Functions of Two variables.
|
|
|
- Ralph Porter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Functions of Two variables. Ferdinánd Filip siva.banki.hu/jegyzetek 27 February 217 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 1 / 36
2 Table of contents Functions of Several Variables Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 2 / 36
3 Definition Suppose D is a set of n-tuples of real numbers (x 1, x 2,..., x n ). A real-valued function f on D is a rule that assigns a unique (single) real number w = f (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) to each element in D. The set D is the function s domain. The set of w-values taken on by f is the function s range. The symbol w is the dependent variable of f, and f is said to be a function of the n independent variables x 1 to x n. We also call the x j s the function s input variables and call w the function s output variable. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 3 / 36
4 Interior and Boundary Points, Open, Closed Definition A point (x, y )in a region (set) R in the xy-plane is an interior point of R if it is the center of a disk of positive radius that lies entirely in R. A point (x, y ) is a boundary point of R if every disk centered at (x, y ) contains points that lie outside of R as well as points that lie in R. (The boundary point itself need not belong to R.) The interior points of a region, as a set, make up the interior of the region. The region s boundary points make up its boundary. A region is open if it consists entirely of interior points. A region is closed if it contains all its boundary points. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 4 / 36
5 Interior and Boundary Points, Open, Closed (x, y ) Interior point of R (x, y ) R (x 1, y 1 ) (x 1, y 1 ) Boundary pointof R Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 5 / 36
6 Bounded and Unbounded Regions in the Plane Definition A region in the plane is bounded if it lies inside a disk of fixed radius. A region is unbounded if it is not bounded. Example: bounded sets: line segments, triangles, interiors of triangles, rectangles, circles, and disks bounded sets: lines, coordinate axes, the graphs of functions defined on infinite intervals, quadrants, half-planes, and the plane itself. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 6 / 36
7 Graphs, Level Curves, and Contours of Functions of Two Variables Definition:Level Curve, Graph, Surface The set of points in the plane where a function f (x, y) has a constant valuef (x, y) = c is called a level curve of f. The set of all points (x, y, f (x, y)) in space, for (x, y) in the domain of f, is called the graph of f. The graph of f is also called the surface z = f (x, y) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 7 / 36
8 Graphs, Level Curves, and Contours of Functions of Two Variables f (x, y) = x + y f (x, y) = x 2 + y x y x y 2 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 8 / 36
9 Graphs, Level Curves, and Contours of Functions of Two Variables f (x, y) = x 2 + y 2 f (x, y) = xe x2 y x y x y 2 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 9 / 36
10 Graphs, Level Curves, and Contours of Functions of Two Variables f (x, y) = y 2 y 4 x 2 f (x, y) = cos x cos ye x 2 +y x y 1 5 x 5 5 y 5 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 1 / 36
11 Definition: Limit of a Function of Two Variables We say that a function f (x, y) approaches the limit L as (x, y) approaches (x, y ), and write lim f (x, y) = L (x,y) (x,y ) if, for every number ε >, there exists a corresponding number δ > such that for all (x, y in the domain of f f (x, y) L < ε wheneever < (x x ) 2 + (y y ) 2 < δ Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 11 / 36
12 Properties of Limits of Functions of Two Variablesi The following rules hold if L, M, and k are real numbers and lim f (x, y) = L, lim (x,y) (x,y ) g(x, y) = M (x,y) (x,y ) lim (f (x, y) + g(x, y)) = L + M (x,y) (x,y ) lim (f (x, y) g(x, y)) = L M (x,y) (x,y ) lim kf (x, y) = kl (x,y) (x,y ) f (x,y) lim (x,y) (x,y ) g(x,y) = L M, ha M. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 12 / 36
13 Definition: Continuous Function of Two Variables A function f (x, y) is continuous at the point (x, y ) if 1 f is defined at (x, y ), 2 lim (x,y) (x,y ) f (x, y) exists 3 lim (x,y) (x,y ) f (x, y) = f (x, y ) A function is continuous if it is continuous at every point of its domain. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 13 / 36
14 Definition: Partial Derivative with Respect to x The partial derivative of f (x, y) with respect to x at the point (x, y ) is f f (x + h, y ) f (x, y ) x = lim (x,y ) h h provided the limit exists. The equivalent expressions for the partial derivative are: f x (x, y ) f x(x, y ) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 14 / 36
15 Definition: Partial Derivative with Respect to y The partial derivative of f (x, y) with respect to y at the point (x, y ) is f f (x, y + h) f (x, y ) y = lim (x,y ) h h provided the limit exists. The equivalent expressions for the partial derivative are:: f y (x, y ) f y (x, y ) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 15 / 36
16 Calculations f x f y differentiating f with respect to x in the usual way while treating y as a constant y differentiating f with respect to x in the usual way while treating y as a constant Examples: Find f x and f y f (x, y) = x 2 + y 3 f (x, y) = x 2 y 3 f (x, y) = x 3 sin(x + y) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 16 / 36
17 Differentiable Function A function z = f (x, y) is differentiable at (x, y ) if f x(x, y ) and f y (x ), y ) exist and z = f (x + x, y + y) f (x, y ) satisfies an equation of the form z = f x(x, y ) x + f y (x, y ) y + ε 1 x + ε 2 y in which each of ε 1, ε 2 as both x, y. We call f differentiable if it is differentiable at every point in its domain. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 17 / 36
18 Theorem: If the partial derivatives f x and f y of a function f (x, y) are continuous throughout an open region R, then f is differentiable at every point of R. Tétel: If a function f (x, y) is differentiable at (x, y ), then f is continuous at (x, y ). Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 18 / 36
19 Linearization, Linear Approximation The linearization of a function f at a point (x, y ) where f is differentiable L(x, y) = f (x, y ) + f x(x, y )(x x ) + f y (x, y )(y y ) The approximation f (x, y) L(x, y) is the standard linear approximation of f at ((x, y ). Find the linearization of f (x, y) = x 2 + y 3 at point ( 2, 1) f (x, y) = x 3 sin(x + y) at point ( π 2, π 2 ) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 19 / 36
20 Plane Tangent to a Surface The plane tangent to the surface z = f (x, y) of a differentiable function f at the point P (x, y, z ) = (x, y, f (x, y )) is z = z + f x(x, y )(x x ) + f y (x, y )(y y ) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 2 / 36
21 Total Differential If we move from (x, y ) to a point (x + dx, y + dy) nearby, the resulting change df = f x(x, y )dx + f y (x, y )dy in the linearization of f f is called the total differential of f. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 21 / 36
22 Estimating Absolut and Percentage Error Let function f (x, y) is differentiable at (x, y ). The absolute error: f df = f x(x, y )dx + f y (x, y )dy f x(x, y ) dx + f y (x, y ) dy Percentage Error: δf = f f f x(x, y ) f (x, y ) dx + f y (x, y ) f (x, y ) dy Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 22 / 36
23 Second-Order Partial Derivatives When we differentiate a function f (x, y) twice, we produce its second-order derivatives. These derivatives are usually denoted by 2 f x 2 vagy f xx; 2 f y x vagy f xy 2 f x y vagy f yx; 2 f y 2 vagy f yy Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 23 / 36
24 The defining equations are 2 f x 2 = ( ) f x x 2 f x y = ( ) f x y 2 f y x = ( ) f y x 2 f y 2 = ( ) f y y Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 24 / 36
25 Examples: Find all the second-order partial derivatives of the functions f (x, y) = x 2 y 3 f (x, y) = x 3 sin(x + y) f (x, y) = x 2 y 3 f (x, y) = (x 2 1)(y + 2) f (x, y) = x 2 + y 2 f (x, y) = (x 2 y 1)(y + 2) f (x, y) = x 3 sin(x + y) f (x, y) = x y f (x, y) = x2 y 1 y 3 f (x, y) = xe x2 y Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 25 / 36
26 Theorem: (Schwarz-Young) If f (x, y) and its partial derivatives f x, f y, f xy and f yx are defined throughout an open region containing a point (a, b) pontot, and are all continuous at (a, b), then f xy(a, b) = f yx(a, b). Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 26 / 36
27 The Chain Rule If w = f (x, y)has continuous partial derivatives f x and f y and if x = x(t), y = y(t) are differentiable functions of t then the composite w = f (x(t), y(t)) is a differ- entiable function of t and df dt = f x[x(t), y(t)]x (t) + f y [x(t), y(t)]y (t) or dw dt = f dx x dt + f dy y dt Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 27 / 36
28 A Formula for Implicit Differentiation Suppose that F (x, y) is differentiable and that the equation F (x, y) = defines y as a differentiable function of x. Then at any point where F y, dy dx = F x F y. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 28 / 36
29 A Formula for Implicit Differentiation Examples Find the value of dy dx at the given point. x 3 2y 2 + xy =, (1, 1) x 2 + xy + y 2 7 =, (1, 2) xe y + sin xy + y ln 2 =, (, ln 2) Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 29 / 36
30 Definition: Local Maximum, Local Minimum Let f (x, y) be defined on a region R containing the point (a, b). Then 1 f (a, b) is a local maximum value of f if f (a, b) f (x, y) for all domain points (x, y) in an open disk centered at (a, b). 2 f (a, b)) is a local minimum value of f if f (a, b) f (x, y) for all domain points (x, y) in an open disk centered at (a, b). Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 3 / 36
31 First Derivative Test for Local Extreme Values If f (x, y) has a local maximum or minimum value at an interior point (a, b) of its domain and if the first partial derivatives exist there, then f x(a, b) = and f y (a, b) =. Definition: An interior point of the domain of a function f (x, y) where both f x and f y are zero or where one or both of f x and f y do not exist is a critical point of f Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 31 / 36
32 Definition: Saddle point A differentiable function f (x, y) has a saddle point at a critical point (a, b) if in every open disk centered at (a, b) there are domain points (x, y) where f (x, y) < f (a, b) and domain points (x, y) where f (x, y) > f (a, b). The corresponding point (a, b, f (a, b)) on the surface f (x, y) > f (a, b) is called a saddle point of the surface. Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 32 / 36
33 lok. max lok. min Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 33 / 36
34 1 nyeregpont Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 34 / 36
35 Second Derivative Test for Local Extreme Values Suppose that f (x, y) and its first and second partial derivatives are continuous throughout a disk centered at (a, b) and that f x(a, b) = f y (a, b) = O. Then i. f has a local maximum at (a, b) if f xxf yy ( f xy) 2 > and f xx <. ii. f has a local minimum at (a, b) if f xxf yy ( f xy) 2 > and f xx >. iii. f has a saddle point at (a, b) if f xxf yy ( f xy) 2 <. iv. The test is inconclusive at (a, b) if f xxf yy ( f xy) 2 = at (a, b). In this case, we must find some other way to determine the behavior of f at (a, b). Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 35 / 36
36 The expression f xxf yy ( f xy) 2 is called the discriminant or Hessian of f. It is sometimes easier to remember it in determinant form, f xxf yy ( f xy ) 2 f = xx f xy f yx f yy Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 36 / 36
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
Daily WeBWorK, #1. This means the two planes normal vectors must be multiples of each other.
 Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES. 4. Function of several variables, their domain. 6. Limit of a function of several variables
 302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
Tangent Planes/Critical Points
 Tangent Planes/Critical Points Christopher Croke University of Pennsylvania Math 115 UPenn, Fall 2011 Problem: Find the tangent line to the curve of intersection of the surfaces xyz = 1 and x 2 + 2y 2
Tangent Planes/Critical Points Christopher Croke University of Pennsylvania Math 115 UPenn, Fall 2011 Problem: Find the tangent line to the curve of intersection of the surfaces xyz = 1 and x 2 + 2y 2
Math 213 Exam 2. Each question is followed by a space to write your answer. Please write your answer neatly in the space provided.
 Math 213 Exam 2 Name: Section: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used other than a onepage cheat
Math 213 Exam 2 Name: Section: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used other than a onepage cheat
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION
 LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers
 3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
The Divergence Theorem
 The Divergence Theorem MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2011 Green s Theorem Revisited Green s Theorem: M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = C R ( N x M ) da y y x Green
The Divergence Theorem MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2011 Green s Theorem Revisited Green s Theorem: M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = C R ( N x M ) da y y x Green
. Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 First Order Partial Derivatives;...
 Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order Partial Derivatives; Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order Partial Derivatives; 2 Application of Gradient; Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order
Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order Partial Derivatives; Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order Partial Derivatives; 2 Application of Gradient; Tutorial Class V 3-10/10/2012 1 First Order
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester Lecture 33 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
x 6 + λ 2 x 6 = for the curve y = 1 2 x3 gives f(1, 1 2 ) = λ actually has another solution besides λ = 1 2 = However, the equation λ
 Math 0 Prelim I Solutions Spring 010 1. Let f(x, y) = x3 y for (x, y) (0, 0). x 6 + y (4 pts) (a) Show that the cubic curves y = x 3 are level curves of the function f. Solution. Substituting y = x 3 in
Math 0 Prelim I Solutions Spring 010 1. Let f(x, y) = x3 y for (x, y) (0, 0). x 6 + y (4 pts) (a) Show that the cubic curves y = x 3 are level curves of the function f. Solution. Substituting y = x 3 in
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 ontents 1 Vector Functions and pace urves 2 1.1 Limits, Derivatives, and Integrals of Vector Functions...................... 2 1.2 Arc Length and urvature..................................... 2 1.3 Motion
ontents 1 Vector Functions and pace urves 2 1.1 Limits, Derivatives, and Integrals of Vector Functions...................... 2 1.2 Arc Length and urvature..................................... 2 1.3 Motion
MATH 104 Sample problems for first exam - Fall MATH 104 First Midterm Exam - Fall (d) 256 3
 MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane
 Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Chain rule Theorem-A: Let x : R R n be differentiable at t 0 and f : R n R be differentiable
Lecture 6: Chain rule, Mean Value Theorem, Tangent Plane Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Chain rule Theorem-A: Let x : R R n be differentiable at t 0 and f : R n R be differentiable
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a
 Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a Sphereoid Parabaloid Hyperboloid Whateveroid Volumes Calculating 3-D Space an Object Occupies Take a cross-sectional slice. Compute the area of the slice. Multiply
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a Sphereoid Parabaloid Hyperboloid Whateveroid Volumes Calculating 3-D Space an Object Occupies Take a cross-sectional slice. Compute the area of the slice. Multiply
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
= w. w u. u ; u + w. x x. z z. y y. v + w. . Remark. The formula stated above is very important in the theory of. surface integral.
 1 Chain rules 2 Directional derivative 3 Gradient Vector Field 4 Most Rapid Increase 5 Implicit Function Theorem, Implicit Differentiation 6 Lagrange Multiplier 7 Second Derivative Test Theorem Suppose
1 Chain rules 2 Directional derivative 3 Gradient Vector Field 4 Most Rapid Increase 5 Implicit Function Theorem, Implicit Differentiation 6 Lagrange Multiplier 7 Second Derivative Test Theorem Suppose
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation
 Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Name: Class: Date: 1. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint.
 . Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
(1) Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14)z = a + 2
 (1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
(1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
Minima, Maxima, Saddle points
 Minima, Maxima, Saddle points Levent Kandiller Industrial Engineering Department Çankaya University, Turkey Minima, Maxima, Saddle points p./9 Scalar Functions Let us remember the properties for maxima,
Minima, Maxima, Saddle points Levent Kandiller Industrial Engineering Department Çankaya University, Turkey Minima, Maxima, Saddle points p./9 Scalar Functions Let us remember the properties for maxima,
13.1. Functions of Several Variables. Introduction to Functions of Several Variables. Functions of Several Variables. Objectives. Example 1 Solution
 13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
(1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives.
 Section 11.3 Partial Derivatives (1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives. MATH 127 (Section 11.3) Partial Derivatives The University of Kansas
Section 11.3 Partial Derivatives (1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives. MATH 127 (Section 11.3) Partial Derivatives The University of Kansas
Find the specific function values. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. f (x,y,z) = x y y 2 + z = (Simplify your answer.) ID: 14.1.
 . Find the specific function values. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. f (x,y,z) = x y y 2 + z 2 (a) f(2, 4,5) = (b) f 2,, 3 9 = (c) f 0,,0 2 (d) f(4,4,00) = = ID: 4..3 2. Given the function f(x,y)
. Find the specific function values. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. f (x,y,z) = x y y 2 + z 2 (a) f(2, 4,5) = (b) f 2,, 3 9 = (c) f 0,,0 2 (d) f(4,4,00) = = ID: 4..3 2. Given the function f(x,y)
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points.
 MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Hw 4 Due Feb 22. D(fg) x y z (
 Hw 4 Due Feb 22 2.2 Exercise 7,8,10,12,15,18,28,35,36,46 2.3 Exercise 3,11,39,40,47(b) 2.4 Exercise 6,7 Use both the direct method and product rule to calculate where f(x, y, z) = 3x, g(x, y, z) = ( 1
Hw 4 Due Feb 22 2.2 Exercise 7,8,10,12,15,18,28,35,36,46 2.3 Exercise 3,11,39,40,47(b) 2.4 Exercise 6,7 Use both the direct method and product rule to calculate where f(x, y, z) = 3x, g(x, y, z) = ( 1
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2
 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Lecture 25 February 28, 2007 Recall Fact Recall Fact If f is a dierentiable function of x and y, then f has a directional derivative in the direction
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Lecture 25 February 28, 2007 Recall Fact Recall Fact If f is a dierentiable function of x and y, then f has a directional derivative in the direction
Direction Fields; Euler s Method
 Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives. Partial Derivatives
 In general, if f is a function of two variables x and y, suppose we let only x vary while keeping y fixed, say y = b, where b is a constant. By the definition of a derivative, we have Then we are really
In general, if f is a function of two variables x and y, suppose we let only x vary while keeping y fixed, say y = b, where b is a constant. By the definition of a derivative, we have Then we are really
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule
 MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
Final Exam - Review. Cumulative Final Review covers sections and Chapter 12
 Final Exam - eview Cumulative Final eview covers sections 11.4-11.8 and Chapter 12 The following is a list of important concepts from each section that will be tested on the Final Exam, but were not covered
Final Exam - eview Cumulative Final eview covers sections 11.4-11.8 and Chapter 12 The following is a list of important concepts from each section that will be tested on the Final Exam, but were not covered
MA FINAL EXAM Green April 30, 2018 EXAM POLICIES
 MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
MA 6100 FINAL EXAM Green April 0, 018 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN! Write the following in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes (and blacken
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
. 1. Chain rules. Directional derivative. Gradient Vector Field. Most Rapid Increase. Implicit Function Theorem, Implicit Differentiation
 1 Chain rules 2 Directional derivative 3 Gradient Vector Field 4 Most Rapid Increase 5 Implicit Function Theorem, Implicit Differentiation 6 Lagrange Multiplier 7 Second Derivative Test Theorem Suppose
1 Chain rules 2 Directional derivative 3 Gradient Vector Field 4 Most Rapid Increase 5 Implicit Function Theorem, Implicit Differentiation 6 Lagrange Multiplier 7 Second Derivative Test Theorem Suppose
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Gradient and Directional Derivatives
 Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Math 241, Final Exam. 12/11/12.
 Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
3. The domain of a function of 2 or 3 variables is a set of pts in the plane or space respectively.
 Math 2204 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives Sec. 14.1: Functions of Several Variables I. Functions and Variables A. Def n : Suppose D is a set of n-tuples of real numbers (x 1, x 2,
Math 2204 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives Sec. 14.1: Functions of Several Variables I. Functions and Variables A. Def n : Suppose D is a set of n-tuples of real numbers (x 1, x 2,
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus 3, Prof. Montero 3450: , Fall 2008
 A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus, Prof. Montero 45:-4, Fall 8 Maxima and minima Let us recall first, that for a function f(x, y), the gradient is the vector ( f)(x, y) = ( ) f f (x, y); (x, y).
A small review, Second Midterm, Calculus, Prof. Montero 45:-4, Fall 8 Maxima and minima Let us recall first, that for a function f(x, y), the gradient is the vector ( f)(x, y) = ( ) f f (x, y); (x, y).
Introduction to PDEs: Notation, Terminology and Key Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction to PDEs: Notation, Terminology and Key Concepts 1.1 Review 1.1.1 Goal The purpose of this section is to briefly review notation as well as basic concepts from calculus. We will also
Chapter 1 Introduction to PDEs: Notation, Terminology and Key Concepts 1.1 Review 1.1.1 Goal The purpose of this section is to briefly review notation as well as basic concepts from calculus. We will also
NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X
 Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
(Section 6.2: Volumes of Solids of Revolution: Disk / Washer Methods)
 (Section 6.: Volumes of Solids of Revolution: Disk / Washer Methods) 6.. PART E: DISK METHOD vs. WASHER METHOD When using the Disk or Washer Method, we need to use toothpicks that are perpendicular to
(Section 6.: Volumes of Solids of Revolution: Disk / Washer Methods) 6.. PART E: DISK METHOD vs. WASHER METHOD When using the Disk or Washer Method, we need to use toothpicks that are perpendicular to
Solution of final examination
 of final examination Math 20, pring 201 December 9, 201 Problem 1 Let v(t) (2t e t ) i j + π cos(πt) k be the velocity of a particle with initial position r(0) ( 1, 0, 2). Find the accelaration at the
of final examination Math 20, pring 201 December 9, 201 Problem 1 Let v(t) (2t e t ) i j + π cos(πt) k be the velocity of a particle with initial position r(0) ( 1, 0, 2). Find the accelaration at the
Calculus 234. Problems. May 15, 2003
 alculus 234 Problems May 15, 23 A book reference marked [TF] indicates this semester s official text; a book reference marked [VPR] indicates the official text for next semester. These are [TF] Thomas
alculus 234 Problems May 15, 23 A book reference marked [TF] indicates this semester s official text; a book reference marked [VPR] indicates the official text for next semester. These are [TF] Thomas
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus
 Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function
 Spring 2019 MA 114 Worksheet 17 Thursday, 7 March 2019 MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function 1. Write down the equation for the average value of an integrable function f(x) on [a, b]. 2. Find
Spring 2019 MA 114 Worksheet 17 Thursday, 7 March 2019 MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function 1. Write down the equation for the average value of an integrable function f(x) on [a, b]. 2. Find
UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES (SOLUTIONS ) CHAPTER 3: Partial derivatives and differentiation
 UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES SOLUTIONS ) 3-1. Find, for the following functions: a) fx, y) x cos x sin y. b) fx, y) e xy. c) fx, y) x + y ) lnx + y ). CHAPTER 3: Partial derivatives
UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES SOLUTIONS ) 3-1. Find, for the following functions: a) fx, y) x cos x sin y. b) fx, y) e xy. c) fx, y) x + y ) lnx + y ). CHAPTER 3: Partial derivatives
True/False. MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY
 MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions
 C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
(c) 0 (d) (a) 27 (b) (e) x 2 3x2
 1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus
 MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals. Textbook: Section 16.2
 Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) Today, We Will: Level Curves. Notes. Notes. Notes.
 Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) 11 February 2015 Today, We Will: Wrap-up our discussion of level curves and contour maps. Define partial derivatives of a function
Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) 11 February 2015 Today, We Will: Wrap-up our discussion of level curves and contour maps. Define partial derivatives of a function
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
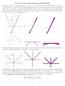
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Be familiar with the definition of a derivative as the slope of a tangent line (the
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Be familiar with the definition of a derivative as the slope of a tangent line (the
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints
 Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
minutes/question 26 minutes
 st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers. Lagrange Multipliers
 In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
In this section we present Lagrange s method for maximizing or minimizing a general function f(x, y, z) subject to a constraint (or side condition) of the form g(x, y, z) = k. Figure 1 shows this curve
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Week 5: Geometry and Applications
 Week 5: Geometry and Applications Introduction Now that we have some tools from differentiation, we can study geometry, motion, and few other issues associated with functions of several variables. Much
Week 5: Geometry and Applications Introduction Now that we have some tools from differentiation, we can study geometry, motion, and few other issues associated with functions of several variables. Much
Exam 2 Preparation Math 2080 (Spring 2011) Exam 2: Thursday, May 12.
 Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Introduction to Functions of Several Variables
 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables Today 1 / 20 Introduction In this section, we extend the definition of
Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables Today 1 / 20 Introduction In this section, we extend the definition of
Surfaces and Integral Curves
 MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
Differentiability and Tangent Planes October 2013
 Differentiability and Tangent Planes 14.4 04 October 2013 Differentiability in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f is differentiable at a f (a + h) f (a) lim exists and = f (a) h 0 h
Differentiability and Tangent Planes 14.4 04 October 2013 Differentiability in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f is differentiable at a f (a + h) f (a) lim exists and = f (a) h 0 h
The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y = 2, below by
 Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
V = 2πx(1 x) dx. x 2 dx. 3 x3 0
 Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
AP Calculus BC. Find a formula for the area. B. The cross sections are squares with bases in the xy -plane.
 AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
Polar (BC Only) They are necessary to find the derivative of a polar curve in x- and y-coordinates. The derivative
 Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
1. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) = 0 implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two:
 Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
Math 113 Exam 1 Practice
 Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials
 2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule
 Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2
 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Marius Ionescu October 26, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part October 2 26, 2012 1 / 12 Recall Fact Marius
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part 2 Marius Ionescu October 26, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Part October 2 26, 2012 1 / 12 Recall Fact Marius
Dr. Allen Back. Aug. 27, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Aug. 27, 2014 Math 2220 Preliminaries (2+ classes) Differentiation (12 classes) Multiple Integrals (9 classes) Vector Integrals (15 classes) Math 2220 Preliminaries (2+ classes) Differentiation
Dr. Allen Back Aug. 27, 2014 Math 2220 Preliminaries (2+ classes) Differentiation (12 classes) Multiple Integrals (9 classes) Vector Integrals (15 classes) Math 2220 Preliminaries (2+ classes) Differentiation
Total. Math 2130 Practice Final (Spring 2017) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8)
 Math 130 Practice Final (Spring 017) Before the exam: Do not write anything on this page. Do not open the exam. Turn off your cell phone. Make sure your books, notes, and electronics are not visible during
Math 130 Practice Final (Spring 017) Before the exam: Do not write anything on this page. Do not open the exam. Turn off your cell phone. Make sure your books, notes, and electronics are not visible during
AP * Calculus Review. Area and Volume
 AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
7/28/2011 SECOND HOURLY PRACTICE V Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011
 7/28/2011 SECOND HOURLY PRACTICE V Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
7/28/2011 SECOND HOURLY PRACTICE V Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
Solution 2. ((3)(1) (2)(1), (4 3), (4)(2) (3)(3)) = (1, 1, 1) D u (f) = (6x + 2yz, 2y + 2xz, 2xy) (0,1,1) = = 4 14
 Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables
 Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
Lagrange multipliers 14.8
 Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals v v Sections: 8.1 Integral as Net Change 8.2 Areas in the Plane v 8.3 Volumes HW Sets Set A (Section 8.1) Pages
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals v v Sections: 8.1 Integral as Net Change 8.2 Areas in the Plane v 8.3 Volumes HW Sets Set A (Section 8.1) Pages
