of translations of ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you describe the properties of orientation and congruence of translations?
|
|
|
- Alaina French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ? LESSN 12.1 Properties of Translations ESSENTIL QUESTIN How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of translations? Two-dimensional shapes Generalize the properties of orientation and congruence of translations of two-dimensional shapes on a coordinate plane. EXPLRE TIVITY Eploring Translations You learned that a function is a rule that assigns eactl one output to each input. transformation is a function that describes a change in the position, size, or shape of a figure. The input of a transformation is the preimage, and the output of a transformation is the image. translation is a transformation that slides a figure along a straight line. The image has the same size and shape as the preimage. The triangle shown on the grid is the preimage (input). The arrow shows the motion of a translation and how point is translated to point. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Image redits: rand X Pictures/lam Images E F Trace triangle onto a piece of paper. ut out our traced triangle. Slide our triangle along the arrow to model the translation that maps point to point. The image of the translation is the triangle produced b the translation. Sketch the image of the translation. The vertices of the image are labeled using prime notation. For eample, the image of is. Label the images of points and. escribe the motion modeled b the translation. Move units right and units down. heck that the motion ou described in part E is the same motion that maps point onto, point onto, and point onto Reflect 1. How is the orientation of the triangle affected b the translation? Lesson
2 EXPLRE TIVITY Properties of Translations Use trapezoid TRP to investigate the properties of translations. Trace the trapezoid onto a piece of paper. ut out our traced trapezoid. Place our trapezoid on top of the trapezoid in the figure. Then translate our trapezoid units to the left and 3 units up. Sketch the image of the translation b tracing our trapezoid in this new location. Label the vertices of the image T, R,, and P T R P Use a ruler to measure the sides of trapezoid TRP in centimeters. TR = R = P = TP = Use a ruler to measure the sides of trapezoid T R P in centimeters. T R = R = P = T P = E What do ou notice about the lengths of corresponding sides of the two figures? F Use a protractor to measure the angles of trapezoid TRP. m T = m R = m = m P = G H I Use a protractor to measure the angles of trapezoid T R P. m T = m R = m = m P = What do ou notice about the measures of corresponding angles of the two figures? Which sides of trapezoid TRP are parallel? How do ou know? Which sides of trapezoid T R P are parallel? What do ou notice? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan 33 Unit
3 Reflect 2. Make a onjecture Use our results from parts E, H, and I to make a conjecture about translations. 3. What can ou sa about translations and congruence? Graphing Translations To translate a figure in the coordinate plane, translate each of its vertices. Then connect the vertices to form the image. EXMPLE 1 The figure shows triangle XYZ. Graph the image of the triangle after a translation of units to the right and 1 unit up Math n the Spot m.hrw.com Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 STEP Translate point X. ount right units and up 1 unit and plot point X. Translate point Y. ount right units and up 1 unit and plot point Y. Translate point Z. ount right units and up 1 unit and plot point Z. onnect X, Y, and Z to form triangle X Y Z. Each verte is moved units right and 1 unit up. X X Z Z X Y X Y Z Z Y Y Math Talk Mathematical Processes Is the image congruent to the preimage? How do ou know? Lesson
4 Personal Math Trainer nline ssessment and Intervention m.hrw.com YUR TURN. The figure shows parallelogram. Graph the image of the parallelogram after a translation of units to the left and 2 units down. - - Guided Practice 1. Vocabular is a change in the position, size, or shape of a figure. 2. Vocabular When ou perform a transformation of a figure on the coordinate plane, the input of the transformation is called the, and the output of the transformation is called the. 3. Joni translates a right triangle 2 units down and units to the right. How does the orientation of the image of the triangle compare with the orientation of the preimage? (Eplore ctivit 1). Rashid drew rectangle PQRS on a coordinate plane. He then translated the rectangle 3 units up and 3 units to the left and labeled the image P Q R S. How do rectangle PQRS and rectangle P Q R S compare? (Eplore ctivit 2)?. The figure shows trapezoid WXYZ. Graph the image of the trapezoid after a translation of units up and 2 units to the left. (Eample 1) ESSENTIL QUESTIN HEK-IN. What are the properties of translations? W Z - Y X Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan 33 Unit
5 Name lass ate 12.1 Independent Practice The figure shows triangle EF. a. Graph the image of the triangle after the translation that maps point to point. m.hrw.com E Personal Math Trainer nline ssessment and Intervention b. How would ou describe the translation? - F c. How does the image of triangle EF compare with the preimage? - 8. a. Graph quadrilateral KLMN with vertices K( 3, 2), L(2, 2), M(0, 3), and N(, 0) on the coordinate grid. b. n the same coordinate grid, graph the image of quadrilateral KLMN after a translation of 3 units to the right and units up. c. Which side of the image is congruent to side _ LM? - Name three other pairs of congruent sides. - Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan raw the image of the figure after each translation. 9. units left and 2 units down 10. units right and 3 units up Q P R - - S - - Lesson
6 11. The figure shows the ascent of a hot air balloon. How would ou describe the translation? ritical Thinking Is it possible that the orientation of a figure could change after it is translated? Eplain FUS N HIGHER RER THINKING 13. a. Multistep Graph triangle XYZ with vertices X( 2, ), Y(2, 2), and Z(, ) on the coordinate grid. b. n the same coordinate grid, graph and label triangle X Y Z, the image of triangle XYZ after a translation of 3 units to the left and units up. c. Now graph and label triangle X Y Z, the image of triangle X Y Z after a translation of 1 unit to the left and 2 units down. - d. nalze Relationships How would ou describe the translation that maps triangle XYZ onto triangle X Y Z? - 1. ritical Thinking The figure shows rectangle P Q R S, the image of rectangle PQRS after a translation of units to the right and 7 units up. Graph and label the preimage PQRS. 1. ommunicate Mathematical Ideas Eplain wh the image of a figure after a translation is congruent to its preimage. - P Q S R Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing ompan Unit
Properties of Rotations 8.10.A. Sketch the image of the rotation. Label the images of points A, B, and C as A, B, and C.
 ? LESSON 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTION Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
? LESSON 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTION Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
Properties of Reflections 8.10.A. What is the line of reflection for this transformation?
 ? LSSN 12.2 SSNTIL QUSTIN Properties of Reflections How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of reflections? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
? LSSN 12.2 SSNTIL QUSTIN Properties of Reflections How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of reflections? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
8.G.1c. Trace triangle ABC onto a piece of paper. Cut out your traced triangle.
 ? LESSON 9.3 Properties of Rotations ESSENTIL QUESTION 8.G.1c Verif eperimentall the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. lso 8.G.1a, 8.G.1b,
? LESSON 9.3 Properties of Rotations ESSENTIL QUESTION 8.G.1c Verif eperimentall the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. lso 8.G.1a, 8.G.1b,
9 LESSON 9.1. Transformations and Congruence. Properties of Translations ESSENTIAL QUESTION
 Transformations and ongruence? MULE 9 LESSN 9.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Translations How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve realworld problems? 8.G.1, 8.G.3 LESSN 9. Properties of
Transformations and ongruence? MULE 9 LESSN 9.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Translations How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve realworld problems? 8.G.1, 8.G.3 LESSN 9. Properties of
Properties of Rotations 8.10.A. Sketch the image of the rotation. Label the images of points A, B, and C as A, B, and C.
 ? LESSN 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
? LESSN 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
Representations of Dilations 8.G.1.3
 ? L E S S N 10. lgebraic Representations of Dilations ESSENTIL QUESTIN.G.1.3 Describe the effect of dilations, on twodimensional figures using coordinates. How can ou describe the effect of a dilation
? L E S S N 10. lgebraic Representations of Dilations ESSENTIL QUESTIN.G.1.3 Describe the effect of dilations, on twodimensional figures using coordinates. How can ou describe the effect of a dilation
Representations of Transformations
 ? L E S S N 9.4 Algebraic Representations of Transformations ESSENTIAL QUESTIN Algebraic Representations of Translations The rules shown in the table describe how coordinates change when a figure is translated
? L E S S N 9.4 Algebraic Representations of Transformations ESSENTIAL QUESTIN Algebraic Representations of Translations The rules shown in the table describe how coordinates change when a figure is translated
Transformations and Similarity
 Transformations and Similarit? MDULE 10 LESSN 10.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Dilations How can ou use dilations and similarit to solve real-world problems? 8.G.3, 8.G. LESSN 10. lgebraic Representations
Transformations and Similarit? MDULE 10 LESSN 10.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Dilations How can ou use dilations and similarit to solve real-world problems? 8.G.3, 8.G. LESSN 10. lgebraic Representations
9.1 Angle Relationships
 ? LESSON 9.1 ngle Relationships ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you use angle relationships to solve problems? Equations, epressions, and relationships 7.11. Write and solve equations using geometry concepts,
? LESSON 9.1 ngle Relationships ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you use angle relationships to solve problems? Equations, epressions, and relationships 7.11. Write and solve equations using geometry concepts,
Unit 4 Performance Tasks
 ? UNIT 4 Stud Guide Review MULE 9 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Transformations and ongruence How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve real-world problems? EXMPLE Translate triangle XYZ left 4 units and
? UNIT 4 Stud Guide Review MULE 9 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Transformations and ongruence How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve real-world problems? EXMPLE Translate triangle XYZ left 4 units and
3.1 Sequences of Transformations
 Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
17.1 Translations. Exploring Translations. Explore
 Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Name Class Date. Congruence and Transformations Going Deeper
 Name lass ate 4-1 ongruence and Transformations Going eeper ssential question: How can ou use transformations to determine whether figures are congruent? Two figures are congruent if the have the same
Name lass ate 4-1 ongruence and Transformations Going eeper ssential question: How can ou use transformations to determine whether figures are congruent? Two figures are congruent if the have the same
Angle Theorems for Triangles 8.8.D
 ? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
13.4 Problem Solving with Trigonometry
 Name lass ate 13.4 Problem Solving with Trigonometr Essential Question: How can ou solve a right triangle? Resource Locker Eplore eriving an rea Formula You can use trigonometr to find the area of a triangle
Name lass ate 13.4 Problem Solving with Trigonometr Essential Question: How can ou solve a right triangle? Resource Locker Eplore eriving an rea Formula You can use trigonometr to find the area of a triangle
Rotate. A bicycle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. ACTIVITY: Three Basic Ways to Move Things
 . Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
. Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
3.2 Proving Figures are Congruent Using Rigid Motions
 Name lass ate 3.2 Proving igures are ongruent Using igid otions ssential uestion: How can ou determine whether two figures are congruent? esource ocker plore onfirming ongruence Two plane figures are congruent
Name lass ate 3.2 Proving igures are ongruent Using igid otions ssential uestion: How can ou determine whether two figures are congruent? esource ocker plore onfirming ongruence Two plane figures are congruent
Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the
 Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the 4 Coordinate Plane WARM UP Determine each product. 1. 21 3 6 2. 2 3 5 (21) LEARNING GOALS Reflect geometric figures on the coordinate plane. Identif and describe
Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the 4 Coordinate Plane WARM UP Determine each product. 1. 21 3 6 2. 2 3 5 (21) LEARNING GOALS Reflect geometric figures on the coordinate plane. Identif and describe
ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you determine when two triangles are similar? 8.8.D
 ? LESSON 7.3 ngle-ngle Similarity ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you determine when two triangles are similar? Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.8.D Use informal arguments to establish facts about
? LESSON 7.3 ngle-ngle Similarity ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you determine when two triangles are similar? Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.8.D Use informal arguments to establish facts about
1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints
 Name lass ate 1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints Essential Question: How do you draw a segment and measure its length? Explore Exploring asic Geometric Terms In geometry, some of the names of figures and
Name lass ate 1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints Essential Question: How do you draw a segment and measure its length? Explore Exploring asic Geometric Terms In geometry, some of the names of figures and
18.1 Sequences of Transformations
 Name lass ate 1.1 Sequences of Transformations ssential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? plore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Name lass ate 1.1 Sequences of Transformations ssential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? plore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
13.4 Classify Quadrilaterals
 ? Name 13.4 lassify Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you sort and classify quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 4.6. MTHEMTIL PROESSES 4.1., 4.1.E Unlock the Problem quadrilateral is a polygon
? Name 13.4 lassify Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you sort and classify quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 4.6. MTHEMTIL PROESSES 4.1., 4.1.E Unlock the Problem quadrilateral is a polygon
Translations. Essential Question How can you translate a figure in a coordinate plane? A B
 . Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
. Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Understanding Rotations
 Lesson 19 Understanding Rotations 8.G.1.a, 8.G.1.b, 8.G.1.c, 8.G., 8.G.3 1 Getting the idea A rotation is a tpe of transformation in which ou turn a figure about a fied point. The image formed b a rotation
Lesson 19 Understanding Rotations 8.G.1.a, 8.G.1.b, 8.G.1.c, 8.G., 8.G.3 1 Getting the idea A rotation is a tpe of transformation in which ou turn a figure about a fied point. The image formed b a rotation
Sequences of Transformations
 OMMON ORE D P j E E F F D F k D E Locker LESSON 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation
OMMON ORE D P j E E F F D F k D E Locker LESSON 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation
23.1 Perpendicular Bisectors of Triangles
 Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
10.5 Perimeter and Area on the Coordinate Plane
 Name lass ate 1.5 Perimeter and rea on the oordinate Plane ssential Question: How do ou find the perimeter and area of polgons in the coordinate plane? Resource Locker plore inding Perimeters of igures
Name lass ate 1.5 Perimeter and rea on the oordinate Plane ssential Question: How do ou find the perimeter and area of polgons in the coordinate plane? Resource Locker plore inding Perimeters of igures
5.2 ASA Triangle Congruence
 Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the
 Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the 4 Coordinate Plane WARM UP Determine each product. 1. 21 3 6 2. 2 3 5 (21) LEARNING GOALS Reflect geometric figures on the coordinate plane. Identif and describe
Mirror, Mirror Reflections of Figures on the 4 Coordinate Plane WARM UP Determine each product. 1. 21 3 6 2. 2 3 5 (21) LEARNING GOALS Reflect geometric figures on the coordinate plane. Identif and describe
Reflections and Translations
 Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram ABC was translated to parallelogram A B C. 2. Alyssa made the design shown below. How many units and in which direction were the x-coordinates of parallelogram ABC moved? A.
Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram ABC was translated to parallelogram A B C. 2. Alyssa made the design shown below. How many units and in which direction were the x-coordinates of parallelogram ABC moved? A.
Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane
 Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane 5 WARM UP 1. Redraw each given figure as described. a. so that it is turned 10 clockwise Before: After: s D b. so that it is turned
Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane 5 WARM UP 1. Redraw each given figure as described. a. so that it is turned 10 clockwise Before: After: s D b. so that it is turned
Size Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Size Transformations in the Coordinate Plane I.e. Dilations (adapted from Core Plus Math, Course 2) Concepts 21-26 Lesson Objectives In this investigation you will use coordinate methods to discover several
Size Transformations in the Coordinate Plane I.e. Dilations (adapted from Core Plus Math, Course 2) Concepts 21-26 Lesson Objectives In this investigation you will use coordinate methods to discover several
6.2 AAS Triangle Congruence
 Name lass ate 6. S Triangle ongruence ssential Question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell ou about two triangles? xplore G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent b appling the ngle-ngle-side
Name lass ate 6. S Triangle ongruence ssential Question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell ou about two triangles? xplore G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent b appling the ngle-ngle-side
Reflecting Any Points on the Coordinate Plane
 ACTIVITY 4.2 Reflecting An Points on the Coordinate Plane NOTES Consider the point (, ) located anwhere in the first quadrant. (, ) 0 1. Use the table to record the coordinates of each point. a. Reflect
ACTIVITY 4.2 Reflecting An Points on the Coordinate Plane NOTES Consider the point (, ) located anwhere in the first quadrant. (, ) 0 1. Use the table to record the coordinates of each point. a. Reflect
Chapter 8 Transformations and Congruence
 Lesson 8-1 Translations Page 559 Graph ABC with vertices A(1, 2), B(3, 1), and C(3, 4). Then graph the image of the triangle after it is translated 2 units left and 1 unit up, and write the coordinates
Lesson 8-1 Translations Page 559 Graph ABC with vertices A(1, 2), B(3, 1), and C(3, 4). Then graph the image of the triangle after it is translated 2 units left and 1 unit up, and write the coordinates
4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations
 4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations Identify Congruence Transformations A congruence transformation is a transformation where the original figure, or preimage, and the transformed
4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations Identify Congruence Transformations A congruence transformation is a transformation where the original figure, or preimage, and the transformed
9.3 Properties of Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares
 Name lass Date 9.3 Properties of Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares Essential Question: What are the properties of rectangles, rhombuses, and squares? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Sides, ngles, and
Name lass Date 9.3 Properties of Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares Essential Question: What are the properties of rectangles, rhombuses, and squares? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Sides, ngles, and
9.2 Conditions for Parallelograms
 Name lass ate 9.2 onditions for Parallelograms Essential Question: What criteria can you use to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? Explore G.6.E Prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram...
Name lass ate 9.2 onditions for Parallelograms Essential Question: What criteria can you use to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? Explore G.6.E Prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram...
ACTIVITY: Frieze Patterns and Reflections. a. Is the frieze pattern a reflection of itself when folded horizontally? Explain.
 . Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
. Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal. ESSENTIAL QUESTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal?
 ? LSSON 7.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal SSNTIL QUSTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal? xpressions, equations, and relationships Use
? LSSON 7.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal SSNTIL QUSTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal? xpressions, equations, and relationships Use
How can you enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate. ACTIVITY: Comparing Triangles in a Coordinate Plane.
 . Dilations How can ou enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate When ou have our ees checked, the optometrist sometimes dilates one or both of the pupils of our ees. ACTIVITY: Comparing
. Dilations How can ou enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate When ou have our ees checked, the optometrist sometimes dilates one or both of the pupils of our ees. ACTIVITY: Comparing
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 * Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Vocabulary Transformation- changes the position or orientation of a figure. Image- the resulting figure after a transformation. Preimage- the original figure.
* Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Vocabulary Transformation- changes the position or orientation of a figure. Image- the resulting figure after a transformation. Preimage- the original figure.
Practice For use with pages
 9. For use with pages 598 605 Use the translation (, ) ( 6, 3).. What is the image of (3, )?. What is the image of (4, )? 3. What is the preimage of 9(, 7)? 4. What is the preimage of 9(3, )? The vertices
9. For use with pages 598 605 Use the translation (, ) ( 6, 3).. What is the image of (3, )?. What is the image of (4, )? 3. What is the preimage of 9(, 7)? 4. What is the preimage of 9(3, )? The vertices
The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations
 The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations that are rigid motions and characteristics of transformations
The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations that are rigid motions and characteristics of transformations
14-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
L3 Rigid Motion Transformations 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date
 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date Pre-Assessment Which of the following could represent a translation using the rule T (, ) = (, + 4), followed b a reflection over the given line? (The pre-image
3.1 Sequences of Transformations Per Date Pre-Assessment Which of the following could represent a translation using the rule T (, ) = (, + 4), followed b a reflection over the given line? (The pre-image
Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane 1. As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A B C D E F. Under this transformation,
Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane 1. As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A B C D E F. Under this transformation,
Understanding Reflections
 Lesson 18 Understanding Reflections 8.G.1.a, 8.G.1.b, 8.G.1.c, 8.G., 8.G.3 1 Getting the idea A reflection is a tpe of transformation in which ou flip a figure across a line called the line of reflection.
Lesson 18 Understanding Reflections 8.G.1.a, 8.G.1.b, 8.G.1.c, 8.G., 8.G.3 1 Getting the idea A reflection is a tpe of transformation in which ou flip a figure across a line called the line of reflection.
7.3 Triangle Inequalities
 Locker LESSON 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: G.5.D Verify the Triangle Inequality theorem using constructions and apply
Locker LESSON 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: G.5.D Verify the Triangle Inequality theorem using constructions and apply
15.2 Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals
 Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Rotations. Essential Question How can you rotate a figure in a coordinate plane?
 11.3 Rotations Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate lane ONSTRUTING VILE RGUMENTS To be proficient in math, ou need to use previousl established
11.3 Rotations Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate lane ONSTRUTING VILE RGUMENTS To be proficient in math, ou need to use previousl established
You can demonstrate the congruence of two figures by using a rigid motion or a sequence of rigid motions to make the figures coincide.
 18 LESSON roperties of Rotations, Reflections, and Translations UNERSTN rigid motion changes the position of a figure without changing its shape or size. sequence of rigid motions can transform a figure
18 LESSON roperties of Rotations, Reflections, and Translations UNERSTN rigid motion changes the position of a figure without changing its shape or size. sequence of rigid motions can transform a figure
Name: Date: Period: Score: Linear Algebra Chapters 7, 8, & 9 Study Guide
 1. Triangle ABC is shown on the coordinate grid. 3. Use the parallelogram shown in the coordinate plane to answer each question. Translate 3 units horizontally. Label the image. How are the values in the
1. Triangle ABC is shown on the coordinate grid. 3. Use the parallelogram shown in the coordinate plane to answer each question. Translate 3 units horizontally. Label the image. How are the values in the
Drawing Polygons in the Coordinate Plane
 Lesson 7 Drawing Polgons in the Coordinate Plane 6.G. Getting the idea The following points represent the vertices of a polgon. A(, 0), B(0, ), C(, ), D(, ), and E(0, ) To draw the polgon, plot the points
Lesson 7 Drawing Polgons in the Coordinate Plane 6.G. Getting the idea The following points represent the vertices of a polgon. A(, 0), B(0, ), C(, ), D(, ), and E(0, ) To draw the polgon, plot the points
Reflections. Reflections in the Coordinate Plane. Translations Battleship Warm Up
 Reflections Translations Battleship Warm Up Phase : Position our battleships on our gameboard according to the following specifications: - Aircraft Carrier - rectangle, area of units, nd quadrant onl -
Reflections Translations Battleship Warm Up Phase : Position our battleships on our gameboard according to the following specifications: - Aircraft Carrier - rectangle, area of units, nd quadrant onl -
Unit 2: Transformations. 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line?
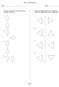 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best represents only a translation (slide) up? 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line? D. D. page 1 3.
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best represents only a translation (slide) up? 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line? D. D. page 1 3.
First published in 2013 by the University of Utah in association with the Utah State Office of Education.
 First published in 013 by the University of Utah in association with the Utah State Office of Education. opyright 013, Utah State Office of Education. Some rights reserved. This work is published under
First published in 013 by the University of Utah in association with the Utah State Office of Education. opyright 013, Utah State Office of Education. Some rights reserved. This work is published under
9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two. a) Tina s shadow is 2.4 m and the first tree s. b) Tina s shadow is 0.
 b) J 1 15 G F 9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two trees. For each tree, she stands so that one end of her shadow coincides with one end of the shadow of the tree. Tina s friend measures the lengths
b) J 1 15 G F 9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two trees. For each tree, she stands so that one end of her shadow coincides with one end of the shadow of the tree. Tina s friend measures the lengths
9-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary
 9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
Practice 8-1. Translations. Use arrow notation to write a rule that describes the translation shown on each graph.
 ame lass ate Practice 8-1 Translations Use arrow notation to write a rule that describes the translation shown on each graph. 1.. 3. Pearson ducation, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ll rights
ame lass ate Practice 8-1 Translations Use arrow notation to write a rule that describes the translation shown on each graph. 1.. 3. Pearson ducation, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ll rights
25.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals
 - - a a 6 Locker LESSON 5. Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Name Class Date 5. Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance
- - a a 6 Locker LESSON 5. Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Name Class Date 5. Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance
9-1. Reflections Going Deeper Essential question: How do you draw the image of a figure under a reflection? EXPLORE. Drawing a Reflection Image
 Nae lass ate 9-1 Reflections Going eeper Essential question: How do you draw the iage of a figure under a reflection? One type of rigid otion is a reflection. reflection is a transforation that oves points
Nae lass ate 9-1 Reflections Going eeper Essential question: How do you draw the iage of a figure under a reflection? One type of rigid otion is a reflection. reflection is a transforation that oves points
11.4 AA Similarity of Triangles
 Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore G.7. pply the ngle-ngle criterion to verify similar triangles and apply the proportionality
Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore G.7. pply the ngle-ngle criterion to verify similar triangles and apply the proportionality
6.3 HL Triangle Congruence
 Name lass ate 6.3 HL Triangle ongruence Essential Question: What does the HL Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about two triangles? Explore Is There a Side-Side-ngle ongruence Theorem? Resource Locker
Name lass ate 6.3 HL Triangle ongruence Essential Question: What does the HL Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about two triangles? Explore Is There a Side-Side-ngle ongruence Theorem? Resource Locker
Unit 5 Lesson 2 Investigation 1
 Name: Investigation 1 Modeling Rigid Transformations CPMP-Tools Computer graphics enable designers to model two- and three-dimensional figures and to also easil manipulate those figures. For eample, interior
Name: Investigation 1 Modeling Rigid Transformations CPMP-Tools Computer graphics enable designers to model two- and three-dimensional figures and to also easil manipulate those figures. For eample, interior
11.4 AA Similarity of Triangles
 Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore xploring ngle-ngle Similarity for Triangles Two triangles are similar when their corresponding
Name lass ate 11.4 Similarity of Triangles ssential Question: How can you show that two triangles are similar? xplore xploring ngle-ngle Similarity for Triangles Two triangles are similar when their corresponding
Plot and connect the points in a coordinate plane to make a polygon. Name the polygon.
 . Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
. Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
Performing Congruence and Similarity Transformations. C m
 9 ig Idea HPTER SUMMRY IG IES Performing ongruence and Similarit Transformations For Your Notebook Translation Translate a figure right or left, up or down. Reflection Reflect a figure in a line. 9 9 9
9 ig Idea HPTER SUMMRY IG IES Performing ongruence and Similarit Transformations For Your Notebook Translation Translate a figure right or left, up or down. Reflection Reflect a figure in a line. 9 9 9
1ACE Exercise 17. Name Date Class. 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry?
 1ACE Exercise 17 Investigation 1 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry? HINT Rotation symmetry means you can turn the object around its center to a position in which it looks the same as the
1ACE Exercise 17 Investigation 1 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry? HINT Rotation symmetry means you can turn the object around its center to a position in which it looks the same as the
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Applications. 44 Stretching and Shrinking
 Applications 1. Look for rep-tile patterns in the designs below. For each design, tell whether the small quadrilaterals are similar to the large quadrilateral. Explain. If the quadrilaterals are similar,
Applications 1. Look for rep-tile patterns in the designs below. For each design, tell whether the small quadrilaterals are similar to the large quadrilateral. Explain. If the quadrilaterals are similar,
ASA Triangle Congruence
 Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Transformations & Basic Geometry Vocabulary
 Transformations & Basic Geometry Vocabulary Key Terms and Concepts Name: Date: Period: Rigid Transformations Toolkit Key Vocabulary- Give a precise definition of each term Parallel lines: Perpendicular
Transformations & Basic Geometry Vocabulary Key Terms and Concepts Name: Date: Period: Rigid Transformations Toolkit Key Vocabulary- Give a precise definition of each term Parallel lines: Perpendicular
1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints
 1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints Essential Question: How do you draw a segment and measure its length? Explore Exploring asic Geometric Terms In geometry, some of the names of figures and other terms will
1.1 Segment Length and Midpoints Essential Question: How do you draw a segment and measure its length? Explore Exploring asic Geometric Terms In geometry, some of the names of figures and other terms will
Describe Plane Shapes
 Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13. Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
Transformation Packet
 Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Rising, Running, Stepping, Scaling Dilating Figures on the Coordinate Plane
 Rising, Running, Stepping, Scaling Dilating Figures on the Coordinate Plane WRM UP Scale up or scale down to determine the value of the variable in each equivalent ratio. 1. 3 : 1 5 5.5 : z. : 5 5 a :
Rising, Running, Stepping, Scaling Dilating Figures on the Coordinate Plane WRM UP Scale up or scale down to determine the value of the variable in each equivalent ratio. 1. 3 : 1 5 5.5 : z. : 5 5 a :
Symmetry Transformations
 Symmetry Transformations You can make symmetric designs by copying a basic figure to produce a balanced pattern. For example, to construct a design with reflection symmetry, start with pentagon and line
Symmetry Transformations You can make symmetric designs by copying a basic figure to produce a balanced pattern. For example, to construct a design with reflection symmetry, start with pentagon and line
2.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals
 Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Relationships and Graphs 7.4.A. Graphing Proportional Relationships You can use a graph to explore proportional relationships.
 ? LESSN.3 Proportional Relationships and Graphs ESSENTIAL QUESTIN Proportionality 7..A Represent constant rates of change in mathematical and real-world problems given pictorial, tabular, verbal, numeric,
? LESSN.3 Proportional Relationships and Graphs ESSENTIAL QUESTIN Proportionality 7..A Represent constant rates of change in mathematical and real-world problems given pictorial, tabular, verbal, numeric,
9 3 Rotations 9 4 Symmetry
 h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
Additional Practice. Name Date Class. 1. Which of these angles are acute, which are obtuse, and which are right? a. b. c. d. e. f. Shapes and Designs
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. Which of these angles are acute, which are obtuse, and which are right? a. b. c. d. e. f. 1 Additional Practice (continued) Investigation 1 2. Use the diagram of
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. Which of these angles are acute, which are obtuse, and which are right? a. b. c. d. e. f. 1 Additional Practice (continued) Investigation 1 2. Use the diagram of
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Patterns are pleasing to the eye. They are used by designers, architects, and engineers to make their products more attractive. Look at the quilt pattern. Which figures are used as quilt blocks? Which
Patterns are pleasing to the eye. They are used by designers, architects, and engineers to make their products more attractive. Look at the quilt pattern. Which figures are used as quilt blocks? Which
19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions
 Name Class Date 19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions Essential Question: What is the effect of the constant a on the graph of f () = a? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding the Parent Quadratic Function
Name Class Date 19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions Essential Question: What is the effect of the constant a on the graph of f () = a? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding the Parent Quadratic Function
19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions
 Name Class Date 19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions Essential Question: What is the effect of the constant a on the graph of f () = a? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding the Parent Quadratic Function
Name Class Date 19.1 Understanding Quadratic Functions Essential Question: What is the effect of the constant a on the graph of f () = a? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding the Parent Quadratic Function
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
7.3 Triangle Inequalities
 Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Resource Locker Explore Exploring
Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Resource Locker Explore Exploring
Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles
 7 5.G.1 5.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles Students can be expected to examine the features of a variety of shapes, such as quadrilaterals,
7 5.G.1 5.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles Students can be expected to examine the features of a variety of shapes, such as quadrilaterals,
Transformations. Transformations. Reflections. Rotations. Composition of Transformations
 Reflections Rotations omposition of Transformations ongruence Transformations ilations Similarity Transformations Transformations Transformations transformation of a geometric figure is a mapping that
Reflections Rotations omposition of Transformations ongruence Transformations ilations Similarity Transformations Transformations Transformations transformation of a geometric figure is a mapping that
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 OMMON ORE Locker LESSON ommon ore Math Standards The student is expected to: OMMON ORE G-O..10 Prove theorems about triangles. Mathematical Practices OMMON ORE 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles MP.3
OMMON ORE Locker LESSON ommon ore Math Standards The student is expected to: OMMON ORE G-O..10 Prove theorems about triangles. Mathematical Practices OMMON ORE 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles MP.3
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
Number of sides Name of polygon Least number of Interior angle sum 3 Triangle
 Name: Period: 6.1 Polygon Sum Polygon: a closed plane figure formed by three or more segments that intersect only at their endpoints. Are these polygons? If so, classify it by the number of sides. 1) 2)
Name: Period: 6.1 Polygon Sum Polygon: a closed plane figure formed by three or more segments that intersect only at their endpoints. Are these polygons? If so, classify it by the number of sides. 1) 2)
Skill: Polygons. Vocabulary: Polygon a closed two-dimensional figure with straight edges
 Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Isometries and Congruence
 Honors Geometr Section.1 Name: Date: Period: Isometries and Congruence transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape, or size.. The original figure is called the preimage. The
Honors Geometr Section.1 Name: Date: Period: Isometries and Congruence transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape, or size.. The original figure is called the preimage. The
Geometry. Transformations. Slide 1 / 154 Slide 2 / 154. Slide 4 / 154. Slide 3 / 154. Slide 6 / 154. Slide 5 / 154. Transformations.
 Slide 1 / 154 Slide 2 / 154 Geometry Transformations 2014-09-08 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 154 Slide 4 / 154 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Transformations Translations Reflections
Slide 1 / 154 Slide 2 / 154 Geometry Transformations 2014-09-08 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 154 Slide 4 / 154 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Transformations Translations Reflections
15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals
 ? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
Chapter 2: Transformations. Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1
 Chapter 2: Transformations Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1 Unit 2: Vocabulary 1) transformation 2) pre-image 3) image 4) map(ping) 5) rigid motion (isometry) 6) orientation 7) line reflection 8) line
Chapter 2: Transformations Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1 Unit 2: Vocabulary 1) transformation 2) pre-image 3) image 4) map(ping) 5) rigid motion (isometry) 6) orientation 7) line reflection 8) line
