Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.
|
|
|
- June Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shadows Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.com Practical & Robust Stenciled Shadow Volumes for Hardware-Accelerated Rendering, Cass Everitt & Mark J. Kilgard, GDC 2002 Shadow Mapping with Today s OpenGL Hardware, Mark Kilgard, CEDEC 2001, Tokyo, Japan Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes, Mark Kilgard, CEDEC 2001, Tokyo, Japan Shadow Mapping, Cass Everitt Reflections, Shadows,Transparency, and Fog, Mark Kilgard, GDC 2000 Tutorial Shadow Mapping with Todays OpenGL Hardware, Mark Kilgard, GDC 2000 Tutorial Shadows Important visual cue All real world scenes have shadows Occlusion from light s point-of-view instead of viewer s Cue for light-object-object relationships CS 4451 Fall
2 Local Illumination & Shadows Typically lack shadow support Ignore occlusion of lights that creates shadows Global lighting models account for shadows Too expensive for interactive use Interactive shadow algorithms typically operate independent of local lighting models Interactive Shadow Simplifications True shadows are expensive, cut corners Simple geometry tricks Projection Volume intersection Pre-compute static shadow results where possible Make simplifying assumptions Treat area light sources as points Exploit hardware features such as stencil CS 4451 Fall
3 Common Real-time Shadow Techniques Projected planar shadows Shadow volumes Hybrid approaches Light maps Problems with Common Techniques Mostly tricks with lots of limitations Light maps totally unsuited for dynamic shadows Projected planar shadows well works only on flat surfaces Stenciled shadow volumes determining the shadow volume is hard work Shadow Maps only works with spotlight frustums shadow acne artifacts CS 4451 Fall
4 Pre-computed Shadow Textures (Light maps, 8.5 in book) Lightmaps are static shadow textures Compute lightmaps off-line with radiosity solver local lighting models evaluated on tight grid can work too Lightmaps with soft shadows can be built faster with convolution approach, accelerated using the Fast Fourier Transform [Soler & Silion 98] Pre-computed shadow textures work well for building interior with lots of diffuse surfaces Aside: Stencil Buffers An extra test for fine-grain pixel control Standard OpenGL and DirectX 6 feature Per-pixel test similar to depth buffering Tests fragment against pixel s stencil value, rejects fragments that fail Also, can modify pixel s stencil buffer value based on stencil/depth test results Hardware accelerates stencil testing Typically free when depth testing too CS 4451 Fall
5 Stencil Testing Similar to Depth Testing but Compares current reference value to pixel s stencil buffer value Same comparison functions as depth test Stencil values controlled by stencil ops stencil side effects of stencil & depth tests Possible operations Increment, Decrement Keep, Replace, Zero, Invert Projected Planar Shadows CS 4451 Fall
6 Projected Planar Shadows Classic computer graphics trick Given Ground plane equation, Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 Light position (x, y, z, w) Construct projective transform that squishes vertices into ground plane based on light position Concatenate this with view transform Rendering 3D object creates shadow-like pile of polygons in ground plane Projected Planar Shadow Issues Shadow must be cast on infinite planes Pile of polygons creates Z-fighting artifacts Polygon offset fixes this, but disturbs Z values Difficult to blend shadow with ground texture Just blending creates double blends Specular highlights can show in shadow Stencil testing can fix most of these issues CS 4451 Fall
7 Projected Planar Shadow Artifacts Bad Good extends off ground region Z fighting double blending Shadow Volumes CS 4451 Fall
8 The Shadow Volume Concept Volumetric shadows, not just planar A single point light source splits the world in two shadowed regions unshadowed regions A shadow volume is the boundary between these shadowed and unshadowed regions First described by [Crow 77] Visualizing the Shadow Volume Occluders and light source cast out a shadow volume Objects within the volume should be shadowed Light source CS 4451 Fall
9 Shadow Volume Result Objects within the volume are shadowed Shadow Volume Algorithm High-level view of the algorithm Given the scene and a light source position, determine the shadow volume Render the scene in two passes Draw scene with the light enabled, updating only fragments in unshadowed region Draw scene with the light disabled, updated only fragments in shadowed region But how to control update of regions? CS 4451 Fall
10 2D Cutaway of a Shadow Volume Light source Shadowing object Surface outside shadow volume (illuminated) Shadow volume (infinite extent) Eye position (note that shadows are independent of the eye position) Partially shadowed object Surface inside shadow volume (shadowed) Counting Shadow Volume Enter/Leaves With a Stencil Buffer Render scene to initialize depth buffer Depth values indicate the closest visible fragments Use a stencil enter/leave counting approach Draw shadow volume twice using face culling 1st pass: render front faces and increment when depth test passes 2nd pass: render back faces and decrement when depth test passes Don t update depth or color Afterward, pixel s stencil is non-zero if pixel in shadow, and zero if illuminated CS 4451 Fall
11 Why Eye-to-Object Stencil Enter/Leave Counting Approach Works Light source Shadowing object zero +1 zero Eye position Illuminated, Behind Shadow Volumes Light source Shadowing object zero +1 zero Eye position Unshadowed object Shadow Volume Count = = 0 CS 4451 Fall
12 Shadowed, Nested in Shadow Volumes Light source Shadowing object zero +1 zero Eye position Shadowed object Shadow Volume Count = = 2 Illuminated, In Front of Shadow Volumes Light source Shadowing object zero +1 zero Eye position Shadowed object Shadow Volume Count = 0 CS 4451 Fall
13 Problems Created by Near Plane Clipping Missed shadow volume intersection due to near clip plane clipping; leads to mistaken count zero Far clip plane zero Near clip plane Visualizing the Stencil Buffer Counts Shadowed scene Stencil buffer contents Stencil counts beyond 1 are possible for multiple or complex occluders. GLUT shadowvol example credit: Tom McReynolds red = stencil value of 1 green = stencil value of 0 CS 4451 Fall
14 Computing Shadow Volumes Harder than you might think Easy for a single triangle, just project out three infinite polygons from the triangle, opposite the light position For complex objects, projecting object s 2D silhouette is a good approximation (flat objects are easy) Static shadow volumes can be pre-compiled Stenciled Shadow Volumes in Practice (1) Scene with shadows. Yellow light is embedded in the green three-holed object. P inf is used for all the following scenes. Same scene visualizing the shadow volumes. CS 4451 Fall
15 Stenciled Shadow Volumes in Practice (2) Details worth noting... Fine details: Shadows of the A, N, and T letters on the knight s armor and shield. Hard case: The shadow volume from the front-facing hole would definitely intersect the near clip plane. Stenciled Shadow Volumes in Practice (3) Alternate view of same scene with shadows. Yellow lines indicate previous view s view frustum boundary. Recall shadows are view-independent. Shadow volumes from the alternate view. CS 4451 Fall
16 Shadow Volume Issues Practical considerations [Bergeron 86] If eye is in shadow volume, need to determine this and flip enabled & disabled lighting passes Shadow volume only as good as its tessellation Shadows tend to magnify limited tessellation of curved surfaces Must cap the shadow volume s intersection with the near clipping plane Open models and non-planar polygons Reconstructing Shadow Volume From a Depth Buffer Very clever idea [McCool 98] Render scene from light source with depth testing Read back the depth buffer Use computer vision techniques to reconstruct the shadow volume geometry from the depth buffer image Very reasonable results for complex scenes CS 4451 Fall
17 Multiple Lights and Shadow Volumes Requires still more rendering passes, but can work! Shadows from different light sources overlap correctly Shadow Volumes from Area Light Sources Make soft shadows Shadow volumes work for point light sources Area light sources are common and make soft shadows Model an area light source as a collection of point light sources [Brotman & Badler 84] Use accumulation buffer or additive blending to accumulate soft shadow Linear cost per shadow volume sample CS 4451 Fall
18 Soft Shadow Example Eight samples (more would be better) Note the banding artifacts Combined Shadow Algorithm Example: Shadow Volume + Planar Projection just logo shadow volume logo lacks shadow on the teapot teapot lacks shadow on the floor combined approach just planar projected shadows CS 4451 Fall
19 Shadow Volume Advantages Omni-directional approach Not just spotlight frustums as with shadow maps Automatic self-shadowing Everything can shadow everything, including self Without shadow acne artifacts as with shadow maps Window-space shadow determination Shadows accurate to a pixel Or sub-pixel if multisampling is available Required stencil buffer broadly supported today OpenGL support since version 1.0 (1991) Direct3D support since DX6 (1998) Shadow Volume Disadvantages Ideal light sources only Limited to local point and directional lights No area light sources for soft shadows Requires polygonal models with connectivity Models must be closed (2-manifold) Models must be free of non-planar polygons Silhouette computations are required Can burden CPU Particularly for dynamic scenes Inherently multi-pass algorithm Consumes lots of GPU fill rate CS 4451 Fall
20 Shadow Mapping Shadow Mapping Image-space shadow determination Lance Williams published the basic idea in 1978 Completely image-space algorithm no knowledge of scene s geometry is required must deal with aliasing artifacts Well known software rendering technique Pixar s RenderMan uses the algorithm Basic shadowing technique for Toy Story, etc. CS 4451 Fall
21 The Shadow Mapping Concept (1) Depth testing from the light s point-of-view Two pass algorithm First, render depth buffer from the light s point-ofview the result is a depth map or shadow map essentially a 2D function indicating the depth of the closest pixels to the light This depth map is used in the second pass The Shadow Mapping Concept (2) Shadow determination with the depth map Second, render scene from the eye s point-of-view For each rasterized fragment determine fragment s XYZ position relative to the light compare the depth value at light position XY in the depth map to fragment s light position Z CS 4451 Fall
22 The Shadow Mapping Concept (3) The Shadow Map Comparison Two values A = Z value from depth map at fragment s light XY position B = Z value of fragment s XYZ light position If B is greater than A, then there must be something closer to the light than the fragment then the fragment is shadowed If A and B are approximately equal, the fragment is lit Shadow Mapping in 2D (1) The A < B shadowed fragment case depth map image plane light source depth map Z = A eye position eye view image plane, a.k.a. the frame buffer fragment s light Z = B CS 4451 Fall
23 Shadow Mapping in 2D (2) The A B unshadowed fragment case depth map image plane light source depth map Z = A eye position fragment s light Z = B eye view image plane, a.k.a. the frame buffer Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (1) A fairly complex scene with shadows the point light source CS 4451 Fall
24 Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (2) Compare with and without shadows with shadows without shadows Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (3) The scene from the light s point-of-view FYI: from the eye s s point-of-view again CS 4451 Fall
25 Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (4) The depth buffer from the light s point-of-view FYI: from the light s s point-of-view again Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (5) Projecting the depth map onto the eye s view FYI: depth map for light s s point-of-view again CS 4451 Fall
26 Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (6) Projecting light s planar distance onto eye s view Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (6) Comparing light distance to light depth map Green is where the light planar distance and the light depth map are approximately equal Non-green is where shadows should be CS 4451 Fall
27 Visualizing the Shadow Mapping Technique (7) Scene with shadows Notice how specular highlights never appear in shadows Notice how curved surfaces cast shadows on each other More Examples Smooth surfaces with object self-shadowing Note object self-shadowing CS 4451 Fall
28 More Examples Complex objects all shadow More Examples Even the floor casts shadow Note shadow leakage due to infinitely thin floor Could be fixed by giving floor thickness CS 4451 Fall
29 Luxo Jr. in Real-time using Shadow Mapping Steve Jobs at MacWorld 2001 Japan shows this on a Mac with OpenGL using hardware shadow mapping Luxo Jr. Demo Details Luxo Jr. has two animated lights and one overhead light Three shadow maps dynamically generated per frame Complex geometry (cords and lamp arms) all correctly shadowed User controls the view, shadowing just works Real-time Luxo Jr. is technical triumph for OpenGL Only available in OpenGL. (Images are from web cast video of Apple s MacWorld Japan announcement.) CS 4451 Fall
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes. CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan
 Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Lecture 17: Shadows. Projects. Why Shadows? Shadows. Using the Shadow Map. Shadow Maps. Proposals due today. I will mail out comments
 Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Last Time. Why are Shadows Important? Today. Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Shadow Volume History (1) Shadow Volumes. Shadow Volume History (2) Shadow Volume History (3) Shadow Volume Basics. Shadow Volume History (4)
 Shadow Volume History (1) Shadow Volumes Invented by Frank Crow [ 77] Software rendering scan-line approach Brotman and Badler [ 84] Software-based depth-buffered approach Used lots of point lights to
Shadow Volume History (1) Shadow Volumes Invented by Frank Crow [ 77] Software rendering scan-line approach Brotman and Badler [ 84] Software-based depth-buffered approach Used lots of point lights to
For Intuition about Scene Lighting. Today. Limitations of Planar Shadows. Cast Shadows on Planar Surfaces. Shadow/View Duality.
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Overview. A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes. Augmented Reality.
 Overview A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes Introduction of Concepts Standard Stenciled Shadow Volumes Method Proposed Approach in AR Application Experimental
Overview A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes Introduction of Concepts Standard Stenciled Shadow Volumes Method Proposed Approach in AR Application Experimental
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Today. Why are Shadows Important? Shadows as a Depth Cue. For Intuition about Scene Lighting
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
Reflections, Shadows, Transparency, and Fog
 GDC Tutorial: Advanced OpenGL Game Development Reflections, Shadows, Transparency, and Fog March 8, 2000 Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation Quick Tutorial on Stencil Testing
GDC Tutorial: Advanced OpenGL Game Development Reflections, Shadows, Transparency, and Fog March 8, 2000 Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation Quick Tutorial on Stencil Testing
Last Time. Reading for Today: Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms
 Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Schedule. Questions? Today. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Textures can Alias. Schedule. Questions? Quiz 1: Tuesday October 26 th, in class (1 week from today!
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
Real-Time Shadows. MIT EECS 6.837, Durand and Cutler
 Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations. Vienna University of Technology 2
 Shadows What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects Vienna University of Technology 2 What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects And
Shadows What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects Vienna University of Technology 2 What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects And
Shadows. Shadows. Spatial relationship between objects. Shadows as depth cue. Spatial relationship between objects
 Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT Shadows Realism Depth cue 1 2 Shadows as depth cue Spatial relationship between objects 3 Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 Spatial relationship between
Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT Shadows Realism Depth cue 1 2 Shadows as depth cue Spatial relationship between objects 3 Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 Spatial relationship between
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #18: More Effects. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #18: More Effects Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements TA evaluations CAPE Final project blog
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #18: More Effects Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements TA evaluations CAPE Final project blog
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Real-Time Shadows. Computer Graphics. MIT EECS Durand 1
 Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering
 Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows. Real-Time Hard Shadows. Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec
 Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
Shadow Algorithms. CSE 781 Winter Han-Wei Shen
 Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker. Herbst 2010
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows
 Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
Optimized Stencil Shadow Volumes. Cass Everitt & Mark J. Kilgard
 Optimized Stencil Shadow Volumes Cass Everitt & Mark J. Kilgard Outline: Complete Lecture Review of Stenciled Shadow Volumes Stenciled Shadow Volumes Optimizations More Information Outline: Review of Stenciled
Optimized Stencil Shadow Volumes Cass Everitt & Mark J. Kilgard Outline: Complete Lecture Review of Stenciled Shadow Volumes Stenciled Shadow Volumes Optimizations More Information Outline: Review of Stenciled
Shadows. Shadows. Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT. Realism Depth cue
 Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT 1 Shadows Realism Depth cue 2 1 Shadows as depth cue 3 Spatial relationship between objects Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 2 Spatial relationship
Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT 1 Shadows Realism Depth cue 2 1 Shadows as depth cue 3 Spatial relationship between objects Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 2 Spatial relationship
Shadows. Shadows. Spatial relationship between objects. Shadows as depth cue. Spatial relationship between objects
 Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT Shadows Realism Depth cue 1 2 Shadows as depth cue Spatial relationship between objects 3 Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 Spatial relationship between
Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT Shadows Realism Depth cue 1 2 Shadows as depth cue Spatial relationship between objects 3 Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 Spatial relationship between
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 10
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
Texture Mapping II. Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1. 7.
 Texture Mapping II Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1 Light Maps Simulates the effect of a local light source + = Can be pre-computed
Texture Mapping II Light maps Environment Maps Projective Textures Bump Maps Displacement Maps Solid Textures Mipmaps Shadows 1 Light Maps Simulates the effect of a local light source + = Can be pre-computed
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Advanced Shading and Texturing
 Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
Shadow Mapping. Render Scene and Access the Depth Texture. What is Projective Texturing? About Projective Texturing (1) About Projective Texturing (3)
 Render Scene and Access the Depth Texture Shadow Mapping Cass Everitt NVIDIA Corporation cass@nvidia.com Realizing the theory in practice Fragment s light position can be generated using eye-linear texture
Render Scene and Access the Depth Texture Shadow Mapping Cass Everitt NVIDIA Corporation cass@nvidia.com Realizing the theory in practice Fragment s light position can be generated using eye-linear texture
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Reading for Today A Practical Model for Subsurface Light Transport, Jensen, Marschner, Levoy, & Hanrahan, SIGGRAPH 2001 Participating Media Measuring BRDFs
Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Reading for Today A Practical Model for Subsurface Light Transport, Jensen, Marschner, Levoy, & Hanrahan, SIGGRAPH 2001 Participating Media Measuring BRDFs
Shadow Mapping. Marc Stamminger, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
 Shadow Mapping Marc Stamminger, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg 1 Idea assumption: spot light with spot angle
Shadow Mapping Marc Stamminger, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg 1 Idea assumption: spot light with spot angle
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007
 Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007 Lightmaps, as do other precomputed lighting methods, provide an efficient and pleasing solution for lighting and shadowing of relatively static
Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007 Lightmaps, as do other precomputed lighting methods, provide an efficient and pleasing solution for lighting and shadowing of relatively static
CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline
 CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline 1 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1! evaluation of linear functions on pixel grid 2! functions defined by parameter values at vertices 3! using extra parameters to determine
CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline 1 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1! evaluation of linear functions on pixel grid 2! functions defined by parameter values at vertices 3! using extra parameters to determine
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018 Announcements Midterm Scores are on TritonEd Exams to be
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018 Announcements Midterm Scores are on TritonEd Exams to be
CS 498 VR. Lecture 18-4/4/18. go.illinois.edu/vrlect18
 CS 498 VR Lecture 18-4/4/18 go.illinois.edu/vrlect18 Review and Supplement for last lecture 1. What is aliasing? What is Screen Door Effect? 2. How image-order rendering works? 3. If there are several
CS 498 VR Lecture 18-4/4/18 go.illinois.edu/vrlect18 Review and Supplement for last lecture 1. What is aliasing? What is Screen Door Effect? 2. How image-order rendering works? 3. If there are several
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Final Projects Proposals due Thursday 4/8 Proposed project summary At least 3 related papers (read & summarized) Description of series of test cases Timeline & initial task assignment The Traditional Graphics
Final Projects Proposals due Thursday 4/8 Proposed project summary At least 3 related papers (read & summarized) Description of series of test cases Timeline & initial task assignment The Traditional Graphics
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques
 Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007
 Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Rendering. Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image. Camera. Light. Rendering. View Plane
 Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Motivation. Culling Don t draw what you can t see! What can t we see? Low-level Culling
 Motivation Culling Don t draw what you can t see! Thomas Larsson Mälardalen University April 7, 2016 Image correctness Rendering speed One day we will have enough processing power!? Goals of real-time
Motivation Culling Don t draw what you can t see! Thomas Larsson Mälardalen University April 7, 2016 Image correctness Rendering speed One day we will have enough processing power!? Goals of real-time
Shadows. COMP 575/770 Spring 2013
 Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
Computing Visibility. Backface Culling for General Visibility. One More Trick with Planes. BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz
 Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Visibility and Occlusion Culling
 Visibility and Occlusion Culling CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University [some slides based on those of Benjamin Mora] Why? To avoid processing geometry that does
Visibility and Occlusion Culling CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University [some slides based on those of Benjamin Mora] Why? To avoid processing geometry that does
Rasterization Overview
 Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Abstract. 2 Description of the Effects Used. 1 Introduction Phong Illumination Bump Mapping
 Developing a Real-Time Renderer With Optimized Shadow Volumes Mátyás Premecz (email: pmat@freemail.hu) Department of Control Engineering and Information Technology, Budapest University of Technolgy Hungary
Developing a Real-Time Renderer With Optimized Shadow Volumes Mátyás Premecz (email: pmat@freemail.hu) Department of Control Engineering and Information Technology, Budapest University of Technolgy Hungary
Volume Shadows Tutorial Nuclear / the Lab
 Volume Shadows Tutorial Nuclear / the Lab Introduction As you probably know the most popular rendering technique, when speed is more important than quality (i.e. realtime rendering), is polygon rasterization.
Volume Shadows Tutorial Nuclear / the Lab Introduction As you probably know the most popular rendering technique, when speed is more important than quality (i.e. realtime rendering), is polygon rasterization.
Lecture 13: Reyes Architecture and Implementation. Kayvon Fatahalian CMU : Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011)
 Lecture 13: Reyes Architecture and Implementation Kayvon Fatahalian CMU 15-869: Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011) A gallery of images rendered using Reyes Image credit: Lucasfilm (Adventures
Lecture 13: Reyes Architecture and Implementation Kayvon Fatahalian CMU 15-869: Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011) A gallery of images rendered using Reyes Image credit: Lucasfilm (Adventures
Stencil Shadow Volumes
 Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory T-111.500 Seminar on Computer Graphics Spring 2002 Rendering of High Quality 3D-Graphics Stencil Shadow Volumes Matti
Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory T-111.500 Seminar on Computer Graphics Spring 2002 Rendering of High Quality 3D-Graphics Stencil Shadow Volumes Matti
A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters
 jgt 2008/7/20 22:19 page 1 #1 Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: 1?? A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters Byungmoon Kim 1, Kihwan Kim 2, Greg Turk 2 1 NVIDIA, 2 Georgia Institute
jgt 2008/7/20 22:19 page 1 #1 Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: 1?? A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters Byungmoon Kim 1, Kihwan Kim 2, Greg Turk 2 1 NVIDIA, 2 Georgia Institute
GUERRILLA DEVELOP CONFERENCE JULY 07 BRIGHTON
 Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 14
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Illumination and Geometry Techniques. Karljohan Lundin Palmerius
 Illumination and Geometry Techniques Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Objectives Complex geometries Translucency Huge areas Really nice graphics! Shadows Graceful degradation Acceleration Optimization Straightforward
Illumination and Geometry Techniques Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Objectives Complex geometries Translucency Huge areas Really nice graphics! Shadows Graceful degradation Acceleration Optimization Straightforward
Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload)
 Lecture 2: Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload) Visual Computing Systems Today Finishing up from last time Brief discussion of graphics workload metrics
Lecture 2: Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload) Visual Computing Systems Today Finishing up from last time Brief discussion of graphics workload metrics
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
Orthogonal Projection Matrices. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Spring 2018 Lecture 11
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Ray Tracing. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662, Fall 2016
 Ray Tracing Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Primitive-partitioning vs. space-partitioning acceleration structures Primitive partitioning (bounding volume hierarchy): partitions node s primitives
Ray Tracing Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Primitive-partitioning vs. space-partitioning acceleration structures Primitive partitioning (bounding volume hierarchy): partitions node s primitives
Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters.
 1 2 Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters. Crowd rendering in large environments presents a number of challenges,
1 2 Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters. Crowd rendering in large environments presents a number of challenges,
This work is about a new method for generating diffusion curve style images. Although this topic is dealing with non-photorealistic rendering, as you
 This work is about a new method for generating diffusion curve style images. Although this topic is dealing with non-photorealistic rendering, as you will see our underlying solution is based on two-dimensional
This work is about a new method for generating diffusion curve style images. Although this topic is dealing with non-photorealistic rendering, as you will see our underlying solution is based on two-dimensional
Shadow Volumes Revisited
 Shadow Volumes Revisited Stefan Roettger, Alexander Irion, and Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart, Faculty of Computer Science Visualization and Interactive Systems Group! ABSTRACT We present a method
Shadow Volumes Revisited Stefan Roettger, Alexander Irion, and Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart, Faculty of Computer Science Visualization and Interactive Systems Group! ABSTRACT We present a method
Hidden surface removal. Computer Graphics
 Lecture Hidden Surface Removal and Rasterization Taku Komura Hidden surface removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles Illumination We cannot see every surface in scene We don t want
Lecture Hidden Surface Removal and Rasterization Taku Komura Hidden surface removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles Illumination We cannot see every surface in scene We don t want
Practical Shadow Mapping
 Practical Shadow Mapping Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken, Germany Abstract In this paper we propose several methods that can greatly improve
Practical Shadow Mapping Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken, Germany Abstract In this paper we propose several methods that can greatly improve
Triangle Rasterization
 Triangle Rasterization Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/07/07 1 From last time Lines and planes Culling View frustum culling Back-face culling Occlusion culling
Triangle Rasterization Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/07/07 1 From last time Lines and planes Culling View frustum culling Back-face culling Occlusion culling
Direct Rendering of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces
 Direct Rendering of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces Hardware Graphics Pipeline 2/ 81 Hardware Graphics Pipeline GPU Video Memory CPU Vertex Processor Raster Unit Fragment Processor Render Target Screen Extended
Direct Rendering of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces Hardware Graphics Pipeline 2/ 81 Hardware Graphics Pipeline GPU Video Memory CPU Vertex Processor Raster Unit Fragment Processor Render Target Screen Extended
VISIBILITY & CULLING. Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH
 VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
3D Rasterization II COS 426
 3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
LOD and Occlusion Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 LOD and Occlusion Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Problem You want to render an enormous island covered in dense vegetation in realtime [Crysis] Scene complexity Many billions of triangles Many gigabytes
LOD and Occlusion Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Problem You want to render an enormous island covered in dense vegetation in realtime [Crysis] Scene complexity Many billions of triangles Many gigabytes
Real Time Rendering of Expensive Small Environments Colin Branch Stetson University
 Real Time Rendering of Expensive Small Environments Colin Branch Stetson University Abstract One of the major goals of computer graphics is the rendering of realistic environments in real-time. One approach
Real Time Rendering of Expensive Small Environments Colin Branch Stetson University Abstract One of the major goals of computer graphics is the rendering of realistic environments in real-time. One approach
FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES. A Thesis CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN
 FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES A Thesis by CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES A Thesis by CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Page 1. Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms
 Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
Accelerated Ambient Occlusion Using Spatial Subdivision Structures
 Abstract Ambient Occlusion is a relatively new method that gives global illumination like results. This paper presents a method to accelerate ambient occlusion using the form factor method in Bunnel [2005]
Abstract Ambient Occlusion is a relatively new method that gives global illumination like results. This paper presents a method to accelerate ambient occlusion using the form factor method in Bunnel [2005]
Intro to OpenGL II. Don Fussell Computer Science Department The University of Texas at Austin
 Intro to OpenGL II Don Fussell Computer Science Department The University of Texas at Austin University of Texas at Austin CS354 - Computer Graphics Don Fussell Where are we? Last lecture, we started the
Intro to OpenGL II Don Fussell Computer Science Department The University of Texas at Austin University of Texas at Austin CS354 - Computer Graphics Don Fussell Where are we? Last lecture, we started the
Computer Graphics. Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal. Taku Komura
 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal Taku Komura 1 Why Hidden Surface Removal? A correct rendering requires correct visibility calculations When multiple opaque polygons cover the same screen
Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal Taku Komura 1 Why Hidden Surface Removal? A correct rendering requires correct visibility calculations When multiple opaque polygons cover the same screen
Projective Textures & Shadow Mapping. Prof. Aaron Lanterman School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
 Projective Textures & Shadow Mapping Prof. Aaron Lanterman School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology What is projective texturing? An intuition for projective texturing
Projective Textures & Shadow Mapping Prof. Aaron Lanterman School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology What is projective texturing? An intuition for projective texturing
Shadow Volumes. Why Shadow Volumes?
 Shado Volumes Why Shado Volumes? Dynamic shados improve your game Dramatic effects Better sense of 3D Most game shados today are very limited Planar projected shados [Blinn 88] Limited to floor planes,
Shado Volumes Why Shado Volumes? Dynamic shados improve your game Dramatic effects Better sense of 3D Most game shados today are very limited Planar projected shados [Blinn 88] Limited to floor planes,
In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms
 In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms Alex Wiens and Gitta Domik, University of Paderborn, Germany Abstract: We are describing two exercises to deepen the understanding of two popular real-time shadow
In- Class Exercises for Shadow Algorithms Alex Wiens and Gitta Domik, University of Paderborn, Germany Abstract: We are describing two exercises to deepen the understanding of two popular real-time shadow
Render-To-Texture Caching. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students)
 TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
Lecture 9: Deferred Shading. Visual Computing Systems CMU , Fall 2013
 Lecture 9: Deferred Shading Visual Computing Systems The course so far The real-time graphics pipeline abstraction Principle graphics abstractions Algorithms and modern high performance implementations
Lecture 9: Deferred Shading Visual Computing Systems The course so far The real-time graphics pipeline abstraction Principle graphics abstractions Algorithms and modern high performance implementations
Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload)
 Lecture 2: Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload) Visual Computing Systems Analyzing a 3D Graphics Workload Where is most of the work done? Memory Vertex
Lecture 2: Parallelizing Graphics Pipeline Execution (+ Basics of Characterizing a Rendering Workload) Visual Computing Systems Analyzing a 3D Graphics Workload Where is most of the work done? Memory Vertex
9. Illumination and Shading
 9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
Shadows in Computer Graphics. by Björn Kühl im/ve University of Hamburg, Germany
 Shadows in Computer Graphics by Björn Kühl im/ve University of Hamburg, Germany Importance of Shadows Shadows provide cues to the position of objects casting and receiving shadows to the position of the
Shadows in Computer Graphics by Björn Kühl im/ve University of Hamburg, Germany Importance of Shadows Shadows provide cues to the position of objects casting and receiving shadows to the position of the
DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/
 DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/2013-11-04 DEFERRED RENDERING? CONTENTS 1. The traditional approach: Forward rendering 2. Deferred rendering (DR) overview 3. Example uses of DR:
DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/2013-11-04 DEFERRED RENDERING? CONTENTS 1. The traditional approach: Forward rendering 2. Deferred rendering (DR) overview 3. Example uses of DR:
Werner Purgathofer
 Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Visible Surface Detection Werner Purgathofer Visibility in the Rendering Pipeline scene objects in object space object capture/creation ti modeling viewing projection
Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Visible Surface Detection Werner Purgathofer Visibility in the Rendering Pipeline scene objects in object space object capture/creation ti modeling viewing projection
Practical Shadows. Outline
 Practical Shadows Out of the demo, into the engine Tom Forsyth RAD Game Tools Outline Shadow volumes (stencil shadows) Fairly brief covered well elsewhere Shadow buffers Scene management of shadow buffers
Practical Shadows Out of the demo, into the engine Tom Forsyth RAD Game Tools Outline Shadow volumes (stencil shadows) Fairly brief covered well elsewhere Shadow buffers Scene management of shadow buffers
Lecturer Athanasios Nikolaidis
 Lecturer Athanasios Nikolaidis Computer Graphics: Graphics primitives 2D viewing and clipping 2D and 3D transformations Curves and surfaces Rendering and ray tracing Illumination models Shading models
Lecturer Athanasios Nikolaidis Computer Graphics: Graphics primitives 2D viewing and clipping 2D and 3D transformations Curves and surfaces Rendering and ray tracing Illumination models Shading models
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
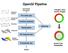 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
Shadow and Environment Maps
 CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #8 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Monday, 28 September 2009 Shadow and Environment Maps Lecture #8: Monday, 28 September 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #8 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Monday, 28 September 2009 Shadow and Environment Maps Lecture #8: Monday, 28 September 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
