Contours of slopes of a rippled water surface
|
|
|
- Holly Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contours of slopes of a rippled water surface Charles Cox* and Xin Zhang Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD 0213, La Jolla, California 9209, USA *cscox@ucsd.edu Abstract: The appearance of a horizontal array of linear lamps below the water surface when viewed from above is approximately in the form of contours of one component of the water surface slope. The degree of approximation is a fraction of one percent when this method is used to describe the slopes of a wind ruffled surface. An extension of the method to image both components of slope requires two arrays of lamps pulsed alternately and in synchronism with a fast camera Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Oceanic optics; ( ) Nonimaging optical systems; ( ) Surface measurements, roughness. References and links 1. P. A. Hwang, D. B. Trizna, and J. Wu, Spatial measurements of short wind waves using a scanning slope sensor, Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 20(1-2), 1 23 (1993). 2. C. Cox and X. Zhang, Optical methods for study of sea surface roughness and microscale turbulence, in Proc. SPIE, Optical Technology in Fluid, Thermal, and Combustion Flow, III, Vol. 3172, S. S. Cha, J. D. Trolinger, and M. Kawahashi, ed. (1997). 3. T. E. Hara, J. Bock, J. B. Edson, and W. R. McGillis, Observation of short wind waves in coastal waters, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 28(7), (1998). 4. C. J. Zappa, M. L. Banner, H. Schultz, A. Corrada-Emmanuel, L. B. Wolff, and J. Yalcin, Retrieval of short ocean wave slope using polarimetric imaging, Meas. Sci. Technol. 19(5), (2008), doi: / /19/5/ F. M. Bréon and N. Henriot, Spaceborne observations of ocean glint reflectance and modeling of wave slope distributions, J. Geophys. Res. 111(C6), C06005 (2006), doi: /2005jc Introduction The shape of the sea surface on all scales is of importance as the roughness regulates the structure and intensity of turbulence in the wind above the sea. These factors in turn control the stresses that the wind exerts on the ocean and the growth of wind waves. The shape also controls the transmission and reflection of sunlight and the scattering of microwaves. Waves of the sea surface have a wide range of scales ranging upwards from a millimeter or less. Waves of large scale, swell and wind waves, have been effectively delineated by many methods including arrays of pressure sensors below the sea surface and scanning laser altimeters from above. Small scale waves are difficult to measure because measuring apparatus tends to distort the waves directly or to modify the air flow which generates them. The difficulties are illustrated by equipment used in the open sea to study the shortest waves [1 3]. All three measure the refraction of light rays from bright light sources by the slopes of the water surface in order to avoid disturbing the surface. Although they successfully resolve the finest scales of the sea surface, they require large support devices close to the water surface that must necessarily disturb water and air flow, and also generate unwanted reflected waves in the region of interest. Another approach that avoids contact with the water involves polarimetric imaging of light reflected from the sea surface [4]. This method uses as a source skylight, preferably from a cloudy sky. The principal limitation is the low intensity of reflected skylight. The movement of short waves during needed exposure times smears the images of the shortest waves. We describe here a method in which bright optical sources and receivers can be kept at considerable distances from the water air interface to avoid disturbances. (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18789
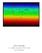
2 Fig. 1. (a) A compressed image of 10 colored fluorescent lamps viewed through the still water surface in a laboratory wind/wave channel. Each lamp is 16 mm in diameter and 1.15 m long. They are separated by 74 mm center to center and are effectively 3 m below the water surface. (b) Part of an image of the lamps when a wind of 3.3 m/s (channel averaged) blows over the water surface. The x axis is parallel to the long axis of the image and the lamps are parallel to the y axis. The area of water surface shown is 176 mm by 80 mm (2816 by 1287 pixels). The camera, mounted with entrance pupil 1.8 m above the mean water surface, was pointed straight down. The photograph is one of 60 exposed in a burst one second long with exposure times of one millisecond. The image has been enhanced by a process that clears the background and identifies the color of individual contour stripes by averaging the color coordinates within each stripe. Stripes containing fewer than 128 pixels are ignored. Contouring one component of slope We mount a horizontal array of long, thin, colored lamps below the water surface, to form the appearance of contours as viewed from above. By mounting the lamps well below the water surface and the optical receiver well above we allow free water and air flow adjacent to the water surface. Each lamp is oriented normal to the direction corresponding to the component of slope to be sensed. For example, if x and y are horizontal components, lamps parallel to the y axis produce contours of the x component of slope. Viewed from above, when the water surface is flat, the lamps appear as almost straight colored lines (Fig. 1(a)). When the water surface is ruffled by wind the lamp images are broken into multiple curved and colored stripes (Fig. 1(b)). In this example, x is positive downwind and the lamps are parallel to the y direction. Each color provides, with a slight degree of uncertainty, a contour of x-slope, the value of which varies slowly in the x direction. We shall refer to such stripes as contour stripes. The uncertainty arises because the true value of x-slope at each point within a contour stripe depends to some extent on the y component of slope at which the refraction of the light ray occurs. (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18790
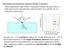
3 Uncertainty of contour value within a contour stripe The contour represented by each contour stripe and its uncertainty can be calculated in the following way. Let N be in an upward directed unit vector normal to the water surface at,, x, y, z is centered on the p( x y z ) (Fig. 2). Here the rectangular coordinate system ( ) entrance pupil of the camera, with z-axis upwards. N has components cos α sin θ, sin α sin θ, cosθ, where θ is the vertical angle of N and α its azimuth. Snell s ( ) law for refraction of light rays is contained in the expression n I R = k N, (1) where n is the index of refraction of the water relative to air, I and R are unit vectors parallel to the incident and refracted rays respectively, and k is positive. Total internal reflection of the incident ray occurs when Ii R 1 n. In terms of the angles summarized in Fig. 2, Ι= R= ( cos β sin φ, sin β sin φ, cos φ), ( γ ψ γ ψ ψ) cos sin, sin sin, cos. Fig. 2. The geometry of refraction. (a) Plan view viewed from above. The origin of coordinates is centered in the entrance pupil of the camera, EP, here treated as negligible in size. An incident ray of light along I originating at the light source LS at S, is refracted at the water surface at p and continues along R to the camera. N is normal to the water surface at p. (b) Side view of three vertical planes respectively containing I, R and N. These three unit vectors are shown extended to illustrate end points on light source, entrance pupil and sea surface. The three components of Eq. (1) are contained in n cos β sinφ cos γ sin ψ = k cos α sin θ, (2a) n sin β sinφ sin γ sin ψ = k sin α sin θ, (2b) n cosφ cos ψ = k cos θ. (2c) (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18791
4 Since k sinθ is positive, Eqs. (2a) and (2b) have the signs of cosα and sinα respectively, and α can be found from the four quadrant arc tangent of the ratio of Eq. (2b) to Eq. (2a). The sum of squares of Eq. (2a) and Eq. (2b) divided by the square of Eq. (2c) leads to the square of the tangent of θ. The (x, y) components of slope of the water surface at p are cos α tan θ and sin α tanθ respectively. The vertical component of distance from the camera entrance pupil to the image point on the water surface, h, must be measured by some means (for example, acoustically) in order to relate pixel coordinates of image points, thus (ψ, γ), to the corresponding (x, y) points on the water surface. In addition the vertical component of distance H to the light source must be known. From these four input data together with the function S(X, Y, -H) describing the shape of the light source we can compute slope components of the water surface which could possibly contribute to every point within a contour stripe at water surface position, (x, y). In general we find that there is a range of true contour values within each contour stripe. The resulting uncertainties of true values are illustrated in Figs. 3 and 4. Fig. 3. The relation of true contours to contour stripes. produced by a single lamp parallel to the y axis and centered below the camera (X = 0). The field of view of the camera is assumed to be 0.30 m by 0.24 m in the x and y dimensions respectively. (a) The mean value of each x-slope contour stripe produced by this lamp depends essentially only on x. (b) The uncertainties of contours expressed as the standard deviation of true values within each contour stripe found by the first method discussed in the text. (c) Standard deviation of probable uncertainties by the second method Here it is assumed that the camera is pointed vertically downward, that its entrance pupil is h = 2.5 m above the water surface (thus assuming the waves on the surface are negligibly high), and that the light source is linear, 1.5 m long, parallel to the y axis and 2.5 m below the water surface. In Fig. 3 the center of the lamp is vertically below the camera (X = 0). In Fig. 4 it is displaced 1.0 m (X = 1.0 m). With either configuration the contour stripes are very nearly true contours of x-slope which vary slowly in the x direction but with a degree of ambiguity depending on the range of possible values of y-slope. There would be no ambiguity if the y- slopes were known within the contour stripe. Without such knowledge we show the uncertainty in two ways. The first assumes that rays of light entering the camera may have originated anywhere along the entire length of the lamp. The uncertainties are represented by (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18792
5 the standard deviation of x-slope for an even distribution of light rays originating along the lamp such that Y < 0.75 m. This would imply a very wide and unlikely range of y-slopes. The other method weighs the deviations in x-slope according to the probability of those y-slopes required to produce rays from any position along the lamp. The y-slope probability is taken as the nearly Gaussian form found in the open sea [5]. The variances of up/downwind and crosswind slope components increase linearly with wind speed. The former is larger than the latter and reaches a value of 0.05 at a wind speed of 15 m/s. As a consequence the ambiguity in x-slope contour stripes is a maximum when the wind is parallel to the y direction and increases with wind speed. The slope probability is known to be skewed: highest slopes are directed upwind and the most probable slope is a small value directed downwind. As a result, when the wind is coming from the positive y direction the uncertainties in x-slope contour stripes are larger at positive y locations than at negative y locations. This is illustrated in Figs. 3(c) and 4(c) where it is assumed the wind is blowing from the positive y direction at 15 m/s (as measured 10 m above the sea). The uncertainties would be reduced at lower windspeeds and when the wind direction is along the x axis. Fig. 4. Similar to Fig. 3 except that the single lamp source is now at X = 1.0 m. The uncertainties shown are roughly one percent of the mean contour value by the first method and one half of one percent from the second method. Lamp spacing and reconstruction from contours In order to reconstruct the entire image field of x-slopes it is necessary to interpolate between contours. Experience, to be related elsewhere, shows that errors inherent in interpolation are related to the ratio of contour spacing to rms slopes and to the extension of the slope spectrum into short wavelengths. The distribution of errors is sharply peaked at zero near contour stripes and reaches maxima far from the contours. In windblown water waves in a laboratory channel where the slope spectrum is sharply limited by viscosity, 95% of errors are less than 8% of rms x-slope when the contour interval is 80% of rms slope. As a result of this favorable circumstance, ten colored lamps are sufficient to create contour stripes covering a useful field of view and a wide range of slopes. (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18793
6 Exposure time and evolution of slopes in time Slope contours of wind waves move at speeds comprised of the inherent phase speeds of capillary waves superposed on the orbital velocities of underlying gravity waves. In laboratory wind wave channels this speed reaches 0.5 m/s. For this reason exposure times must be as short as one millisecond. The focal ratio needed for adequate depth of focus (f/8) then puts a lower limit to lamp intensity. Fifty watt fluorescent lamps have been found to provide sufficient light intensity to meet the need. Contouring both slope components The contour stripes shown in Fig. 1(b) were generated by an array of fluorescent lamps that are inherently steady state devices. The recent development of strips of high power light emitting diodes that can be switched on and off at millisecond rates presents the opportunity of switching between two arrays of lamps, one y parallel and one x parallel. A single high speed camera, with exposures synchronized with the lamps can then image x-slope and y- slope contour stripes in alternate images. Spectral range Our method requires resolution of individual contour stripes. The separation of contours is governed by very short waves. On a windblown water surface capillary waves with wavenumbers extending up to 2 per mm (wavelength 3 mm) have been resolved when the image magnification in the camera corresponds to 16 pixels per millimeter on the water surface, and contour stripes are well separated. The long wavelength limit is then set by the number of pixels in each dimension of the full image. Figure 1(b) was made by a camera with 2816 by 2112 pixels in the x and y directions. Thus the longest waves to be encompassed in the image were 176 mm and 132 mm in the x and y directions (wavenumbers and per mm). Multiple cameras or cameras with higher resolution can extend these long wavelength limits. Possible use at sea The contouring method described here has the advantage for open sea work that both light sources and camera or cameras can be kept far enough from the sea surface to avoid disturbing air flow, water flow or waves in the region of measurement. The requirements for a platform able to support the sources and cameras at sea are stringent. It should also not affect wind, waves or currents in the region of interest and must follow the vertical motions of large wind waves and swells to maintain the geometry of sources and cameras with some degree of uniformity. Acknowledgment Support from the National Science Foundation (grants no. OCE and OCE ) is acknowledged. (C) 2011 OSA 26 September 2011 / Vol. 19, No. 20 / OPTICS EXPRESS 18794
The influence of coherent waves on the remotely sensed reflectance
 The influence of coherent waves on the remotely sensed reflectance J. Ronald V. Zaneveld and Emmanuel Boss College of Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University, Corvallis OR 97330 zaneveld@oce.orst.edu,
The influence of coherent waves on the remotely sensed reflectance J. Ronald V. Zaneveld and Emmanuel Boss College of Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University, Corvallis OR 97330 zaneveld@oce.orst.edu,
Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging
 Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science Phone: (413) 545-3482, Fax:
Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science Phone: (413) 545-3482, Fax:
Optics Vac Work MT 2008
 Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Extraction of surface normal and index of refraction using a pair of passive infrared polarimetric sensors
 Extraction of surface normal and index of refraction using a pair of passive infrared polarimetric sensors Firooz Sadjadi Lockheed Martin Corporation Saint Paul, Minnesota firooz.sadjadi@ieee.org Farzad
Extraction of surface normal and index of refraction using a pair of passive infrared polarimetric sensors Firooz Sadjadi Lockheed Martin Corporation Saint Paul, Minnesota firooz.sadjadi@ieee.org Farzad
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging
 Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science Phone: (413) 545-3482 fax:
Equipment in Support for Polarimetric Imaging Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science Phone: (413) 545-3482 fax:
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION. Wave Fronts and Rays
 Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE
 58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
Chapter 37. Wave Optics
 Chapter 37 Wave Optics Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics. Sometimes called physical optics These phenomena include:
Chapter 37 Wave Optics Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics. Sometimes called physical optics These phenomena include:
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Chapter 18 Ray Optics
 Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
FLAP P6.2 Rays and geometrical optics COPYRIGHT 1998 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY S570 V1.1
 F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
Polarization of light
 Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Interference and Diffraction of Light
 Name Date Time to Complete h m Partner Course/ Section / Grade Interference and Diffraction of Light Reflection by mirrors and refraction by prisms and lenses can be analyzed using the simple ray model
Name Date Time to Complete h m Partner Course/ Section / Grade Interference and Diffraction of Light Reflection by mirrors and refraction by prisms and lenses can be analyzed using the simple ray model
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean
 1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean LONG-TERM GOALS Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean LONG-TERM GOALS Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Condenser Optics for Dark Field X-Ray Microscopy
 Condenser Optics for Dark Field X-Ray Microscopy S. J. Pfauntsch, A. G. Michette, C. J. Buckley Centre for X-Ray Science, Department of Physics, King s College London, Strand, London WC2R 2LS, UK Abstract.
Condenser Optics for Dark Field X-Ray Microscopy S. J. Pfauntsch, A. G. Michette, C. J. Buckley Centre for X-Ray Science, Department of Physics, King s College London, Strand, London WC2R 2LS, UK Abstract.
Geometrical Optics. Theory. N = normal to surface. n r > n i. n i. n r. PHY 192 Geometrical Optics Spring
 PHY 192 Geometrical Optics Spring 2017 1 Geometrical Optics The light source for this experiment is a low-power helium-neon laser with a wavelength of 632.8 nm. ever look directly at a laser beam nor permit
PHY 192 Geometrical Optics Spring 2017 1 Geometrical Optics The light source for this experiment is a low-power helium-neon laser with a wavelength of 632.8 nm. ever look directly at a laser beam nor permit
Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms
 Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms Ping Zhou* and Jim Burge College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721, USA *Corresponding author:
Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms Ping Zhou* and Jim Burge College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721, USA *Corresponding author:
Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Part Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. This Chapter. Phys. 281B Geometric Optics. Chapter 2 : Image Formation. Chapter 2: Image Formation
 Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
1. Particle Scattering. Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes
 1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
Spectrographs. C. A. Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution.
 Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
The image is virtual and erect. When a mirror is rotated through a certain angle, the reflected ray is rotated through twice this angle.
 1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
Stable simulations of illumination patterns caused by focusing of sunlight by water waves
 Stable simulations of illumination patterns caused by focusing of sunlight by water waves Sjoerd de Ridder ABSTRACT Illumination patterns of underwater sunlight have fascinated various researchers in the
Stable simulations of illumination patterns caused by focusing of sunlight by water waves Sjoerd de Ridder ABSTRACT Illumination patterns of underwater sunlight have fascinated various researchers in the
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference
 LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
Ray Optics. Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors
 Ray Optics Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors 1 Ray optics Optical imaging and color in medicine Integral
Ray Optics Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors 1 Ray optics Optical imaging and color in medicine Integral
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Lecture Ray Model of Light. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org
 Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean
 A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean Lian Shen Department of Civil Engineering Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-5033 fax: (410) 516-7473 email: LianShen@jhu.edu
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean Lian Shen Department of Civil Engineering Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-5033 fax: (410) 516-7473 email: LianShen@jhu.edu
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Distortion Correction for Conical Multiplex Holography Using Direct Object-Image Relationship
 Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. ROC(A) Vol. 25, No. 5, 2001. pp. 300-308 Distortion Correction for Conical Multiplex Holography Using Direct Object-Image Relationship YIH-SHYANG CHENG, RAY-CHENG CHANG, AND SHIH-YU
Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. ROC(A) Vol. 25, No. 5, 2001. pp. 300-308 Distortion Correction for Conical Multiplex Holography Using Direct Object-Image Relationship YIH-SHYANG CHENG, RAY-CHENG CHANG, AND SHIH-YU
PH880 Topics in Physics
 PH880 Topics in Physics Modern Optical Imaging (Fall 2010) The minimum path principle n(x,y,z) Γ Γ has the minimum optical path length, compared to the alternative paths. nxyzdl (,, ) Γ Thelaw of reflection
PH880 Topics in Physics Modern Optical Imaging (Fall 2010) The minimum path principle n(x,y,z) Γ Γ has the minimum optical path length, compared to the alternative paths. nxyzdl (,, ) Γ Thelaw of reflection
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Experiment 9. Law of reflection and refraction of light
 Experiment 9. Law of reflection and refraction of light 1. Purpose Invest light passing through two mediums boundary surface in order to understand reflection and refraction of light 2. Principle As shown
Experiment 9. Law of reflection and refraction of light 1. Purpose Invest light passing through two mediums boundary surface in order to understand reflection and refraction of light 2. Principle As shown
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XIII Refraction of light Snell s law Dispersion and rainbow Mirrors and lens Plane mirrors Concave and convex mirrors Thin lenses http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XIII Refraction of light Snell s law Dispersion and rainbow Mirrors and lens Plane mirrors Concave and convex mirrors Thin lenses http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/
Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness: Innovative Polarization Measurement
 Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness: Innovative Polarization Measurement Christopher J. Zappa Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Ocean and Climate Physics Division 61 Route 9W, Palisades,
Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness: Innovative Polarization Measurement Christopher J. Zappa Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Ocean and Climate Physics Division 61 Route 9W, Palisades,
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3. Chapter 20. Classic and Modern Optics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Effect of 3-D instrument casing shape on the self-shading of in-water upwelling irradiance
 Effect of 3-D instrument casing shape on the self-shading of in-water upwelling irradiance Jacek Piskozub Institute of Oceanology PAS, ul. Powstancow Warszawy 55, 81-712 Sopot, Poland piskozub@iopan.gda.pl
Effect of 3-D instrument casing shape on the self-shading of in-water upwelling irradiance Jacek Piskozub Institute of Oceanology PAS, ul. Powstancow Warszawy 55, 81-712 Sopot, Poland piskozub@iopan.gda.pl
Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurements
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurements Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurements Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
Physical Optics. You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra ( )
 Physical Optics You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra (1925-2015) OBJECTIVES To observe some interference and diffraction phenomena with visible light. THEORY In a previous experiment you
Physical Optics You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra (1925-2015) OBJECTIVES To observe some interference and diffraction phenomena with visible light. THEORY In a previous experiment you
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Formulas of possible interest
 Name: PHYS 3410/6750: Modern Optics Final Exam Thursday 15 December 2011 Prof. Bolton No books, calculators, notes, etc. Formulas of possible interest I = ɛ 0 c E 2 T = 1 2 ɛ 0cE 2 0 E γ = hν γ n = c/v
Name: PHYS 3410/6750: Modern Optics Final Exam Thursday 15 December 2011 Prof. Bolton No books, calculators, notes, etc. Formulas of possible interest I = ɛ 0 c E 2 T = 1 2 ɛ 0cE 2 0 E γ = hν γ n = c/v
CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION. 4.1 Normal Computation
 CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION Ray computation is the second stage of the ray tracing procedure and is composed of two steps. First, the normal to the current wavefront is computed. Then the intersection of
CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION Ray computation is the second stage of the ray tracing procedure and is composed of two steps. First, the normal to the current wavefront is computed. Then the intersection of
Chapter 37. Interference of Light Waves
 Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch ) Diffraction (Ch )
 Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction
 Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
2/26/2016. Chapter 23 Ray Optics. Chapter 23 Preview. Chapter 23 Preview
 Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves
 PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
Lecture 14: Refraction
 Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Refraction of Light. This bending of the ray is called refraction
 Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
The geometry of reflection and refraction Wave conversion and reflection coefficient
 7.2.2 Reflection and Refraction The geometry of reflection and refraction Wave conversion and reflection coefficient The geometry of reflection and refraction A wave incident on a boundary separating two
7.2.2 Reflection and Refraction The geometry of reflection and refraction Wave conversion and reflection coefficient The geometry of reflection and refraction A wave incident on a boundary separating two
To determine the wavelength of laser light using single slit diffraction
 9 To determine the wavelength of laser light using single slit diffraction pattern 91 Apparatus: Helium-Neon laser or diode laser, a single slit with adjustable aperture width, optical detector and power
9 To determine the wavelength of laser light using single slit diffraction pattern 91 Apparatus: Helium-Neon laser or diode laser, a single slit with adjustable aperture width, optical detector and power
22.1. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.1. Solve: (a)
 22.. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.. Solve: (a) (b) The initial light pattern is a double-slit interference pattern. It is centered behind the midpoint of the slits. The slight decrease in intensity
22.. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex22.. Solve: (a) (b) The initial light pattern is a double-slit interference pattern. It is centered behind the midpoint of the slits. The slight decrease in intensity
PHYS1004 Problem Sheet - Optics - with Solutions
 PHYS004 Problem Sheet - Optics - with Solutions Do not write on these question sheets - there is not enough room to do a good job of answering these questions. The answers need to be written in your life
PHYS004 Problem Sheet - Optics - with Solutions Do not write on these question sheets - there is not enough room to do a good job of answering these questions. The answers need to be written in your life
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
Wave Optics. April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1
 Wave Optics April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Exam tomorrow! We/Thu: Relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday, April 30, 8-10 PM Location: WH B115 (Wells Hall)
Wave Optics April 11, 2014 Chapter 34 1 Announcements! Exam tomorrow! We/Thu: Relativity! Last week: Review of entire course, no exam! Final exam Wednesday, April 30, 8-10 PM Location: WH B115 (Wells Hall)
Downloaded from UNIT 06 Optics
 1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
SPECTRAL APPROACH TO CALCULATE SPECULAR REFLECTION OF LIGHT FROM WAVY WATER SURFACE
 in Optics of Natural Waters (ONW 1), St. Petersburg, Russia, 1. SPECTRAL APPROACH TO CALCULATE SPECULAR REFLECTION OF LIGHT FROM WAVY WATER SURFACE V. I. Haltrin, W. E. McBride III, and R. A. Arnone Naval
in Optics of Natural Waters (ONW 1), St. Petersburg, Russia, 1. SPECTRAL APPROACH TO CALCULATE SPECULAR REFLECTION OF LIGHT FROM WAVY WATER SURFACE V. I. Haltrin, W. E. McBride III, and R. A. Arnone Naval
Optics of Vision. MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1.
 Optics of Vision MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1. www.physics.uoguelph.ca/phys1070/webst.html Text: Chap. 3, pp. 1-39 (NB: pg. 3-37 missing) Chap. 5 pp.1-17 Handbook: 1. study guide 3 2. lab 3 Optics of the eye
Optics of Vision MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1. www.physics.uoguelph.ca/phys1070/webst.html Text: Chap. 3, pp. 1-39 (NB: pg. 3-37 missing) Chap. 5 pp.1-17 Handbook: 1. study guide 3 2. lab 3 Optics of the eye
Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM B Winter 2009
 Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM B Winter 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book exam. You may consult four (two-sided) 8 1/2" 11" sheets of paper of personal notes. However, you may not collaborate and/or
Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM B Winter 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book exam. You may consult four (two-sided) 8 1/2" 11" sheets of paper of personal notes. However, you may not collaborate and/or
Interference. Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location.
 Interference Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location. Thus, interacting electromagnetic waves also add together.
Interference Electric fields from two different sources at a single location add together. The same is true for magnetic fields at a single location. Thus, interacting electromagnetic waves also add together.
Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness Innovative Measurement and Modeling
 Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness Innovative Measurement and Modeling Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science
Ocean Surface Wave Optical Roughness Innovative Measurement and Modeling Howard Schultz Aerial Imaging and Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Massachusetts, Amherst Department of Computer Science
Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation
 Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics P.O. Box 1385, GR-71110 Heraklion,
Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics P.O. Box 1385, GR-71110 Heraklion,
The Elimination of Correlation Errors in PIV Processing
 9 th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, July, 1998 The Elimination of Correlation Errors in PIV Processing Douglas P. Hart Massachusetts Institute
9 th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, July, 1998 The Elimination of Correlation Errors in PIV Processing Douglas P. Hart Massachusetts Institute
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
Digital Image Correlation of Stereoscopic Images for Radial Metrology
 Digital Image Correlation of Stereoscopic Images for Radial Metrology John A. Gilbert Professor of Mechanical Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Huntsville, AL 35899 Donald R. Matthys Professor
Digital Image Correlation of Stereoscopic Images for Radial Metrology John A. Gilbert Professor of Mechanical Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Huntsville, AL 35899 Donald R. Matthys Professor
Chapter 33 cont. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
The main problem of photogrammetry
 Structured Light Structured Light The main problem of photogrammetry to recover shape from multiple views of a scene, we need to find correspondences between the images the matching/correspondence problem
Structured Light Structured Light The main problem of photogrammetry to recover shape from multiple views of a scene, we need to find correspondences between the images the matching/correspondence problem
Experiment 6. Snell s Law. Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite.
 Experiment 6 Snell s Law 6.1 Objectives Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite. Observe total internal reflection and calculate the critical angle. Explain the basis of how optical
Experiment 6 Snell s Law 6.1 Objectives Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite. Observe total internal reflection and calculate the critical angle. Explain the basis of how optical
Chapter 33. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian The Nature of Light Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles
Chapter 33 The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian The Nature of Light Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles
LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 14 2 Reading chapter 33-5 & 33-8 Phasors n Addition of two harmonic waves n Interference pattern from multiple sources n Single slit diffraction
LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 14 2 Reading chapter 33-5 & 33-8 Phasors n Addition of two harmonic waves n Interference pattern from multiple sources n Single slit diffraction
1. What is the law of reflection?
 Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
The branch of physics which studies light
 Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Quantitative flow visualization using the hydraulic analogy
 Experiments in Fluids 27 (2000) 165 169 Springer-Verlag 2000 Quantitative flow visualization using the hydraulic analogy S. L. Rani, M. S. Wooldridge 165 Abstract The current work describes the development
Experiments in Fluids 27 (2000) 165 169 Springer-Verlag 2000 Quantitative flow visualization using the hydraulic analogy S. L. Rani, M. S. Wooldridge 165 Abstract The current work describes the development
Fundamental Optics for DVD Pickups. The theory of the geometrical aberration and diffraction limits are introduced for
 Chapter Fundamental Optics for DVD Pickups.1 Introduction to basic optics The theory of the geometrical aberration and diffraction limits are introduced for estimating the focused laser beam spot of a
Chapter Fundamental Optics for DVD Pickups.1 Introduction to basic optics The theory of the geometrical aberration and diffraction limits are introduced for estimating the focused laser beam spot of a
Physics 202, Lecture 23
 Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign
 Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti 1-4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
The liquid s index of refraction is. v liquid = nm = = 460 nm 1.38
 HMWK 5 Ch 17: P 6, 11, 30, 31, 34, 42, 50, 56, 58, 60 Ch 18: P 7, 16, 22, 27, 28, 30, 51, 52, 59, 61 Ch. 17 P17.6. Prepare: The laser beam is an electromagnetic wave that travels with the speed of light.
HMWK 5 Ch 17: P 6, 11, 30, 31, 34, 42, 50, 56, 58, 60 Ch 18: P 7, 16, 22, 27, 28, 30, 51, 52, 59, 61 Ch. 17 P17.6. Prepare: The laser beam is an electromagnetic wave that travels with the speed of light.
Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law
 Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
Wave properties The wave speed A two-dimensional traveling wave is a disturbance of a medium, which can be expressed
 Wave phenomena: ripple tank experiments References: PASCO Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for Ripple Generator and Ripple Tank System G. Kuwabara, T. Hasegawa, K. Kono: Water waves in a ripple
Wave phenomena: ripple tank experiments References: PASCO Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for Ripple Generator and Ripple Tank System G. Kuwabara, T. Hasegawa, K. Kono: Water waves in a ripple
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light. Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle
 Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Solutions PHYS1252 Exam #1, Spring 2017, V hbs. Problem I: Multiple Choice Questions, 20P total = 5P(Q.1) + 5P(Q.2) + 5P(Q.3) + 5P(Q.
 Problem I: Multiple Choice Questions, 20P total = 5P(Q1) + 5P(Q2) + 5P(Q3) + 5P(Q4) Exam Version: 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F Q1 [5P] B B C D C B Q2 [5P] D D C E A B Q3 [5P] A C C B B D Q4 [5P] D D E E A E Detailed
Problem I: Multiple Choice Questions, 20P total = 5P(Q1) + 5P(Q2) + 5P(Q3) + 5P(Q4) Exam Version: 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F Q1 [5P] B B C D C B Q2 [5P] D D C E A B Q3 [5P] A C C B B D Q4 [5P] D D E E A E Detailed
PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 7: DIFFRACTION & INTERFERENCE
 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 7: DIFFRACTION & INTERFERENCE Object: To investigate the diffraction and interference of light, Apparatus: Lasers, optical bench, single and double slits. screen and mounts. Theory:
PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 7: DIFFRACTION & INTERFERENCE Object: To investigate the diffraction and interference of light, Apparatus: Lasers, optical bench, single and double slits. screen and mounts. Theory:
Diffraction. Introduction: Diffraction is bending of waves around an obstacle (barrier) or spreading of waves passing through a narrow slit.
 Introduction: Diffraction is bending of waves around an obstacle (barrier) or spreading of waves passing through a narrow slit. Diffraction amount depends on λ/a proportion If a >> λ diffraction is negligible
Introduction: Diffraction is bending of waves around an obstacle (barrier) or spreading of waves passing through a narrow slit. Diffraction amount depends on λ/a proportion If a >> λ diffraction is negligible
