Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f 1, f 2,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i.
|
|
|
- Ada Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HdPlot.nb? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4, PlotRange, 3 4 Plot Sin x, Cos x, x,,
2 HdPlot.nb Plot Sin x, x,, yvalues Table Sin x, x,,,. ;? ListPlot ListPlot y, y, plots points corresponding to a list of values, assumed to correspond to x coordinates,,. ListPlot x, y, x, y, plots a list of points with specified x and y coordinates. ListPlot list, list, plots several lists of points. ListPlot yvalues ListPlot yvalues, PlotJoined True
3 HdPlot.nb 3? ParametricPlot ParametricPlot f x, f y, u, u min, u max generates a parametric plot of a curve with x and y coordinates f x and f y as a function of u. ParametricPlot f x, f y, g x, g y,, u, u min, u max plots several parametric curves. ParametricPlot f x, f y, u, u min, u max, v, v min, v max plots a parametric region. ParametricPlot f x, f y, g x, g y,, u, u min, u max, v, v min, v max plots several parametric regions. z t_ : 3 Exp I t ParametricPlot Re z t, Im z t, t,, Pi, AspectRatio 3 3
4 HdPlot.nb 4 ParametricPlot Cosh t, Sinh t, t,,, AspectRatio ParametricPlot t 3 Sin t, 3 t, t, 5 Pi, 5 Pi 4
5 HdPlot.nb ? ContourPlot ContourPlot f, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max generates a contour plot of f as a function of x and y. ContourPlot f g, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots contour lines for which f g. ContourPlot f g, f g,, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots several contour lines.
6 HdPlot.nb 6 ContourPlot x ^ y ^, x,,, y,, ContourPlot x ^ y ^, x,,, y,,
7 HdPlot.nb 7 ContourPlot x ^ y ^, x,,, y,,, ContourShading False, Contours ContourPlot x ^ y ^ 3, x,,, y,,
8 HdPlot.nb 8 ContourPlot x ^ y ^, x,,, y,,, Contours, PlotPoints 5? ContourPlot3D ContourPlot3D f, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max, z, z min, z max produces a three dimensional contour plot of f as a function of x, y and z. ContourPlot3D f g, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max, z, z min, z max plots the contour surface for which f g.
9 HdPlot.nb 9 ContourPlot3D z x ^ y ^, x,,, y,,, z,,, AxesLabel "x", "y", "z" x..5 z..5. y? Plot3D Plot3D f, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max generates a three dimensional plot of f as a function of x and y. Plot3D f, f,, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots several functions.
10 HdPlot.nb Plot3D Sin x y, x, 3, 3, y,.5, Plot3D x ^ y ^, x,,, y,,, AxesLabel "x", "y", "z" x 5 z y? ParametricPlot3D ParametricPlot3D f x, f y, f z, u, u min, u max produces a three dimensional space curve parametrized by a variable u which runs from u min to u max. ParametricPlot3D f x, f y, f z, u, u min, u max, v, v min, v max produces a three dimensional surface parametrized by u and v. ParametricPlot3D f x, f y, f z, g x, g y, g z plots several objects together.
11 HdPlot.nb ParametricPlot3D Cos t, Sin t, t 3, t,,
12 HdPlot.nb x Cos v Sin u Sin v Sin u Cos v ; y Cos v Sin u Sin v Sin u Sin v ; z Sin v Sin u Cos v Sin u ; ParametricPlot3D x, y, z, u,, Pi, v,, Pi? Clear Clear symbol, symbol, clears values and definitions for the symbol i. Clear " form ", " form ", clears values and definitions for all symbols whose names match any of the string patterns form i. x Cos v Cos v Sin u Sin u Sin v Clear x, y, z y y VectorAnalysis`? Grad Grad f gives the gradient, f, of the scalar function f in the default coordinate system. Grad f, coordsys gives the gradient of f in the coordinate system coordsys. Grad x y z, Cartesian x, y, z y z, x z, x y Grad 5 x ^ y ^ 3 z ^ 4, Cartesian x, y, z x y 3 z 4, 5 x y z 4, x y 3 z 3
13 HdPlot.nb 3? VectorPlot VectorPlot v x, v y, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max generates a vector plot of the vector field v x, v y as a function of x and y. VectorPlot v x, v y, w x, w y,, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots several vector fields. VectorPlot y, y, x,, 3, y, 3, 3 3 3? ContourPlot ContourPlot f, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max generates a contour plot of f as a function of x and y. ContourPlot f g, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots contour lines for which f g. ContourPlot f g, f g,, x, x min, x max, y, y min, y max plots several contour lines. P : ContourPlot Log x ^ y ^, x, 6, 6, y, 6, 6 Grad Log x ^ y ^, Cartesian x, y, z x, 4 y, x y x y x P : VectorPlot, 4 y, x, 6, 6, y, 6, 6 x y x y? Show Show graphics, options shows graphics with the specified options added. Show g, g, shows several graphics combined.
14 HdPlot.nb 4 Show P, P
Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f 1, f 2,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i.
 HdPlot.nb In[]:=? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. In[]:= Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5
HdPlot.nb In[]:=? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. In[]:= Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5
Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica
 Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica Bill Kinney, Bethel University, St. Paul, MN 2 KinneyComplexAnalysisLabCourse.nb
Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica Bill Kinney, Bethel University, St. Paul, MN 2 KinneyComplexAnalysisLabCourse.nb
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES
 9- Graphical representation of surfaces 1 9 GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES 9.1. Figures defined in Mathematica ô Graphics3D[ ] ø Spheres Sphere of centre 1, 1, 1 and radius 2 Clear "Global` " Graphics3D
9- Graphical representation of surfaces 1 9 GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES 9.1. Figures defined in Mathematica ô Graphics3D[ ] ø Spheres Sphere of centre 1, 1, 1 and radius 2 Clear "Global` " Graphics3D
A plane. Or, with more details, NotebookDirectory. C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_225\
 In[1]:= NotebookDirectory Out[1]= C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_5\ A plane Given a point in R 3 (below it is vr) and two non-collinear vectors (below uu and vv) the parametric equation
In[1]:= NotebookDirectory Out[1]= C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_5\ A plane Given a point in R 3 (below it is vr) and two non-collinear vectors (below uu and vv) the parametric equation
Lab 2B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 2374 University of Minnesota Questions to:
 Lab_B.nb Lab B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 37 University of Minnesota http://www.math.umn.edu/math37 Questions to: rogness@math.umn.edu Introduction As in last week s lab, there is no calculus in this
Lab_B.nb Lab B Parametrizing Surfaces Math 37 University of Minnesota http://www.math.umn.edu/math37 Questions to: rogness@math.umn.edu Introduction As in last week s lab, there is no calculus in this
REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM
 - Representation of curves in parametric form 1 REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM.1. Parametrization of curves in the plane Given a curve in parametric form, its graphical representation in a
- Representation of curves in parametric form 1 REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM.1. Parametrization of curves in the plane Given a curve in parametric form, its graphical representation in a
CurvesGraphics. A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni. Arrows on 2D curves. Motivation
 CurvesGraphics A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni Motivation As a teacher of Calculus and Mathematical Analysis at college and university level, I feel that Mathematica
CurvesGraphics A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni Motivation As a teacher of Calculus and Mathematical Analysis at college and university level, I feel that Mathematica
Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics
 Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics Fall 2016 In[213]:= Clear "Global`*" 2 2450notes2_fall2016.nb Parametric Equations In chapter 9, we introduced parametric equations so that we could easily
Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics Fall 2016 In[213]:= Clear "Global`*" 2 2450notes2_fall2016.nb Parametric Equations In chapter 9, we introduced parametric equations so that we could easily
Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented by Mathematical Equations
 American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 01,, 199-06 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/ajcm.01.305 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm) Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented
American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 01,, 199-06 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/ajcm.01.305 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm) Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented
ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.
![ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.](/thumbs/75/71742148.jpg) Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
Plots & Animations. Simple 2d plots x
 Plots & Animations Simple 2d plots Physical processes and corresponding mathematical formulas can be visualized by plots. The simplest plot of a single function f[x] can be created as follows f@x_d :=
Plots & Animations Simple 2d plots Physical processes and corresponding mathematical formulas can be visualized by plots. The simplest plot of a single function f[x] can be created as follows f@x_d :=
Introduction to Mathematica and Graphing in 3-Space
 1 Mathematica is a powerful tool that can be used to carry out computations and construct graphs and images to help deepen our understanding of mathematical concepts. This document will serve as a living
1 Mathematica is a powerful tool that can be used to carry out computations and construct graphs and images to help deepen our understanding of mathematical concepts. This document will serve as a living
H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P. H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L
 Define and plotting a point and vector H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L Graphics3D@8PointSize@0.05D, Red, Point@PD
Define and plotting a point and vector H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L Graphics3D@8PointSize@0.05D, Red, Point@PD
Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces
 The Mathematica Journal Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces Alan Horwitz In this article, we demonstrate makehole, a program which removes points from any Graphics or Graphics3D picture whose coordinates
The Mathematica Journal Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces Alan Horwitz In this article, we demonstrate makehole, a program which removes points from any Graphics or Graphics3D picture whose coordinates
Algebra. Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C. Solving Equations. Factoring. Exact Solutions to single equation:
 Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C Algebra Solving Equations Exact Solutions to single equation: In[88]:= Solve@x^3 + 5 x - 6 ã 0, xd Out[88]= :8x Ø 1, :x Ø 1 2 I-1 + Â 23
Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C Algebra Solving Equations Exact Solutions to single equation: In[88]:= Solve@x^3 + 5 x - 6 ã 0, xd Out[88]= :8x Ø 1, :x Ø 1 2 I-1 + Â 23
HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20;
 In[1]:= HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20; In[2]:= In[3]:= VincristineDoses 0, 0.00032`, 0.000507`, 0.0008`, 0.00127`, 0.002`, 0.0032`, 0.00507`,
In[1]:= HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20; In[2]:= In[3]:= VincristineDoses 0, 0.00032`, 0.000507`, 0.0008`, 0.00127`, 0.002`, 0.0032`, 0.00507`,
Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points
 Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points We know that an analytic function f(z) is conformal (preserves angles and orientation) at all points where the derivative f (z) is not zero. Here we look
Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points We know that an analytic function f(z) is conformal (preserves angles and orientation) at all points where the derivative f (z) is not zero. Here we look
Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine
 Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine Kenderdine Maths Tutoring 1 December 01 This note shows some interesting curves not usually encountered. Most of the examples exist as families that can be altered by changing
Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine Kenderdine Maths Tutoring 1 December 01 This note shows some interesting curves not usually encountered. Most of the examples exist as families that can be altered by changing
MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Parametrizations
 MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Goals of the lab: To learn some basic operations in Mathematica, such as how to define a function, and how to produce various
MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Goals of the lab: To learn some basic operations in Mathematica, such as how to define a function, and how to produce various
OffPlot::"plnr"; OffGraphics::"gptn"; OffParametricPlot3D::"plld" Needs"Graphics`Arrow`" Needs"VisualLA`"
 Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser of.: Transformation of Functions In this section, we will explore three types of transformations:.) Shifting.) Reflections (or flips).) Stretches and compressions
Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser of.: Transformation of Functions In this section, we will explore three types of transformations:.) Shifting.) Reflections (or flips).) Stretches and compressions
Lecture 2. Dr John Armstrong
 Computing for Geometry and Number Theory Lecture 2 Dr John Armstrong King's College London December 6, 2018 Last week we used Mathematica as a calculator Using the workbook, for example to type SHIFT +
Computing for Geometry and Number Theory Lecture 2 Dr John Armstrong King's College London December 6, 2018 Last week we used Mathematica as a calculator Using the workbook, for example to type SHIFT +
Representations of Curves and Surfaces, and of their Tangent Lines, and Tangent Planes in R 2 and R 3 Robert L.Foote, Fall 2007
 CurvesAndSurfaces.nb Representations of Curves and Surfaces, and of their Tangent Lines, and Tangent Planes in R and R 3 Robert L.Foote, Fall 007 Curves and Surfaces Graphs ü The graph of f : Æ is a curve
CurvesAndSurfaces.nb Representations of Curves and Surfaces, and of their Tangent Lines, and Tangent Planes in R and R 3 Robert L.Foote, Fall 007 Curves and Surfaces Graphs ü The graph of f : Æ is a curve
1 An introduction to Mathematica
 An introduction to Mathematica Mathematica is a very large and seemingly complex system. It contains hundreds of functions for performing various tasks in science, mathematics, and engineering, including
An introduction to Mathematica Mathematica is a very large and seemingly complex system. It contains hundreds of functions for performing various tasks in science, mathematics, and engineering, including
Computational methods in Mathematics
 Computational methods in Mathematics José Carlos Díaz Ramos Cristina Vidal Castiñeira June 13, 2014 1 Graphics Mathematica represents all graphics in terms of a collection of graphics primitives. The primitives
Computational methods in Mathematics José Carlos Díaz Ramos Cristina Vidal Castiñeira June 13, 2014 1 Graphics Mathematica represents all graphics in terms of a collection of graphics primitives. The primitives
Problem #130 Ant On Cylinders
 Problem #130 Ant On Cyliners The Distance The Ant Travels Along The Surface John Snyer November, 009 Problem Consier the soli boune by the three right circular cyliners x y (greenish-yellow), x z (re),
Problem #130 Ant On Cyliners The Distance The Ant Travels Along The Surface John Snyer November, 009 Problem Consier the soli boune by the three right circular cyliners x y (greenish-yellow), x z (re),
23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages
 23. Procedures and Packages 2015-06-15 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages In a typical Mathematica package there are generally two kinds
23. Procedures and Packages 2015-06-15 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages In a typical Mathematica package there are generally two kinds
Copyright 1996,1997, All rights reserved, Izumi Ohzawa,
 CXmodelWhyBB-BD.ma 1 This Mathematica Notebook contains computations and derivations used to create plots in Figs. 8, 9 and 10 of our paper Ohzawa, DeAngelis, Freeman, Encoding of Binocular Disparity by
CXmodelWhyBB-BD.ma 1 This Mathematica Notebook contains computations and derivations used to create plots in Figs. 8, 9 and 10 of our paper Ohzawa, DeAngelis, Freeman, Encoding of Binocular Disparity by
A Mathematica Tutorial
 A Mathematica Tutorial -3-8 This is a brief introduction to Mathematica, the symbolic mathematics program. This tutorial is generic, in the sense that you can use it no matter what kind of computer you
A Mathematica Tutorial -3-8 This is a brief introduction to Mathematica, the symbolic mathematics program. This tutorial is generic, in the sense that you can use it no matter what kind of computer you
Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation
 The following notes are complements for the book Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation Albert Tarantola Society of Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), 2005 11.4.3 Probabilistic
The following notes are complements for the book Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation Albert Tarantola Society of Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), 2005 11.4.3 Probabilistic
PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES
 PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES Suppose we want to plot the path of a particle moving in a plane. This path looks like a curve, but we cannot plot it like we would plot any other type of curve in the
PARAMETERIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES Suppose we want to plot the path of a particle moving in a plane. This path looks like a curve, but we cannot plot it like we would plot any other type of curve in the
Assignment 1. Prolog to Problem 1. Two cylinders. ü Visualization. Problems by Branko Curgus
 Assignment In[]:= Problems by Branko Curgus SetOptions $FrontEndSession, Magnification Prolog to Problem. Two cylinders In[]:= This is a tribute to a problem that I was assigned as an undergraduate student
Assignment In[]:= Problems by Branko Curgus SetOptions $FrontEndSession, Magnification Prolog to Problem. Two cylinders In[]:= This is a tribute to a problem that I was assigned as an undergraduate student
Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
PLoT Manual. PLT 209 Released December 2004
 PLoT Manual PLT (scheme@plt-scheme.org) 209 Released December 2004 Copyright notice Copyright c 1996-2004 PLT Permission to make digital/hard copies and/or distribute this documentation for any purpose
PLoT Manual PLT (scheme@plt-scheme.org) 209 Released December 2004 Copyright notice Copyright c 1996-2004 PLT Permission to make digital/hard copies and/or distribute this documentation for any purpose
Explore 3D Figures. Dr. Jing Wang (517) , Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA
 Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
Mathematica Assignment 1
 Math 21a: Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2000 Mathematica Assignment 1 Support Welcome to this Mathematica computer assignment! In case of technical problems with this assignment please consult first the
Math 21a: Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2000 Mathematica Assignment 1 Support Welcome to this Mathematica computer assignment! In case of technical problems with this assignment please consult first the
Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection. Visualization and Graphics
 Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection Visualization and Graphics For use with Wolfram Mathematica 7.0 and later. For the latest updates and corrections to this manual: visit reference.wolfram.com For
Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection Visualization and Graphics For use with Wolfram Mathematica 7.0 and later. For the latest updates and corrections to this manual: visit reference.wolfram.com For
1 The Inverse Problem
 The Inverse Problem We have learned that a general solution of a first-order differential equation y = f H, yl (..) is a one-parameter family of (either eplicit or implicit) solutions. Finding a general
The Inverse Problem We have learned that a general solution of a first-order differential equation y = f H, yl (..) is a one-parameter family of (either eplicit or implicit) solutions. Finding a general
Examples of Fourier series
 Examples of Fourier series Preliminaries In[]:= Below is the definition of a periodic extension of a function defined on L, L. This definition takes a function as a variable. The function has to be inputted
Examples of Fourier series Preliminaries In[]:= Below is the definition of a periodic extension of a function defined on L, L. This definition takes a function as a variable. The function has to be inputted
Glossary. T his glossary is intended to supplement the chapter glossaries found throughout. Commands
 Glossary T his glossary is intended to supplement the chapter glossaries found throughout the book. In those, you found a roster of commands, options, and packages that were particularly useful in solving
Glossary T his glossary is intended to supplement the chapter glossaries found throughout the book. In those, you found a roster of commands, options, and packages that were particularly useful in solving
1 Basic Plotting. Radii Speeds Offsets 1, 1, 1 2, 5, 19 0, 0, 0 1, 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2 1, 10, 17, 26, 28, 37 0, Π, Π, 0, 0, Π
 1 Basic Plotting Placing wheels on wheels on wheels and giving them different rates of spin leads to some interesting parametric plots. The images show four examples. They arise from the values below,
1 Basic Plotting Placing wheels on wheels on wheels and giving them different rates of spin leads to some interesting parametric plots. The images show four examples. They arise from the values below,
Math 21a Homework 22 Solutions Spring, 2014
 Math 1a Homework Solutions Spring, 014 1. Based on Stewart 11.8 #6 ) Consider the function fx, y) = e xy, and the constraint x 3 + y 3 = 16. a) Use Lagrange multipliers to find the coordinates x, y) of
Math 1a Homework Solutions Spring, 014 1. Based on Stewart 11.8 #6 ) Consider the function fx, y) = e xy, and the constraint x 3 + y 3 = 16. a) Use Lagrange multipliers to find the coordinates x, y) of
Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L
 Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) Clear@"Global`*"D H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L H* Define vector functions in 3D of one variable t, i.e.
Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) Clear@"Global`*"D H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L H* Define vector functions in 3D of one variable t, i.e.
Graphing on the Riemann Sphere
 The Mathematica Journal Graphing on the Riemann Sphere Djilali Benayat We give a procedure to plot parametric curves on the sphere whose advantages over classical graphs in the Cartesian plane are obvious
The Mathematica Journal Graphing on the Riemann Sphere Djilali Benayat We give a procedure to plot parametric curves on the sphere whose advantages over classical graphs in the Cartesian plane are obvious
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
MATH Harrell. Which way is up? Lecture 9. Copyright 2008 by Evans M. Harrell II.
 MATH 2401 - Harrell Which way is up? Lecture 9 Copyright 2008 by Evans M. Harrell II. A set does not necessarily have boundaries If it does have boundaries Are the boundaries part of the set or not? Sets
MATH 2401 - Harrell Which way is up? Lecture 9 Copyright 2008 by Evans M. Harrell II. A set does not necessarily have boundaries If it does have boundaries Are the boundaries part of the set or not? Sets
Graphs of Functions, Limits, and
 Chapter Continuity Graphs of Functions, Limits, and ü. Plotting Graphs Students should read Chapter of Rogawski's Calculus [] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü.. Basic
Chapter Continuity Graphs of Functions, Limits, and ü. Plotting Graphs Students should read Chapter of Rogawski's Calculus [] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü.. Basic
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral
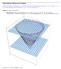 Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Lagrange multipliers October 2013
 Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 1 1 3/2 Example: Optimization
Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 1 1 3/2 Example: Optimization
Daily WeBWorK, #1. This means the two planes normal vectors must be multiples of each other.
 Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
Daily WeBWorK, #1 Consider the ellipsoid x 2 + 3y 2 + z 2 = 11. Find all the points where the tangent plane to this ellipsoid is parallel to the plane 2x + 3y + 2z = 0. In order for the plane tangent to
Fine Arts in Solow Model. Abstract
 Fine Arts in Solow Model Tetsuya Saito Department of Economics, SUNY at Buffalo Abstract Applying some built-in functions of Mathematica, this note provides some graphics derived from convergent paths
Fine Arts in Solow Model Tetsuya Saito Department of Economics, SUNY at Buffalo Abstract Applying some built-in functions of Mathematica, this note provides some graphics derived from convergent paths
Lagrange multipliers 14.8
 Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Functions f and g are called a funny cosine and a funny sine if they satisfy the following properties:
 Assignment problems by Branko Ćurgus posted on 2070720 Problem. Funny trigonometry and its beauty ü Few Mathematica comments There are several standard Mathematica functions that can be useful here. For
Assignment problems by Branko Ćurgus posted on 2070720 Problem. Funny trigonometry and its beauty ü Few Mathematica comments There are several standard Mathematica functions that can be useful here. For
Maple: Plotting graphs
 Maple: Plotting graphs System Maple provides many possibilities for graphical representation of data and mathematical relations, using different modifications of function plots for plotting graphs. Among
Maple: Plotting graphs System Maple provides many possibilities for graphical representation of data and mathematical relations, using different modifications of function plots for plotting graphs. Among
Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives. Directional Derivatives
 Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Recall that if z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as and represent the rates of change of z in the x- and y-directions, that is, in the directions of the unit vectors i and
Basic Exercises about Mathematica
 Basic Exercises about Mathematica 1. Calculate with four decimal places. NB F. 2.23607 2.23607 Ë We can evaluate a cell by placing the cursor on it and pressing Shift+Enter (or Enter on the numeric key
Basic Exercises about Mathematica 1. Calculate with four decimal places. NB F. 2.23607 2.23607 Ë We can evaluate a cell by placing the cursor on it and pressing Shift+Enter (or Enter on the numeric key
Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression]
![Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression] Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression]](/thumbs/82/86424514.jpg) Mathematica Basics To evaluate a Mathematica command, press [Shift]+[Enter]. Pay attention to spaces! Mathematica interprets some of them as multiplication. Syntax, capitalization and punctuation are meaningful.
Mathematica Basics To evaluate a Mathematica command, press [Shift]+[Enter]. Pay attention to spaces! Mathematica interprets some of them as multiplication. Syntax, capitalization and punctuation are meaningful.
Functions and Graphs. The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996.
 Functions and Graphs The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996. Launch Mathematica. Type
Functions and Graphs The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996. Launch Mathematica. Type
Overview: The original Mathematica was a computer algebra system (CAS) released by Stephen Wolfram in 1988.
 Mathematica 7.0.1 Overview: The original Mathematica was a computer algebra system (CAS) released by Stephen Wolfram in 1988. Modern releases have augmented the CAS with powerful numerical and graphical
Mathematica 7.0.1 Overview: The original Mathematica was a computer algebra system (CAS) released by Stephen Wolfram in 1988. Modern releases have augmented the CAS with powerful numerical and graphical
6.2.1 Plotting Curves in Parametric Representation in 3-Dimensional Space
 6.2 Drawing Three-Dimensional Objects $Version 2015-04 - 21 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 1. Curves in space may be drawn in perspective. (ParametricPlot3D,ListPointPlot3D). 2. 2-dimensional
6.2 Drawing Three-Dimensional Objects $Version 2015-04 - 21 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 1. Curves in space may be drawn in perspective. (ParametricPlot3D,ListPointPlot3D). 2. 2-dimensional
Visualization of Complex Functions
 complexvis.nb Visualization of Complex Functions Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria Source: This article appeared first in The Mathematica Journal 7(), 63-8 (998), The package ComplexPlot.m described
complexvis.nb Visualization of Complex Functions Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria Source: This article appeared first in The Mathematica Journal 7(), 63-8 (998), The package ComplexPlot.m described
Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica
 Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica Complex functions Real and Imaginary parts of functions can be obtained using ComplexExpand, which treats all variables (here x and y) as
Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica Complex functions Real and Imaginary parts of functions can be obtained using ComplexExpand, which treats all variables (here x and y) as
4. Mathematica. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Starting Mathematica Starting Mathematica from an X-terminal (Maths)
 4. Mathematica 4.1 Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
4. Mathematica 4.1 Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
Math 2A Vector Calculus Chapter 11 Test Fall 07 Name Show your work. Don t use a calculator. Write responses on separate paper.
 Math A Vector Calculus Chapter Test Fall 7 Name Show our work. Don t use a calculator. Write responses on separate paper.. Consider the nice, smooth unction z, whose contour map is shown at right. a. Estimate
Math A Vector Calculus Chapter Test Fall 7 Name Show our work. Don t use a calculator. Write responses on separate paper.. Consider the nice, smooth unction z, whose contour map is shown at right. a. Estimate
Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September 2, 2013
 Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September, 0 Contents. Getting Started. Basic plotting. Solving equations, approximating
Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September, 0 Contents. Getting Started. Basic plotting. Solving equations, approximating
11.5 Cylinders and cylindrical coordinates
 11.5 Cylinders and cylindrical coordinates Definition [Cylinder and generating curve] A cylinder is a surface composed of the lines that pass through a given plane curve parallel to a given line in space.
11.5 Cylinders and cylindrical coordinates Definition [Cylinder and generating curve] A cylinder is a surface composed of the lines that pass through a given plane curve parallel to a given line in space.
1. How Mathematica works
 Departments of Civil Engineering and Mathematics CE 109: Computing for Engineering Mathematica Session 1: Introduction to the system Mathematica is a piece of software described by its manufacturers as
Departments of Civil Engineering and Mathematics CE 109: Computing for Engineering Mathematica Session 1: Introduction to the system Mathematica is a piece of software described by its manufacturers as
MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3
 MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3 List of important Definitions and Theorems 1 Foundations Definition 1. By a function f one understands a mathematical object consisting of (i) a set X, called
MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3 List of important Definitions and Theorems 1 Foundations Definition 1. By a function f one understands a mathematical object consisting of (i) a set X, called
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
Chapter 3 Functions of Several Variables 3.1 Definitions and Examples of Functions of two or More Variables In this section, we extend the definition of a function of one variable to functions of two or
Version 5.0. Alexander Friedman and Jamie Raymond. June 6, 2010
 PLoT: Graph Plotting Version 5.0 Alexander Friedman and Jamie Raymond June 6, 2010 PLoT (a.k.a. PLTplot) provides a basic interface for producing common types of plots such as line and vector field plots
PLoT: Graph Plotting Version 5.0 Alexander Friedman and Jamie Raymond June 6, 2010 PLoT (a.k.a. PLTplot) provides a basic interface for producing common types of plots such as line and vector field plots
Mathematical Computing
 IMT2b2β Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna A.W.L. Pubudu Thilan Graphics in Maxima Introduction Gnuplot is a comand-line oriented plot program. Maxima s plotting is based on the Gnuplot, which
IMT2b2β Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna A.W.L. Pubudu Thilan Graphics in Maxima Introduction Gnuplot is a comand-line oriented plot program. Maxima s plotting is based on the Gnuplot, which
14.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
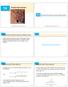 14 Partial Derivatives 14.6 and the Gradient Vector Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and the Gradient Vector In this section we introduce
14 Partial Derivatives 14.6 and the Gradient Vector Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and the Gradient Vector In this section we introduce
ENGI Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01
 ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
Lagrange Multipliers
 Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Lagrange Multipliers Introduction and Goals: The goal of this lab is to become more familiar with the process and workings of Lagrange multipliers. This lab is designed more to help you understand the
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 27 / 45
 : Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD
 The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD Brainnetome Workshop 9-10 October 015, Beijing, China Init The 1-D Gaussian kernel: gauss[x_, Σ_ /; Σ > 0] := Σ 1 Π e - x Σ ; The
The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD Brainnetome Workshop 9-10 October 015, Beijing, China Init The 1-D Gaussian kernel: gauss[x_, Σ_ /; Σ > 0] := Σ 1 Π e - x Σ ; The
surface length L = 1 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD
 inflow y H i,n y outflow i,1 i,0 starting length Xs surface length L = 1 Figure 1: Eternal boundary layer control volume. 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD Listed below is a Mathematica
inflow y H i,n y outflow i,1 i,0 starting length Xs surface length L = 1 Figure 1: Eternal boundary layer control volume. 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD Listed below is a Mathematica
Taschenrechner. Ganzzahlarithmetik N Pi, 500. In[1]:= Out[1]= In[2]:=
![Taschenrechner. Ganzzahlarithmetik N Pi, 500. In[1]:= Out[1]= In[2]:= Taschenrechner. Ganzzahlarithmetik N Pi, 500. In[1]:= Out[1]= In[2]:=](/thumbs/80/81586012.jpg) Taschenrechner In[]:=... Out[]=.99 In[]:= NPi, Out[]=.99999999999999 999999999 9999999 999999999 9999999999999 Ganzzahlarithmetik In[]:= Out[]= 9 9 99 9 9 9 9 9 99 99 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 In[]:= Out[]= 9 9 9
Taschenrechner In[]:=... Out[]=.99 In[]:= NPi, Out[]=.99999999999999 999999999 9999999 999999999 9999999999999 Ganzzahlarithmetik In[]:= Out[]= 9 9 99 9 9 9 9 9 99 99 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 In[]:= Out[]= 9 9 9
Lecture 34: Curves defined by Parametric equations
 Curves defined by Parametric equations When the path of a particle moving in the plane is not the graph of a function, we cannot describe it using a formula that express y directly in terms of x, or x
Curves defined by Parametric equations When the path of a particle moving in the plane is not the graph of a function, we cannot describe it using a formula that express y directly in terms of x, or x
Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Yeung-Nan Shieh 2008 Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification Yeung-Nan Shieh, San Jose State University Jason Kao Available at: https://works.bepress.com/yeung-nan_shieh/9/
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Yeung-Nan Shieh 2008 Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification Yeung-Nan Shieh, San Jose State University Jason Kao Available at: https://works.bepress.com/yeung-nan_shieh/9/
4. Dynamic Interactivity
 4. Dynamic Interactivity Mathematica has several dynamic elements. It is very useful for visualization of the results if the problem contains some parameters and one wants to study it under the change
4. Dynamic Interactivity Mathematica has several dynamic elements. It is very useful for visualization of the results if the problem contains some parameters and one wants to study it under the change
Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points
 Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points Project Template Chapter 10 of Anton/Rorres, Elementary Linear Algebra, 10th edition, consists of 20 sections of Applications, the first of which
Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points Project Template Chapter 10 of Anton/Rorres, Elementary Linear Algebra, 10th edition, consists of 20 sections of Applications, the first of which
Part V Appendices c Copyright, Todd Young and Martin Mohlenkamp, Department of Mathematics, Ohio University, 2017
 Part V Appendices c Copyright, Todd Young and Martin Mohlenkamp, Department of Mathematics, Ohio University, 2017 Appendix A Glossary of Matlab Commands Mathematical Operations + Addition. Type help plus
Part V Appendices c Copyright, Todd Young and Martin Mohlenkamp, Department of Mathematics, Ohio University, 2017 Appendix A Glossary of Matlab Commands Mathematical Operations + Addition. Type help plus
A Brief Introduction to Mathematica
 A Brief Introduction to Mathematica Objectives: (1) To learn to use Mathematica as a calculator. (2) To learn to write expressions in Mathematica, and to evaluate them at given point. (3) To learn to plot
A Brief Introduction to Mathematica Objectives: (1) To learn to use Mathematica as a calculator. (2) To learn to write expressions in Mathematica, and to evaluate them at given point. (3) To learn to plot
Norman Bleistein. *MATHEMATICA is a trademark of Wolfram Research Inc. %,- BUTisbutC4 ST l'ted A
 AD-A2 5 2 779 /$i/i~i/u/llli///i/lll/ui/lllc"l-.,3p., Mathematica Tm and the Method of Steepest Descents Part I by Norman Bleistein DTIC S ELECTED S JUL 6 1992 U C *MATHEMATICA is a trademark of Wolfram
AD-A2 5 2 779 /$i/i~i/u/llli///i/lll/ui/lllc"l-.,3p., Mathematica Tm and the Method of Steepest Descents Part I by Norman Bleistein DTIC S ELECTED S JUL 6 1992 U C *MATHEMATICA is a trademark of Wolfram
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Big Ideas. What We Are Doing Today... Notes. Notes. Notes
 Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
MATLAB Tutorial. Mohammad Motamed 1. August 28, generates a 3 3 matrix.
 MATLAB Tutorial 1 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131 August 28, 2016 Contents: 1. Scalars, Vectors, Matrices... 1 2. Built-in variables, functions,
MATLAB Tutorial 1 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131 August 28, 2016 Contents: 1. Scalars, Vectors, Matrices... 1 2. Built-in variables, functions,
Curvilinear Coordinates
 Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Calculus III. 1 Getting started - the basics
 Calculus III Spring 2011 Introduction to Maple The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar with some of the tools the Maple software package offers for visualizing curves and surfaces in
Calculus III Spring 2011 Introduction to Maple The purpose of this document is to help you become familiar with some of the tools the Maple software package offers for visualizing curves and surfaces in
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
{σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]]
![{σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]] {σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]]](/thumbs/87/97226018.jpg) g[x_, y_] := f[x_, y_] := x 1 2 +y 2 2 * π * σ * 2 e- 2*σ 2 ; 10 g[x, y] + g[x + i, y] + g[x, y + i] + g[x + 10, y + 10] /. {σ 1}; i=1 10 i=1 Hessian2D[f_] := D[D[f[x, y], {x}], {x}] D[D[f[x, y], {x}],
g[x_, y_] := f[x_, y_] := x 1 2 +y 2 2 * π * σ * 2 e- 2*σ 2 ; 10 g[x, y] + g[x + i, y] + g[x, y + i] + g[x + 10, y + 10] /. {σ 1}; i=1 10 i=1 Hessian2D[f_] := D[D[f[x, y], {x}], {x}] D[D[f[x, y], {x}],
Graphics. Graphics. Graphics. Graphics
 T T T E T E T X E E X E X E X X and and and and and and Graphics Graphics Graphics Graphics Graphics c, 3, Trivandrum 6954, INDIA /3 7. Plotting Tricks We have seen how we can join points to produce curves
T T T E T E T X E E X E X E X X and and and and and and Graphics Graphics Graphics Graphics Graphics c, 3, Trivandrum 6954, INDIA /3 7. Plotting Tricks We have seen how we can join points to produce curves
This notebook "MathematicaDemo.nb" can be downloaded from the course web page.
 Mathematica demo http://www.wolfram.com/ This notebook "MathematicaDemo.nb" can be downloaded from the course web page. Basics Evaluate cells by pressing "shift-enter" / shift-return In[]:= + 3 Out[]=
Mathematica demo http://www.wolfram.com/ This notebook "MathematicaDemo.nb" can be downloaded from the course web page. Basics Evaluate cells by pressing "shift-enter" / shift-return In[]:= + 3 Out[]=
AMS Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I
 ams-511-ws01-sol.nb 1 AMS 691.02 - Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I Workshop 01 Solution Robert J Frey, Research Professor Stony Brook University, Applied Mathematics and Statistics frey@ams.sunysb.edu
ams-511-ws01-sol.nb 1 AMS 691.02 - Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I Workshop 01 Solution Robert J Frey, Research Professor Stony Brook University, Applied Mathematics and Statistics frey@ams.sunysb.edu
II. grafika. grafikuli obieqtebis ageba: funqcia Graphics
 II. grafika grafikuli obieqtebis ageba: fuqcia Graphics wia leqciasi Cve gavixilet Mathematica sistemis grafikuli fuqciebi Plot (grafikis ageba sibrtkeze) da Plot3D (grafikis ageba sivrcesi). agretve gaxiluli
II. grafika grafikuli obieqtebis ageba: fuqcia Graphics wia leqciasi Cve gavixilet Mathematica sistemis grafikuli fuqciebi Plot (grafikis ageba sibrtkeze) da Plot3D (grafikis ageba sivrcesi). agretve gaxiluli
Solids of Revolution
 > Solids of Revolution > restart; > with(plots); Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined [ animate, animate3d, animatecurve, changecoords, complexplot, complexplot3d, conformal, contourplot,
> Solids of Revolution > restart; > with(plots); Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined [ animate, animate3d, animatecurve, changecoords, complexplot, complexplot3d, conformal, contourplot,
Outcomes List for Math Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring
 Outcomes List for Math 200-200935 Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring 2009-2010 The purpose of the Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and
Outcomes List for Math 200-200935 Multivariable Calculus (9 th edition of text) Spring 2009-2010 The purpose of the Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and
You can drag the graphs using your mouse to rotate the surface.
 The following are some notes for relative maxima and mimima using surfaces plotted in Mathematica. The way to run the code is: Select Menu bar -- Evaluation -- Evaluate Notebook You can drag the graphs
The following are some notes for relative maxima and mimima using surfaces plotted in Mathematica. The way to run the code is: Select Menu bar -- Evaluation -- Evaluate Notebook You can drag the graphs
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 28 / 46
 Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
f for Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y).
 Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y). For a function f(x,y), the gradient vector, denoted as f (pronounced grad f ) is
Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y). For a function f(x,y), the gradient vector, denoted as f (pronounced grad f ) is

 Overview of Basic Graphics Commands In[]:=
Overview of Basic Graphics Commands In[]:=