A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L 1 Optical Flow
|
|
|
- Clementine Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Duality Base Approach for Realtime TV-L 1 Optical Flow C. Zach 1, T. Pock 2, an H. Bischof 2 1 VRVis Research Center 2 Institute for Computer Graphics an Vision, TU Graz Abstract. Variational methos are among the most successful approaches to calculate the optical flow between two image frames. A particularly appealing formulation is base on total variation (TV) regularization an the robust L 1 norm in the ata fielity term. This formulation can preserve iscontinuities in the flow fiel an offers an increase robustness against illumination changes, occlusions an noise. In this work we present a novel approach to solve the TV-L 1 formulation. Our metho results in a very efficient numerical scheme, which is base on a ual formulation of the TV energy an employs an efficient point-wise thresholing step. Aitionally, our approach can be accelerate by moern graphics processing units. We emonstrate the real-time performance (30 fps) of our approach for vieo inputs at a resolution of pixels. 1 Introuction The recovery of motion from images is a major task of biological an artificial vision systems. The main objective of optical flow methos is to compute a flow fiel estimating the motion of pixels in two consecutive image frames. Since optical flow is an highly ill-pose inverse problem, using pure intensity-base constraints generally results in an uner-etermine system of equations, which is generally known as the aperture problem. In orer to solve this problem some kin of regularization is neee to obtain physically meaningful isplacement fiels. In their seminal work [13], Horn an Schunck stuie a variational formulation of the optical flow problem. { } min u u λ (I 1 (x + u(x)) I 0 (x)) 2. (1) u I 0 an I 1 is the image pair, u = (u 1 (x), u 2 (x)) T is the two-imensional isplacement fiel an λ is a free parameter. The first term (regularization term) penalizes high variations in u to obtain smooth isplacement fiels. The secon term (ata term) is also known as the optical flow constraint. It assumes, that the intensity values of I 0 (x) o not change uring its motion to I 1 (x + u(x)).
2 Since the Horn-Schunck moel penalizes eviations in a quaratic way, it has two major limitations. It oes not allow for iscontinuities in the isplacement fiel, an it oes not hanle outliers in the ata term robustly. To overcome these limitations, several moels incluing robust error norms an higher orer ata terms have been propose. Since iscontinuities in the optical flow appear often in conjunction with high image graients, several authors replace the homogeneous regularization in the Horn-Schunck moel with an anisotropic iffusion approach [15, 19]. Other propose moifications substitute the square penalty functions in the Horn-Schunck moel with more robust variants. Blake an Ananan [5] apply estimators from robust statistics an obtain a robust an iscontinuity preserving formulation for the optical flow energy. Aubert et al. [3] analyze energy functionals for optical flow incorporating an L 1 ata fielity term an a general class of iscontinuity preserving regularization forces. Papenberg et al. [16] employ a ifferentiable approximation of the TV (resp. L 1 ) norm an formulate a neste iteration scheme to compute the isplacement fiel. Most approaches for optical flow computation replace the nonlinear intensity profile I 1 (x + u(x)) by a first orer Taylor approximation to linearize the problem locally. Since such approximation is only vali for small isplacements, aitional techniques are require to etermine the optical flow correctly for large isplacements. Scale-space approaches [1] an coarse-to-fine warping (e.g. [2, 14, 7]) provie solutions to optical flow estimation with large isplacements. In several applications, such as autonomous robot navigation, it is necessary to calculate isplacement fiels in real-time. Real-time optical flow techniques typically consier only the ata fielity term to generate isplacement fiels [10, 18]. One of the first variational approaches to compute the optical flow in realtime was presente by Bruhn et al. [8, 9]. In their work a highly efficient multigri approach is employe to obtain real-time or near real-time performance. The aim of their approach is very similar to our objective: obtaining robust an iscontinuity preserving solutions for optical flow with highly efficient implementations. Nevertheless, we utilize a completely ifferent solution strategy as escribe in the next sections. 2 TV-L 1 Optical Flow In the basic setting two image frames I 0 an I 1 : ( R 2 ) R are given. The objective is to fin the isparity map u : R 2, which minimizes an imagebase error criterion together with a regularization force. In this work we focus on the plain intensity ifference between pixels as the image similarity score. Hence, the target isparity map u is the minimizer of { } λφ (I 0 (x) I 1 (x + u(x))) + ψ(u, u,...) x, (2) where φ (I 0 (x) I 1 (x + u(x))) is the image ata fielity, an ψ(u, u,...) epicts the regularization term inucing the shape prior. λ weights between the
3 ata fielity an the regularization force. Selecting φ(x) = x 2 an ψ( u) = u 2 results in the Horn-Schunck moel [13]. The choice of φ(x) = x an ψ( u)) = u yiels to the following functional consisting of an L 1 ata penalty term an total variation regularization: E = { } λ I 0 (x) I 1 (x + u(x)) + u x. (3) Although Eq. 3 seems to be simple, it offers some computational ifficulties. The main reason is that both the regularization term an the ata term are not continuously ifferentiable. One approach is to replace φ(x) = x an ψ( u) with ifferentiable approximations φ ε (x 2 ) = x 2 + ε 2 an ψ ε ( u) = u 2 + ε 2, an to apply a numerical optimization technique on this slightly moifie functional (e.g. [12, 7]). In this paper we employ a rather ifferent approach. In [11] Chambolle propose an efficient an exact numerical scheme to solve the Ruin-Osher-Fatemi energy [17] for total variation base image enoising. In the following, we will escribe how to aopt this approach for the optical flow case. 2.1 The 1D Stereo Case In this section we restrict the isparities to be non-zero only in the horizontal irection, e.g. a normalize stereo image pair is provie. Hence, u(x) reuces to a scalar u(x), an we use the (sloppy) notation x + u(x) for x + (u(x), 0) T. The following erivation is base on [4], but aapte to the stereo/optical flow setting. At first, we linearize image I 1 near x + u 0, i.e. I 1 (x + u) = I 1 (x + u 0 ) + (u u 0 ) I x 1 (x + u 0 ), where u 0 is a given isparity map an I1 x is the erivative of the image intensity I 1 wrt. the x-irection. Using the first orer Taylor approximation for I 1 means, that the following proceure nees to be embee into an iterative warping approach to compensate for image nonlinearities. Aitionally, a multi-level approach is employe to allow large isparities between the images. For fixe u 0 an using the linear approximation for I 1, the TV-L 1 functional (Eq. 3) now reas as: E = { } λ u I1 x + I 1 (x + u 0 ) u 0 I1 x I 0 + u x. (4) In the following, we enote the current resiual I 1 (x + u 0 ) + (u u 0 ) I1 x I 0 by ρ(u, u 0, x) (or just ρ(u) by omitting the explicit epenency on u 0 an x). Moreover, we introuce an auxiliary variable v an propose to minimize the following convex approximation of Eq. 4: { E θ = u + 1 } 2θ (u v)2 + λ ρ(v) x, (5)
4 where θ is a small constant, such that v is a close approximation of u. This convex minimization problem can be optimize by alternating steps upating either u or v in every iteration: 1. For v being fixe, solve min u { u + 12θ } (u v)2 x. (6) This is the total variation base image enoising moel of Ruin, Osher an Fatemi [17]. 2. For u being fixe, solve min v { } 1 2θ (u v)2 + λ ρ(v) x. (7) This minimization problem can be solve point-wise, since it oes not epen on spatial erivatives of v. An efficient solution for the first step (Eq. 6) was propose in [11], which uses a ual formulation of Eq. 6 to erive an efficient an globally convergent scheme. Since this algorithm is an essential part of our metho, we reprouce the relevant results from [11]: Proposition 1 The solution of Eq. (6) is given by where p = (p 1, p 2 ) fulfills u = v θ iv p, (8) (θ iv p v) = (θ iv p v) p, (9) which can be solve by the following iterative fixe-point scheme: where p 0 = 0 an the time step τ 1/8. p k+1 = p k + τ (iv p k v/θ) 1 + τ (iv p k v/θ), (10) The next proposition characterizes the minimizer of the secon part (Eq. 7): Proposition 2 The solution of the minimization task in Eq. 7 is given by the following thresholing step: λ θ I1 x if ρ(u) < λ θ (I1 x ) 2 v = u + λ θ I1 x if ρ(u) > λ θ (I1 x ) 2 (11) ρ(u)/i1 x if ρ(u) λ θ (I1 x ) 2. This means, that the image resiual ρ(v) is allowe to vanish, if the require step from u to v is sufficiently small. Otherwise, v makes a boune step from u, such that the magnitue of the resiual ecreases. The proposition above can be shown irectly by analyzing the three possible cases, ρ(v) > 0 (inucing v = u λ θ I x 1 ), ρ(v) < 0 (v = u + λ θ I x 1 ) an ρ(v) = 0 (v = u ρ(u)/i x 1 ).
5 2.2 Generalization to Higher Dimensions In this section we exten the metho introuce in the previous section to optical flow estimation, i.e. an N-imensional isplacement map u is etermine from two given N-D images I 0 an I 1. The first orer image resiual ρ(u, u 0, x) wrt. a given isparity map u 0 is now I 1 (x+u 0 )+ I 1, u u 0 I 0 (x). Aitionally, we write u for the -th component of u ( {1,..., N}). The generalization of Eq. 5 to more imensions is the following energy: E θ = { u + 1 2θ (u v ) 2 + λ ρ(v) } x. (12) Similar to the stereo setting, minimizing this energy can be performe by alternating optimization steps: 1. For every an fixe v, solve min { u + u 12θ } (u v ) 2 x. (13) This minimization problem is ientical to Eq. 6 an can be solve by the same proceure. Note, that the ual variables are introuce for every imension, e.g. Eq. 8 now reas as u = v θ iv p. (14) 2. For u being fixe, solve min v 1 2θ (u v ) 2 + λ ρ(v). (15) The following proposition generalizes the thresholing step from Proposition 2 to higher imensions: Proposition 3 The solution of the minimization task in Eq. 15 is given by the following thresholing step: λ θ I 1 if ρ(u) < λ θ I 1 2 v = u + λ θ I 1 if ρ(u) > λ θ I 1 2 (16) ρ(u) I 1 / I 1 2 if ρ(u) λ θ I 1 2. This proposition essentially states, that the N-imensional optimization problem can be reuce to a one-imensional thresholing step, since v always lies on the line l going through u with irection I 1 (for every x). This can be seen as follows: The first part in Eq. 15, (u v ) 2 /2θ, is basically the square istance of v to u, an the secon part, λ ρ(v), is the unsigne istance to the line l : ρ(w) = 0, i.e. I 1 (x + u 0 ) + I 1, w u 0 I 0 (x) = 0. If we consier all v µ with a fixe istance µ to u, then the functional in Eq. 15 is minimize for the v µ closest to the line l (with minimal normal istance). This is also vali for the true minimizer, hence the optimum for Eq. 15 is on l. In aition, the one-imensional thresholing step in graient irection can be applie (Proposition 2), resulting in the presente scheme.
6 3 Implementation This section gives etails on the employe numerical proceure an on the GPUaccelerate implementation for the propose TV-L 1 optical flow approach. Although the iscussion in Section 2.2 is vali for any image imension N 2, our GPU-base implementation is specifically tailore for the case N = Numerical Scheme The generally non-convex energy functional for optical flow (Eq. 3) becomes a convex minimization problem after linearization of the image intensities (Eq. 4), but this linearization is only vali for small isplacements. Hence, the energy minimization proceure is embee into a coarse-to-fine approach to avoi convergence to unfavorable local minima. We employ image pyramis with a ownsampling factor of 2 for this purpose. Beginning with the coarsest level, we solve Eq. 3 at each level of the pyrami an propagate the solution to the next finer level. This solution is further use to compute the coefficients of the linear resiual function ρ by sampling I 0 an I 1 using the corresponing pyrami levels. Hence, the warping step for I 1 takes place only once per level. I 1 is approximate by central ifferences. At the beginning of a new level, v is initialize with u, an all p are set to 0. At the coarsest level, the isplacement fiel u starts with 0. Avoiing poor local minima is not the only avantage of the coarse-to-fine approach. It turns out, that the filling-in process inuce by the regularization occurring in textureless region is substantially accelerate by a hierarchical scheme as well. The minimization proceure alternates one step of the fixe-point scheme to upate all p (an therefore u, Eq. 10) with the thresholing step from Proposition 3 to improve v. The implementation of the fixe-point upate (Eq. 10) uses backwar ifferences to approximate iv p an forwar ifferences for the numerical graient computation in orer to have mutually ajoint operators [11]. 3.2 Acceleration by Graphics Processing Units Numerical methos working on regular gris, e.g. rectangular image omains, can be effectively accelerate by moern graphics processing units (GPUs). We employ the huge computational power an the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs to obtain a fully accelerate implementation of our optical flow approach. The GPU-base proceure is essentially a straightforwar Cg implementation of the numerical schemes (Eqs. 10 an 16) with few moifications escribe as follows.
7 If we write own the alternating minimization steps explicitly, iteration k performs the following upates on u, v an p : 1a. v k+1 T H(u k ) 1b. u k+1 v k+1 θ iv p k for {1, 2} 2. p k+1 pk + τ/θ uk τ/θ u k+1 for {1, 2}, (17) where T H( ) enotes the thresholing step from Eq. 16. These steps can be immeiately implemente on the GPU by appropriate fragment programs using two renering passes. 3 The first pass implements steps 1a an 1b from Eq. 17. The values v k+1 are use only temporarily within the shaer program an nee not to be save explicitly. u k+1 is written to the target texture. The secon shaer program correspons with step 2 from Eq. 17. It turns out, that the utilization of the fragment processors can be improve by upating u an p for two pixels simultaneously. The shaer programs work on the left an on the right half of the images in parallel, with appropriate hanling of borer pixels. Our implementation encoes the two components of u using full 32-bit precision, an the overall four components of p 1 an p 2 are compresse to 16-bit half precision floating point numbers. We currently use a fixe but tunable number of iterations on each level in our implementation, since etermining the maximum upate u k+1 u k still requires an expensive reuction operation even on moern GPUs. 4 Results At first, we provie timing results for our optical flow approach epicte in Table 1. Two harware setups were use to obtain the timing results: a esktop PC equippe with a NViia GeForce 7800 GS car, an a high-en laptop supplie with a NViia GeForce Go 7900 GTX graphics boar. The timing results were obtaine uner the Linux operating system with recent OpenGL graphics rivers an the Cg 1.5 toolkit. The timings in Table 1 are given in frames per secon for the epicte fixe number of iterations on each level of the image pyrami. The measure times inclue the texture uploas to vieo memory an the final visualization of the obtaine isplacement fiel. The timing results inicate, that real-time performance with more than 30 frames per secon can be achieve at pixels resolution with our approach. Frames from a live vieo emo application are shown in Figure 1, which continuously reas images from a firewire camera an visualizes the optical flow for ajacent frames. Real-time performance can be achieve with the mobile harware setup. Figure 2 shows common test sequences for optical flow, in particular the Ettlinger Tor, the Rheinhafen an the Yosemite sequences, an their respective flow 3 A single pass variant using only one shaer program is possible as well, but the observe performance is inferior in almost all cases.
8 GeForce 7800 GS GeForce Go 7900 GTX Image resolution 50 It It Table 1. Observe frame rates at ifferent image resolutions an with varying number of iterations on our teste harware. (a) First frame (b) Secon frame (c) Optical flow fiel Fig. 1. Capture frames an generate optical flow fiel using our live vieo application. The image resolution is , an 50 iterations are performe on each level of the image pyrami. The framerate is close to 30 frames per secon in this setting. The flow fiel is visualize using hue to inicate the irection an intensity for the magnitue. fiels. The results for these atasets inicate, that the reuce 16-bit resolution for the ual variables p oes not severely affect the quality of the obtaine flow fiels. Table 2 specifies the obtaine average angular error (AAE) of the flow fiel for the Yosemite ataset wrt. the provie groun truth. If the completely homogeneous sky region is exclue from the AAE calculation, the flow fiel is essentially converge after 50 iterations. Enabling more iterations yiels to slightly inferior results, since the TV-L 1 energy favors piecewise constant flow fiels in the limit. If the sky region is inclue in the evaluation, the AAE error ecreases by increasing the number of iterations. In this case the flow fiel in the sky region converges relatively slowly to the zero isplacement. 50 It Without sky With sky Table 2. Average angular error for frame 8 an 9 of the Yosemite sequence at ifferent number of iterations.
9 (a) Frame 5 (b) Frame 6 (c) Flow fiel, 9.3 fps () Frame 1130 (e) Frame 1131 (f) Flow fiel, 29.1 fps (g) Frame 8 (h) Frame 9 (i) Flow fiel, 27.2 fps Fig. 2. Sample images an obtaine flow fiels for the Ettlinger Tor ( pixels), the Rheinhafen ( pixels) an the Yosemite ( pixels) sequences. 5 Conclusion We presente a novel approach for efficient optical flow estimation using a TV- L 1 energy functional. We evelope a novel fast numerical scheme which can be efficiently implemente on moern graphics processing units. With this we can show real-time performance using online vieo streams. The correctness an quality of our implementation is emonstrate on several atasets. Future work inclues the extension of our approach to hanle color images as well. Aitionally, other image similarity measures, e.g. base on intensity graients, nee to be further explore. The ege preserving nature of total variation can be enhance, if a suitable weighte TV-norm/active contour moel is applie [6]. Future work will aress the incorporation of these feature for stereo an optical flow estimation. Finally, switching from an OpenGL-base implementation to the newer CUDA GPU programming framework is expecte to increase the observe performance substantially.
10 References 1. L. Alvarez, J. Weickert, an J. Sánchez. A scale-space approach to nonlocal optical flow calculations. In Proceeings of the Secon International Conference on Scale- Space Theories in Computer Vision, pages , P. Ananan. A computational framework an an algorithm for the measurement of visual motion. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 2: , G. Aubert, R. Deriche, an P. Kornprobst. Computing optical flow via variational techniques. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 60(1): , J.-F. Aujol, G. Gilboa, T. Chan, an S. Osher. Structure-texture image ecomposition moeling, algorithms, an parameter selection. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 67(1): , M.J. Black an P. Ananan. A framework for the robust estimation of optical flow. In ICCV93, pages , X. Bresson, S. Eseoglu, P. Vanergheynst, J. Thiran, an S. Osher. Fast Global Minimization of the Active Contour/Snake Moel. Journal of Mathematical Imaging an Vision, T. Brox, A. Bruhn, N. Papenberg, an J. Weickert. High accuracy optical flow estimation base on a theory for warping. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 25 36, A. Bruhn, J. Weickert, C. Feern, T. Kohlberger, an C. Schnörr. Variational optical flow computation in real time. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 14(5): , A. Bruhn, J. Weickert, T. Kohlberger, an C. Schnörr. A multigri platform for real-time motion computation with iscontinuity-preserving variational methos. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 70(3): , T. A. Camus. Real-time quantize optical flow. Journal of Real-Time Imaging, 3:71 86, Special Issue on Real-Time Motion Analyis. 11. A. Chambolle. An algorithm for total variation minimization an applications. Journal of Mathematical Imaging an Vision, 20(1 2):89 97, T. F. Chan, G. H. Golub, an P. Mulet. A nonlinear primal-ual metho for total variation-base image restoration. In ICAOS 96 (Paris, 1996),, volume 219, pages , B.K.P. Horn an B.G. Schunck. Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence, 17: , E. Mémin an P. Pérez. Hierarchical estimation an segmentation of ense motion fiels. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 46(2): , H.-H. Nagel an W. Enkelmann. An investigation of smoothness constraints for the estimation of isplacement vector fiels from image sequences. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis an Machine Intelligence (PAMI), 8: , N. Papenberg, A. Bruhn, T. Brox, S. Dias, an J. Weickert. Highly accurate optic flow computation with theoretically justifie warping. Int l J. Computer Vision, pages , L. I. Ruin, S. Osher, an E. Fatemi. Nonlinear total variation base noise removal algorithms. Physica D, 60: , R. Strzoka an C. Garbe. Real-time motion estimation an visualization on graphics cars. In IEEE Visualization 2004, pages , J. Weickert an T. Brox. Diffusion an regularization of vector- an matrix-value images. Inverse Problems, Image Analysis an Meical Imaging. Contemporary Mathematics, 313: , 2002.
A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration
 A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration Thomas Pock 1, Martin Urschler 1, Christopher Zach 2, Reinhard Beichel 3, and Horst Bischof 1 1 Institute for Computer Graphics & Vision,
A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration Thomas Pock 1, Martin Urschler 1, Christopher Zach 2, Reinhard Beichel 3, and Horst Bischof 1 1 Institute for Computer Graphics & Vision,
Shift-map Image Registration
 Shift-map Image Registration Linus Svärm Petter Stranmark Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Lun University {linus,petter}@maths.lth.se Abstract Shift-map image processing is a new framework base on energy
Shift-map Image Registration Linus Svärm Petter Stranmark Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Lun University {linus,petter}@maths.lth.se Abstract Shift-map image processing is a new framework base on energy
Shift-map Image Registration
 Shift-map Image Registration Svärm, Linus; Stranmark, Petter Unpublishe: 2010-01-01 Link to publication Citation for publishe version (APA): Svärm, L., & Stranmark, P. (2010). Shift-map Image Registration.
Shift-map Image Registration Svärm, Linus; Stranmark, Petter Unpublishe: 2010-01-01 Link to publication Citation for publishe version (APA): Svärm, L., & Stranmark, P. (2010). Shift-map Image Registration.
Notes 9: Optical Flow
 Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Dense Disparity Estimation in Ego-motion Reduced Search Space
 Dense Disparity Estimation in Ego-motion Reuce Search Space Luka Fućek, Ivan Marković, Igor Cvišić, Ivan Petrović University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering an Computing, Croatia (e-mail:
Dense Disparity Estimation in Ego-motion Reuce Search Space Luka Fućek, Ivan Marković, Igor Cvišić, Ivan Petrović University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering an Computing, Croatia (e-mail:
Transient analysis of wave propagation in 3D soil by using the scaled boundary finite element method
 Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23r Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures an Materials 214 Transient analysis of wave propagation in 3D soil by using the scale bounary finite
Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23r Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures an Materials 214 Transient analysis of wave propagation in 3D soil by using the scale bounary finite
A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration
 A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration Thomas Pock 1,MartinUrschler 1, Christopher Zach 2, Reinhard Beichel 3, and Horst Bischof 1 1 Institute for Computer Graphics & Vision,
A Duality Based Algorithm for TV-L 1 -Optical-Flow Image Registration Thomas Pock 1,MartinUrschler 1, Christopher Zach 2, Reinhard Beichel 3, and Horst Bischof 1 1 Institute for Computer Graphics & Vision,
Technion - Computer Science Department - Tehnical Report CIS
 Over-Parameterized Variational Optical Flow Tal Nir Alfred M. Bruckstein Ron Kimmel {taln, freddy, ron}@cs.technion.ac.il Department of Computer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion
Over-Parameterized Variational Optical Flow Tal Nir Alfred M. Bruckstein Ron Kimmel {taln, freddy, ron}@cs.technion.ac.il Department of Computer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion
6 Gradient Descent. 6.1 Functions
 6 Graient Descent In this topic we will iscuss optimizing over general functions f. Typically the function is efine f : R! R; that is its omain is multi-imensional (in this case -imensional) an output
6 Graient Descent In this topic we will iscuss optimizing over general functions f. Typically the function is efine f : R! R; that is its omain is multi-imensional (in this case -imensional) an output
Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Smoothing Approach for Solving a Class of Bi-Level Multiobjective Programming Problem
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 17, No 3 Sofia 017 Print ISSN: 1311-970; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-017-0030 Particle Swarm Optimization Base
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 17, No 3 Sofia 017 Print ISSN: 1311-970; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-017-0030 Particle Swarm Optimization Base
Fast Window Based Stereo Matching for 3D Scene Reconstruction
 The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 0, No. 3, May 203 209 Fast Winow Base Stereo Matching for 3D Scene Reconstruction Mohamma Mozammel Chowhury an Mohamma AL-Amin Bhuiyan Department
The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 0, No. 3, May 203 209 Fast Winow Base Stereo Matching for 3D Scene Reconstruction Mohamma Mozammel Chowhury an Mohamma AL-Amin Bhuiyan Department
Image Segmentation using K-means clustering and Thresholding
 Image Segmentation using Kmeans clustering an Thresholing Preeti Panwar 1, Girhar Gopal 2, Rakesh Kumar 3 1M.Tech Stuent, Department of Computer Science & Applications, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra,
Image Segmentation using Kmeans clustering an Thresholing Preeti Panwar 1, Girhar Gopal 2, Rakesh Kumar 3 1M.Tech Stuent, Department of Computer Science & Applications, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra,
Using the disparity space to compute occupancy grids from stereo-vision
 The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots an Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Using the isparity space to compute occupancy gris from stereo-vision Mathias Perrollaz,
The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots an Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Using the isparity space to compute occupancy gris from stereo-vision Mathias Perrollaz,
Classifying Facial Expression with Radial Basis Function Networks, using Gradient Descent and K-means
 Classifying Facial Expression with Raial Basis Function Networks, using Graient Descent an K-means Neil Allrin Department of Computer Science University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9237 nallrin@cs.ucs.eu
Classifying Facial Expression with Raial Basis Function Networks, using Graient Descent an K-means Neil Allrin Department of Computer Science University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9237 nallrin@cs.ucs.eu
Part II: Modeling Aspects
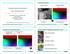 Yosemite test sequence Illumination changes Motion discontinuities Variational Optical Flow Estimation Part II: Modeling Aspects Discontinuity Di ti it preserving i smoothness th tterms Robust data terms
Yosemite test sequence Illumination changes Motion discontinuities Variational Optical Flow Estimation Part II: Modeling Aspects Discontinuity Di ti it preserving i smoothness th tterms Robust data terms
Refinement of scene depth from stereo camera ego-motion parameters
 Refinement of scene epth from stereo camera ego-motion parameters Piotr Skulimowski, Pawel Strumillo An algorithm for refinement of isparity (epth) map from stereoscopic sequences is propose. The metho
Refinement of scene epth from stereo camera ego-motion parameters Piotr Skulimowski, Pawel Strumillo An algorithm for refinement of isparity (epth) map from stereoscopic sequences is propose. The metho
Real Time On Board Stereo Camera Pose through Image Registration*
 28 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Einhoven University of Technology Einhoven, The Netherlans, June 4-6, 28 Real Time On Boar Stereo Camera Pose through Image Registration* Fai Dornaika French National
28 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Einhoven University of Technology Einhoven, The Netherlans, June 4-6, 28 Real Time On Boar Stereo Camera Pose through Image Registration* Fai Dornaika French National
Multimodal Stereo Image Registration for Pedestrian Detection
 Multimoal Stereo Image Registration for Peestrian Detection Stephen Krotosky an Mohan Trivei Abstract This paper presents an approach for the registration of multimoal imagery for peestrian etection when
Multimoal Stereo Image Registration for Peestrian Detection Stephen Krotosky an Mohan Trivei Abstract This paper presents an approach for the registration of multimoal imagery for peestrian etection when
Motion Estimation with Adaptive Regularization and Neighborhood Dependent Constraint
 0 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications Motion Estimation with Adaptive Regularization and Neighborhood Dependent Constraint Muhammad Wasim Nawaz, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum, Son Lam Phung ICT
0 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications Motion Estimation with Adaptive Regularization and Neighborhood Dependent Constraint Muhammad Wasim Nawaz, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum, Son Lam Phung ICT
Robust Camera Calibration for an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
 obust Camera Calibration for an Autonomous Unerwater Vehicle Matthew Bryant, Davi Wettergreen *, Samer Aballah, Alexaner Zelinsky obotic Systems Laboratory Department of Engineering, FEIT Department of
obust Camera Calibration for an Autonomous Unerwater Vehicle Matthew Bryant, Davi Wettergreen *, Samer Aballah, Alexaner Zelinsky obotic Systems Laboratory Department of Engineering, FEIT Department of
Exercises of PIV. incomplete draft, version 0.0. October 2009
 Exercises of PIV incomplete raft, version 0.0 October 2009 1 Images Images are signals efine in 2D or 3D omains. They can be vector value (e.g., color images), real (monocromatic images), complex or binary
Exercises of PIV incomplete raft, version 0.0 October 2009 1 Images Images are signals efine in 2D or 3D omains. They can be vector value (e.g., color images), real (monocromatic images), complex or binary
Video Super Resolution using Duality Based TV-L 1 Optical Flow
 Video Super Resolution using Duality Based TV-L 1 Optical Flow Dennis Mitzel 1,2, Thomas Pock 3, Thomas Schoenemann 1 Daniel Cremers 1 1 Department of Computer Science University of Bonn, Germany 2 UMIC
Video Super Resolution using Duality Based TV-L 1 Optical Flow Dennis Mitzel 1,2, Thomas Pock 3, Thomas Schoenemann 1 Daniel Cremers 1 1 Department of Computer Science University of Bonn, Germany 2 UMIC
Estimation of large-amplitude motion and disparity fields: Application to intermediate view reconstruction
 c 2000 SPIE. Personal use of this material is permitte. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for avertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or
c 2000 SPIE. Personal use of this material is permitte. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for avertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or
A Plane Tracker for AEC-automation Applications
 A Plane Tracker for AEC-automation Applications Chen Feng *, an Vineet R. Kamat Department of Civil an Environmental Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA * Corresponing author (cforrest@umich.eu)
A Plane Tracker for AEC-automation Applications Chen Feng *, an Vineet R. Kamat Department of Civil an Environmental Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA * Corresponing author (cforrest@umich.eu)
Bends, Jogs, And Wiggles for Railroad Tracks and Vehicle Guide Ways
 Ben, Jogs, An Wiggles for Railroa Tracks an Vehicle Guie Ways Louis T. Klauer Jr., PhD, PE. Work Soft 833 Galer Dr. Newtown Square, PA 19073 lklauer@wsof.com Preprint, June 4, 00 Copyright 00 by Louis
Ben, Jogs, An Wiggles for Railroa Tracks an Vehicle Guie Ways Louis T. Klauer Jr., PhD, PE. Work Soft 833 Galer Dr. Newtown Square, PA 19073 lklauer@wsof.com Preprint, June 4, 00 Copyright 00 by Louis
Skyline Community Search in Multi-valued Networks
 Syline Community Search in Multi-value Networs Rong-Hua Li Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing, China lironghuascut@gmail.com Jeffrey Xu Yu Chinese University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China yu@se.cuh.eu.h
Syline Community Search in Multi-value Networs Rong-Hua Li Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing, China lironghuascut@gmail.com Jeffrey Xu Yu Chinese University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China yu@se.cuh.eu.h
Research Article Inviscid Uniform Shear Flow past a Smooth Concave Body
 International Engineering Mathematics Volume 04, Article ID 46593, 7 pages http://x.oi.org/0.55/04/46593 Research Article Invisci Uniform Shear Flow past a Smooth Concave Boy Abullah Mura Department of
International Engineering Mathematics Volume 04, Article ID 46593, 7 pages http://x.oi.org/0.55/04/46593 Research Article Invisci Uniform Shear Flow past a Smooth Concave Boy Abullah Mura Department of
Estimating Velocity Fields on a Freeway from Low Resolution Video
 Estimating Velocity Fiels on a Freeway from Low Resolution Vieo Young Cho Department of Statistics University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720-3860 Email: young@stat.berkeley.eu John Rice Department
Estimating Velocity Fiels on a Freeway from Low Resolution Vieo Young Cho Department of Statistics University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720-3860 Email: young@stat.berkeley.eu John Rice Department
TV-L1 Optical Flow Estimation
 214/7/1 v.5 IPOL article class Published in Image Processing On Line on 213 7 19. Submitted on 212 7 5, accepted on 212 1 29. ISSN 215 1232 c 213 IPOL & the authors CC BY NC SA This article is available
214/7/1 v.5 IPOL article class Published in Image Processing On Line on 213 7 19. Submitted on 212 7 5, accepted on 212 1 29. ISSN 215 1232 c 213 IPOL & the authors CC BY NC SA This article is available
A multiple wavelength unwrapping algorithm for digital fringe profilometry based on spatial shift estimation
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences 214 A multiple wavelength unwrapping algorithm for
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences 214 A multiple wavelength unwrapping algorithm for
Digital fringe profilometry based on triangular fringe patterns and spatial shift estimation
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences 4 Digital fringe profilometry base on triangular
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering an Information Sciences 4 Digital fringe profilometry base on triangular
Chapter 5 Proposed models for reconstituting/ adapting three stereoscopes
 Chapter 5 Propose moels for reconstituting/ aapting three stereoscopes - 89 - 5. Propose moels for reconstituting/aapting three stereoscopes This chapter offers three contributions in the Stereoscopy area,
Chapter 5 Propose moels for reconstituting/ aapting three stereoscopes - 89 - 5. Propose moels for reconstituting/aapting three stereoscopes This chapter offers three contributions in the Stereoscopy area,
BIJECTIONS FOR PLANAR MAPS WITH BOUNDARIES
 BIJECTIONS FOR PLANAR MAPS WITH BOUNDARIES OLIVIER BERNARDI AND ÉRIC FUSY Abstract. We present bijections for planar maps with bounaries. In particular, we obtain bijections for triangulations an quarangulations
BIJECTIONS FOR PLANAR MAPS WITH BOUNDARIES OLIVIER BERNARDI AND ÉRIC FUSY Abstract. We present bijections for planar maps with bounaries. In particular, we obtain bijections for triangulations an quarangulations
Queueing Model and Optimization of Packet Dropping in Real-Time Wireless Sensor Networks
 Queueing Moel an Optimization of Packet Dropping in Real-Time Wireless Sensor Networks Marc Aoun, Antonios Argyriou, Philips Research, Einhoven, 66AE, The Netherlans Department of Computer an Communication
Queueing Moel an Optimization of Packet Dropping in Real-Time Wireless Sensor Networks Marc Aoun, Antonios Argyriou, Philips Research, Einhoven, 66AE, The Netherlans Department of Computer an Communication
Approximation with Active B-spline Curves and Surfaces
 Approximation with Active B-spline Curves an Surfaces Helmut Pottmann, Stefan Leopolseer, Michael Hofer Institute of Geometry Vienna University of Technology Wiener Hauptstr. 8 10, Vienna, Austria pottmann,leopolseer,hofer
Approximation with Active B-spline Curves an Surfaces Helmut Pottmann, Stefan Leopolseer, Michael Hofer Institute of Geometry Vienna University of Technology Wiener Hauptstr. 8 10, Vienna, Austria pottmann,leopolseer,hofer
Comparison of Methods for Increasing the Performance of a DUA Computation
 Comparison of Methos for Increasing the Performance of a DUA Computation Michael Behrisch, Daniel Krajzewicz, Peter Wagner an Yun-Pang Wang Institute of Transportation Systems, German Aerospace Center,
Comparison of Methos for Increasing the Performance of a DUA Computation Michael Behrisch, Daniel Krajzewicz, Peter Wagner an Yun-Pang Wang Institute of Transportation Systems, German Aerospace Center,
Sampling the Disparity Space Image
 Accepte for publication, June 2003. To appear in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis an Machine Intelligence (PAMI) Sampling the Disparity Space Image Richar Szeliski Daniel Scharstein Microsoft Research
Accepte for publication, June 2003. To appear in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis an Machine Intelligence (PAMI) Sampling the Disparity Space Image Richar Szeliski Daniel Scharstein Microsoft Research
Solving Vision Tasks with variational methods on the GPU
 Solving Vision Tasks with variational methods on the GPU Horst Bischof Inst. f. Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology Joint work with Thomas Pock, Markus Unger, Arnold Irschara and
Solving Vision Tasks with variational methods on the GPU Horst Bischof Inst. f. Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology Joint work with Thomas Pock, Markus Unger, Arnold Irschara and
Parallel Directionally Split Solver Based on Reformulation of Pipelined Thomas Algorithm
 NASA/CR-1998-208733 ICASE Report No. 98-45 Parallel Directionally Split Solver Base on Reformulation of Pipeline Thomas Algorithm A. Povitsky ICASE, Hampton, Virginia Institute for Computer Applications
NASA/CR-1998-208733 ICASE Report No. 98-45 Parallel Directionally Split Solver Base on Reformulation of Pipeline Thomas Algorithm A. Povitsky ICASE, Hampton, Virginia Institute for Computer Applications
Exploring Context with Deep Structured models for Semantic Segmentation
 1 Exploring Context with Deep Structure moels for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Anton van en Hengel, Ian Rei between an image patch an a large backgroun image region. Explicitly moeling
1 Exploring Context with Deep Structure moels for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Anton van en Hengel, Ian Rei between an image patch an a large backgroun image region. Explicitly moeling
Exploring Context with Deep Structured models for Semantic Segmentation
 APPEARING IN IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, APRIL 2017. 1 Exploring Context with Deep Structure moels for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Anton van en
APPEARING IN IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, APRIL 2017. 1 Exploring Context with Deep Structure moels for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Anton van en
Tight Wavelet Frame Decomposition and Its Application in Image Processing
 ITB J. Sci. Vol. 40 A, No., 008, 151-165 151 Tight Wavelet Frame Decomposition an Its Application in Image Processing Mahmu Yunus 1, & Henra Gunawan 1 1 Analysis an Geometry Group, FMIPA ITB, Banung Department
ITB J. Sci. Vol. 40 A, No., 008, 151-165 151 Tight Wavelet Frame Decomposition an Its Application in Image Processing Mahmu Yunus 1, & Henra Gunawan 1 1 Analysis an Geometry Group, FMIPA ITB, Banung Department
Bayesian localization microscopy reveals nanoscale podosome dynamics
 Nature Methos Bayesian localization microscopy reveals nanoscale poosome ynamics Susan Cox, Ewar Rosten, James Monypenny, Tijana Jovanovic-Talisman, Dylan T Burnette, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Gareth
Nature Methos Bayesian localization microscopy reveals nanoscale poosome ynamics Susan Cox, Ewar Rosten, James Monypenny, Tijana Jovanovic-Talisman, Dylan T Burnette, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Gareth
Multilevel Linear Dimensionality Reduction using Hypergraphs for Data Analysis
 Multilevel Linear Dimensionality Reuction using Hypergraphs for Data Analysis Haw-ren Fang Department of Computer Science an Engineering University of Minnesota; Minneapolis, MN 55455 hrfang@csumneu ABSTRACT
Multilevel Linear Dimensionality Reuction using Hypergraphs for Data Analysis Haw-ren Fang Department of Computer Science an Engineering University of Minnesota; Minneapolis, MN 55455 hrfang@csumneu ABSTRACT
A Convex Clustering-based Regularizer for Image Segmentation
 Vision, Moeling, an Visualization (2015) D. Bommes, T. Ritschel an T. Schultz (Es.) A Convex Clustering-base Regularizer for Image Segmentation Benjamin Hell (TU Braunschweig), Marcus Magnor (TU Braunschweig)
Vision, Moeling, an Visualization (2015) D. Bommes, T. Ritschel an T. Schultz (Es.) A Convex Clustering-base Regularizer for Image Segmentation Benjamin Hell (TU Braunschweig), Marcus Magnor (TU Braunschweig)
FTSM FAST TAKAGI-SUGENO FUZZY MODELING. Manfred Männle
 FTS FAST TAKAGI-SUGENO FUZZY ODELING anfre ännle Institute for Computer Design an Fault Tolerance University of Karlsruhe, D-7628 Karlsruhe, Germany anfre.aennle@informatik.uni-karlsruhe.e Abstract Takagi-Sugeno
FTS FAST TAKAGI-SUGENO FUZZY ODELING anfre ännle Institute for Computer Design an Fault Tolerance University of Karlsruhe, D-7628 Karlsruhe, Germany anfre.aennle@informatik.uni-karlsruhe.e Abstract Takagi-Sugeno
EXTRACTION OF MAIN AND SECONDARY ROADS IN VHR IMAGES USING A HIGHER-ORDER PHASE FIELD MODEL
 EXTRACTION OF MAIN AND SECONDARY ROADS IN VHR IMAGES USING A HIGHER-ORDER PHASE FIELD MODEL Ting Peng a,b, Ian H. Jermyn b, Véronique Prinet a, Josiane Zerubia b a LIAMA & PR, Institute of Automation,
EXTRACTION OF MAIN AND SECONDARY ROADS IN VHR IMAGES USING A HIGHER-ORDER PHASE FIELD MODEL Ting Peng a,b, Ian H. Jermyn b, Véronique Prinet a, Josiane Zerubia b a LIAMA & PR, Institute of Automation,
Design of Policy-Aware Differentially Private Algorithms
 Design of Policy-Aware Differentially Private Algorithms Samuel Haney Due University Durham, NC, USA shaney@cs.ue.eu Ashwin Machanavajjhala Due University Durham, NC, USA ashwin@cs.ue.eu Bolin Ding Microsoft
Design of Policy-Aware Differentially Private Algorithms Samuel Haney Due University Durham, NC, USA shaney@cs.ue.eu Ashwin Machanavajjhala Due University Durham, NC, USA ashwin@cs.ue.eu Bolin Ding Microsoft
EXACT SIMULATION OF A BOOLEAN MODEL
 Original Research Paper oi:10.5566/ias.v32.p101-105 EXACT SIMULATION OF A BOOLEAN MODEL CHRISTIAN LANTUÉJOULB MinesParisTech 35 rue Saint-Honoré 77305 Fontainebleau France e-mail: christian.lantuejoul@mines-paristech.fr
Original Research Paper oi:10.5566/ias.v32.p101-105 EXACT SIMULATION OF A BOOLEAN MODEL CHRISTIAN LANTUÉJOULB MinesParisTech 35 rue Saint-Honoré 77305 Fontainebleau France e-mail: christian.lantuejoul@mines-paristech.fr
Generalized Edge Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks
 Generalize Ege Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks Chun-Chen Hsu Institute of Information Science Acaemia Sinica Taipei, Taiwan Da-wei Wang Jan-Jan Wu Institute of Information Science
Generalize Ege Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks Chun-Chen Hsu Institute of Information Science Acaemia Sinica Taipei, Taiwan Da-wei Wang Jan-Jan Wu Institute of Information Science
SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD
 SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD M.E-II, Department of Computer Engineering, PICT, Pune ABSTRACT: Optical flow as an image processing technique finds its applications
SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD M.E-II, Department of Computer Engineering, PICT, Pune ABSTRACT: Optical flow as an image processing technique finds its applications
Online Appendix to: Generalizing Database Forensics
 Online Appenix to: Generalizing Database Forensics KYRIACOS E. PAVLOU an RICHARD T. SNODGRASS, University of Arizona This appenix presents a step-by-step iscussion of the forensic analysis protocol that
Online Appenix to: Generalizing Database Forensics KYRIACOS E. PAVLOU an RICHARD T. SNODGRASS, University of Arizona This appenix presents a step-by-step iscussion of the forensic analysis protocol that
ATV-L1OpticalFlowMethod with Occlusion Detection
 ATV-L1OpticalFlowMethod with Occlusion Detection Coloma Ballester 1, Lluis Garrido 2, Vanel Lazcano 1, and Vicent Caselles 1 1 Dept Information and Communication Technologies, University Pompeu Fabra 2
ATV-L1OpticalFlowMethod with Occlusion Detection Coloma Ballester 1, Lluis Garrido 2, Vanel Lazcano 1, and Vicent Caselles 1 1 Dept Information and Communication Technologies, University Pompeu Fabra 2
An Anti-Aliasing Technique for Splatting
 An Anti-Aliasing Technique for Splatting J. Ewar Swan II 1,2,3 Klaus Mueller 2 Torsten Möller 1,2 Naeem Shareef 1,2 Roger Crawfis 1,2 Roni Yagel 1,2 1 Avance Computing Center for the Arts an Design 2 Department
An Anti-Aliasing Technique for Splatting J. Ewar Swan II 1,2,3 Klaus Mueller 2 Torsten Möller 1,2 Naeem Shareef 1,2 Roger Crawfis 1,2 Roni Yagel 1,2 1 Avance Computing Center for the Arts an Design 2 Department
The Journal of Systems and Software
 The Journal of Systems an Software 83 (010) 1864 187 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Journal of Systems an Software journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jss Embeing capacity raising
The Journal of Systems an Software 83 (010) 1864 187 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect The Journal of Systems an Software journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jss Embeing capacity raising
Regularized Laplacian Zero Crossings as Optimal Edge Integrators
 Regularize aplacian Zero rossings as Optimal Ege Integrators R. KIMME A.M. BRUKSTEIN Department of omputer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion ity, Haifa 32, Israel Abstract We view
Regularize aplacian Zero rossings as Optimal Ege Integrators R. KIMME A.M. BRUKSTEIN Department of omputer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion ity, Haifa 32, Israel Abstract We view
Parts Assembly by Throwing Manipulation with a One-Joint Arm
 21 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots an Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, October, 21. Parts Assembly by Throwing Manipulation with a One-Joint Arm Hieyuki Miyashita, Tasuku Yamawaki an Masahito
21 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots an Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, October, 21. Parts Assembly by Throwing Manipulation with a One-Joint Arm Hieyuki Miyashita, Tasuku Yamawaki an Masahito
A Versatile Model-Based Visibility Measure for Geometric Primitives
 A Versatile Moel-Base Visibility Measure for Geometric Primitives Marc M. Ellenrieer 1,LarsKrüger 1, Dirk Stößel 2, an Marc Hanheie 2 1 DaimlerChrysler AG, Research & Technology, 89013 Ulm, Germany 2 Faculty
A Versatile Moel-Base Visibility Measure for Geometric Primitives Marc M. Ellenrieer 1,LarsKrüger 1, Dirk Stößel 2, an Marc Hanheie 2 1 DaimlerChrysler AG, Research & Technology, 89013 Ulm, Germany 2 Faculty
Classical Mechanics Examples (Lagrange Multipliers)
 Classical Mechanics Examples (Lagrange Multipliers) Dipan Kumar Ghosh Physics Department, Inian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400076 September 3, 015 1 Introuction We have seen that the
Classical Mechanics Examples (Lagrange Multipliers) Dipan Kumar Ghosh Physics Department, Inian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400076 September 3, 015 1 Introuction We have seen that the
Generalized Edge Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks
 TR-IIS-05-021 Generalize Ege Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks Chun-Chen Hsu, Pangfeng Liu, Da-Wei Wang, Jan-Jan Wu December 2005 Technical Report No. TR-IIS-05-021 http://www.iis.sinica.eu.tw/lib/techreport/tr2005/tr05.html
TR-IIS-05-021 Generalize Ege Coloring for Channel Assignment in Wireless Networks Chun-Chen Hsu, Pangfeng Liu, Da-Wei Wang, Jan-Jan Wu December 2005 Technical Report No. TR-IIS-05-021 http://www.iis.sinica.eu.tw/lib/techreport/tr2005/tr05.html
Software Reliability Modeling and Cost Estimation Incorporating Testing-Effort and Efficiency
 Software Reliability Moeling an Cost Estimation Incorporating esting-effort an Efficiency Chin-Yu Huang, Jung-Hua Lo, Sy-Yen Kuo, an Michael R. Lyu -+ Department of Electrical Engineering Computer Science
Software Reliability Moeling an Cost Estimation Incorporating esting-effort an Efficiency Chin-Yu Huang, Jung-Hua Lo, Sy-Yen Kuo, an Michael R. Lyu -+ Department of Electrical Engineering Computer Science
Yet Another Parallel Hypothesis Search for Inverse Entailment Hiroyuki Nishiyama and Hayato Ohwada Faculty of Sci. and Tech. Tokyo University of Scien
 Yet Another Parallel Hypothesis Search for Inverse Entailment Hiroyuki Nishiyama an Hayato Ohwaa Faculty of Sci. an Tech. Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki, Noa-shi, CHIBA, 278-8510, Japan hiroyuki@rs.noa.tus.ac.jp,
Yet Another Parallel Hypothesis Search for Inverse Entailment Hiroyuki Nishiyama an Hayato Ohwaa Faculty of Sci. an Tech. Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki, Noa-shi, CHIBA, 278-8510, Japan hiroyuki@rs.noa.tus.ac.jp,
AnyTraffic Labeled Routing
 AnyTraffic Labele Routing Dimitri Papaimitriou 1, Pero Peroso 2, Davie Careglio 2 1 Alcatel-Lucent Bell, Antwerp, Belgium Email: imitri.papaimitriou@alcatel-lucent.com 2 Universitat Politècnica e Catalunya,
AnyTraffic Labele Routing Dimitri Papaimitriou 1, Pero Peroso 2, Davie Careglio 2 1 Alcatel-Lucent Bell, Antwerp, Belgium Email: imitri.papaimitriou@alcatel-lucent.com 2 Universitat Politècnica e Catalunya,
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization Douglas Comer Computer Science Department Purue University 250 N. University Street West Lafayette, IN 47907-2066 http://www.cs.purue.eu/people/comer Copyright 2006. All rights reserve.
Computer Organization Douglas Comer Computer Science Department Purue University 250 N. University Street West Lafayette, IN 47907-2066 http://www.cs.purue.eu/people/comer Copyright 2006. All rights reserve.
Characterizing Decoding Robustness under Parametric Channel Uncertainty
 Characterizing Decoing Robustness uner Parametric Channel Uncertainty Jay D. Wierer, Wahee U. Bajwa, Nigel Boston, an Robert D. Nowak Abstract This paper characterizes the robustness of ecoing uner parametric
Characterizing Decoing Robustness uner Parametric Channel Uncertainty Jay D. Wierer, Wahee U. Bajwa, Nigel Boston, an Robert D. Nowak Abstract This paper characterizes the robustness of ecoing uner parametric
ILLUMINATION ROBUST OPTICAL FLOW ESTIMATION BY ILLUMINATION-CHROMATICITY DECOUPLING. Sungheon Park and Nojun Kwak
 ILLUMINATION ROBUST OPTICAL FLOW ESTIMATION BY ILLUMINATION-CHROMATICITY DECOUPLING Sungheon Park and Nojun Kwak Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Korea
ILLUMINATION ROBUST OPTICAL FLOW ESTIMATION BY ILLUMINATION-CHROMATICITY DECOUPLING Sungheon Park and Nojun Kwak Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Korea
CAMERAS AND GRAVITY: ESTIMATING PLANAR OBJECT ORIENTATION. Zhaoyin Jia, Andrew Gallagher, Tsuhan Chen
 CAMERAS AND GRAVITY: ESTIMATING PLANAR OBJECT ORIENTATION Zhaoyin Jia, Anrew Gallagher, Tsuhan Chen School of Electrical an Computer Engineering, Cornell University ABSTRACT Photography on a mobile camera
CAMERAS AND GRAVITY: ESTIMATING PLANAR OBJECT ORIENTATION Zhaoyin Jia, Anrew Gallagher, Tsuhan Chen School of Electrical an Computer Engineering, Cornell University ABSTRACT Photography on a mobile camera
Non-homogeneous Generalization in Privacy Preserving Data Publishing
 Non-homogeneous Generalization in Privacy Preserving Data Publishing W. K. Wong, Nios Mamoulis an Davi W. Cheung Department of Computer Science, The University of Hong Kong Pofulam Roa, Hong Kong {wwong2,nios,cheung}@cs.hu.h
Non-homogeneous Generalization in Privacy Preserving Data Publishing W. K. Wong, Nios Mamoulis an Davi W. Cheung Department of Computer Science, The University of Hong Kong Pofulam Roa, Hong Kong {wwong2,nios,cheung}@cs.hu.h
I. Introuction With the evolution of imaging technology, an increasing number of image moalities becomes available. In remote sensing, sensors are use
 A multivalue image wavelet representation base on multiscale funamental forms P. Scheuners Vision Lab, Department ofphysics, University ofantwerp, Groenenborgerlaan 7, 00 Antwerpen, Belgium Tel.: +3/3/8
A multivalue image wavelet representation base on multiscale funamental forms P. Scheuners Vision Lab, Department ofphysics, University ofantwerp, Groenenborgerlaan 7, 00 Antwerpen, Belgium Tel.: +3/3/8
Solution Representation for Job Shop Scheduling Problems in Ant Colony Optimisation
 Solution Representation for Job Shop Scheuling Problems in Ant Colony Optimisation James Montgomery, Carole Faya 2, an Sana Petrovic 2 Faculty of Information & Communication Technologies, Swinburne University
Solution Representation for Job Shop Scheuling Problems in Ant Colony Optimisation James Montgomery, Carole Faya 2, an Sana Petrovic 2 Faculty of Information & Communication Technologies, Swinburne University
SURVIVABLE IP OVER WDM: GUARANTEEEING MINIMUM NETWORK BANDWIDTH
 SURVIVABLE IP OVER WDM: GUARANTEEEING MINIMUM NETWORK BANDWIDTH Galen H Sasaki Dept Elec Engg, U Hawaii 2540 Dole Street Honolul HI 96822 USA Ching-Fong Su Fuitsu Laboratories of America 595 Lawrence Expressway
SURVIVABLE IP OVER WDM: GUARANTEEEING MINIMUM NETWORK BANDWIDTH Galen H Sasaki Dept Elec Engg, U Hawaii 2540 Dole Street Honolul HI 96822 USA Ching-Fong Su Fuitsu Laboratories of America 595 Lawrence Expressway
Spherical Billboards and their Application to Rendering Explosions
 Spherical Billboars an their Application to Renering Explosions Tamás Umenhoffer László Szirmay-Kalos Gábor Szijártó Department of Control Engineering an Information Technology Buapest University of Technology,
Spherical Billboars an their Application to Renering Explosions Tamás Umenhoffer László Szirmay-Kalos Gábor Szijártó Department of Control Engineering an Information Technology Buapest University of Technology,
New Geometric Interpretation and Analytic Solution for Quadrilateral Reconstruction
 New Geometric Interpretation an Analytic Solution for uarilateral Reconstruction Joo-Haeng Lee Convergence Technology Research Lab ETRI Daejeon, 305 777, KOREA Abstract A new geometric framework, calle
New Geometric Interpretation an Analytic Solution for uarilateral Reconstruction Joo-Haeng Lee Convergence Technology Research Lab ETRI Daejeon, 305 777, KOREA Abstract A new geometric framework, calle
Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu Microsoft Research New England
 Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu celiu@microsoft.com Microsoft Research New England Last time Motion perception Motion representation Parametric motion: Lucas-Kanade T I x du dv = I x I T x I y I x T I y
Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu celiu@microsoft.com Microsoft Research New England Last time Motion perception Motion representation Parametric motion: Lucas-Kanade T I x du dv = I x I T x I y I x T I y
Stereo Matching Using Tree Filtering
 1 Stereo Matching Using Tree Filtering Qingxiong Yang, Member, IEEE, Abstract Matching cost aggregation is one of the olest an still popular methos for stereo corresponence. While effective an efficient,
1 Stereo Matching Using Tree Filtering Qingxiong Yang, Member, IEEE, Abstract Matching cost aggregation is one of the olest an still popular methos for stereo corresponence. While effective an efficient,
Coupling the User Interfaces of a Multiuser Program
 Coupling the User Interfaces of a Multiuser Program PRASUN DEWAN University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill RAJIV CHOUDHARY Intel Corporation We have evelope a new moel for coupling the user-interfaces
Coupling the User Interfaces of a Multiuser Program PRASUN DEWAN University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill RAJIV CHOUDHARY Intel Corporation We have evelope a new moel for coupling the user-interfaces
Reversible Image Watermarking using Bit Plane Coding and Lifting Wavelet Transform
 250 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science an Network Security, VOL.9 No.11, November 2009 Reversible Image Watermarking using Bit Plane Coing an Lifting Wavelet Transform S. Kurshi Jinna, Dr.
250 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science an Network Security, VOL.9 No.11, November 2009 Reversible Image Watermarking using Bit Plane Coing an Lifting Wavelet Transform S. Kurshi Jinna, Dr.
Fuzzy Clustering in Parallel Universes
 Fuzzy Clustering in Parallel Universes Bern Wisweel an Michael R. Berthol ALTANA-Chair for Bioinformatics an Information Mining Department of Computer an Information Science, University of Konstanz 78457
Fuzzy Clustering in Parallel Universes Bern Wisweel an Michael R. Berthol ALTANA-Chair for Bioinformatics an Information Mining Department of Computer an Information Science, University of Konstanz 78457
Image compression predicated on recurrent iterated function systems
 2n International Conference on Mathematics & Statistics 16-19 June, 2008, Athens, Greece Image compression preicate on recurrent iterate function systems Chol-Hui Yun *, Metzler W. a an Barski M. a * Faculty
2n International Conference on Mathematics & Statistics 16-19 June, 2008, Athens, Greece Image compression preicate on recurrent iterate function systems Chol-Hui Yun *, Metzler W. a an Barski M. a * Faculty
A Discrete Search Method for Multi-modal Non-Rigid Image Registration
 A Discrete Search Metho for Multi-moal on-rigi Image Registration Alexaner Shekhovtsov Juan D. García-Arteaga Tomáš Werner Center for Machine Perception, Dept. of Cybernetics Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
A Discrete Search Metho for Multi-moal on-rigi Image Registration Alexaner Shekhovtsov Juan D. García-Arteaga Tomáš Werner Center for Machine Perception, Dept. of Cybernetics Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
Intensive Hypercube Communication: Prearranged Communication in Link-Bound Machines 1 2
 This paper appears in J. of Parallel an Distribute Computing 10 (1990), pp. 167 181. Intensive Hypercube Communication: Prearrange Communication in Link-Boun Machines 1 2 Quentin F. Stout an Bruce Wagar
This paper appears in J. of Parallel an Distribute Computing 10 (1990), pp. 167 181. Intensive Hypercube Communication: Prearrange Communication in Link-Boun Machines 1 2 Quentin F. Stout an Bruce Wagar
THE APPLICATION OF ARTICLE k-th SHORTEST TIME PATH ALGORITHM
 International Journal of Physics an Mathematical Sciences ISSN: 2277-2111 (Online) 2016 Vol. 6 (1) January-March, pp. 24-6/Mao an Shi. THE APPLICATION OF ARTICLE k-th SHORTEST TIME PATH ALGORITHM Hua Mao
International Journal of Physics an Mathematical Sciences ISSN: 2277-2111 (Online) 2016 Vol. 6 (1) January-March, pp. 24-6/Mao an Shi. THE APPLICATION OF ARTICLE k-th SHORTEST TIME PATH ALGORITHM Hua Mao
Texture Defect Detection System with Image Deflection Compensation
 Texture Defect Detection System with Image Deflection Compensation CHUN-CHENG LIN CHENG-YU YEH Department of Electrical Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology 35, Lane 15, Sec. 1, Chungshan
Texture Defect Detection System with Image Deflection Compensation CHUN-CHENG LIN CHENG-YU YEH Department of Electrical Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology 35, Lane 15, Sec. 1, Chungshan
Lakshmish Ramanna University of Texas at Dallas Dept. of Electrical Engineering Richardson, TX
 Boy Sensor Networks to Evaluate Staning Balance: Interpreting Muscular Activities Base on Inertial Sensors Rohith Ramachanran Richarson, TX 75083 rxr057100@utallas.eu Gaurav Prahan Dept. of Computer Science
Boy Sensor Networks to Evaluate Staning Balance: Interpreting Muscular Activities Base on Inertial Sensors Rohith Ramachanran Richarson, TX 75083 rxr057100@utallas.eu Gaurav Prahan Dept. of Computer Science
Synthesis Distortion Estimation in 3D Video Using Frequency and Spatial Analysis
 MITSUBISHI EECTRIC RESEARCH ABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Synthesis Distortion Estimation in 3D Vieo Using Frequency an Spatial Analysis Fang,.; Cheung, N-M; Tian, D.; Vetro, A.; Sun, H.; Yu,. TR2013-087
MITSUBISHI EECTRIC RESEARCH ABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Synthesis Distortion Estimation in 3D Vieo Using Frequency an Spatial Analysis Fang,.; Cheung, N-M; Tian, D.; Vetro, A.; Sun, H.; Yu,. TR2013-087
Tracking and Regulation Control of a Mobile Robot System With Kinematic Disturbances: A Variable Structure-Like Approach
 W. E. Dixon e-mail: wixon@ces.clemson.eu D. M. Dawson e-mail: awson@ces.clemson.eu E. Zergeroglu e-mail: ezerger@ces.clemson.eu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
W. E. Dixon e-mail: wixon@ces.clemson.eu D. M. Dawson e-mail: awson@ces.clemson.eu E. Zergeroglu e-mail: ezerger@ces.clemson.eu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 31, NO. 4, APRIL
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 1, NO. 4, APRIL 01 74 Towar Efficient Distribute Algorithms for In-Network Binary Operator Tree Placement in Wireless Sensor Networks Zongqing Lu,
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 1, NO. 4, APRIL 01 74 Towar Efficient Distribute Algorithms for In-Network Binary Operator Tree Placement in Wireless Sensor Networks Zongqing Lu,
Improving Spatial Reuse of IEEE Based Ad Hoc Networks
 mproving Spatial Reuse of EEE 82.11 Base A Hoc Networks Fengji Ye, Su Yi an Biplab Sikar ECSE Department, Rensselaer Polytechnic nstitute Troy, NY 1218 Abstract n this paper, we evaluate an suggest methos
mproving Spatial Reuse of EEE 82.11 Base A Hoc Networks Fengji Ye, Su Yi an Biplab Sikar ECSE Department, Rensselaer Polytechnic nstitute Troy, NY 1218 Abstract n this paper, we evaluate an suggest methos
Variational Recursive Joint Estimation of Dense Scene Structure and Camera Motion from Monocular High Speed Traffic Sequences
 Variational Recursive Joint Estimation of Dense Scene Structure an Camera Motion from Monocular High Spee Traffic Sequences Florian Becker, Frank Lenzen, Jo rg H. Kappes an Christoph Schno rr HCI an IPA,
Variational Recursive Joint Estimation of Dense Scene Structure an Camera Motion from Monocular High Spee Traffic Sequences Florian Becker, Frank Lenzen, Jo rg H. Kappes an Christoph Schno rr HCI an IPA,
A Comparative Evaluation of Iris and Ocular Recognition Methods on Challenging Ocular Images
 A Comparative Evaluation of Iris an Ocular Recognition Methos on Challenging Ocular Images Vishnu Naresh Boeti Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 naresh@cmu.eu Jonathon M Smereka Carnegie Mellon
A Comparative Evaluation of Iris an Ocular Recognition Methos on Challenging Ocular Images Vishnu Naresh Boeti Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 naresh@cmu.eu Jonathon M Smereka Carnegie Mellon
Optimization Beyond the Convolution: Generalizing Spatial Relations with End-to-End Metric Learning
 Optimization Beyon the Convolution: Generalizing Spatial Relations with En-to-En Metric Learning Philipp Jun, Anreas Eitel, Nichola Abo an Wolfram Burgar 1 Abstract To operate intelligently in omestic
Optimization Beyon the Convolution: Generalizing Spatial Relations with En-to-En Metric Learning Philipp Jun, Anreas Eitel, Nichola Abo an Wolfram Burgar 1 Abstract To operate intelligently in omestic
Wavelet-Based Multiscale Anisotropic Diffusion with Adaptive Statistical Analysis for Image Restoration
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Wavelet-Base Multiscale Anisotropic Diffusion with Aaptive Statistical Analysis for Image Restoration Junmei Zhong Huifang Sun TR008-067 November
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Wavelet-Base Multiscale Anisotropic Diffusion with Aaptive Statistical Analysis for Image Restoration Junmei Zhong Huifang Sun TR008-067 November
On the Placement of Internet Taps in Wireless Neighborhood Networks
 1 On the Placement of Internet Taps in Wireless Neighborhoo Networks Lili Qiu, Ranveer Chanra, Kamal Jain, Mohamma Mahian Abstract Recently there has emerge a novel application of wireless technology that
1 On the Placement of Internet Taps in Wireless Neighborhoo Networks Lili Qiu, Ranveer Chanra, Kamal Jain, Mohamma Mahian Abstract Recently there has emerge a novel application of wireless technology that
Study of Network Optimization Method Based on ACL
 Available online at www.scienceirect.com Proceia Engineering 5 (20) 3959 3963 Avance in Control Engineering an Information Science Stuy of Network Optimization Metho Base on ACL Liu Zhian * Department
Available online at www.scienceirect.com Proceia Engineering 5 (20) 3959 3963 Avance in Control Engineering an Information Science Stuy of Network Optimization Metho Base on ACL Liu Zhian * Department
Feature Extraction and Rule Classification Algorithm of Digital Mammography based on Rough Set Theory
 Feature Extraction an Rule Classification Algorithm of Digital Mammography base on Rough Set Theory Aboul Ella Hassanien Jafar M. H. Ali. Kuwait University, Faculty of Aministrative Science, Quantitative
Feature Extraction an Rule Classification Algorithm of Digital Mammography base on Rough Set Theory Aboul Ella Hassanien Jafar M. H. Ali. Kuwait University, Faculty of Aministrative Science, Quantitative
SMART IMAGE PROCESSING OF FLOW VISUALIZATION
 SMAR IMAGE PROCESSING OF FLOW VISUALIZAION H Li (A Rinoshika) 1, M akei, M Nakano 1, Y Saito 3 an K Horii 4 1 Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering, Yamagata University, Yamagata 99-851, JAPAN Department
SMAR IMAGE PROCESSING OF FLOW VISUALIZAION H Li (A Rinoshika) 1, M akei, M Nakano 1, Y Saito 3 an K Horii 4 1 Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering, Yamagata University, Yamagata 99-851, JAPAN Department
PM-Huber: PatchMatch with Huber Regularization for Stereo Matching
 PM-Huber: PatchMatch with Huber Regularization for Stereo Matching Philipp Heise, Sebastian Klose, Brian Jensen, Alois Knoll Department of Informatics, Technische Uniersita t Mu nchen, Germany {heise,kloses,jensen,knoll}@intume
PM-Huber: PatchMatch with Huber Regularization for Stereo Matching Philipp Heise, Sebastian Klose, Brian Jensen, Alois Knoll Department of Informatics, Technische Uniersita t Mu nchen, Germany {heise,kloses,jensen,knoll}@intume
Rough Set Approach for Classification of Breast Cancer Mammogram Images
 Rough Set Approach for Classification of Breast Cancer Mammogram Images Aboul Ella Hassanien Jafar M. H. Ali. Kuwait University, Faculty of Aministrative Science, Quantitative Methos an Information Systems
Rough Set Approach for Classification of Breast Cancer Mammogram Images Aboul Ella Hassanien Jafar M. H. Ali. Kuwait University, Faculty of Aministrative Science, Quantitative Methos an Information Systems
An Algorithm for Building an Enterprise Network Topology Using Widespread Data Sources
 An Algorithm for Builing an Enterprise Network Topology Using Wiesprea Data Sources Anton Anreev, Iurii Bogoiavlenskii Petrozavosk State University Petrozavosk, Russia {anreev, ybgv}@cs.petrsu.ru Abstract
An Algorithm for Builing an Enterprise Network Topology Using Wiesprea Data Sources Anton Anreev, Iurii Bogoiavlenskii Petrozavosk State University Petrozavosk, Russia {anreev, ybgv}@cs.petrsu.ru Abstract
Unknown Radial Distortion Centers in Multiple View Geometry Problems
 Unknown Raial Distortion Centers in Multiple View Geometry Problems José Henrique Brito 1,2, Rolan Angst 3, Kevin Köser 3, Christopher Zach 4, Pero Branco 2, Manuel João Ferreira 2, Marc Pollefeys 3 1
Unknown Raial Distortion Centers in Multiple View Geometry Problems José Henrique Brito 1,2, Rolan Angst 3, Kevin Köser 3, Christopher Zach 4, Pero Branco 2, Manuel João Ferreira 2, Marc Pollefeys 3 1
