controlling Humanoid Robots with Human Motion Data: Experimental Validation
 21 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots Nashville, TN, USA, December 6-8, 21 Controlling Humanoid Robots with Human Motion Data: Experimental Validation Katsu Yamane, Stuart O. Anderson,
21 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots Nashville, TN, USA, December 6-8, 21 Controlling Humanoid Robots with Human Motion Data: Experimental Validation Katsu Yamane, Stuart O. Anderson,
Motion Planning of Emergency Stop for Humanoid Robot by State Space Approach
 Motion Planning of Emergency Stop for Humanoid Robot by State Space Approach Mitsuharu Morisawa, Kenji Kaneko, Fumio Kanehiro, Shuuji Kajita, Kiyoshi Fujiwara, Kensuke Harada, Hirohisa Hirukawa National
Motion Planning of Emergency Stop for Humanoid Robot by State Space Approach Mitsuharu Morisawa, Kenji Kaneko, Fumio Kanehiro, Shuuji Kajita, Kiyoshi Fujiwara, Kensuke Harada, Hirohisa Hirukawa National
A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System J. Baltes*, P. Kopacek**,M. Schörghuber** *Department of Computer
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System J. Baltes*, P. Kopacek**,M. Schörghuber** *Department of Computer
Control Approaches for Walking and Running
 DLR.de Chart 1 > Humanoids 2015 > Christian Ott > 02.11.2015 Control Approaches for Walking and Running Christian Ott, Johannes Englsberger German Aerospace Center (DLR) DLR.de Chart 2 > Humanoids 2015
DLR.de Chart 1 > Humanoids 2015 > Christian Ott > 02.11.2015 Control Approaches for Walking and Running Christian Ott, Johannes Englsberger German Aerospace Center (DLR) DLR.de Chart 2 > Humanoids 2015
Physical Interaction between Human And a Bipedal Humanoid Robot -Realization of Human-follow Walking-
 Physical Interaction between Human And a Bipedal Humanoid Robot -Realization of Human-follow Walking- *Samuel Agus SEIAWAN **Sang Ho HYON ***Jin ichi YAMAGUCHI * ***Atsuo AKANISHI *Department of Mechanical
Physical Interaction between Human And a Bipedal Humanoid Robot -Realization of Human-follow Walking- *Samuel Agus SEIAWAN **Sang Ho HYON ***Jin ichi YAMAGUCHI * ***Atsuo AKANISHI *Department of Mechanical
Developing a Robot Model using System-Level Design
 Developing a Robot Model using System-Level Design What was once the stuff of dreams, being secretly developed in high-security government labs for applications in defense and space exploration, is now
Developing a Robot Model using System-Level Design What was once the stuff of dreams, being secretly developed in high-security government labs for applications in defense and space exploration, is now
Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots
 28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots Oussama Khatib, 1 Peter Thaulad,
28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots Oussama Khatib, 1 Peter Thaulad,
Upper Body Joints Control for the Quasi static Stabilization of a Small-Size Humanoid Robot
 Upper Body Joints Control for the Quasi static Stabilization of a Small-Size Humanoid Robot Andrea Manni, Angelo di Noi and Giovanni Indiveri Dipartimento Ingegneria dell Innovazione, Università di Lecce
Upper Body Joints Control for the Quasi static Stabilization of a Small-Size Humanoid Robot Andrea Manni, Angelo di Noi and Giovanni Indiveri Dipartimento Ingegneria dell Innovazione, Università di Lecce
Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters
 Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters Vincent Hugel and Nicolas Jouandeau LISV, University of Versailles and LIASD, University of Paris 8 Abstract. This paper describes a procedure
Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters Vincent Hugel and Nicolas Jouandeau LISV, University of Versailles and LIASD, University of Paris 8 Abstract. This paper describes a procedure
Falling forward of humanoid robot based on similarity with parametric optimum
 Acta Technica 62 (2017), No. 5A, 201212 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Falling forward of humanoid robot based on similarity with parametric optimum Xiaokun Leng 1, Songhao Piao 2, Lin
Acta Technica 62 (2017), No. 5A, 201212 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Falling forward of humanoid robot based on similarity with parametric optimum Xiaokun Leng 1, Songhao Piao 2, Lin
KINEMATIC MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF 5 DOF ROBOTIC ARM
 International Journal of Robotics Research and Development (IJRRD) ISSN(P): 2250-1592; ISSN(E): 2278 9421 Vol. 4, Issue 2, Apr 2014, 17-24 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. KINEMATIC MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF 5 DOF ROBOTIC
International Journal of Robotics Research and Development (IJRRD) ISSN(P): 2250-1592; ISSN(E): 2278 9421 Vol. 4, Issue 2, Apr 2014, 17-24 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. KINEMATIC MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF 5 DOF ROBOTIC
Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped Robot. Jinrong Zhang *, Chenxi Wang and Jianhua Zhang
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 014, 6, 1685-1690 1685 Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 014, 6, 1685-1690 1685 Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped
Interpolation and extrapolation of motion capture data
 Interpolation and extrapolation of motion capture data Kiyoshi Hoshino Biological Cybernetics Lab, University of the Ryukyus and PRESTO-SORST, Japan Science and Technology Corporation Nishihara, Okinawa
Interpolation and extrapolation of motion capture data Kiyoshi Hoshino Biological Cybernetics Lab, University of the Ryukyus and PRESTO-SORST, Japan Science and Technology Corporation Nishihara, Okinawa
Using the Generalized Inverted Pendulum to generate less energy-consuming trajectories for humanoid walking
 Using the Generalized Inverted Pendulum to generate less energy-consuming trajectories for humanoid walking Sahab Omran, Sophie Sakka, Yannick Aoustin To cite this version: Sahab Omran, Sophie Sakka, Yannick
Using the Generalized Inverted Pendulum to generate less energy-consuming trajectories for humanoid walking Sahab Omran, Sophie Sakka, Yannick Aoustin To cite this version: Sahab Omran, Sophie Sakka, Yannick
An Interactive Software Environment for Gait Generation and Control Design of Sony Legged Robots
 An Interactive Software Environment for Gait Generation and Control Design of Sony Legged Robots Dragos Golubovic and Huosheng Hu Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Colchester CO4 3SQ,
An Interactive Software Environment for Gait Generation and Control Design of Sony Legged Robots Dragos Golubovic and Huosheng Hu Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Colchester CO4 3SQ,
Robot body. Robot Body. Wireless LAN Access point. Battery. communication. User PC. Power. Drawing 1 Wired mode configuration.
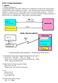 HOAP-2 Design Specification 1. System 1.1 System configuration The following illustration shows both available forms of configuration, the wired mode and the wireless modem (wireless mode is available
HOAP-2 Design Specification 1. System 1.1 System configuration The following illustration shows both available forms of configuration, the wired mode and the wireless modem (wireless mode is available
MEAM 620: HW 1. Sachin Chitta Assigned: January 10, 2007 Due: January 22, January 10, 2007
 MEAM 620: HW 1 Sachin Chitta (sachinc@grasp.upenn.edu) Assigned: January 10, 2007 Due: January 22, 2006 January 10, 2007 1: MATLAB Programming assignment Using MATLAB, write the following functions: 1.
MEAM 620: HW 1 Sachin Chitta (sachinc@grasp.upenn.edu) Assigned: January 10, 2007 Due: January 22, 2006 January 10, 2007 1: MATLAB Programming assignment Using MATLAB, write the following functions: 1.
Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League
 Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League Armita Sabeti Ashraf, Atieh Alsadat Moosavian, Fatemeh Gerami Gohar, Fatima Tafazzoli Shadpour, Romina Moradi, Sama Moayeri Farzanegan
Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League Armita Sabeti Ashraf, Atieh Alsadat Moosavian, Fatemeh Gerami Gohar, Fatima Tafazzoli Shadpour, Romina Moradi, Sama Moayeri Farzanegan
INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR
 INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR Mohammad Afif Ayob 1, Wan Nurshazwani Wan Zakaria 1, Jamaludin Jalani 2 and Mohd Razali Md Tomari 1 1 Advanced Mechatronics Research Group
INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR Mohammad Afif Ayob 1, Wan Nurshazwani Wan Zakaria 1, Jamaludin Jalani 2 and Mohd Razali Md Tomari 1 1 Advanced Mechatronics Research Group
Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns
 1 Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns Jinsu Liu 1, Xiaoping Chen 1 and Manuela Veloso 2 1 Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
1 Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns Jinsu Liu 1, Xiaoping Chen 1 and Manuela Veloso 2 1 Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm
 Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm Mohammed Z. Al-Faiz,MIEEE Computer Engineering Dept. Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mohammed S.Saleh
Inverse Kinematics Analysis for Manipulator Robot With Wrist Offset Based On the Closed-Form Algorithm Mohammed Z. Al-Faiz,MIEEE Computer Engineering Dept. Nahrain University Baghdad, Iraq Mohammed S.Saleh
Kinematics. Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position.
 Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Using Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction Of Dynamic Human Motion
 ABSTRACT Using Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction Of Dynamic Human Motion Researchers in robotics and other human-related fields have been studying human motion behaviors to understand and mimic
ABSTRACT Using Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction Of Dynamic Human Motion Researchers in robotics and other human-related fields have been studying human motion behaviors to understand and mimic
Evolutionary Motion Design for Humanoid Robots
 Evolutionary Motion Design for Humanoid Robots Toshihiko Yanase Department of Frontier Informatics The University of Tokyo Chiba 277-8561, Japan yanase@iba.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp Hitoshi Iba Department of Frontier
Evolutionary Motion Design for Humanoid Robots Toshihiko Yanase Department of Frontier Informatics The University of Tokyo Chiba 277-8561, Japan yanase@iba.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp Hitoshi Iba Department of Frontier
Imitation Control for Biped Robot Using Wearable Motion Sensor
 Imitation Control for Biped Robot Using Wearable Motion Sensor Tao Liu e-mail: liu.tao@kochi-tech.ac.jp Yoshio Inoue Kyoko Shibata Department of Intelligent Mechanical Systems Engineering, Kochi University
Imitation Control for Biped Robot Using Wearable Motion Sensor Tao Liu e-mail: liu.tao@kochi-tech.ac.jp Yoshio Inoue Kyoko Shibata Department of Intelligent Mechanical Systems Engineering, Kochi University
Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots. Talk Overview
 Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner, Jr. Carnegie Mellon University Koichi Nishiwaki The University of Tokyo Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Lab (AIST) Masayuki Inaba
Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner, Jr. Carnegie Mellon University Koichi Nishiwaki The University of Tokyo Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Lab (AIST) Masayuki Inaba
Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot
 Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot Jung-Yup Kim *, Christopher G. Ateson *, Jessica K. Hodgins *, Darrin C. Bentivegna *,** and Sung Ju Cho * * Robotics
Online Gain Switching Algorithm for Joint Position Control of a Hydraulic Humanoid Robot Jung-Yup Kim *, Christopher G. Ateson *, Jessica K. Hodgins *, Darrin C. Bentivegna *,** and Sung Ju Cho * * Robotics
Cecilia Laschi The BioRobotics Institute Scuola Superiore Sant Anna, Pisa
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
A CONTROL ARCHITECTURE FOR DYNAMICALLY STABLE GAITS OF SMALL SIZE HUMANOID ROBOTS. Andrea Manni,1, Angelo di Noi and Giovanni Indiveri
 A CONTROL ARCHITECTURE FOR DYNAMICALLY STABLE GAITS OF SMALL SIZE HUMANOID ROBOTS Andrea Manni,, Angelo di Noi and Giovanni Indiveri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Innovazione, Università di Lecce, via
A CONTROL ARCHITECTURE FOR DYNAMICALLY STABLE GAITS OF SMALL SIZE HUMANOID ROBOTS Andrea Manni,, Angelo di Noi and Giovanni Indiveri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Innovazione, Università di Lecce, via
Study on Dynamics Identification of the Foot Viscoelasticity of a Humanoid Robot
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 24-29, 214 Study on Dynamics Identification of the Foot Viscoelasticity of a Humanoid
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 24-29, 214 Study on Dynamics Identification of the Foot Viscoelasticity of a Humanoid
Motion Simulation of a Modular Robotic System
 Motion Simulation of a Modular Robotic System Haruhisa KUROKAWA, Kohji TOMITA, Eiichi YOSHIDA, Satoshi MURATA and Shigeru KOKAJI Mechanical Engineering Laboratory, AIST, MITI Namiki 1-2, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Motion Simulation of a Modular Robotic System Haruhisa KUROKAWA, Kohji TOMITA, Eiichi YOSHIDA, Satoshi MURATA and Shigeru KOKAJI Mechanical Engineering Laboratory, AIST, MITI Namiki 1-2, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2
 Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2 Yutaro Fukase Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan fukase@shimz.co.jp Junichiro Maeda Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan
Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2 Yutaro Fukase Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan fukase@shimz.co.jp Junichiro Maeda Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan
Lecture Note 6: Forward Kinematics
 ECE5463: Introduction to Robotics Lecture Note 6: Forward Kinematics Prof. Wei Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ohio State University Columbus, Ohio, USA Spring 2018 Lecture 6 (ECE5463
ECE5463: Introduction to Robotics Lecture Note 6: Forward Kinematics Prof. Wei Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ohio State University Columbus, Ohio, USA Spring 2018 Lecture 6 (ECE5463
Ann L. Torres. at the. June others the right to do so.
 Virtual Model Control of a Hexapod Walking Robot by Ann L. Torres Submitted to the Department of Mechanical Engineering in partial fulllment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science in
Virtual Model Control of a Hexapod Walking Robot by Ann L. Torres Submitted to the Department of Mechanical Engineering in partial fulllment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science in
Humanoid Robotics. Path Planning and Walking. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Path Planning and Walking Maren Bennewitz 1 Introduction Given the robot s pose in a model of the environment Compute a path to a target location First: 2D path in a 2D grid map representation
Humanoid Robotics Path Planning and Walking Maren Bennewitz 1 Introduction Given the robot s pose in a model of the environment Compute a path to a target location First: 2D path in a 2D grid map representation
Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot
 Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot Yuan Xu and Heinrich Mellmann Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche Intelligenz Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany {xu,mellmann}@informatik.hu-berlin.de
Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot Yuan Xu and Heinrich Mellmann Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche Intelligenz Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany {xu,mellmann}@informatik.hu-berlin.de
Motion Planning for Whole Body Tasks by Humanoid Robots
 Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 5 Motion Planning for Whole Body Tasks by Humanoid Robots Eiichi Yoshida 1, Yisheng Guan 1, Neo
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 5 Motion Planning for Whole Body Tasks by Humanoid Robots Eiichi Yoshida 1, Yisheng Guan 1, Neo
Modeling of Humanoid Systems Using Deductive Approach
 INFOTEH-JAHORINA Vol. 12, March 2013. Modeling of Humanoid Systems Using Deductive Approach Miloš D Jovanović Robotics laboratory Mihailo Pupin Institute Belgrade, Serbia milos.jovanovic@pupin.rs Veljko
INFOTEH-JAHORINA Vol. 12, March 2013. Modeling of Humanoid Systems Using Deductive Approach Miloš D Jovanović Robotics laboratory Mihailo Pupin Institute Belgrade, Serbia milos.jovanovic@pupin.rs Veljko
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo. Humanoid Robots 2: Dynamic Modeling
 Autonomous and Mobile Robotics rof. Giuseppe Oriolo Humanoid Robots 2: Dynamic Modeling modeling multi-body free floating complete model m j I j R j ω j f c j O z y x p ZM conceptual models for walking/balancing
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics rof. Giuseppe Oriolo Humanoid Robots 2: Dynamic Modeling modeling multi-body free floating complete model m j I j R j ω j f c j O z y x p ZM conceptual models for walking/balancing
A Walking Pattern Generator for Biped Robots on Uneven Terrains
 A Walking Pattern Generator for Biped Robots on Uneven Terrains Yu Zheng, Ming C. Lin, Dinesh Manocha Albertus Hendrawan Adiwahono, Chee-Meng Chew Abstract We present a new method to generate biped walking
A Walking Pattern Generator for Biped Robots on Uneven Terrains Yu Zheng, Ming C. Lin, Dinesh Manocha Albertus Hendrawan Adiwahono, Chee-Meng Chew Abstract We present a new method to generate biped walking
Rolling Locomotion of Deformable Tensegrity Structure
 1 Rolling Locomotion of Deformable Tensegrity Structure M. SHIBATA and S. HIRAI Department of Robotics, Ritsumeikan University, Kusatsu, Shiga 525-8577, Japan E-mail: mizuho-s@se.ritsumei.ac.jp http://greenhand.web.infoseek.co.jp/school/english/index.html
1 Rolling Locomotion of Deformable Tensegrity Structure M. SHIBATA and S. HIRAI Department of Robotics, Ritsumeikan University, Kusatsu, Shiga 525-8577, Japan E-mail: mizuho-s@se.ritsumei.ac.jp http://greenhand.web.infoseek.co.jp/school/english/index.html
INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR
 www.arpnjournals.com INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR Mohammad Afif Ayob 1a, Wan Nurshazwani Wan Zakaria 1b, Jamaludin Jalani 2c, Mohd Razali Md Tomari 1d 1 ADvanced Mechatronics
www.arpnjournals.com INVERSE KINEMATICS ANALYSIS OF A 5-AXIS RV-2AJ ROBOT MANIPULATOR Mohammad Afif Ayob 1a, Wan Nurshazwani Wan Zakaria 1b, Jamaludin Jalani 2c, Mohd Razali Md Tomari 1d 1 ADvanced Mechatronics
Interaction Mesh Based Motion Adaptation for Biped Humanoid Robots
 Interaction Mesh Based Motion Adaptation for Biped Humanoid Robots Shin ichiro Nakaoka 12 and Taku Komura 1 Abstract Adapting human motion data for humanoid robots can be an efficient way to let them conduct
Interaction Mesh Based Motion Adaptation for Biped Humanoid Robots Shin ichiro Nakaoka 12 and Taku Komura 1 Abstract Adapting human motion data for humanoid robots can be an efficient way to let them conduct
Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics
 Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics z z y x z y x z y y x x In Industrial terms Robot Manipulators The study of robot manipulators involves dealing with the positions and orientations
Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics z z y x z y x z y y x x In Industrial terms Robot Manipulators The study of robot manipulators involves dealing with the positions and orientations
An Optimal Planning of Falling Motions of a Humanoid Robot
 Proceedings of the 27 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems San Diego, CA, USA, Oct 29 - Nov 2, 27 TuB5.3 An Optimal Planning of Falling Motions of a Humanoid Robot Kiyoshi
Proceedings of the 27 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems San Diego, CA, USA, Oct 29 - Nov 2, 27 TuB5.3 An Optimal Planning of Falling Motions of a Humanoid Robot Kiyoshi
ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution. Total Points: 30
 Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
Research and Literature Review on Developing Motion Capture System for Analyzing Athletes Action
 International Conference on Education Technology, Management and Humanities Science (ETMHS 2015) Research and Literature Review on Developing Motion Capture System for Analyzing Athletes Action HAN Fang
International Conference on Education Technology, Management and Humanities Science (ETMHS 2015) Research and Literature Review on Developing Motion Capture System for Analyzing Athletes Action HAN Fang
FORWARD AND INVERSE DISPLACEMENT ANALYSIS OF A NOVEL THREE- LEGGED MOBILE ROBOT BASED ON THE KINEMATICS OF IN-PARALLEL MANIPULATORS
 Proceedings of the ASME 7 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 7 September 4-7, 7, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA DETC7-3466 FORWARD
Proceedings of the ASME 7 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 7 September 4-7, 7, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA DETC7-3466 FORWARD
Simultaneous Tracking and Balancing of Humanoid Robots for Imitating Human Motion Capture Data
 The 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 11-15, 2009 St. Louis, USA Simultaneous Tracking and Balancing of Humanoid Robots for Imitating Human Motion Capture
The 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 11-15, 2009 St. Louis, USA Simultaneous Tracking and Balancing of Humanoid Robots for Imitating Human Motion Capture
MTRX4700 Experimental Robotics
 MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming
 214 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 214) September 14-18, 214, Chicago, IL, USA Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming X Xinjilefu, Siyuan Feng and
214 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 214) September 14-18, 214, Chicago, IL, USA Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming X Xinjilefu, Siyuan Feng and
Mobile Robots Locomotion
 Mobile Robots Locomotion Institute for Software Technology 1 Course Outline 1. Introduction to Mobile Robots 2. Locomotion 3. Sensors 4. Localization 5. Environment Modelling 6. Reactive Navigation 2 Today
Mobile Robots Locomotion Institute for Software Technology 1 Course Outline 1. Introduction to Mobile Robots 2. Locomotion 3. Sensors 4. Localization 5. Environment Modelling 6. Reactive Navigation 2 Today
CS 231. Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation. Articulated rigid-body dynamics
 CS 231 Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation Articulated rigid-body dynamics F = ma No control 1 No control Ragdoll effects, joint limits RT Speed: many sims at real-time rates on today
CS 231 Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation Articulated rigid-body dynamics F = ma No control 1 No control Ragdoll effects, joint limits RT Speed: many sims at real-time rates on today
Keyframing an IK Skeleton Maya 2012
 2002-2012 Michael O'Rourke Keyframing an IK Skeleton Maya 2012 (This tutorial assumes you have done the Creating an Inverse Kinematic Skeleton tutorial in this set) Concepts Once you have built an Inverse
2002-2012 Michael O'Rourke Keyframing an IK Skeleton Maya 2012 (This tutorial assumes you have done the Creating an Inverse Kinematic Skeleton tutorial in this set) Concepts Once you have built an Inverse
Dynamically Balanced Omnidirectional Humanoid Robot Locomotion. An Honors Paper for the Department of Computer Science. By Johannes Heide Strom
 Dynamically Balanced Omnidirectional Humanoid Robot Locomotion An Honors Paper for the Department of Computer Science By Johannes Heide Strom Bowdoin College, 2009 c 2009 Johannes Heide Strom Contents
Dynamically Balanced Omnidirectional Humanoid Robot Locomotion An Honors Paper for the Department of Computer Science By Johannes Heide Strom Bowdoin College, 2009 c 2009 Johannes Heide Strom Contents
Inverse Kinematics. Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector
 Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Articulated Robots! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems! MAE 345, Princeton University, 2017
 Articulated Robots! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems! MAE 345, Princeton University, 2017 Robot configurations Joints and links Joint-link-joint transformations! Denavit-Hartenberg representation
Articulated Robots! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems! MAE 345, Princeton University, 2017 Robot configurations Joints and links Joint-link-joint transformations! Denavit-Hartenberg representation
THE POSITION AND ORIENTATION MEASUREMENT OF GONDOLA USING A VISUAL CAMERA
 THE POSITION AND ORIENTATION MEASUREMENT OF GONDOLA USING A VISUAL CAMERA Hwadong Sun 1, Dong Yeop Kim 1 *, Joon Ho Kwon 2, Bong-Seok Kim 1, and Chang-Woo Park 1 1 Intelligent Robotics Research Center,
THE POSITION AND ORIENTATION MEASUREMENT OF GONDOLA USING A VISUAL CAMERA Hwadong Sun 1, Dong Yeop Kim 1 *, Joon Ho Kwon 2, Bong-Seok Kim 1, and Chang-Woo Park 1 1 Intelligent Robotics Research Center,
DETC ANALYSIS, SYNTHESIS, AND EXPERIMENTS OF STANDING UP METHODS FOR A TRIPEDAL ROBOT
 roceedings of the ASME 2009 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference roceedings of ASME 2009 International Design Engineering Technical
roceedings of the ASME 2009 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference roceedings of ASME 2009 International Design Engineering Technical
Inverse Kinematics Software Design and Trajectory Control Programming of SCARA Manipulator robot
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
Development of Wall Mobile Robot for Household Use
 The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Development of Wall Mobile Robot for Household Use Takahiro DOI* 1, Kenta
The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Development of Wall Mobile Robot for Household Use Takahiro DOI* 1, Kenta
CSIS 0801 Final Year Project. Implementation of An Intelligent Hexapod Robot. Individual Final Report - Kinematics
 CSIS 0801 Final Year Project Implementation of An Intelligent Hexapod Robot Individual Final Report - Kinematics FYP Account: fyp14013 Name: Yip Sit Wun (Terry) UID: 3035009744 HKU CS FYP14013 Implementation
CSIS 0801 Final Year Project Implementation of An Intelligent Hexapod Robot Individual Final Report - Kinematics FYP Account: fyp14013 Name: Yip Sit Wun (Terry) UID: 3035009744 HKU CS FYP14013 Implementation
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention
 Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
Leg Motion Primitives for a Dancing Humanoid Robot
 Leg Motion Primitives for a Dancing Humanoid Robot Shinichiro Nakaoka, Atsushi Nakazawa, Kazuhito Yokoi and Katsushi Ikeuchi Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo 4-6-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku,
Leg Motion Primitives for a Dancing Humanoid Robot Shinichiro Nakaoka, Atsushi Nakazawa, Kazuhito Yokoi and Katsushi Ikeuchi Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo 4-6-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku,
DETC WORKSPACE ANALYSIS FOR THE LIMBS OF A HEXAPEDAL ROBOT WALKING GAIT GENERATION ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
 Proceedings of the ASME 008 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 008 August 3-6, 008, Brooklyn, New York, USA DETC008-49615
Proceedings of the ASME 008 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 008 August 3-6, 008, Brooklyn, New York, USA DETC008-49615
Kinematics and Orientations
 Kinematics and Orientations Hierarchies Forward Kinematics Transformations (review) Euler angles Quaternions Yaw and evaluation function for assignment 2 Building a character Just translate, rotate, and
Kinematics and Orientations Hierarchies Forward Kinematics Transformations (review) Euler angles Quaternions Yaw and evaluation function for assignment 2 Building a character Just translate, rotate, and
Self-Collision Detection. Planning for Humanoid Robots. Digital Human Research Center. Talk Overview
 Self-Collision Detection and Motion Planning for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner (CMU & AIST Japan) Digital Human Research Center Self-Collision Detection Feature-based Minimum Distance Computation: Approximate
Self-Collision Detection and Motion Planning for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner (CMU & AIST Japan) Digital Human Research Center Self-Collision Detection Feature-based Minimum Distance Computation: Approximate
Real-time gait planner for human walking using a lower limb exoskeleton and its implementation on Exoped robot
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Real-time gait planner for human walking using a lower limb exoskeleton and its implementation on Exoped robot
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Real-time gait planner for human walking using a lower limb exoskeleton and its implementation on Exoped robot
An Efficient Method for Composing Whole Body Motions of a Humanoid Robot
 An Efficient Method for Composing Whole Body Motions of a Humanoid Robot Shinichiro NAKAOKA Atsushi NAKAZAWA Katsushi IKEUCHI Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo {nakaoka, ki}@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
An Efficient Method for Composing Whole Body Motions of a Humanoid Robot Shinichiro NAKAOKA Atsushi NAKAZAWA Katsushi IKEUCHI Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo {nakaoka, ki}@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
[2] J. "Kinematics," in The International Encyclopedia of Robotics, R. Dorf and S. Nof, Editors, John C. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1988.
![[2] J. Kinematics, in The International Encyclopedia of Robotics, R. Dorf and S. Nof, Editors, John C. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1988. [2] J. Kinematics, in The International Encyclopedia of Robotics, R. Dorf and S. Nof, Editors, John C. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1988.](/thumbs/90/102406247.jpg) 92 Chapter 3 Manipulator kinematics The major expense in calculating kinematics is often the calculation of the transcendental functions (sine and cosine). When these functions are available as part of
92 Chapter 3 Manipulator kinematics The major expense in calculating kinematics is often the calculation of the transcendental functions (sine and cosine). When these functions are available as part of
Robotics. SAAST Robotics Robot Arms
 SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
7 Modelling and Animating Human Figures. Chapter 7. Modelling and Animating Human Figures. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 7-1
 Modelling and Animating Human Figures 7-1 Introduction Modeling and animating an articulated figure is one of the most formidable tasks that an animator can be faced with. It is especially challenging
Modelling and Animating Human Figures 7-1 Introduction Modeling and animating an articulated figure is one of the most formidable tasks that an animator can be faced with. It is especially challenging
Research on time optimal trajectory planning of 7-DOF manipulator based on genetic algorithm
 Acta Technica 61, No. 4A/2016, 189 200 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Research on time optimal trajectory planning of 7-DOF manipulator based on genetic algorithm Jianrong Bu 1, Junyan
Acta Technica 61, No. 4A/2016, 189 200 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Research on time optimal trajectory planning of 7-DOF manipulator based on genetic algorithm Jianrong Bu 1, Junyan
Leg Motion Primitives for a Humanoid Robot to Imitate Human Dances
 Leg Motion Primitives for a Humanoid Robot to Imitate Human Dances Shinichiro Nakaoka 1, Atsushi Nakazawa 2, Kazuhito Yokoi 3 and Katsushi Ikeuchi 1 1 The University of Tokyo,Tokyo, Japan (nakaoka@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp)
Leg Motion Primitives for a Humanoid Robot to Imitate Human Dances Shinichiro Nakaoka 1, Atsushi Nakazawa 2, Kazuhito Yokoi 3 and Katsushi Ikeuchi 1 1 The University of Tokyo,Tokyo, Japan (nakaoka@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp)
Optimization of Six Bar Knee Linkage for Stability of Knee Prosthesis
 Optimization of Six Bar Knee Linkage for Stability of Knee Prosthesis Narjes.Ghaemi 1, Morteza. Dardel 2, Mohammad Hassan Ghasemi 3, Hassan.Zohoor 4, 1- M.sc student, Babol Noshirvani University of Technology,
Optimization of Six Bar Knee Linkage for Stability of Knee Prosthesis Narjes.Ghaemi 1, Morteza. Dardel 2, Mohammad Hassan Ghasemi 3, Hassan.Zohoor 4, 1- M.sc student, Babol Noshirvani University of Technology,
Fuzzy Control for Bipedal Robot Considering Energy Balance
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol., 28, no. 39, 945-952 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/.2988/ces.28.837 Fuzzy Control for Bipedal Robot Considering Energy Balance Jhonattan Gordillo
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol., 28, no. 39, 945-952 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/.2988/ces.28.837 Fuzzy Control for Bipedal Robot Considering Energy Balance Jhonattan Gordillo
Visuo-Motor Learning for Face-to-face Pass between Heterogeneous Humanoids
 Visuo-Motor Learning for Face-to-face Pass between Heterogeneous Humanoids Masaki Ogino a,, Masaaki Kikuchi a, Minoru Asada a,b a Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems b HANDAI Frontier Research Center Graduate
Visuo-Motor Learning for Face-to-face Pass between Heterogeneous Humanoids Masaki Ogino a,, Masaaki Kikuchi a, Minoru Asada a,b a Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems b HANDAI Frontier Research Center Graduate
IVR: Open- and Closed-Loop Control. M. Herrmann
 IVR: Open- and Closed-Loop Control M. Herrmann Overview Open-loop control Feed-forward control Towards feedback control Controlling the motor over time Process model V B = k 1 s + M k 2 R ds dt Stationary
IVR: Open- and Closed-Loop Control M. Herrmann Overview Open-loop control Feed-forward control Towards feedback control Controlling the motor over time Process model V B = k 1 s + M k 2 R ds dt Stationary
Person identification from spatio-temporal 3D gait
 200 International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies Person identification from spatio-temporal 3D gait Yumi Iwashita Ryosuke Baba Koichi Ogawara Ryo Kurazume Information Science and Electrical
200 International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies Person identification from spatio-temporal 3D gait Yumi Iwashita Ryosuke Baba Koichi Ogawara Ryo Kurazume Information Science and Electrical
Design & Kinematic Analysis of an Articulated Robotic Manipulator
 Design & Kinematic Analysis of an Articulated Robotic Manipulator Elias Eliot 1, B.B.V.L. Deepak 1*, D.R. Parhi 2, and J. Srinivas 2 1 Department of Industrial Design, National Institute of Technology-Rourkela
Design & Kinematic Analysis of an Articulated Robotic Manipulator Elias Eliot 1, B.B.V.L. Deepak 1*, D.R. Parhi 2, and J. Srinivas 2 1 Department of Industrial Design, National Institute of Technology-Rourkela
Rising Motion Controllers for Physically Simulated Characters
 Rising Motion Controllers for Physically Simulated Characters by Benjamin James Jones B.S. Computer Science, B.S. Engineering Physics, Colorado School of Mines, 2009 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Rising Motion Controllers for Physically Simulated Characters by Benjamin James Jones B.S. Computer Science, B.S. Engineering Physics, Colorado School of Mines, 2009 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
This week. CENG 732 Computer Animation. Warping an Object. Warping an Object. 2D Grid Deformation. Warping an Object.
 CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
Robot mechanics and kinematics
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2017/18 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2017/18 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
