Represent and interpret data. Lesson 85 CC.5.MD.2 Line Plots...169
|
|
|
- Patrick Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Measurement and Data Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Lesson 78 CC.5.MD. Customary Length Lesson 79 CC.5.MD. Customary Capacity Lesson 80 CC.5.MD. Weight Lesson 8 CC.5.MD. Multistep Measurement Problems Lesson 82 CC.5.MD. Metric Measures Lesson 83 CC.5.MD. Problem Solving Customary and Metric Conversions Lesson 8 CC.5.MD. Elapsed Time Represent and interpret data. Lesson 85 CC.5.MD.2 Line Plots Geometric measurement: understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition. Lesson 86 CC.5.MD.3 Three-Dimensional Figures Lesson 87 CC.5.MD.3a Unit Cubes and Solid Figures Lesson 88 CC.5.MD.3b Understand Volume Lesson 89 CC.5.MD. Estimate Volume Lesson 90 CC.5.MD.5a Volume of Rectangular Prisms Lesson 9 CC.5.MD.5b Algebra Apply Volume Formulas Lesson 92 CC.5.MD.5b Problem Solving Compare Volumes Lesson 93 CC.5.MD.5c Find Volume of Composed Figures vi
3 Customary Length LESSON 78 CC.5.MD. OBJECTIVE Compare, contrast, and convert customary units of length. You can convert one customary unit of length to another customary unit of length by multiplying or dividing. Multiply to change from larger to smaller units of length. Divide to change from smaller to larger units of length. Customary Units of Length foot (ft) = 2 inches (in.) yard (yd) = 3 feet mile (mi) = 5,280 feet mile =,760 yards Convert 3 feet to inches. Step Decide: Multiply or Divide feet larger inches smaller Step 2 Think: ft = 2 in., so 3 ft = (3 2 ) in. Step 3 Multiply. 3 2 = 36 So, 3 feet = 36 inches. Convert 363 feet to yards. Step Decide: Multiply or Divide feet smaller yards larger Step 2 Think: 3 ft = yd, so 363 ft = (363 3 ) yd. Step 3 Divide = 2 So, 363 feet = 2 yards. Convert.. 33 yd = 99 ft mi = 528,000 yd 3. 6 in. = 3 ft 0 in.. 96 yd = 288 ft 5. 8 ft = 6 yd 6. 2 mi 20 yd = 3,50 yd Compare. Write <, >, or = yd < 7 ft mi = 7,920 yd yd < 800 ft 0. yd 2 ft > 6 ft. 3 ft 0 in. < 58 in mi 8 ft > 8,800 yd Measurement and Data 55
4 Customary Length Convert.. 2 yd = 36 ft 2. 5 ft = 60 in. total yards feet in yard total feet CC.5.MD mi = 26,00 ft 2 3 = 36 2 yards = 36 feet. 20 in. = 20 ft yd = 300 ft 6. 0 ft = 20 in in. = 2 ft 6 in yd 2 ft = 23 ft 9. 0 mi = 52,800 ft Compare. Write <, >, or = in. < 2 ft. 25 yd = 75 ft 2. 6,200 ft > mi 900 ft in. < 3 yd ft Problem Solving 6. Marita orders 2 yards of material to make banners. If she needs foot of fabric for each banner, how many banners can she make?.,000 ft > 300 yd in. > 0 ft 7. Christy bought an 8-foot piece of lumber to trim a bookshelf. Altogether, she needs 00 inches of lumber for the trim. Did Christy buy enough lumber? Explain. 36 banners No. She bought only 96 inches of trim. 56 Lesson 78
5 Customary Capacity LESSON 79 CC.5.MD. OBJECTIVE Compare, contrast, and convert customary units of capacity. You can convert one unit of customary capacity to another by multiplying or dividing. Multiply to change from larger to smaller units. Divide to change from smaller to larger units. Convert 8 cups to quarts. Step Decide: Multiply or Divide cups smaller quarts larger Step 2 Think: c = qt, so 8 c = (8 ) qt. Customary Units of Capacity cup (c) = 8 fluid ounces (fl oz) pint (pt) = 2 cups quart (qt) = 2 pints quart = cups gallon (gal) = quarts Step 3 Divide. 8 = 2 So, 8 cups = 2 quarts. Convert 9 gallons to quarts. Step Decide: Multiply or Divide gallons larger quarts smaller Step 2 Think: gal = qt, so 9 gal = (9 ) qt. Step 3 Multiply. 9 = 76 So, 9 gallons = 76 quarts. Convert.. pt = 7 qt qt = 28 c 3. 7 c = 56 fl oz. 28 c = pt 5. 9 gal = 36 qt 6. 6 c = qt Compare. Write <, >, or = qt > 60 c fl oz = c 9. 3 gal > 0 qt qt > 5 c. 66 fl oz < 9 c 2. 6 gal = 6 qt Measurement and Data 57
6 Customary Capacity Convert.. 5 gal = 0 pt fl oz = 2 pt CC.5.MD pt = 30 c Think: gallon = quarts quart = 2 pints. 20 fl oz = 30 c qt = 8 gal 6. 0 qt = 0 c 7. 8 c = 2 qt pt = 9 gal fl oz = 8 pt Compare. Write <, >, or = qt > gal. 96 fl oz < 8 pt pt < 00 gal fl oz < 6 pt Problem Solving 6. Vickie made a recipe for fluid ounces of scented candle wax. How many -cup candle molds can she fill with the recipe?. 7 fl oz > 8 c 5. 2 c = 3 qt 7. A recipe calls for 32 fluid ounces of heavy cream. How many -pint containers of heavy cream are needed to make the recipe? 8 candle molds 2 pints 58 Lesson 79
7 LESSON 80 Weight OBJECTIVE Compare, contrast, and convert customary units of weight. CC.5.MD. You can convert one customary unit of weight to another by multiplying or dividing. Multiply to change from larger to smaller units. Divide to change from smaller to larger units. Customary Units of Weight pound (lb) = 6 ounces (oz) ton (T) = 2,000 pounds Convert 96 ounces to pounds. Step Step 2 Step 3 Decide: Multiply or Divide ounces smaller pounds larger Think: 6 oz = lb so 96 oz = (96 6 ) lb. Divide = 6 So, 96 ounces = 6 pounds. Convert pounds to ounces. Step Step 2 Step 3 Decide: Multiply or Divide pounds larger ounces smaller Think: lb = 6 oz, so lb = ( 6 ) oz. Multiply. 6 = 6 So, pounds = 6 ounces. Convert.. lb = 22 oz 2. 2,000 lb = 6 T 3. 2 T =,000 lb. 7 lb = 2 oz lb = 352 oz 6. 6 oz = lb Compare. Write <, >, or =. 7. T < 3,000 lb 8. 3 lb > 3 oz 9. 5 T = 0,000 lb 0. 3 T = 6,000 lb. 6 lb = 96 oz 2. 6 T > 6,00 lb Measurement and Data 59
8 Weight Convert. CC.5.MD.. 96 oz = 6 lb 2. 6 T = 2,000 lb 3. 8 lb = 288 oz total oz oz in lb total lb 96 6 = 6. 3,200 oz = 200 lb 5. 2 T = 2,000 lb 6. 9 lb = oz 7. 5 lb = 80 oz lb =,600 oz 9. 60,000 lb = 30 T Compare. Write <, >, or = oz < lb. 80 oz = 5 lb 2. 5,000 lb < 5 T 3. 8,000 lb = 9 T. 25 lb > 350 oz oz < 2 lb Problem Solving 6. Mr. Fields ordered 3 tons of gravel for a driveway at a factory. How many pounds of gravel did he order? 7. Sara can take no more than 22 pounds of luggage on a trip. Her suitcase weighs 2 ounces. How many more pounds can she pack without going over the limit? 6,000 pounds 5 pounds 60 Lesson 80
9 LESSON 8 Multistep Measurement Problems OBJECTIVE Convert measurement units to solve multistep problems. CC.5.MD. An ice cream parlor donated 6 containers of ice cream to a local elementary school. Each container holds 3 gallons of ice cream. If each student is served cup of ice cream, how many students can be served? Step Record the information you are given. There are 6 Each container holds containers of ice cream. gallons of ice cream. Step 2 Find the total amount of ice cream in the 6 containers. 6 3 gallons = 8 gallons of ice cream Step 3 Convert from gallons to cups. 3 There are quarts in gallon, so 8 gallons = 72 quarts. There are 2 pints in quart, so 72 quarts = pints. There are 2 cups in pint, so pints = 288 cups. So, 288 students can be served cup of ice cream. Solve.. A cargo truck weighs 8,750 pounds. The weight limit for a certain bridge is 5 tons. How many pounds of cargo can be added to the truck before it exceeds the weight limit for the bridge?,250 pounds 3. Larry has 9 gallons of paint. He uses 0 quarts to paint his kitchen and 3 gallons to paint his living room. How many pints of paint will be left? 2. A plumber uses 6 inches of tubing to connect each washing machine in a laundry to the water source. He wants to install 8 washing machines. How many yards of tubing will he need? 8 yards. Ketisha is practicing for a marathon by running around a track that is 0 yards long. Yesterday she ran around the track 20 times. How many miles did she run? 28 pints 5 miles Measurement and Data 6
10 Multistep Measurement Problems Solve. CC.5.MD.. A cable company has 5 miles of cable to install. How many 00-yard lengths of cable can be cut? Think:,760 yards = mile. So the cable company has 5,760, or 8,800 yards of cable. Divide. 8, = lengths 2. Afton made a chicken dish for dinner. She added a 0-ounce package of vegetables and a -ounce package of rice to 0 ounces of chicken. What was the total weight of the chicken dish in pounds? pounds 3. A jar contains 26 fluid ounces of spaghetti sauce. How many cups of spaghetti sauce do jars contain? 3 cups. Coach Kent brings 3 quarts of sports drink to soccer practice. He gives the same amount of the drink to each of his 6 players. How many ounces of the drink does each player get? 6 ounces 5. Leslie needs 32 inches of fringe to put around the edge of a tablecloth. The fringe comes in lengths of 0 yards. If Leslie buys package of fringe, how many feet of fringe will she have left over? 6. Darnell rented a moving truck. The weight of the empty truck was 7,860 pounds. When Darnell filled the truck with his items, it weighed 6 tons. What was the weight in pounds of the items that Darnell placed in the truck? Problem Solving 3 feet 7. A pitcher contains 0 fluid ounces of iced tea. Shelby pours 3 cups of iced tea. How many pints of iced tea are left in the pitcher?,0 pounds 8. Olivia ties 2.5 feet of ribbon onto one balloon. How many yards of ribbon does Olivia need for 8 balloons? pint 5 yards 62 Lesson 8
11 LESSON 82 Metric Measures OBJECTIVE Compare, contrast, and convert metric units. CC.5.MD. The metric system is based on place value. To convert between units, you multiply or divide by a power of 0. You multiply to change larger units to smaller units, such as liters to centiliters. You divide to change smaller units to larger units, such as meters to kilometers. Convert 566 millimeters to decimeters. Think about how the two units are related. decimeter = 00 millimeters Think: Should I multiply or divide? Millimeters are smaller than decimeters. So divide, or move the decimal point left for each power of = 5.66 millimeters mm in dm total decimeters So, 566 mm = 5.66 dm. kilo- (k) Metric Units of Length centimeter (cm) = 0 millimeters (mm) decimeter (dm) = 0 centimeters (cm) meter (m) =,000 millimeters (mm) kilometer (km) =,000 meters (m) hecto- (h) deka- (da) meter liter gram deci- (d) centi- (c) milli- (m) Complete the equation to show the conversion.. 5 km 0 =,50 hm 2. 8 cl 0 =.8 dl 5 km 00 =,500 dam 8 cl 00 =.8 L 5 km,000 = 5,000 m 8 cl,000 = 0.8 dal Convert. 5, or 3. 0 cm = 00 mm. 500 ml = 5.00 dl kg = 56,000 g 50, or 6. 5,000 cl = L 7. kg = 0 hg mm = 20, or 20.0 cm Measurement and Data 63
12 Metric Measures CC.5.MD. Convert.. 6 m = 6,000 mm 2. 6,500 cl = 65 L 3. 5 cm = 50 mm number of millimeters number of meters in meter millimeters 6,000 = 6,000 6 m = 6,000 mm. 3,200 g = 3.2 kg 5. 2 L = 2,000 ml cm = 2 m 7. 70,000 g = 70 kg dl = 0 L m = 60,000 mm Compare. Write <, >, or = cm = 9,000 mm. 600 km > 5 m 2. 5,000 cm > 5 m 3. 8,000 g > 0 kg. 8,56 ml < 9 L 5. 2 m < 275 cm Problem Solving 6. Bria ordered 5 centimeters of fabric. Jayleen ordered.5 meters of fabric. Who ordered more fabric? 7. Ed fills his sports bottle with.2 liters of water. After his bike ride, he drinks 200 milliliters of the water. How much water is left in Ed s sports bottle? Jayleen L, or,000 ml 6 Lesson 82
13 LESSON 83 Problem Solving Customary and Metric Conversions OBJECTIVE Solve problems about customary and metric conversions using the strategy make a table. You can use the strategy make a table to help you solve problems about customary and metric conversions. Jon s faucet is dripping at the rate of 2 centiliters in a day. How many milliliters of water will have dripped from Jon s faucet in 2 hours? CC.5.MD. Read the Problem Solve the Problem What do I need to find? I need to find how many milliliters of water will have dripped from Jon s faucet in 2 hours. What information do I need to use? I need to use How will I use the information? I will make a table to show the relationship between the number of of milliliters. the number of cl that have dripped in 2 hr and the number of ml in a cl. centiliters and the number Make a table to help you solve the problems.. Fernando has a bucket that holds 3 gallons of water. He is filling the bucket using a -pint container. How many times will he have to fill the pint container in order to fill the bucket? Conversion Table L dl cl ml L 0 00,000 dl 0 cl 00 ml, I can use the Conversion Table to find the number of milliliters in centiliter. There are 0 centiliter. cl 2 2 ml milliliters in So, 20 milliliters of water will have dripped from Jon s faucet in 2 hours. Check students tables. 2. Lexi has a roll of shelf paper that is 800 cm long. She wants to cut the paper into -m strips to line the shelves in her pantry. How many -meter strips can she cut? 2 times 8 strips Measurement and Data 65
14 Problem Solving Customary and Metric Conversions CC.5.MD. Solve each problem by making a table. Possible tables are given.. Thomas is making soup. His soup pot holds 8 quarts of soup. How many -cup servings of soup will Thomas make? 32 -cup servings Number of Quarts Number of Cups Paulina works out with a 2.5-kilogram mass. What is the mass of the 2.5-kilogram mass in grams? 2,500 grams Number of Kilograms Number of Grams 2 2.5,000 2,000 2, Alex lives 500 yards from the park. How many inches does Alex live from the park? Yards Inches ,000 8,000 inches. Emma uses a 250-meter roll of crepe paper to make streamers. How many dekameters of crepe paper does Emma use? 25 dekameters 5. A flatbed truck is loaded with 7,000 pounds of bricks. How many tons of brick are on the truck? 3.5 tons Meters Dekameters Pounds 2,000 3,000,000 7,000 Tons Lesson 83
15 LESSON 8 Elapsed Time OBJECTIVE Convert units of time to solve elapsed time problems. CC.5.MD. You can solve elapsed time problems by converting units of time. Starting at :20 P.M., Connie practiced piano for 90 minutes. At what time did Connie stop practicing piano? Convert 90 minutes to hours and minutes. Then find the end time. Step To convert minutes to hours, divide is with a remainder of min = hr 30 min Step 2 Count forward by hours until you reach hour. Step 3 Count forward by minutes until you reach 30 minutes. Connie stops practicing piano at 5:50 P.M.. Units of Time 60 seconds (s) minute (min) 60 minutes hour (hr) 2 hours day (d) 7 days week (wk) 52 weeks year (yr) 2 months (mo) year 365 days year :20 5:20 = hour 5:20 5:30 = hour 0 minutes 5:30 5:0 = hour 20 minutes 5:0 5:50 = hour 30 minutes Convert.. 80 min = 8 hr 2. d = 96 hr hr = 5 d 5 hr Find the start, elapsed, or end time.. Start time: 7:5 A.M. 5. Start time: 6:28 A.M. Elapsed time: 2 hr 20 min Elapsed time: 3 hr 0 min End time: 9:35 A.M. End time: 0:08 A.M. 6. Start time: 2:05 P.M. 7. Start time: 5:2 P.M. Elapsed time: 5 hr 50 min End time: 7:55 P.M. Elapsed time: 6 hr End time: :2 P.M. Measurement and Data 67
16 Elapsed Time CC.5.MD. Convert.. 5 days = 20 hr 2. 8 hr = 80 min min =,800 s Think: day = 2 hours 5 2 = hr = 900 min 5. 5 yr =,825 d 6. 7 d = 68 hr or, hr =,0 min s = 0 min 9. 60,000 min =,000 hr Find the start, elapsed, or end time. 0. Start time: :00 A.M. Elapsed time: hours 5 minutes. Start time: 6:30 P.M. Elapsed time: 2 hours 8 minutes End time: 3:05 P.M. End time: 8:8 P.M. 2. Start time: Elapsed time: 9 3_ hours End time: 6:00 P.M. Problem Solving 8:5 A.M.. Kiera s dance class starts at :30 P.M. and ends at 6:5 P.M. How long is her dance class? 3. Start time: 2:00 P.M. 6 hr 30 min, or 6 _ Elapsed time: 2 hr End time: 8:30 P.M. 5. Julio watched a movie that started at :30 A.M. and ended at 2:2 P.M. How long was the movie? hr 5 min 2 hr 2 min 68 Lesson 8
17 LESSON 85 Line Plots OBJECTIVE Make and use line plots with fractions to solve problems. CC.5.MD.2 A line plot is a graph that shows the shape of a data set by placing s above each data value on a number line. You can make a line plot to represent a data set and then use the line plot to answer questions about the data set. Students measure the lengths of several seeds. The length of each seed is listed below. 2 inch, 3 inch, 2 inch, inch, 3 inch, 3 inch, 3 inch, inch, 2 inch What is the combined length of the seeds that are _ inch long? Step To represent the different lengths of the seeds, draw and label a line plot with the data values _, _ 2, and 3_. Then use an to represent each seed. The line plot has been started for you. Step 2 There are 2 s above _ on the line plot. Multiply to find the combined length of the seeds: 2 2 =, or 2 inch The combined length of the seeds that are _ inch long is _ 2 inch. 2 Length of Seeds (in inches) 3 You can use the same process to find the combined lengths of the seeds that are _ 2 inch long and 3_ inch long. Use the data and the line plot above to answer the questions.. What is the total length of all the seeds that the students measured? 5 inches 2. What is the average length of one of the seeds that the students measured? 5 9 inch Measurement and Data 69
18 Line Plots CC.5.MD.2 Use the data to complete the line plot. Then answer the questions. A clerk in a health food store makes bags of trail mix. The amount of trail mix in each bag is listed below. lb, lb, 3 lb, 2 lb, lb, 3 lb, 3 lb, 3 lb, 2 lb, lb, 2 lb, 2 lb. What is the combined weight of the _ -lb bags? 2 Weight of Trail Mix (in pounds) lb 3 Think: There are four _ -pound bags. 2. What is the combined weight of the _ 2 -lb bags? 3. What is the combined weight of the 3_ -lb bags? 2 lb 3 lb. What is the total weight of the trail mix used in all the bags? 6 lb 5. What is the average amount of trail mix in each bag? _ 2 lb Julie uses crystals to make a bracelet. The lengths of the crystals are shown below. 2 in., 5 8 in., 3 in., 2 in., 3 8 in., 2 in., 3 in., 3 8 in., 3 in., 5 8 in., 2 in., 3 8 in., 5 8 in., 3 in. 6. What is the combined length of the _ 2 -in. crystals? 7. What is the combined length of the 5_ 8 -in. crystals? 8. What is the total length of all the crystals in the bracelet? 9. What is the average length of each crystal in the bracelet? Lengths of Crystals (in inches) 2 in. 7 8 in. 8 in. 7 in Lesson 85
19 LESSON 86 Three-Dimensional Figures OBJECTIVE Identify, describe, and classify three-dimensional figures. CC.5.MD.3 A polyhedron is a solid figure with faces that are polygons. You can identify a polyhedron by the shape of its faces. A pyramid is a polyhedron with one polygon base. The lateral faces of a pyramid are triangles that meet at a common vertex. triangular pyramid rectangular pyramid square pyramid The base and faces are triangles. The base is a rectangle. The base is a square. A prism is a polyhedron with two congruent polygons as bases. The lateral faces of a prism are rectangles. triangular prism rectangular prism square prism or cube The two bases are triangles. All faces are rectangles. All faces are squares. pentagonal pyramid hexagonal pyramid The base is a pentagon. The base is a hexagon. pentagonal prism hexagonal prism A solid figure with curved surfaces is not a polyhedron. cone The one base is a circle. cylinder sphere There is no base. The two bases are pentagons. The two bases are hexagons. The two bases are circles. Classify the solid figure. Write prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder, or sphere. The solid figure has one base. The rest of its faces are triangles. So, the solid figure is a pyramid. Classify each solid figure. Write prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder, or sphere cylinder pyramid rectangular prism cone Measurement and Data 7
20 Three-Dimensional Figures Classify the solid figure. Write prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder, or sphere. CC.5.MD There are no bases. There is curved surface. It is a sphere rectangular prism cone triangular pyramid pentagonal pyramid cylinder rectangular prism Problem Solving 0. Darrien is making a solid figure out of folded paper. His solid figure has six congruent faces that are all squares. What solid figure did Darrien make? cone hexagonal prism. Nanako said she drew a square pyramid and that all of the faces are triangles. Is this possible? Explain. cube No. The base of the pyramid is a square that has sides, not Lesson 86
21 LESSON 87 Unit Cubes and Solid Figures OBJECTIVE Understand unit cubes and how they can be used to build a solid figure. CC.5.MD.3a A unit cube is a cube that has a length, width, and height of unit. You can use unit cubes to build a rectangular prism. unit unit unit Count the number of cubes used to build the rectangular prism. The length of the prism is made up of The width of the prism is made up of The height of the prism is made up of 8 2 unit cubes. unit cubes. unit cube. The number of unit cubes used to build the rectangular prism is 6. Count the number of unit cubes used to build each solid figure unit cubes 8. unit cubes 5 unit cubes 7 unit cubes Measurement and Data 73
22 Unit Cubes and Solid Figures Count the number of cubes used to build each solid figure. CC.5.MD.3a unit cubes 20 unit cubes unit cubes 6 unit cubes 8 unit cubes 7 unit cubes Compare the number of unit cubes in each solid figure. Use <, >, or = unit cubes > unit cubes 5 unit cubes = 5 unit cubes Problem Solving 9. A carton can hold,000 unit cubes that measure inch by inch by inch. Describe the dimensions of the carton using unit cubes. 0. Peter uses unit cubes to build a figure in the shape of the letter X. What is the fewest unit cubes that Peter can use to build the figure? Possible answer: The dimensions of the carton are 0 inches by 0 inches by 0 inches. 5 unit cubes 7 Lesson 87
23 LESSON 88 Understand Volume OBJECTIVE Count unit cubes that fill a solid figure to find volume. CC.5.MD.3b The volume of a rectangular prism is equal to the number of unit cubes that make up the prism. Each unit cube has a volume of cubic unit. Find the volume of the prism. unit cube = cubic inch Step Count the number of unit cubes in the bottom layer of the prism. There are unit cubes that make up the length of the first layer. There are 2 unit cubes that make up the width of the first layer. There is unit cube that makes up the height of the first layer. So, altogether, there are 8 unit cubes that make up the bottom layer of the prism. Step 2 Count the number of layers of cubes that make up the prism. The prism is made up of 3 layers of unit cubes. Step 3 Find the total number of cubes that fill the prism. Multiply the number of layers by the number of cubes in each layer. 3 8 = 2 unit cubes Each unit cube has a volume of cubic inch. So, the volume of the prism is 2, or 2 cubic inches. Use the unit given. Find the volume ft cm 3 ft 5 ft 3 cm 6 cm Each cube = cu ft Each cube = cu cm Volume = 5 cu ft Volume = 72 cu cm Measurement and Data 75
24 Understand Volume Use the unit given. Find the volume. CC.5.MD.3b. 3 cm 2. 3 in. 5 cm Each cube = cu cm 7 cm 8 in. Each cube = cu in. 2 in. Volume = 05 cu cm 3. 2 ft. ft 7 ft Each cube = cu ft Volume = 56 cu ft 5. Compare the volumes. Write <, >, or =. Volume = 8 cu in. 5 cm 5 cm 5 cm Each cube = cu cm Volume = 25 cu cm ft 3 ft 5 ft Each cube = cu ft Problem Solving 60 cu ft 6. A manufacturer ships its product in boxes with edges of inches. If 2 boxes are put in a carton and completely fill the carton, what is the volume of the carton? = 60 cu ft 6 ft Each cube = cu ft 5 ft 2 ft 7. Matt and Mindy each built a rectangular prism that has a length of 5 units, a width of 2 units, and a height of units. Matt used cubes that are cm on each side. Mindy used cubes that are in. on each side. What is the volume of each prism? 768 cubic inches Matt: 0 cu cm, Mindy: 0 cu in. 76 Lesson 88
25 LESSON 89 Estimate Volume OBJECTIVE Estimate the volume of a rectangular prism. CC.5.MD. You can estimate the volume of a larger box by filling it with smaller boxes. Mario packs boxes of markers into a large box. The volume of each box of markers is 5 cubic inches. Estimate the volume of the large box. Markers Markers Markers Markers The volume of one box of markers is 5 cubic inches. Use the box of markers to estimate the volume of the large box. The large box holds 2 layers of boxes of markers, a top layer and a bottom layer. Each layer contains 0 boxes of markers. So, the large box holds about 2 0, or 20 boxes of markers. Multiply the volume of box of markers by the estimated number of boxes of markers that fit in the large box = 300 So, the volume of the large box is about 300 cubic inches. Estimate the volume.. Each box of toothpaste has a volume of 25 cubic inches. Toothpaste Toothpaste Toothpaste Toothpaste Toothpaste Toothpaste There are 30 boxes of toothpaste in the large box. The estimated volume of the large box is = 750 cubic inches. 2. Volume of case: 80 cu cm Volume of large box: about,800 cu cm Measurement and Data 77
26 Estimate Volume Estimate the volume. CC.5.MD.. Volume of package of paper: 200 cu in. 2. Volume of rice box: 500 cu cm Paper Paper Paper Paper Paper Paper Paper Paper Think: Each package of paper has a volume of 200 cu in. There are 8 packages of paper in the larger box. So, the volume of the large box is about 8 200, or,600 cubic inches. Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Rice Volume of large box:,600 cu in. Volume of large box: 2,000 cu cm 3. Volume of tea box: 0 cu in.. Volume of DVD case: 20 cu in. Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea Tea DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD DVD Volume of large box: 2,000 cu in. Volume of large box: 960 cu in. Problem Solving 5. Theo fills a large box with boxes of staples. The volume of each box of staples is 20 cu cm. Estimate the volume of the large box. Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples Staples 6. Lisa uses pudding boxes to estimate the volume of the box below. The volume of each pudding box is 50 cu in. Estimate the volume of the large box. Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding Pudding 3,600 cu cm 6,000 cu in. 78 Lesson 89
27 LESSON 90 Volume of Rectangular Prisms OBJECTIVE Find the volume of rectangular prisms. CC.5.MD.5a Jorge wants to find the volume of this rectangular prism. He can use cubes that measure centimeter on each side to find the volume. Step The base has a length of 2 centimeters and a width of 3 centimeters. Multiply to find the area of the base. Base = 2 3 Base = 6 cm 2 Step 2 The height of the prism is centimeters. Add the number of cubes in each layer to find the volume. Remember: Each layer has 6 cubes. Step 3 Count the cubes. 2 cubes Multiply the base and the height to check your answer. Volume = 6 Volume = 2 cubic centimeters So, the volume of Jorge s rectangular prism is 2 cubic centimeters. Find the volume cm 2 ft 2 ft 3 cm 2 cm 5 ft Volume: 8 cm 3 Volume: 20 ft 3. in. 3 cm 3 cm 2 in. 6 cm in. Volume: 32 in. 3 Volume: 5 cm 3 Measurement and Data 79
28 Volume of Rectangular Prisms Find the volume. CC.5.MD.5a. 3 cm 2. in. 6 cm 5 cm 2 in. 2 in. Volume: 90 cm 3 Volume: 96 in ft. 6 ft 6 cm 7 ft 5 cm 5 cm Volume: 8 ft 3 Volume: 50 cm in. 6. ft 5 in. Volume: 20 in. 3 Problem Solving 8 in. 7. Aaron keeps his baseball cards in a cardboard box that is 2 inches long, 8 inches wide, and 3 inches high. What is the volume of this box? 6 ft Volume: ft 3 6 ft 8. Amanda s jewelry box is in the shape of a cube that has 6-inch edges. What is the volume of Amanda s jewelry box? 288 in in Lesson 90
29 LESSON 9 Algebra Apply Volume Formulas OBJECTIVE Use a formula to find the volume of a rectangular prism. CC.5.MD.5b You can use a formula to find the volume of a rectangular prism. Volume = length width height V = (l w) h Find the volume of the rectangular prism. Step Identify the length, width, and height of the rectangular prism. length = 9 in. width = 3 in. height = in. Step 2 Substitute the values of the length, width, and height into the formula. V = (l w) h 9 in. 3 in. in. V = ( 9 3 ) Step 3 Multiply the length by the width. V = (9 3) V = 27 Step Multiply the product of the length and width by the height. V = 27 = 08 So, the volume of the rectangular prism is Find the volume ft ft 2 ft 08 8 cm 8 cm 8 cm cubic inches. V = 20 ft 3 V = 52 cm 3 Measurement and Data 8
30 Apply Volume Formulas Find the volume. CC.5.MD.5b ft 5 in. 2 ft 6 ft 2 in. 2 in. V = l w h V = 20 in. 3 V = V = 36 ft cm. 5 ft 5 cm 5 cm 2 ft 3 ft V = 25 cm 3 V = 80 ft 3 5. in cm V = 9 in. 26 in. 3 Problem Solving 6 in. 7. A construction company is digging a hole for a swimming pool. The hole will be 2 yards long, 7 yards wide, and 3 yards deep. How many cubic yards of dirt will the company need to remove? 252 yd 3 V = 8 cm 7 cm 50 cm 3 8. Amy rents a storage room that is 5 feet long, 5 feet wide, and 8 feet high. What is the volume of the storage room? 600 ft 3 82 Lesson 9
31 LESSON 92 Problem Solving Compare Volumes OBJECTIVE Use the strategy make a table to compare volumes. CC.5.MD.5b A company makes aquariums that come in three sizes of rectangular prisms. The length of each aquarium is three times its width and depth. The depths of the aquariums are foot, 2 feet, and 3 feet. What is the volume of each aquarium? Read the Problem What do I need to find? I need to find the of each aquarium. What information do I need to use? I can use the formula for volume, V = l w h, or V = B h. I can use ft, 2 ft, and 3 ft volume as the depths. I can use the clues the length is three times the width and depth How will I use the information?. Solve the Problem Think: The depth of an aquarium is the same as the height of the prism formed by the aquarium. Length (ft) Width (ft) Depth, or Height (ft) Volume (cu ft) So, the volumes of the aquariums are 3 cubic feet, 2 cubic feet, and 8 cubic feet. I will use the volume formula and a table to list all of the possible combinations of lengths, widths, and depths.. Jamie needs a bin for her school supplies. A blue bin has a length of 2 inches, a width of 5 inches, and a height of inches. A green bin has a length of 0 inches, a width of 6 inches, and a height of 5 inches. What is the volume of the bin with the greatest volume? 2. Suppose the blue bin that Jamie found had a length of 5 inches, a width of 5 inches, and a height of 2 inches. Would one bin have a greater volume than the other? Explain. No. Both bins have the same 300 in. 3 volume; 300 in. 3 Measurement and Data 83
32 Problem Solving Compare Volumes Make a table to help you solve each problem. CC.5.MD.5b. Amita wants to make a mold for a candle. She wants the shape of the candle to be a rectangular prism with a volume of exactly 28 cubic centimeters. She wants the sides to be in whole centimeters. How many different molds can she make? 0 molds 2. Amita decides that she wants the molds to have a square base. How many of the possible molds can she use? 2 molds 3. Raymond wants to make a box that has a volume of 360 cubic inches. He wants the height to be 0 inches and the other two dimensions to be whole numbers of inches. How many different-sized boxes can he make? 5 boxes. Jeff put a small box that is 2 inches long, 8 inches wide, and inches tall inside a box that is 20 inches long, 5 inches wide, and 9 inches high. How much space is left in the larger box? 2,36 cu in. 5. Mrs. Nelson has a rectangular flower box that is 5 feet long and 2 feet tall. She wants the width of the box to be no more than 5 feet. If the width is a whole number, what are the possible volumes for the flower box? 6. Sophina bought 3 yards of trim to put around a rectangular scarf. She wants the width of the scarf to be a whole number that is at least 6 inches and at most 2 inches. If she uses all the trim, what are the possible dimensions of her scarf? Write your answers in inches. 0 cu ft, 20 cu ft, 30 cu ft, 0 cu ft, and 50 cu ft 6 by 8, 7 by 7, 8 by 6, 9 by 5, 0 by, by 3, and 2 by 2 8 Lesson 92
33 LESSON 93 Find Volume of Composed Figures OBJECTIVE Find the volume of combined rectangular prisms. CC.5.MD.5c A composite figure is a solid made up of two or more solids. To find the volume of a composite figure, first find the volume of each solid that makes up the figure. Then find the sum of the volumes of the figures. in. Find the volume of the composite figure at right. Step Break apart the composite figure into two rectangular prisms. Label the dimensions of each prism. Prism Prism 2 8 in. in. 20 in. 8 in. in. 20 in. 8 in. Step 2 Find the volume of each prism. 0 ft 8 ft Prism Prism 2 V = (l w) h V = (l w) h V = 8 V = 20 8 V = 28 in. 3 V = 60 in. 3 Step 3 Find the sum of the volumes of the two prisms. Volume of Prism + Volume of Prism 2 = Volume of Composite Figure = Volume of Composite Figure So, the volume of the composite figure is 768 in. 3 Find the volume of the composite figure.. 28 ft 2 ft ft 8 ft 2 ft = Volume of Composite Figure in. 7 in. 6 in. 3 in. in. V = 2,00 ft 3 V = 05 in. 3 Measurement and Data 85
34 Find Volume of Composed Figures Find the volume of the composite figure. CC.5.MD.5c. in. 2. cm 2 cm 2 cm 3 in. in. 6 cm cm in. 2 in. V = 2 cu in. V = 38 cu cm 3. in.. 6 ft 6 in. ft 2 ft 8 ft ft in. 8 in. 3 in. V = 39 cu in. V = 6 cu ft Problem Solving 5. As part of her shop class, Jules made the figure below out of pieces of wood. How much space does the figure she made take up? 6 cm 9 cm 2 cm 30 cm 9 cm 6. What is the volume of the composite figure below? 6 ft 6 ft 9 ft 27 ft 2 ft 2,96 cu cm 2,592 cu ft 86 Lesson 93
Problem Solving Find Unknown Lengths OBJECTIVE Solve problems using the strategy guess, check, and revise. Read the Problem.
 LESSON 72 Problem Solving Find Unknown Lengths OBJECTIVE Solve problems using the strategy guess, check, and revise. CC.5.NF.5b Zach built a rectangular deck in his backyard. The area of the deck is 00
LESSON 72 Problem Solving Find Unknown Lengths OBJECTIVE Solve problems using the strategy guess, check, and revise. CC.5.NF.5b Zach built a rectangular deck in his backyard. The area of the deck is 00
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
not regular Lesson 11.1 Polygons Name 4 sides, 4 vertices, 4 angles means it is a Chapter 11 P219
 Name Polygons Lesson 11.1 COMMON CORE STANDARD MACC.5.G.2.3 Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. Name each polygon. Then tell whether it is a regular polygon or not
Name Polygons Lesson 11.1 COMMON CORE STANDARD MACC.5.G.2.3 Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. Name each polygon. Then tell whether it is a regular polygon or not
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. no no R89. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Measurement and Geometry
 8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
5th Grade. Measurement & Data.
 1 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015 11 23 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of
1 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015 11 23 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of
5th Grade Measurement & Data
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement
5th Grade. Standard Measurement Conversions. Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115. Slide 4 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Slide 5 / 115.
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes click on the
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes click on the
5th Grade. Slide 1 / 115. Slide 2 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Measurement & Data. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 115 Metric Measurement
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 115 Metric Measurement
5th Grade. Standard Measurement Conversions. Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115. Slide 4 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Slide 5 / 115.
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of a
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of a
GRADE 5. Mathematics. Administered April 2018 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered April 2018 RELEASED Copyright 2018, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work
STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered April 2018 RELEASED Copyright 2018, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work
Measurement and Geometry
 Name Date Class Review for Mastery: Converting Customary Units You can use the table below to convert customary units. Length 1 foot = 1 inches 1 yard = 36 inches 1 yard = 3 feet 1 mile = 5,80 feet 1 mile
Name Date Class Review for Mastery: Converting Customary Units You can use the table below to convert customary units. Length 1 foot = 1 inches 1 yard = 36 inches 1 yard = 3 feet 1 mile = 5,80 feet 1 mile
Math Tool: Grid Paper
 Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
The School District of Palm Beach County Fifth Grade Mathematics Scope rd Trimester
 Unit & Go Math! & lessons from each Measurement and Data MA.5.G.5.3 MD.1.1 Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within
Unit & Go Math! & lessons from each Measurement and Data MA.5.G.5.3 MD.1.1 Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 11 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
10-1. Enrichment. You Can Count On It!
 10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
2-dimensional figure. 3-dimensional figure. about. acute angle. addend. addition. angle. area. array. bar graph. capacity
 2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
THIRD TERM EXAM REVISION WORKSHEET AY Grade 5 Mathematics ` SECTION A: VOCABULARY. Line graph origin ordered pair prism milliliter
 THIRD TERM EXAM REVISION WORKSHEET AY 2015-2016 Grade 5 Mathematics ` Name: Section: SECTION A: VOCABULARY Choose the best term from the box. Line graph origin ordered pair prism milliliter Milligram polyhedron
THIRD TERM EXAM REVISION WORKSHEET AY 2015-2016 Grade 5 Mathematics ` Name: Section: SECTION A: VOCABULARY Choose the best term from the box. Line graph origin ordered pair prism milliliter Milligram polyhedron
Grade 6: Geometry and Algebra. 1. Choose an appropriate customary unit for measuring the area of a classroom. B. Square Feet D.
 6.8.1 Name Grade 6: Geometry and Algebra 1. Choose an appropriate customary unit for measuring the area of a classroom. A. Cubic Feet C. Square Inches B. Square Feet D. Square Acres 2. What is the measure
6.8.1 Name Grade 6: Geometry and Algebra 1. Choose an appropriate customary unit for measuring the area of a classroom. A. Cubic Feet C. Square Inches B. Square Feet D. Square Acres 2. What is the measure
5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z
 o o o. 5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
o o o. 5TH GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids. Use the formula. Substitute for l and w. Use the formula. Substitute for B and h.
 ? LESSON 10.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids How do you find the volume of a rectangular prism and a rectangular pyramid? Finding the Volume of a Rectangular Prism Remember
? LESSON 10.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Pyramids How do you find the volume of a rectangular prism and a rectangular pyramid? Finding the Volume of a Rectangular Prism Remember
The School District of Palm Beach County 5 th Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester. 13 days: August 18 September 6
 1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) OA.1.1 OA.1.2 NBT.1.1 Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) OA.1.1 OA.1.2 NBT.1.1 Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES. The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power.
 UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
North Adams Public Schools
 Unit 1: Place Value and Multi-Digit Addition and Subtraction Place value drawings to represent numbers. Place value drawings to add and subtract whole numbers. Different methods to add and subtract whole
Unit 1: Place Value and Multi-Digit Addition and Subtraction Place value drawings to represent numbers. Place value drawings to add and subtract whole numbers. Different methods to add and subtract whole
11. Jason ran 325 meters farther than Kim ran. Kim ran 4.2 kilometers. How many meters did Jason run? Estimate to check your answer.
 8-1 Complete. 1. 75 cm = m 3. 251 km = 251,000 5. 0.46 cm = mm 7. 58 mm = m 9. 35.6 mm = cm 2. 802 cm = m 4. 0.95 mm = cm 6. 32 m = mm 8. 2,581 m = km 10. 2.92 cm = 29.2 Solve. 11. Jason ran 325 meters
8-1 Complete. 1. 75 cm = m 3. 251 km = 251,000 5. 0.46 cm = mm 7. 58 mm = m 9. 35.6 mm = cm 2. 802 cm = m 4. 0.95 mm = cm 6. 32 m = mm 8. 2,581 m = km 10. 2.92 cm = 29.2 Solve. 11. Jason ran 325 meters
GRADE 5. Mathematics. Administered March 2017 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered March 017 RELEASED Copyright 017, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is
STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered March 017 RELEASED Copyright 017, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is
The School District of Palm Beach County 5 th Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester. 13 days: August 20 September 8
 1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) OA.1.1 OA.1.2 NBT.1.1 Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) OA.1.1 OA.1.2 NBT.1.1 Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
Surface Area and Volume of Solids
 Surface Area and Volume of Solids? MODULE 5 LESSON 5. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Nets and Surface Area How can a model help you to solve surface area and volume problems? 6.G. LESSON 5. Volume of Rectangular Prisms
Surface Area and Volume of Solids? MODULE 5 LESSON 5. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Nets and Surface Area How can a model help you to solve surface area and volume problems? 6.G. LESSON 5. Volume of Rectangular Prisms
CHAPTER. Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC. Three-Dimensional Figures 217
 CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
FIFTH GRADE Mathematics Curriculum Map Unit 5
 FIFTH GRADE Mathematics Curriculum Map Unit 5 VOCABULARY additive area Associative Property attribute base capacity centimeter convert/conversions cubic units cup customary data decimeter edge lengths
FIFTH GRADE Mathematics Curriculum Map Unit 5 VOCABULARY additive area Associative Property attribute base capacity centimeter convert/conversions cubic units cup customary data decimeter edge lengths
The Next Step. Mathematics Applications for Adults. Book Measurement
 The Next Step Mathematics Applications for Adults Book 14019 Measurement OUTLINE Mathematics - Book 14019 Measurement The Metric System use correct metric units to measure length, volume, capacity, mass,
The Next Step Mathematics Applications for Adults Book 14019 Measurement OUTLINE Mathematics - Book 14019 Measurement The Metric System use correct metric units to measure length, volume, capacity, mass,
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade
 Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
3 rd Grade Hinojosa Math Vocabulary Words
 Topic 1 Numeration Word Definition Picture Digits The symbol used to write the numbers 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8, and 9 are called digits. 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Standard Form Standard form is a way to write a number
Topic 1 Numeration Word Definition Picture Digits The symbol used to write the numbers 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8, and 9 are called digits. 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Standard Form Standard form is a way to write a number
,525 m. Possible estimate: 4,300 m cm
 8-1 Complete. 1. 75 cm = 0.75 m 2. 802 cm = 8.02 m 3. 251 km = 251,000 m 4. 0.95 mm = 0.095 cm 5. 0.46 cm = 4.6 mm 6. 32 m = 32,000 mm 7. 58 mm = 0.058 m 8. 2,581 m = 2.581 km 9. 35.6 mm = 3.56 cm 10.
8-1 Complete. 1. 75 cm = 0.75 m 2. 802 cm = 8.02 m 3. 251 km = 251,000 m 4. 0.95 mm = 0.095 cm 5. 0.46 cm = 4.6 mm 6. 32 m = 32,000 mm 7. 58 mm = 0.058 m 8. 2,581 m = 2.581 km 9. 35.6 mm = 3.56 cm 10.
GRADE 5. Operations & Algebraic Thinking - Domain
 Write and interpret numerical expressions. CLUSTERS: 1. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. 2. Write simple expressions that record
Write and interpret numerical expressions. CLUSTERS: 1. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. 2. Write simple expressions that record
Brunswick School Department: Grade 5
 Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
3. Draw the orthographic projection (front, right, and top) for the following solid. Also, state how many cubic units the volume is.
 PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
English 5 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 4/13/18
 English 5 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 4/13/18 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
English 5 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 4/13/18 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
Surface Area and Volume
 Name: Chapter Date: Surface Area and Volume Practice 1 Building Solids Using Unit Cubes Find the number of unit cubes used to build each solid. Some of the cubes may be hidden. 1. 2. unit cubes 3. 4. unit
Name: Chapter Date: Surface Area and Volume Practice 1 Building Solids Using Unit Cubes Find the number of unit cubes used to build each solid. Some of the cubes may be hidden. 1. 2. unit cubes 3. 4. unit
Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes
 26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
{[2 x (3+5)] 9}= {[2 x 8] 9}= {16 9}=
![{[2 x (3+5)] 9}= {[2 x 8] 9}= {16 9}= {[2 x (3+5)] 9}= {[2 x 8] 9}= {16 9}=](/thumbs/96/126592427.jpg) {[2 x (3+5)] 9}= {[2 x 8] 9}= {16 9}= 7 5.OA.1 Subtract 6 from 24 = 24-6 Add 12 and 13 = 12 + 13 Multiply 8 by 2 = 8 x 2 Divide 36 by 6 = 36 6 5.OA.2 X and Y Start at O Rule for X- Add 3 Rule for Y- Add
{[2 x (3+5)] 9}= {[2 x 8] 9}= {16 9}= 7 5.OA.1 Subtract 6 from 24 = 24-6 Add 12 and 13 = 12 + 13 Multiply 8 by 2 = 8 x 2 Divide 36 by 6 = 36 6 5.OA.2 X and Y Start at O Rule for X- Add 3 Rule for Y- Add
12-4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders. Find the volume of each prism.
 Find the volume of each prism. 3. the oblique rectangular prism shown at the right 1. The volume V of a prism is V = Bh, where B is the area of a base and h is the height of the prism. If two solids have
Find the volume of each prism. 3. the oblique rectangular prism shown at the right 1. The volume V of a prism is V = Bh, where B is the area of a base and h is the height of the prism. If two solids have
Surface Area and Volume
 14 CHAPTER Surface Area and Volume Lesson 14.1 Building Solids Using Unit Cubes How many unit cubes are used to build each solid? 1. unit cubes 2. unit cubes Extra Practice 5B 121 3. unit cubes 4. 5. unit
14 CHAPTER Surface Area and Volume Lesson 14.1 Building Solids Using Unit Cubes How many unit cubes are used to build each solid? 1. unit cubes 2. unit cubes Extra Practice 5B 121 3. unit cubes 4. 5. unit
4th Grade Math Curriculum Map BENCHMARKS TERMINOLOGY. Lesson assessments pre and post test. Check My Progress. Benchmark Test
 4th Grade Math Curriculum Map Course Title: Math UNIT/ORGANIZING PRINCIPLE: Numbers and Operation in Base Ten PACING: 9 days UNIT NUMBER: Ch. 1 Place Value 4.NBT.1 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.2 I can identify
4th Grade Math Curriculum Map Course Title: Math UNIT/ORGANIZING PRINCIPLE: Numbers and Operation in Base Ten PACING: 9 days UNIT NUMBER: Ch. 1 Place Value 4.NBT.1 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.2 I can identify
3 rd Grade Mathematics Learning Targets By Unit PA CORE STANDARD ADDRESSED
 INSTRUCTIONAL UNIT UNIT 1: NUMBERS TO 10,000 PA CORE STANDARD ADDRESSED LEARNING TARGETS I can use base ten blocks to count, read and write numbers to 10,000. I can use a place-value chart to read, write
INSTRUCTIONAL UNIT UNIT 1: NUMBERS TO 10,000 PA CORE STANDARD ADDRESSED LEARNING TARGETS I can use base ten blocks to count, read and write numbers to 10,000. I can use a place-value chart to read, write
Associative Property of Addition. Associative Property of Multiplication and 1
 Page 1 1. Find the property that each equation shows. Write the equation in the correct box. 11 ( 6) = (11 ) 6 1 + 27 + 18 = 27 + 1 + 18 1 + (12 + 11) = (1 + 12) + 11 18 2 = 2 18 1 = 72 + 0 = 72 Commutative
Page 1 1. Find the property that each equation shows. Write the equation in the correct box. 11 ( 6) = (11 ) 6 1 + 27 + 18 = 27 + 1 + 18 1 + (12 + 11) = (1 + 12) + 11 18 2 = 2 18 1 = 72 + 0 = 72 Commutative
Acute Angle. Angle. An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint.
 Acute Angle An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. Geometry Angle A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint. 5 Geometry Area The number of square units
Acute Angle An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. Geometry Angle A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint. 5 Geometry Area The number of square units
Lesson PROBLEM SOLVING
 Name Problem Solving Compare Volumes Essential Question: How can you use the strategy make a table to compare different rectangular prisms with the same volume? Unlock the Problem PROBLEM SOLVING Lesson
Name Problem Solving Compare Volumes Essential Question: How can you use the strategy make a table to compare different rectangular prisms with the same volume? Unlock the Problem PROBLEM SOLVING Lesson
Three-Dimensional Figures and Nets
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Three-Dimensional Figures and Nets Solid figures have three dimensions length, width, and height. They can be named by the shapes of their bases, the number of bases, and the shapes
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Three-Dimensional Figures and Nets Solid figures have three dimensions length, width, and height. They can be named by the shapes of their bases, the number of bases, and the shapes
1.0 Fractions Review Name: Date: Goal: to review some key fractions skills in preparation for the upcoming unit. Main Ideas: b)!!
 1.0 Fractions Review Name: Date: Goal: to review some key fractions skills in preparation for the upcoming unit Toolkit: Working with integers Operations with fractions Main Ideas: Reducing Fractions To
1.0 Fractions Review Name: Date: Goal: to review some key fractions skills in preparation for the upcoming unit Toolkit: Working with integers Operations with fractions Main Ideas: Reducing Fractions To
Polygon Practice. E90 Grade 5. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygon Practice Write the number of sides and the number of angles that each polygon has. Then match each description to one of the polygons drawn below. Label the polygon with the exercise
Lesson 11.1 Polygon Practice Write the number of sides and the number of angles that each polygon has. Then match each description to one of the polygons drawn below. Label the polygon with the exercise
Unit. 8 Days : August 24 September 2
 1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Geometry (G) OA.3.5 Generate and analyze patterns. Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the
1 st Trimester Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Geometry (G) OA.3.5 Generate and analyze patterns. Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the
UNIT 12. Volume and Surface Area CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Vocabulary 2. Basics of 3-D Figures 3 8
 UNIT 12 Volume and Surface Area 2016 2017 CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept(s) Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Basics of 3-D Figures 3 8 Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Finding Missing
UNIT 12 Volume and Surface Area 2016 2017 CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept(s) Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Basics of 3-D Figures 3 8 Volume of Rectangular Prisms and Finding Missing
Math 6: Geometry 3-Dimensional Figures
 Math 6: Geometry 3-Dimensional Figures Three-Dimensional Figures A solid is a three-dimensional figure that occupies a part of space. The polygons that form the sides of a solid are called a faces. Where
Math 6: Geometry 3-Dimensional Figures Three-Dimensional Figures A solid is a three-dimensional figure that occupies a part of space. The polygons that form the sides of a solid are called a faces. Where
MATHEMATICS Grade 2 Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations. Organizing Topic Benchmark Indicator Number and Number Systems
 Standard: Number, Number Sense and A. Use place value concepts to represent whole numbers using numerals, words and physical models. 1. Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers
Standard: Number, Number Sense and A. Use place value concepts to represent whole numbers using numerals, words and physical models. 1. Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers
TEACHER GUIDE INCLUDES. Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Correlations. Diagnostic Interviews for Every Common Core Cluster
 TEACHER GUIDE FOR THE COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3 INCLUDES Tier Tier Tier 3 Correlations Diagnostic Interviews for Every Common Core Cluster Tier Lessons, Tier Prerequisite Skills, and
TEACHER GUIDE FOR THE COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3 INCLUDES Tier Tier Tier 3 Correlations Diagnostic Interviews for Every Common Core Cluster Tier Lessons, Tier Prerequisite Skills, and
Georgia Department of Education P a g e 1
 P a g e CC.5.OA. Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces Grade Difference in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. GA.4.N.7 Students
P a g e CC.5.OA. Write and interpret numerical expressions. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces Grade Difference in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. GA.4.N.7 Students
CCM6+ Unit 12 Surface Area and Volume page 1 CCM6+ UNIT 12 Surface Area and Volume Name Teacher Kim Li
 CCM6+ Unit 12 Surface Area and Volume page 1 CCM6+ UNIT 12 Surface Area and Volume Name Teacher Kim Li MAIN CONCEPTS Page(s) Unit 12 Vocabulary 2 3D Figures 3-8 Volume of Prisms 9-19 Surface Area 20-26
CCM6+ Unit 12 Surface Area and Volume page 1 CCM6+ UNIT 12 Surface Area and Volume Name Teacher Kim Li MAIN CONCEPTS Page(s) Unit 12 Vocabulary 2 3D Figures 3-8 Volume of Prisms 9-19 Surface Area 20-26
Groveport Madison Local School District Second Grade Math Content Standards Planning Sheets
 Standard: Measurement A. Explain the need for standard units of measure. B. Select appropriate units for length, weight, volume (capacity) and time, using: objects; i.e., non-standard units Second Grade
Standard: Measurement A. Explain the need for standard units of measure. B. Select appropriate units for length, weight, volume (capacity) and time, using: objects; i.e., non-standard units Second Grade
Houston County Schools Grade 4 Math
 Grade 4 Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking [OA] Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Gain familiarity with factors and multiples. Generate and analyze patterns. Number and
Grade 4 Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking [OA] Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Gain familiarity with factors and multiples. Generate and analyze patterns. Number and
Surface Area and Volume
 8 Surface Area and Volume 8. Three-Dimensional Figures 8. Surface Areas of Prisms 8. Surface Areas of Pyramids 8. Volumes of Rectangular Prisms I petitioned my owner for a doghouse with greater volume.
8 Surface Area and Volume 8. Three-Dimensional Figures 8. Surface Areas of Prisms 8. Surface Areas of Pyramids 8. Volumes of Rectangular Prisms I petitioned my owner for a doghouse with greater volume.
English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14
 English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 10-1 Solid Geometry
 10A Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 10-1 Solid Geometry face edge vertex prism cylinder pyramid cone cube net cross
10A Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 10-1 Solid Geometry face edge vertex prism cylinder pyramid cone cube net cross
Write Euler s Theorem. Solving Problems Using Surface Area and Volume. Figure Surface Area Volume. Cl V 5 1 } 3
 CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
Practice A Introduction to Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Revision Booklet. Grade 6
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Russell County Schools Pacing Guide Grade 5 Math. Overview
 ussell County Schools Pacing Guide Overview Operations and Algebraic hinking [OA] Write and interpret numerical expressions. Analyze patterns and relationships. Number and Operations in Base en [NB] Understand
ussell County Schools Pacing Guide Overview Operations and Algebraic hinking [OA] Write and interpret numerical expressions. Analyze patterns and relationships. Number and Operations in Base en [NB] Understand
English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 3, 2013
 English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 3, 2013 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah
English 4 th Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: June 3, 2013 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah
Unit 7: Area and Volume
 Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
ADW GRADE 5 Math Standards, revised 2017
 NUMBER SENSE (NS) Students compute with whole numbers, decimals and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers.
NUMBER SENSE (NS) Students compute with whole numbers, decimals and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions and percents. They understand the relative magnitudes of numbers.
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
5 th Grade Common Core. Math Review. 40 Pages. All Standards. Jennifer Findley
 5 th Grade Common Core Math Review 40 Pages All Standards Jennifer Findley The first 30 pages contain standards in all 5 domains, grouped this way: The last ten pages contain only Number and Operation
5 th Grade Common Core Math Review 40 Pages All Standards Jennifer Findley The first 30 pages contain standards in all 5 domains, grouped this way: The last ten pages contain only Number and Operation
Revision Booklet. Grade 6
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Length, Width, and Depth
 Length, Width, and Depth Deepening Understanding of Volume 1 WARM UP Determine the least common multiple of the numbers in each pair. 1., 10. 3, 8 3. 6, 1 LEARNING GOALS Determine the volume of right rectangular
Length, Width, and Depth Deepening Understanding of Volume 1 WARM UP Determine the least common multiple of the numbers in each pair. 1., 10. 3, 8 3. 6, 1 LEARNING GOALS Determine the volume of right rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS
 MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
Engage NY Lesson 15: Representing Three-Dimensional Figures Using Nets
 Name: Surface Area & Volume Packet Engage NY Lesson 15: Representing Three-Dimensional Figures Using Nets Classwork Cereal Box Similarities: Cereal Box Differences: Exercise 1 1. Some of the drawings below
Name: Surface Area & Volume Packet Engage NY Lesson 15: Representing Three-Dimensional Figures Using Nets Classwork Cereal Box Similarities: Cereal Box Differences: Exercise 1 1. Some of the drawings below
A mathematics resource for parents, teachers, and students
 Encourage your student to record and graph the number of windows, doors, chairs, etc. in your home. If your student gets an allowance, ask her to make a graph of how she spends her money. Groovy Graphing
Encourage your student to record and graph the number of windows, doors, chairs, etc. in your home. If your student gets an allowance, ask her to make a graph of how she spends her money. Groovy Graphing
We want students to understand that all numbers have parts, values, uses, types, and we use operations and reasonableness to work with them.
 Grade 4 - Fractions Essential Questions: 1. Why do we use numbers, what are their properties, and how does our number system function? 2. Why do we use estimation and when is it appropriate? 3. What makes
Grade 4 - Fractions Essential Questions: 1. Why do we use numbers, what are their properties, and how does our number system function? 2. Why do we use estimation and when is it appropriate? 3. What makes
C in. 2. D in Find the volume of a 7-inch tall drinking glass with a 4-inch diameter. C lateral faces. A in. 3 B in.
 Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Lesson 14.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 14.1 Skills Practice Name Date Cut, Fold, and Voila! Nets Vocabulary Define each term in your own words. 1. geometric solids 2. net 3. prototype 4. edge 5. face 6. vertex Problem Set Sketch and
Lesson 14.1 Skills Practice Name Date Cut, Fold, and Voila! Nets Vocabulary Define each term in your own words. 1. geometric solids 2. net 3. prototype 4. edge 5. face 6. vertex Problem Set Sketch and
Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs
 Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs 1. Given the rule: Complete the table for the function rule for the following input values: input 0 2 4 6 8 10 output 2. Here is an input-output rule: Complete the
Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs 1. Given the rule: Complete the table for the function rule for the following input values: input 0 2 4 6 8 10 output 2. Here is an input-output rule: Complete the
Plainfield Public School District Mathematics/3 rd Grade Curriculum Guide
 NJCCCS: STANDARD 4.2 (GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT) ALL STUDENTS WILL DEVELOP SPATIAL SENSE AND THE ABILITY TO USE GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES, RELATIONSHIPS, AND MEASUREMENT TO MODEL, DESCRIBE AND ANALYZE PHENOMENA.
NJCCCS: STANDARD 4.2 (GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT) ALL STUDENTS WILL DEVELOP SPATIAL SENSE AND THE ABILITY TO USE GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES, RELATIONSHIPS, AND MEASUREMENT TO MODEL, DESCRIBE AND ANALYZE PHENOMENA.
8th Grade. Slide 1 / 97. Slide 2 / 97. Slide 3 / 97. 3D Geometry. Table of Contents. 3-Dimensional Solids. Volume. Glossary & Standards
 Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
1 Measurement - Nets, Surface Area and Volume. Terms
 1 Measurement - Nets, Surface Area and Volume Terms 2 Measurement - Nets, Surface Area and Volume Nets 1. Draw a net for the following shape. Include all measurements and symbols. 2. 3. 4. 3 Measurement
1 Measurement - Nets, Surface Area and Volume Terms 2 Measurement - Nets, Surface Area and Volume Nets 1. Draw a net for the following shape. Include all measurements and symbols. 2. 3. 4. 3 Measurement
CHAPTER 10 EXAMPLES AND DEFINITIONS
 MATH 20063 CHAPTER 10 EXAMPLES AND DEFINITIONS Section 10.1 Systems of Measurement It can be helpful to have an everyday approximate equivalent to units of measure. These are called benchmarks. Some benchmarks
MATH 20063 CHAPTER 10 EXAMPLES AND DEFINITIONS Section 10.1 Systems of Measurement It can be helpful to have an everyday approximate equivalent to units of measure. These are called benchmarks. Some benchmarks
The Grade 5 Common Core State Standards for Measurement and Data specify that students should
 Measurement and Data Students have learned that measurement is the process of comparing a quantity to a standard unit. In fifth grade, students convert units within a given measurement system and use these
Measurement and Data Students have learned that measurement is the process of comparing a quantity to a standard unit. In fifth grade, students convert units within a given measurement system and use these
8-3. A butterfly house at a local zoo is a rectangular prism with dimensions 20' 15' 10' and contains 625 butterflies.
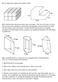 8-1. Compute the volume of the figures below. 8-2. Carefully draw the prisms below onto your paper. One way to do this is to draw the two bases first and then to connect the corresponding vertices of the
8-1. Compute the volume of the figures below. 8-2. Carefully draw the prisms below onto your paper. One way to do this is to draw the two bases first and then to connect the corresponding vertices of the
Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education
 Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
Geometry: Notes
 Geometry: 11.5-11.8 Notes NAME 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Date: Define Vocabulary: volume Cavalieri s Principle density similar solids Examples: Finding Volumes of Prisms 1 Examples: Finding
Geometry: 11.5-11.8 Notes NAME 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Date: Define Vocabulary: volume Cavalieri s Principle density similar solids Examples: Finding Volumes of Prisms 1 Examples: Finding
3 Dimensional Solids. Table of Contents. 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres
 Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
MFM2P Measurement Checklist
 MFM2P Measurement Checklist 1 Goals for this unit: I can work in Imperial measure and convert between Metric and Imperial. I can determine the volume of simple prisms. I can determine the surface area
MFM2P Measurement Checklist 1 Goals for this unit: I can work in Imperial measure and convert between Metric and Imperial. I can determine the volume of simple prisms. I can determine the surface area
Math Lesson Plan 4th Grade Curriculum Total Activities: 204
 TimeLearning Online Learning for Homeschool and Enrichment www.timelearning.com Languages Arts, Math and more Multimedia s, Interactive Exercises, Printable Worksheets and Assessments Student Paced Learning
TimeLearning Online Learning for Homeschool and Enrichment www.timelearning.com Languages Arts, Math and more Multimedia s, Interactive Exercises, Printable Worksheets and Assessments Student Paced Learning
Second Grade Mathematics Indicators Class Summary
 Mathematics Indicators Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Number and Number System Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers using physical models, numerals and words,
Mathematics Indicators Number, Number Sense and Operations Standard Number and Number System Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers using physical models, numerals and words,
Unit 5. Area & Volume. Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume. Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18. Name: Math Teacher:
 Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Math Lesson Plan 4th Grade Curriculum Total Activities: 214
 TimeLearning Online Learning for Homeschool and Enrichment www.timelearning.com Languages Arts, Math and more Multimedia s, Interactive Exercises, Printable Worksheets and Assessments Student Paced Learning
TimeLearning Online Learning for Homeschool and Enrichment www.timelearning.com Languages Arts, Math and more Multimedia s, Interactive Exercises, Printable Worksheets and Assessments Student Paced Learning
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED: Volume of Cylinders Volume of Cones Volume of Spheres Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Cylinders Accelerated Mathematics
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED: Volume of Cylinders Volume of Cones Volume of Spheres Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Cylinders Accelerated Mathematics
