Chapter 33 cont. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
|
|
|
- Luke Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
2 Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction in which the electric field is vibrating In this example, the direction of polarization is along the y-axis
3 Unpolarized Light, Example All directions of vibration from a wave source are possible The resultant em wave is a superposition of waves vibrating in many different directions This is an unpolarized wave The arrows show a few possible directions of the waves in the beam
4 Polarization of Light, cont. A wave is said to be linearly polarized if the resultant electric field E vibrates in the same direction at all times at a particular point The plane formed by E and the direction of propagation is called the plane of polarization of the wave
5 Methods of Polarization It is possible to obtain a linearly polarized beam from an unpolarized beam by removing all waves from the beam except those whose electric field vectors oscillate in a single plane Processes for accomplishing this include selective absorption reflection double refraction scattering
6 Polarization by Selective Absorption The most common technique for polarizing light Uses a material that transmits waves whose electric field vectors lie in the plane parallel to a certain direction and absorbs waves whose electric field vectors are perpendicular to that direction
7 Active Figure (SLIDESHOW MODE ONLY)
8 Selective Absorption, cont. E. H. Land discovered a material that polarizes light through selective absorption He called the material polaroid The molecules readily absorb light whose electric field vector is parallel to their lengths and allow light through whose electric field vector is perpendicular to their lengths
9 Selective Absorption, final It is common to refer to the direction perpendicular to the molecular chains as the transmission axis In an ideal polarizer, All light with E parallel to the transmission axis is transmitted All light with E perpendicular to the transmission axis is absorbed
10 Intensity of a Polarized Beam The intensity of the polarized beam transmitted through the second polarizing sheet (the analyzer) varies as I = I max cos 2 θ (Malus s Law) I o is the intensity of the polarized wave incident on the analyzer Malus s law applies to any two polarizing materials whose transmission axes are at an angle of θ to each other
11 Intensity of a Polarized Beam, cont. The intensity of the transmitted beam is a maximum when the transmission axes are parallel θ = 0 or 180 o The intensity is zero when the transmission axes are perpendicular to each other This would cause complete absorption
12 Intensity of Polarized Light, Examples On the left, the transmission axes are aligned and maximum intensity occurs In the middle, the axes are at 45 o to each other and less intensity occurs On the right, the transmission axes are perpendicular and the light intensity is a minimum
13 Polarization by Reflection When an unpolarized light beam is reflected from a surface, the reflected light may be Completely polarized Partially polarized Unpolarized It depends on the angle of incidence If the angle is 0, the reflected beam is unpolarized For other angles, there is some degree of polarization For one particular angle, the beam is completely polarized
14 Polarization by Reflection, cont. The angle of incidence for which the reflected beam is completely polarized is called the polarizing angle, θ p Brewster s law relates the polarizing angle to the index of refraction for the material sin θp n = = tan θp cos θ p θ p may also be called Brewster s angle
15 Polarization by Reflection, Partially Polarized Example Unpolarized light is incident on a reflecting surface The reflected beam is partially polarized The refracted beam is partially polarized
16 Polarization by Reflection, Completely Polarized Example Unpolarized light is incident on a reflecting surface The reflected beam is completely polarized The refracted beam is perpendicular to the reflected beam The angle of incidence is Brewster s angle
17 Polarization by Double Refraction In certain crystalline structures, the speed of light is not the same in all directions Such materials are characterized by two indices of refraction They are often called double-refracting or birefringent materials
18 Polarization by Double Refraction, cont. Unpolarized light splits into two planepolarized rays The two rays are in mutual perpendicular directions Indicated by the dots and arrows
19 Polarization by Double Refraction, Rays The ordinary (O) ray is characterized by an index of refraction of n o This is the same in all directions The second ray is the extraordinary (E) ray which travels at different speeds in different directions Characterized by an index of refraction of n E that varies with the direction of propagation
20 Polarization by Double Refraction, Optic Axis There is one direction, called the optic axis, along which the ordinary and extraordinary rays have the same speed n O = n E The difference in speeds for the two rays is a maximum in the direction perpendicular to the optic axis
21 Some Indices of Refraction
22 Optical Stress Analysis Some materials become birefringent when stressed When a material is stressed, a series of light and dark bands is observed The light bands correspond to areas of greatest stress Optical stress analysis uses plastic models to test for regions of potential weaknesses
23 Polarization by Scattering When light is incident on any material, the electrons in the material can absorb and reradiate part of the light This process is called scattering An example of scattering is the sunlight reaching an observer on the Earth being partially polarized
24 Polarization by Scattering, cont. The horizontal part of the electric field vector in the incident wave causes the charges to vibrate horizontally The vertical part of the vector simultaneously causes them to vibrate vertically If the observer looks straight up, he sees light that is completely polarized in the horizontal direction
25 Scattering, cont. Short wavelengths (blue) are scattered more efficiently than long wavelengths (red) When sunlight is scattered by gas molecules in the air, the blue is scattered more intensely than the red When you look up, you see blue At sunrise or sunset, much of the blue is scattered away, leaving the light at the red end of the spectrum
26 Optical Activity Certain materials display the property of optical activity A material is said to be optically active if it rotates the plane of polarization of any light transmitted through it Molecular asymmetry determines whether a material is optically active
27 Huygens s Principle Huygens assumed that light is a form of wave motion rather than a stream of particles Huygens s Principle is a geometric construction for determining the position of a new wave at some point based on the knowledge of the wave front that preceded it
28 Huygens s Principle, cont. All points on a given wave front are taken as point sources for the production of spherical secondary waves, called wavelets, which propagate outward through a medium with speeds characteristic of waves in that medium After some time has passed, the new position of the wave front is the surface tangent to the wavelets
29 Huygens s Construction for a Plane Wave At t = 0, the wave front is indicated by the plane AA The points are representative sources for the wavelets After the wavelets have moved a distance cδt, a new plane BB can be drawn tangent to the wavefronts
30 Huygens s Construction for a Spherical Wave The inner arc represents part of the spherical wave The points are representative points where wavelets are propagated The new wavefront is tangent at each point to the wavelet
31 Huygens s Principle and the Law of Reflection The law of reflection can be derived from Huygens s principle AB is a wave front of incident light The wave at A sends out a wavelet centered on A toward D The wave at B sends out a wavelet centered on B toward C AD = BC = cδt
32 Huygens s Principle and the Law of Reflection, cont. Triangle ABC is congruent to triangle ADC cos γ = BC / AC cos γ = AD / AC Therefore, cos γ = cos γ and γ = γ This gives θ 1 = θ 1 This is the law of reflection
33 Huygens s Principle and the Law of Refraction Ray 1 strikes the surface and at a time interval Δt later, ray 2 strikes the surface During this time interval, the wave at A sends out a wavelet, centered at A, toward D
34 Huygens s Principle and the Law of Refraction, cont. The wave at B sends out a wavelet, centered at B, toward C The two wavelets travel in different media, therefore their radii are different From triangles ABC and ADC, we find 1 2 sin BC v Δ t 1 and sin AD v Δ θ = = θ t 2 = = AC AC AC AC
35 Huygens s Principle and the Law of Refraction, final The preceding equation can be simplified to sin θ1 v1 = sin θ2 v2 sin θ1 cn1 n2 But = = sin θ2 cn2 n1 and so n sin θ = n sin θ This is Snell s law of refraction
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Lecture Ray Model of Light. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org
 Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 33. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian The Nature of Light Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles
Chapter 33 The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 1) Dr. Armen Kocharian The Nature of Light Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles
Review: 22.4: Dispersion. Refraction in a Prism. Announcements
 Announcements The second midterm exam is coming Monday, Nov 8 Will cover from 18.1 thru 22.7 Same format as Exam 1 20 multiple choice questions Room assignments TBA QUESTIONS? PLEASE ASK! Review: Light
Announcements The second midterm exam is coming Monday, Nov 8 Will cover from 18.1 thru 22.7 Same format as Exam 1 20 multiple choice questions Room assignments TBA QUESTIONS? PLEASE ASK! Review: Light
Introduction to Light
 Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer from the source to the observer. Images in mirrors Reflection
Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer from the source to the observer. Images in mirrors Reflection
Chapter 22. Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Dispersion Polarization
 Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3. Chapter 20. Classic and Modern Optics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal
 The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal the underlying symmetry structure of the object that diffracts
The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal the underlying symmetry structure of the object that diffracts
Basic Optics : Microlithography Optics Part 4: Polarization
 Electromagnetic Radiation Polarization: Linear, Circular, Elliptical Ordinary and extraordinary rays Polarization by reflection: Brewster angle Polarization by Dichroism Double refraction (Birefringence)
Electromagnetic Radiation Polarization: Linear, Circular, Elliptical Ordinary and extraordinary rays Polarization by reflection: Brewster angle Polarization by Dichroism Double refraction (Birefringence)
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
10.5 Polarization of Light
 10.5 Polarization of Light Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These fields can take many different directions
10.5 Polarization of Light Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These fields can take many different directions
Image Formation by Refraction
 Image Formation by Refraction If you see a fish that appears to be swimming close to the front window of the aquarium, but then look through the side of the aquarium, you ll find that the fish is actually
Image Formation by Refraction If you see a fish that appears to be swimming close to the front window of the aquarium, but then look through the side of the aquarium, you ll find that the fish is actually
Polarization. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Polarization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Polaroid sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (see [link]). Polaroids have this ability
Polarization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Polaroid sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (see [link]). Polaroids have this ability
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu
 Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
Wavefronts and Rays. When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to
 Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics
 B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics UNIT III Polarization Introduction:- Interference and diffraction phenomena proved that light is a wave motion. These phenomena are
B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics UNIT III Polarization Introduction:- Interference and diffraction phenomena proved that light is a wave motion. These phenomena are
Physics 202, Lecture 23
 Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 4-3 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS Reading Activity Questions? Essential Idea: All waves can be described by the same sets of mathematical ideas.
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 4-3 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS Reading Activity Questions? Essential Idea: All waves can be described by the same sets of mathematical ideas.
OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES
 Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
OpenStax-CNX module: m Polarization * Bobby Bailey. Based on Polarization by OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m52456 1 27.9 Polarization * Bobby Bailey Based on Polarization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m52456 1 27.9 Polarization * Bobby Bailey Based on Polarization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light 24.1 Waves Versus Particles; Huygens Principle and Diffraction Huygens principle: Every point on a wave front acts as a point source; the wavefront as it develops is
Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light 24.1 Waves Versus Particles; Huygens Principle and Diffraction Huygens principle: Every point on a wave front acts as a point source; the wavefront as it develops is
Electromagnetic waves
 Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Chapter 35. The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics
 Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Chapter 35. The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics
 Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics
 Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Properties of Light. 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization
 Chapter 33 - Light Properties of Light 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap33-Light - Revised: 6-24-2012 2 Electromagnetic
Chapter 33 - Light Properties of Light 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap33-Light - Revised: 6-24-2012 2 Electromagnetic
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Be careful not to leave your fingerprints on the optical surfaces of lenses or Polaroid sheets.
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision An optical Tuning Fork Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Where does light actually come
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision An optical Tuning Fork Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Where does light actually come
The Propagation of Light:
 Lecture 8 Chapter 4 The Propagation of Light: Transmission Reflection Refraction Macroscopic manifestations of scattering and interference occurring at the atomic level Reflection Reflection Inside the
Lecture 8 Chapter 4 The Propagation of Light: Transmission Reflection Refraction Macroscopic manifestations of scattering and interference occurring at the atomic level Reflection Reflection Inside the
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch ) Diffraction (Ch )
 Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Internal Reflection. Total Internal Reflection. Internal Reflection in Prisms. Fiber Optics. Pool Checkpoint 3/20/2013. Physics 1161: Lecture 18
 Physics 1161: Lecture 18 Internal Reflection Rainbows, Fiber Optics, Sun Dogs, Sun Glasses sections 26-8 & 25-5 Internal Reflection in Prisms Total Internal Reflection Recall Snell s Law: n 1 sin( 1 )=
Physics 1161: Lecture 18 Internal Reflection Rainbows, Fiber Optics, Sun Dogs, Sun Glasses sections 26-8 & 25-5 Internal Reflection in Prisms Total Internal Reflection Recall Snell s Law: n 1 sin( 1 )=
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
4.4 Polarisation [26 marks]
![4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 4.4 Polarisation [26 marks]](/thumbs/89/98671418.jpg) 4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 1. Unpolarized light of intensity I 0 is incident on the first of two polarizing sheets. Initially the planes of polarization of the sheets are perpendicular. Which sheet must
4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 1. Unpolarized light of intensity I 0 is incident on the first of two polarizing sheets. Initially the planes of polarization of the sheets are perpendicular. Which sheet must
Chapter 24. Geometric optics. Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24
 Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
1. Particle Scattering. Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes
 1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
IB-2 Polarization Practice
 Name: 1. Plane-polarized light is incident normally on a polarizer which is able to rotate in the plane perpendicular to the light as shown below. In diagram 1, the intensity of the incident light is 8
Name: 1. Plane-polarized light is incident normally on a polarizer which is able to rotate in the plane perpendicular to the light as shown below. In diagram 1, the intensity of the incident light is 8
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L Polarization of Light (P.532-537) What is Polarized Light? Polarized sunglasses eliminate the glare of reflected light off the surface of a stream while
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L Polarization of Light (P.532-537) What is Polarized Light? Polarized sunglasses eliminate the glare of reflected light off the surface of a stream while
Polarization. OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58525 1 Polarization OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m58525 1 Polarization OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS
 Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS I. POLARIZATION Natural unpolarized light is made up of waves vibrating in all directions. When a beam of unpolarized light is
Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS I. POLARIZATION Natural unpolarized light is made up of waves vibrating in all directions. When a beam of unpolarized light is
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Polarization of waves on ropes
 Polarization of waves on ropes Youtube clip one: the gentleman excites first a wave of vertical polarization, and next of horizontal polarization. Youtube clip two: vertical, horizontal, and even circular
Polarization of waves on ropes Youtube clip one: the gentleman excites first a wave of vertical polarization, and next of horizontal polarization. Youtube clip two: vertical, horizontal, and even circular
Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation
 Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation Chen-Bin Huang Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Various slides under courtesy
Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation Chen-Bin Huang Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Various slides under courtesy
Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee. Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction
 Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction Okay, this is the third lecture of the five lecture series
Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction Okay, this is the third lecture of the five lecture series
WAVE OPTICS-I. A linear source produces cylindrical wavefront. (Draw diagram).
 WAVE OPTICS-I Wavefront: It is the locus of points in space which are simultaneously disturbed and are vibrating in same phase. Wavefront can be spherical, plane or cylindrical. Note that the wavefront
WAVE OPTICS-I Wavefront: It is the locus of points in space which are simultaneously disturbed and are vibrating in same phase. Wavefront can be spherical, plane or cylindrical. Note that the wavefront
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc
 Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Optics Polarization Birefringence
 Optics Polarization Birefringence Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 21, 2018 Last time the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization Brewster angle Overview polarization birefringence Rayleigh
Optics Polarization Birefringence Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 21, 2018 Last time the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization Brewster angle Overview polarization birefringence Rayleigh
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other.
 CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Polarization. Components of Polarization: Malus Law. VS203B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization
 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, 013 011 Topic: Polarization Polarization Recall that I stated that we had to model light as a transverse wave so that we could use the model to explain polarization. The electric
VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, 013 011 Topic: Polarization Polarization Recall that I stated that we had to model light as a transverse wave so that we could use the model to explain polarization. The electric
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea?
 How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea? www.digital-photography-tips.net/stay_focussed-newsletter-march-2013.html Discover the answer to this
How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea? www.digital-photography-tips.net/stay_focussed-newsletter-march-2013.html Discover the answer to this
Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch : E&M Waves
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch.33.6 10: E&M Waves Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don t ordinarily feel pressure
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch.33.6 10: E&M Waves Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don t ordinarily feel pressure
CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate
 CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Construction Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate POLARISATION Huygens Theory of Double Refraction
CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Construction Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate POLARISATION Huygens Theory of Double Refraction
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
! "To accept Huygens's principle requires abandoning the idea that a ray has much intrinsic physical significance..." (pg. 5.)
 02. Malus and Polarization. 1. The Optical Ray. Pre-17th Century: The ray as the physical foundation of light.! Euclid: "visual rays" proceed from the eye to object of sight. 1690. Huygens's Traite de
02. Malus and Polarization. 1. The Optical Ray. Pre-17th Century: The ray as the physical foundation of light.! Euclid: "visual rays" proceed from the eye to object of sight. 1690. Huygens's Traite de
PY106 Class31. Index of refraction. Refraction. Index of refraction. Sample values of n. Rays and wavefronts. index of refraction: n v.
 Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter
![1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter 1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter](/thumbs/81/83191942.jpg) Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
Polarisation and Diffraction
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
Understanding the Propagation of Light
 [ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
[ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
Polarization of light
 Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Course Updates. Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today. 2) Polarization, dispersion. 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today 2) Polarization, dispersion 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd n 1 n 2 Total
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today 2) Polarization, dispersion 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd n 1 n 2 Total
DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE. Utsav Hanspal. Physics Honors Research Paper
 DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE Utsav Hanspal Physics Honors Research Paper Dr. Watson Hanspal 2 INTRODUCTION When light moves between
DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE Utsav Hanspal Physics Honors Research Paper Dr. Watson Hanspal 2 INTRODUCTION When light moves between
θ =θ i r n sinθ = n sinθ
 θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n sin θ Total Internal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n 1 =1.5) to air (n =1.0) n 1 incident ray θ 1 θ r reflected ray GLASS sinθ sinθ 1 > 1 = n n 1 θ > θ 1 n θ refracted
θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n sin θ Total Internal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n 1 =1.5) to air (n =1.0) n 1 incident ray θ 1 θ r reflected ray GLASS sinθ sinθ 1 > 1 = n n 1 θ > θ 1 n θ refracted
Light. Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction
 Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Physics 1502: Lecture 28 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1502: Lecture 28 Today s Agenda Announcements: Midterm 2: Monday Nov. 16 Homework 08: due next Friday Optics Waves, Wavefronts, and Rays Reflection Index of Refraction 1 Waves, Wavefronts, and
Physics 1502: Lecture 28 Today s Agenda Announcements: Midterm 2: Monday Nov. 16 Homework 08: due next Friday Optics Waves, Wavefronts, and Rays Reflection Index of Refraction 1 Waves, Wavefronts, and
History of Light. 5 th Century B.C.
 History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
Chapter 36. Diffraction. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Polarization Exploration #10600
 1550 Finntown Road Waldoboro ME 04572 www.envisionlabs.com Polarization Exploration #10600 the light wave is always present, but it s omission from the diagrams and figures is solely for clarity of understanding
1550 Finntown Road Waldoboro ME 04572 www.envisionlabs.com Polarization Exploration #10600 the light wave is always present, but it s omission from the diagrams and figures is solely for clarity of understanding
Lecture 14: Refraction
 Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Ch. 22 Properties of Light HW# 1, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, 22, 29, 37, 38
 Ch. 22 Properties of Light HW# 1, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, 22, 29, 37, 38 Brief History of the Nature of Light Up until 19 th century, light was modeled as a stream of particles. Newton was a proponent of
Ch. 22 Properties of Light HW# 1, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, 22, 29, 37, 38 Brief History of the Nature of Light Up until 19 th century, light was modeled as a stream of particles. Newton was a proponent of
θ =θ i r n sinθ = n sinθ
 θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n2 sin θ 2 Index of Refraction Speed of light, c, in vacuum is 3x10 8 m/s Speed of light, v, in different medium can be v < c. index of refraction, n = c/v. frequency, f, does not
θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n2 sin θ 2 Index of Refraction Speed of light, c, in vacuum is 3x10 8 m/s Speed of light, v, in different medium can be v < c. index of refraction, n = c/v. frequency, f, does not
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
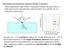 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Polarization. Lecture outline
 Polarization Lecture outline Why is polarization important? Classification of polarization Four ways to polarize EM waves Polarization in active remote sensing systems 1 Definitions Polarization is the
Polarization Lecture outline Why is polarization important? Classification of polarization Four ways to polarize EM waves Polarization in active remote sensing systems 1 Definitions Polarization is the
Refraction of Light. This bending of the ray is called refraction
 Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Light II. Physics 2415 Lecture 32. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Light II Physics 2415 Lecture 32 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Huygens principle and refraction Snell s law and applications Dispersion Total internal reflection Huygens Principle Newton s contemporary
Light II Physics 2415 Lecture 32 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Huygens principle and refraction Snell s law and applications Dispersion Total internal reflection Huygens Principle Newton s contemporary
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 02 Unit-4 Phase contrast, Polarized
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 02 Unit-4 Phase contrast, Polarized
Light. Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see
 Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide. From Last time. Huygen s principle. Overlapping diffraction patterns. Diffraction from other objects
 New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide From Last time Two-source interference: Interference-like pattern from a single slit. For a slit: a θ central width ~ 2 Diffraction grating Week3HW on Mastering
New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide From Last time Two-source interference: Interference-like pattern from a single slit. For a slit: a θ central width ~ 2 Diffraction grating Week3HW on Mastering
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Rules for Deviation of Light Rays During Refraction
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
LIGHT. Descartes particle theory, however, could not be used to explain diffraction of light.
 1 LIGHT Theories of Light In the 17 th century Descartes, a French scientist, formulated two opposing theories to explain the nature of light. These two theories are the particle theory and the wave theory.
1 LIGHT Theories of Light In the 17 th century Descartes, a French scientist, formulated two opposing theories to explain the nature of light. These two theories are the particle theory and the wave theory.
LECTURE 13 REFRACTION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 13 REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 13 2 Reading chapter 26.5 Index of refraction Snell s law Total internal reflection Total polarization Index of refraction 3 The speed of light in
LECTURE 13 REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 13 2 Reading chapter 26.5 Index of refraction Snell s law Total internal reflection Total polarization Index of refraction 3 The speed of light in
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT REFRACTION When light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, it bends from
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT REFRACTION When light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, it bends from
