Spatial Data Structures for GIS Visualization. Ed Grundy
|
|
|
- Caroline Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spatial Data Structures for GIS Visualization Ed Grundy
2 GIS Data Elevation maps Satellite imagery (as texture data) Other data we may wish to visualise, such as temperature, population, etc In GIS terms data sets are draped over a base (usually the elevation or satellite image)
3 Elevation data Typically from NASA SRTM shuttle mission 1201x1201 tiles ~1.5m vertices + normals Have been tiled to larger dimensions Typical methods use distance based triangulation to effect continuous level of detail
4 Texture data Large images ~8000x~9000 Multi-channel (usually we are only interested in RGB) Difficult to register onto elevation maps
5 Direct Rendering OpenGL cannot handle textures this size Requires resizing the image, causing loss of data
6 Quadtrees Data structure of choice for 2D subdivision Literature usually discusses Black and White quadtrees where the tree encodes a binary image (internal nodes are called Grey nodes) Leaf data can be approximated in internal nodes to produce discrete level of detail Nodes can be pruned if all siblings have the same data
7 Quadtrees Nodes can be rendered as fans, strips or quads Allows fine level of detail control Geometry is not tied to the tree, i.e. nodes can contain indices into a vertex array
8 Quadtrees Storage requirements can be large for deep trees Constant value of 4 pointers + growth rate of the tree For a 1024x1024 image with 64x64 sized nodes 43k is needed just for pointers (this is a small tree!) Dynamic allocation strategies often cause heap fragmentation, encouraging page faults leafcount treedepth log l log (256) 4 nodecount d 4 i 0 4 i size 4n* sizeof ( ptr) 4*337*32 ~ 43k 4
9 Linear Quadtrees Using expressions from the previous slide we can calculate the size of the tree and allocate a contiguous block of memory Two problems: How should the nodes be ordered? How do we locate a node?
10 Linear Quadtrees Depth-first ordering Nodes are stored in depth first search order Useful for recursive searching Breadth-first ordering Useful for adjacent searching (GIS problem) Nodes can be located with Location codes (similar to Huffman encoding) as described in Octrees for faster isosurface generation, Wilhelms and Van Gelder, 1992
11 Location Codes Code describes the path from the root to a leaf by storing the branch factor at each level; i.e. the code is a sequence of branch factors Quadtrees use base 4 values, octrees use base 8. Rule of thumb: base = 2^data dimensionality or 2^child count. i.e. binary trees use base 2 in Huffman encoding Location codes have many useful properties Encodes the path to all ancestors Slight modification allows us to locate siblings Further modification allows locating general neighbours Also encodes the array index when the tree is stored in a breadth first manner (
12 Location Codes Ancestor = removing least significant digit A ( q i n ) q n i Siblings = change least significant digit S { 0,1,2,3} ( qn) q i n 1 i Neighbours = performing a carry operation on the code and modifying up to a point Array index given by transforming from base 4 to base 10 Must be careful to note 0s are significant: i 0 i I( q n ) 4 q n i 1
13 Location Codes Faster than traditional tree browsing methods Complexity is linear to the length of the code, i.e. depth of the tree Codes can be constructed by dividing the unit square, removing all need for the tree representation Image co-ordinates can be retrieved from the code
14 Location Codes Codes are valid for different trees (as long as underlying data is aligned and subdivision methods are equal) Solves a problem of finding related data in GIS drapes i.e. find a location in the elevation data, and the code will present texture, normals, population, temperature, etc
15 Summary Linear quadtree and location codes are a fast and efficient indexing method Can be extended to higher dimensions, (usually by changing 4 to 2^n where n is the dimensionality of the data)
16 Results
CSE 554 Lecture 5: Contouring (faster)
 CSE 554 Lecture 5: Contouring (faster) Fall 2016 CSE554 Contouring II Slide 1 Review Iso-contours Points where a function evaluates to be a given value (iso-value) Smooth thresholded boundaries Contouring
CSE 554 Lecture 5: Contouring (faster) Fall 2016 CSE554 Contouring II Slide 1 Review Iso-contours Points where a function evaluates to be a given value (iso-value) Smooth thresholded boundaries Contouring
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Organizing Spatial Data
 Organizing Spatial Data Spatial data records include a sense of location as an attribute. Typically location is represented by coordinate data (in 2D or 3D). 1 If we are to search spatial data using the
Organizing Spatial Data Spatial data records include a sense of location as an attribute. Typically location is represented by coordinate data (in 2D or 3D). 1 If we are to search spatial data using the
CS535 Fall Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Spatial Data Structures and Hierarchies CS535 Fall 2010 Daniel G Aliaga Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Spatial Data Structures Store geometric information Organize geometric
Spatial Data Structures and Hierarchies CS535 Fall 2010 Daniel G Aliaga Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Spatial Data Structures Store geometric information Organize geometric
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
Main Memory and the CPU Cache
 Main Memory and the CPU Cache CPU cache Unrolled linked lists B Trees Our model of main memory and the cost of CPU operations has been intentionally simplistic The major focus has been on determining
Main Memory and the CPU Cache CPU cache Unrolled linked lists B Trees Our model of main memory and the cost of CPU operations has been intentionally simplistic The major focus has been on determining
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Algorithms for GIS:! Quadtrees
 Algorithms for GIS: Quadtrees Quadtree A data structure that corresponds to a hierarchical subdivision of the plane Start with a square (containing inside input data) Divide into 4 equal squares (quadrants)
Algorithms for GIS: Quadtrees Quadtree A data structure that corresponds to a hierarchical subdivision of the plane Start with a square (containing inside input data) Divide into 4 equal squares (quadrants)
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
EE 368. Weeks 5 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
1. Meshes. D7013E Lecture 14
 D7013E Lecture 14 Quadtrees Mesh Generation 1. Meshes Input: Components in the form of disjoint polygonal objects Integer coordinates, 0, 45, 90, or 135 angles Output: A triangular mesh Conforming: A triangle
D7013E Lecture 14 Quadtrees Mesh Generation 1. Meshes Input: Components in the form of disjoint polygonal objects Integer coordinates, 0, 45, 90, or 135 angles Output: A triangular mesh Conforming: A triangle
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
Subdivision Of Triangular Terrain Mesh Breckon, Chenney, Hobbs, Hoppe, Watts
 Subdivision Of Triangular Terrain Mesh Breckon, Chenney, Hobbs, Hoppe, Watts MSc Computer Games and Entertainment Maths & Graphics II 2013 Lecturer(s): FFL (with Gareth Edwards) Fractal Terrain Based on
Subdivision Of Triangular Terrain Mesh Breckon, Chenney, Hobbs, Hoppe, Watts MSc Computer Games and Entertainment Maths & Graphics II 2013 Lecturer(s): FFL (with Gareth Edwards) Fractal Terrain Based on
Announcements. Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday
 Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Image Rotation Using Quad Tree
 80 Image Rotation Using Quad Tree Aashish Kumar, Lec. ECE Dept. Swami Vivekanand institute of Engneering & Technology, Ramnagar Banur ABSTRACT This paper presents a data structure based technique of rotating
80 Image Rotation Using Quad Tree Aashish Kumar, Lec. ECE Dept. Swami Vivekanand institute of Engneering & Technology, Ramnagar Banur ABSTRACT This paper presents a data structure based technique of rotating
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
An undirected graph is a tree if and only of there is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices.
 Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Spatial Data Structures
 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
An iterative, octree-based algorithm for distance computation between polyhedra with complex surfaces 1
 An iterative, octree-based algorithm for distance computation between polyhedra with complex surfaces 1 André Borrmann, Stefanie Schraufstetter, Christoph van Treeck, Ernst Rank {borrmann, schraufstetter,
An iterative, octree-based algorithm for distance computation between polyhedra with complex surfaces 1 André Borrmann, Stefanie Schraufstetter, Christoph van Treeck, Ernst Rank {borrmann, schraufstetter,
Motivation for B-Trees
 1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
9. Three Dimensional Object Representations
 9. Three Dimensional Object Representations Methods: Polygon and Quadric surfaces: For simple Euclidean objects Spline surfaces and construction: For curved surfaces Procedural methods: Eg. Fractals, Particle
9. Three Dimensional Object Representations Methods: Polygon and Quadric surfaces: For simple Euclidean objects Spline surfaces and construction: For curved surfaces Procedural methods: Eg. Fractals, Particle
Ray Tracing III. Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University
 Ray Tracing III Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University Shirley, Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Chap 10 Doug James CG slides, I-Chen Lin s CG slides Ray-tracing Review For each pixel,
Ray Tracing III Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University Shirley, Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Chap 10 Doug James CG slides, I-Chen Lin s CG slides Ray-tracing Review For each pixel,
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students)
 TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
CS 151. Binary Trees. Friday, October 5, 12
 CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering
 1 Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering Project Plan Final Group: May13-11 Christopher Jeffers Eric Jensen Joel Rausch Client: Siemens PLM Software Client Contact: Michael Carter Adviser: Simanta Mitra 4/29/13
1 Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering Project Plan Final Group: May13-11 Christopher Jeffers Eric Jensen Joel Rausch Client: Siemens PLM Software Client Contact: Michael Carter Adviser: Simanta Mitra 4/29/13
Quadtrees and Meshing
 Computational Geometry Lecture INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK FAKULTÄT FÜR INFORMATIK Tamara Mchedlidze Darren Strash 14.12.2015 Motivation: Meshing PC Board Layouts To simulate the heat produced
Computational Geometry Lecture INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK FAKULTÄT FÜR INFORMATIK Tamara Mchedlidze Darren Strash 14.12.2015 Motivation: Meshing PC Board Layouts To simulate the heat produced
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
CPSC / Sonny Chan - University of Calgary. Collision Detection II
 CPSC 599.86 / 601.86 Sonny Chan - University of Calgary Collision Detection II Outline Broad phase collision detection: - Problem definition and motivation - Bounding volume hierarchies - Spatial partitioning
CPSC 599.86 / 601.86 Sonny Chan - University of Calgary Collision Detection II Outline Broad phase collision detection: - Problem definition and motivation - Bounding volume hierarchies - Spatial partitioning
Introduction. Choice orthogonal to indexing technique used to locate entries K.
 Tree-Structured Indexes Werner Nutt Introduction to Database Systems Free University of Bozen-Bolzano 2 Introduction As for any index, three alternatives for data entries K : Data record with key value
Tree-Structured Indexes Werner Nutt Introduction to Database Systems Free University of Bozen-Bolzano 2 Introduction As for any index, three alternatives for data entries K : Data record with key value
Lecture 25 of 41. Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees
 Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre Public
Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre Public
Scene Management. Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development
 Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development Chap. 5 Scene Management Overview Scene Management vs Rendering This chapter is about rendering
Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development Chap. 5 Scene Management Overview Scene Management vs Rendering This chapter is about rendering
An improvement in the build algorithm for Kd-trees using mathematical mean
 An improvement in the build algorithm for Kd-trees using mathematical mean Priyank Trivedi, Abhinandan Patni, Zeon Trevor Fernando and Tejaswi Agarwal School of Computing Sciences and Engineering, VIT
An improvement in the build algorithm for Kd-trees using mathematical mean Priyank Trivedi, Abhinandan Patni, Zeon Trevor Fernando and Tejaswi Agarwal School of Computing Sciences and Engineering, VIT
Code Transformation of DF-Expression between Bintree and Quadtree
 Code Transformation of DF-Expression between Bintree and Quadtree Chin-Chen Chang*, Chien-Fa Li*, and Yu-Chen Hu** *Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Chung Cheng University
Code Transformation of DF-Expression between Bintree and Quadtree Chin-Chen Chang*, Chien-Fa Li*, and Yu-Chen Hu** *Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Chung Cheng University
Solid Modeling. Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall Represent solid interiors of objects
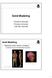 Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
1 Introduction Interactive visualization is of major importance to scientific users, but the sheer size of volume data sets can tax the resources of c
 Octrees for Faster Isosurface Generation Λ Jane Wilhelms and Allen Van Gelder University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract The large size of many volume data sets often prevents visualization algorithms
Octrees for Faster Isosurface Generation Λ Jane Wilhelms and Allen Van Gelder University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract The large size of many volume data sets often prevents visualization algorithms
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Topic 18 Binary Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb
 Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Second degree equations - quadratics. nonparametric: x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = r 2
 walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 20 Slide 1 Three Dimensional Representations Quadric Surfaces Superquadrics Sweep Representations Constructive Solid Geometry Octrees Quadric Surfaces Second degree
walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 20 Slide 1 Three Dimensional Representations Quadric Surfaces Superquadrics Sweep Representations Constructive Solid Geometry Octrees Quadric Surfaces Second degree
Real-Time Reyes: Programmable Pipelines and Research Challenges. Anjul Patney University of California, Davis
 Real-Time Reyes: Programmable Pipelines and Research Challenges Anjul Patney University of California, Davis Real-Time Reyes-Style Adaptive Surface Subdivision Anjul Patney and John D. Owens SIGGRAPH Asia
Real-Time Reyes: Programmable Pipelines and Research Challenges Anjul Patney University of California, Davis Real-Time Reyes-Style Adaptive Surface Subdivision Anjul Patney and John D. Owens SIGGRAPH Asia
Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures
 Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures Sumair Ahmed October 29, 2009 Ray Tracing is very time-consuming because of the ray-object intersection calculations. With the brute force method, each ray has
Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures Sumair Ahmed October 29, 2009 Ray Tracing is very time-consuming because of the ray-object intersection calculations. With the brute force method, each ray has
Contouring and Isosurfaces. Ronald Peikert SciVis Contouring 2-1
 Contouring and Isosurfaces Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Contouring 2-1 What are contours? Set of points where the scalar field s has a given value c: Examples in 2D: height contours on maps isobars on
Contouring and Isosurfaces Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Contouring 2-1 What are contours? Set of points where the scalar field s has a given value c: Examples in 2D: height contours on maps isobars on
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
Tree-Structured Indexes. Chapter 10
 Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k 25, [n1,v1,k1,25] 25,
Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k 25, [n1,v1,k1,25] 25,
Tree-Structured Indexes ISAM. Range Searches. Comments on ISAM. Example ISAM Tree. Introduction. As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*:
 Introduction Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Introduction Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Real time 3D display of hydrographic data for QA and QC.
 Real time 3D display of hydrographic data for QA and QC. Roland Arsenault Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping & Joint Hydrographic Center University of New Hampshire roland@ccom.unh.edu Figure 1 Data
Real time 3D display of hydrographic data for QA and QC. Roland Arsenault Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping & Joint Hydrographic Center University of New Hampshire roland@ccom.unh.edu Figure 1 Data
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
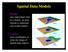 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
Tree-Structured Indexes
 Introduction Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Introduction Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Mesh Generation. Quadtrees. Geometric Algorithms. Lecture 9: Quadtrees
 Lecture 9: Lecture 9: VLSI Design To Lecture 9: Finite Element Method To http://www.antics1.demon.co.uk/finelms.html Lecture 9: To Lecture 9: To component not conforming doesn t respect input not well-shaped
Lecture 9: Lecture 9: VLSI Design To Lecture 9: Finite Element Method To http://www.antics1.demon.co.uk/finelms.html Lecture 9: To Lecture 9: To component not conforming doesn t respect input not well-shaped
Data Structure. IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017
 Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
REGION BASED SEGEMENTATION
 REGION BASED SEGEMENTATION The objective of Segmentation is to partition an image into regions. The region-based segmentation techniques find the regions directly. Extract those regions in the image whose
REGION BASED SEGEMENTATION The objective of Segmentation is to partition an image into regions. The region-based segmentation techniques find the regions directly. Extract those regions in the image whose
A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset
 32 A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset Zhou Kai, and Tian Feng School of Computer and Information Technology, Northeast Petroleum University,
32 A Real-time Rendering Method Based on Precomputed Hierarchical Levels of Detail in Huge Dataset Zhou Kai, and Tian Feng School of Computer and Information Technology, Northeast Petroleum University,
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Tree-Structured Indexes
 Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 9 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: ➀ Data record with key value k ➁
Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 9 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: ➀ Data record with key value k ➁
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
) $ f ( n) " %( g( n)
 CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
8 Three-Dimensional Object Representations. Chapter 8. Three-Dimensional Object Representations. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 8-1
 Chapter 8 Three-Dimensional Object Representations 8-1 8.1 Overview The main goal of three-dimensional computer graphics is to generate two-dimensional images of a scene or of an object based on a a description
Chapter 8 Three-Dimensional Object Representations 8-1 8.1 Overview The main goal of three-dimensional computer graphics is to generate two-dimensional images of a scene or of an object based on a a description
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26. Graphs. CS 441 Discrete mathematics for CS. Final exam
 CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
Spatial Data Management
 Spatial Data Management Chapter 28 Database management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite
Spatial Data Management Chapter 28 Database management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite
Bioinformatics Programming. EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang)
 Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
Terrain rendering (part 1) Due: Monday, March 10, 10pm
 CMSC 3700 Winter 014 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 February 5 Terrain rendering (part 1) Due: Monday, March 10, 10pm 1 Summary The final two projects involves rendering large-scale outdoor
CMSC 3700 Winter 014 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 February 5 Terrain rendering (part 1) Due: Monday, March 10, 10pm 1 Summary The final two projects involves rendering large-scale outdoor
Cga-LoD Developer Documentation
 Cga-LoD Developer Documentation Introduction Cga-LoD was programmed 2009/10 as a Praktikum. The purpose of the program is to create LoD models of models that were created with Markus Lipp's Cga program.
Cga-LoD Developer Documentation Introduction Cga-LoD was programmed 2009/10 as a Praktikum. The purpose of the program is to create LoD models of models that were created with Markus Lipp's Cga program.
Decision trees. Decision trees are useful to a large degree because of their simplicity and interpretability
 Decision trees A decision tree is a method for classification/regression that aims to ask a few relatively simple questions about an input and then predicts the associated output Decision trees are useful
Decision trees A decision tree is a method for classification/regression that aims to ask a few relatively simple questions about an input and then predicts the associated output Decision trees are useful
CSE 530A. B+ Trees. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2. CIS565 Fall 2012 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li
 Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2 CIS565 Fall 202 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li Jim Scott 2009 Spatial cceleration Structures: KD-Trees *Some portions of these
Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2 CIS565 Fall 202 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li Jim Scott 2009 Spatial cceleration Structures: KD-Trees *Some portions of these
Trees. Introduction & Terminology. February 05, 2018 Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Spatial Data Structures for Computer Graphics
 Spatial Data Structures for Computer Graphics Page 1 of 65 http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sharat November 2008 Spatial Data Structures for Computer Graphics Page 1 of 65 http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sharat November
Spatial Data Structures for Computer Graphics Page 1 of 65 http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sharat November 2008 Spatial Data Structures for Computer Graphics Page 1 of 65 http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sharat November
Isosurface Rendering. CSC 7443: Scientific Information Visualization
 Isosurface Rendering What is Isosurfacing? An isosurface is the 3D surface representing the locations of a constant scalar value within a volume A surface with the same scalar field value Isosurfaces form
Isosurface Rendering What is Isosurfacing? An isosurface is the 3D surface representing the locations of a constant scalar value within a volume A surface with the same scalar field value Isosurfaces form
Oblique Image Processing in SURE - First Experiments and Results
 EuroSDR / ISPRS Workshop, Southampton 2015 Oblique Image Processing in SURE - First Experiments and Results Mathias Rothermel Outline» General Workflow» 2.5D Meshing» Mesh Texturing» 3D Workflow» First
EuroSDR / ISPRS Workshop, Southampton 2015 Oblique Image Processing in SURE - First Experiments and Results Mathias Rothermel Outline» General Workflow» 2.5D Meshing» Mesh Texturing» 3D Workflow» First
Data Structures Question Bank Multiple Choice
 Section 1. Fundamentals: Complexity, Algorthm Analysis 1. An algorithm solves A single problem or function Multiple problems or functions Has a single programming language implementation 2. A solution
Section 1. Fundamentals: Complexity, Algorthm Analysis 1. An algorithm solves A single problem or function Multiple problems or functions Has a single programming language implementation 2. A solution
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
FMM Data Structures. Content. Introduction Hierarchical Space Subdivision with 2 d -Trees Hierarchical Indexing System Parent & Children Finding
 FMM Data Structures Nail Gumerov & Ramani Duraiswami UMIACS [gumerov][ramani]@umiacs.umd.edu CSCAMM FAM4: 4/9/4 Duraiswami & Gumerov, -4 Content Introduction Hierarchical Space Subdivision with d -Trees
FMM Data Structures Nail Gumerov & Ramani Duraiswami UMIACS [gumerov][ramani]@umiacs.umd.edu CSCAMM FAM4: 4/9/4 Duraiswami & Gumerov, -4 Content Introduction Hierarchical Space Subdivision with d -Trees
M-ary Search Tree. B-Trees. B-Trees. Solution: B-Trees. B-Tree: Example. B-Tree Properties. Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height =
 M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Multi-way Search Trees
 Multi-way Search Trees Kuan-Yu Chen ( 陳冠宇 ) 2018/10/24 @ TR-212, NTUST Review Red-Black Trees Splay Trees Huffman Trees 2 Multi-way Search Trees. Every node in a binary search tree contains one value and
Multi-way Search Trees Kuan-Yu Chen ( 陳冠宇 ) 2018/10/24 @ TR-212, NTUST Review Red-Black Trees Splay Trees Huffman Trees 2 Multi-way Search Trees. Every node in a binary search tree contains one value and
Tree-Structured Indexes
 Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 9 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 9 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing (Cnt(
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing (Cnt( Cnt.) Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing (Cnt( Cnt.) Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition
CIS 4930/ SCIENTIFICVISUALIZATION
 CIS 4930/6930-902 SCIENTIFICVISUALIZATION ISOSURFACING Paul Rosen Assistant Professor University of South Florida slides credits Tricoche and Meyer ADMINISTRATIVE Read (or watch video): Kieffer et al,
CIS 4930/6930-902 SCIENTIFICVISUALIZATION ISOSURFACING Paul Rosen Assistant Professor University of South Florida slides credits Tricoche and Meyer ADMINISTRATIVE Read (or watch video): Kieffer et al,
Real-Time Voxelization for Global Illumination
 Lecture 26: Real-Time Voxelization for Global Illumination Visual Computing Systems Voxelization to regular grid Input: scene triangles Output: surface information at each voxel in 3D grid - Simple case:
Lecture 26: Real-Time Voxelization for Global Illumination Visual Computing Systems Voxelization to regular grid Input: scene triangles Output: surface information at each voxel in 3D grid - Simple case:
Recursion Problems. Warm Ups. Enumeration 1 / 7
 1 / 7 Recursion Problems Warm Ups 1. Write a recursive implementation of the factorial function. Recall that n! = 1 2 n, with the special case that 0! = 1. 2. Write a recursive function that, given a number
1 / 7 Recursion Problems Warm Ups 1. Write a recursive implementation of the factorial function. Recall that n! = 1 2 n, with the special case that 0! = 1. 2. Write a recursive function that, given a number
A Comparison of Two Fully-Dynamic Delaunay Triangulation Methods
 A Comparison of Two Fully-Dynamic Delaunay Triangulation Methods Michael D Adams Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Victoria Victoria, BC, V8W 3P6, Canada Web: http://wwweceuvicca/
A Comparison of Two Fully-Dynamic Delaunay Triangulation Methods Michael D Adams Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Victoria Victoria, BC, V8W 3P6, Canada Web: http://wwweceuvicca/
Out-of-core Multi-resolution Terrain Modeling
 2 Out-of-core Multi-resolution Terrain Modeling Emanuele Danovaro 1,2, Leila De Floriani 1,2, Enrico Puppo 1, and Hanan Samet 2 1 Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Genoa - Via
2 Out-of-core Multi-resolution Terrain Modeling Emanuele Danovaro 1,2, Leila De Floriani 1,2, Enrico Puppo 1, and Hanan Samet 2 1 Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Genoa - Via
GPU Memory Model. Adapted from:
 GPU Memory Model Adapted from: Aaron Lefohn University of California, Davis With updates from slides by Suresh Venkatasubramanian, University of Pennsylvania Updates performed by Gary J. Katz, University
GPU Memory Model Adapted from: Aaron Lefohn University of California, Davis With updates from slides by Suresh Venkatasubramanian, University of Pennsylvania Updates performed by Gary J. Katz, University
Geometric Compression Through Topological Surgery
 Geometric Compression Through Topological Surgery GABRIEL TAUBIN IBM T. J. Watson Research Center and JAREK ROSSIGNAC GVU, Georgia Institute of Technology The abundance and importance of complex 3-D data
Geometric Compression Through Topological Surgery GABRIEL TAUBIN IBM T. J. Watson Research Center and JAREK ROSSIGNAC GVU, Georgia Institute of Technology The abundance and importance of complex 3-D data
Visibility and Occlusion Culling
 Visibility and Occlusion Culling CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University [some slides based on those of Benjamin Mora] Why? To avoid processing geometry that does
Visibility and Occlusion Culling CS535 Fall 2014 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University [some slides based on those of Benjamin Mora] Why? To avoid processing geometry that does
Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Dr. Michael Wimmer
 Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Dr. Michael Wimmer wimmer@cg.tuwien.ac.at Visibility Overview Basics about visibility Basics about occlusion culling View-frustum culling / backface culling Occlusion
Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Dr. Michael Wimmer wimmer@cg.tuwien.ac.at Visibility Overview Basics about visibility Basics about occlusion culling View-frustum culling / backface culling Occlusion
( ) ( ) C. " 1 n. ( ) $ f n. ( ) B. " log( n! ) ( ) and that you already know ( ) ( ) " % g( n) ( ) " #&
 CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
Tree-Structured Indexes
 Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Tree-Structured Indexes Chapter 10 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record with key value k
Computing 3D Geometry Directly From Range Images
 Computing 3D Geometry Directly From Range Images Sarah F. Frisken and Ronald N. Perry Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Geometry from Range Data A Classic Approach Subject Range images Range surfaces
Computing 3D Geometry Directly From Range Images Sarah F. Frisken and Ronald N. Perry Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Geometry from Range Data A Classic Approach Subject Range images Range surfaces
