ECS Baruch Lab 2 Fall 2019 Name
|
|
|
- Doris Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECS Baruch Lab 2 Fall 2019 Name I. Review Recall that in lab 1, you created a folder on your H: drive, Document/Apps-SU/Python Programs The reason you need to save programs here on the lab computers is a) So they won t be erased when you log off. b) So they will run. (On your own laptop, you can put them anywhere you want.) Answer these by remembering what happened in lab If I enter at the shell prompt >>> 34 what will the shell print? 2. If I enter at the shell prompt>>> # what will the shell print? Why? II. A. Variables Open IDLE for Python 3.7 (NOT 2.7!) You see the Python Shell. (From the title bar at the top you can see that is says Python Shell ) At the prompt (>>>) type # your name (use your actual name!) At the prompt set >>> area=3*4 Evaluate by asking >>> area Create two more variables by assigning length the value 7 and width the value 5. Have the shell evaluate length and width and see that their values are 7 and 5. At the prompt set >>> area=length * width Evaluate. What did you get? Notice that the former value of area (12) has been replaced with a new value.
2 Give length a new value, 10 Without telling the shell to recompute area, have the shell evaluate the area. What value did it give for area? Did it use the new value of length? Once again tell it to compute area using area=length * width What value did it give for area? Did it use the new value of length? (Changing a value of a variable does not change previous computations, only those going forward.) B. Restarting the Shell From the Shell menu select Restart Shell. Notice that what you typed before is still visible in the window, but there is a line indicating where the shell was restarted. So what does restart mean? At the prompt type area Did it remember the value? (Everything that was defined in the earlier incarnation of the shell has been wiped out.) III. Some data types and commands A. Enter each of these at the prompts, as indicated. Record what the computer responds. Include single or double quotes if they are part of the output. >>> 27 >>> "27" >>> apples = 6 >>> apples >>> "apples" >>> oranges = "navel" >>> oranges >>> >>>type(apples)
3 >>>type(oranges) >>>type(3.14) >>>type("something in quotes") A string is a sequence of characters. We tell the computer we mean a string by enclosing the string in single quotes ' ' or double quotes: " ". The computer indicates a string by enclosing them in quotes. Above, a sequence of characters without quotes, like oranges, is the name of a variable. A variable could be holding an int, like 27, a float, like , or even a string, like "navel". B. We can tell the computer to print something to the screen. Try >>>print(234) >>>print("pizza and salad") >>>print(apples) >>>print(oranges) >>>print( ) >>>print("i like " + oranges) >>>print(apples + oranges) (What happens?) Answer by looking at the examples above: What happens when you add two strings? What happens when you add a string to a number? >>>print(3, 2, 1) >>>print(apples, oranges, "plums") >>>print(apples,oranges,"plums") >>>print(apples, oranges, "plums") C. Some input. Try the following >>>name = input("enter your name: ") When the computer asks you to enter you name, type it in, followed by the enter key. Now evaluate name >>>name
4 Write similar code to ask for someone's age. Enter an age when asked. Evaluate age. Are there any quotation marks around the output? Is the computer interpreting your age as a number or as a string? Try >>>age2=eval(input("enter your age ")) >>>age2 Are there any quotation marks around the output? This time, is the computer interpreting your age as a number or as a string? D. Time to write your own program. Restart the shell. (Shell -> Restart shell) Write a sequence of statements that will Ask a user for their name and store it in a variable. Ask the user for the length and width of a rectangle. Compute the area of the rectangle Compute the perimeter of the rectangle Print results like this (but with your values): Hi Michelle! Your rectangle has area 50 Your rectangle has perimeter 30 IV. Congratulations! You have written a program - almost. The problem is, if you want to run it again, you will have to type it all in again. So lets do it again, but this time we will save the statements in a file, so we can reuse them. Select File -> New File A new Python editor window will open. Type in some comments like these (but use your name, not mine): # ProcessRectangle.py # by Marjory Baruch # Compute the area and perimeter of a rectangle. # Ask for name. # Ask for length and width. # Compute area and perimeter. # Print results.
5 The first three lines are the file name, your name, and a brief description of what the program does. Starting with the comment #Ask for name go back and retype the Python statements you typed in part D. Now there are no prompts. Put the statements right after the comments that describe them, for example # Ask for name. name = input("enter your name ") Do this for all the comments, providing Python statements that will actually do what the comments describe. Select File-> Save In the window that opens, navigate to the folder Documents\Apps-SU\Python Programs on your H: drive that you set up in lab 1. Name the file ProcessRectangle.py and click the Save button. With the ProcessRectangle.py file window selected, select Run-> Run Module from the menu. If all went well, the Python shell window restarted and you are asked to enter your name! Answer the questions when asked, pressing enter key each time, and your program should print some answers! If all didn't go well (which is usually the case), fix errors, save again, and run again. You may have to repeat this step several times. To appreciate that this script can be run over and over choose Run->Run Module again and enter different values. When you run this module, you are just giving the shell lots of lines of code at once. You can still enter commands. At the prompt type >>>length and see that you get the value you entered when you ran the module. Print the file ProcessRectangle.py to hand in later. Close the file window. V. Writing and running a program with a main. From the shell menu select File -> New File. (In the future I will just say open a new file.) Type the following in the window (use your name where it says your name) Don't cut and paste.
6 # miletokm.py # your name # Converts distance in miles to kilometers # Ask for the distance in miles miles = eval( input( "Enter distance in miles: ")) # Convert to kilometers km = miles * # Print the result print(miles, "miles equals", km, "kilometers") Save the module file as milestokm.py in your Python Programs folder on your H: drive. (Recall H:Documents/Apps-SU/Python Programs ) Whenever I say to save a file, this is where you should save it. Select Run-> Run Module from the menu. (I will say Run the Module). Fix errors if there are any. When it is running properly, the shell will be selected and You should see the program's prompt. (Enter distance in miles not >>>) Enter a value, like 1 (where you know the answer) and see what the program says. Did you get a good answer? Run the module again. Did the shell restart? Give a different value. Record the input value (miles) and the output value (kilometers) miles: km: At the shell prompt type miles. What is the output? Save the Python shell window (not the module) in Python Programs as lab2shell.py. Frequently throughout lab save it again, by pressing the control key and s together. That way it won't be lost.
7 B. Writing a main function. We would like to be able to run a program several times without restarting the shell. Click on the module window. (It says milestokm.py on the title bar.) Click File->Save As. Add v2 (for version 2) to the name (miletokmv2.py), and make sure it is being saved in the python programs folder. Modify your program so it looks like the program below. Indentation matters. To indent a bunch of lines: highlight them and from the menu bar select Format -> indent region. # miletokmv2.py # your name # Converts distance in miles to kilometers def main(): # Ask for the distance in miles miles = eval( input( "Enter distance in miles: ")) main() # Convert to kilometers km = miles * # Print the result print(miles, "miles equals", km, "kilometers") Run the module milestokmv2.py. Did the shell restart? Enter data when asked. Now to call main. At the shell prompt type main() and press enter >>> main() Does the program run again? Did the shell restart? C. While we can now convert lots of miles by running the program over and over, lets have the program do it. Save the program again as milestokmv3.py.
8 Modify the program so it looks like # miletokmv3.py # your name # Converts distances in miles to kilometers def main(): for i in range(4): # Ask for the distance in miles miles = eval( input( "Enter distance in miles: ")) main() # Convert to kilometers km = miles * # Print the result print(miles, "miles equals", km, "kilometers") Run the module milestokmv3.py Enter data as asked. How many time does the program ask you for miles? List the values you enter and the answers: miles KM Once again, save the shell. VI. Submitting your work. Print the file lab2shell.txt to printer CST Print (if you didn't earlier) the module ProcessRectangle.py Make sure your name is on the lab packet. Staple them together in the order: packet on top, then ProcessRectangle, then Lab2Shell. Just outside the lab is a file cabinet with a slot on top and BARUCH ECS102 written on the front. Put your lab in the slot.
ECS Baruch Lab 3 Spring 2019 Name
 ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 3 Spring 2019 Name I. You can't ask a computer to do something you can't do. Now it is your turn to step through a program, without a computer. DO NOT ENTER THIS PROGRAM ON THE COMPUTER.
ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 3 Spring 2019 Name I. You can't ask a computer to do something you can't do. Now it is your turn to step through a program, without a computer. DO NOT ENTER THIS PROGRAM ON THE COMPUTER.
ECS Baruch Lab 9 Spring 2019 Name
 ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 9 Spring 2019 Name I. Reading input files A. infile.read() Copy the file exploreinputfiles.txt from the webpage, change to.py. Run it. I hope you got an error FileNotFoundError: [Errno
ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 9 Spring 2019 Name I. Reading input files A. infile.read() Copy the file exploreinputfiles.txt from the webpage, change to.py. Run it. I hope you got an error FileNotFoundError: [Errno
Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners. Chapter 1. by Warren Sande and Carter Sande. Copyright 2009 Manning Publications
 Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners by Warren Sande and Carter Sande Chapter 1 Copyright 2009 Manning Publications brief contents Preface xiii Acknowledgments xix About this
Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners by Warren Sande and Carter Sande Chapter 1 Copyright 2009 Manning Publications brief contents Preface xiii Acknowledgments xix About this
Using IDLE for
 Using IDLE for 15-110 Step 1: Installing Python Download and install Python using the Resources page of the 15-110 website. Be sure to install version 3.3.2 and the correct version depending on whether
Using IDLE for 15-110 Step 1: Installing Python Download and install Python using the Resources page of the 15-110 website. Be sure to install version 3.3.2 and the correct version depending on whether
ECS Baruch Lab 5 Spring 2019 Name NetID (login, like , not your SUID)
 ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 5 Spring 2019 Name NetID (login, like email, not your SUID) Today you will be doing some more experiments in the shell. Create a file Lab5.txt. In this file you will be asked to save
ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 5 Spring 2019 Name NetID (login, like email, not your SUID) Today you will be doing some more experiments in the shell. Create a file Lab5.txt. In this file you will be asked to save
Lab 1: Input, Processing, and Output This lab accompanies Chapter 2 of Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design.
 Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design 1 Lab 1: Input, Processing, and Output This lab accompanies Chapter 2 of Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design. Lab 1.1 Algorithms Name: Critical Review
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design 1 Lab 1: Input, Processing, and Output This lab accompanies Chapter 2 of Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design. Lab 1.1 Algorithms Name: Critical Review
Once you define a new command, you can try it out by entering the command in IDLE:
 1 DEFINING NEW COMMANDS In the last chapter, we explored one of the most useful features of the Python programming language: the use of the interpreter in interactive mode to do on-the-fly programming.
1 DEFINING NEW COMMANDS In the last chapter, we explored one of the most useful features of the Python programming language: the use of the interpreter in interactive mode to do on-the-fly programming.
Getting Started. Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners
 Getting Started Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners EARLY ACCESS EDITION Warren D. Sande and Carter Sande MEAP Release: May 2008 Softbound print: November 2008
Getting Started Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners EARLY ACCESS EDITION Warren D. Sande and Carter Sande MEAP Release: May 2008 Softbound print: November 2008
Semester 2, 2018: Lab 1
 Semester 2, 2018: Lab 1 S2 2018 Lab 1 This lab has two parts. Part A is intended to help you familiarise yourself with the computing environment found on the CSIT lab computers which you will be using
Semester 2, 2018: Lab 1 S2 2018 Lab 1 This lab has two parts. Part A is intended to help you familiarise yourself with the computing environment found on the CSIT lab computers which you will be using
Intro to Programming. Unit 7. What is Programming? What is Programming? Intro to Programming
 Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Computer and Programming: Lab 1
 01204111 Computer and Programming: Lab 1 Name ID Section Goals To get familiar with Wing IDE and learn common mistakes with programming in Python To practice using Python interactively through Python Shell
01204111 Computer and Programming: Lab 1 Name ID Section Goals To get familiar with Wing IDE and learn common mistakes with programming in Python To practice using Python interactively through Python Shell
Creating a Project in XCode
 ECS 102 Lab 2 for Mac Spring 2018 Name Creating a Project in XCode 1. Creating a project and program file, and running a program. (a) If you have already installed XCode skip to Part b. Go to the App store
ECS 102 Lab 2 for Mac Spring 2018 Name Creating a Project in XCode 1. Creating a project and program file, and running a program. (a) If you have already installed XCode skip to Part b. Go to the App store
CMSC 201 Fall 2016 Lab 09 Advanced Debugging
 CMSC 201 Fall 2016 Lab 09 Advanced Debugging Assignment: Lab 09 Advanced Debugging Due Date: During discussion Value: 10 points Part 1: Introduction to Errors Throughout this semester, we have been working
CMSC 201 Fall 2016 Lab 09 Advanced Debugging Assignment: Lab 09 Advanced Debugging Due Date: During discussion Value: 10 points Part 1: Introduction to Errors Throughout this semester, we have been working
Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and installing Python
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and
Lecture 05 I/O statements Printf, Scanf Simple statements, Compound statements
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 05 I/O statements Printf, Scanf Simple
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 05 I/O statements Printf, Scanf Simple
Lecture 3. Input, Output and Data Types
 Lecture 3 Input, Output and Data Types Goals for today Variable Types Integers, Floating-Point, Strings, Booleans Conversion between types Operations on types Input/Output Some ways of getting input, and
Lecture 3 Input, Output and Data Types Goals for today Variable Types Integers, Floating-Point, Strings, Booleans Conversion between types Operations on types Input/Output Some ways of getting input, and
ECS Baruch Lab 12 Spring 2019 Name
 ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 12 Spring 2019 Name I. More input files. Download the file cookiesales.txt and the code file processcookies.py. cookiesales has information about some scouts and how many cookie orders
ECS 102 - Baruch Lab 12 Spring 2019 Name I. More input files. Download the file cookiesales.txt and the code file processcookies.py. cookiesales has information about some scouts and how many cookie orders
Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling
 Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling Now that the main concepts of programming have been explained, it's time to actually do some programming. In order for you to "edit" and "compile" a program, you'll need
Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling Now that the main concepts of programming have been explained, it's time to actually do some programming. In order for you to "edit" and "compile" a program, you'll need
6.S189 Homework 1. What to turn in. Exercise 1.1 Installing Python. Exercise 1.2 Hello, world!
 6.S189 Homework 1 http://web.mit.edu/6.189/www/materials.html What to turn in Do the warm-up problems for Days 1 & 2 on the online tutor. Complete the problems below on your computer and get a checkoff
6.S189 Homework 1 http://web.mit.edu/6.189/www/materials.html What to turn in Do the warm-up problems for Days 1 & 2 on the online tutor. Complete the problems below on your computer and get a checkoff
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015)
 CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7
 Anatomy of a class Oliver W. Layton CS231: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7 Follow-up Python is also cross-platform. What s the advantage of Java? It s true: Python
Anatomy of a class Oliver W. Layton CS231: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7 Follow-up Python is also cross-platform. What s the advantage of Java? It s true: Python
CSI Lab 02. Tuesday, January 21st
 CSI Lab 02 Tuesday, January 21st Objectives: Explore some basic functionality of python Introduction Last week we talked about the fact that a computer is, among other things, a tool to perform high speed
CSI Lab 02 Tuesday, January 21st Objectives: Explore some basic functionality of python Introduction Last week we talked about the fact that a computer is, among other things, a tool to perform high speed
Starting. Read: Chapter 1, Appendix B from textbook.
 Read: Chapter 1, Appendix B from textbook. Starting There are two ways to run your Python program using the interpreter 1 : from the command line or by using IDLE (which also comes with a text editor;
Read: Chapter 1, Appendix B from textbook. Starting There are two ways to run your Python program using the interpreter 1 : from the command line or by using IDLE (which also comes with a text editor;
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to
 A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
Exploring Python Basics
 CptS 111 Lab #1 Fall 2017 Exploring Python Basics Learning Objectives: - Use the IDLE Shell window to run Python interactively - Use the IDLE Editor window to write a Python program (script) - Run Python
CptS 111 Lab #1 Fall 2017 Exploring Python Basics Learning Objectives: - Use the IDLE Shell window to run Python interactively - Use the IDLE Editor window to write a Python program (script) - Run Python
3 Getting Started with Objects
 3 Getting Started with Objects If you are an experienced IDE user, you may be able to do this tutorial without having done the previous tutorial, Getting Started. However, at some point you should read
3 Getting Started with Objects If you are an experienced IDE user, you may be able to do this tutorial without having done the previous tutorial, Getting Started. However, at some point you should read
CMSC 201 Fall 2018 Lab 04 While Loops
 CMSC 201 Fall 2018 Lab 04 While Loops Assignment: Lab 04 While Loops Due Date: During discussion, September 24 th through September 27 th Value: 10 points (8 points during lab, 2 points for Pre Lab quiz)
CMSC 201 Fall 2018 Lab 04 While Loops Assignment: Lab 04 While Loops Due Date: During discussion, September 24 th through September 27 th Value: 10 points (8 points during lab, 2 points for Pre Lab quiz)
S206E Lecture 19, 5/24/2016, Python an overview
 S206E057 Spring 2016 Copyright 2016, Chiu-Shui Chan. All Rights Reserved. Global and local variables: differences between the two Global variable is usually declared at the start of the program, their
S206E057 Spring 2016 Copyright 2016, Chiu-Shui Chan. All Rights Reserved. Global and local variables: differences between the two Global variable is usually declared at the start of the program, their
Lesson 4: Who Goes There?
 Lesson 4: Who Goes There? In this lesson we will write a program that asks for your name and a password, and prints a secret message if you give the right password. While doing this we will learn: 1. What
Lesson 4: Who Goes There? In this lesson we will write a program that asks for your name and a password, and prints a secret message if you give the right password. While doing this we will learn: 1. What
Arduino 02: Using the Arduino with Python. Jeffrey A. Meunier University of Connecticut
 Arduino 02: Using the Arduino with Python Jeffrey A. Meunier jeffm@engr.uconn.edu University of Connecticut About: How to use this document I designed this tutorial to be tall and narrow so that you can
Arduino 02: Using the Arduino with Python Jeffrey A. Meunier jeffm@engr.uconn.edu University of Connecticut About: How to use this document I designed this tutorial to be tall and narrow so that you can
CSC105, Introduction to Computer Science I. Introduction. Perl Directions NOTE : It is also a good idea to
 CSC105, Introduction to Computer Science Lab03: Introducing Perl I. Introduction. [NOTE: This material assumes that you have reviewed Chapters 1, First Steps in Perl and 2, Working With Simple Values in
CSC105, Introduction to Computer Science Lab03: Introducing Perl I. Introduction. [NOTE: This material assumes that you have reviewed Chapters 1, First Steps in Perl and 2, Working With Simple Values in
SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer
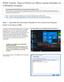 SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer Only Computers That DO NOT Have an Internet Connection Need to Do This If the computer you want to activate SPSS on does
SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer Only Computers That DO NOT Have an Internet Connection Need to Do This If the computer you want to activate SPSS on does
How To Test Your Code A CS 1371 Homework Guide
 Introduction After you have completed each drill problem, you should make it a habit to test your code. There are good ways of testing your code and there are bad ways of testing your code. This guide
Introduction After you have completed each drill problem, you should make it a habit to test your code. There are good ways of testing your code and there are bad ways of testing your code. This guide
Introduction to Computer Programming for Non-Majors
 Introduction to Computer Programming for Non-Majors CSC 2301, Fall 2016 Chapter 1 Instructor: Long Ma The Department of Computer Science Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software
Introduction to Computer Programming for Non-Majors CSC 2301, Fall 2016 Chapter 1 Instructor: Long Ma The Department of Computer Science Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software
CS 1110, LAB 3: MODULES AND TESTING First Name: Last Name: NetID:
 CS 1110, LAB 3: MODULES AND TESTING http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs11102013fa/labs/lab03.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: The purpose of this lab is to help you better understand functions, and to
CS 1110, LAB 3: MODULES AND TESTING http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs11102013fa/labs/lab03.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: The purpose of this lab is to help you better understand functions, and to
Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-1004 Introduction to Programming for Non-Majors
 First Python Program Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-1004 Introduction to Programming for Non-Majors (Slides include materials from Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science, 2 nd edition, by
First Python Program Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-1004 Introduction to Programming for Non-Majors (Slides include materials from Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science, 2 nd edition, by
StudioPrompter Tutorials. Prepare before you start the Tutorials. Opening and importing text files. Using the Control Bar. Using Dual Monitors
 StudioPrompter Tutorials Prepare before you start the Tutorials Opening and importing text files Using the Control Bar Using Dual Monitors Using Speed Controls Using Alternate Files Using Text Markers
StudioPrompter Tutorials Prepare before you start the Tutorials Opening and importing text files Using the Control Bar Using Dual Monitors Using Speed Controls Using Alternate Files Using Text Markers
Python is available at: https://www.python.org/ Why Python is awesome: https://www.python.org/about/success/
 The Python IDLE: Introduction This tutorial assumes you have a PYTHON 3 version of the programming language installed. (Current version at of this writing is Python 3.6) Python is available at: https://www.python.org/
The Python IDLE: Introduction This tutorial assumes you have a PYTHON 3 version of the programming language installed. (Current version at of this writing is Python 3.6) Python is available at: https://www.python.org/
Introduction to Computation for the Humanities and Social Sciences. CS 3 Chris Tanner
 Introduction to Computation for the Humanities and Social Sciences CS 3 Chris Tanner Lecture 5 But I ve got a blank space [in my text String] baby Taylor Swift Lecture 5 Reading Input From Users Reading
Introduction to Computation for the Humanities and Social Sciences CS 3 Chris Tanner Lecture 5 But I ve got a blank space [in my text String] baby Taylor Swift Lecture 5 Reading Input From Users Reading
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) First Name: Last Name: NetID:
 CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
Part 6b: The effect of scale on raster calculations mean local relief and slope
 Part 6b: The effect of scale on raster calculations mean local relief and slope Due: Be done with this section by class on Monday 10 Oct. Tasks: Calculate slope for three rasters and produce a decent looking
Part 6b: The effect of scale on raster calculations mean local relief and slope Due: Be done with this section by class on Monday 10 Oct. Tasks: Calculate slope for three rasters and produce a decent looking
9.2 Linux Essentials Exam Objectives
 9.2 Linux Essentials Exam Objectives This chapter will cover the topics for the following Linux Essentials exam objectives: Topic 3: The Power of the Command Line (weight: 10) 3.3: Turning Commands into
9.2 Linux Essentials Exam Objectives This chapter will cover the topics for the following Linux Essentials exam objectives: Topic 3: The Power of the Command Line (weight: 10) 3.3: Turning Commands into
Programming for Engineers in Python. Autumn
 Programming for Engineers in Python Autumn 2011-12 Plan Administration: Course site Homework submission guidelines Working environment Python: Variables Editor vs. shell Homework 0 Python Cont. Conditional
Programming for Engineers in Python Autumn 2011-12 Plan Administration: Course site Homework submission guidelines Working environment Python: Variables Editor vs. shell Homework 0 Python Cont. Conditional
ASCII Art. Introduction: Python
 Python 1 ASCII Art All Code Clubs must be registered. Registered clubs appear on the map at codeclub.org.uk - if your club is not on the map then visit jumpto.cc/18cplpy to find out what to do. Introduction:
Python 1 ASCII Art All Code Clubs must be registered. Registered clubs appear on the map at codeclub.org.uk - if your club is not on the map then visit jumpto.cc/18cplpy to find out what to do. Introduction:
Notepad++ The COMPSCI 101 Text Editor for Windows. What is a text editor? Install Python 3. Installing Notepad++
 Notepad++ The COMPSCI 101 Text Editor for Windows The text editor that we will be using in the Computer Science labs for creating our Python programs is called Notepad++ and is freely available for the
Notepad++ The COMPSCI 101 Text Editor for Windows The text editor that we will be using in the Computer Science labs for creating our Python programs is called Notepad++ and is freely available for the
Notes By: Shailesh Bdr. Pandey, TA, Computer Engineering Department, Nepal Engineering College
 Preparing to Program You should take certain steps when you're solving a problem. First, you must define the problem. If you don't know what the problem is, you can't find a solution! Once you know what
Preparing to Program You should take certain steps when you're solving a problem. First, you must define the problem. If you don't know what the problem is, you can't find a solution! Once you know what
In further discussion, the books make other kinds of distinction between high level languages:
 Max and Programming This essay looks at Max from the point of view of someone with a bit of experience in traditional computer programming. There are several questions that come up from time to time on
Max and Programming This essay looks at Max from the point of view of someone with a bit of experience in traditional computer programming. There are several questions that come up from time to time on
The Domino Designer QuickStart Tutorial
 The Domino Designer QuickStart Tutorial 1. Welcome The Domino Designer QuickStart Tutorial You've installed Domino Designer, you've taken the Designer Guided Tour, and maybe you've even read some of the
The Domino Designer QuickStart Tutorial 1. Welcome The Domino Designer QuickStart Tutorial You've installed Domino Designer, you've taken the Designer Guided Tour, and maybe you've even read some of the
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Class Website http://www.cs.umb.edu/~jane/cs114/ Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Class Website http://www.cs.umb.edu/~jane/cs114/ Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming
Lecture 3. Functions & Modules
 Lecture 3 Functions & Modules Labs this Week Lab 1 is due at the beginning of your lab If it is not yet by then, you cannot get credit Only exception is for students who added late (Those students should
Lecture 3 Functions & Modules Labs this Week Lab 1 is due at the beginning of your lab If it is not yet by then, you cannot get credit Only exception is for students who added late (Those students should
Programming. We will be introducing various new elements of Python and using them to solve increasingly interesting and complex problems.
 Plan for the rest of the semester: Programming We will be introducing various new elements of Python and using them to solve increasingly interesting and complex problems. We saw earlier that computers
Plan for the rest of the semester: Programming We will be introducing various new elements of Python and using them to solve increasingly interesting and complex problems. We saw earlier that computers
CS 105 Lab As a review of what we did last week a. What are two ways in which the Python shell is useful to us?
 1 CS 105 Lab 3 The purpose of this lab is to practice the techniques of making choices and looping. Before you begin, please be sure that you understand the following concepts that we went over in class:
1 CS 105 Lab 3 The purpose of this lab is to practice the techniques of making choices and looping. Before you begin, please be sure that you understand the following concepts that we went over in class:
Chapter 2 The SAS Environment
 Chapter 2 The SAS Environment Abstract In this chapter, we begin to become familiar with the basic SAS working environment. We introduce the basic 3-screen layout, how to navigate the SAS Explorer window,
Chapter 2 The SAS Environment Abstract In this chapter, we begin to become familiar with the basic SAS working environment. We introduce the basic 3-screen layout, how to navigate the SAS Explorer window,
NCMail: Microsoft Outlook User s Guide
 NCMail: Microsoft Outlook 2007 Email User s Guide Revision 1.1 3/9/2009 This document covers how to use Microsoft Outlook 2007 for accessing your email with the NCMail Exchange email system. The syntax
NCMail: Microsoft Outlook 2007 Email User s Guide Revision 1.1 3/9/2009 This document covers how to use Microsoft Outlook 2007 for accessing your email with the NCMail Exchange email system. The syntax
Functions Structure and Parameters behind the scenes with diagrams!
 Functions Structure and Parameters behind the scenes with diagrams! Congratulations! You're now in week 2, diving deeper into programming and its essential components. In this case, we will talk about
Functions Structure and Parameters behind the scenes with diagrams! Congratulations! You're now in week 2, diving deeper into programming and its essential components. In this case, we will talk about
Not-So-Mini-Lecture 6. Modules & Scripts
 Not-So-Mini-Lecture 6 Modules & Scripts Interactive Shell vs. Modules Launch in command line Type each line separately Python executes as you type Write in a code editor We use Atom Editor But anything
Not-So-Mini-Lecture 6 Modules & Scripts Interactive Shell vs. Modules Launch in command line Type each line separately Python executes as you type Write in a code editor We use Atom Editor But anything
CS 1110, LAB 1: PYTHON EXPRESSIONS.
 CS 1110, LAB 1: PYTHON EXPRESSIONS Name: Net-ID: There is an online version of these instructions at http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2012fa/labs/lab1 You may wish to use that version of the instructions.
CS 1110, LAB 1: PYTHON EXPRESSIONS Name: Net-ID: There is an online version of these instructions at http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2012fa/labs/lab1 You may wish to use that version of the instructions.
Heuristic Evaluation of [Pass It On]
![Heuristic Evaluation of [Pass It On] Heuristic Evaluation of [Pass It On]](/thumbs/93/112469320.jpg) Heuristic Evaluation of [Pass It On] Evaluator #A: Janette Evaluator #B: John Evaluator #C: Pascal Evaluator #D: Eric 1. Problem Pass It On aims to transform some of the numerous negative and stressful
Heuristic Evaluation of [Pass It On] Evaluator #A: Janette Evaluator #B: John Evaluator #C: Pascal Evaluator #D: Eric 1. Problem Pass It On aims to transform some of the numerous negative and stressful
Lesson 3 Transcript: Part 2 of 2 Tools & Scripting
 Lesson 3 Transcript: Part 2 of 2 Tools & Scripting Slide 1: Cover Welcome to lesson 3 of the DB2 on Campus Lecture Series. Today we are going to talk about tools and scripting. And this is part 2 of 2
Lesson 3 Transcript: Part 2 of 2 Tools & Scripting Slide 1: Cover Welcome to lesson 3 of the DB2 on Campus Lecture Series. Today we are going to talk about tools and scripting. And this is part 2 of 2
Introduction to computers and Python. Matthieu Choplin
 Introduction to computers and Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ 1 Objectives To get a brief overview of what Python is To understand computer basics and programs
Introduction to computers and Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ 1 Objectives To get a brief overview of what Python is To understand computer basics and programs
CpSc 1111 Lab 4 Part a Flow Control, Branching, and Formatting
 CpSc 1111 Lab 4 Part a Flow Control, Branching, and Formatting Your factors.c and multtable.c files are due by Wednesday, 11:59 pm, to be submitted on the SoC handin page at http://handin.cs.clemson.edu.
CpSc 1111 Lab 4 Part a Flow Control, Branching, and Formatting Your factors.c and multtable.c files are due by Wednesday, 11:59 pm, to be submitted on the SoC handin page at http://handin.cs.clemson.edu.
Exploring Python Basics
 CptS 111 Lab #1 Exploring Python Basics Learning Objectives: - Use the IDLE Shell window to run Python interactively - Use the IDLE Editor window to write a Python program (script) - Run Python programs
CptS 111 Lab #1 Exploring Python Basics Learning Objectives: - Use the IDLE Shell window to run Python interactively - Use the IDLE Editor window to write a Python program (script) - Run Python programs
Flow Control: Branches and loops
 Flow Control: Branches and loops In this context flow control refers to controlling the flow of the execution of your program that is, which instructions will get carried out and in what order. In the
Flow Control: Branches and loops In this context flow control refers to controlling the flow of the execution of your program that is, which instructions will get carried out and in what order. In the
Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows
 Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows Using Windows The Windows start-up screen should look something like Figure 1-1. Several standard desktop icons will always appear on start up. Note
Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows Using Windows The Windows start-up screen should look something like Figure 1-1. Several standard desktop icons will always appear on start up. Note
1. Please, please, please look at the style sheets job aid that I sent to you some time ago in conjunction with this document.
 1. Please, please, please look at the style sheets job aid that I sent to you some time ago in conjunction with this document. 2. W3Schools has a lovely html tutorial here (it s worth the time): http://www.w3schools.com/html/default.asp
1. Please, please, please look at the style sheets job aid that I sent to you some time ago in conjunction with this document. 2. W3Schools has a lovely html tutorial here (it s worth the time): http://www.w3schools.com/html/default.asp
Introduction to: Computers & Programming: Review prior to 1 st Midterm
 Introduction to: Computers & Programming: Review prior to 1 st Midterm Adam Meyers New York University Summary Some Procedural Matters Summary of what you need to Know For the Test and To Go Further in
Introduction to: Computers & Programming: Review prior to 1 st Midterm Adam Meyers New York University Summary Some Procedural Matters Summary of what you need to Know For the Test and To Go Further in
CS1046 Lab 4. Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to:
 CS1046 Lab 4 Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to: Define the terms: function, calling and user-defined function and predefined function
CS1046 Lab 4 Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to: Define the terms: function, calling and user-defined function and predefined function
NCMail: Microsoft Outlook User s Guide
 NCMail: Microsoft Outlook 2003 Email User s Guide Revision 1.0 11/10/2007 This document covers how to use Microsoft Outlook 2003 for accessing your email with the NCMail Exchange email system. The syntax
NCMail: Microsoft Outlook 2003 Email User s Guide Revision 1.0 11/10/2007 This document covers how to use Microsoft Outlook 2003 for accessing your email with the NCMail Exchange email system. The syntax
15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation
 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Lab 0 Navigating your account in Linux Tom Cortina, Rob Simmons Unlike typical graphical interfaces for operating systems, here you are entering commands directly
15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Lab 0 Navigating your account in Linux Tom Cortina, Rob Simmons Unlike typical graphical interfaces for operating systems, here you are entering commands directly
CSE 101 Introduction to Computers Development / Tutorial / Lab Environment Setup
 CSE 101 Introduction to Computers Development / Tutorial / Lab Environment Setup Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to setup software that you will be using throughout the term for learning about Python
CSE 101 Introduction to Computers Development / Tutorial / Lab Environment Setup Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to setup software that you will be using throughout the term for learning about Python
CSCI 161: Introduction to Programming I Lab 1b: Hello, World (Eclipse, Java)
 Goals - to learn how to compile and execute a Java program - to modify a program to enhance it Overview This activity will introduce you to the Java programming language. You will type in the Java program
Goals - to learn how to compile and execute a Java program - to modify a program to enhance it Overview This activity will introduce you to the Java programming language. You will type in the Java program
CS Lab 8. Part 1 - Basics of File I/O
 CS 105 - Lab 8 Today, you will be doing a lot with files! We will start with the basics of reading and writing and then expand upon the pixel value work that you did in a previous lab by working on image
CS 105 - Lab 8 Today, you will be doing a lot with files! We will start with the basics of reading and writing and then expand upon the pixel value work that you did in a previous lab by working on image
Drupal Cloud Getting Started Guide Creating a Lab site with the MIT DLC Theme
 Introduction Drupal Cloud Getting Started Guide Creating a Lab site with the MIT DLC Theme In this Getting Started Guide, you can follow along as a website is built using the MIT DLC Theme. Whether you
Introduction Drupal Cloud Getting Started Guide Creating a Lab site with the MIT DLC Theme In this Getting Started Guide, you can follow along as a website is built using the MIT DLC Theme. Whether you
Introduction to Python
 Islamic University Of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Lab 1 Introduction to Python Eng. Ibraheem Lubbad September 17, 2016 Introduction: Python is a high-level, object-oriented
Islamic University Of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Lab 1 Introduction to Python Eng. Ibraheem Lubbad September 17, 2016 Introduction: Python is a high-level, object-oriented
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
MEMBERSHIP & PARTICIPATION
 MEMBERSHIP & PARTICIPATION What types of activities can I expect to participate in? There are a variety of activities for you to participate in such as discussion boards, idea exchanges, contests, surveys,
MEMBERSHIP & PARTICIPATION What types of activities can I expect to participate in? There are a variety of activities for you to participate in such as discussion boards, idea exchanges, contests, surveys,
Adafruit's Raspberry Pi Lesson 1. Preparing an SD Card for your Raspberry Pi
 Adafruit's Raspberry Pi Lesson 1. Preparing an SD Card for your Raspberry Pi Created by Simon Monk Last updated on 2013-07-08 12:15:38 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview You Will Need Downloading
Adafruit's Raspberry Pi Lesson 1. Preparing an SD Card for your Raspberry Pi Created by Simon Monk Last updated on 2013-07-08 12:15:38 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview You Will Need Downloading
Table of Contents EVALUATION COPY
 Table of Contents Introduction... 1-2 A Brief History of Python... 1-3 Python Versions... 1-4 Installing Python... 1-5 Environment Variables... 1-6 Executing Python from the Command Line... 1-7 IDLE...
Table of Contents Introduction... 1-2 A Brief History of Python... 1-3 Python Versions... 1-4 Installing Python... 1-5 Environment Variables... 1-6 Executing Python from the Command Line... 1-7 IDLE...
Importing source database objects from a database
 Importing source database objects from a database We are now at the point where we can finally import our source database objects, source database objects. We ll walk through the process of importing from
Importing source database objects from a database We are now at the point where we can finally import our source database objects, source database objects. We ll walk through the process of importing from
Programming Fundamentals and Python
 Chapter 2 Programming Fundamentals and Python This chapter provides a non-technical overview of Python and will cover the basic programming knowledge needed for the rest of the chapters in Part 1. It contains
Chapter 2 Programming Fundamentals and Python This chapter provides a non-technical overview of Python and will cover the basic programming knowledge needed for the rest of the chapters in Part 1. It contains
BEGINNER PHP Table of Contents
 Table of Contents 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Introduction Getting Setup Your first PHP webpage Working with text Talking to the user Comparison & If statements If & Else Cleaning up the game Remembering values Finishing
Table of Contents 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Introduction Getting Setup Your first PHP webpage Working with text Talking to the user Comparison & If statements If & Else Cleaning up the game Remembering values Finishing
GEO 425: SPRING 2012 LAB 9: Introduction to Postgresql and SQL
 GEO 425: SPRING 2012 LAB 9: Introduction to Postgresql and SQL Objectives: This lab is designed to introduce you to Postgresql, a powerful database management system. This exercise covers: 1. Starting
GEO 425: SPRING 2012 LAB 9: Introduction to Postgresql and SQL Objectives: This lab is designed to introduce you to Postgresql, a powerful database management system. This exercise covers: 1. Starting
15-110: Principles of Computing, Spring 2018
 15-110: Principles of Computing, Spring 2018 Programming Assignment 11 (PA11) Due: Tuesday, May 1 by 9PM IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT You cant drop this assignment even if it is your lowest PA score. Failure
15-110: Principles of Computing, Spring 2018 Programming Assignment 11 (PA11) Due: Tuesday, May 1 by 9PM IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT You cant drop this assignment even if it is your lowest PA score. Failure
Tutorial How to upgrade firmware on Phison S8 controller MyDigitalSSD
 Tutorial How to upgrade firmware on Phison S8 controller MyDigitalSSD Version 1.4 This tutorial will walk you through how to create a bootable USB drive and how to apply the newest firmware 4.6 to your
Tutorial How to upgrade firmware on Phison S8 controller MyDigitalSSD Version 1.4 This tutorial will walk you through how to create a bootable USB drive and how to apply the newest firmware 4.6 to your
3. Now go to Edit => Effects => Brightness/Contrast... and notice that you can modify the colors you created above.
 The Background Note: This lesson is created for version 3.2 of HyperStudio for Macintosh. Some features may not be present in the version you may have. You may download updates for your HyperStudio version
The Background Note: This lesson is created for version 3.2 of HyperStudio for Macintosh. Some features may not be present in the version you may have. You may download updates for your HyperStudio version
Chapter 2 Input, Processing and Output. Hong Sun COSC 1436 Spring 2017 Jan 30, 2017
 Chapter 2 Input, Processing and Output Hong Sun COSC 1436 Spring 2017 Jan 30, 2017 Designing a Program Designing a Program o Programs must be carefully designed before they are written. Before beginning
Chapter 2 Input, Processing and Output Hong Sun COSC 1436 Spring 2017 Jan 30, 2017 Designing a Program Designing a Program o Programs must be carefully designed before they are written. Before beginning
PYTHON. Varun Jain & Senior Software Engineer. Pratap, Mysore Narasimha Raju & TEST AUTOMATION ARCHITECT. CenturyLink Technologies India PVT LTD
 PYTHON Varun Jain & Senior Software Engineer Pratap, Mysore Narasimha Raju & TEST AUTOMATION ARCHITECT CenturyLink Technologies India PVT LTD 1 About Python Python is a general-purpose interpreted, interactive,
PYTHON Varun Jain & Senior Software Engineer Pratap, Mysore Narasimha Raju & TEST AUTOMATION ARCHITECT CenturyLink Technologies India PVT LTD 1 About Python Python is a general-purpose interpreted, interactive,
Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving
 Class 3: The Eclipse IDE Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward What is an IDE? An integrated development environment (IDE) is an environment in
Class 3: The Eclipse IDE Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward What is an IDE? An integrated development environment (IDE) is an environment in
Lecture 3. Functions & Modules
 Lecture 3 Functions & Modules Labs this Week Lab 1 is due at the beginning of your lab If it is not yet by then, you cannot get credit Only exception is for students who added late (Those students should
Lecture 3 Functions & Modules Labs this Week Lab 1 is due at the beginning of your lab If it is not yet by then, you cannot get credit Only exception is for students who added late (Those students should
CS 1110, LAB 1: EXPRESSIONS AND ASSIGNMENTS First Name: Last Name: NetID:
 CS 1110, LAB 1: EXPRESSIONS AND ASSIGNMENTS http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2018sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Learning goals: (1) get hands-on experience using Python in
CS 1110, LAB 1: EXPRESSIONS AND ASSIGNMENTS http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2018sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Learning goals: (1) get hands-on experience using Python in
STAT 113: R/RStudio Intro
 STAT 113: R/RStudio Intro Colin Reimer Dawson Last Revised September 1, 2017 1 Starting R/RStudio There are two ways you can run the software we will be using for labs, R and RStudio. Option 1 is to log
STAT 113: R/RStudio Intro Colin Reimer Dawson Last Revised September 1, 2017 1 Starting R/RStudio There are two ways you can run the software we will be using for labs, R and RStudio. Option 1 is to log
Max and Programming Is Max a Programming Language?
 There are several questions that come up from time to time on the Max discussion list. Is Max a real programming language? if so how do I do [loop, switch, bitmap, recursion] and other programming tricks
There are several questions that come up from time to time on the Max discussion list. Is Max a real programming language? if so how do I do [loop, switch, bitmap, recursion] and other programming tricks
Invent Your Own Computer Games with Python
 Hello Wor ld! Invent Your Own Computer Games with Python Taesoo Kwon Heejin Park Hanyang University Introduction to Python Python Easier to learn than C. Serious programming language. Many expert programmers
Hello Wor ld! Invent Your Own Computer Games with Python Taesoo Kwon Heejin Park Hanyang University Introduction to Python Python Easier to learn than C. Serious programming language. Many expert programmers
nostarch.com/pfk For bulk orders, please contact us at
 nostarch.com/pfk For bulk orders, please contact us at sales@nostarch.com. Teacher: Date/Period: Subject: Python Programming Class: Topic: #1 - Getting Started Duration: Up to 50 min. Objectives: Install
nostarch.com/pfk For bulk orders, please contact us at sales@nostarch.com. Teacher: Date/Period: Subject: Python Programming Class: Topic: #1 - Getting Started Duration: Up to 50 min. Objectives: Install
MITOCW watch?v=0jljzrnhwoi
 MITOCW watch?v=0jljzrnhwoi The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=0jljzrnhwoi The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Temple University Computer Science Programming Under the Linux Operating System January 2017
 Temple University Computer Science Programming Under the Linux Operating System January 2017 Here are the Linux commands you need to know to get started with Lab 1, and all subsequent labs as well. These
Temple University Computer Science Programming Under the Linux Operating System January 2017 Here are the Linux commands you need to know to get started with Lab 1, and all subsequent labs as well. These
Algorithms and Programming I. Lecture#12 Spring 2015
 Algorithms and Programming I Lecture#12 Spring 2015 Think Python How to Think Like a Computer Scientist By :Allen Downey Installing Python Follow the instructions on installing Python and IDLE on your
Algorithms and Programming I Lecture#12 Spring 2015 Think Python How to Think Like a Computer Scientist By :Allen Downey Installing Python Follow the instructions on installing Python and IDLE on your
Control Panel software usage guide (v beta)
 Control Panel software usage guide (v 1.012 beta) (note: the pictures throughout the guide may not directly correspond with your server installation, however all features are covered) 1. Connecting to
Control Panel software usage guide (v 1.012 beta) (note: the pictures throughout the guide may not directly correspond with your server installation, however all features are covered) 1. Connecting to
Lecture 4. Defining Functions
 Lecture 4 Defining Functions Academic Integrity Quiz Reading quiz about the course AI policy Go to http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs11110/ Click Academic Integrity in side bar Read and take quiz in
Lecture 4 Defining Functions Academic Integrity Quiz Reading quiz about the course AI policy Go to http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs11110/ Click Academic Integrity in side bar Read and take quiz in
Introduction to Python Code Quality
 Introduction to Python Code Quality Clarity and readability are important (easter egg: type import this at the Python prompt), as well as extensibility, meaning code that can be easily enhanced and extended.
Introduction to Python Code Quality Clarity and readability are important (easter egg: type import this at the Python prompt), as well as extensibility, meaning code that can be easily enhanced and extended.
