11.5 Cylinders and cylindrical coordinates
|
|
|
- Ross Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11.5 Cylinders and cylindrical coordinates Definition [Cylinder and generating curve] A cylinder is a surface composed of the lines that pass through a given plane curve parallel to a given line in space. The curve is a generating curve for the cylinder. Definition [Cylindrical coordinates] Cylindrical coordinates represent a point in P space by ordered triples ( r, θ, z) in which r and θ are polar coordinates for the vertical projection of P on the xy-plane, and z is the rectangular vertical coordinate. Equations relating rectangular and cylindrical coordinates x=r cos( θ ), y=r sin( θ ), z=z r 2 = x 2 + y 2 tan( θ) = y x Plotting in other coordinate systems Worksheet by Mike May, S.J.- maymk@slu.edu > restart: It is worthwhile to look at how we can plot with Maple in other coordinate systems. The trick is that maple has a coords option in its plot commands. Functions of one variable Cartesian Coordinates We start with the standard cartesian coordinate system. Maple assumes that we will write y as a function of x. We can also plot parametrically using [x(t), y(t), t=trange]. > plot((x-1)^2-2, x=-1..3); plot([t, (t-1)^2-2,t=-1..3]);
2 Polar Coordinates If we want to use polar coordinates we should note that Maple expects r to be a function of theta. If we are plotting parametrically Maple expects [r(t), theta(t), t=trange].
3 > plot(1+2*cos(theta), theta=0..2*pi, coords=polar); plot([1+2*cos(t), t, t=0..2*pi], coords=polar); Mixed Coordinates One of the useful things we can do is to put plots done with different coordinate
4 systems together with the display command. Note that we want to end the commands of the named plots with a colon rather than a semicolon. (Otherwise we get an ugly list of the postscript commands that make up the plot structures.) To use display we first need to load it with the plots command. > with(plots); plota:= plot((x-1)^2-2, x=-1..3, color=red): plotb:= plot(1+2*cos(theta), theta=0..2*pi, coords=polar, color=blue): display({plota, plotb}); Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined [ animate, animate3d, animatecurve, changecoords, complexplot, complexplot3d, conformal, contourplot, contourplot3d, coordplot, coordplot3d, cylinderplot, densityplot, display, display3d, fieldplot, fieldplot3d, gradplot, gradplot3d, implicitplot, implicitplot3d, inequal, listcontplot, listcontplot3d, listdensityplot, listplot, listplot3d, loglogplot, logplot, matrixplot, odeplot, pareto, pointplot, pointplot3d, polarplot, polygonplot, polygonplot3d, polyhedra_supported, polyhedraplot, replot, rootlocus, semilogplot, setoptions, setoptions3d, spacecurve, sparsematrixplot, sphereplot, surfdata, textplot, textplot3d, tubeplot] Exercises: 1) Plot the graph of a 5 petal rose of radius 2 with a petal cut by the positive x-axis.
5 (You should remember the formula for this from pre-calculus. > 2) Plot the cartioid defined by r=1-sin(theta) on the same axes as the graph of y=2+sin(pi*x) to create a picture of a heart with a hat. > Functions of two variables Cartesian Coordinates We start surfaces that are the plots of functions in two variables with cartesian coordiantes. In a parallel fashion, Maple assumes that we will write z as a function of x and y. If we are going to parameterize the surface, it is assumed to be in the form ([x(u,v), y(u, v), z(u, v)], u=urange, v=vrange). > plot3d(sin(x^2+y^2), x=-3..3, y=-3..3, style=patch, axes=boxed, grid=[60,60]); plot3d([u, v, sin(u^2+v^2)], u=-3..3, v=-3..3, style=patch, axes=boxed, grid=[60,60]);
6 Cylindrical Coordinates The next coordinate system we want to look at is the cylindrical coordinates. Maple assumes that we will express r as a function of theta and z. (in class we typically express z as a function of r and theta.) This means that we have to use the parametric form if we want to do the sombrero surface above. (The graph above has many r values corresponding to a single value of theta and z, so r is not a function of theta and z.) Interestingly, the parametric form arranges the variables in the more familiar (r, theta, z) pattern so the form is ([r(u,v), theta(u,v), z(u,v)], u=urange, v=vrange). > plot3d([r, theta, sin(r^2)], r=0..4, theta=0..2*pi, coords=cylindrical, style=patch, axes=boxed, grid=[100,100]);
7 The cylindrical form is useful for plotting surfaces obtained by rotating curves around the z axis. Cylinders are the easiest example of this. They are obtained by rotating lines of the form y=c about the x-axis. > plot3d({1, 3+sin(z)}, theta=0..2*pi, z=-4..4, style=patch, axes=boxed, coords=cylindrical, grid=[60,60]);
8 > Spherical coordiantes Maple assumes that spherical coordinates will express rho as a function of theta and phi. The easiest surface to graph is, as the name of the system suggests, a sphere centered at the origin. > plot3d(2, theta=0..2*pi, phi=0..pi, coords=spherical, style=patch, axes=boxed, grid=[60,60],scaling=constrained);
9 If we are doing a more complicated surface we may want to use the parametric form. In that Case Maple asumes that the form will be ([rho(u,v), theta(u,v), phi(u,v)], u=urange, v=vrange). > plot3d(4+5*cos(2*phi)+3*sin(3*theta), theta=0..2*pi, phi=0..pi, coords=spherical, style=patch, axes=boxed, grid=[60,60]); plot3d([4+5*cos(2*phi)+3*sin(3*theta), theta, phi], theta=0..2*pi, phi=0..pi, coords=spherical, style=patchnogrid, axes=boxed, grid=[40,40], lightmodel=light1);
10 Mixed coordinates Once again, a nice trick is to use display3d to put together surfaces that are easy to describe in different coordinate systems. The code below putes togeter the plane z=x+y (cartesian coordinates), the cylinder r=2 (cylindrical coordinates), and the sphere rho = 3 (spherical coordinates). > plotplane := plot3d(x+y, x=-4..4, y=-4..4, style=patch, color=yellow, axes=boxed, grid=[60,60]): plotcyl := plot3d(2, theta=0..2*pi, z=-8..8, style=patch, color=pink, axes=boxed,
11 coords=cylindrical, grid=[60,60]): plotsph := plot3d(3, theta=0..2*pi, phi=0..pi, style=patch, color=green, axes=boxed, coords=spherical, grid=[60,60]): display3d({plotplane, plotcyl, plotsph}); Exercises: 3) Plot a sphere of radius 3 centered at the origin in each of the three coordinate systems we have discussed. Which is easiest? > 4) Plot a cone with point at the origin, height 4 and radius 3 using your favorite coordinate system. >
Solids of Revolution
 > Solids of Revolution > restart; > with(plots); Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined [ animate, animate3d, animatecurve, changecoords, complexplot, complexplot3d, conformal, contourplot,
> Solids of Revolution > restart; > with(plots); Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined [ animate, animate3d, animatecurve, changecoords, complexplot, complexplot3d, conformal, contourplot,
Basic Maple Tutorial
 Basic Maple Tutorial The purpose of this document is to introduce some basic Maple commands, syntax, and programming concepts for Maple V Release 9.5. 1 Some Basic Maple Commands After you log on to your
Basic Maple Tutorial The purpose of this document is to introduce some basic Maple commands, syntax, and programming concepts for Maple V Release 9.5. 1 Some Basic Maple Commands After you log on to your
Convergence of Algorithms
 Convergence of Algorithms Unstable Exponential Growth The recursive equation has the solution p n = 0 p n K 3 p n = c 3 K p n K 2 for n = 2, 3,... n C c 2 3 n for any constants c. Let's compute p 2 thru
Convergence of Algorithms Unstable Exponential Growth The recursive equation has the solution p n = 0 p n K 3 p n = c 3 K p n K 2 for n = 2, 3,... n C c 2 3 n for any constants c. Let's compute p 2 thru
More on Basic Maple Commands
 More on Basic Maple Commands A. J. Meir Copyright (C) A. J. Meir. All rights reserved. This worksheet is for educational use only. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted for profit
More on Basic Maple Commands A. J. Meir Copyright (C) A. J. Meir. All rights reserved. This worksheet is for educational use only. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted for profit
2. Introduction to Maple
 2. Introduction to Maple What is Maple? Maple is a computer algebra system (CAS). What is a CAS? As the name suggests, it is a computer software program that manipulates sophisticated algebraic symbols
2. Introduction to Maple What is Maple? Maple is a computer algebra system (CAS). What is a CAS? As the name suggests, it is a computer software program that manipulates sophisticated algebraic symbols
Maple: Plotting graphs
 Maple: Plotting graphs System Maple provides many possibilities for graphical representation of data and mathematical relations, using different modifications of function plots for plotting graphs. Among
Maple: Plotting graphs System Maple provides many possibilities for graphical representation of data and mathematical relations, using different modifications of function plots for plotting graphs. Among
A Quick Introduction to Maple 11
 A Quick Introduction to Maple Introduction Maple is a tool for doing nearly anything you think of as computational in mathematics, as well as many things you may be surprised to find a machine doing. Examples
A Quick Introduction to Maple Introduction Maple is a tool for doing nearly anything you think of as computational in mathematics, as well as many things you may be surprised to find a machine doing. Examples
Maple Manual for Fundamentals of Differential Equations, 8e, and Fundamentals of Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 6e.
 Maple Manual for Fundamentals of Differential Equations, 8e, and Fundamentals of Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 6e.. Introduction The study of mathematics can be greatly enhanced with
Maple Manual for Fundamentals of Differential Equations, 8e, and Fundamentals of Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 6e.. Introduction The study of mathematics can be greatly enhanced with
MATH 4503/6503 Worksheet 1: An introduction to Maple
 > restart; MATH 4503/6503 Worksheet : An introduction to Maple Sanjeev S. Seahra revised: February 2, 204 This worksheet is meant to serve as a brief introduction to the Maple symbolic computation package.
> restart; MATH 4503/6503 Worksheet : An introduction to Maple Sanjeev S. Seahra revised: February 2, 204 This worksheet is meant to serve as a brief introduction to the Maple symbolic computation package.
An Introduction to MAPLE
 > restart; An Introduction to MAPLE Sanjeev S. Seahra These notes are meant to serve as a brief introduction to the MAPLE symbolic computation package. You might ask yourself: how can MAPLE improve my
> restart; An Introduction to MAPLE Sanjeev S. Seahra These notes are meant to serve as a brief introduction to the MAPLE symbolic computation package. You might ask yourself: how can MAPLE improve my
Visual Problem Solving with Maple
 Visual Problem Solving with Maple by Paul Eakin, paul@ms.uky.edu and Carl Eberhart, carl@ms.uky.edu Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky First edition June 1997 Second Edition February 2009
Visual Problem Solving with Maple by Paul Eakin, paul@ms.uky.edu and Carl Eberhart, carl@ms.uky.edu Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky First edition June 1997 Second Edition February 2009
An Introduction to MAPLE
 > restart; An Introduction to MAPLE Sanjeev S. Seahra These notes are meant to serve as a brief introduction to the MAPLE symbolic computation package. You might ask yourself: how can MAPLE improve my
> restart; An Introduction to MAPLE Sanjeev S. Seahra These notes are meant to serve as a brief introduction to the MAPLE symbolic computation package. You might ask yourself: how can MAPLE improve my
General Information. Variables. Description of expressions: ! """ "" " $ ** * + -. / < <= <> =
 General Information expressions index of descriptions for Maple expressions expression sequences expression sequences functions index of Maple functions statements index of descriptions for Maple statements
General Information expressions index of descriptions for Maple expressions expression sequences expression sequences functions index of Maple functions statements index of descriptions for Maple statements
Practice with Parameterizing Curves and Surfaces. (Part 1)
 M:8 Spring 7 J. Simon Practice with Parameterizing Curves and Surfaces (Part ) A "parameter" is a number used to measure something. In particular, if we want to describe and analyzie some curve or surface
M:8 Spring 7 J. Simon Practice with Parameterizing Curves and Surfaces (Part ) A "parameter" is a number used to measure something. In particular, if we want to describe and analyzie some curve or surface
13.6 Directional derivatives,
 13.5 The chain rule Theorem [Chain Rule for Functions of Two Variables] If w = f ( x, y ) is differentiable and x and y are differentiable functions of t, then w is a differentiable function of t and dw
13.5 The chain rule Theorem [Chain Rule for Functions of Two Variables] If w = f ( x, y ) is differentiable and x and y are differentiable functions of t, then w is a differentiable function of t and dw
Lagrange Multipliers
 Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Big Ideas. What We Are Doing Today... Notes. Notes. Notes
 Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
Calculus III. 1 Getting started - the basics
 Calculus III Spring 2011 Introduction to Maple The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar with some of the tools the Maple software package offers for visualizing curves and surfaces in
Calculus III Spring 2011 Introduction to Maple The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar with some of the tools the Maple software package offers for visualizing curves and surfaces in
The Calcplot Package for Maple V
 The Calcplot Package for Maple V Timothy A. Murdoch Department of Mathematics Washington and Lee University Lexington, Virginia 24450 E-mail: murdoch@wlu.edu August 10, 2000 Introduction The contents of
The Calcplot Package for Maple V Timothy A. Murdoch Department of Mathematics Washington and Lee University Lexington, Virginia 24450 E-mail: murdoch@wlu.edu August 10, 2000 Introduction The contents of
Math 382: Scientific Computing 1. Intro to Maple
 Math 382: Scientific Computing 1 Intro to Maple Preliminaries Start Maple from the Start button -> Programs -> Math -> Maple 11.0 -> Maple 11. Go to the Tools menu and select Options. A dialog window will
Math 382: Scientific Computing 1 Intro to Maple Preliminaries Start Maple from the Start button -> Programs -> Math -> Maple 11.0 -> Maple 11. Go to the Tools menu and select Options. A dialog window will
Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Cylindrical Volume Element d V
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Maple for Math Majors. 5. Graphs of functions and equations
 Maple for Math Majors Roger Kraft Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Purdue University Calumet roger@purduecal.edu 5.1. Introduction 5. Graphs of functions and equations We define
Maple for Math Majors Roger Kraft Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Purdue University Calumet roger@purduecal.edu 5.1. Introduction 5. Graphs of functions and equations We define
FIND RECTANGULAR COORDINATES FROM POLAR COORDINATES CALCULATOR
 29 June, 2018 FIND RECTANGULAR COORDINATES FROM POLAR COORDINATES CALCULATOR Document Filetype: PDF 464.26 KB 0 FIND RECTANGULAR COORDINATES FROM POLAR COORDINATES CALCULATOR Rectangular to Polar Calculator
29 June, 2018 FIND RECTANGULAR COORDINATES FROM POLAR COORDINATES CALCULATOR Document Filetype: PDF 464.26 KB 0 FIND RECTANGULAR COORDINATES FROM POLAR COORDINATES CALCULATOR Rectangular to Polar Calculator
but both the "what" and the "how" can get quite complicated.
 plot3d Maple's plot3d command is used for drawing graphs of surfaces in three-dimensional space. The syntax and usage of the command is very similar to the plot command (which plots curves in the two-dimensional
plot3d Maple's plot3d command is used for drawing graphs of surfaces in three-dimensional space. The syntax and usage of the command is very similar to the plot command (which plots curves in the two-dimensional
Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates Math 251, Fall 2017 Juergen Gerlach Radford University Parametric Curves We will investigate several aspects of parametric curves in the plane. The curve given by
Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates Math 251, Fall 2017 Juergen Gerlach Radford University Parametric Curves We will investigate several aspects of parametric curves in the plane. The curve given by
Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates Math 251, Fall 2017 Juergen Gerlach Radford University Parametric Curves We will investigate several aspects of parametric curves in the plane. The curve given by
Parametric Curves and Polar Coordinates Math 251, Fall 2017 Juergen Gerlach Radford University Parametric Curves We will investigate several aspects of parametric curves in the plane. The curve given by
14 Vector Calculus Parametric Equations of Curves
 8 14 Vector Calculus 14.1 Parametric Equations of Curves In this section we will see how Maple V can be used to plot interesting curves using parametric representation. First of all consider the circle
8 14 Vector Calculus 14.1 Parametric Equations of Curves In this section we will see how Maple V can be used to plot interesting curves using parametric representation. First of all consider the circle
Math Exam III Review
 Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus
 Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Spherical Coordinates (ρ, φ, θ)
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
E-BOOK // CONVERT TO RECTANGULAR COORDINATES DOCUMENT
 19 February, 2018 E-BOOK // CONVERT TO RECTANGULAR COORDINATES DOCUMENT Document Filetype: PDF 533.05 KB 0 E-BOOK // CONVERT TO RECTANGULAR COORDINATES DOCUMENT For more help a students can connect to
19 February, 2018 E-BOOK // CONVERT TO RECTANGULAR COORDINATES DOCUMENT Document Filetype: PDF 533.05 KB 0 E-BOOK // CONVERT TO RECTANGULAR COORDINATES DOCUMENT For more help a students can connect to
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
16.6. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Vector Calculus. Parametric Surfaces and Their Areas
 16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 10.1 Parametric Equations
 MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 27 / 45
 : Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
Maple for Math Majors. 6. How Maple draws graphs
 Maple for Math Majors Roger Kraft Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Purdue University Calumet roger@calumet.purdue.edu 6.1. Introduction 6. How Maple draws graphs By now you should
Maple for Math Majors Roger Kraft Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Purdue University Calumet roger@calumet.purdue.edu 6.1. Introduction 6. How Maple draws graphs By now you should
Goals: Course Unit: Describing Moving Objects Different Ways of Representing Functions Vector-valued Functions, or Parametric Curves
 Block #1: Vector-Valued Functions Goals: Course Unit: Describing Moving Objects Different Ways of Representing Functions Vector-valued Functions, or Parametric Curves 1 The Calculus of Moving Objects Problem.
Block #1: Vector-Valued Functions Goals: Course Unit: Describing Moving Objects Different Ways of Representing Functions Vector-valued Functions, or Parametric Curves 1 The Calculus of Moving Objects Problem.
MATH203 Calculus. Dr. Bandar Al-Mohsin. School of Mathematics, KSU
 School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Introduction to Mathematica and Graphing in 3-Space
 1 Mathematica is a powerful tool that can be used to carry out computations and construct graphs and images to help deepen our understanding of mathematical concepts. This document will serve as a living
1 Mathematica is a powerful tool that can be used to carry out computations and construct graphs and images to help deepen our understanding of mathematical concepts. This document will serve as a living
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations
 Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area
 Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
Chapter 15 Notes, Stewart 7e
 Contents 15.2 Iterated Integrals..................................... 2 15.3 Double Integrals over General Regions......................... 5 15.4 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates..........................
Contents 15.2 Iterated Integrals..................................... 2 15.3 Double Integrals over General Regions......................... 5 15.4 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates..........................
Applications of Triple Integrals
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
5. y 2 + z 2 + 4z = 0 correct. 6. z 2 + x 2 + 2x = a b = 4 π
 M408D (54690/95/00), Midterm #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions (20 points) See last two pages. Question #1 (25 points) Dene the vector-valued function r(t) = he t ; 2; 3e t i: a) At what point P (x
M408D (54690/95/00), Midterm #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions (20 points) See last two pages. Question #1 (25 points) Dene the vector-valued function r(t) = he t ; 2; 3e t i: a) At what point P (x
Outcomes List for Math Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring
 Outcomes List for Math 200-200935 Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring 2009-2010 The purpose of the Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and
Outcomes List for Math 200-200935 Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring 2009-2010 The purpose of the Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and
Visualizing Regions of Integration in 2-D Cartesian Coordinates
 Classroom Tips and Techniques: Visualizing Regions of Integration Robert J. Lopez Emeritus Professor of Mathematics and Maple Fellow Maplesoft Introduction Five of the new task templates in Maple 14 are
Classroom Tips and Techniques: Visualizing Regions of Integration Robert J. Lopez Emeritus Professor of Mathematics and Maple Fellow Maplesoft Introduction Five of the new task templates in Maple 14 are
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 8 Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 8.5 Polar Equations and Graphs Polar Coordinate System Graphs of Polar Equations Conversion
8 Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 8.5 Polar Equations and Graphs Polar Coordinate System Graphs of Polar Equations Conversion
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Mathematics 205 HWK 21 Solutions Section 16.5 p766
 Mathematics 5 HK 1 Solutions Section 16.5 p766 Problem 5, 16.5, p766. For the region shown (a rectangular slab of dimensions 1 5; see the text), choose coordinates and set up a triple integral, including
Mathematics 5 HK 1 Solutions Section 16.5 p766 Problem 5, 16.5, p766. For the region shown (a rectangular slab of dimensions 1 5; see the text), choose coordinates and set up a triple integral, including
Curvilinear Coordinates
 Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Visualizing Linear Transformations in R 3
 Visualizing Linear Transformations in R 3 Worksheet by Michael K. May, S. J., revised by Russell Blyth restart: with(linearalgebra): with(plots): with(plottools): Warning, the name changecoords has been
Visualizing Linear Transformations in R 3 Worksheet by Michael K. May, S. J., revised by Russell Blyth restart: with(linearalgebra): with(plots): with(plottools): Warning, the name changecoords has been
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Chapter 2 Vectors and Graphics
 Chapter 2 Vectors and Graphics We start this chapter by explaining how to use vectors in MATLAB, with an emphasis on practical operations on vectors in the plane and in space. Remember that n-dimensional
Chapter 2 Vectors and Graphics We start this chapter by explaining how to use vectors in MATLAB, with an emphasis on practical operations on vectors in the plane and in space. Remember that n-dimensional
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 28 / 46
 Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems
 Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems You can skip this boot camp if you can answer the following question: Staying on a sphere of radius R, what is the shortest distance between the point (0, 0, R) on the
Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems You can skip this boot camp if you can answer the following question: Staying on a sphere of radius R, what is the shortest distance between the point (0, 0, R) on the
ENGI Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01
 ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate
 1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Lab 2B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 2374 University of Minnesota Questions to:
 Lab_B.nb Lab B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 37 University of Minnesota http://www.math.umn.edu/math37 Questions to: rogness@math.umn.edu Introduction As in last week s lab, there is no calculus in this
Lab_B.nb Lab B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 37 University of Minnesota http://www.math.umn.edu/math37 Questions to: rogness@math.umn.edu Introduction As in last week s lab, there is no calculus in this
YOUR MATLAB ASSIGNMENT 4
 YOUR MATLAB ASSIGNMENT 4 Contents GOAL: USING MATLAB TO SKETCH THE GRAPHS OF A PARAMETERIZED SURFACES IN SPACE USE THE FOLLOWING STEPS: HERE IS AN ACTUAL EXAMPLE OF A CLOSED SURFACE DRAWN PARAMETERICALLY
YOUR MATLAB ASSIGNMENT 4 Contents GOAL: USING MATLAB TO SKETCH THE GRAPHS OF A PARAMETERIZED SURFACES IN SPACE USE THE FOLLOWING STEPS: HERE IS AN ACTUAL EXAMPLE OF A CLOSED SURFACE DRAWN PARAMETERICALLY
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral
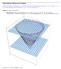 Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives
 Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives Introduction and Goals: The main goal of this lab is to help you visualize surfaces in three dimensions. We investigate how one can use Maple to evaluate
Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives Introduction and Goals: The main goal of this lab is to help you visualize surfaces in three dimensions. We investigate how one can use Maple to evaluate
Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Homework 1 - Solutions 3. 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 13
 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
Classes 7-8 (4 hours). Graphics in Matlab.
 Classes 7-8 (4 hours). Graphics in Matlab. Graphics objects are displayed in a special window that opens with the command figure. At the same time, multiple windows can be opened, each one assigned a number.
Classes 7-8 (4 hours). Graphics in Matlab. Graphics objects are displayed in a special window that opens with the command figure. At the same time, multiple windows can be opened, each one assigned a number.
PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES
 PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES Suppose we want to plot the path of a particle moving in a plane. This path looks like a curve, but we cannot plot it like we would plot any other type of curve in the
PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES Suppose we want to plot the path of a particle moving in a plane. This path looks like a curve, but we cannot plot it like we would plot any other type of curve in the
7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011
 7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
Exam 2 Preparation Math 2080 (Spring 2011) Exam 2: Thursday, May 12.
 Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates
 Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Math Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates
 Math 213 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 2, 218 Homework Re-read section 15.7 Work on section 15.7, problems 1-13 (odd), 17-21 (odd) from Stewart
Math 213 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 2, 218 Homework Re-read section 15.7 Work on section 15.7, problems 1-13 (odd), 17-21 (odd) from Stewart
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, and are graphed in Cartesian coordinates.
 Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
1 Programs for double integrals
 > restart; Double Integrals IMPORTANT: This worksheet depends on some programs we have written in Maple. You have to execute these first. Click on the + in the box below, then follow the directions you
> restart; Double Integrals IMPORTANT: This worksheet depends on some programs we have written in Maple. You have to execute these first. Click on the + in the box below, then follow the directions you
Put your initials on the top of every page, in case the pages become separated.
 Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.
![ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.](/thumbs/75/71742148.jpg) Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
The points (2, 2, 1) and (0, 1, 2) are graphed below in 3-space:
 Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems The plane is a two-dimensional coordinate system in the sense that any point in the plane can be uniquely described using two coordinates (usually x and y, but we have
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems The plane is a two-dimensional coordinate system in the sense that any point in the plane can be uniquely described using two coordinates (usually x and y, but we have
Workbook. MAT 397: Calculus III
 Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 2017 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 2017 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0.
 Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
Equation of tangent plane: for explicitly defined surfaces
 Equation of tangent plane: for explicitly defined surfaces Suppose that the surface z = f(x,y) has a non-vertical tangent plane at a point (a, b, f(a,b)). The plane y = b intersects the surface at a curve
Equation of tangent plane: for explicitly defined surfaces Suppose that the surface z = f(x,y) has a non-vertical tangent plane at a point (a, b, f(a,b)). The plane y = b intersects the surface at a curve
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 252 FALL 2008 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 125 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY % POSSIBLE
 QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
Pre-Calc Unit 14: Polar Assignment Sheet April 27 th to May 7 th 2015
 Pre-Calc Unit 14: Polar Assignment Sheet April 27 th to May 7 th 2015 Date Objective/ Topic Assignment Did it Monday Polar Discovery Activity pp. 4-5 April 27 th Tuesday April 28 th Converting between
Pre-Calc Unit 14: Polar Assignment Sheet April 27 th to May 7 th 2015 Date Objective/ Topic Assignment Did it Monday Polar Discovery Activity pp. 4-5 April 27 th Tuesday April 28 th Converting between
Curves: We always parameterize a curve with a single variable, for example r(t) =
 Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots
 Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots The Maple part of the assignment is to plot the graphs corresponding to the following problems. I ll note some syntax here to get you started see tutorials for more. Problem
Graded Assignment 2 Maple plots The Maple part of the assignment is to plot the graphs corresponding to the following problems. I ll note some syntax here to get you started see tutorials for more. Problem
Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form
 Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f 1, f 2,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i.
 HdPlot.nb? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5 3 4.5 Plot Sin
HdPlot.nb? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5 3 4.5 Plot Sin
Winter 2012 Math 255 Section 006. Problem Set 7
 Problem Set 7 1 a) Carry out the partials with respect to t and x, substitute and check b) Use separation of varibles, i.e. write as dx/x 2 = dt, integrate both sides and observe that the solution also
Problem Set 7 1 a) Carry out the partials with respect to t and x, substitute and check b) Use separation of varibles, i.e. write as dx/x 2 = dt, integrate both sides and observe that the solution also
Lecture 34: Curves defined by Parametric equations
 Curves defined by Parametric equations When the path of a particle moving in the plane is not the graph of a function, we cannot describe it using a formula that express y directly in terms of x, or x
Curves defined by Parametric equations When the path of a particle moving in the plane is not the graph of a function, we cannot describe it using a formula that express y directly in terms of x, or x
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). Surfaces will need two parameters.
 Math 55 - Vector Calculus II Notes 14.6 urface Integrals Let s develop some surface integrals. First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). urfaces
Math 55 - Vector Calculus II Notes 14.6 urface Integrals Let s develop some surface integrals. First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). urfaces
9.5 Polar Coordinates. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 9.5 Polar Coordinates Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Introduction Representation of graphs of equations as collections of points (x, y), where x and y represent the directed distances
9.5 Polar Coordinates Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Introduction Representation of graphs of equations as collections of points (x, y), where x and y represent the directed distances
Explore 3D Figures. Dr. Jing Wang (517) , Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA
 Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
